Cucumbers are parasitized by 2 types of pathogenic fungi that cause diseases with a similar name. Both diseases are extremely harmful and affect greenhouse cucumbers more often than ground cucumbers. Powdery mildew sometimes appears in the open field, but downy mildew on the street is rare.
Features of the disease

Treatment should be started at the first sign of illness. Photo: What does the disease look like, how it develops:
- Downy mildew or downy mildew of cucumbers - an infection caused by the pseudo fungus (mycoid) Pseudoperonospora. It affects all groups of cultivated plants, but pumpkin seeds are the least resistant. Pseudo-fungi parasitize on stems and leaves, very rarely infect flowers and fruits.
- Spores do not die in the soil in winter. When warmth comes, they are carried by the wind, insects. Easily fall into the ground with seedlings contaminated with seeds.
- Falling on a plant microscopic organisms penetrate into the pores through which gas exchange with the environment takes place, and begin to multiply rapidly. The overgrown mycelium picks up moisture and trace elements from the stems and leaves. The plant begins to die.
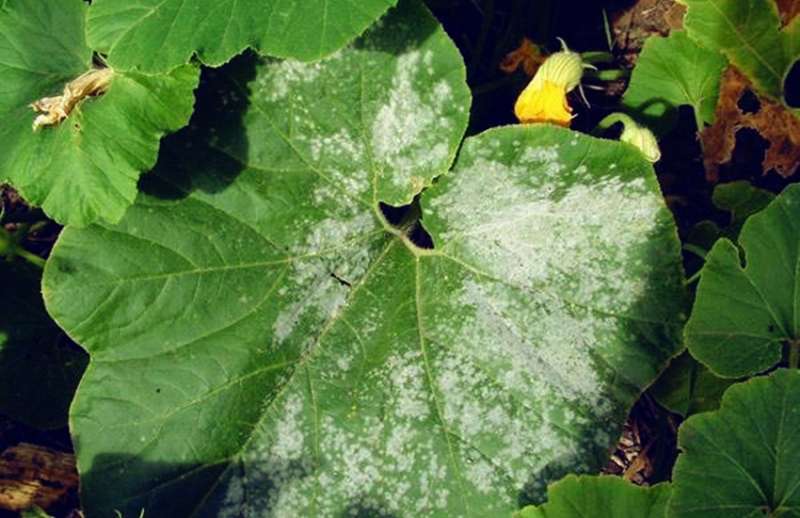
- The first signs of infection - yellow dots on the outside of the leaves. If the conditions for the development of the fungus are favorable, the spots grow rapidly and turn brown. A grayish bloom with black blotches appears on the inside of the leaf plate - these are fungal spores. Then the leaves turn brown and dry.
- The fungus may not manifest itself for a long time. But with the onset of conditions favorable for its development (high humidity, temperature drops), it can destroy the plant in 3 days.
- You need to start treating plants immediately. The late stages of the disease are not amenable to treatment even with chemical drugs. In this case, the cucumbers are dug up and burned to prevent infestation of other bushes.
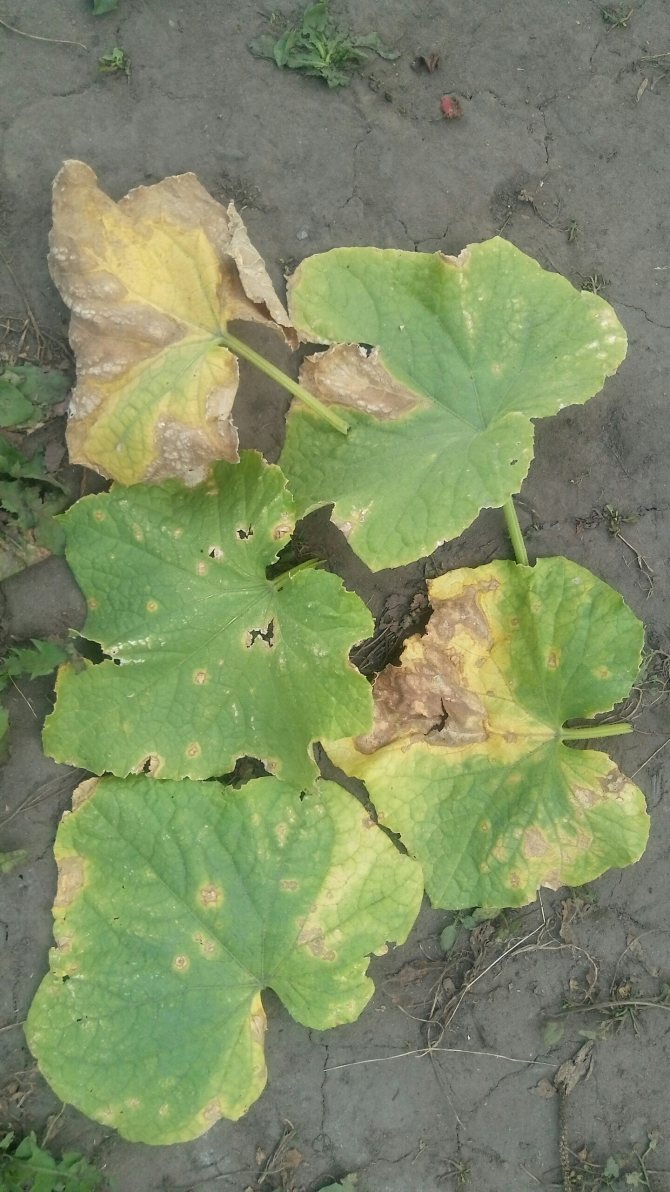


In 70% of cases, downy mildew affects crops grown in greenhouses.
The author of the video tells what needs to be done to prolong the yield and save the plants:
Who is guilty?
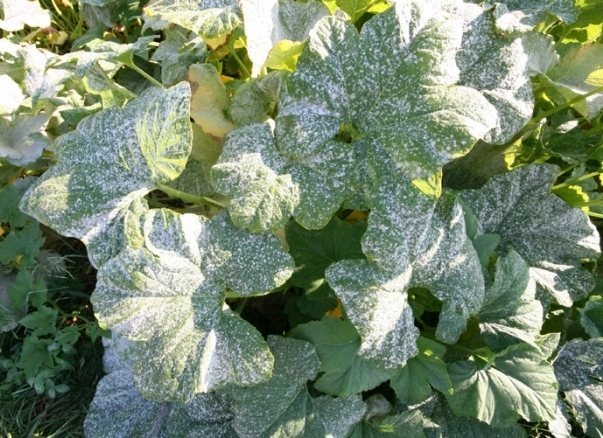
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease. The spores that cause it are passed from one plant to another. Infected parts of plants become covered with a whitish bloom, as if a little flour was sprinkled on a leaf. Over time, the "flour" becomes more, and the leaf itself withers, turns yellow and soon dies off. The first to suffer are those leaves that are closer to the ground, gradually the infection moves upward, capturing the entire plant as a whole, affecting not only the leaves and their petioles, but also flowers, ovaries, fruits. If the disease is not stopped in time, then most of the crop perishes, and the surviving fruits develop poorly, their taste is spoiled.


Apply chemicals
Before processing, it is imperative to remove all deformed leaves and burn them. If the plant is severely affected, it is dug up and destroyed.
How to process:
| Biofungicides Alirin-B, Gamair, Fitosporin-M, Planriz are most effective against downy mildew:
|
| Fungicides Long-acting chemicals that suppress the development of the fungus - Raek, Topsin, Topaz, Fundazol, Skor:
|
How to prevent infection
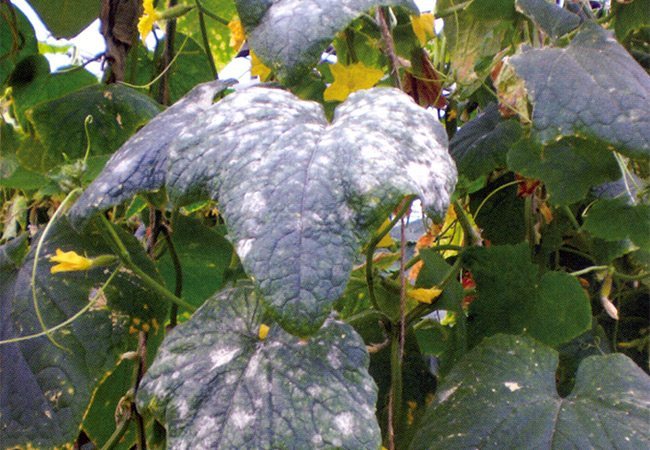


Better than any treatment is prevention. Some advise growing hybrid varieties of cucumbers that are not susceptible to powdery mildew and peronosporosis, but, unfortunately, guaranteed resistance to these infections has not yet been obtained.
What to do to reduce the likelihood of developing fungal diseases in cucumbers in the summer:
- disinfect open ground or in a greenhouse before sowing with an aqueous solution of a complex of active iodine with Pharmayod;
- prepare the soil in advance, clear the site of weeds and diseased crops;
- helps the use for seedlings of those seeds that have been stored for several years (if there was a fungus, it dies);
- some specialists process seeds in thermostats;
- change landing sites every season;
- in greenhouses, observe the temperature regime and monitor the optimal ventilation regime;
- after harvesting, the seeds are soaked in a concentrated solution of potassium permanganate.
Thus, by carefully preparing the soil and the greenhouse for planting cucumbers, and carefully monitoring the growth of the crop, you can reduce the likelihood of powdery mildew or neutralize it at the very first signs.
Reviews of gardeners
Evgeny
Downy mildew at the initial stage can disguise itself as other diseases (powdery mildew, chlorosis, bacteriosis ...), but one thing is invariable: a grayish-violet felt plaque forms on the lower side of the leaf, on which dark dots are distinguishable.
In our country house, local old-timers are saved from such an infection in the following way. They take a liter of kefir 1%, it stands in the room for a day, then it is diluted with a bucket of water and all this is poured onto the plant through a watering can.
Powdery mildew (ash)
This is perhaps the most common disease in greenhouse cucumbers. In protected ground, it spreads instantly and its harmfulness is enormous. In open ground, powdery mildew is less common, does not spread so rapidly, and therapeutic measures give a much greater effect than in a greenhouse.
Description of the pathogen.
- Powdery mildew on cucumbers is caused by the pathogenic fungi powdery mildew. Several strains of this pathogen can parasitize pumpkin seeds.


- The pathogen hibernates in the soil and on plant debris, where it can persist for up to 5-7 years.
- It affects cucumbers starting from the germination phase. Infection can occur during the entire growing season, but more often occurs in the second half of summer.
- Distributed with soil and water. During the sporulation period, spores can be carried by the wind.
Conditions for the onset of the disease
Favorable factors for the development of the disease on cucumbers are strong temperature drops - more than 10 ° C. High humidity contributes to the spread of powdery mildew. It spreads most strongly in damp summers. Even if the weather is hot, but rainy, with high humidity, the powdery mildew still affects the plants, though not so much than in a cold and damp summer. The first foci appear:
- in the greenhouse - at the doors, vents, film breaks;
- outdoors - in the wettest places of the borage. Most often, lesions appear a few days after heavy rainfall;
- thickened plantings, both in open and protected ground, are the first to be affected by powdery mildew.
The incubation period lasts 3-5 days, when the cucumbers are already infected, but there are no signs of the disease yet.
Signs of damage to cucumbers with powdery mildew


- Leaves, petioles and stems of cucumbers are affected.
- On the leaves, spots of white powdery bloom appear on the upper side, which are initially easily erased from the surface. But after a few hours they appear again.
- The spots gradually merge with each other, the edges of the leaves are slightly bent downwards and dry.
- Severely affected leaves become wavy, dry and fall off.
- With widespread powdery mildew, the stems are affected. Pads of white fluffy bloom appear on them, but not as thick as with white rot. The lashes begin to dry.
Zelentsy do not get sick with powdery mildew, but the yield when affected by the pathogen decreases by 40-50%. The greens themselves become small and bitter.
Fighting disease with chemicals
Processing is carried out immediately upon detection of the first signs. It should be taken into account that the infection of healthy plants occurs rapidly, and the slightest delay can lead to a shortage of crops and the death of plants.
- Colloidal sulfur - the main drug against powdery mildew - is not used in the greenhouse. In a greenhouse, where the temperature and humidity are high, even a normal concentration of the drug can cause severe burns to cucumbers, and if the concentration is exceeded, even slightly, the plants can be destroyed. In the open field, treatment with sulfur preparations is best done in cloudy weather. Prepare a working solution strictly according to the instructions. When processing sulfur and its derivatives, the air temperature should be at least 20 ° C and not more than 32 ° C. At low temperatures, the drugs will not work, at high temperatures they are phytotoxic, that is, they kill plants. Colloidal sulfur is sold in garden stores in its pure form, a preparation based on it - Tiovit Jet. All pumpkin crops and cucumber, in particular, are very sensitive to sulfur, so a one-time treatment is carried out. It is impossible to spray cucumbers with sulfur-containing preparations several times during the growing season.
- Application of fungicides: Raek, Tilt, Topsin-M, Topaz, Bayleton. Re-treatment is carried out after 14 days, changing the drug, since the pathogen very quickly becomes resistant to drugs.
- At an early stage, the biological product Alirin B is used. The soil bacteria contained in it at the earliest stage are capable of destroying the pathogen. It is usually used if there is a high risk of developing the disease. Processing is carried out 2-3 days after heavy rains.
Folk remedies
Used for the prevention and treatment of the initial stage of the disease.
- When the first signs appear or with sharp fluctuations in day and night temperatures, cucumbers are treated with an alcohol solution of iodine (sold in pharmacies). The iodine solution contains alcohol and iodine. Iodine is an antiseptic and causes the death of pathogenic microflora, alcohol is also an antiseptic, it suppresses the development of a pathogen, although it does not kill it. 10 ml of 5% iodine solution is diluted in 10 liters of water.

- Spraying cucumbers with a strong raspberry solution of potassium permanganate. It is a strong disinfecting agent and prevents the penetration of the pathogen into plant tissues, and at the initial stage it kills germinating spores of the fungus.
- Preventive treatment of cucumbers with kefir (1 l / 10 l of water). Lactic acid bacteria are antagonists of pathogenic microflora and prevent its growth and spread.
- Using soda ash. The drug has a strong alkaline reaction, which parasitic fungi cannot tolerate. Preparation of a working solution: 50 g of soda ash is diluted in 10 liters of water, 40 g of soap is added there as an adhesive. Processing is carried out with a freshly prepared solution. Sick plants are treated every 7 days in cloudy weather.For the prevention of powdery mildew, cucumbers are sprayed 2-3 times during the growing season.
With any method of treatment, all affected leaves must be removed.
Disease prevention
- If powdery mildew appears in the greenhouse from year to year, then a layer of earth of at least 10 cm is removed, replacing it with a new one.
- All plant residues are removed in autumn.
- The greenhouse is disinfected by setting fire to sulfur bombs in it, or the structures are washed using disinfectants.
- Thinning of thickened crops, since it is there that the first foci of the disease most often appear.
- Thorough ventilation of greenhouses. Reducing humidity also reduces the risk of powdery mildew.
- Removing weeds around the perimeter of the borage.
Powdery Mildew Resistant Varieties
At present, a sufficient number of them have been bred, both hybrids and bee-pollinated varieties. Resistance means that cucumbers are not affected by the small spread of the pathogen. With a strong outbreak of the disease, only individual leaves on a cucumber are affected, while the bulk of the cucumbers does not get sick.
| Powdery Mildew Resistant Hybrids | |
|
|
| Varietal bee-pollinated cucumbers with disease resistance | |
|
|
Signs of the disease
Peronosporosis fungi feed on plant sap and plant nutrients.
A sign of their settlement on cucumbers is the appearance of yellowish oily spots of various shapes on the leaves.
On the underside of diseased leaves, plaque (spore accumulations of the fungus) is observed, which during the incubation period changes its color and can be white, gray or with a purple tint.
The peak of abundant sporulation occurs already on the 5th day, and the death of the plant may occur on the seventh day.
Over time, focal lesions grow in diameter, capturing the central vein. The damaged leaf changes color to red-brown, dries up and falls off.
Stems of diseased plants crack and deform. The areas affected by the fungus acquire a faded color and become limp.
The first signs of the disease are often confused with the symptoms of black spot. But unlike a fungus, the bacterium leaves not spores on the lower part of the leaf, but a yellow exudate.
Signs in the later stages:
- inflorescences turn black and deform
- damaged fruits stop in growth and development, in most cases do not ripen
- ripe fruits lose their bright color, become pale and lose their usual taste.
- infection (albeit less frequently) affects the cotyledons.
Conditions for growing cucumbers and caring for them
The preparation of the garden for cucumbers in the greenhouse and in the open field begins in the fall. All debris and plant residues are carefully removed, the walls of the greenhouse are washed with a disinfectant solution.
In a greenhouse, it is better to completely replace the top layer of soil 5-7 cm thick, it is in it that the bulk of pests and pathogenic bacteria are contained. Mullein, humus, wood ash are added to the garden bed, after which the earth is dug up together with fertilizer. During spring preparation, the soil is loosened and additionally fertilized with minerals, adding 2 tbsp for each square meter. l. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. l. urea and potassium sulfate.
On a note! The soil for this culture must be permeable and nutritious at the same time, have a slightly acidic reaction. It is recommended to place a garden bed on a bright, level place, where there are no winds and a lot of sun.
After that, the bed is watered and covered with a film for 5-6 days. During this time, fertilizers will be evenly distributed in the soil, and the earth itself will warm up. Seedlings should be planted when the soil temperature reaches 14-15 ° C. In the open ground of the middle lane, landing is carried out in the second half of May, after the threat of frost has disappeared. For the greenhouse, this period is shifted two weeks earlier. By this time, the plants should have four formed leaves.
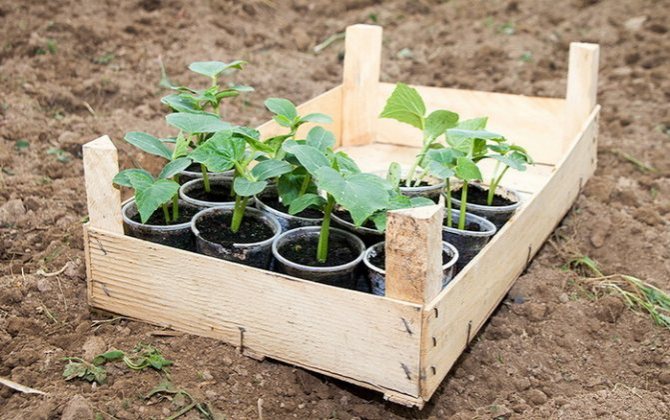


Planting seedlings of cucumbers
Bushes are planted at a distance of 30-40 cm from each other, leaving 50 cm between rows. A little organic matter, yeast solution, mineral fertilizers can be added to the hole before planting. After planting, metal arcs are installed on the garden bed, which are covered with a film for the first week to create a warm and humid microclimate.
Cucumber care is as follows:
- regular watering;
- top dressing;
- loosening;
- formation.
Immediately after planting seedlings grown at home, the plants are not fertilized, the root system is allowed to take root thoroughly. The soil still contains a sufficient supply of nutrients. After 1-1.5 weeks, the first feeding is carried out, consisting of mullein infusion (0.5 liters per bucket of water). In the future, you can alternate organic and mineral fertilizers. In total, cucumbers are fed 3-4 times per season.


Feeding cucumbers
Watering is done often, cucumbers are very fond of moisture. In this case, you need to take into account the weather conditions. If the air temperature drops to 15 ° C, the bushes temporarily stop watering. Watering should be done before 4-5 pm, then the moisture on the leaves will have time to dry before nightfall.
Advice! On hot days, it is recommended to moisten the cucumber garden using the sprinkler method. The rest of the time, it is better to water the cucumbers in the grooves so that the water does not erode the roots.
The formation of plants makes it easier for the summer resident to care for them. The method of tying to trellises is gaining popularity every year. While the plants are young, they need loosening. This must be done carefully, to a depth of no more than 4 cm, so as not to damage the roots. Loosening is carried out immediately after watering, at the same time doing weeding. Compliance with agricultural technology will save plants from many diseases.
Advice! Cucumbers that require pollination in the flowering phase are useful to spray with a honey solution to attract insects. You can prepare "honey water" by adding 1 tbsp. l. honey per liter of warm water.
























