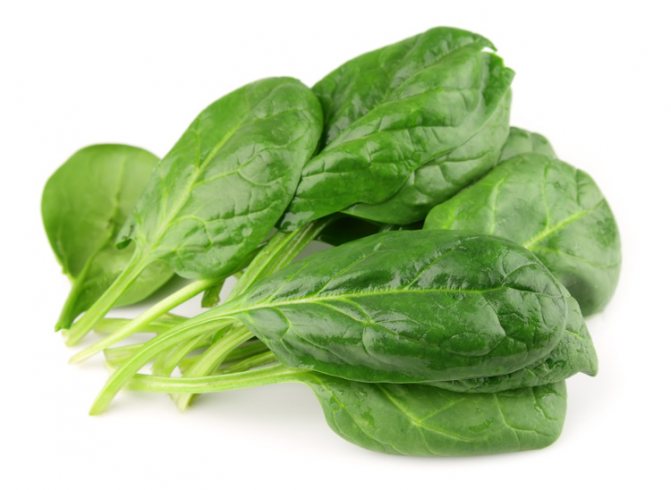
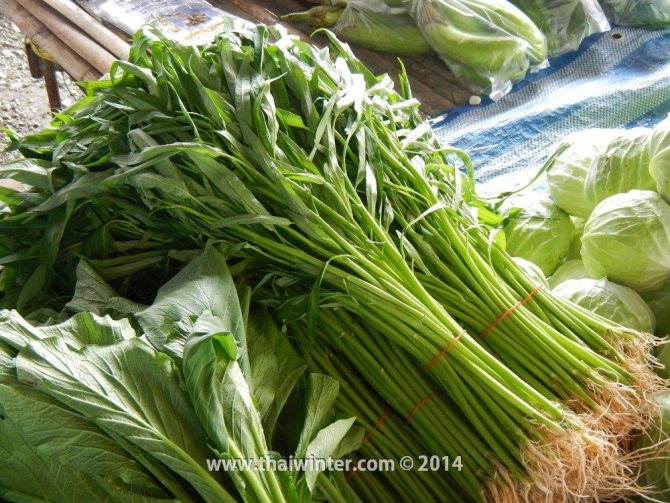
Spinach
The main variety of spinach that can be bought at the market or in the supermarket is vegetable garden. It is the most abundant and nutritious. The first species of spinach grew wild in Asia. Then, when people realized the usefulness of this plant, they began to cultivate it in Persia. The name is translated from Persian as "green hand". Further along the Silk Road, it spread to China, and there it was nicknamed the Persian vegetable.
Over time, this vegetable green was widespread in Europe, many wealthy lords, kings and other influential persons demanded this product to the table. It got its distribution in Europe later than in Asia, but it became more popular. And then breeders began to try to bring the variety better, so that it was less bitter and did not go into the stem with the onset of summer.
In Russia, this Persian vegetable began to be eaten even later, and it was more in demand at the table of noble people, but it was not as popular as in Europe. It was more of a decoration when serving food.
How to choose the right product?
When buying spinach, first of all, you need to pay attention to the appearance of the product and its storage conditions. In a fresh plant, the leaves are bright green in color, they are elastic to the touch and crack slightly when pressed.
If the spinach looks sluggish, the ends of the leaves are dry, and the stems have darkening, this product is not suitable for consumption.

Gallery: types of spinach (25 photos)
Growing
Spinach grows best in moist, nitrogen-rich soil. Spinach plants form a deep taproot, so for better growth, dig up at least 30 centimeters of soil before planting.
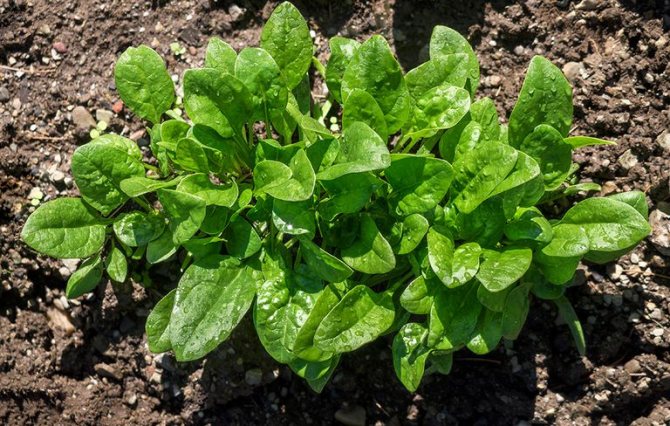


Garden spinach should be planted from seed in the spring, 6 weeks after the last frost. To make this process easier, the soil must be prepared in the fall.
In warm climates, spinach should be planted in the shade of tall crops such as corn or beans. In this case, the leaves will be protected from the hot sun and will retain their beautiful, rich green color by the time of harvesting.
Seeds should be sown intensively, as they will sprout up to about 50%. In warm weather, you need to water the seed holes often - (once or twice a day). Watering will help cool the soil, which in turn will keep the crop from drought and make it richer. You can harvest the crop within a year after the first shoots have grown (up to the first autumn frosts).


Types of spinach
There are many species of this green plant that were bred at one time by breeders. But there are main varieties that are more common in the world today. Now we will consider them.
- The first grade, the most common is the garden one. More palatable than the others, it has a mild sweet aftertaste.
- New Zealand is distinguished by its thick and fleshy leaves.
- Multifoliate or jminda. It can reach a height of up to 8 centimeters and has berries that look like raspberries.
- Ceylon spinach or basella grows up to 3 meters in length and grows in the form of a vine.
Botanical description
Garden spinach (Spinacia oleracea) is a herb with edible leaves, belonging to the Marevykh subfamily, the closest relative of beets.It is one of the most common leafy vegetables.
The plant has a two-year development cycle. In the first year, leaves appear, in the second, flowers and seeds. Seeds can form in the first year.
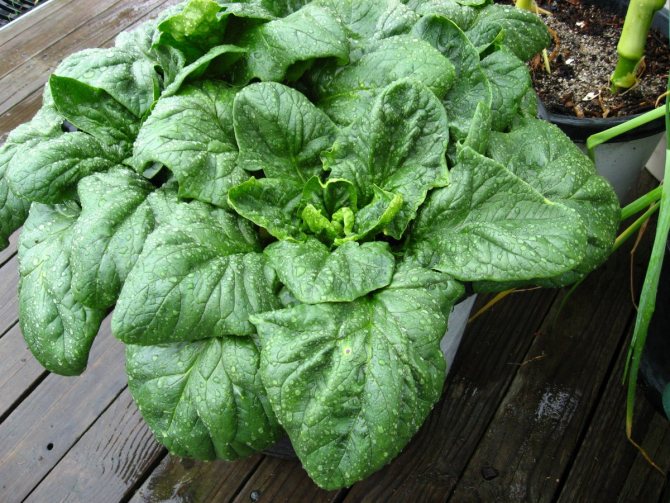
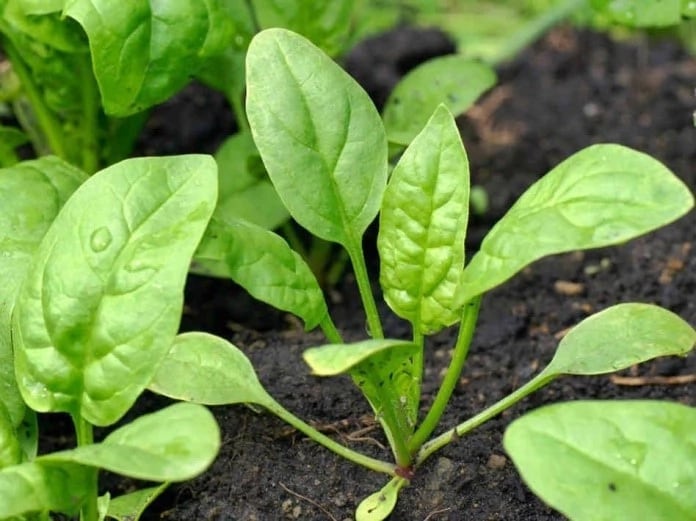
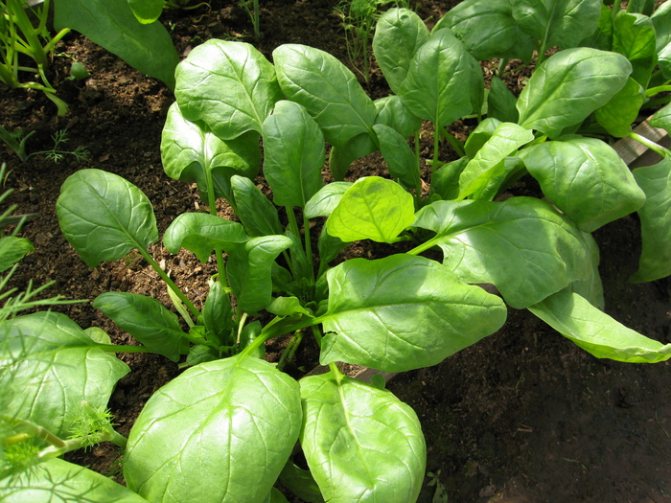
Now gardeners grow spinach infrequently, many do not even know what it looks like. It has smooth or bubbly, depending on the variety, leaves growing from one common point - similar to a root collar, from which the pivotal root extends downward.
The bush, on which peduncles have already appeared, becomes inedible. Its leaves become coarse as the plant prepares for fruiting.
The leaves of the culture are large, juicy, triangular in shape, sometimes with ears. Their length, together with the petiole, can reach 25 cm.
Flowers are collected in panicle inflorescences, nondescript, cream-colored, small. The fruits are large, spherical in shape.
The culture is dioecious, that is, it has male and female specimens. Males form leaves earlier than females, and after flowering they die off. Women are tying fruit.
Photo of spinach:


There are few types of spinach. In addition to the usual, connoisseurs grow strawberry or multifoliate spinach Blítum virgátum. This is a plant from the same family that can be eaten with leaves and fruit-berries. Because of the red color of the fruit, Blítum virgátum is sometimes called "spinach-raspberry".
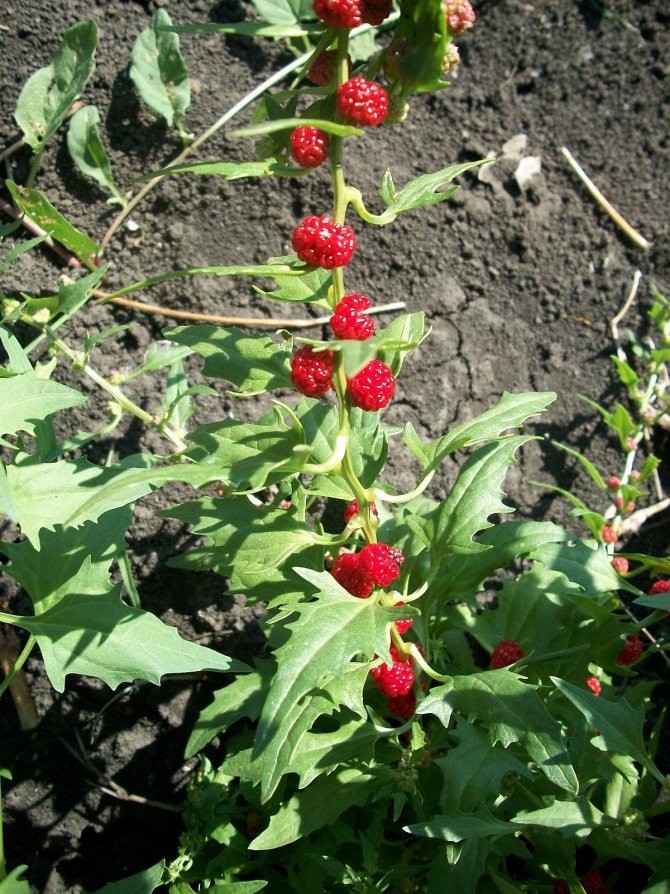


Photo: Strawberry spinach
Garden spinach has many fruitful varieties that give the gardener the opportunity to receive up to 2.5 kg of products per square meter. m.
The most popular are:
- Gigantic - early maturing, medium spreading with large, slightly bubbly light green leaves.


- Fat-leaved - early maturing, with raised large-bubble leaves of intense green color.


- Matador - leaves are round, light green, delicate taste, medium early ripening.


Micronutrients that are included in spinach
The composition of this vegetable greens includes a fairly large number of various useful elements that are very rarely found in other vegetables and greens. A set of essential trace elements, acids, minerals, vitamins and other irreplaceable elements makes spinach a source of beneficial properties. Spinach has a low calorie content, but at the same time it contains some elements in very large quantities, which, of course, speaks of the high natural value of spinach. Now let's look at the amount of micronutrients per 100 grams of spinach. We will not write the exact grammar of these elements, we will just list them.
- Manganese.
- Zinc.
- Selenium.
- Iron.
- Copper.
- Phosphorus.
- Calcium.
- Sodium.
- Potassium.
- Magnesium.
- Beta carotene.
- Vitamin A.
- Vitamin B1.
- Vitamin B2.
- Vitamin B5.
- Vitamin B6.
- Vitamin B9.
- Vitamin C.
- Vitamin E.
- Vitamin N.
- Vitamin K.
- Vitamin PP.
- Vitamin B1.
- Choline.
Application in medicine


Doctors recommend including spinach in therapeutic diets for various diseases, as well as to strengthen immunity, give vitality to the body, and increase stress resistance.
For medicinal purposes, spinach is used internally in raw or poached form, as well as externally in the form of a decoction, infusion, lotions, compresses, rinses.
Application for pathologies of the digestive tract
Spinach is called a "stomach brush" and is included in the menu for problems with stool: fiber and chlorophyll increase the volume of intestinal contents, which stimulates its activity. In the intestinal lumen, the vegetable binds cholesterol and toxic waste products and removes them from the intestines, performing the function of an absorbent.
The anti-inflammatory properties of the substances contained in spinach are used for therapeutic nutrition for gastritis with low acidity and enterocolitis.
Application for pathologies of the heart and blood vessels
By binding cholesterol in the blood, spinach helps to lower cholesterol levels.Therefore, it has an anti-cholesterol and anti-atherosclerotic effect, which is used in the complex treatment of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Vitamins A, E and C strengthen the walls of blood vessels, increase their elasticity, due to which they have a hypotensive effect in hypertension. The high content of B vitamins stimulates cerebral circulation.
Application for eye diseases
The high content of "eye" vitamin A allows the use of spinach as the main ingredient in dishes for eye diseases (night blindness, deterioration of visual acuity, macular degeneration, conjunctivitis). Regular consumption of this vegetable in food helps to improve the state of vision for people who often work at a computer.
Application for anemia


The iron and chlorophyll contained in this green leafy plant increase the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, having an antianemic effect. Spinach is indicated for use by people suffering from or at risk of anemia:
- women of childbearing age (due to monthly blood loss);
- pregnant women;
- women who are breastfeeding;
- athletes;
- children;
- weakened and emaciated people;
- after prolonged illness;
- in the postoperative period;
- To old people.
Influence on metabolism
The chemical composition of a vegetable affects the metabolism of various substances in the body, so it can be used for metabolic disorders:
- fat (hypercholesterolemia, obesity);
- carbohydrates (diabetes mellitus);
- proteins (deficiency of essential amino acids);
- iodine (hypofunction of the thyroid gland);
- calcium and phosphorus (osteoporosis, osteomalacia).
Vitamin K (anti-hemorrhagic), which is part of the vegetable, increases blood clotting, therefore, it has an anti-hemorrhagic effect and is used when there is a tendency to bleeding.
The low sodium content of spinach increases the elimination of fluids from the body, providing a mild diuretic effect.
Topical application of spinach


Spinach leaves, decoctions and infusions from it are used as lotions and compresses on painful areas of the body when:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- rheumatism;
- bruises;
- abrasions;
- diaper rash;
- burns.
The active substances of the vegetable have an anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effect on the skin, accelerate the epithelization of wounds and abrasions, and exhibit a light analgesic effect.
Applying fresh spinach leaves to the site of an insect bite (bees, mosquitoes) relieves swelling and pain.
Rinsing the mouth with a decoction of spinach accelerates the healing of wounds on the gums, treats periodontal disease and gingivitis.
A massage using a decoction of spinach (instead of a massage cream) improves the elasticity and firmness of the skin and prevents the appearance of “orange peel” - cellulite on it.
Masks made from this vegetable have a rejuvenating effect on the skin of the face, neck and décolleté, therefore they are popular among women in adulthood.
Benefits of spinach
This green plant has long been used to prevent certain diseases. Since since ancient times, people have guessed about the beneficial properties of this plant, and what effect it has on the human body. In any form, greens have the best effect on the body. But despite all the usefulness of this plant, many people underestimate this greenery and pass by. To be sure that this is a big mistake, just look at the list of useful properties of a fresh product. And then the benefits of this green plant will not raise any doubts.
So what is it useful for the human body:
- Participates in the production of basic hormones for human life.
- Prevents the appearance of cataracts and reduces eye fatigue.
- Cleans the digestive tract and fights constipation, helps regulate the level of carbohydrates in the body.
- Helps fight certain diseases: enterocolitis, gastritis, migraine, hypertension, osteoporosis, asthma, anemia, arthritis.
- Improves immunity.
- Reduces nervous tension and increases the body's resistance to stress.
- Reduces the negative effects of carcinogens and helps in the prevention of cancer.
- Improves the functioning of the musculoskeletal system and strengthens it.
- Enriches the body with oxygen and gives the body energy and strength.
- Improves appetite and helps to recover better after surgeries.
Many health benefits of spinach have been described, but these are far from all the benefits of a green plant. And also it has a number of useful functions to improve the daily state of the body:
- Diuretic.
- Laxative.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Calming.
- Toning.
Harvesting
Early-maturing varieties can be harvested 20 days after sowing with hatched seeds. Mid-ripening and late-ripening varieties ripen in 40-50 days. By this time, the plants usually form a rosette of four to five leaves.
Spinach is harvested by a bush, pulling it out of the ground with its roots. It is best to do this early in the morning, before the onset of the heat. The earth is shaken off, non-standard leaves are removed and the bushes are laid with the roots down. In the refrigerator in this form, they are stored for up to 2 weeks. Storage temperature +1.
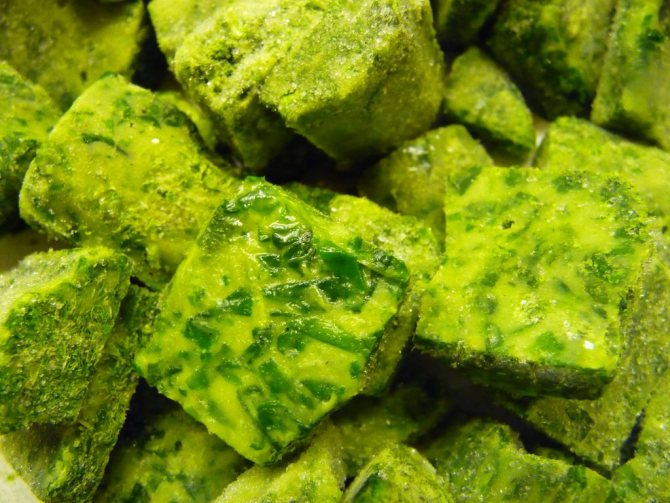
Leaves can be frozen. At a temperature of -2, they are stored for up to 3 months.
Knowing how you can grow spinach on the windowsill, and what kind of care you need in the open field, you can get an excellent harvest of useful leaves all year round.
Spinach plant. Growing spinach. Spinach care
The most famous and most popular type of green vegetable is spinach. It has significant advantages and beneficial substances. A herbaceous plant (the main varieties are annuals) belongs to the Amaranth family.
For the first time, spinach began to be used in food in Persia, the whole of Asia can be considered the homeland. Greens became very popular after the adoption of Christianity, as they were considered the mainstay of the diet during Lent. Now I grow spinacht and used fresh as a spice or for pickling.


Description and benefits of spinach
Depending on the varietal variety, spinach can be one year old or two year old. Reaches 25-50 cm in height, appearance - naked, simple, branched. The leaves are collected in a neat petiole, can be rounded, oval, oblong, sharp or wedge-shaped edges.
The flowers are miniature, collected in inflorescences, stamens and pistils are placed in dense sinuses. The plant can be either unisexual or bisexual. The fruits are small, of various shapes: in the form of a ball, with horns or with roundness.
Spinach is considered to be one of the crops (vegetables, greens) that have the highest amount of nutrients. Only cut leaves are a unique antioxidant. The plant is saturated with magnesium, calcium, iron, vitamins A, C and E.
Spinach is considered the main store of folic acid among all other foods. Contains kerotin, acids (ascorbic, oxalic, oleic, linolenic), manganese, phosphorus, iodine, copper.


In combination with other dietary products, spinach is used for gastrointestinal problems, with a poor blood formula, to increase appetite, to strengthen the nervous system. Young children, the elderly and people with chronic ailments of the liver and kidneys must be very careful with it.
Growing spinach from seeds
Spinach perfectly grown from seed, the germination is excellent, but for reassurance, they are sown in two passes. Before sowing, the seeds are prepared: they are placed in warm water (room temperature) for two days. Then they are dried well with a napkin, removing excess moisture.
The first sowing of seeds is carried out in the fall, and the second - in the spring. Spinach planted in the fall will show its first shoots when the snow melts. Sowed in April / May, there are two typical methods - on ridges and in rows.The first method is used when the soil is very compacted (with an oily structure), the second - for all other types of soils.


Growing conditions for spinach will depend on the zone. For example, in the northern regions, where the summer temperature does not rise above +20 C, spinach is grown in August / September. Already at the end of spring, you can get a full-fledged green harvest.
Planting and caring for spinach outdoors
Growing spinach outdoors, special attention should be paid to the soil. He loves soil rich in organic matter and with good drainage, the optimum acidity should be pH 6.7-7.0. The compacted soil will "clog" the growth, so the plant can be lost.
In the fall, they resort to the introduction of potash-phosphorus fertilizers, rotted manure is used as organic matter (at the rate of 5-6 kg per 1 sq. M.) The process of introducing fertilizers is combined with digging the soil. It is important to know that spinach, like any other greens, quickly accumulates nitrate toxins, therefore minerals are introduced in a strictly normalized manner.


Rows are made on the ground at a distance of 25-30 cm, grooves no more than 2-3 cm deep. Sowing is carried out and covered with loose earth. If spinach is grown by seedlings, then the landing is carried out in April / May, at a distance of 5-10 cm from each other.
As soon as the first shoots are pierced, make sure that the soil is not "clogged". Access to the root system of oxygen is very important. Weeds should not be allowed among the crops, the latter carry spinach viruses or carry pests.


In hot weather, two-time watering is carried out in the morning and in the evening, after rain - at the end of the day. Watering is systematic, this will help to avoid plant stemming.
Spinach is used for food (phase 6-8 leaves), harvesting the entire crop. Eat fresh (you cannot store it in the refrigerator for more than a week), freeze for the winter, mix with salt.
Growing and care in general for spinach not whimsical. The only thing that must be adhered to is not to oversaturate the soil with nitrogen-type fertilizers, it is they that the plant accumulates most of all.
Since the end of January, spinach is grown in a greenhouse... The plant perfectly tolerates cold, even frosts down to -7 ° С, germination at + 2 ... + 3 ° С. In greenhouses, a non-seedling method is used.


During the growing season, the rows are thinned out twice. They regularly loosen the soil and make abundant watering (once a week). The collection of the leaf is carried out 25-30 days after germination, the greenhouse is regularly ventilated.
Types and varieties of spinach
Growing spinach at home, the gardener strives to choose the most efficient variety from a yield point of view. Therefore, spinach has different stages of ripening: it ripens quickly, ripens late and has average ripening rates.
* Gigantic spinach - an early ripening spinach variety, the leaves are used for food already on the 30-35 day of the growing season. It is planted in late autumn or early spring and has many benefits.


* Matador. Grow spinach, mainly outdoors, ready for use 3 weeks after sprouting. Differs in special frost resistance and excellent quality taste. Demanding on moisture, it is appreciated by culinary experts, great for drying or freezing.


* Strong spinach... It belongs to the variety (with average time indicators), you can harvest it for 25-30 days. Suitable for planting in the northern regions of the country, it is resistant to frost. Leaves have many useful properties, they are boiled, stewed, dried and frozen.
*New Zealand spinach... Grown in the driest and hottest regions, the plant reaches a height of 1 meter, the stems spread along the ground. Leaves are small, rounded, edges are pointed, jagged. It requires high-quality soil and a lot of moisture, the leaves are cut off on the 25-30th day of the growing season, it gives several harvests per season.
* Spinach victoria... This variety of spinach is late ripening, the leaves are edible for 30-35 days. Very picky about the soil, loves moisture.Possesses good resistance to powdery mildew and arrow development.


* Fat-leaved. By cultivating this sort spinach, gardeners love it for its miniature outlet, pleasant taste and light aroma. Suitable for food one month after the emergence of sprouts.
* Strawberry spinach... This variety with a light strawberry flavor is more exotic than for industrial purposes. The people call this plant "multifoliate", the leaves are exactly like spinach, the stems are covered with berries that resemble raspberries, but have neither taste nor smell.


Diseases and pests of spinach
A variety of rot is a common spinach disease. It can be both root rot and rot of the upper part of the plant. Fusarium rot, peronosporosis, anthracnose, viral (curl, cucumber mosaic) - a list of the main diseases.
Especially susceptible to decay spinach, windowsill-grownwhere there is central heating. Breeders believe that the best remedy for fungal infections is to create the latest varieties that are highly resistant to infection.
The mining fly, or rather its larvae, which it lays on the leaves, brings tangible harm to crops. To prevent this harm, spinach is planted away from sugar beets and the affected leaf plates are systematically disposed of.