Author rating
The author of the article
Yakov Pavlovich
Professor, Head of the Department of Vegetable Growing
Articles written
153
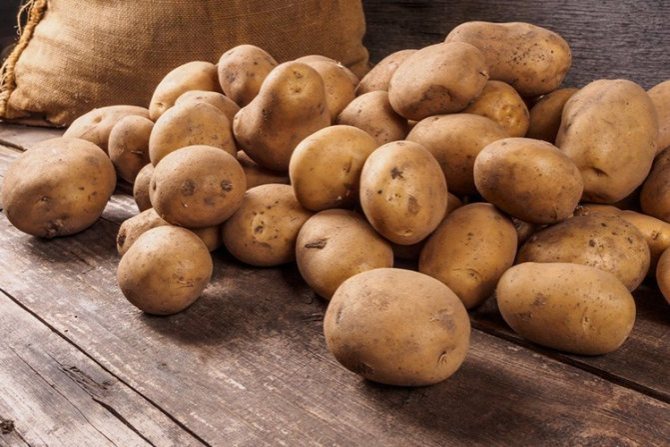
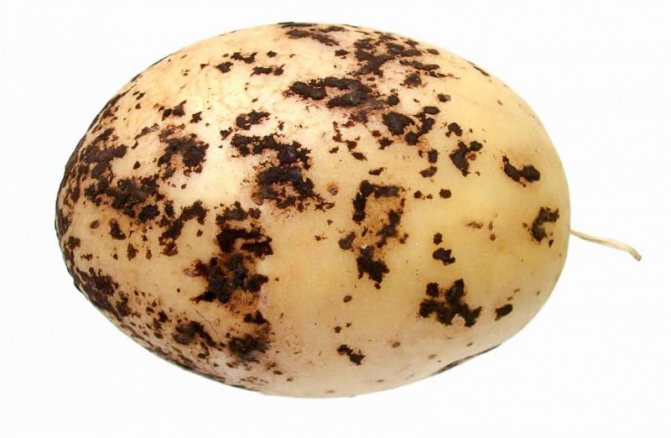
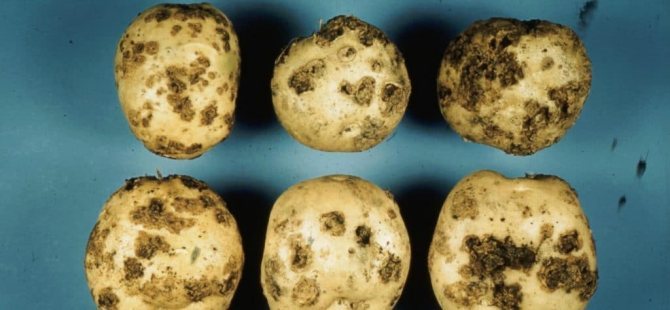
Potato seedlings are susceptible to various fungal and bacterial diseases. The result of the impact of pathogenic organisms is a sharp decrease in the quantity and quality of the crop. One of the most common diseases is potato scab, which infects tubers and makes them unsuitable for food. It is impossible to cure a vegetable during the growth process, therefore, the need for high-quality prevention is growing.
Types of potato scab
Scab is a potato disease caused by fungal spores. They are in the ground and after planting the crop, they begin to infect the tubers, the root system, and occasionally rise to the stem. This disease is divided into several types, each of which has its own signs and methods of treatment.
Ordinary
This type of scab develops in dry alkaline soil when the air temperature reaches 25-30 ° C. Spores of the fungus live in the ground, organic debris and tubers, while they are in the upper layers of the soil. The fungus affects the seedlings through small cracks in the peel. Penetrating inside, it begins to reproduce when favorable conditions develop. Otherwise, the spores are simply dormant in the ground or tubers.
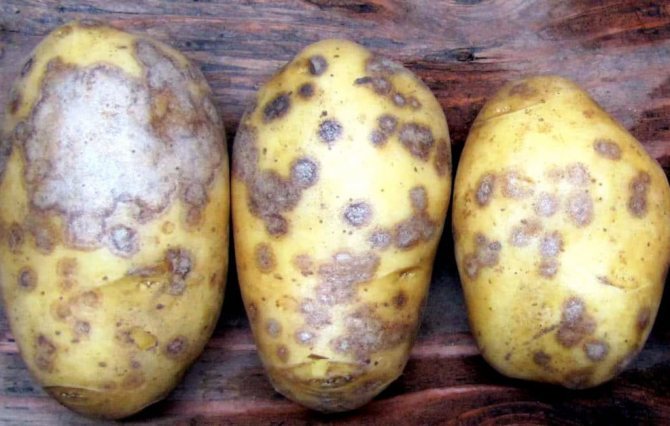
Common scab most often affects potato varieties that have a pink or thin light skin. Hard ulcers appear on the tubers, over time they form a solid crust on the fruit, which is intersected by cracks. Thanks to the scab, a favorable environment is created for the growth and development of pernicious bacteria in the root system of the vegetable and over time the potatoes become covered with gray rot.
Silvery
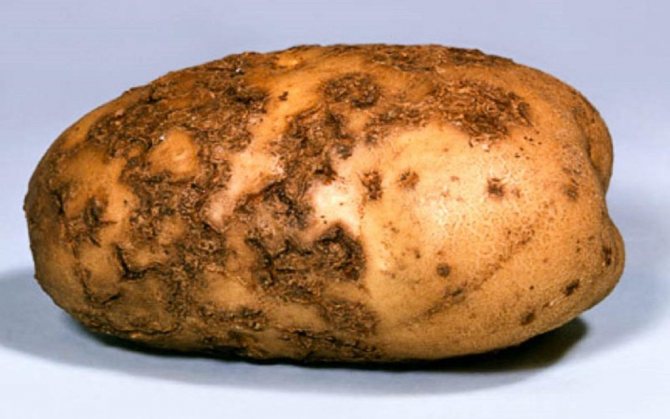
This type of fungus is common on sandy loam, hard and clay soils. Favorable conditions for its growth and development are air temperature + 18-32 ° C and high 85-100% humidity. Spores of the fungus live in the soil, penetrating through small lesions into the tuber, affecting the entire root system of the seedlings. A characteristic feature of this fungal disease is the silvery hue that the affected areas acquire.

Potato varieties with white and red skins are especially vulnerable to disease. Lesions appear as gray-brown spots that are slightly depressed and do not clear from the surface. At this time, black spots spread on the pulp of the vegetable, which eventually cover the entire tuber. In this case, the peel is strongly wrinkled.
Potatoes that are affected by silvery scab not only rot during storage, but also lose all moisture, quickly drying out. The affected vegetable becomes an excellent breeding ground for bacteria and can be quickly attacked by wet or gray mold.
Lumpy
This type of disease is transmitted by the fungus Oospora pustulans Owen. Tubers are affected through the eyes or any damage to the skin (cracks, chips, cuts). In places where the pathogenic organism enters, brown bumps are formed, which eventually turn into real growths. In this case, some pustules may, on the contrary, be depressed into the pulp. There are no black spots or other lesions under the skin.


The optimal conditions for the development of fungal spores are marshy and soddy-podzolic soils, whose temperature reaches + 4-11˚C and at 100% humidity.Infection of tubers occurs at the moment they enter the soil and as they grow, however, when digging up, there are no characteristic signs of damage - they appear after 2-3 months of storage.
Black
This type of scab is called rhizoctonia - it develops in cool, humid weather, a temperature of + 17 ° C. The fungus is widespread in loamy soils of neutral acidity. This species is the most dangerous of all, as it leads to the complete death of the bushes.


Infection occurs immediately after the seedlings get into the ground, after which the fungus immediately begins to develop and affects the root system of the culture. This affects seedlings - about 20% of tubers do not sprout, and the rest sprout unevenly. Immediately after the potato, the spores move to the forming stem, almost completely destroying it.
Infected tubers are covered with black spots that look like soil, but are not peeled off. There are no lesions under the skin, but at the same time, the infected bushes begin to wilt slowly, their leaves curl, and the stems become covered with white spots.
Powdery
The most common potato scab, which is carried and developed by the pathogen fungus. At the same time, it is quite large in size and is able to move independently. It lives in the soil, is dormant in the harvested crop and is found in manure - the life cycle of the parasite is 5 years and even withstands passage through the digestive system of animals.
The ideal conditions for its reproduction are: heavy loamy soils, high humidity and an air temperature of + 12-18 ° C. When potatoes are damaged, ugly white growths begin to appear on its bushes, which then change color to brown. Tubers are overgrown with pustules, which differ in shape, color and relief. They burst over time and turn into ulcers, which contain dusty remnants of spores and vegetable pulp.


Scab - signs of the disease and methods of treatment
But in the spring, loosening is necessary, because the larvae do not tolerate direct sunlight either, and the egg-laying of beetles also perishes. You can arrange simple traps: in April, fill small pits with half-matured grass, moisten and cover with boards. The wireworm willingly settles in such holes, and after a few days, the grass with the larvae can be selected and burned. And put a new batch of grass in the hole.
Good harvests!
A trip to Turkey for 10 days with the "Velvet Season" club - the city of Bodrum on the Aegean coast!
Fill out an application
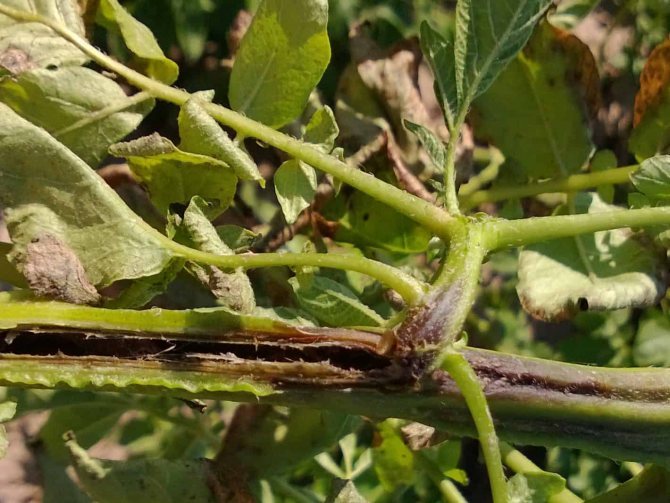
It got its name from the black formations on the tuber, which can be confused with lumps of adhered soil. The fungus can penetrate green shoots, as a result, brown spots and pits are formed on them. From such a defeat, the sprouts quickly die even before they emerge from the ground. Black scab can infect the root system of mature plants. As a result, the plant withers, its leaves turn yellow and it dies.
The pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani) requires high soil moisture - 80-100%. Temperatures are average enough for spring or summer - 17-20 ° C. Most of all, the pathogen likes loamy soils. More often, the disease develops with a late and rainy spring. The peculiarity of the disease is that there are no potato varieties resistant to the pathogen. Often, the fungus destroys the plants before germination.
Control measures should be taken depending on the type of fungal infection. Since each type of pathogen has its own preferences for temperature and humidity. However, there are general principles of struggle that help with any type of scab.
1. Planting exceptionally healthy tubers in spring. Infected or damaged tubers (cracked, chipped, eroded) should be discarded.
2. Potatoes for planting should be stored in a dry, dark, cool place.such conditions prevent the formation of condensation.
3. Before sowing, keep the tubers in the light to germinate the sprouts.
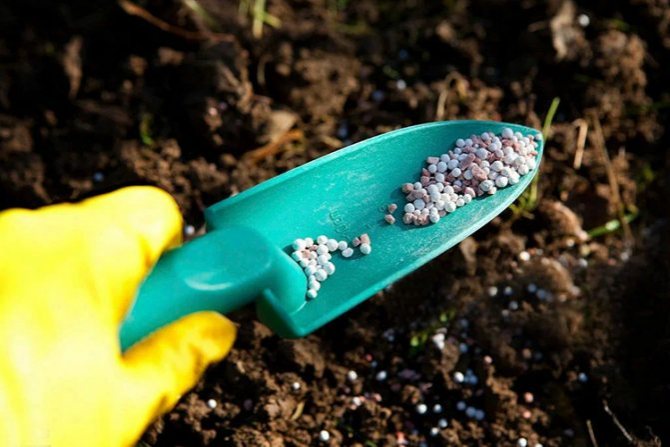
4. It is advisable to apply fertilizers taking into account the substances already contained in it (determine them by the type of soil or by chemical analysis)
5. In case of development of the disease in the beds. Potatoes can be planted again in the same place after 4-5 years.


Black scab
6. Fresh manure cannot be used to fertilize potato soils. You need to use it in advance for a year, for the culture preceding the sowing of potatoes.
7. Lupine, clover, soybeans, mustard can be used as green manure.
8. It is undesirable to constantly grow potatoes in the same place. It is necessary to periodically change the sown area.
9. Carry out deep loosening of row spacings, especially 10-12 days before the emergence of sprouts
10. It is advisable to pickle potato seeds before sowing with polycarbacin, TMTD or other special preparations against fungal diseases.
11. If a certain type of scab is found for the next year, varieties resistant to the pathogen can be grown. But you need to understand that this method of struggle cannot be independent and replace other methods, since an absolutely resistant variety does not exist.
12. Fungi need an alkaline environment, so you can acidify the soil by adding ammonium sulfate (20 grams per 10 liters) to the irrigation water.
13. It is useful to sow legumes on contaminated soil, as they noticeably oxidize it, reducing the preservation of spores.
14. When planting, you can add manganese, copper or boron to the seed.
15. Mowing the tops of potatoes 10-15 days before harvesting will increase the thickness of the peel and, accordingly, its protection.
A plant whose roots are affected by scab:
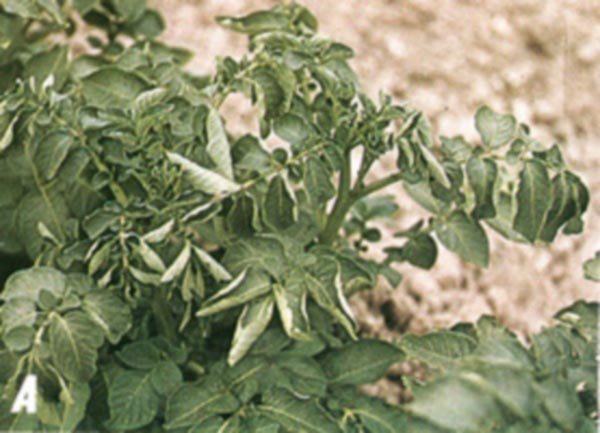


Individual control of scab species:
1. Common scab. Since the pathogen loves dry sandy soils, it is advisable to water thoroughly. It should be done immediately after planting, and carried out regularly until adult plants grow with a stem thickness at the root of 1.5-2 cm.
2. Powdered scab. In the garden for several years, you can grow potato varieties resistant to powdery scab: majestic, lorkh, cardinal, yubel. Before planting the tubers, it is advisable to hold for 5-7 minutes in a 0.2% formalin solution. After aging, cover the potatoes with a tarp for 2-3 hours.
3. The scab is silvery. Treating potatoes just before planting and immediately after harvesting helps a lot. For processing, you can use "Titusim", "Botran", "Celest", "Nitrafen" and "Fundazol".
4. Black scab.
How to identify a lesion
Signs of potato scab disease cannot be seen in the early stages of growth... First, small, almost imperceptible dots of brown, dark red and purple appear on the skin. The surface of the root crop acquires a rough surface. As the disease progresses, small bumps appear on the peel, which soon grow in size and crack. At the last stage of the development of the fungus, the roots begin to rot.
When the scab is black, the roots and stems of the plant are affected and the leaves are sometimes damaged. If the upper part of the bush becomes infected, there is no way to save it. The infectious tuber must be destroyed.
The silver scab fungus is the most tenacious of all, has the ability to infect root crops even during storage.


Causes of tuber damage
Fungus occurs due to infections and adverse conditions. In some cases, the person himself is to blame for the appearance of the disease due to improper care of the culture.
The main causes of the disease:
- infection through diseased planting material;
- high moisture content of the earth;
- a high level of alkali in the soil (after adding lime or ash to the soil);
- sudden changes in temperature;
- an increase in the content of nitrogen and calcium in the soil;
- the ground before planting was infected with a fungus;
- lack of minerals (boron, manganese).
A dry, hot climate is especially conducive to the reproduction and development of the fungus. The disease develops more often in an alkaline environment than in an acidic one.
Causes of the disease
The main causes of scab damage to potatoes are:
- poorly cleaned, infected soil;
- diseased tubers that are used for planting;
- too much nitrogen in the soil;
- non-compliance with crop rotation;
- increased soil temperature;
- high acidity of the soil;
- fertilization with fresh cow dung of the garden;
- high soil moisture.
Fungal spores can live in potatoes or soil for up to 5 years, while they are in a dormant state, but as soon as conditions around become favorable (humidity and temperature increase), the pathogen begins to develop, infecting all seedlings.

Where and when is it formed?
The scab causative agent is in the soil, so it is not always possible to completely destroy it. Bacteria mainly hibernate in fallen leaves, and the peak of the exacerbation of the disease falls in the spring, when it becomes warm and humid outside.
Also, for the successful development of such an ailment, certain parameters are important:
- air temperature + 25-30 ° С;
- sandy, loose, dry soil;
- the presence of a large amount of organic fertilizers in the soil, in particular humus;
- alkaline earth;
- lack of manganese and boron in the soil, and an excess of calcium and nitrogen;
- air humidity not less than 70%;
- lack of immunity in the root crop to this disease.
Preventive measures
It is impossible to completely get rid of the scab. It is necessary to direct all measures to create such conditions under which these viruses will not spread. Compliance with crop rotation shows good results. According to the rules, in places where potatoes grew, its next planting can be done in 3-4 years.
However, this rule does not apply to small towns. In this case, it is recommended to plant green manure plants in this place after harvesting: oats, radishes, mustard, soybeans or clover. The listed plants have specific substances that negatively affect the scab.
You can protect your potato crop from scab with an integrated approach. Only a combination of several methods can give a positive result.
How to cure scab soil
Slightly acidic soils are ideal soil for potato growth. Many gardeners do not understand why potatoes yield poor crops. They just don't know that the ground may not be suitable. But, despite this, you can grow a good harvest if you improve the soil.
If the soil is alkaline, then it must be gypsum. This must be done so that the tubers are not hit by scab.
In order to get rid of the scab, it is not necessary to process the bushes. It is enough to plaster the soil. For this, about 200 grams of gypsum is applied for each square meter. Then the soil should be dug up. It should be noted that salts interacting with gypsum become mobile and if you just add it, then there will be no result. To achieve the effect, after applying the gypsum, it is also necessary to water the soil well several times, this will wash out the salts in the soil. You should know that this method has been valid for several years.
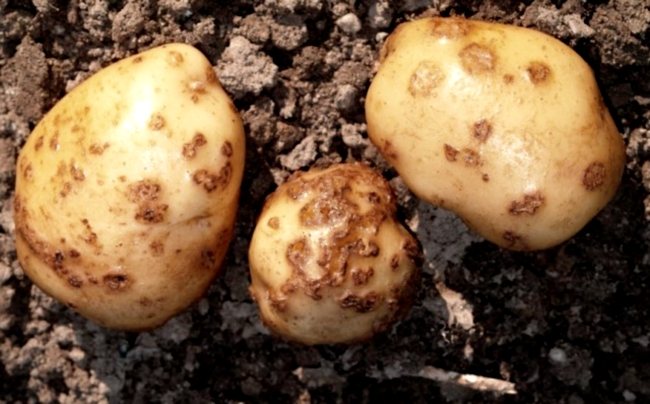


If the tubers are slightly affected by scab, then fallen pine needles will help to cope with the problem. When decomposed, it gives the soil all the acidic reaction. You can add needles in any quantity.
In addition, ordinary sulfur can acidify the soil. It is introduced into the soil regardless of the season. When sulfur reacts with air, oxides are formed from it, which turn into acids when interacting with water.
Signs of appearance
Infection of new seedlings occurs at the time of planting it in the ground, but this is imperceptible to the eye - the spores initially capture only tubers.Over time, farmers can detect the disease based on the following characteristics:
- Potato sprouts do not germinate uniformly, 20-30% of the seed does not germinate at all.
- The tubers are covered with pustules (their color and shape depends on the type of disease), which grow over time throughout the vegetable.
- The dug up potatoes are covered with white mycelium.
- The leaves on the bushes begin to grow small and curl up into a tube.
- White spots appear on stems and leaves.
- The potatoes in the basement after 2 months begin to dry out and rot.
Since most types of scab affect only the root system and tubers, its spread is imperceptible. But if you suspect that the seedlings are infected, it is best to dig up a couple of bushes and check the tubers for fungus.
Why is it dangerous?


Potato tubers affected by a fungal disease do not harm human health. I.e if you eat the contaminated product, you definitely won't get to the hospital... However, whether it will be pleasant to cook it is another question.
Scab is an unpleasant phenomenon that lowers the nutritional value of potatoes, it loses a significant amount of starch. It also reduces the keeping quality of the root crop and causes rotting. The scab is the cause of the loss of the quality of the crop, the loss of the presentation, infects the seeds, affects the resistance of plants to other diseases.
Methods of dealing with rhizoctonia on potatoes
Universal methods of scab control are the use of fungicides, adherence to agricultural practices and the use of high-quality seed.
Agrotechnical measures
It is difficult to fight the fungus on potatoes, so it is best to follow agrotechnical rules that significantly reduce the risk of damage.


Among them:
- The choice of healthy planting material.
- Observance of crop rotation - it is best to plant potatoes after legumes, onions and grains.
- Soil acidification.
- Growing potatoes in one area no more than once every 5 years.
- Timely fertilization of seedlings.
- Harvesting tops 10 days before harvest.
It is best not to plant potatoes too early and water in moderation so that the soil does not become marshy.
Chemical and biological products
To get rid of fungal spores, you can use modern chemical fungicides. Among them, farmers recommend:
- Maxim is a contact fungicide that kills only the fungus and does not affect the soil microflora;
- Agata25K - the tubers are treated with the drug before planting;
- Fitosporin M - the agent is sprayed with bushes 3 times per season;
- Cuprosat - they are treated with bushes when watering 2 times per season, but no later than 20 days before harvesting.
Biological preparations are no less effective. Among them are Circo and FitoPlus, which are sprayed on all seedlings without harming the crop.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
Gardener with 17 years of experience and our expert
Ask a Question
Important! It is necessary to make a solution for spraying bushes strictly according to the instructions and observing the indicated proportions.
Traditional methods
If it is not always possible to spray seedlings with chemicals, then treatment with folk remedies is available and safe at any time. The best ways are:
- Treatment of planting holes with a solution of chicken manure (1 liter per 15 ml of droppings).
- Re-treatment with manure solution when shoots reach 10 cm.
- Watering seedlings during active growth with nettle infusion (1:10).
- Pouring over the bushes during the formation of buds with a solution of wood ash (10 liters of water and 3 tablespoons of ash).
The manure that is used in solutions should be 1-2-year-old rotted, since fresh can contain spores of the fungus.
How to deal with potato scab without chemicals
If you follow the rules for caring for potato plantings, scab can be fought without the use of potent drugs. Treatment is as follows:
- compliance with crop rotation;
- correct application of various types of fertilizers;
- quality control of seed potatoes.
Crop rotation
Scab spores live in contaminated soil for 5-7 years. For 3-4 years, the infected soil cannot be used for planting potatoes due to the activity of the fungus.
If it is impossible to take a break, then immediately after the autumn harvest, it is necessary to sow siderates (green fertilizers). These are legumes, mustard, lupine, rapeseed, oats and other cereals. The waste products of these plants are saprophytic microorganisms. They successfully suppress the growth of all types of potato scab pathogen.
Correct application of different types of fertilizers
To combat the scab pathogen, it is necessary to acidify the contaminated soil. This is done with acid fertilizers - sulfate-containing preparations, superphosphates.
Good plant resistance is facilitated by the enrichment of the soil with preparations of copper, manganese, boron. For this, plants are watered with water containing these elements.
Organic fertilizers should be applied with caution. You cannot add fresh straw manure (rotted within 2-3 years is suitable). Large amounts of lime or wood ash will also lead to the progression of the infection.
Quality control of seed potatoes
One of the main causes of infection is poor quality seed. Spring bulkheading of seed potatoes and killing diseased plants will help isolate infected tubers. Tubers of an infected crop should not be allowed to seed, even if they seem healthy. They can also contain spores of the pathogen.
Use of drugs
The development of this disease can be prevented by treating the tubers with special fungicidal agents. The drugs Maxim and Fitosporin have proven themselves well.
Moreover, the latter option is used not only during planting, but also as a sprayer during the growing season. To prepare the composition, you will need to mix the contents of the package with 3 liters of water.


Treatment of tubers with potent drugs: Fenorami or Kolfugo will help to increase immunity to black scab. For other varieties of this disease, less serious drugs can be used. For this purpose, any growth regulators (for example, Zircon) are suitable.
Important! The use of chemicals quickly normalizes the condition of the soil, but has a short-term effect.
Which culture is striking?
Fungal disease is not only a disease of vegetable crops, but also the main enemy in the garden. Pathogenic microorganisms affect:
- potatoes;
- beets;
- carrot;
- citrus fruit;
- apples;
- pears;
- cherries;
- grapes;
- houseplants.
This disease causes the greatest damage to potatoes, apples, pears, impairing their appearance and quality of fruits. In this case, the fungal infection is different in each case. This disease occurs mainly in temperate latitudes.
Prevention measures
The main method of preventing scab infestation is the selection of high-quality seed and its preliminary treatment with fungicides. Only potatoes clean from spores will be able to give a high-quality harvest, provided that the soil for planting has also been pre-treated with preparations for fungal infections. In addition, you can take the following steps:
- Grow between rows of green manure - mustard, lupine and peas protect the soil from fungal spores.
- Store crops only in a cool and ventilated area.
- Grow scab resistant varieties.
- Observe the crop rotation.


These methods will preserve the crop and protect the soil and seedlings from fungal spores.
Scab on potatoes: how to heal the earth to avoid this scourge
There are no varieties resistant to the pathogen.To increase the resistance of potatoes before planting, they are treated with antifungal agents: "Maxim", "Planriz", "Vivatax", "Baktofit", "Integral" and "Fenoram". It is necessary to plant potatoes exclusively in warm ground, with a temperature of more than 8 ° C. They also follow the rules for planting depth.
It got its name from the black formations on the tuber, which can be confused with lumps of adhered soil. The fungus can penetrate green shoots, as a result, brown spots and pits are formed on them. From such a defeat, the sprouts quickly die even before they emerge from the ground. Black scab can infect the root system of mature plants. As a result, the plant withers, its leaves turn yellow and it dies.
The pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani) requires high soil moisture - 80-100%. Temperatures are average enough for spring or summer - 17-20 ° C. Most of all, the pathogen likes loamy soils. More often, the disease develops with a late and rainy spring. The peculiarity of the disease is that there are no potato varieties resistant to the pathogen.
Highly resistant varieties
If all efforts to prevent scab do not lead to the expected result, you can not waste time and change the variety of potatoes. None of the existing varieties has complete resistance to this infectious disease, but there are more resistant ones. These include:
- Bryansk novelty;
- Is vain;
- Spring;
- Vesnik;
- Aspia and others.
From foreign similar varieties, you can choose: Mentor, Prokura, Patrones, Krostotr and others.
Advice! even when choosing resistant varieties, it is important to keep prevention in mind.
Can infected potatoes be eaten?
Can you eat scab-infected potatoes? Or should they be thrown away? Not at all. Select them, remove the damaged parts. You can safely fry potatoes or make mashed potatoes for dinner.
On the contrary, it is not recommended to eat potatoes affected by dry rot. Even if you have a tuber affected only on one side, you should not eat the supposedly healthy side of the other half. Throw away the entire tuber without any pity.
To keep your potatoes healthy, select or buy quality seed for planting. Pay attention to the characteristics of the variety, to the resistance to a particular disease. Dig up potatoes intended for future planting earlier than for food and storage, since the longer it stays in the ground, the more likely it is to become infected. Try to follow the crop rotation.
POTATO PARCH - FIGHTING TIPS AND REVIEWS ON WAYS TO GET RID OF HER
In our area last summer, the weather was extraordinary, to which we have already begun to get used to. May, June were cold, with an air temperature of 5-10 °. Without waiting for the warmth, I had to plant potatoes in late May - early June. But somewhere in the 20th of June, the heat came, and the drought lasted three months - July, August, September. Light rains passed, but they could not even wet the earth.
I have a rather big plot, surrounded on all sides by vegetation, which creates a shelter for various pests. The worst are wireworms and slugs. I fight the wireworm every year, coming up with a variety of tricks for him. Last year, I decided to put more ash in the holes and watered the ground with a biological preparation against wireworms and other harmful insects. I don't know which worked better, but the wireworm has become much smaller.
However, to my great chagrin, the potatoes were attacked by another disease - the common scab. This has never happened before. What caused this disease?
Large amounts of ash in dry weather. In July I watered the potatoes, but in August I had to leave, and the whole month the potatoes grew by themselves. There is a saying that you cannot spoil porridge with butter, but it turns out that ash can spoil potatoes. The truth is right: everything is good in moderation.
But life is twofold, and in every minus you can see the pluses.For example, I now know which potatoes are more resistant to scab and which ones are less, and I can share this information with you.


The following varieties turned out to be resistant to scab:
Galaxy (in the photo you can see his harvest taken from one bush), Unica (in the photo you can see the harvest from one ridge 8 m long). From the varieties that I first grown, Aladdin simply mesmerized, such huge balls have grown. Cecile is also a very attractive variety, similar to a long red club (the length of the largest tuber is 23 cm).
I grow potatoes in the ridges. In some there is already loose black soil - here I plant proven varieties with excellent yields. But there are also ridges with loam, which is strongly compressed in the heat and becomes very hard.
Here I plant the varieties that first appeared with me, and immediately, in the very first year, it turns out whether this variety should be left or not. So last year I planted new items on these ridges: even in such conditions, the Fidelia variety managed to grow in 2-3 tiers, Sharvari, Piroshka, Nikse, Red Scarlett, Bars, Jelly showed themselves well.
<л.андреева>


























