Sweet pepper, like a true southerner, does not tolerate the climatic conditions of central Russia and higher latitudes too well.
In order not to be left without a crop due to sudden cold snaps, they successfully cultivate pepper in a polycarbonate greenhouse.
General recommendations
To grow a plant in a covered garden, you must:
- Prepare the soil Fertilize, apply phosphorus fertilization. Then humus in proportions of 10 liters. solution for 1 sq.m.
You cannot use manure! In pepper, it causes a drop in yield.
- Before planting small seedlings, warm up the greenhouse and the ground with the help of natural heat, heaters.
- Saplings survive better if the seeds are grown in glasses of peat.
- Greenhouse peppers require maintenance. It is important to follow the recommendations for watering, feeding, seating scheme.
Planting peppers in a greenhouse has advantages: thick walls of an artificial greenhouse protect seedlings from wind, frost, and excess moisture. The double material scatters the light, in this case the sun does not burn the leaves, but evenly illuminates the room.


Varieties
The following types of overseas vegetables are prepared for greenhouse growing conditions:
| Variety | Characteristic |
| Claudio | Ripens 73-76 days after planting, is not susceptible to fungi, perfectly tolerates heat, small frosts. |
| Cow's ear | Elongated fruit, weight - 120 -140 g. Seedlings are transported without loss of properties. |
| Atlant | A highly fertile hybrid, the shape of the fruit is conical. Stores well, freezes. |
| Cockatoo | Fruits are large in size, weighing up to 500 grams, red. The height of the bush is about 60 cm. |
| Winnie the Pooh | Not capricious, has good immunity. The fruits are well stored, transported, have excellent taste, contain vitamin C. |
| Health | Growing and caring for this pepper in a greenhouse is easy. He is unpretentious to light, watering. Produces a high yield. |
| California miracle | Fruits ripen in 100 days from the date of transplanting pepper seedlings. Vegetable mass up to 140 gr. |
| Orange miracle | Fruit color is orange, resistant to frost. Used for the seedless method. |
| Hercules | Early ripening, ripening takes 3 months from sowing, the shape of the fruit is cubic, shade green, red. |


Three components of success
It is grown on personal plots a lot and with pleasure, experimenting with varieties, methods and planting site. But the highest yields are obtained by those who grow peppers, observing three conditions.
- Growing through seedlings.
- Growing in a greenhouse.
- The correct choice of variety.
Choosing the right variety is important for several reasons. Different varieties not only have different color, taste, size, shape, weight. They also ripen at different times and the growing season is different for them.
Peppers are bred today:
- long and narrow;
- plump and wide;
- like balls;
- like cones;
- curved in the form of a prism.
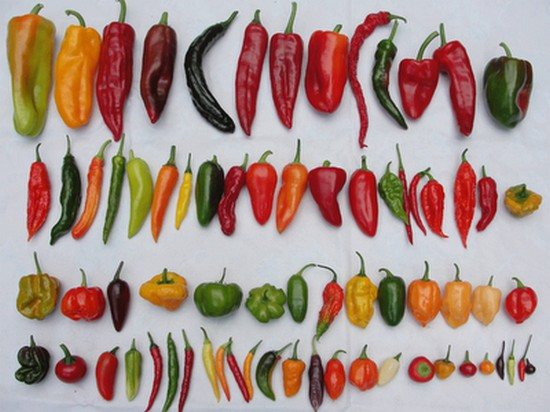


Pepper types
Their weight can be in the range from 5 to 300 g. And the color palette even includes shades of blue-violet and black-brown.
Seedlings can be grown for all varieties of vegetable peppers, but peppers with a long growing season especially need this method of agricultural technology. Like many garden crops, peppers have three large groups, classified according to their ripening times:
- early ripening;
- mid-season;
- long-ripening.
In the conditions of our not the hottest summer, cool spring and rainy autumn, it is ideal to grow pepper seedlings in a greenhouse, even if it is an ultra-early ripening variety. It is desirable to choose a greenhouse from polycarbonate. The old film structures have long been replaced by durable, lightweight structures with a polycarbonate coating that completely protect plants and maintain an optimal microclimate.


Polycarbonate greenhouses protect plants and maintain an optimal microclimate
The most popular greenhouse peppers
Of course, there are peppers that are most suitable for greenhouse cultivation. There are many of them, but some are especially popular. Tested by more than one generation of gardeners, these varieties have firmly taken a leading position. When buying seeds, most summer residents prefer them.
| Name | Description |
| Sweet vegetable varieties | |
| "Alyonushka" | Hybrid mid-early. Pyramidal shape in the fetus, intense red color |
| "Orange miracle" | Hybrid variety with early ripeness. Pepper color - dazzling yellow, cubic shape |
| "California miracle" | Medium early ripeness. Fruit - prism, bright scarlet |
| "Buratino" | Ultra early maturing. The shape is conical, highly elongated. Muted red color |
| "Swallow" | Medium ripeness, red-fruited, cone-shaped fruit |
| "Winnie the Pooh" | Pretty early. The shape is also a cone, but shortened. Color yellowish red |
| "Negociant" | Hybrid early maturing. Prismatic fruitlets of burgundy-red color |
| "Night" | Hybrid, medium ripeness. Pyramid fruits. Dark red coloration |
| "Tenderness" | Very early, with a very juicy and tender middle. The fruit is a pyramid. Color - light red |
| Spicy varieties | |
| "Elephant trunk" | Average ripening time. The fruits resemble a trunk, drooping and long. Classic red color. Medium pungency |
| "Astrakhansky" | Mid-season, very spicy variety. Pyramidal shape, deep red color. The pulp is tough, coarse |
Temperature regime
A polycarbonate greenhouse installed in the yard provides conditions for this due to good light transmission and heat retention inside.
To get a good harvest, you need to maintain the following temperature regime:
- The temperature for pepper seedlings - inside the greenhouse is not lower than + 22 ° С and + 14 ° С - on the ground.
- For rapid growth, a temperature of 27-28 ° C is required.
- A decrease in temperature to a minimum (14-16 ° C) will not cause the death of seedlings, but will lead to wilting, cessation of growth.
Sowing dates for pepper
Due attention is paid to the timing of the sowing of seeds. After all, this will affect the further growth and development of the crop.
For the correct calculation of the timing, you need to take into account the variety of grown peppers:
- it takes 60 days before the day of transplanting for early maturing varieties;
- about 75 days for mid and late ripening varieties.
Important! Many gardeners take into account the lunar calendar when sowing, but the scientific fact of the influence of the moon on the growth of planted plants has not been confirmed.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that when diving seedlings, the period of its development will lag by about 10 days.
Soil preparation
Planting pepper seedlings in a polycarbonate greenhouse requires soil preparation. The soil is ennobled in advance, the first time in the fall, then in the spring. For this:
- Dig in, saturating with fertilizers.
Observe the dose of organic matter: 5 kg per 1 sq. M.
- In April-May, the site is dug up again, fertilizers are applied.
Add phosphorus and potassium: 40-50 g per sq.m. Or humus.
- Before planting seedlings, they loosen the ground, dig holes, fill them with water.
The beds are heated to a minimum temperature of 15-18 ° C. Better up to 23-25 ° C.
Remember to ventilate the greenhouse and periodically loosen the ground until the plants take root. This saturates the soil with oxygen and increases resistance to disease.


Growing healthy seedlings
How to grow seedlings? Peppers, like many other crops, are grown using seedlings. In terms of time, the material is sown in the first - second decade of March. First of all, you should prepare the necessary components, namely:
- Taru - it is best to use boxes made of wood.
- Saturated Soil - Experienced growers find a moist compost mixture to be the best option, as these vegetables are very demanding to get a complete diet.
- Purchased seeds.
The selected soil is evenly distributed over the containers, and the planting material is sent to soak in a stimulant solution overnight. Next, the seeds are washed with clean water and placed on a pre-moistened material.


Small depressions of about 1.5 cm are created in the ground and the seed is spread. Peppers are sown according to the 2x2 scheme. The pits are then covered using dry compost and placed under film or glass, thereby creating a greenhouse effect.
In this form, the seedlings are left until they give the first shoots. This usually takes 2-3 weeks. During this period, the soil must be watered periodically, avoiding waterlogging or drying out.
In the room where the sown pepper is located, there should be the correct temperature regime - about 20-21 o C. After a while, when the seedlings grow and become strong, they need to be cut down. It is recommended to use pots with a diameter of up to 20 cm as containers, so the roots of plants can fully develop.
Do not forget to keep a distance, from one pot to another there should be a gap of about 40 cm. Temperature is also important, optimal indicators are 18–20 o C, no less. Young seedlings need good lighting, when they do not receive solar energy, the plantings stretch and turn pale.
It is necessary to contain sweet peppers in accordance with all the rules and regulations. It is imperative to water and fertilize the soil. When the cultivation technology is strictly followed, vegetables develop and branch quickly.
However, an excessive set of greenery on the bushes should be prevented. From the moment they grow more than 10 cm in height, you should get rid of the apical bud - pinch. This procedure will help in the correct formation of plants. Future fruiting depends on how well the side shoots grow. The more there are, the more abundant the harvest.
If you prefer to cultivate tall varieties, build a support for them by tying them to pegs, otherwise the bushes will break from the weight of the vegetables. Now let's look at the technique of growing and caring for bell peppers in a greenhouse.
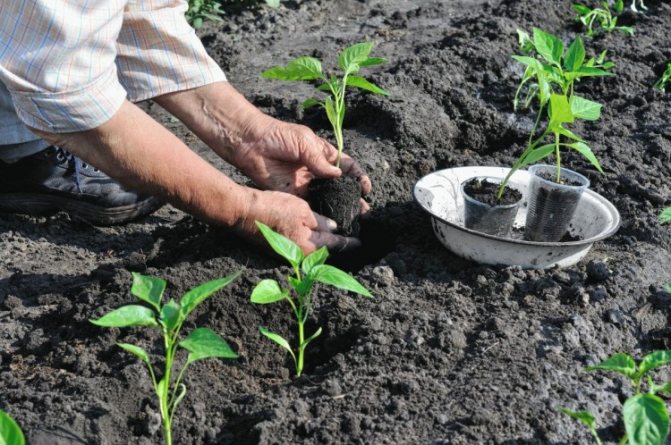
Disembarkation scheme
To know exactly at what distance you can plant peppers in a greenhouse, you need to follow the planting scheme of bushes. Gardeners use different methods:
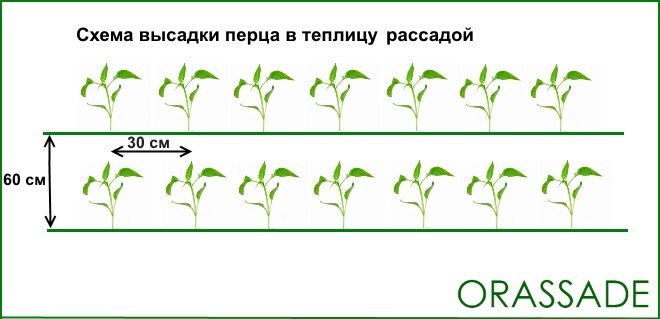
Seedling
It is considered the most popular and convenient. Row spacing - 70-60 cm, between seedlings - from 30 to 40 cm. The higher the plant, the more space it needs. As a result, it turns out that 1 sq. M. will accommodate from 3 to 5 bushes.
The hole is dug deep so that the seedlings with a clod of earth fit into it.
Before planting, pour 1 liter of water into the hole, wait for absorption and place the finished bush in the depression. You can put a piece of peat, humus inside the hole.

Seedless
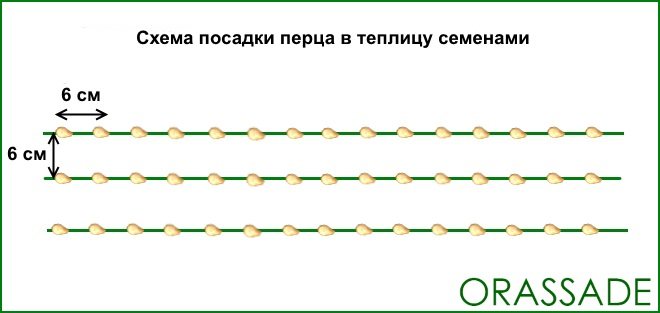
Seeds are planted in the ground. First of all, the root system develops in them. The seeds are pre-soaked in water with fertilizers. Ash, peat, nitrogen are added to the hole. Observe the planting density (6 cm by 6 cm) and depth (no more than 1 cm). Seedlings will appear in 14-16 days.
For the seedless method, prepare the soil in advance in October. Warm up the soil to 22 ° C.

Bush
This is a method of planting two bushes in one hole. Not suitable for greenhouses and cold climates. Plants are infected with fungi from each other, give a reduced yield.
Selection of materials for planting
Suitable varieties for growing in a greenhouse:


- parthenocarpic: do not need pollination;
- compact, but tall: planting spreading bushes, due to limited space, would be irrational;
- early and mid-early, if the greenhouse is unheated and is located in central Russia or to the north;
- with any ripening period, if heated.
Seeds are planted up to 2 years old - the older ones lose their germination.
They act in the following sequence:
- having dissolved table salt in water at the rate of 40 g per liter, the seeds are dipped into it. After waiting 10 minutes, the floating seeds are thrown away - they are unusable, the rest are washed and dried;
- soak the seeds for half an hour in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate. As a result, the pathogens on them are destroyed;
- after washing the seeds, immerse them in a growth stimulator. Soaking time depends on the type of stimulant and is indicated in the instructions for it;
- lay the seed on wet gauze and cover the same on top. Here the seeds hatch for several days.
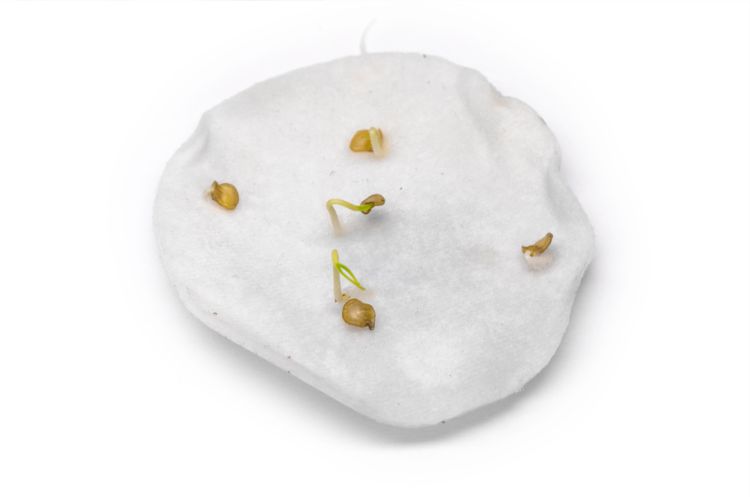


Sprouted pepper seeds
Sprouted seeds are ready to be planted in pots.
Peppers should not be planted next to beans, kohlrabi, or fennel. But tomatoes, eggplants, carrots, basil, onions, coriander, green manure plants are quite acceptable neighbors.
How to form a bush
Greenhouse peppers require care and proper bush formation. This will allow you to achieve a rich harvest. Competent pinching occurs according to the following rules:
- Agricultural work is carried out only on bushes that have grown up to 25 cm.
- The crown flower (first) must be removed mercilessly. This will help the vegetable develop other shoots.
- Create the skeletal base of the bush.
- To do this, collect powerful shoots, pinch the rest, cut them off.
- Skeletal shoots develop and a primrose appears on them. Repeat the plucking procedure one more time.
- Treat the rest of the branches in the same way.
- Remove flowers inside the bush. They interfere, reduce yields.
This method of formation is suitable for tall plants. On undersized, only sluggish, weak shoots, diseased parts should be removed.
See tips on how to pinch peppers of the candidate of agricultural sciences Fursov Nikolai Petrovich. Please note that he advises leaving no more than 12-15 fruits on each pepper bush.
Watering
To achieve maximum yield, you need to know how to properly water the pepper in the greenhouse. Observe the following guidelines:
- Watering the planted bushes is done at the root.
- Do not use rain water. This leads to the sterilization of the seedlings.
- Do not allow the soil to dry out during flowering. The buds will wither, the fruits will turn out to be thin, small in size.
- Prefer drip irrigation.
- For one bush, increase the amount of water from 1 liter to 2 as it grows.
- Do not use cold water. It must be heated to a temperature comfortable for the plant of 22-24 ° C.
- Work in the morning.
- On cool days, water the pepper 2 times a week, 3-4 times in the heat.
- Mineral dressing can be added to the water 1-2 times a month. This will increase the plant's immunity and yield.
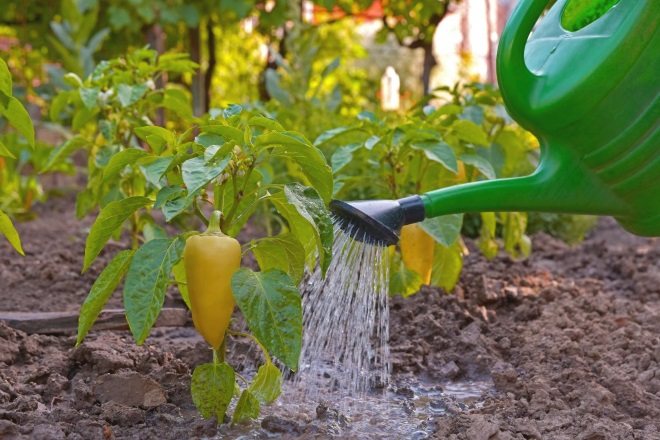
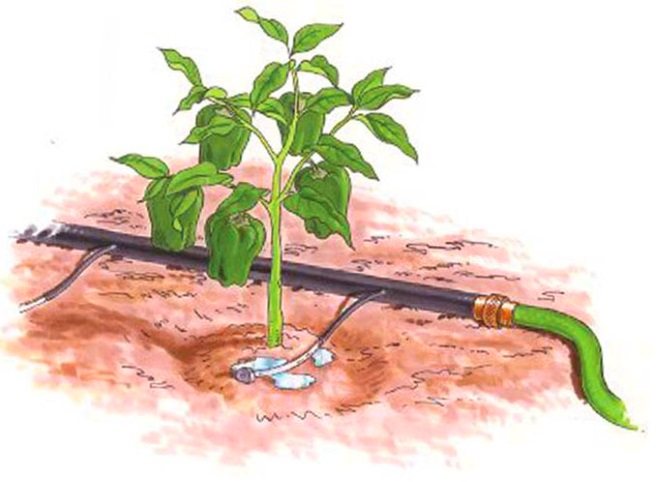




Automatic Polycarbonate Greenhouse Irrigation System
Top dressing
Many gardeners are wondering how to feed the pepper after planting in the greenhouse and during the period of active growth of the bush. There are several stages of fertilization:
- 3-4 weeks after planting the seedlings in the greenhouse. Superphosphate 5 grams mixed with 10 liters of water and 10 grams of urea is suitable. Pour 1 liter of solution under each bush.
- During the flowering period. Use a mixture of superphosphate (9-10 grams), potassium sulfate - 3 grams, water - 10 liters. Fertilize each bush with 1 liter of solution.
- Harvesting. Mix phosphorus 1 tsp. and potassium 1 tsp. with 10 lira of water. 1 liter of solution is poured under each root.
Top dressing requires a competent approach.Do not use chicken manure or cattle manure. They can burn the root system, disrupt the metabolism, which will lead to a decrease in yield and overgrowth of leaves.
Correct care
It is easy to care for greenhouse peppers if you know the rules and features of care.
- Place the seedlings comfortably. Closely planted seedlings will not give a good harvest due to a lack of space for the fruits, the root system.
- Plant the seedlings along with the peat from the glass.
- Loosen the soil 2 to 3 cm deep more often. Pepper loves oxygen, fresh air.
- The soil must be moist.
- Maintain the microclimate in the greenhouse at 22 ° C during the flowering period, 25-27 ° C during the ripening of the fruit.
- Provide the seedlings with plenty of light.
- Do not plant peppers in cold soil. He will die.
- Inspect the leaves periodically for bugs and parasites.
- Use the dressing in moderation, keeping the proportions.
- Form the bushes in the morning to give the skeleton time to heal.
- Tie up the bushes before fruit begins to appear.
- Remove all limp, diseased leaves and fruits from the bush.
- Remove ripe peppercorns in time so as not to weigh down the stem.
Harvesting
The fruits are harvested at the stages of biological or technical maturity. Peppers of biological maturity are fully ripe fruits that are immediately used for food. In technical maturity, the crop is harvested for storage, long-term transportation (while the pepper grows to the desired size and shape, but retains a green or even white tint).
It is recommended to cut the pepper together with the stalk - while the fruits are preserved longer, retain their useful qualities.
Compatibility with other cultures
Often gardeners ask themselves the question: “Is it possible to plant several crops in one greenhouse? For example, tomatoes and peppers, cucumbers and bell peppers? " These crops are thermophilic, but their compatibility also depends on other growing conditions.
- Do not plant bell peppers in a hot chili greenhouse at the same time. Seedlings are pollinated.
- Planting cucumbers and peppers in the same greenhouse is not the best option for experienced gardeners. Cucumbers do not require airing, and peppers love fresh air. Cucumbers need heat, while peppers need a moderate, constant temperature.
- Tomatoes and peppers do not get along well together. They need different conditions for staying in the greenhouse. Sweet vegetables need moisture, and tomatoes are killed by water.
Thus, it is better to plant crops in different parts of a large greenhouse or arrange an individual greenhouse for each.
Growing features
Growing conditions for peppers are about the same as for tomatoes. Pepper grows outdoors only in regions with a mild climate. In order for your vegetable to delight you with beautiful and healthy fruits, you need to prepare a special soil for it.


Pepper care
Rotten manure, compost, which are mixed with turf, are suitable for this purpose. Light soil is suitable for growing peppers, so the soil with high acidity needs to be limed.
Diseases
To find out why pepper grows poorly in the greenhouse, why it turns yellow, a thorough analysis of the greenhouse microclimate and an external examination will help. Most often, fungi and infections affect plants that are in a poorly ventilated area, are filled with water.
The main diseases of peppers are:
- Mosaic. Leaves lose transpiration and yield decreases.
- White rot. Plaque is formed on the root part, the death of seedlings occurs in 3-4 days. The reason is high humidity, rare ventilation of the greenhouse.
- Late blight. Holes appear on the leaves, dark purple spots on the fruits, crown. The culprit is considered a cold snap at night, excess moisture.
- Black spot. Leaves, peppercorns become covered with tubercles, which turn black, causing the death of the plant.
They fight infections by dusting the damaged areas with charcoal and chalk. It is important to establish an irrigation regime, to constantly maintain a comfortable atmosphere inside the greenhouse.Immediately remove diseased bushes away from healthy ones, do not regret throwing them away. This will help keep yields high.
Disease protection


The beds are regularly inspected in order to detect harmful insects or signs of disease in time. Due to the high humidity, pepper can be affected by late blight, fusarium, apical or white rot. Closer to autumn, there is a risk of developing Alternaria. It is recognized by the black areas on fruits and leaves. Bell pepper is susceptible to the tobacco mosaic virus, the development of bacterial cancer.
If the bush is strongly affected by the fungus, it is better to get rid of it, because the infection in the greenhouse spreads quickly. At the first manifestations of the disease, the following measures are taken:
- Remove infected fruits and green parts of plants.
- With bacterial cancer, the bushes are treated with a solution of copper sulfate.
- Peppers infected with tobacco mosaic or fusarium are destroyed.
- In case of fungal diseases, the bushes are irrigated with a solution of a fungicide or a copper-containing preparation.


































