Types of greenhouse beds
Depending on how it turns out to fill the greenhouse space, beds are distinguished:
- unpaved, located on the ground;
- shelving, located in boxes.
At dachas and personal plots, the first option is more often used.
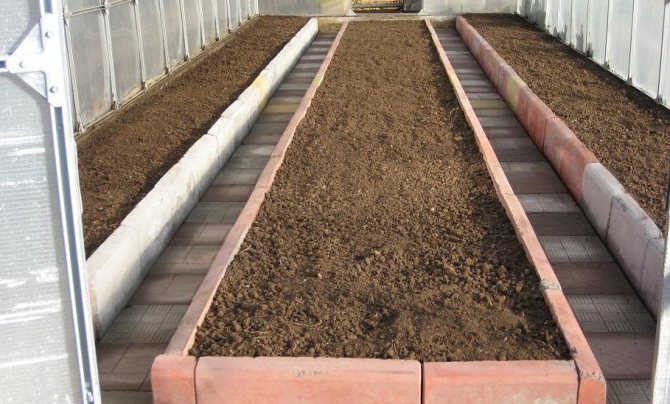

Depending on how the striping was carried out, there are:
- wide rows, between which there is a narrow passage;
- middle rows with a passage, the width of which allows you to move freely;
- narrow rows with sides and a wide passage along the Meatlider;
- narrow raised (warm) bed-boxes according to Lyadov;
- rows up to 40 cm wide with a distance of 50–80 cm according to Pikalevsky;
- original.
Did you know? There are also greenhouses in the Sahara Desert, but they protect the plants not from the cold, but from the heat.
There are the following types of the original design of the rows:
- in the form of a pyramid;
- vertical;
- French;
- warm;
- "Bosquet".
Pyramid beds
Pyramidal beds can be arranged in 2 versions:
- Small... A large-diameter pipe is installed and covered with earth in the form of a slide. Along the pipe on both sides, in the form of steps, it is necessary to strengthen the cultures planted in rectangular boxes.
- Large... Four rectangular rows of the same size are connected in the form of a square. The next 4 rows should have a length of 20 cm less than the first, they are also connected in a square and installed inside the previous square in the form of a step leading in height, etc.
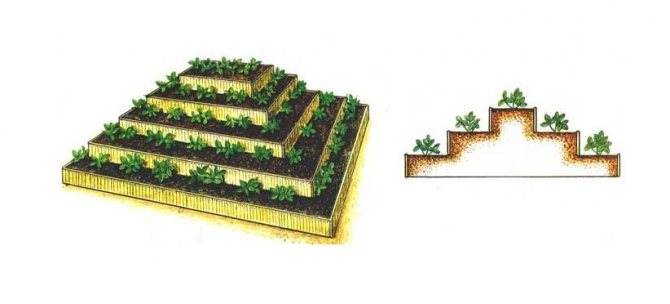

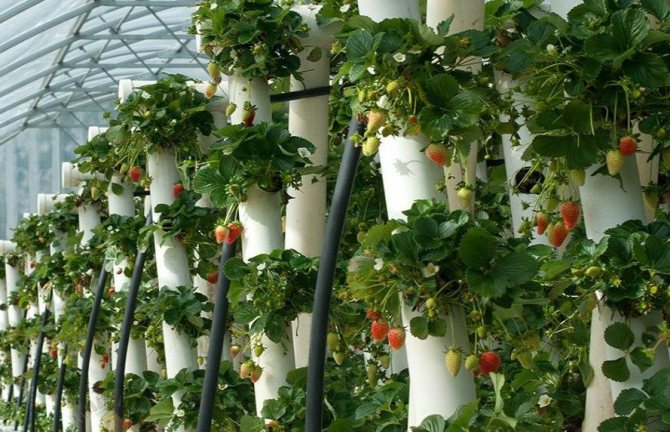
Vertical
Vertical stripes, like pyramidal stripes, are installed in the form of steps, but on one side. In addition, there are options for planting crops in a vertically installed pipe with drilled holes for their growth. You can also plant plants in "pockets" made of insulation, sewn in rows on the base.


French
French beds resemble pizza in shape - they are a circle that is divided into sectors, like pizza to pieces. Different types of plants can be planted in each sector. There are curbs or paths between the sectors that are directed outward from the center of the circle. Such beds will be the best option for round or domed greenhouses.


Warm beds
Warm beds are a way of growing plants that warms the soil.
Did you know? In the Netherlands, a project is being developed to use the surplus heat generated in greenhouses for heating residential buildings, and condensate for drinking water.
Depending on which method of insulation is chosen, there are:
- Warming of the soil at depth.
- Warming by building up the soil layer.
- Combining the two previous options.
- Growing using this option has three advantages:
- you can get the harvest earlier;
- in larger quantities;
- protect it from pests and diseases.


Bosquet beds
"Bosquet" - the beds are a derivative of the French type. In this case, the landing area should not be divided into sectors, but into parts of the same arbitrary shape - circles, hexagons, squares, rectangles, etc.


Secrets of the device of beds, depending on their type
You can plan and break up the beds with your own hands according to schemes developed for different conditions.Gardeners are constantly trying out more convenient options and creating new ways to grow crops. For greenhouses, practical and compact device methods are most suitable.
Meatlider beds
The American vegetable grower, Doctor of Agricultural Sciences J. Mitlider has been developing optimal planting schemes for 50 years. On its ridges, each sprout receives the maximum amount of light and is well ventilated. The special structure allows not to lose water and fertilizers during watering.
For greenhouses of the Meathlider ridge, it is recommended to do this:
- orient landings along the north-south axis;
- level the soil level horizontally;
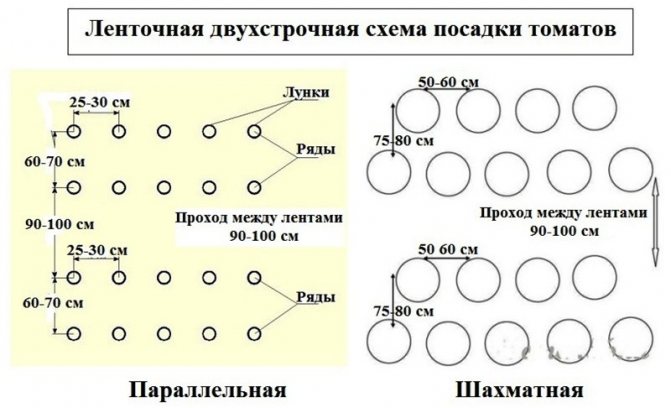
- the width of each strip for landing - no more than 45-50 cm;
- the bushes are planted in 2 rows, along the long sides of the strip, leaving the middle free (the distance between the shoots is approximately equal to 30-40 cm);
- along the edge of the ridge, a board with a height of about 10 cm is formed (they fill in the earth or put formwork);
- the ground level does not exceed the level of the passage;
- a 90 cm wide passage is left between the ridges.
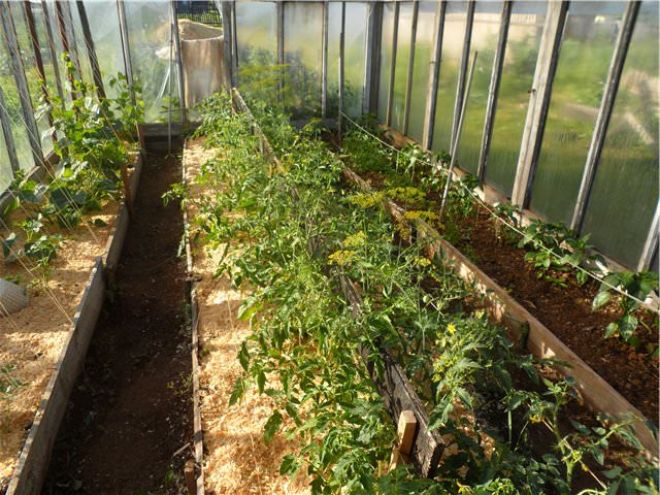


The Meathlider ridges are well suited for drip irrigation: the pipe is laid along the centerline of each strip and moisture is evenly distributed in the middle.
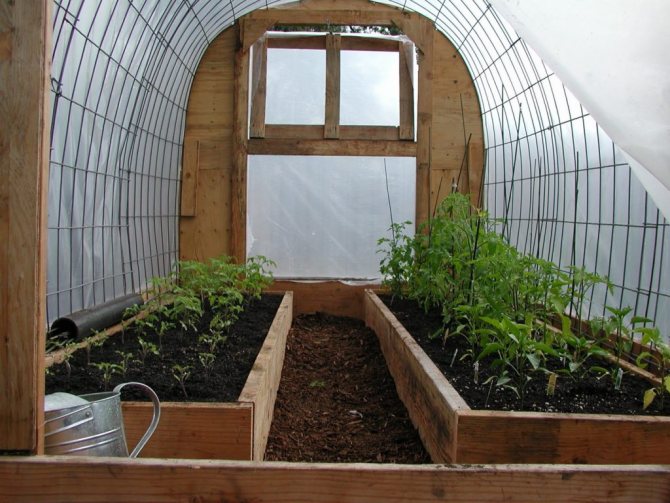
High beds
This type of polycarbonate beds is suitable when the groundwater level is raised on the site or the soil is of little use for agriculture. With this method, each strip is fenced with durable material, and fertile soil of the desired composition is poured inside. They can be formed using the principles of Meatlider, and without them. A variant of a high ridge is considered a rack, on which there is a distance between the bottom of the box and the ground.
Warm beds
Warmed varieties are used for forcing early greens and radishes, growing seedlings, etc. Biofuel helps to warm the soil: manure, bird droppings and other materials that rot with the release of heat. On warm ridges, 2 planting methods are used:
- in holes made in a biofuel layer;
- in a bulk soil layer (about 30 cm), on top of biofuel.
Basic principles of creating beds
The choice of a suitable greenhouse design option should be based on:
- the size of the stripes;
- idea of how many there will be;
- relation to the cardinal points;
- the types of crops that are planned to be grown.
Important! Ideally, you should first plan the interior design of the greenhouse and the crops grown, and then decide on the size and shape of the greenhouse.
Width and height of the bed
The lane division is based on the following principles:
- In the process of caring for the garden bed, you cannot step on it, therefore, the outer rows should not be wider than 50 cm, and the central ones - 120 cm.
- The optimal width of the aisles is 50-60 cm, this width will allow better use of the space. Narrower passages will not make it possible to move normally, since overgrown plants will hang over them.
- The number of rows in the garden should allow for high-quality care of crops, and plants in adjacent rows should not interfere with each other's growth. Ideally, the planting width should be 25-30 cm, but it all depends on the type of crops.
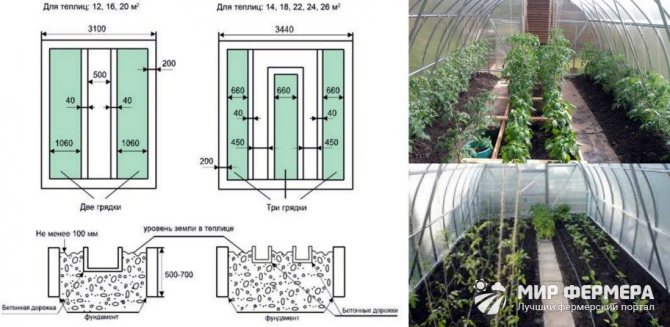
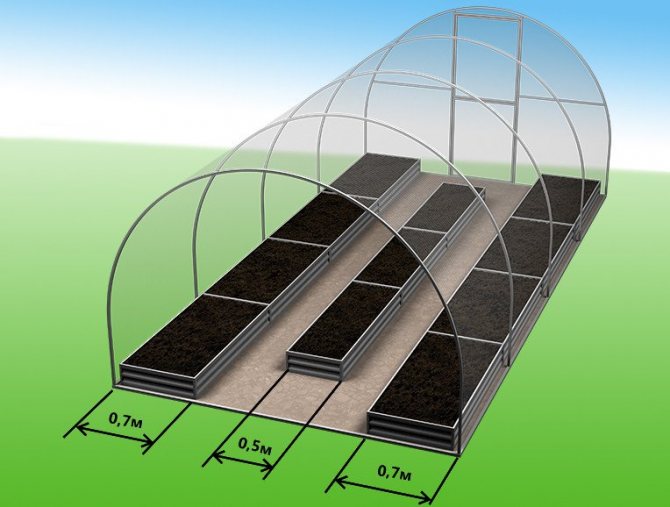
The planning of the strips in the finished greenhouse depends on the size of the greenhouse. The most common size is 3 by 6 m - this is the standard size of polycarbonate greenhouses, related to the size of the polycarbonate sheets. In this case, you can arrange 2 narrow strips of 0.5 m at the edges and a strip 1 m wide between them. Then there will be 2 50 cm passages. If opposite the entrance to make a strip perpendicular to them, then you can form an inverted letter Ш.
Video: How to arrange the beds in the greenhouse
The height of the rows can be as follows:
- Flush with the ground or up to 10 cm for soil that has a good level of fertility, a low level of groundwater, a composition suitable for this crop.
- Up to 30 cm, if it is planned to grow plants in which the root system is located close to the surface, there is a high level of groundwater, the soil is characterized by a poor composition.
- Up to 60 cm, if the soil is very poor, the water table is very high, it is planned to grow root crops.
The same approach can be applied for greenhouses measuring 3 x 4 or 3 x 8 m.
Reasonable use of vertical
It is possible to increase the efficiency of space use by filling the volume:
- Place racks. If you equip bed-shelves up to 50 cm wide, then you can grow seedlings on the upper shelves, and store tools under the lower ones. You just need to make sure that there is sufficient distance between the shelves for the growth of crops, access to light, and care for them.
- Hang growing containers from the ceiling. The hanging rope must be strong and long so that the plants do not fall and burn near the top of the greenhouse.
- Make the vertical or pyramid beds described above.
Important! All of the above methods of vertical filling of the greenhouse lead to accelerated drying of the earthen coma, so plantings need more frequent watering.
Such options are suitable for annual crops, the root system of which does not grow much.
We make warm beds
Warm beds allow you to get a greenhouse effect.
For their arrangement:
- Mark the boundaries of the future bed.
- If you are planning an in-depth or combined version of insulation, dig a hole 70 cm deep for the first and 45 cm for the second option, if not, equip walls with a height of about 70 cm.
- The bottom layer will be a mesh with small holes through which rodents cannot crawl.
- Drain with sand, small stone, or bricks.
- Lay out thick branches, pieces of wood on a thickness of 20 cm.
- Put small branches, sawdust on a thickness of up to 10 cm.
- Lay leaves, grass, turf, straw to a thickness of up to 5 cm, press down well.
- Place humus, plant waste (excluding tomatoes and potatoes), compost, bird droppings on a thickness of 20 cm.
- Apply a soil mixture suitable for the type of crops you have planned.
Each layer must be watered thoroughly.


Warm beds require careful observance of crop rotation:
- plant watermelons, melons, pumpkins, zucchini on them for the first year;
- the second - zucchini, tomatoes, cabbage, cucumbers;
- the third - onions, carrots, radishes, potatoes;
- fourth - legumes, greens;
- fifth - equip anew.
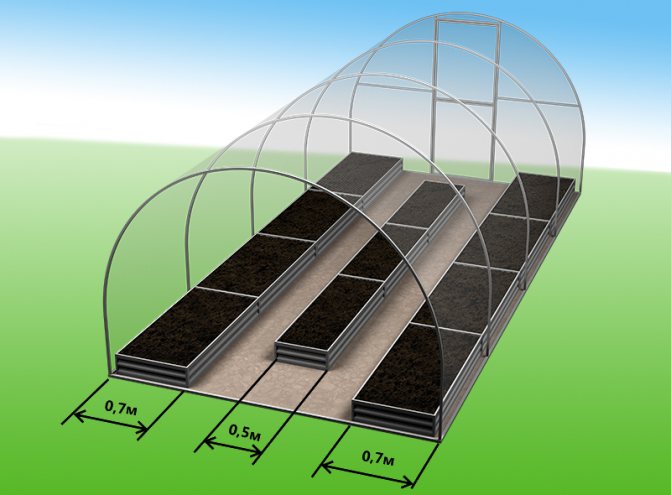
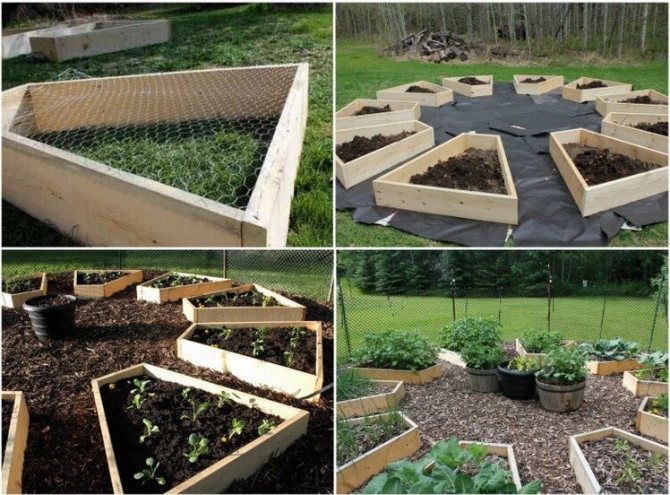
Seedling in three beds
This method is the most popular, since in this case the entire site can be rationally used. If the edges of the beds are compact, then you can make the paths a little wider. This will give more access to plants.
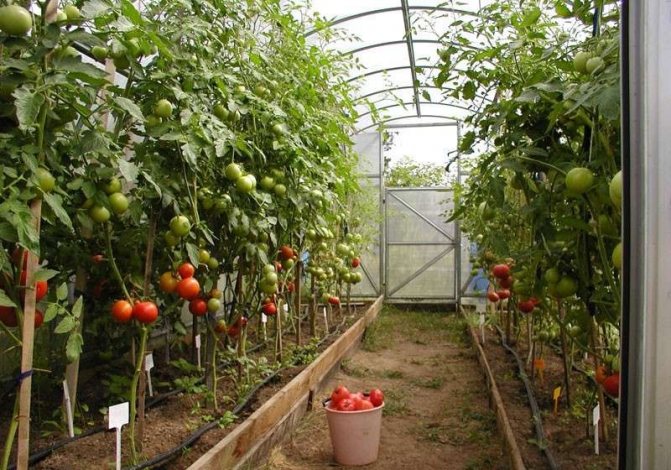
If you want to plant tomatoes, then it is better to plant low varieties around the edges., since the height near the walls is small compared to the center. The best option for planting in greenhouses are medium-sized, early ripening tomatoes. They will not take up much space, and the harvest will begin to delight you very soon after planting.


What to make fences for the beds
Row fences can be made from the following materials:
- Planks - the disadvantage is fragility, the ability to be affected by fungi and serve as a shelter for pests, but they are cheap and quickly installed.
- Brick - the disadvantage is the high cost, large expenditure of time and effort for installation.
- Slate - not particularly attracted by its appearance, it can emit harmful substances, brittle, has sharp edges, heats up very much, but it is durable.
- Polycarbonate - high cost, may deform.
- Zinc coated metals - have a high cost, can get very hot, but at the same time they are durable and easy to install.
Reasonable use of vertical
It is not at all necessary to place the beds exclusively in one plane. You have an excellent opportunity to organize a shelving structure in the greenhouse. It is the vertical layout of the beds that allows you to use all the free space very effectively. However, there are some complications here as well. It is imperative to distribute all plants and soil containers so that the lower tiers are not overshadowed by the upper ones.
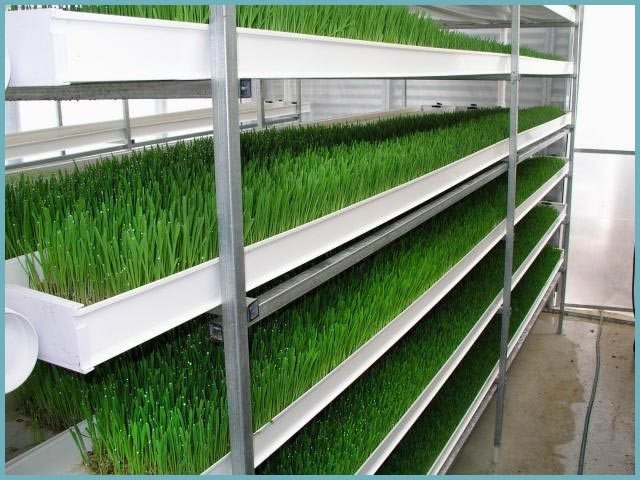


Greenhouse racks
Here are three simple rules for shelving.
- Directly under the shelves, you can create a niche like a warehouse for storing the necessary fixtures.
- Lower, middle tiers are ideal for mature plants. You can also put containers with fertile soil there, in which young bushes are planted. For example, this is a good solution when growing Dutch strawberries.
- Seedling containers most of all need warmth and light. That is why they should be placed on the uppermost tiers when placing the beds in a rack. In accordance with the growth, development, they can be gradually moved lower.
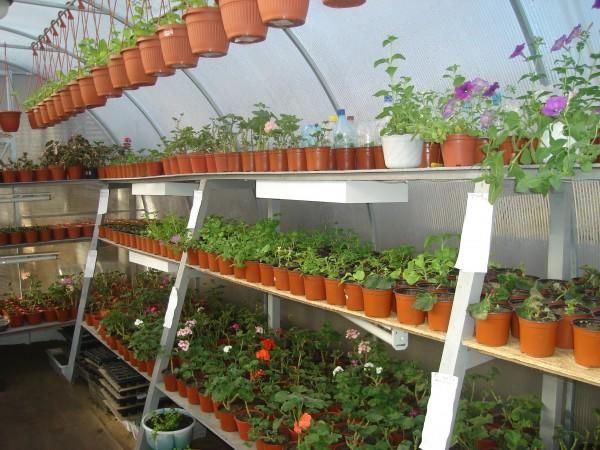


Racks and pots for plants in the arrangement of a greenhouse
It is important! Stick to a certain standard. The depth of the rack should be no more than 50 cm. Then the shelves will not shade the plants.
The vertical can also be used for terraced beds. This is a good option for those who want to gradually switch to shelving. In the greenhouse, on one side, the beds are left traditional. For this, the southeast or south side is more suitable. But the terrace can be made from the opposite side of the greenhouse.


An example of creating terrace beds
It should be noted that such experimental designs are appropriate in cases where the combined cultivation of different crops is carried out within the same greenhouse. If you are growing one crop, you need to create uniform conditions throughout the area.
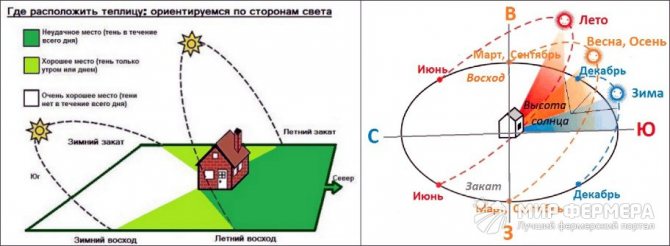
How to properly arrange the beds relative to the cardinal points
The orientation to the cardinal points should be as follows:
- For a set of crops of small stature, north-south is better.
- For those who can shade each other - east-west.

Thus, even in a small greenhouse, you can increase the yield if you carefully consider the arrangement of the rows and fill its volume as efficiently as possible. There is no unequivocal answer to the question of how to do this in your particular case, it is a matter of personal preference. We hope that our recommendations will inspire you to choose the option that suits you.
Correct arrangement of beds between greenhouses
It happens when it is not possible to build greenhouses on one site for any type of plants that you want to grow in your garden. Then each gardener begins to stuff the greenhouses with different sprouts, it turns out a flower garden. Tomatoes on one side, cucumbers a little further, and something for dessert across the path. It is worth forgetting about this situation, and to restore the initially great order in the greenhouse.


Classification of plants in greenhouses and beds:
- Endurance. The adaptability of plants to cold, warmth, increased solar activity.
- The height and size of the plant. Avoid growing large bushy cucumbers next to small fluffy radishes. Larger plant shade can negatively affect a shorter plant.
- Compatibility with neighbors. For example, eggplants and tomatoes will not be able to find a common language when ripe in the same greenhouse and outside. It is also worth considering how many years certain crops have been planted in one place. For example, beets cannot be planted in the same place for 4 years in a row.
- Priority. Many vegetables are incompatible not only in the neighborhood, but also in order. Cucumbers will never grow after a radish, and tomatoes should not be planted in the ground after a potato. Some vegetables are not at all friendly with each other, both in the neighborhood and in absentia.
You can plant some plants in greenhouses, and some in between, protecting them from the wind or strong sun. For example, eggplants are "creepy curmudgeons", they rarely carry other crops nearby. It is not logical to rebuild a greenhouse just for the sake of one crop, or to plant everything with eggplants, and then throw out the surplus.
It is better to plant them outside the greenhouse space, but modestly and alone.
Placing vegetables in a greenhouse is a big work and a whole scientific achievement. It is very difficult to choose the best options, given the availability and variety of greenhouses and options for seating each resident in his own garden, from spiral beds to an ordinary grandmother's garden, with a land on the sides. It all depends on the financial component, the amount of available space and space in the greenhouse, as well as on imagination and desire.
It is much easier to grow crops in a greenhouse, because you don't have to worry about night frosts. The scorching sun is not so scary if the greenhouse is made of a frame and glass. Many pests will not be able to get into the greenhouse, and most importantly, they will not have to run around the garden from garden to garden, watering everything. You can just concentrate some plants in one place and gradually take care of them.
Modern beds of V.N.
Today, the warm beds of Rozum V.N. are in great demand, who, thanks to his own research, has developed a method by which large yields of the highest quality are grown. The idea for this master was an abandoned vegetable garden and unkempt land. Having achieved excellent results, Rozum began to spread the idea, which since its inception began to gain popularity.


Warm-looking beds have their own specific classification:
- There are buried structures that are equipped by removing the top layer of the earth - sod. A trench is dug, and then it is filled with organic matter. The top of the bed should be filled with fertile soil, which is compared to the level of the removed soil.
- There are raised beds that are formed in boxes. In this case, a box is made of slate, boards or any other material, and then the container is also filled with organic substances.
- There are warm beds of the combined type. The lower layer is buried in the ground, and the upper part is raised.
- Warm beds in the form of elongated hills require the removal of the top layer of soil, but it is not required to make a box. Organic matter is poured directly onto the ground.
There are many reasons to make Rozum's beds, and it's worth getting to know each one individually. The demand for the beds is growing due to the fact that their creator is a trainee in organic farming, and he proved by personal example that his methods work. Even the most substandard soil can be made fertile. Particularly well suited are those lands that have not been planted for many years and only weeds have grown. With the help of special technologies, it is possible to make excellent soil from such soil in just 2 seasons. It is permissible to make a good vegetable garden even from the school site.
The yield of such beds is simply incredibly high, and they are suitable for growing completely different crops, especially for tomatoes, peppers and the like. It doesn't take too much effort, time or nerves to make fertile soil. In other words, the garden bed is done 1 time and for the entire time, and then it is simply used every year.
You can create such beds in different seasons, both in spring, and in summer or autumn.
What else is the popularity of Rozum's beds? Their peculiarity is that each garden bed is a whole store of knowledge, wisdom and research on organic fertilizers from specialist Rozum. There are basic principles that are important to consider when creating warm beds.You need to cultivate the soil with a flat cutter. It is necessary to carry out mulching and composting. Plants can be grown even if the area is not well lit. Creates an edging effect. Mixed plantings can be carried out. Plants will be protected from plants and pathogenic bacteria.