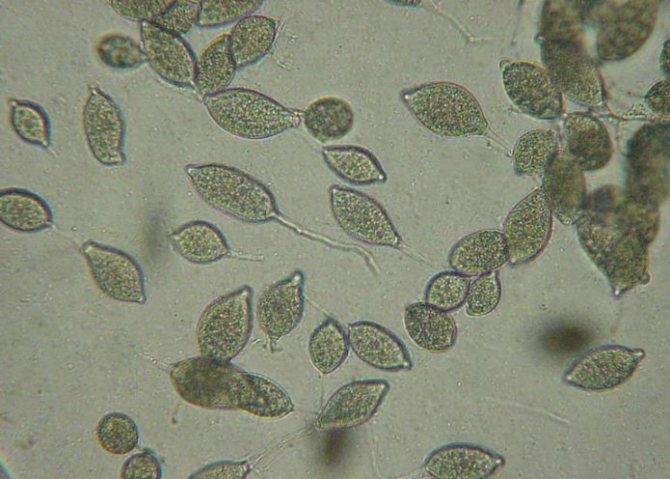
Among the fungal infections that affect vegetable crops, the most insidious is late blight on potatoes, tomatoes, and other plants. Now we will talk about root crops. Through my many years of experience in growing nutritious tubers, I have learned to cope with this scourge. Although it is not possible to completely exterminate the pathogen, prevention helps to keep the disease "in check." In unfavorable conditions, the crop can be saved if treatment is started on time.

Description of the disease


Phytophthora is a fungal disease caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans. The class is isolated from the kingdom of fungi, since the structure of the mycelial organisms of the oomycete is slightly different. Reproduction is through zoosporangia, the incubation period is from 3 to 16 days.
Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
The infection affects tubers, leaves, and plant shoots. Sources of infection:
- seed potatoes;
- tubers left in the soil after harvesting;
- plant residues.
The pathogen is distinguished by its vitality, resistance to subzero temperatures. Risk group - representatives of the nightshade family, among which, in addition to potatoes, sweet peppers, tomatoes, eggplants. Late blight occurs everywhere, with annual losses from fungal infection amounting to 15%.
Classification of preparations for processing potato tubers before and after planting
Treatment of potatoes from late blight before planting is carried out with special means. They affect the causative agent of the disease in different ways. It depends on the classification of the drug:
- Protective. From these chemicals, the spores die immediately, without having time to infect the bush or root crops after planting. Stems and leaves are treated with fungicide. On the bushes, the agent should be applied until the moment of infection. If this moment is missed, then the drug will not work.
- Medicinal. They are also called curative, designed to suppress the pathogen. It is also applied before the culture is infected.
- Eradicating. They destroy existing spores and prevent the emergence of new ones.

Varieties of drugs for mobility in potato tissues.
Translaminar
They only need to process the leaf plates of the bush, and it remains there until the next processing. The following are considered popular:
The active ingredients of the first drug are Mancozeb with Dimethomorph. The second has Famoxadon with Cymoxanil. Endowed with a combined action, contact activity.


Contact
The stems and leaves of the plant are processed. This group includes:
- "Bordeaux mixture";
- Kurzat R;
- copper sulfate;
- "Cupricol KOLR";
- "Ditan M-45";
- Shirlan.
The last two drugs belong to a group of substances that contain copper. The active ingredient of Ditan M-45 is Mankotseb, Fluazinam at Shirlan.


Systemic
The components of the drug move through the vessels of the plant: stems, foliage, tubers, returning back to the vessels of the tops. This group includes:
The active ingredient of the first drug Metaxil + Mancozeb. The second has Mefenoxam + Mancozeb.
Treatment of potatoes before planting against late blight is chosen independently by each gardener on the basis of these characteristics to the preparations, during each of the growing periods. Solutions are made according to the instructions attached to the preparations.It is advisable to process the potatoes before planting, if this has not been done, then this procedure should be started after the first shoots appear.
If you use it more often, then there is a risk of a new strain of spores, which, unlike the existing ones, will have greater resistance and endurance to late blight drugs.


Features and causes of occurrence
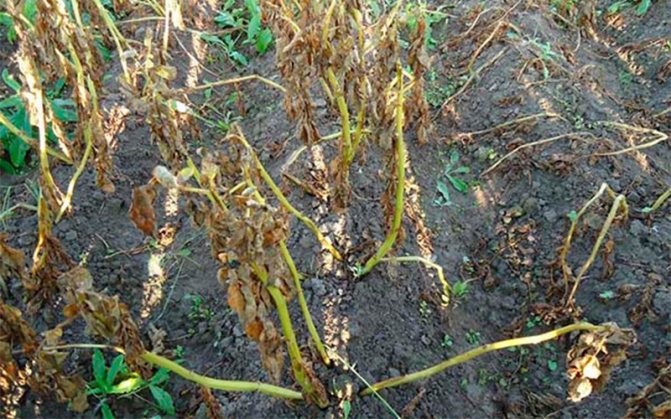


Over a long period, the fungus mutated, which led to the emergence of numerous phenotypes, more aggressive and dangerous. Previously, late blight on potatoes usually appeared in July, nowadays, from the beginning of summer in a number of regions, gardeners begin to notice signs of infection.
The new population is resistant to sudden changes in temperature, not so dependent on moisture indicators. The infection is aggressive, quickly spreading throughout the site.
On a note! If the degree of infection of the plant is 10-12%, then they get rid of the bushes (dig up and burn).
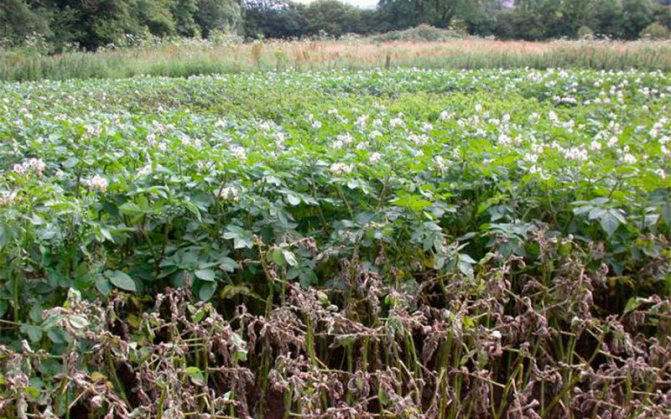


Reasons for the appearance of the pathogen:
- high humidity (especially if it rains for a long period);
- abundant dew;
- excess nitrogen fertilizers in the soil;
- deficiency of potassium, phosphorus, copper;
- thickened plantings.
The causative agent often passes from potatoes to ridges with tomatoes, eggplants, which leads to significant crop losses also on these crops.
What late blight looks like and what excites it
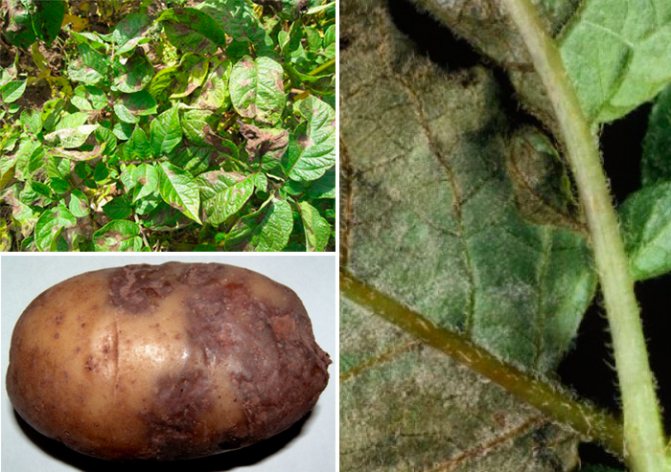
The fungus appears in the form of brown-gray spots on the potatoes. May develop on stems or foliage. It is forbidden to eat such potatoes. The causative agent is the pathogenic fungus Phytophthora infestans of the oomecitis species. Scientists believe that Mexico is considered its homeland. There are two strains:
- A1 - tolerates wintering well, does not form a spore;
- A2 - also tolerates wintering well, forms spores in comparison with the previous one.
Crossing oomecytes contributes to the emergence of more resistant strains to fungicides and severe frosts.


Signs of late blight
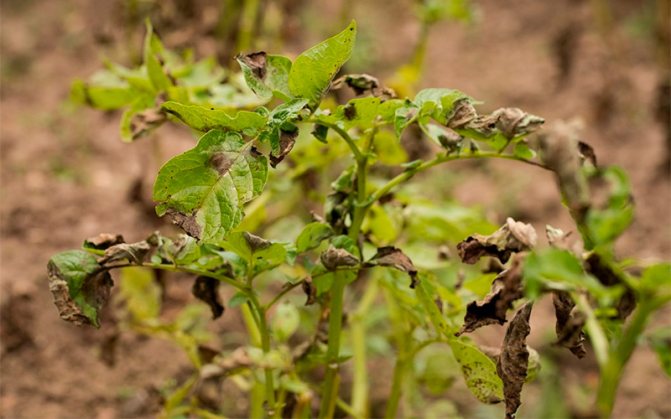


It is easy to determine that a dangerous fungus has appeared on potato bushes:
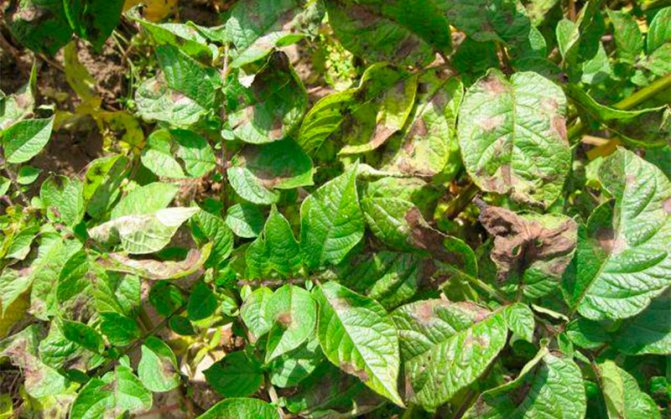
- the lower layer of leaves changes color, brown and black-brown spots appear. Single blotches gradually grow, a grayish-white bloom forms on the back of the leaf plates (see photo of the leaves);
- leaves curl, wither;
- dark spots appear on the shoots; in dry weather, the stems become brittle. If it rains, the stems rot, die off;
- discoloration of flowers, color loss;
- dense dry spots form on the tubers, on the peel and under it. With a strong infection, they capture all the pulp, changing its color to brown-rusty. Potatoes rots, softens.
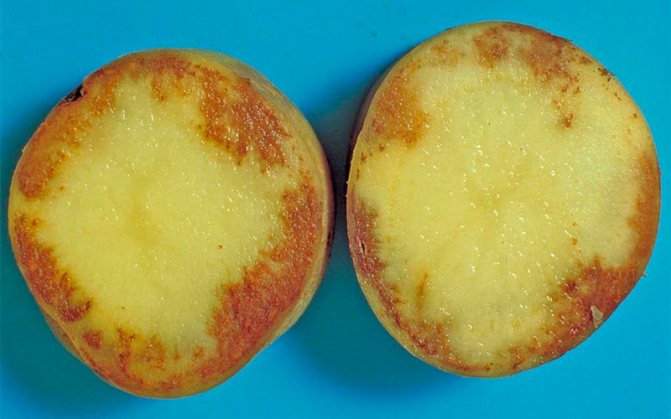


Healthy potatoes put in storage in the fall can rot if at least a few tubers infected with the pathogen get into the cellar or basement.
The harmfulness of the disease for potatoes
The harmful effect of the pathogen is to reduce the area of the plant's assimilation organs. Since it is in them that the accumulation of organic substances and the process of photosynthesis take place, the formation and accumulation of nutrients during the period of tuberization stops. Infected plants produce fewer fruits. When potatoes are damaged by late blight, the yield can be only 15-25%.
After the defeat of the assimilation surface of the plant, obligates infect young tubers. If you do not treat potatoes, you will not be able to save the crop. Root crops will be struck by pathogenic spores and become unsuitable for eating. Even 2-3% infected tubers are poorly preserved, after 50-60 days at an air temperature of +4 - + 8 degrees they rot.
Treatment
The fight against late blight on potatoes includes mainly agricultural techniques and prevention. Infection, especially with severe infection, is incurable.In the early stages of infection, plants can be saved by applying fungicides. Folk remedies are ineffective and "work" more for prevention.
Treatment scheme
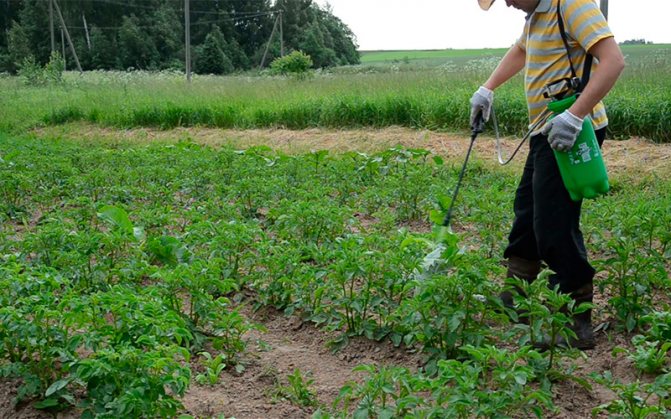


If in previous years late blight was noticed on potatoes, then in the new season, ridges and plantings are compulsorily processed.
Main steps:
- spraying bushes when they reach a height of 30 cm. Copper-containing compositions are selected (Bordeaux liquid 1%, copper sulfate);
- at the beginning of budding, the ridges are sprayed with solutions of Exiol, Epin (to protect and enhance immunity);
- after about 14 days, treatment with Efal-Aliett;
- after the end of flowering - two-time treatment with Bravo (interval - two weeks). For reprocessing Bravo can be replaced with Shirlan.


If there is a strong defeat of the bushes, then you will have to remove the plants from the site. The rest of the potato plantings are treated with fungicides Ridomil Gold MC, Oksikhom.
Attention! When using, they must follow the instructions, take into account the permitted processing times of the crop, taking into account the future harvest.
Application of fungicides
Gardeners use various drugs for late blight in the areas. It is necessary to study the instructions, a description of the action, and only then carry out the treatment.


Popular fungicides:
- Ridomil Gold;
- Artsdil;
- Oxyhom;
- Cuproxat;
- Ditamin;
- Acrobat MC;
- Metaxil.
Used for treatments Agat 25K, Immunocytophyte. The use of Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate is effective against pathogenic fungus.
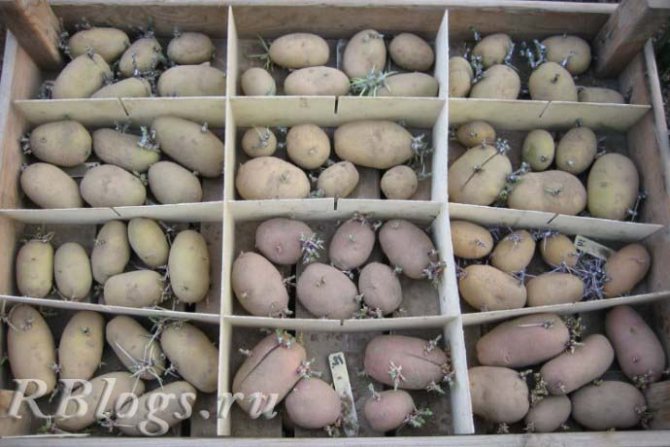
Preparations for dressing tubers:
- Prestige;
- Kolfugo is super;
- Maxim;
- Quadro.


For spraying seed material, biological products Gamair, Alirin-B, containing strains of beneficial soil bacteria, are also recommended. These products are also suitable for pre-planting soil treatment on ridges.
Folk remedies


From the means prepared according to folk recipes, from phytophthora on potatoes, they will partly help:
- garlic infusion;
- a solution of whey, sour milk or kefir (diluted with water in a 1: 1 ratio, add a few drops of iodine);
- decoction of marsh horsetail;
- infusion of hay and urea.
The aisles are powdered with ash, which is additionally a fertilizing crop.
Folk remedies
Wood ash, various pharmaceutical preparations, whey with iodine, yeast, horsetail decoction, table salt, tinder fungus, infusion of rotted hay - these are all popular ways to defeat the disease and increase plant immunity.
Ash
The soil around the bushes of potatoes and tomatoes is powdered with ash, and the ashes are infused in water and sprayed on the leaves - you can water the soil with the solution to reduce the activity of spores.
Milk and iodine
The bushes are sprayed with milk with iodine, adding grated laundry soap to keep the mixture on the leaves. A mixture of 10 liters of water, a liter of milk and 15 - 20 drops of iodine can kill spores. The procedure is carried out every 2 weeks .. The procedure is carried out on a cloudy day in the late afternoon. If it rains, the spraying is repeated.
Salt
A glass of salt in a bucket of water is a prophylactic agent, therefore, before spraying, all diseased plants are removed and burned. 100 g of tinder fungus is crushed and poured with boiling water. When the infusion has cooled, it is poured into a bucket of water and sprayed with tops. The effect is best manifested during the period of fruit setting of tomatoes or the formation of tubers.
Urea
Add 1 kg of hay and 2 - 3 tablespoons of carbamide (urea) to a bucket of water. The liquid is infused for 4 days, then the potatoes are sprayed at intervals of 10 - 14 days.
Yeast
When symptoms of late blight appear, dilute 100 g of yeast in 10 liters of water. The drug is used carefully, since yeast bacteria intensively absorb potassium from the soil, therefore, additional fertilizers are added to the garden.
Prophylaxis


To prevent the appearance of late blight on the site, you can use the following methods:
- observe crop rotation, alternating planting in the garden. This applies not only to potatoes, but also to all crops;
- disinfection of the soil at the site, planting green manure for the improvement of the soil;
- use for planting healthy seed;
- planting potato varieties resistant to late blight (see table);
- regular change of seed tubers;
- choice for potatoes well-lit by the sun beds, without close proximity to groundwater;
- planting plants of the Solanaceae family at a considerable distance from each other;
- regular weeding and loosening;
- application of potash and phosphorus fertilizers to the ridges, exclusion of excess nitrogen additives;
- obligatory hilling of potatoes;
- cleaning from the site of plant residues, tops;
- preventive treatments to prevent infection (from the very beginning of the growing season);
- trimming bots about 1.5-2 weeks before harvesting. During this time, the skin on the tubers will become coarse, there will be less mechanical damage to the potatoes.
Spores of the pathogen are present in varying amounts at many sites. The task of the gardener is to exclude the creation of favorable conditions for them, to avoid soil moisture on the ridges.
Sequencing


Cultivation of the land after harvesting potatoes should be done in the following sequence:
- Collect and burn the tops and rotten tubers.
- At the request of the gardener, dig up the soil a little or loosen it with a flat cutter.
- Spill places of growth of bushes affected by late blight with hot water, solutions of copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture. Ordinary boiling water, which is preferred by supporters of organic farming, is still better than poisoning the soil with copper salts, although it also kills the beneficial microflora.
- A day after watering with boiling water or 7-10 days after treatment with copper sulfate, it is recommended to spill the beds with a solution of any biological product. If the weather is still warm, EM fertilizers will do. "Trichodermin" and "Trichophyte" are incompatible with alkalizing fertilizers and are effective only for acidic soils. The universal and cheapest preparation of those that can be used in autumn to cultivate the land after potato phytophthora is Fitosporin-M.
- In the spring, fertilize the soil and shed again with a biological product. Apply organic and inorganic fertilizers as usual.
Potato varieties resistant to late blight
Planting crop varieties resistant to pathogenic fungus helps to solve the problem with late blight. At the same time, not only the resistance of the variety, hybrid to various diseases, but also recommendations for the region of cultivation are taken into account.


| Ripening terms | Variety name | Features of the |
| Early | Spring | Two varieties have been bred, differing in the color of the pulp - Spring white and yellow |
| Isora | ||
| Bullfinch | Pink rind, white flesh | |
| Luck | Excellent taste characteristics | |
| Desiree (Holland) | Yellow pulp | |
| Latona (Holland) | Very early with white flesh | |
| Lotus (Poland) | High yielding | |
| Timo (Finland) | ||
| Medium early | Sorcerer | High yield |
| Orederzhsky | ||
| Story | Good taste | |
| Rainbow | Red tubers, tasty, fruitful | |
| Nikita | ||
| Santa | High-yielding but satisfying taste | |
| Impala | Yellow pulp | |
| Mid-season | Lugovsky | |
| Shaman | Red and blue tubers, great taste | |
| Petersburg | ||
| Resource | White pulp and rind | |
| Gatchinsky | ||
| Svitanok (Ukraine) | Stores well | |
| Olevi (Denmark) | Excellent taste | |
| Granola (Germany) | Fast growth, great taste | |
| Symphony (Holland) | Red tubers | |
| Peter's riddle | Oval red tubers | |
| Equator | Pink tubers, small eyes | |
| Late and mid-late | Lorch | High starchy grade (up to 20%) |
| Robin | ||
| Purple | Blue pulp, great taste | |
| Saturn | ||
| Atlant |
Late varieties of potatoes are suitable for growing in the southern regions, since most of them do not have time to ripen in the conditions of the North-West, the middle lane. There are no varieties completely resistant to pathogens; preference should be given to early and mid-season varieties.
Growing potatoes and protecting them from late blight is a difficult task, but doable. Compliance with agricultural techniques, the use of healthy planting material, prevention - these are the three "whales" that will help you get an excellent harvest.
Natalia Severova