Features of growing tomatoes that affect the soil
Tomatoes are demanding on the content of nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus and calcium in the soil. Therefore, after them, it is better to plant plants that restore these substances.
You can get a good harvest of tomatoes on almost any soil, but sandy loam and loamy lands are the best option for them. For tomatoes, the moisture permeability of the soil, its lightness and enrichment with organic fertilizers are important.
For sandy and clayey areas, additional humus and compost will be required. And on heavy calcareous soils, you need to replace 30 cm of the top layer. The acidity of the soil should be in the range of 6-6.8.

Crop rotation rules
- annual crop change on the planting area, the exception is corn and potatoes, which can grow in one place for several years in a row;
- after root crops, fruit plants are grown, and vice versa, to make it easier to remember: we alternate "tops and roots";
- we plant crops with a high need for nutrients after those whose need is lower;
- there are cultures that heal the soil (for example, garlic and onions), you must ensure that they are consistently planted in all areas of the garden;
- with an annual change of landings, it is necessary take into account belonging plants to certain botanical families - "inheritance" of land within the same family is undesirable.


Planting plants from the Solanaceae family after tomatoes is undesirable
Make it a rule to keep a planting diary, which will allow you to analyze the changes in yield and the causes of diseases of different crops. It will not be superfluous to draw up a schematic plan of your garden and mark the plantings on it.
You can plant crops based on the most suitable predecessor for them - this is a very time-consuming method, but the most effective... In addition to alternating plantings, it is important to pay attention to how vegetables get along with each other in neighboring beds.
What crops can be planted after tomato
There is one simple rule in crop rotation - every year you need to alternate plants that take nutrients from different layers of the soil. Based on this, after the tomato, it is recommended to plant the following crops:
- Root vegetables - carrots, beets, radishes, root celery.
- Vegetables - squash, cabbage, legumes, cucumbers and squash.
- Greens - parsley, dill, onions, garlic, lettuce.
- Siderata - phacelia, mustard, rye, winter wheat, oats, vetch.
Root crops and vegetables are planted the next year, while greens and siderates can be planted in the same season, after harvest.
Now let's see what are the recommendations, what is better to plant after a tomato next year in different conditions.
In the open field
To restore nitrogen in the soil, greens and legumes are planted on the site - peas, beans, soybeans or beans. They are less demanding on the nutrient layer of the earth, so they can be safely planted after tomatoes.
Onions and garlic will have a positive effect on the soil after tomato. And root crops, due to the fact that they consume nutrients from the lower layers, can also be planted in this area.
Now read:
- What to plant after zucchini. Then plant the zucchini
- Strawberry crop rotation schemes. What to plant after her on ...
- What to plant after cucumbers. Then plant cucumbers
- What to plant after carrots. Then plant the carrots
- What to plant after onions. Then plant onions
For representatives of pumpkin seeds, it is necessary to carry out restorative actions with the soil, making additional fertilizing. After that, they can also be planted after the tomatoes.
In the greenhouse
Cabbage and cucumbers are not susceptible to late blight and nitrogen deficiency, so they can be safely planted. Siderata and greens will also contribute to the restoration of soil fertility. And pumpkin, as in the previous subtitle, on the contrary, will require additional fertilizing before planting.
As a result, the following crops are better suited for a polycarbonate greenhouse after a tomato:
- Zucchini and radish.
- All kinds of cabbage and cucumbers.
- Various types of greenery.
- Any siderate herbs.
After patients with late blight tomato


It takes at least 3 years to restore the fertile soil layer in the area where tomatoes with late blight grew. This process can be accelerated by planting plants that have a beneficial effect on fertility.
These are siderate herbs:
- Cereals. Winter wheat and rye are sown in the fall after the tomato harvest, and in the spring the earth is dug up.
- Representatives of crucifers. Pancake radish is planted in spring or autumn and can be mowed or dug up.
- Legumes. Phacelia is excellent for disease control and pest prevention due to its phytoncidal properties. Actively planted in September.
- A good and cheaper option is mustard, which is sown both in the greenhouse in the spring and in the open area in the fall before winter. It is mown as soon as it grows up to 20 cm. Mustard prevents late blight, scab and other diseases from developing in the soil.
If the cultivation is carried out in a greenhouse or the place is very limited, then disinfection or change of the topsoil is carried out every year. After sick tomatoes with late blight, a 10-centimeter layer of earth is removed in the greenhouse, and the entire plot is watered with a solution of copper sulfate. Then a fertile layer is poured with humus, sand and turf.


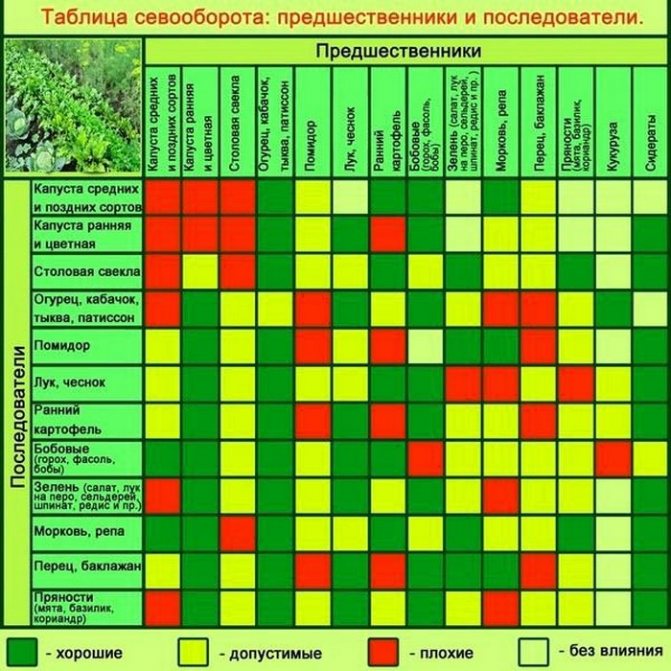
Crop rotation table
Basic information about culture
Tomatoes belong to the plants of the nightshade family, in South America, where they come from, wild varieties of this plant are common. The vegetable came to Europe in the middle of the 16th century, to Russia - 200 years later and was used as an exotic plant, and was considered extremely poisonous. On the territory of European countries, tomatoes were also considered poisonous, and only thanks to the work of the Russian botanist Andrei Timofeevich Bolotov, who was able to develop methods for fruit ripening, this species began to be used for growing for food purposes.


Tomato fruit
Fruits, depending on the variety, have different sizes, shapes and tastes. Tomatoes have gained a strong position in the cuisine of different nations; it is simply impossible to imagine some national cuisines without them, for example, Italian. They are used in salads raw, added to soups and roasts, stewed, pickled, juices and sauces are made.
The popularity of this species is due not only to the peculiar taste, they contain many essential vitamins, trace elements and have a low calorie content, which is in demand in our time. The systematic consumption of vegetables in food helps prevent hypertension, the high content of coarse fibers contributes to the work of the gastrointestinal tract and cleansing the body of toxins, reduces the likelihood of developing cancer.
Due to their excellent taste, a variety of uses for food purposes and the presence of vitamins and trace elements, tomatoes in our country are grown from southern regions to northern latitudes.However, not everyone and not always manage to get good harvests, this culture requires attention, knowledge of the characteristics of agricultural technology and hard work.
Planting tomatoes
The popularity of tomatoes in our country is so great that they are grown in all regions of the country, where they cannot grow in open ground, they are grown in hotbeds, greenhouses, in indoor conditions.
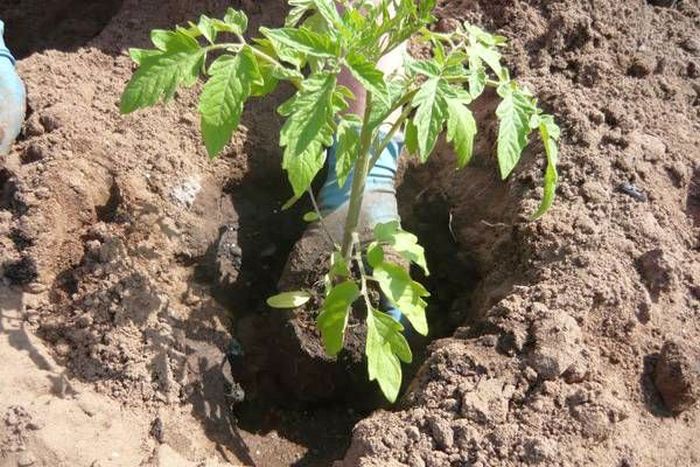


Planting tomatoes
Given the region of origin of vegetables, it is clear that they are a heat-loving crop.
Important! For normal development, they need temperatures of 20-25 degrees, at temperatures below 15 degrees, the fruits do not set, at a temperature of -1 the plant dies.
A plot of land for planting is chosen well-cultivated, with loose, fertilized soil. Before planting tomatoes, it is possible to place any crops on the site, except for those belonging to the nightshade family, such as potatoes, for example. Also, do not forget that not every crop will be able to be planted after tomatoes, if you expect to get a harvest.
Tomatoes are planted when the soil warms up to 10 degrees. They choose an open sunny area for planting, tomatoes are very responsive to sunlight. You can plant tomatoes in any land, but it is preferable to choose loose, fertile, well-heated soils.
The soil for planting is prepared in the fall, cleaned of the remnants of dry plants, dug in, fertilizers are applied, humus in the amount of 4 kg per square meter and superphosphate, 70 g. Tomatoes are demanding and responsive to feeding. Nitrogen fertilizers stimulate the growth of green mass, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers contribute to the development and ripening of fruits. Fertilization should not be overused.


Soil preparation in autumn
Companion plants for tomatoes
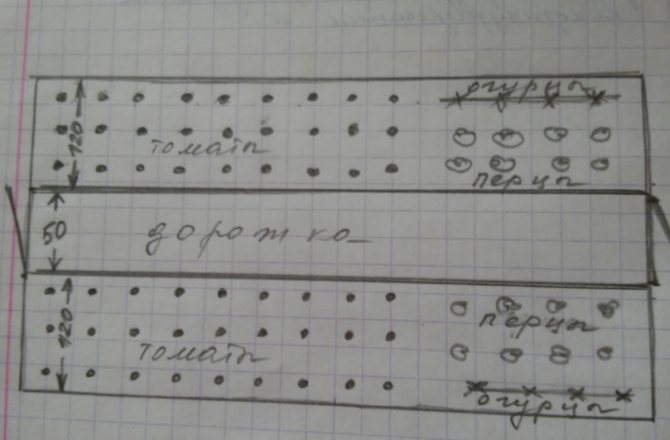
Arranging plants on the site so that their neighborhood is only beneficial is probably the most difficult task. There are recommendations and tips for a tomato:
- Corn or legumes planted nearby will protect the tomatoes from the wind.
- Vegetables include beets, radishes, carrots, celery and asparagus.
- Some flowers - tansy, nasturtium, marigolds, calendula and coriander - are a useful neighborhood for tomatoes from pests.
- For greens, lettuce and parsley will be a good neighbor. Basil will have a positive effect on the taste of fruits, and garlic and onions will protect against late blight and various pests.
- Tomatoes can help gooseberries because they keep the flames away.
- Any green manure is also suitable.
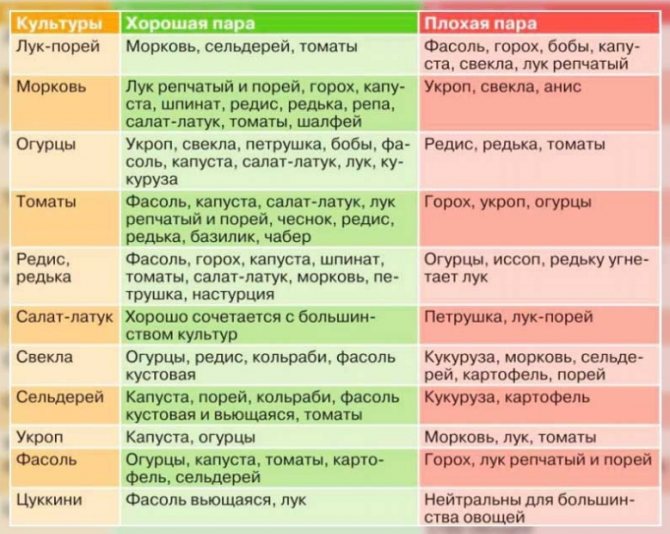
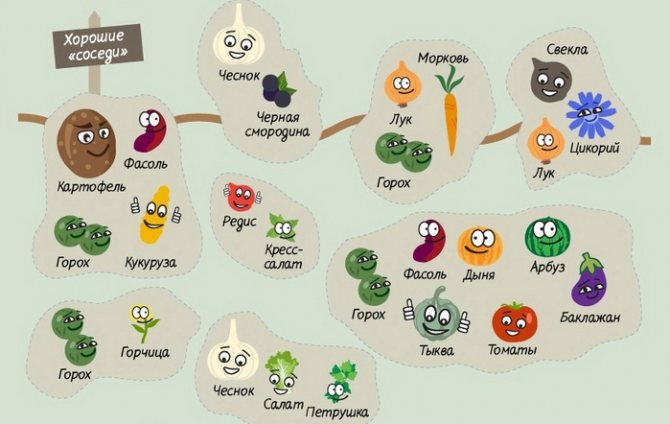
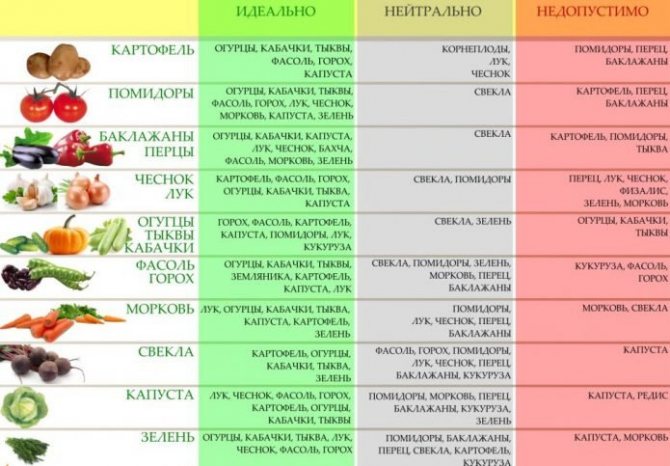
Useful table: which crops can be planted side by side and which not.


What can be planted immediately after harvesting tomatoes in the fall, including in a greenhouse
Cucumbers are not relatives of tomatoes, therefore they do not have common diseases with them and are quite suitable for growing the next year after the tomato. One has only to take into account that cucumbers are sensitive to soil nutrition and require fertilization. Compost is best suited for these purposes.
About cucumbers with tomatoes, we can say that they are "friends". They can be grown either after each other or within the same greenhouse. To do this, it is better to divide the planting zone into two parts and alternate between these two crops annually. At the end of each season, the soil in the greenhouse is thoroughly disinfected to prevent fungal diseases.
Cucumbers can be grown in place of the tomato. They are not susceptible to late blight, but are sensitive to soil quality. Before planting them, compost or rotted humus is introduced into the soil.
In the greenhouse, as well as in the open field, cucumbers can grow in place of a tomato after a complex of nutrients has been restored in the soil.
A characteristic feature of growing tomatoes can be considered the use of stationary premises. Such greenhouses create a favorable climate for the growth and development of this crop, increasing fertility and shortening the time for harvesting.With properly organized ventilation and heating system, you can pick tomatoes until late autumn, and in some cases - all winter. However, this option also has negative sides.


First of all, we are talking about the depletion of the soil. This process in greenhouse conditions occurs much faster than in open ground, because the earth is isolated from external influences. Gradually, nutrients and trace elements become deficient, so the plants need regulatory feeding.
The second danger when growing tomatoes in a greenhouse is the accumulation of harmful bacteria and fungal spores. In a confined space, even after pre-treatment of the soil, there is a risk of contamination of the tomato with late blight and other characteristic diseases. In the favorable humid "climate" of the greenhouse, the spread is faster and the plants can no longer be saved. Simple recipes can come to the rescue, as well as regular activities to help avoid ailments.
Basic rules for using the greenhouse:
- The soil for greenhouses must be treated from pests and disinfected so that bacteria do not get inside. The most commonly used method is the thermal method (calcining the earth at high temperatures) and the use of disinfectant solutions.


Greenhouse soil - The inner surface of the structure must be protected from corrosion and treated with an antiseptic. At the beginning and end of each season, it is advisable to repeat the treatment, replacing worn parts if necessary.
- Good ventilation is a must! This will help prevent the spread of harmful bacteria and mold, as well as circulate the oxygen that plants need.


Greenhouse ventilation - To prevent the accumulation of harmful substances in the greenhouse, it is recommended to completely renew the soil about once every 5 to 7 years. Such events are undoubtedly time-consuming, but they fully justify themselves.
- To prevent the plants from getting sick, it is recommended to alternate planting tomatoes with herbs, parsley, onions and beans. You can plant lettuce, radishes and spinach at the beginning and end of the season to make the most of your greenhouse area. These crops are characterized by an early ripening period, so they will not interfere with the tomatoes.
- The use of fertilizers should be strictly dosed and not exceed the specified rates. In the greenhouse, there is a danger of the accumulation of harmful organic compounds that cannot be absorbed into the soil, as in the open field. That is why small, frequent portions are used to fertilize tomatoes.


Fertilizer application in the greenhouse - To ensure a good harvest, it is best to plant cruciferous, leguminous and leguminous plants after tomatoes. An exception will be peas, which will not bear fruit well after a tomato.
If you plan to use your greenhouse exclusively for growing tomatoes and do not want to use agricultural principles, you can use the following tips. First of all, regularly check the acidity of the soil, which becomes acidic in the place of constant growth of tomatoes. This leads to a drop in yields, so additional liming of the land is used. The second important point is the need for periodic rest.
After tomatoes, it is best to plant mustard, rapeseed, oil radish, and they can be sown on an uncleared garden bed from late August to October. Both vetch-oat mixture and winter rye are suitable for healing the soil.
After what crops can tomatoes be planted


After all of the above, we can draw the first conclusions that the best predecessors for tomatoes will be crops that restore the soil. These are legumes and green crops, siderates.
You can also plant tomatoes after:
- Representatives of the pumpkin family - zucchini, pumpkins, cucumbers. Since organic fertilizers are applied under them.
- Onion and garlic.
- Turnips, carrots, beets and radishes.
- Any kind of cabbage.
What soil and growing conditions do tomatoes need?


Lighting
Tomatoes are a heat-loving and light-loving vegetable crop.
During the period of fruit ripening, the plant needs bright, intense lighting, otherwise the fruits will be less tasty.
- The seeds of this vegetable plant can germinate at a temperature of at least + 14 ° C, but at higher temperatures (within 20-22 ° C) sprouts appear faster.
- And the growth of adult plants begins to slow down at temperatures below + 12 ° С, the shoots completely stop growing when the thermometer drops below + 9 ° С.
If the plants do not have enough lighting, then they begin to stretch, weaken. As a result, flowering and fruiting of these plants will be delayed. The lack of lighting is especially dangerous when growing seedlings at home.
Air humidity
The next requirement is optimal air and soil moisture.
The humidity level of the air should not exceed 60%, and the soil - 70-75%.
High humidity in the air or soil can lead to the development of various fungal diseases, root rot, black leg. Some of these diseases cannot be cured, so the plants have to be destroyed.
Fertilizer
Tomatoes also require nutrients, plants can only get them from the soil. Therefore, the beds on which the tomatoes will grow must be pre-fertilized.
- In autumn, when digging, organic matter (compost, humus, manure) is introduced into the soil at the rate of 10 kg per square.
- In the spring, when re-digging, complex mineral fertilizers are introduced into the soil, and then beds are formed in which tomato seedlings will be planted.
During the growth of seedlings, a large amount of phosphorus is required for the normal development of the root system, which is part of the nutrient substrate.
And then the seedlings are fed with a solution of complex mineral fertilizers twice before they are transplanted into open ground.


After transplanting seedlings to the beds during flowering and the formation of ovaries, growing bushes require potassium and phosphorus.
These minerals contribute to:
- active flowering;
- the appearance of a large number of ovaries;
- strengthening immunity.
As a result, tomato bushes develop faster, more ovaries are formed, and the plants themselves practically do not get sick, which also has a positive effect on the yield of this vegetable crop.
Effects of nitrogen on tomatoes:
- This macronutrient has a beneficial effect on any crop plant.
- Activates the growth of vegetative mass and root system.
But it is necessary to introduce it into the soil with caution. An excess of nitrogen leads to an increase in the development of green mass to the detriment of flowering and fruiting, and a lack of nitrogen leads to a slowdown in growth, lightening of foliage, and the fruits will be too small.
Priming
The best types of soil for this vegetable crop are sandy loam and loamy with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction.
In such conditions, the first fruits on tomato bushes can ripen 1-1.5 months after the flowers appear.
What to plant after plants with late blight to improve the soil?


Onion garlic. Bulbous plants are rich in natural phytoncides that disinfect and heal the earth. After the tomato planting season, it is enough to let the ground rest once by planting onions or garlic, and by the next year you can plant the tomatoes again.- Siderata (mustard, cereals, phacelia). Mustard and phacelia are natural disinfectants. Cereals renew and improve the soil.
These plants restore the microflora after diseased tomatoes and create favorable conditions for the growth of subsequent plants.
What crops will do better in the garden?
For a high yield after tomatoes, it is better to plant:
- different types of cabbage;
- legumes;
- cucumbers;
- roots.
To improve the soil, it is better to plant after tomatoes:
- onion;
- garlic;
- mustard;
- phacelia.
What is absolutely forbidden to cultivate?
- Solanaceous plants (potatoes, peppers, eggplants, physalis). Plants of the same family with tomatoes have similar nutritional requirements, take the same trace elements from the soil, and are affected by the same diseases. All this negatively affects the harvest.
- Strawberries, strawberries. Strawberries are sensitive to late blight, which affects tomatoes. Tomatoes acidify the ground a lot. In such an environment, strawberries will not be able to fully grow and bear fruit.
- Melons (watermelons, melons, pumpkins). The roots of tomatoes and melons are located at about the same depth, and deplete the same layer of soil. Therefore, melons will grow poorly and develop after tomatoes, will give a weak harvest.
Not all plants can be planted after tomatoes. Some crops develop well in the place where tomatoes grew. It is not recommended to plant certain plants after tomatoes. In cases where it is not possible to change the planting site, you can avoid a drop in yield if you correctly apply fertilizers and process the land and plants on time from pathogens. Knowing and applying the principles of crop rotation in the garden, you can always get a good result.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Not recommended crops
The following crops should not be grown in the place where the tomatoes were planted:
- other or similar varieties of tomatoes;
- potatoes;
- tobacco;
- physalis;
- strawberries;
- strawberries;
- eggplant.


This recommendation is due to the fact that tomatoes with the listed crops are affected by similar diseases and pests. Therefore, even after disinfection of the soil, signs of pathologies that previously affected planted tomatoes may appear on new plants grown.
In order to avoid this, the listed crops should be planted away from the places of growth and the former growing area of tomatoes.
There is another argument against the planting of these crops in the former place of growing tomatoes. The fact is that tomatoes make the soil more acidic, and in such an environment the listed plants cannot fully grow, develop, and most importantly, bear fruit. Because of this, crops planted in the wrong place either die or give a poor harvest.
See also
Planting tomatoes for seedlings according to the lunar calendarRead
What can be planted after a tomato from melons? The answer to this question is unequivocal: nothing. This is due to the fact that watermelons, melons or pumpkins planted on the former tomato site will bear poor fruit, and the summer resident will receive a very modest harvest.
Many summer residents plant bell peppers next to the tomatoes. It is not recommended to carry out such a planting on a garden bed on which tomatoes were previously grown for only one reason: the yield of bell peppers can be significantly reduced. If such a prospect does not frighten the gardener, he can plant this plant culture in place of tomatoes without fear of disease or pest damage to the bush.
When is it time to change the place of planting tomatoes
For nightshades, a loamy, easily warming soil, loose, without a certain level of acidity is needed. Gardeners consider transplanting tomatoes to a new location annually as an ideal option. Individual plot owners are forced to resort to a little trick to get a sufficient harvest when planting tomatoes in the same garden for several seasons in a row:
- replace the top layers of the soil - they are sent to a place reserved for growing radishes, which grows best after tomatoes;
- apply certain nitrogen fertilizers - in accordance with the scheme indicated on the package;
- legumes and fragrant greens are planted next to tomatoes - the condition allows you to partially restore the land and prevent its massive impoverishment;
- plant a culture according to the Kizima method - with the formation of a deep root system, in plastic wrap;
- after removing tomato bushes, legumes and mustard varieties are planted in the fall.
Reviews of gardeners
Oleg, Novosibirsk
After picking the tomatoes and removing the tops, he also sowed white mustard, no diseases of the tomatoes were observed. In recent years, we have switched to growing tomatoes in the open field, where, after harvesting, we harvest the tops, dig up and sow either mustard or rye. Tomatoes do not get sick, while late blight is rampant among its neighbors.
Sergey, Omsk
Phacelia I sow when it is necessary to loosen the soil. She is able to loosen even a rolled road.