Each of us who is at least a little familiar with biology understands that the success of growing horticultural crops depends immediately on a combination of many versatile factors. Climatic conditions, planting dates, variety, timeliness and literacy of agrotechnical techniques - this is not all that has a direct impact on the harvest.

Chernozem, humus-rich soil.
One of the fundamental factors that often play a dominant role in the outcome of gardening and planting a vegetable garden is the type of soil. The possibility of growing certain crops, the need for certain fertilizers, the frequency of watering and weeding will depend on what kind of soil is on your site. Yes Yes! All this can have significant differences and be beneficial or harmful if you do not know what kind of soil you are dealing with.
The main types of soils
The main types of soils that Russian gardeners most often encounter are: clay, sandy, sandy loam, loamy, calcareous and swampy. Each of them has both positive and negative properties, which means it differs in recommendations for improving and selecting crops. In their pure form, they are rare, mainly in combination, but with a predominance of certain characteristics. Knowledge of these properties accounts for 80% of the success of a good harvest.


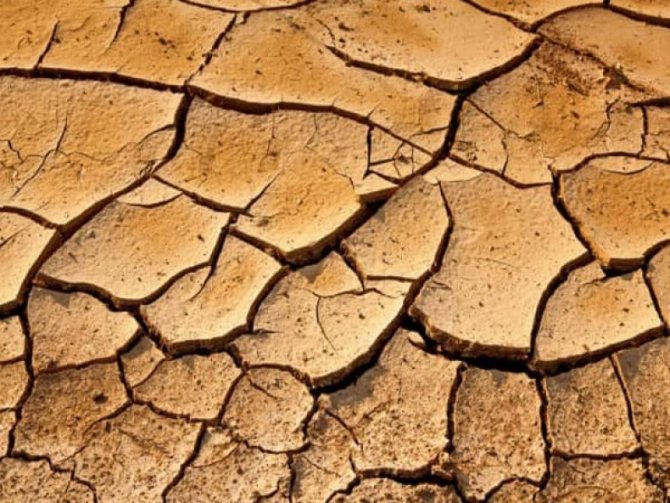
Clay soil. <>
Determine the mechanical composition of the soil


The mechanical composition of the soil is determined by the ratio of the amount of sand and clay particles. Depending on this, light soils are distinguished - sandy and sandy loam, loamy and heavy - clayey. The composition of the soil affects the way it is processed and the methods of growing cultivated plants. It is very easy to define it. A soil sample is taken, - just one teaspoon - it is moistened with water to a doughy state and a ball rolls off.
- The ball did not work out, it crumbled, which means the soil is sandy.
- If the ball works out, you need to try to roll it out between your palms. If a cord does not come out of the ball, the soil is sandy loam.
- It turned out - let's try to roll it into a ring. The ring does not come out - the soil is light loamy.
- Cracks strongly, but holds - medium loamy.
- The ring cracks slightly - the soil is heavy loamy.
- You can give any shape - clay soil.
Sandy and sandy loam soils thaw earlier in spring, melt water leaves them faster and they quickly become suitable for planting. In these soils, plant residues rot very quickly and fertilizers that plants did not have time to assimilate are quickly washed out. To increase the fertility of such soils, it is necessary to apply a large amount of organic and mineral fertilizers. Heavy loamy and clayey soils thaw and warm up more slowly, poorly letting water through. It lingers under the arable layer, so air does not penetrate well to the roots of plants. In such soils, plant residues slowly decompose and do not reach a form that is available for assimilation by plants. For agriculture, the most favorable properties are in loamy soils. In them, all processes are carried out optimally and favorably for all cultures.
Clay soil
It is quite easy to determine the clay soil: after digging it has a coarse, dense structure, sticks greasy to the feet in the rains, does not absorb water well, easily sticks together. If you roll a long sausage from a handful of such earth (wet), it can be easily bent into a ring, while it will not crumble or crack.
Due to its high density, such soil is considered heavy. It warms up slowly, is poorly ventilated, and has a low water absorption coefficient. Therefore, it is quite problematic to grow crops on it. However, if the clay soil is properly cultivated, it can become fertile enough.
To facilitate and enrich this type of soil, it is recommended to periodically apply sand, peat, ash and lime. Sand reduces moisture holding values. Ash enriches with nutrients. Peat loosens and increases water absorption properties. Lime reduces acidity and improves soil air conditions.
How much to add is an individual question, directly related to the indicators of your soil, which can be accurately determined only in laboratory conditions. But, in general: sand - no more than 40 kg per 1 m², lime - about 300-400 g per m², for deep digging once every 4 years (on soils with a weakly acidic reaction), there are no restrictions for peat and ash. If there is a choice of organic matter, then horse manure is the best option for increasing the fertility of clay soils. Sowing siderates such as mustard, rye, oats will not be useless either.
Plants on clay soils do not have an easy time. Poor heating of the roots, lack of oxygen, stagnant moisture, the formation of a soil crust do not work for the benefit of the crop. But still, trees and shrubs, having a sufficiently powerful root system, tolerate this type of soil well. From vegetables on clay, potatoes, beets, peas and Jerusalem artichoke feel good.
For other crops, it is possible to recommend high beds, planting on ridges, using a shallow depth of planting seeds and tubers in the soil, planting seedlings in an inclined way (for better heating of the root system). Among the agrotechnical methods, special attention should be paid to loosening and mulching on clay soils.


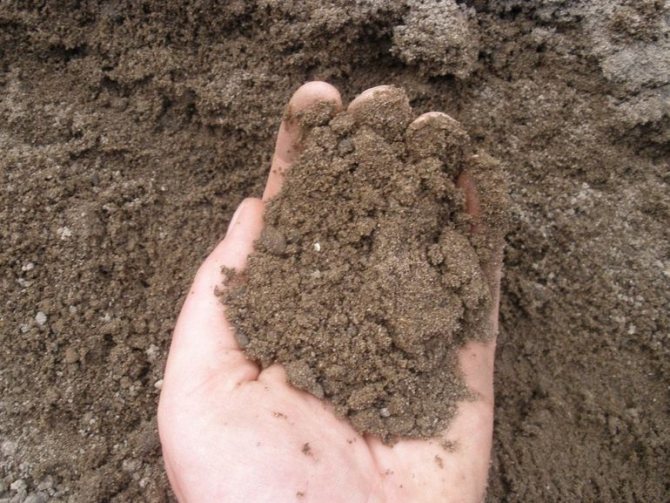
Sandy soil. <>
Acid balance
The acidity of the soil is of great importance for the cultivation of crops., the optimal value of which is called the acid-base balance. It is one of the most important indicators of the quality of fertile land. Indicate acidity with a "pH". When this value is seven units, the acidity is called neutral. If the pH is below seven, the earth is acidic. Above pH 7 is called alkaline.
Read also: Practical tips for growing nightshade in your home
With an increase in acidity, there is an increase in the content of aluminum and its salts in the soil, as well as manganese and other minerals. This does not allow plants to develop normally. Moreover, pathogenic bacteria, microorganisms and pests begin to actively multiply in such soil. The applied fertilizers do not decompose. All this leads to a disturbance in the imbalance of the soil.
Determining acidity is very easy at home. For this, a simple litmus indicator method is used. Soils are acidified very often. The most common method is liming. At the same time, lime displaces aluminum and its salts from the upper layer of the earth, replacing them with calcium and magnesium. This reduces the toxic effect on the plant.
The amount of lime per square meter depends on the type of soil and its characteristics. The table shows the application rates for lime to reduce acidity..
Sandy soil
Sandy soil refers to light soil types. It will not be difficult to recognize it either: it is loose, free-flowing, it easily passes water.If you take a handful of such earth in your hands and try to form a lump, nothing will work.
All the qualities inherent in sandy soils are both their plus and their minus. Such soils quickly warm up, are well aerated, easily processed, but at the same time quickly cool, dry out soon, and weakly retain mineral substances in the root zone (nutrients are washed out by water into the deep layers of the soil). As a result, they are poor in the presence of useful microflora and poorly suited for growing any crops.
To increase the fertility of such soils, it is necessary to constantly take care of improving their compacting and binding properties. Regular application of peat, compost, humus, clay or drill meal (up to two buckets per 1 m²), the use of green manure (embedded in the soil), high-quality mulching give a decent stable result after 3 - 4 years.
But even if the site is still in the process of domestication, it is possible to grow carrots, onions, melons, strawberries, currants, fruit trees on it. Cabbage, peas, potatoes and beets will feel somewhat worse on sandy soils, but if you fertilize them with fast-acting fertilizers, in small doses and often enough, you can achieve good results.
For those who do not want to bother with cultivation, there is another way to improve these soils - the creation of an artificial fertile layer by clay. To do this, on the site of the beds, it is necessary to arrange a clay castle (lay out the clay with a layer of 5-6 cm) and pour 30-35 cm of sandy loam or loamy soil on it, taken from the side.


Sandy loam soil. <>
What is the importance of soil in nature
The existence of life in its present state is possible only due to the emergence of soil on Earth. The main contribution of soil to the maintenance of the planet's biosphere is that it is a direct source of nutrition for plants and an indirect source of food for animals and humans.


The presence or absence of soil has a critical impact on the environment. By absorbing and retaining rainwater, the earth prevents first floods and then drought. Another feature of the earth is the function of a filter that purifies water from impurities.
The earth influences the stabilization of the climate by binding carbon in its composition. Even in desert areas, cyanobacteria, lichens and mosses absorb significant amounts of carbon during photosynthesis. Degradation of the soil layer promotes the transition of carbon from a bound to a free state. This increases the greenhouse effect, one of the causes of global warming.
The surface and thickness of the earth is the habitat of a huge number of species, including humans. Without soil, the existence of a significant part of the planet's biosphere will become impossible.
That is why the number of measures taken to protect the soil is growing. Only an improvement in the quality of soil protection from natural and anthropogenic destructive processes will allow future generations to continue life on Earth.
Sandy loam soil
Sandy loam soil is another option for light-textured soils. In terms of its qualities, it is similar to sandy soils, but it contains a slightly higher percentage of clay inclusions, which means it has a better holding capacity for mineral and organic substances, not only warms up quickly, but also retains heat for a long time, passes moisture less and dries out more slowly, is well aerated and easy to process.
It can be determined by the same method of squeezing a handful of moist earth into a sausage or lump: if it forms, but does not hold its shape poorly, you have sandy loam soil in front of you.
Anything can grow on such soils, with the usual methods of agricultural technology and the choice of zoned varieties. This is one of the good options for gardens and vegetable gardens. However, the methods of increasing and maintaining fertility for these soils will also not be superfluous.It is recommended to regularly introduce organic matter on them (in usual doses), sow green manure crops, and carry out mulching.


Loamy soil. <>
Most common soil types
Of course, for a good harvest, the climatic zone, the timing of planting crops, and competent agricultural technology matter. But the most important is the composition of the soil mixture.
Knowing the constituents of the soil, fertilizers and appropriate care for the planted plants are easily selected. Russian summer residents most often encounter such types of soils as: sandy, sandy loam, clayey, loamy, peaty-boggy, calcareous and black soil.
In their pure form, they are quite rare, but knowing about the main component, one can draw a conclusion about what this or that type needs.
Sandy
The easiest to handle. Loose and free-flowing, they admit water remarkably, warm up quickly, and let air through to the roots well. But all positive qualities are negative at the same time. The soil quickly cools and dries up. Nutrients are washed out during rains and during irrigation, go into deep soil layers, the earth becomes empty and barren.


To increase fertility, several methods are used:
- the introduction of compost, humus, peat crumbs (1-2 buckets for spring-autumn digging per 1 sq. m of the plot) mixed with clay flour;
- sowing siderates (mustard, vetch, alfalfa), followed by embedding of green mass in the ground during digging. Its structure improves, it is saturated with microorganisms and minerals;
- creation of a man-made "clay castle". The method is laborious, but it gives quick and good results. In place of future beds, a layer of ordinary clay, 5-6 cm thick, is crumbled. A mixture of compost, sandy soil, chernozem, peat chips is placed on top and ridges are formed. Clay will retain moisture, the plants will be comfortable.
But already at the initial stage of the cultivation of sandy soils, it is possible to plant strawberries on them, pouring humus or compost under each bush. Onions, carrots and pumpkin seeds thrive on such lands. Fruit trees and berry bushes grow without problems on sandstones. In this case, it is necessary to correctly fertilize the planting pit.
Sandy loam
Sandstones are as easy to cultivate as sandy soils. But they have a much higher content of humus and binding components. Clay components retain nutrients better.
In composition, sandy loam soils differ slightly, depending on the area of the site, but the main characteristics correspond to the name. They warm up quickly, but cool down more slowly than sandy ones. They retain moisture, minerals and organics well.


This species is optimal for growing horticultural crops. But still, do not forget about the introduction of mineral fertilizers, compost and humus, which provide plants with everything they need for normal growth, development and fruiting.
Do not forget about the renewal of the soil layer, periodically, once every 3-4 years, sow green manures on free plots. They contribute to an increase in soil fertility, cleaning it from many viral diseases and parasites.
Growing zoned varieties on sandy loam soil and observing agricultural techniques appropriate to the climatic zone, it is possible to get excellent yields from the summer cottage.
Clayey
Considered heavy soils, difficult to cultivate. In the spring they dry and warm up for a long time, hardly letting air through to the roots of plants. In rainy weather, moisture is poorly passed through, in a dry period the earth resembles a stone, it is difficult to loosen it, as it dries up.
By purchasing such a site, it must be domesticated over several seasons, making:
- compost (humus) - 1-2 buckets per sq. meter of beds annually, to increase fertility;
- sand to improve the transmission of moisture into the ground, up to 40 kg per sq. plot meter;
- peat chips to improve soil looseness and reduce clay density;
- lime and ash are added without restriction;
- once every 3-4 years, green manures are sown on free plots, followed by incorporation of green mass during digging.
Fruit trees and berry bushes, with their powerful and branched roots, tolerate clay soils well, provided that the planting holes are properly prepared.


During the cultivation of the site, you can plant potatoes, beets, Jerusalem artichoke, peas on it. The rest of the vegetables are planted on high ridges or ridges. So the roots will warm up well, and the earth dries out faster after the spring stagnation of moisture.
All planted plants are periodically loosened and mulched. Loosening is best done after rains or watering, until the ground is covered with a hard crust. Mulch with chopped straw, old sawdust or peat chips.
Loamy
Loams are ideal for growing all horticultural crops. Due to its optimally balanced composition (60-80% impurities and 40-20% clay), it is easy to process. The advantage is that loams have a balanced content of mineral and nutrients, which allows them to maintain normal soil acidity.
After digging, the fine-grained structure remains loose for a long time, passes air well to the roots of plants, quickly warms up and retains heat. Clay components retain water for a long time, without stagnation, and maintain soil moisture.


Due to the fact that it is not required to domesticate loams, all garden crops feel good on them. But do not forget about the introduction of organic matter for the autumn digging and mineral dressing of the plants planted in the spring. To preserve moisture, all plantings are mulched with old sawdust, peat chips or chopped straw.
Peat boggy
Plots cut in peat boggy areas require domestication. First of all, it is necessary to carry out reclamation work. Put on must be ditched for moisture outflow, otherwise, over time, the gardening partnership will turn into a swamp.
The soils in such areas are acidic, therefore they require annual liming. In terms of composition, the soil is sufficiently saturated with nitrogen and phosphorus, but it is not suitable for growing cultivated plants, since it is not assimilated in this form.


To improve the fertility of the site, he needs sand, fresh slurry, a large amount of humus or compost, for the rapid development of microorganisms that improve the condition and structure of peat-boggy soil.
To lay out the garden, special preparation of the planting pits is required. They include a cushion of a properly formulated nutritional formula. Another option is to plant trees and bushes on loose mounds. The height is not less than 0.8-1 m.
The method is used, as with sandstones, when the ridges are arranged on a "clay castle", and peat-boggy soil is poured on top, mixed with sand, humus or old sawdust, lime.
Bushes of currants, gooseberries, and black chokeberries are planted on uncultivated soils. Garden strawberries bear fruit well. With minimal care, consisting of watering and weeding, you can get a good harvest of berries.
The rest of the garden plants can be planted the next year after domestication.
Lime
The most unsuitable soil for gardening. It is poor in humus components; plants lack iron and manganese.
A distinctive feature is the light brown color of the soil, which includes many poorly broken lumps. If acidic soils require liming, then calcareous ones require leaching with organic matter.It is possible to improve such a structure with the help of fresh sawdust, which, moreover, acidifies the lime soil well.


The earth heats up quickly without giving up nutrients to the plants. As a result, young seedlings turn yellow, develop poorly and grow. Potatoes, carrots, tomatoes, sorrel, salad greens, radishes, cucumbers suffer from a lack of nutrients and a high alkaline environment. Of course, they can be grown with abundant watering, frequent loosening, mineral and organic fertilizing, but the yield will be much lower than on other types.
To improve the fertility and structure of the soil, humus is used, the introduction of a large amount of manure for winter digging. Sowing green manure with the subsequent incorporation of green mass into the soil will save the day and cultivate the area with limestone.
The application of potash fertilizers will improve the situation with fertility. Increase the acidity of nitrogen fertilization of plants with urea or ammonium sulfate, mulching after watering and fertilizing.
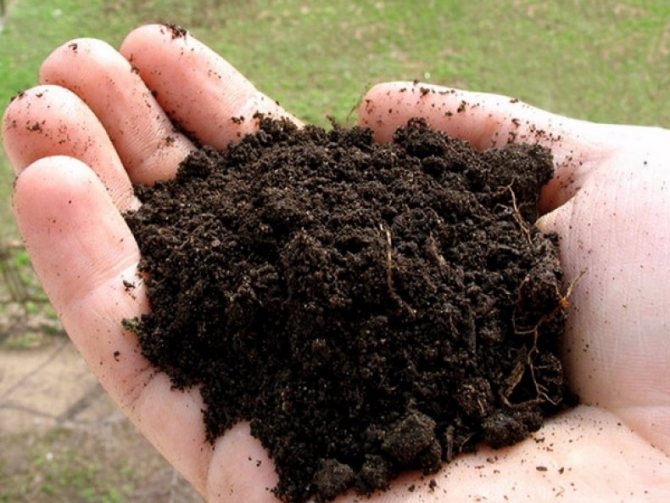
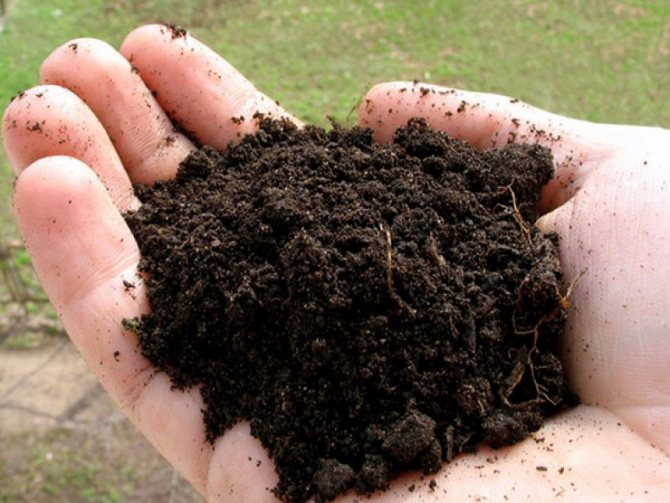
Chernozem
The standard of garden soil. In the middle zone of the country, areas with chernozem soils are extremely rare.
The grainy-lumpy structure is easy to process. It warms up well and retains heat, high water-absorbing and water-retaining properties enable plants not to feel drought.


The balanced content of humus and mineral and nutrients requires constant maintenance. Timely application of humus, compost, mineral fertilizers will make it possible to use the site with black earth soil for a long time. To reduce the density, sand and peat chips are scattered on the site.
The acidity of chernozems is different, therefore, in order to comply with the permissible indicators, a special analysis is carried out or guided by the weeds growing on the site.
Loamy soil
Loamy soil is the most suitable type of soil for growing orchard crops. It is easy to process, contains a large percentage of nutrients, has high air and water permeability, is able not only to retain moisture, but also to distribute it evenly over the thickness of the horizon, and retains heat well. If you take a handful of such earth in your palm and roll it, you can easily form a sausage, which, however, cannot be bent into a ring, since it will fall apart when deformed.
Due to the totality of the available properties, the loamy soil does not need to be improved, but it is only necessary to maintain its fertility: mulch, apply manure for autumn digging (3-4 kg per 1 sq. M.) And, if necessary, feed the crops planted on it with mineral fertilizers. Anything can be grown on loamy soils.
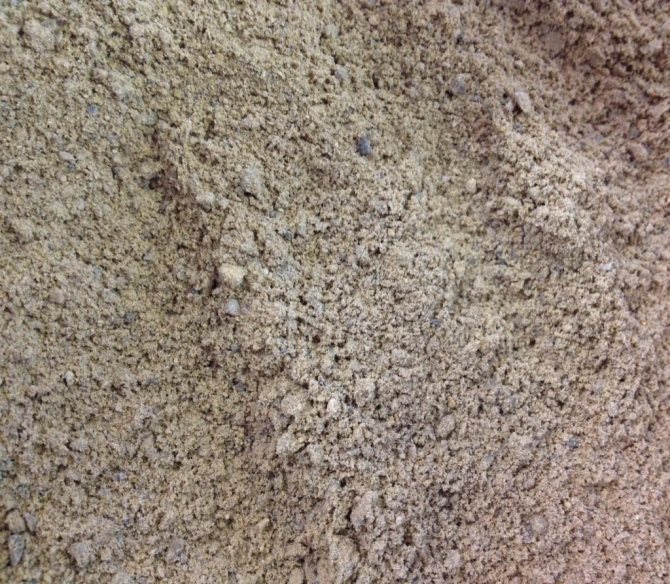


Calcareous soil. <>
Lime soil
Calcareous soil is classified as poor soil. Usually it has a light brown color, a large number of stony inclusions, is characterized by an alkaline environment, it quickly heats up and dries out at elevated temperatures, gives off iron and manganese poorly to plants, and can have a heavy or light composition. In crops grown on such soil, foliage turns yellow and growth is unsatisfactory.
To improve the structure and increase the fertility of calcareous soils, it is necessary to regularly apply organic fertilizers, not only for the main processing, but also in the form of mulch, sow green manures, and apply potash fertilizers.
Everything can be grown on this type of soil, but with frequent loosening of row spacings, timely watering and the thoughtful use of mineral and organic fertilizers. Weak acidity will suffer: potatoes, tomatoes, sorrel, carrots, pumpkin, radish, cucumbers and salads, so they need to be fed with fertilizers that tend to acidify, not alkalize the soil (for example, ammonium sulfate, urea).
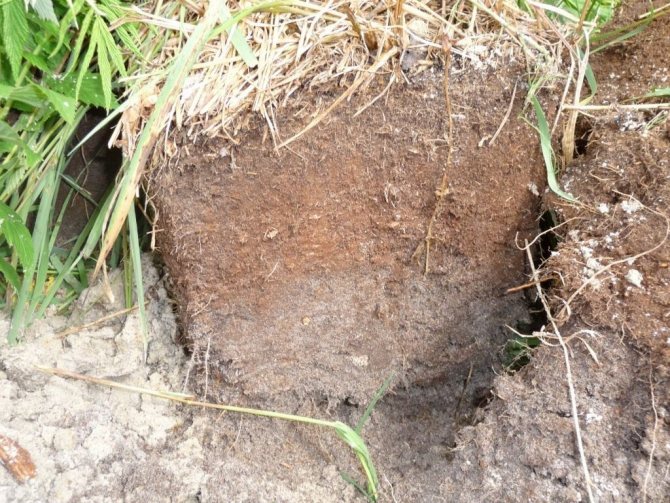


Medium decomposed peat horizon of sod-podzolic soil.
Natural areas of the world
Natural zones are natural complexes that occupy large areas and are characterized by a general type of landscape. The climate has a great influence on their formation, with the peculiarities of the ratio of moisture and heat.
The main characteristic of any natural zone is the unique plants and animals that inhabit this territory, but, above all, the unique composition of the soil.
The structure of the soil, the characteristics of its origin and the level of fertility underlie the soil classification.
Swampy soil
Swampy or peaty soils are also used for the breakdown of garden plots. However, it is rather difficult to call them good for growing crops: the nutrients they contain are not readily available for plants, they absorb water quickly, but they give up just as quickly, they warm up poorly, and often have a high acidity index. On the other hand, such soils retain mineral fertilizers well and are easily amenable to cultivation.
To improve the fertility of marshy soils, it is necessary to saturate the earth with sand (for this, it is necessary to carry out deep digging so as to raise the sand from the lower layers) or clay flour, in especially acidic versions, apply abundant liming, take care of increasing the content of beneficial microorganisms in the earth (apply manure, slurry, compost, do not bypass microbiological additives), do not forget about potassium-phosphorus fertilizers.
If you lay a garden on peat soils, then it is better to plant trees either in pits with soil individually laid for culture, or in bulk hills, with a height of 0.5 to 1 m.
Carefully cultivate the land under the garden, or, as in the version with sandy soils, lay a clay layer and pour loam, organic fertilizers and lime mixed with peat on it. But if you grow only gooseberries, currants, black chokeberries and garden strawberries, then you can do nothing - just water and weed out the weeds, since these crops on such soils are successful without domestication.
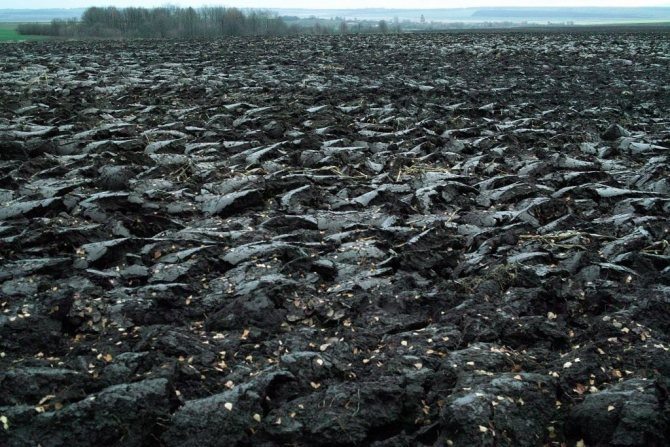


Chernozem. <>
Bog and peat - bog soils. Drainage of the site


And now, finally, you have acquired a piece of land. We went with trepidation to look at our property! They looked and their hands dropped. We thought with regret: there is so much good land in the country. Why did you get this miserable piece of swamp! And now what to do with it! Do not be discouraged for a long time, but get down to drainage of the site.Bog and peat - bog soils not the worst soil! How to drain over a damp area has already been described in the article on clay soils. Let me remind you briefly. You need to put on rubber boots, take a shovel (mechanization will hardly be possible to use) and dig a net
grooves along and across the section. They must be arranged so that the water is diverted outside the site. Later, when the area is drained, drainage can be arranged in part of the grooves. To do this, use chopped dry branches, crushed stumps, sprinkled with gravel or coarse sand. Leave the grooves open only around the perimeter of the area. By the end of summer, when the water and soil come down
dries up, you can finally start to improve the soil. Just as in the case of clay soils, sand is added to peat soils, and also clay. This will improve the structure of the soil. Clay is applied dry, ground into powder. At the same moment, lime is added, since peat on boggy soils is usually acidic.
- For 1 sq.m. 1 bucket of sand and clay is introduced.
- Lime for 1 sq. m. is applied from 0.3 kg to 1.5 kg, depending on the acidity.
After that, the site is shallow, up to 18 cm, dug up. Later, during the main processing, manure, humus or garden soil are introduced.
- Manure is applied in small doses - 1 kg / sq. m, since peat is rich in organic matter, and manure or humus is introduced in order to start the process of its decomposition with the help of bacteria.
Mineral fertilizers must also be applied, since there are few trace elements in peat soils. Copper and boron are especially low. Over time, when using the site, the peat layer gradually decreases. This is due to the fact that organic residues are mineralized, they become less and the soil is compacted. There is a poor soil layer under the peat layer, in
which contains an increased amount of iron, manganese, aluminum, etc., which is harmful to plants. It is not worth digging it up together with peat. If there is a layer of sand under the peat, then during digging it is captured, about 1/3 of the peat layer. And the clay under the peat, every time they add 2-3 cm. This is how they develop bog and peat-bog soils.
Chernozems
And, of course, speaking of soils, it is difficult not to mention black soil. On our summer cottages, they are not so common, but deserve special attention.
Chernozems are soils of high potential fertility. Stable granular-lumpy structure, high humus content, high percentage of calcium, good water-absorbing and water-retaining capacity allow us to recommend them as the best option for growing crops. However, like any other soils, they tend to deplete from constant use, therefore, in 2-3 years after their development, it is recommended to apply organic fertilizers to the beds, sow green manures.
In addition, chernozems can hardly be called light soils, based on this, they are often loosened by adding sand or peat. They can also be acidic, neutral and alkaline, which also requires adjustment.
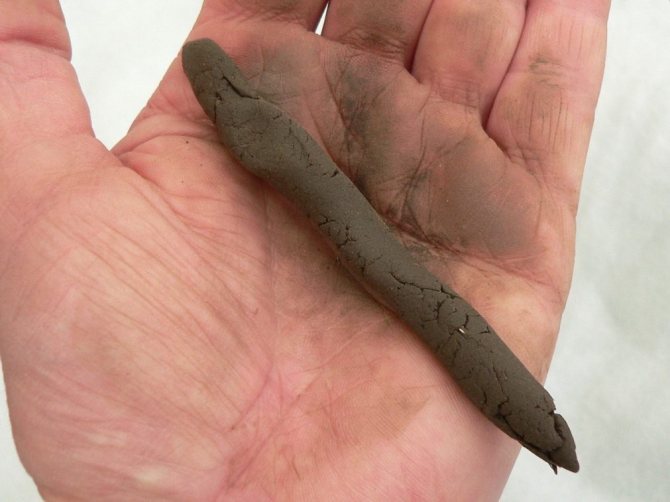


Chernozem.
To understand that you really have black soil in front of you, you need to take a guest of the earth and squeeze it in your palm, a black bold imprint should remain on your hand.
Some people confuse chernozem with peat - here, too, there is a method for checking: a wet lump of soil must be squeezed out in the hand and placed in the sun - the peat will dry out instantly, while chernozem will retain moisture for a long time.