Home / Pests and diseases
Back to
Published: 03.07.2019
Reading time: 13 min
0
609
Even people far from truck farming know that there is such an insidious infection as potato late blight. What can we say about those who had to do their best to save plantings and crops from fungus in practice. The disease is easier to prevent, so it is important to know the causes of the appearance, the description and signs of the disease, and preventive measures.
- 1 Description of the disease
- 2 Features and causes of occurrence
- 3 Signs of late blight
- 4 Treatment 4.1 Treatment Scheme
- 4.2 Application of fungicides
- 4.3 Folk remedies
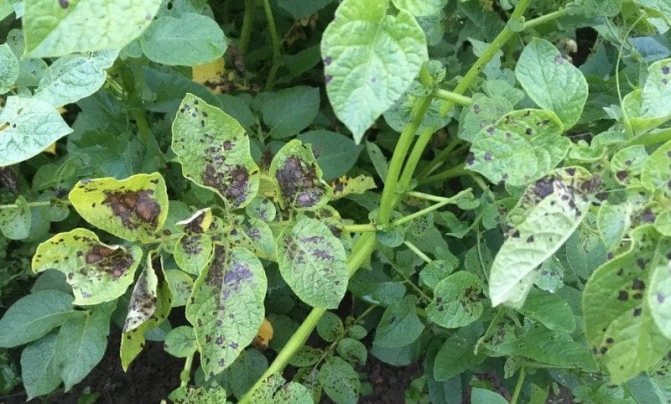
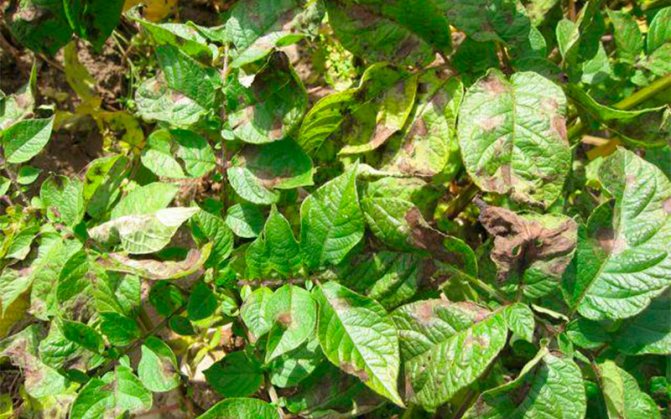
Signs of infection
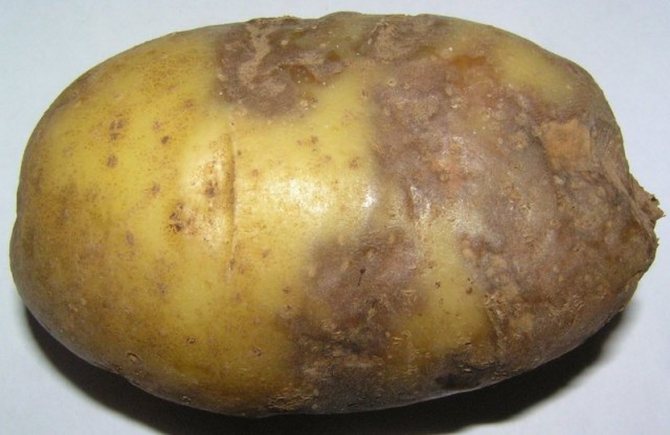
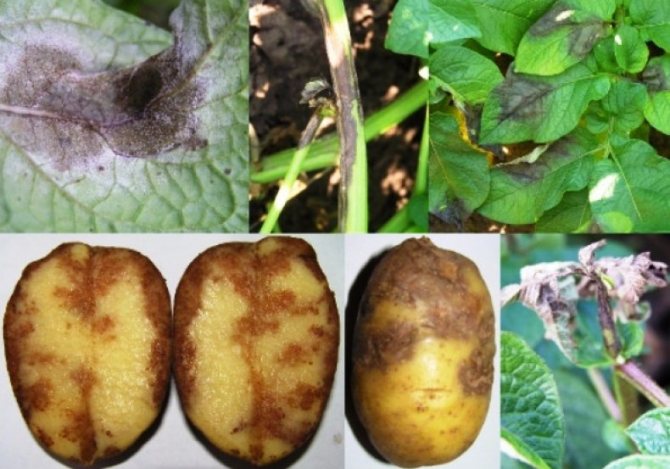
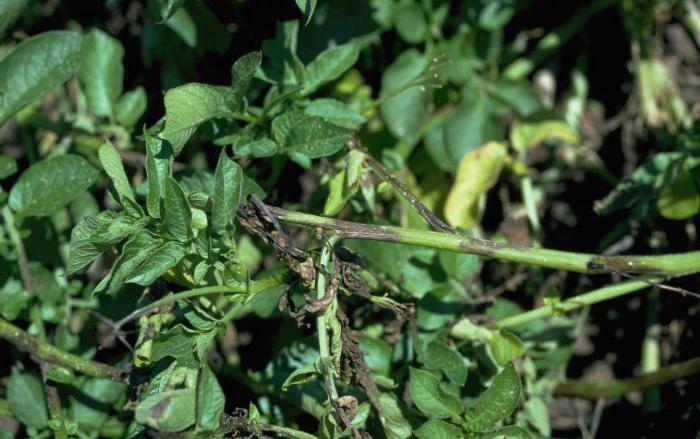
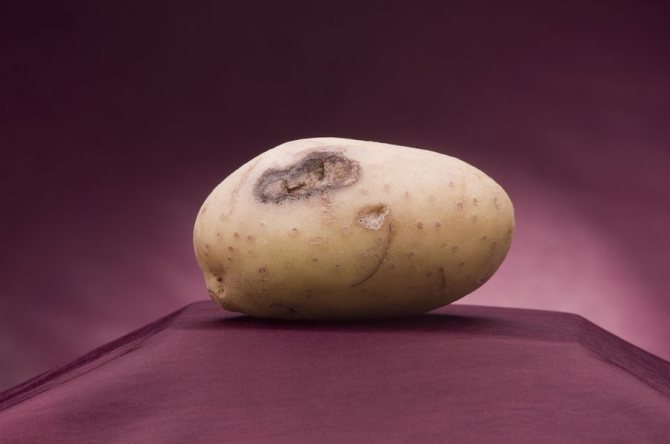
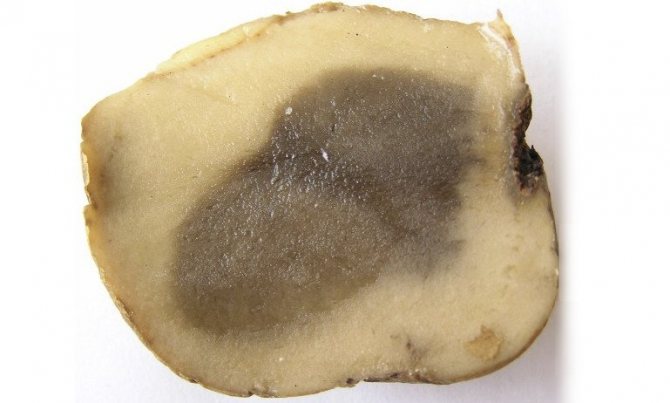
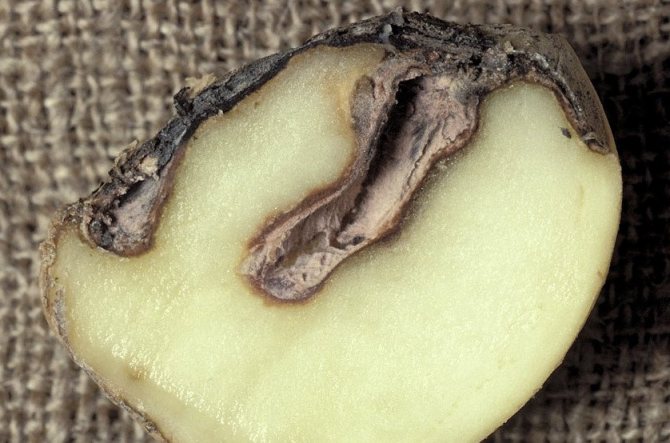
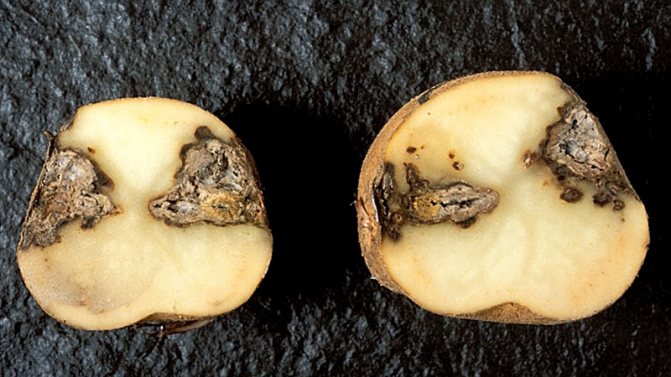
The disease first manifests itself on the lower leaves of potato bushes in the form of brown spots with a barely noticeable fluffy light bloom. Then it spreads to the rest of the leaves and tubers. The stems are covered with dark stripes. The affected tuber looks darkened, as if ulcerated. If such symptoms appear, the plant may die without treatment in a day or two.

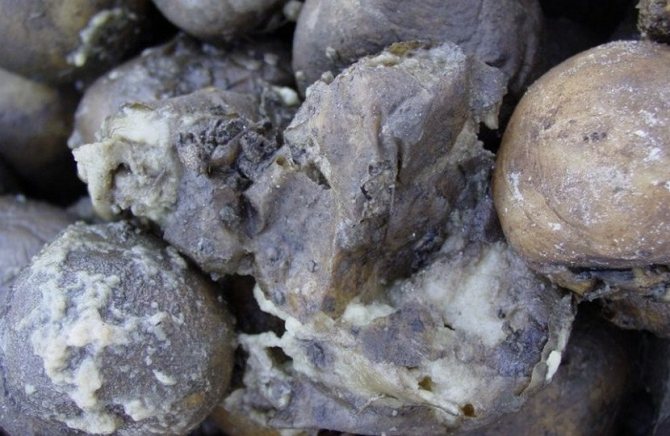
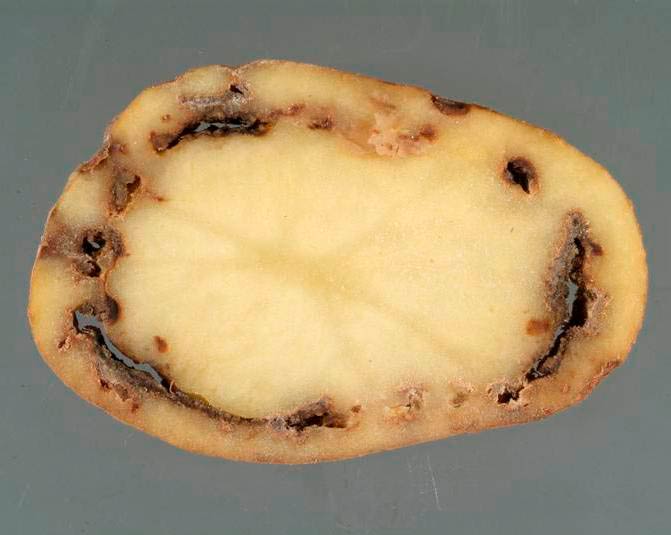
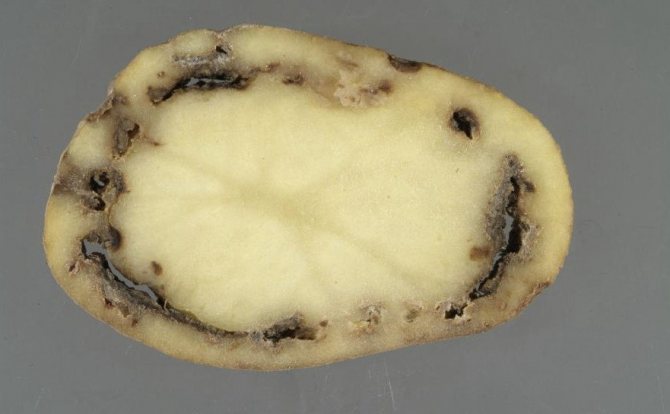
Phoma rot
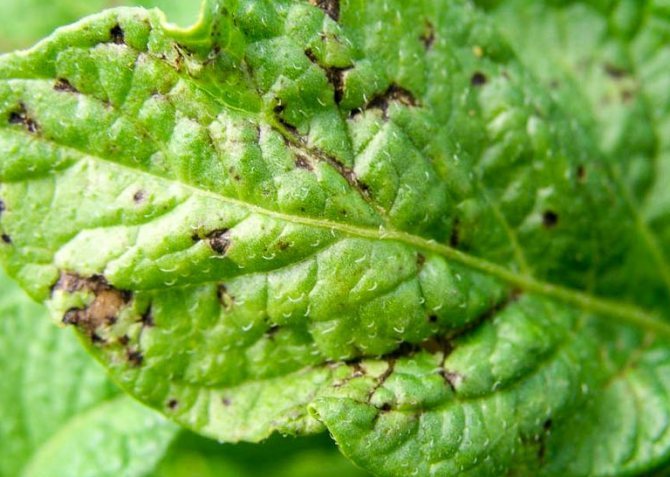
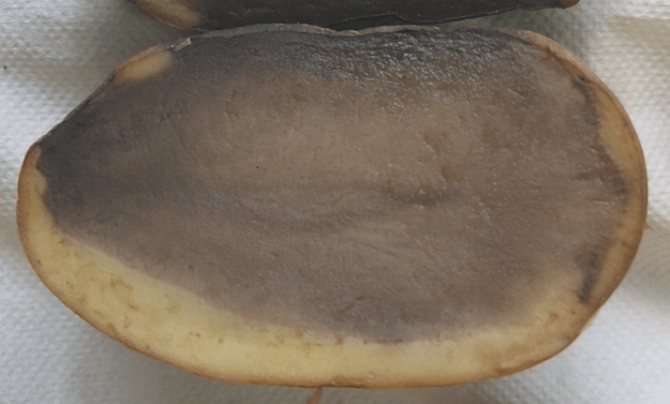
It is activated if during the growing season there was a low air temperature and a lot of precipitation. Sometimes in warm climates, elongated spots of light yellow or brown color appear on the stem at the base of the petioles.
Symptoms On the tuber affected by phoma rot, depressed rounded spots with a diameter of 2-5 cm appear, the peel in the infected places remains taut, but inside the rot destroys almost all the pulp.
Prevention. Maintain the recommended temperature in the potato storage, preventing the development of fungi.
Phoma rot is not always visible on the surface
Effective drugs and remedies for the fight and treatment
Since the disease spreads very quickly and can destroy almost the entire crop within a week, chemicals are the most effective in controlling it. The agrochemical industry, as it develops, offers new tools that combine efficiency and environmental safety. The descriptions below will help you navigate the choice.
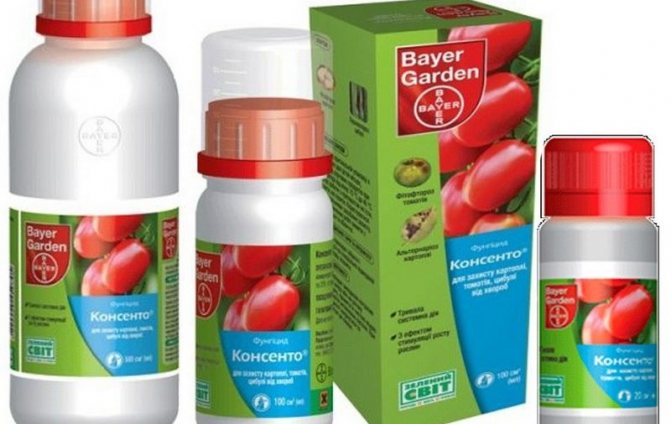
"Consento"
It is a systemic fungicide based on fenamidone and propamocarb hydrochloride. The first does not allow the cells of the fungus to breathe, and the second destroys the biosynthesis of their phospholipids and fatty acids. The remedy is more effective for the prevention of late blight than for treatment.


Infinito
Another systemic fungicide with active substances propamocarb hydrochloride and fluopicolide, which protects plants for a long time. You can effectively treat potatoes with it: zoospores die as soon as the agent hits the surface of the leaves.
"Quadris"
Fungicide, which allows you to control not only late blight of potatoes, but also other diseases of garden crops. The main active ingredient is azoxystrobin, which provides not only long-term protection of the plants treated with it, but also:
- increased productivity due to increased photosynthesis;
- improving the quality of root crops.
It is most effective if used prophylactically or in the early stages of late blight.
"Energodar-Ukravit"
A product based on propamocarb hydrochloride and aluminum fosetyl protects even untreated parts of the bushes and new growth. At the same time it helps to strengthen the immune system and stimulates plant growth.
"Fitosporin"
Biofungicide containing a strain of hay bacillus - bacteria Bacillus subtilis 26 D. From different types of means for potatoes are used:
- powder "Fitosporin-M";
- paste "Fitosporin-M Universal";
- paste "Fitosporin-M Potato".


The tool can be used at any stage of the growing season of the crop and even eat root crops by washing them with water immediately after processing.
Copper sulfate
Due to its low cost and availability, it is one of the most popular fungicides. It is applicable at any stage of crop cultivation: not only plants are treated with it, but tubers are also treated with it before planting, and the soil and storage facilities are disinfected.
The product should be diluted in containers made of enamel, plastic, ceramics or glass. In metal containers, copper sulfate oxidizes the metal, forming ferrous sulfate and pure copper.
Bordeaux liquid
Another proven and cheap remedy for late blight is a mixture of copper sulfate and slaked lime, dissolved in water. Both ingredients react with metals, so containers made of other materials are used to prepare the solution.


For people and animals, Bordeaux mixture is low-toxic, and for bees it is safe a few hours after application.
"Revus"
Modern systemic fungicide that protects potatoes from major diseases, including late blight. Deingredients: mandipropamide and difenoconazole. Long-term protection against the disease - up to two weeks after treatment. It is used at the end of flowering and at the beginning of tuberization.
"Hom"
In fact, this tool is an analogue of the Bordeaux mixture, since the main active ingredient is copper oxychloride. Accordingly, the rules for its use are similar to those for Bordeaux mixture.


"Bravo"
Organochlorine pesticide with active ingredient chlorothalonil. Has excellent rain resistance.
"Oxyhom"
A variation of the drug "Hom", supplemented by a chemical compound of systemic influence, oxadixil. It spreads into leaves and stems, destroying pathogenic microorganisms and providing long-term internal plant protection.
Shirlan
A contact fungicide used primarily for disease prevention. The active substance is fluazinam. It has a high resistance to washing off, and therefore guarantees the protection of potatoes from late blight, even in case of precipitation or under irrigation conditions.
"Ditan M-45"
Another prophylactic agent based on mancozeb, which destroys fungal spores as a result of affecting the metabolism in their cells. Additionally, manganese and zinc enhance photosynthesis in the leaves and improve the development of the leaf apparatus.
Metaxil
Two-component fungicide (active substances - mancozeb and metalaxyl), which protects against infection by pathogenic organisms both from the outside and from the inside. The drug is used prophylactically. It is toxic: for industrial use, it is not recommended to spray it by air, and its use in the sanitary zone around fish farms is completely prohibited.
Rapid Gold
Highly effective two-component fungicide with the main active ingredients mancozeb and cymoxanil. The first forms a protective film against pathogens on the surface of leaf plates and stems, and the second blocks the growth of mycelium and the formation of spores.
The drug decomposes quickly in the soil. Toxic to humans, low-hazard to bees.
"Profit Gold"
Similar to the previous contact-systemic action of the fungicide, in which famoxadone provides long-term surface protection.
Thanos
Like other two-component fungicides, the action of Thanos is local-systemic: it penetrates deeply into plant tissues, remaining in the treatment area. This ability is provided by the "duet" of active substances - cymoxanil and famoxadone. The tool destroys spores of fungi that have sprouted into leaves and shoots and the entire adult mycelium at any stage of its development. Thus, it is effective for the prevention of late blight and for the treatment of plants.
Ridomil Gold
The active ingredients of the drug are mancozeb and mefenoxam. It is a preventive and curative fungicide. It performs systemic and translaminar action, protecting not only the aerial parts of the potato, but also the tubers. Also protects root crops from infection when stored in storage.
"Acrobat MC"
The Swiss-made drug combines two active ingredients - dimethomorph and mancozeb - which provide contact and local-systemic effects on not only late blight pathogens, but also many other fungal infections. At the same time, "Acrobat" remains safe for bees and other beneficial insects.
Kurzat R
This fungicide, produced by the American firm DuPont, acts even on those pathogenic strains that have developed resistance to phenylamide pesticides. The product contains active ingredients:
- copper oxychloride, which destroys the pogogenic flora on the leaf surface;
- cymoxanil, which impregnates the tops and helps the drug to be distributed more evenly.
Expert opinion
Stanislav Pavlovich
17 years of experience gardener and our expert See also How to grow potatoes from seeds and when to harvest them
Ask a Question
Potatoes are eaten no earlier than 3 weeks after processing.
"Ordan"
Russian-made effective analogue of the above-mentioned drug, which has a lower cost.
"Alirin-B"
Biological product (biological pesticide), the active ingredient of which is the Bacillus subtilis strain 10VIZR. It is able not only to suppress the activity of pathogens of fungal and bacterial infections, but also to stimulate plant growth. The tool is inexpensive, safe and effective no worse than chemical fungicides.
"Gamair"
Another biopesticide based on the same aerobic soil bacteria Bacillus subtilis.
"Trichodermin"
Spores and mycelium of a fungus from the genus Trichoderma viride — the basis of the biological product "Trichodermin", which inhibits development of phytophthora and potato yield-promoting growth. The tool blocks the development of pathogens by direct parasitism - it releases enzymes, natural antibiotics, and other bioactive substances that inhibit many types of pathogens.
What is late blight
Late blight is a disease caused by the late blight fungus. Mycelial lower organisms lead a parasitic way of life, destroying plant tissues.
Historical reference. In 1845-1849, the fungus Phytophthora infestans caused a significant spread of late blight, which led to the Great Famine in Ireland.
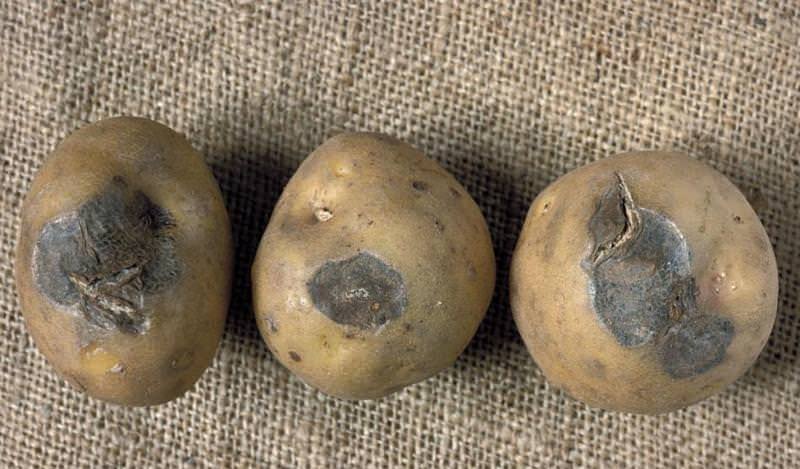
The photo shows potatoes affected by late blight.


Description and characteristics of the disease
For the first time, the disease was discovered practically simultaneously in the USA and Europe in 1842-1843. Presumably, phytophthora was brought from Peru during the export of Chilean nitrate in the early 1840s. The German scientist de Bary, who described the pathogen, called it "phytophthora", which literally means "plant eater."
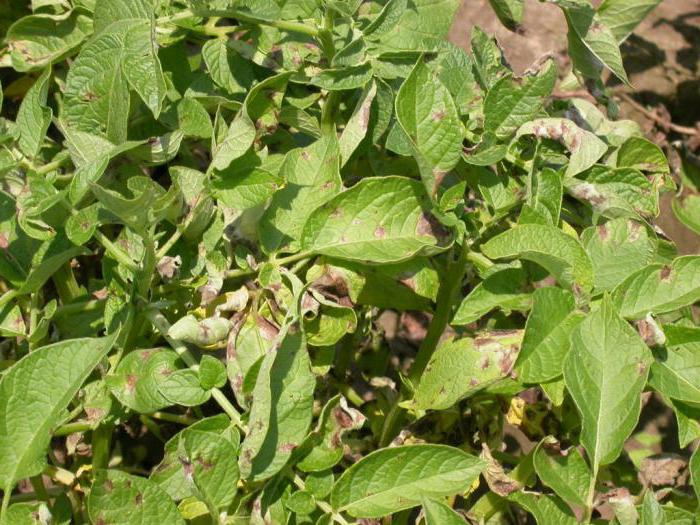
Potato plantings are affected by the fungus Phytophthora infestans Mont. de Bary, named after the same scientist. The pathogen is activated from the end of May to August and spreads with lightning speed in conditions of high air and soil humidity, sudden changes in day and night temperatures, morning dews and fogs. Simply put, wet and cool weather is the optimal environment for the development of phytophthora. In the southern regions, it spreads to abundantly irrigated areas.
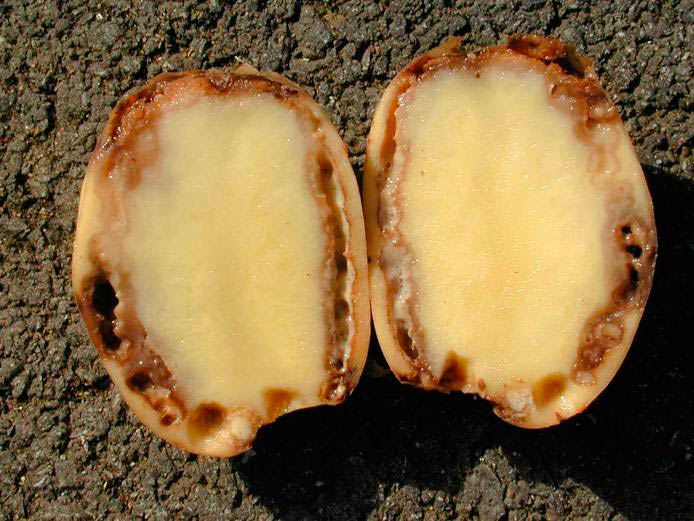
Potatoes are sick with late blight of tops and tubers... Damage to greens is observed at 20-50% of plantings, and tubers - by 8-23%. Crop losses are 30-50%.
Phytophthora, introduced to Europe in the 19th century, was the only causative agent of the disease of the same name until the 80s of the 20th century. In Switzerland and other European countries, a new genotype of the fungus, A2, was discovered, which differs from the previous ones in aggressiveness and the ability to easily adapt to adverse conditions.
As a result of the joint development of both forms, new sexual structures, oospores, were formed. They have a thick two-layer shell, for a long period remain viable in low temperature conditions, overwinter on tubers, leaf residues and in the ground.
The disease began to be detected on the stems 1-4 weeks earlier than usual, the level of infection of tubers increased.
Reference. With the appearance of the A2 fungus form, the disease is diagnosed in the germination phase. Oospores remain viable for 4 years, accumulate in the ground and, under favorable conditions, cause an outbreak of the disease.
Traditional methods and recipes
Preventive measures based on the old folk methods proven over the years are very effective for owners of small potato plots. Moreover, they are completely safe for people, domestic animals, beneficial insects, including bees.
Milk whey and iodine
Serum is considered one of the best remedies in the fight against late blight. It creates a thin film on the foliage that protects against fungi. At the same time, lactic acid bacteria are unpleasant for pathogens: it does not spread to areas with an acidic environment.


Disadvantage of the method: whey inhibits phytophthora, but does not fight it. The first light rain will wash away the protective layer, so you need to repeat the treatments constantly every 10 days: 10 liters of water and 20 drops of iodine are added to a liter of serum.
Yeast feeding
The remedy is valuable for potatoes by the content of unicellular fungi in it, which prevent the reproduction of pathogenic "brothers", including late blight pathogens, but at the same time do not interfere with the development of beneficial soil bacteria.
In 3 liters of water, dissolve 100 g of pressed yeast and the same amount of sugar, insist for a week. Then a glass of the resulting "mash" is bred in a bucket of water and watered with each bush of potatoes.
Wood ash
Ash is both a protection against late blight and a fertilizer for potatoes. It can be used at any stage of the growing season. To keep it on young shoots longer, it is diluted in water along with laundry soap and sprayed with plantings.
Mature hay
A mushroom-antagonist of late blight pathogen - a hay bacillus - lives in slightly dried hay or grass, so mulching the beds with such material is an additional tool in the fight against infection.
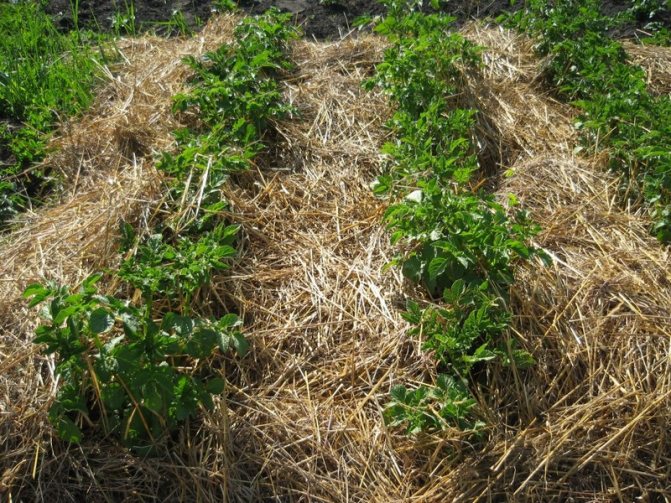


Skim milk or peroxidized kefir
Natural (not store-bought) skim milk is used as a replacement for whey. The proportions of the recipe are about the same: a liter of milk per bucket of water plus 15 drops of iodine.
The use of fresh kefir will not give an effect, and the peroxide is diluted in 10 liters of water in the same proportion as whey or milk.
Garlic
This is an excellent remedy for the prevention of many fungal diseases. The arrows are crushed in a meat grinder and 10 liters of water are added to one and a half glasses of gruel. Insist day, make 1.5 g of potassium permanganate and process potato bushes.
Trichopolus
A solution of the antimicrobial drug Trichopolum with brilliant green is effective for the prevention of late blight and at the very early stage of its development.
10 tablets of Trichopolum are kneaded to a powder state and diluted in 10 liters of water. Root vegetables can be eaten 10 days after processing.
Field horsetail
It is also able to stop the spread of the fungus in the early stages, and at the same time increase the immunity of potatoes.To prepare the product, 250 g of chopped herbs are poured with a liter of boiling water and kept on low heat for half an hour. Strain and dilute in a bucket of water.


Soap-ash solution
The soap in the recipe is used to hold ash on the leaves and stems of potatoes:
- for three days, 2 liters of ash are insisted in a bucket of water;
- filter and dissolve 50 g of grated simple laundry soap in this liquid.
Zelenka
It also helps fight late blight on potatoes. A few drops are diluted in a bucket of water and sprayed on the bushes.
Flaxseed oil or fish oil
One of the recent discoveries is that seed potatoes treated with flaxseed oil or cod liver oil are less likely to suffer from late blight.


Causes, symptoms of potato lesions by late blight
First, a few words about how disputes are spread. In addition to the wind, they are carried by:
- rodents;
- people on clothes, shoes;
- pets;
- birds;
- insects, the same Colorado potato beetle, butterflies.
The infection can be introduced into the soil:
- when planting infected seed, the insidious late blight on the tubers does not appear immediately;
- using raw tools, containers;
- if you add compost from rotted diseased tops;
- with manure;
- when irrigating with contaminated water from open reservoirs, barrels; when favorable conditions arise: the temperature drops, it starts to rain.
At high humidity, contrast of night and daytime temperatures, mycelium swell and begin to develop. Burst, sowing nearby plants. Even a single, point appearance of rot is dangerous. By the way, if tomatoes are affected in a greenhouse or spotting appears on apple trees or berry fields, you urgently need to control the planting of potatoes, spray them to prevent late blight.
By the way, it is better to dig up the affected potatoes ahead of time if these are single bushes. Harvested from infected plants and stored separately from the rest of the potatoes. Consumed first.
The infection spreads through the plant from the bottom up, first the leaf plates located near the ground, then the trunk, the top. The cells dry out, dehydrate, the leaves, the trunk become fragile.
Treatment scheme
The processing time for potato seedlings depends on many factors - weather, crop variety, pickling of raw materials and others. Usually, for prevention, the following rules are followed:
- the first spraying is carried out when the potato sprouts are extended by 20-25 cm, until the rows close. Apply drugs of local systemic action;
- the second treatment is carried out a week or ten days after the first with one of the systemic preparations containing phenylamides;
- further processing is carried out according to the instructions of the selected drug. Usually at least five procedures are performed per season.
Given the toxicity of most chemicals, the last treatment is carried out no later than three weeks before digging up the potato crop (usually no later than the end of July).
If the plants are already sick, they can be saved only when the infection is "captured" at the very beginning.
Spread
Late blight and Alternaria are common in all areas of potato cultivation.
Late blight significantly damages crops in the Central Black Earth Region, Central Russia, North Caucasus, Northwest, Urals, Siberia, Far East, Kamchatka and Sakhalin.
Alternaria causes the greatest harm in the Far East, Sakhalin, Eastern Siberia, as well as in Belarus, Moldova, Ukraine, Tambov, Oryol, Belgorod, Smolensk, Volgograd, Rostov, Saratov, Astrakhan regions, Kabardino-Balkaria.
Prevention measures
In addition to treatment with special drugs, preventive measures include the following:
- the right choice of a place for planting potatoes, taking into account the crop rotation,
- the use of late blight-resistant crop varieties,
- agrotechnical techniques,
- pre-sowing processing of seed material.
Agrotechnical techniques
Their complex application can significantly reduce the risk of outbreaks of potato late blight disease. Let's list these techniques:
- early landings;
- sparseness of bushes;
- mulching the beds;
- timely application of potash fertilizers in the correct dosage;
- quick utilization of tops after harvesting;
- regular soil greening;
- disinfection of holes during planting and others.


The most effective measure remains the pre-planting treatment of tubers.
Crop rotation
Potatoes are planted away from other vegetable crops of the nightshade family (peppers, tomatoes, eggplants and others) and planted in the same place no earlier than 4-6 years later. Cereal and legume-cereal mixtures are considered the best predecessors.
Early planting dates
Early sowing of potatoes provides an early harvest, since it is possible to harvest it before the end of July - at this time there are outbreaks of late blight.


Cultivation of very early varieties
Another way to get a crop of potatoes before the onset of massive epidemics of late blight, where early sowing is impossible. True, early maturing crop species have worse keeping quality and taste, and the seed fund is more difficult to protect from excessive germination before planting.
Healthy planting material
It has been experimentally established that the presence of 1% of tubers affected by late blight in the seed fund leads to a decrease in yield by 10%, and 5% of such potatoes will ensure that a fifth of the harvest is not obtained. Therefore, when preparing potatoes for planting, they are not only germinated, but also warmed up: already at 15-17 ° C, small late blight specks are clearly visible, diseased tubers can be removed.
Preplanting tubers
To limit the development of soil infection, potato seed tubers should be treated with fungicides before planting according to the attached instructions. When it comes to planting in personal plots, this method of preventing late blight remains the most effective.


Planting without thickening
The high density of potato plantings creates favorable conditions for the development of late blight - increased humidity and temperature. A planting scheme with wider row spacings, despite the seeming uneconomic use of space, ultimately allows you to get a higher yield.
Timely weeding
Weeds in the potato beds create the above thickening. In addition, they also accumulate a large number of spores. Therefore, regular weeding is another way to protect root crops from late blight.


Hilling
Hilling potatoes solves several problems at once:
- loosening the soil prevents the penetration of spores washed off by sediments from the foliage to the tubers;
- additionally, a volume is created for the formation of tubers in it;
- weeds are removed.
Timely watering
Since dampness is the best friend of phytophthora, watering dry cool weather is carried out only under the stem, so that moisture, if possible, does not get on the potato tops.


Disinfection of tools and shoes
This factor in the prevention of the disease is rarely paid attention to and, while fighting the outbreak of late blight, at the same time it is spread on shoes and tools to “clean” areas of the garden.
Preventive and curative treatments
If other agrotechnical methods of curbing the development of late blight are unavailable or ineffective, the potato plots are protected by multiple (at least 5-6 treatments per season) application of fungicides.
Spraying crops before storing
For seed potatoes, taste is not important, the main thing is that it must be healthy in the spring.Therefore, tubers can be sprayed with the simplest means - brilliant green, copper sulfate, and if they are collected from recovered plants, potent preparations are needed for autumn dressing.
Hardy varieties
Planting potatoes resistant to late blight reduces the risk of death and damage to the crop. Such properties of it are best revealed when taking into account the zoning of varieties. According to the degree and type of resistance to pathogenic fungus, varieties are distinguished in which tops, tubers are more "hardy", or those in which all parts of the plant are immune to phytophthora.
Tops
Potato tubers receive useful substances not only from the soil through the roots, but also through photosynthesis in the leaves from the tops. Therefore, varieties with tops that are resistant to late blight give a high yield.
Bolvinsky
Domestic mid-season potato variety. The cultivation technique is standard, preferably in the Central Region.


Valor
British selection potato variety of medium late maturity. Also targeted for cultivation in the Central Region.
See also Potato pests: description and control of them
Master
Another Russian mid-season table potato. The best regions for cultivation are Central, Volgo-Vyatka.
Onega
Medium resistant to late blight potato variety bred in Russia - medium early, excellent keeping quality. Suitable for growing in the Northern region.
Russian souvenir
Domestic selection of medium early ripening variety. Cultivation is preferable in the North Caucasian, Middle Volga regions.
Tubers
The immunity to late blight of tubers of certain varieties is fully manifested only if the rules of agricultural technology are observed.
Arrow
The name of the Dutch variety means "arrow". Ripening early, the first digging can be done after 45 days. The climate of the Central region of the country is optimal for cultivation.
Asterix
Another well-proven Dutch potato variety with consistent yields. The climate of the Middle Volga and Far Eastern regions allows for the highest yields.
Snow White
An unpretentious variety bred in Russia. Medium early, starchy. The Central and Far Eastern regions are more suitable for cultivation.
Visa
Medium early potato variety, obtained in Russia. The best regions for cultivation are the North, Volgo-Vyatka.


Elizabeth
One of the long-lived varieties has been cultivated for a long time and remains popular. Russian breeders have bred really wonderful mid-early potatoes: suitable for growing in most regions of the country, good taste, with pulp that does not darken in air or in contact with metal.
Pretty boy
Russian variety of medium-early ripening potatoes. Resistant to drought and tolerates mechanical damage well. The recommended cultivation region is Central Black Earth.
Lasunak
Excellent taste and high resistance to the Colorado potato beetle. The most popular of the mid-late species bred in Belarus. Poor drought tolerance, but suitable for all types of soil. The most productive cultivation is in the Central and Far Eastern regions.
Madeline
A very promising medium-early maturing Dutch potato variety. Resistant to mechanical damage, can adapt to climate and soil. Tubers do not germinate for a long time. The Central, Far Eastern regions are recommended for cultivation.
Manitou
This "Dutchman" is a late-ripening variety. The optimum climate for cultivation is in the Central Black Earth and North Caucasian regions.
Meteor
Super early domestic variety. Gives stable yields under different climatic conditions, grows well on loams, undemanding to watering. Included in the State Register for the Central, Central Black Earth, Volgo-Vyatka and West Siberian regions.


Mustang
Medium late variety of Dutch selection.In the Central and East Siberian regions it gives the highest yields.
Flint
An early maturing product of the selection of Russian specialists. Cultivation in the Volgo-Vyatka region is preferable.
Oredezhsky
Medium early collection Russian variety. The tubers are very good keeping quality: 99% preservation. The undoubted plus of the variety is a stable yield regardless of the weather. The Ural region is preferable for cultivation.
Polonaise
Medium late domestic variety, focused on cultivation in the Central region of the country.
Fresco
The harvest of this early maturing variety of Dutch selection in the southern regions can be harvested twice a season. Disadvantage: prone to early germination. Suitable for most regions of Russia - from the North to the Far East.
Jarl
Early maturing Dutch potato variety. The climate of the Central and Lower Volga regions is best suited for its cultivation.
Complex endurance
This term means that both the tops and tubers of the variety are immune to late blight, subject to the usual agrotechnical rules for growing potatoes. It is these types of culture that are preferred in areas where late blight is common. Experienced potato growers advise planting several varieties on the site, different in terms of ripening.
Dad
Medium ripening potato variety of domestic selection. Recommended for the Central region of Russia.


Bryansk novelty
Another Russian variety with similar characteristics. Suitable for the Central and Central Black Earth regions.
Bryansk jubilee
This mid-early potato variety is the result of the work of Russian breeders. Keeping quality is excellent (98%). Included in the State Register of the Volgo-Vyatka region.
Burnovsky
The variety, bred in Bashkiria, is resistant to drought and many diseases, in addition to late blight. Colorado potato beetle is slightly affected, suffers mechanical damage without decay. The best region for cultivation is the Ural region.
Vega
A wonderful early potato variety that came to us from Germany. A special feature is smooth, beautiful tubers. The rest period is long (safety until spring - 99%). Light frosts, heat, drought do not affect its productivity. It is only harmed by stagnation of water in the soil. Cultivation in the Central region is preferred.
Vector
The Belarusian medium late variety was "born" in 2013. Resistant to most potato diseases, yields on any soil, tolerates heat and drought normally. Suitable for growing in all regions of the country.
Wendy
German breeding medium-early high-yield potato variety with beautiful tubers. Resistant to many potato infections and mechanical damage. Can adapt to soil and climate. The best growing area is Central.
Detskoselsky
Medium early domestic variety. It also has a remarkable ability to adapt to climate and soil.


Eurostarch
Another product of the selection of German scientists is a medium-late potato variety, recommended for regions with problematic climates and soil conditions.
Zekura
A very unpretentious variety of medium early ripening, originally from Germany. Gives high yields of root crops with excellent taste in almost all regions of Russia.
Inara
Another fruit of German breeding: early maturing, beautiful-looking variety.
Karatop
This early German variety, despite its small tuber mass, is distinguished by the fact that it gives stable yields even on problem soils. Well transported and mechanically cleaned.
Caruso
Early ripe "German", the best region for its cultivation is the Middle Volga.
Kemerovo resident
Bred especially for Siberia, a medium early, unpretentious potato variety. It tolerates mechanical damage well.
Beauty
Early ripe potatoes of Russian selection with dark red peel. Preferred cultivation in the Central region of the country
Bodywork
Medium ripening, domestic selection. Resistant to many diseases of culture. Recommended for cultivation in the Ural region.
Lazarus
A mid-season, drought-resistant potato variety - the result of the work of Russian breeders. Suitable for starch processing.


Lina
The mid-early domestic variety is especially popular in the Urals, in Siberia due to its high yield even under difficult weather conditions. The tubers are smooth, beautiful. It tolerates transportation well. Its cultivation is also effective in the North Caucasus and the Far East.
Lugovskoy
A mid-season variety, bred by Ukrainian breeders, is widely popular among potato growers due to the fact that it gives consistently high yields in all regions of Russia, regardless of climatic conditions. Tubers are smooth, large, with long keeping quality.
Beloved
The variety is still of Soviet selection (created in 1958) - medium early, universal, proven. Therefore, it is widespread, despite its mediocre taste.
Mother
Domestic early ripe potato variety. Due to its high drought resistance, it is preferable for cultivation from the Middle Volga region.
Musinsky
Medium late variety, with high keeping quality, excellent taste. Recommended for the regions of the North Caucasus.
Nalchik
Another mid-season potato variety suitable for the North Caucasus region.


Newton
An early ripe potato variety from American breeders. It is unpretentious in leaving. Focused on cultivation in the Central region of the country.
Omega
German mid-season variety of excellent taste, also the most suitable for the Central region of Russia.
Patriot
Potato variety of medium early ripening, high keeping quality. The result of Russian selection. The preferred cultivation region is Central.
Prestige
Mid-season, excellent taste and good keeping quality potatoes of domestic selection. Included in the State Register for the Central Region.
Prize-winner
Medium early potatoes with very large tubers (up to 400 g) and a lot of them in the bush. Also focused on cultivation in the Central region.
Rosara
The product of the selection of German scientists now occupies the 4th place in the world in terms of yield. Early potato variety with excellent taste. Adapts to the climatic conditions of different regions.
Russian beauty
Medium late Russian potato variety with good taste. Located in the State Register of the Central Region.


Santa
Medium-ripening Dutch potato variety. The yield is high. Designed for mechanical cleaning and processing. Adapted for the climate of the middle zone and southern regions of Russia.
Northern Lights
Medium early potatoes. The tubers have good taste. In the West Siberian region, it is included in the State Register for household and small farms.
Favorite
Medium ripening potatoes. Unpretentious care. Most suitable for cultivation in the Central region.
Purple
Purple potato varieties do not belong to the nightshade, but to the bindweed family. The culture was bred in South America, has medicinal qualities, the taste of the tubers is similar to ordinary potatoes, but with a creamy texture and a mild nutty flavor.


Fokinsky
Mid-season potato variety with large tubers. Located in the State Register for the Central Region.
Sorcerer
Combines good taste and unpretentious care. Suitable for most regions of the country. Medium early ripening.
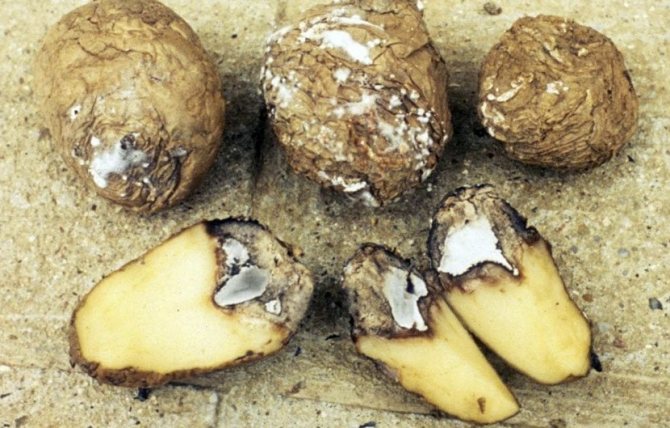
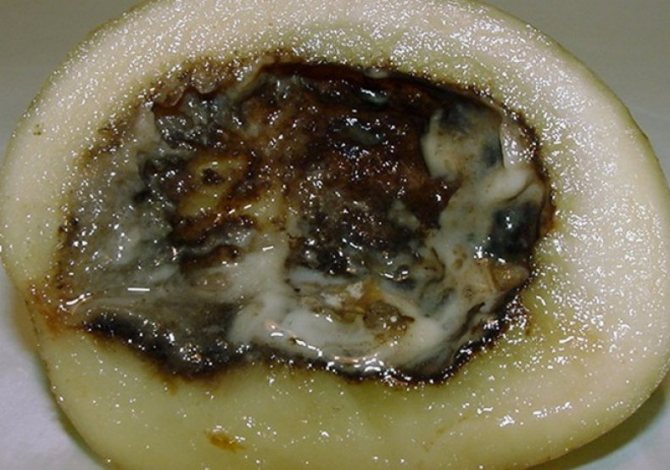
Bacterial disease of potato tops - black leg
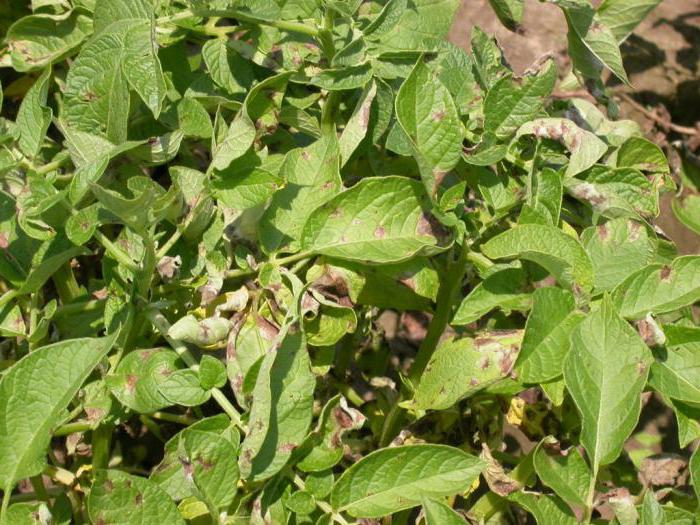
The black leg (lat.Ewinia chrysanthemi) is dangerous because it further affects the entire plant as a whole, destroying the crop. The main signs of potato diseases: the plants gradually wither, the leaves curl into a tube, turn yellow and die, the stems turn black and begin to rot, the bush is easily pulled out of the ground.Having found curly potato leaves, treatment must be started immediately.


Signs of black leg potatoes on the stem
The causative agent of the disease is the special bacteria of the genus Pectobacterium. They are the main reason why the leaves of the potato curl; treatment of the affected bush is useless, since it will no longer be possible to save the plant. The bush is completely removed, and the seed tubers for the next season, before laying in the storage, are treated with the Maxim fungicide, then dried.
Potato diseases - leaf curl, curl treatment
There is a popular recipe for fighting blackleg: use a teaspoon of copper sulfate for 1 glass of wood ash. The infected plant is removed along with the tubers, and the remaining hole is sprinkled with the resulting mixture.
Preventive measures for black leg infection are:
- mowing tops 2 weeks before harvest;
- removal of plant residues from the soil;
- drying the fruit before storing it.
Such varieties as Lazurite, Rosinka are resistant to black leg.
Additional tips and tricks
In addition to the above:
- fresh manure should be carefully applied under the potatoes, as this leads to an overdose of nitrogen in the soil and causes excessive growth of tops with delayed tuberization. The microclimate in the "cared for" rows creates favorable conditions for the development of late blight, and the tubers that did not have time to form a dense skin are easily damaged during harvesting and become infected;
- 7-10 days before harvesting, the tops should be mowed and immediately removed from the beds;
- tubers after harvesting must be dried and sorted out damaged or with signs of disease;
- autumn plowing and the application of organic fertilizers accelerate the mineralization of infected plant residues.


Late blight is an extremely dangerous disease. It is almost impossible to cure plants captured by an epidemic of the disease. But it is possible to prevent or capture prophylactically at the earliest stages of development. After critically assessing the situation and choosing the most appropriate measures from the above list, every effort should be made to prevent infection in the beds or destroy it at the very beginning of the growth of potato bushes, even before their flowering begins.
Next
Potato Description and Treatment of Potato Disease
Description of the disease


Phytophthora is a fungal disease caused by the oomycete Phytophthora infestans. The class is isolated from the kingdom of fungi, since the structure of the mycelial organisms of the oomycete is slightly different. Reproduction is through zoosporangia, the incubation period is from 3 to 16 days.
Have questions? Ask and get useful advice from professional gardeners and experienced summer residents. Ask a question >>
The infection affects tubers, leaves, and plant shoots. Sources of infection:
- seed potatoes;
- tubers left in the soil after harvesting;
- plant residues.
The pathogen is distinguished by its vitality, resistance to subzero temperatures. Risk group - representatives of the nightshade family, among which, in addition to potatoes, sweet peppers, tomatoes, eggplants. Late blight occurs everywhere, with annual losses from fungal infection amounting to 15%.
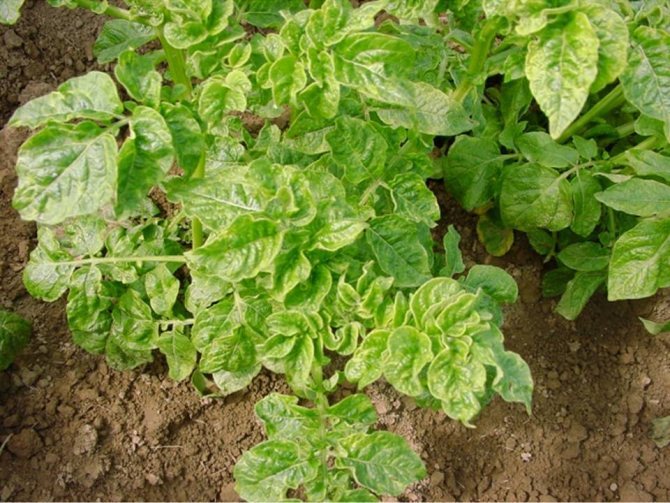
Alfalfa Mosaic Virus (AMV)
|
AMV is widespread in potatoes, but fortunately does not do much harm. It causes the loss of chlorophyll in a significant part of the leaves of the plant; large, irregularly shaped yellow spots appear on them. The natural reservoir of the virus is wild alfalfa and clover, from where aphids transfer it to potatoes. Like other viruses, it is capable of persisting in tubers. >>>
Related articles:
Zeyruk V.N. VVKK-one of the factors of degeneration of the variety