Classification of varieties by growth
There are many classifications of potato varieties. The culture is divided by purpose, region of growth, yield, ripening time and many other parameters.
Depending on the purpose, potatoes are divided by varieties into:
- dining room. These are species intended for human consumption and possessing high enhanced qualities;
- technical. Types of potatoes used to make alcohol and starch;
- stern. Received specifically for livestock;
- universal. This potato is suitable for any application.
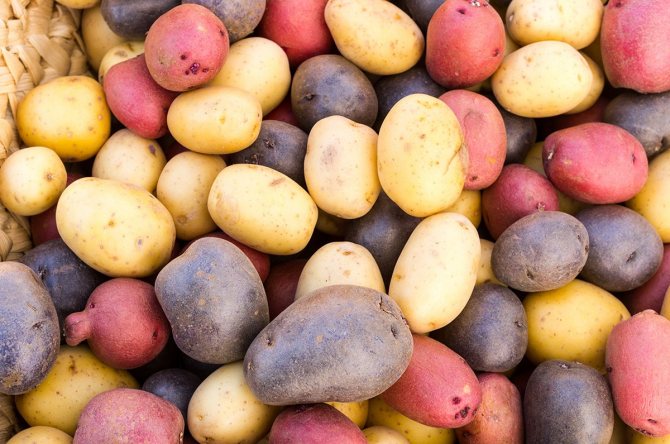

There are a great many varieties of potatoes.
Note! An important condition when choosing a variety is its ability to grow in a certain area. Southern ones will not produce crops in Siberian climates, and species suitable for growing in cold conditions will not be able to withstand heat and drought.
Varieties suitable for Central Russia
Moderate climatic conditions in the Middle Lane make it possible to pick up many suitable varieties of potatoes. However, it should be borne in mind that the summer in these regions is not too long, so the types of culture should be early maturing. Otherwise, it will be difficult to get a decent harvest. Gardeners in the Middle Lane should pay attention to the following varieties:
- Rocco. An excellent variety with a high yield. Resistant to fungi and viruses, normally survives drought, is not susceptible to potato cancer. The mass of tubers reaches 120 g, from 1 plant up to 12 fruits are obtained. Rocco is versatile, can be used in cooking and for feeding animals;
- Adretta was obtained abroad, but is excellent for the Middle Lane. This type of potato is distinguished by increased productivity, resistance to many specific diseases and excellent taste. Adretta quickly adjusts to changing climatic conditions, keeps well until spring;
- Rosara. Refers to especially early species. Full maturation occurs 70 days after germination. It is appreciated by farmers for its increased yield. Potatoes are not susceptible to fungi and nematodes. Infection with viral diseases is possible, but this can be avoided by timely prevention.
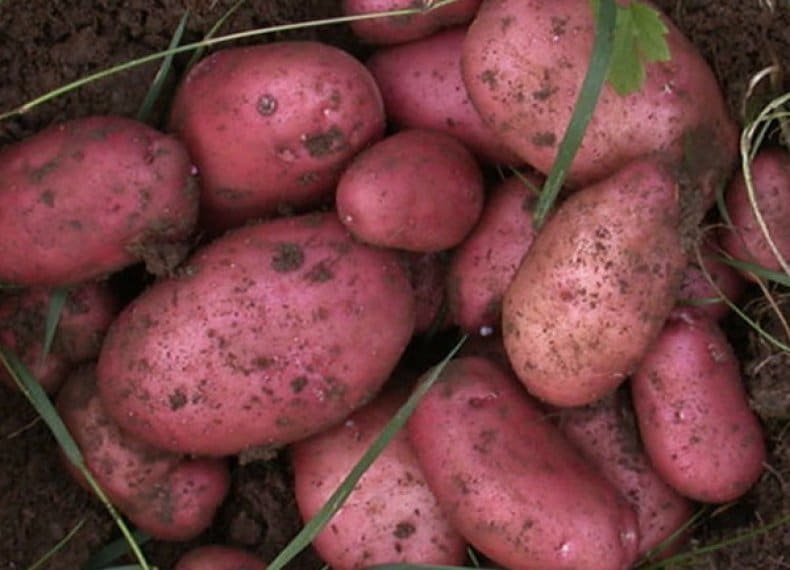


Rocco potatoes
Advantages and Disadvantages of Seed Growing
The main advantages of this method of potato propagation include the following:
- obtaining inexpensive high-quality planting material - mini tubers grown from seedlings and planted for the next season will yield super-super-elite tubers, which is the highest category of planting material used in personal and summer cottages;
- improvement of seed potatoes - the resulting planting material does not contain pathogens of various dangerous viral diseases;
- increase in yield - the use of highly productive planting material obtained from mini tubers allows you to get the maximum yield characteristic of the variety.
The disadvantages of this potato propagation method are:
- sensitivity of potato bushes grown from seeds to environmental conditions - temperature, humidity, illumination;
- high exactingness of seedlings to the soil - its structure, moisture, nutrient content;
- two-year cultivation cycle - with seed reproduction of potatoes, mini tubers are grown in one season, of which they will receive full-fledged planting material only next year;
- fragility of sprouts and seedlings - delicate potato bushes grown from seeds, if handled carelessly, break and injure very easily;
- susceptibility to various diseases (rot, black leg);
- more careful care of seedlings in the early stages of development.


Also, another disadvantage of this method of reproduction is the possible sterility (non-germination) of independently harvested seeds.
However, despite the large number of shortcomings, this method of reproduction and improvement of potatoes has recently become very popular, as evidenced by the appearance on sale of a large number of potato seeds of various varieties, numerous videos for obtaining mini tubers and super-super-elite planting material.
Varieties suitable for the Moscow region
The climate of the Moscow region is diverse: both prolonged rains and prolonged drought with high temperatures are possible. The soil is not particularly fertile, so unpretentious and disease-resistant varieties of potatoes, whose tubers ripen quickly, will be the best choice. These include:
- Nevsky. This potato is medium early, the tubers ripen in about 85 days. On average, 12-15 potatoes weighing up to 140 g can be obtained from a bush. Nevsky can be used for any purpose, it has excellent taste and is stored unchanged for a long time;
- Lorkh belongs to the late, but enjoys great love among gardeners and farmers of the Moscow region because of its pleasant taste. Potatoes last for a long period are versatile. Tuber weight 140 g;
- Sineglazka. Medium early type of potato with high yield. The vegetable has excellent taste characteristics and the possibility of long storage (but only in small quantities). Potatoes are not susceptible to fungi. It belongs to the table types.
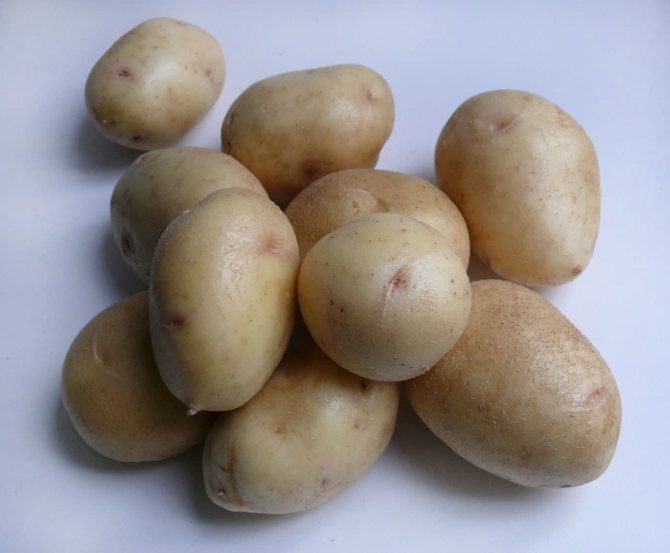


Potatoes Nevsky
Popular varieties of potatoes for Siberia
In Siberia, conditions for growing potatoes are more severe: late spring, early autumn, and very short summers. However, thanks to selection, many types and varieties of potatoes have been bred, which allow you to get a good harvest even in such areas. The following have performed well:
- Red Scarlett. A high-yielding variety with beautiful pink-skinned tubers. Potatoes are not susceptible to fungal diseases, they are resistant to nematodes. Able to withstand prolonged drought;
- Gloria. Medium early potatoes with excellent taste characteristics. It is stored for a long time. More than 370 centners of selected tubers can be obtained from 1 hectare. This type of potato is resistant to nematodes, scab, potato crayfish. However, it does not tolerate late blight too successfully, therefore it requires preventive treatments;
- Ermak. Variety with high yield and good taste. This is a variety of the Early Rose. It is quite resistant to many pathologies and parasites. Potatoes adapt easily to low temperatures and endure unfavorable climatic conditions.
Growing potatoes from seeds in the open field
Agricultural technology for growing potatoes from seeds in the open field includes careful selection of a site and soil preparation, sowing seeds.
Site selection and soil preparation
For growing seedlings and picking them, they choose areas well-lit by the sun with loose fertile soil. It is undesirable to sow seeds and dive seedlings into strongly shaded areas with heavy floating soil.
Sowing seeds
In open ground, seeds are sown both superficially and with a slight depth (up to 1.0 cm). Before germination, the seedbed is covered with foil. As soon as the first shoots appear, the film begins to be periodically removed, gently water the small seedlings with warm water
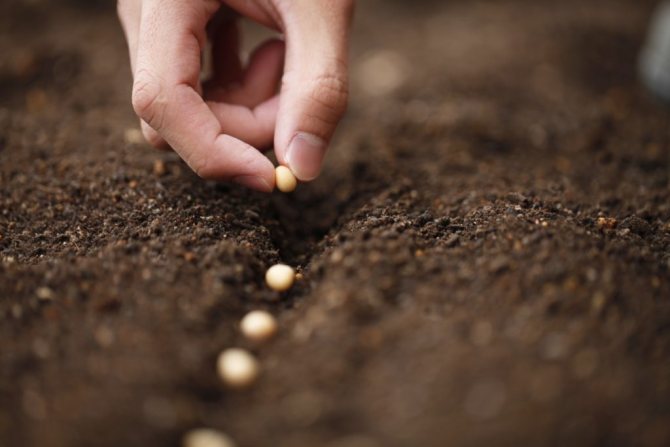


Grown seedlings, when 3-4 true leaves appear on them, dive to a permanent place. In this case, the planting is carried out according to the scheme 20 × 40 cm.
Types by yield
Another important characteristic of potatoes is their yield. The lower this indicator, the less tubers grow on the bush. Farmers and gardeners prefer varieties that can produce high yields.


Lorkh potatoes
Red potatoes with yellow flesh
Tubers of these species are covered with a reddish skin and have a yellow flesh. These varieties include:
- Red Scarlet. On average, you can get up to 660 c / ha;
- Rosara. With proper care, it gives up to 530 centners per hectare;
- Bellarosa. Productivity up to 350 centners per hectare.
Crumbly
Such varieties of potatoes contain a high concentration of starch; during heat treatment they often lose their shape, but at the same time they have an excellent taste:
- Idaho. The average amount is 550 c / ha;
- Share. From 1 hectare, up to 380 centners are obtained, the weight of one potato can reach 400 g.
High-yielding
These types of potatoes always yield a good harvest when properly cared for:
- Rosara - up to 530 c / ha;
- Adretta - up to 450 c / ha;
- Luck - up to 500 c / ha.
Pink potato
The most popular of this category is Picasso. Potatoes have a slightly pinkish skin around their eyes. It is late ripening, up to 300 centners can be obtained per hectare.


Sineglazka potatoes
Types of potatoes. Why do purple and red potatoes have their unusual color?


But today breeders offer very unusual types of potatoes with multi-colored pulp for planting. The amazing color range of potatoes is due to the biochemical composition, or rather, anthocyanins and carotenoids. Whereas tubers with traditional white flesh contain no more than 100 mg of provitamin A per 100 grams of potatoes, varieties with a yellow core contain twice as much of this substance. And the brighter the color of the tuber, the higher the concentration of provitamin A. In orange and red potatoes, its content reaches 500-2000 mg.
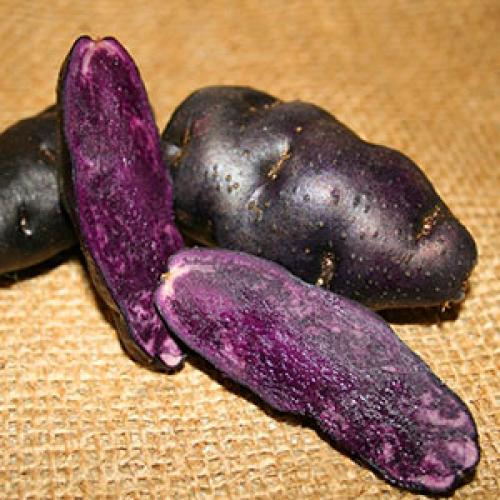


The concentration of anthocyanins, which provide a purple, lilac or violet color of the pulp and rind, in brightly colored tubers is two dozen times higher than in light-colored table varieties. For 100 grams of purple or blue potatoes, there can be 9 to 40 mg of anthocyanins. Moreover, the concentration of this natural dye and carotene is always higher in the peel. But inside the pulp, these substances can be unevenly distributed, which made it possible for breeders to get plants with variegated tubers both outside and inside.


In addition, red, blue or purple potatoes have twice the amount of bioflavonoids than traditional varieties with a light-colored pulp. But the starch in colored tubers is much less, so they can be used for dietary and medical nutrition, and sometimes even raw. Active selection of all new colored varieties and their growing popularity among gardeners allow us to say that not all the beneficial aspects of potatoes have been studied and used. Studies conducted by biologists and physicians in Korea and the United States have shown that the introduction of purple and red tubers into the diet helps the body resist atherosclerosis and cancer.
The substances in the composition of red and purple potatoes have a beneficial effect on the condition of the organs of vision and blood vessels, prevent premature aging and help fight heart disease.
Ripening classification
Before planting, it is required to take into account the ripening period of the tubers. This will allow you to be sure that the crop will have time to reach the required ripeness in the possible time. Therefore, many are interested in the names of varieties that can bear fruit quickly.
Early
This group includes potatoes that can mature in a period of 40 to 56 days. The growth and development of tubers takes up to 3.5 months.These include:
- Impala is a table variety that, with proper care, gives an excellent yield, up to 600 c / ha. In warm climates, 2 plantings are possible in one summer;
- Arrow. Bred in Holland. With good care, the crop can be harvested twice per season. It is resistant to disease;
- Dnipryanka. It rarely gets sick. You can get a re-harvest in a season.
Medium early
Young tubers appear after a couple of months, on average, the ripening period is 3.5 months. The most famous:
- Agatha. Tubers are medium in size and round, in mass they reach 120 g. Agate is resistant to fungal diseases;
- Fun. The fruits are covered with a pink skin, the flesh is yellow. The weight of one tuber reaches 120 g. It is well stored, easily transported;
- Lileya. Large tubers up to 200 g oval or pear-shaped. Under good conditions, this Belarusian variety yields up to 40 tons per hectare.
For your information! The mid-season potatoes also include La strada potatoes, the description of which is similar, but this variety is not resistant to many potato diseases.
Mid late
Such varieties are characterized by full ripening in 125-140 days. Mid-late varieties include:
- Scarb is a high-yielding variety with large and tasty fruits. Susceptible to late blight, therefore, special treatments are necessary;
- Sap. It tolerates drought well, but does not tolerate stagnant moisture;
- Yanka. Gives a very high yield, up to 630 kg / ha. The tubers have excellent taste and can be stored for a long time. Often sick with late blight and wet rot.
Elite potato varieties for increased yield
The elite varieties include potatoes, which are distinguished by good taste, ripen quickly and are not susceptible to many pathologies and pests. There are many alphabetical lists of the most popular potato varieties on the Internet. The most common varieties are described below.
- Nevsky. These potatoes can be grown in all weather conditions. It is unpretentious and gives a good harvest, up to 15 tubers from one bush. Nevsky is resistant to many diseases. The peel is light yellow, the flesh is creamy;
- Zhukovsky early. The variety is suitable for growing in any territory of Russia, unpretentious to the soil and climate. Tubers are pink in color, their weight reaches 120 g. Refers to fruitful, bringing up to 60 kg / ha.
- Lugovskoy. Grows well on light soil. With quality care, it gives a large yield of up to 50 centners per hectare. The peel is pink, the flesh is yellow. Contains a high concentration of starch.
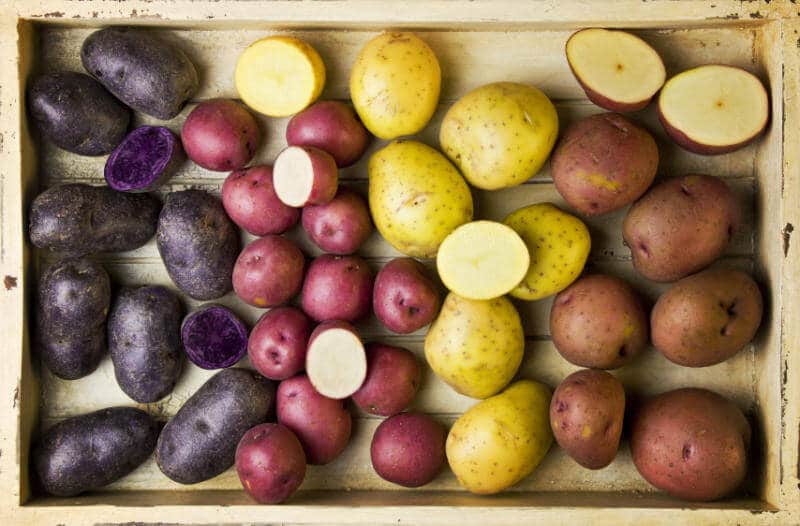


A variety of potatoes can stump any gardener
It is recommended to choose a variety of potatoes for planting, taking into account all the features. It is important to take into account climatic conditions, type of soil, yield, ability to resist diseases and pests. If the rules are not followed, it is difficult to get good potatoes.
Dependence on climatic zones
The territory of our state is located in four zones depending on the climate: arctic, subarctic, temperate and subtropical zones. The arctic and subarctic zones are not suitable for growing tubers due to severe frosts even in summer.
In subtropical regions (the Caucasus, the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea), potatoes can be planted twice a year. The warm and mild climate contributes to high yields of different varieties of potatoes. In the temperate climate, which covers the main part of Russia, the regions are divided into several regions, where the weather conditions are insignificant, but differ.


Of the many seeds for planting, it is better to choose zoned breeding:
- For central Russia (Moscow region, Volga region): Arosa, Adretta, Belarosa, Orbita, Vesna, Zarya. Early for the Moscow region - Vyatka, Domodedovsky, Slavyanka.
- For the Urals: Alena, Veneta, Zhukovsky early, Lorkh, Lyubava, Nevsky, Rozara.
- For Siberia (West Siberian regions): Meteor, Zekura, Nevsky, Adretta.
Seed potatoes are zoned according to the named regions and are marked by a high degree of resistance to low temperatures. All of them belong to early or medium ripening periods. Bushes begin to bloom in June, and ripe fruits appear no later than August-September. The stages and phases of potato development occur at an accelerated pace due to the improvement of the varietal qualities of the "parents" from which new hybrids were obtained.
Attention!
In order to grow a rich crop of potatoes, vegetable growers need to fulfill three main conditions: to purchase high-quality seeds, zoned to their place of residence, to observe crop rotation and cultivation techniques.
High-yielding


The most productive potato varieties are determined empirically over a long period. These data are indicated by the originators in their annotations when submitting an application for inclusion in the State Register. A high yield is considered to be from 300 centners of tubers and more from 1 hectare of potato plantations.
These include: Aurora, Kolobok, Adretta, Atlant, Chaika, Zhuravinka.
The most stable and hardy
Immunity to diseases and pests is an important indicator when choosing seeds. Potato varieties that are resistant to the Colorado potato beetle have priority in marketing, because it is better to grow potatoes that the Colorado potato beetle does not eat.
According to the originators, these are: Lasunok, Zarevo, Temp, Kamensky, Early Morning.
The most beautiful
Such fruits can be identified by every gardener by their appearance. These tubers should be medium to large in size, without a large number of eyes on the surface, smooth, even and attractive to buyers.
Vegetable growers who have tested many varieties of potatoes on their plots consider tubers of varieties as such: Irbitsky, Rodrigo, Lasunok, Nevsky, Zhukovsky, Red Scarlet.
The most delicious


According to the originators, potatoes with a high starch content are considered the most delicious. It is used to prepare first and second courses (soups, mashed potatoes, casseroles). The highest rates of starch in tubers are above 20 percent.
Champions in taste are: Picasso, Tuleevsky, Zhuravinka, Kiwi, Kolobok, Impala, Skazka.
The newest
The State Register of Plant Seeds is updated every year with new varieties of potatoes. In 2020 and early 2020, it includes:
- early: Gulliver, Capri, Christelle, Mishka, Madison, Sandrine;
- average ripening period: Grandma, Arctic, Elena, Granada, Smolyanochka;
- late: Masai, Kazachok, Cerata KVS.
Potatoes are being tested in different regions of Russia for at least 10 years before being included in the register. During this time, some gardeners could already test the quality of new varieties in their garden plots.
Elite


Domestic selection: Lux, Romano, Slavyanka, Zarnitsa, Luck, Gala, Nevsky, Zhukovsky, Rosara, Golubizna.
Foreign selection:
- Holland - Evolution, Prior, Santa, Red Scarlet;
- Germany - Karatop, Sprint, Vitara, Rosara.
Planting material of different varieties of potatoes is purchased through retail sale, in online stores, from friends and acquaintances. The main thing is that these sources are reliable, and their proposals correspond to the varietal indicators of the declared species. The guarantor will be the Quality Certificate of the seeds sold in the store.