Experienced gardeners and farmers know that before each sowing season it is important not only to properly fertilize the site, but also to distribute crops on it according to the rules of crop rotation. Why is it important? If the alternation of vegetables in the garden is not correct, problems will inevitably arise and crop losses are very likely.
Today we'll talk about what can be planted after potatoes next year. The table that we have placed on this page will help you plan the planting of vegetables according to the rules of crop rotation. You will also find out where you can plant potatoes next year. This is an important question, because this crop usually takes up most of the garden. Yes, it is not easy to find out what is better to plant next year: schemes and calculations will be needed. But these efforts will certainly be rewarded with the health of the crops grown and their high yields.

Can potatoes be planted after potatoes?


Potatoes can be planted in the same area after 3-4 years. If the site is small, then it can grow in one place, but not more than 3 years.
At the same time, organic and mineral fertilizers are introduced into the soil, compensating for all the nutrients taken by potatoes from the ground. In addition, we must not forget about soil disinfection, since diseases and pests will infect potatoes with renewed vigor every year.
After harvesting the potatoes, a deep digging of the earth is carried out with a complete overturn of the layer. This contributes to the freezing of the ground and the destruction of diseases and pests.
In the spring, after warming up the earth, compost or humus is brought in and dug up again. Mineral dressing is applied at planting.
After harvesting early potatoes, green manures are sown in its place, they will improve the soil for the next plantings.
What is crop rotation
Growing the same crop in a permanent place for several years in a row leads to adverse consequences. Over time, the soil begins to deplete and accumulate pests and plant pathogens. To avoid this, it is necessary, observing the rules of crop rotation, to plant crops in other beds for the next season.
Crop rotation is the scientifically based rotation of crops in the territory and in time.
There are several good reasons why you need to comply with it:
- reducing the level of soil contamination by pests, diseases and weed plants;
- improving the structure of the topsoil;
- saturation of the soil with the necessary nutrients.
Some types of plants receive nutrients from the lower layers of the soil, others from the upper ones. Planting different crops each year in the same place will improve the health of the soil and ensure a more rational use of nutrients.
What to plant after potatoes next year?


When choosing crops that can grow after potatoes, one should not forget about the rules of crop rotation.
According to the rules of alternation, cultures are divided into 4 groups:
- Root vegetables (potatoes, onions, beets, carrots). They give a good yield with a high potassium content in the soil.
- Fruit (cucumbers, pumpkin, peppers, eggplants, zucchini). Demanding on the presence of phosphorus in the earth.
- Leafy (greens, cabbage, lettuce, spinach). Demanding to the content of nitrogen in the soil.
- Legumes that saturate the soil with nitrogen. Most suitable for crop rotation.
Any crops are planted in accordance with their needs for nutrients, for example, leafy plants are planted after legumes. And legumes, in turn, grow well after onions and garlic. And they give a good harvest after potatoes.
Vegetable crop rotation table
| Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet | Cabbage |
| Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes |
| Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic |
| Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes |
| Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato |
| Carrot | Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini |
| Beet | Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot |
| Cabbage | Potatoes | Onion garlic | Legumes | Pepper, eggplant, tomato | Cucumbers, zucchini | Carrot | Beet |
Can I plant onions, strawberries, cucumbers, tomatoes, cabbage after potatoes?


When crop rotation, you can alternate tops and roots, for example, greens, legumes, carrots, beets, lettuce, garlic, zucchini, cucumbers, cabbage and pumpkin are planted in place of potatoes and tomatoes.
In the spring, the former potato beds can be planted: onions, radishes, garlic, radishes, spinach, beets, lettuce, turnips, cabbage, daikon, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, legumes and melons.
In the place of onions, garlic, legumes, you can sow and plant any crops. Re-planting them in one place is undesirable.
It is not recommended to plant strawberries and strawberries in place of potatoes.
In place of melons, squash, squash, cucumbers, it grows well: potatoes, legumes, radishes, tomatoes, garlic, onions and cabbage.
Carrots are grown in the place of a tomato or cabbage.
What to plant in the fall?
In autumn, after harvesting potatoes, you can sow greens, winter cereals, peas. All of these crops allow the restoration of deep soil layers and grow well in the place of potatoes.
Before winter
To improve the composition of the soil, green manure can be sown:
- alfalfa
- oats
- lupine
- rape
- mustard
- peas
- phacelia
They not only improve the composition of the earth, but also loosen it and fight diseases and pests.
From the wireworm
The larvae of the click beetle (wireworms) are widespread, not only in the potato beds.
It is undesirable to fight the pest with pesticides. In this case, toxic substances enter the plants. In addition, they destroy not only the larvae, but also the living ones useful for the soil.
Therefore, various agrotechnical methods of control are more often used. Digging the soil in the fall reduces the number of insects. In this case, the larvae die from the cold.


- Early spring digging also helps in the fight against wireworms.
- Properly organized crop rotation helps to get rid of the wireworm.
- On heavily infested areas, green manures are sown after harvest.
- The wireworm does not like crops such as buckwheat, mustard, rapeseed, rape, sweet clover, oil radish, black beans, chickpeas, beans, soybeans, peas, soybeans and spinach.
These crops are sown on the site for 2-3 years. During this period, all wireworm larvae die or turn into beetles and leave.
Sown siderates attract pests, after which the plants are dug up and removed from the site.
Marigolds and white mustard, sown in the aisles or along the edges of the beds, will also help to fight the wireworm.
Instead of pesticides, ammonia fertilizers are introduced into the soil in spring, which destroy the pest.
Siderata and onions after potatoes: video
The importance of proper crop rotation
To avoid exhaustion and not be left without a crop next year, agronomists recommend using crop rotation. It consists in the rational sequence of the arrangement of crops in the garden. This method is necessary in order for the land to rest and recover after harvesting the potatoes. Fruit change allows not only to eliminate diseases and pest attacks, but also to increase plant productivity.
In the practice of farming, the need to alternate potatoes with other crops is caused by prerequisites that are associated with:
- Features of soil nutrition: the "diet" of a vegetable consists of ash elements, potassium and nitrogen. After digging up the tubers, these elements in the soil will decrease.
- The influence of potatoes on subsequent plantings and adjacent plants.
- Restoration of the water-resistant structure of the soil, the need for which is caused by the compaction and destruction of the soil during the growth of potato bushes.
- Cleansing the area from weeds and getting rid of diseases. With the permanent method of cultivation, the plantings of potatoes are clogged, and pests and fungal colonies (rhizoctonia, scab) again occupy the bushes.
Improving the fertility and quality of vegetables depends on the correct crop rotation.
After which crop should you plant potatoes?
The best precursors for potatoes are various root crops, cabbage, and green crops.
You can alternate with potatoes onions, beets, carrots, peas, zucchini, beans, cucumbers and beans.
After strawberries, watermelons?

In place of strawberries and strawberries, you can plant potatoes and other root crops, legumes, next year you can plant zucchini, cucumbers, pumpkin here, and then onions and tomatoes.
After watermelons, melons, celery, cucumbers, carrots and parsley are planted: potatoes, tomatoes, legumes, onions and garlic.
What if planted after the "wrong" predecessor?
It is important to follow the recommendations. But what if the potatoes have already been planted in the place where tomatoes or peppers grew last season?
- First, to nourish the soil with mineral fertilizers (potassium, urea, superphosphates), which is necessary for the growth and development of the plant.
- Secondly, 3-4 times per season to process potato plantations, spraying with fungicides, as a method of combating late blight.
- Thirdly, remove the tops 2 weeks before harvesting. And after digging up, dry the tubers well, to avoid decay and long storage in winter.
All of the above features of planting plants one after the other have already been tested many times in practice by gardeners and are advisory in nature. Indeed, for their observance, the area of the site may simply not be enough. But you need to try, and then your efforts will be rewarded with an excellent harvest.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
We tried to write the best article. If you liked it, please share it with your friends or leave your comment below. Thank you! Excellent article 10
After which you can't plant potatoes?


During the growing season, potatoes take phosphorus and potassium from the soil. After harvesting, it is necessary to replenish the lack of these substances in the soil by making appropriate dressings.
Potatoes should not be planted after tomato, pepper, eggplant, physalis and tobacco. They are related crops and have common pathogens and pests. At the same time, spores of late blight, macrosporiosis accumulate in the soil, various rot and plants begin to hurt.
What should not be planted after potatoes?
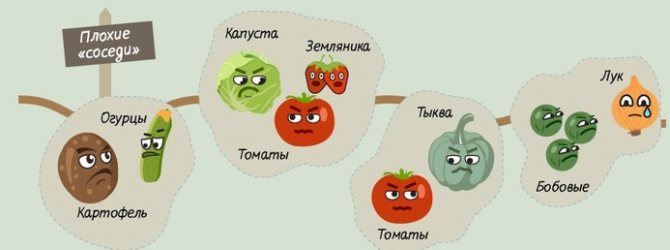

Potatoes as a precursor are not suitable for strawberries and strawberries. Strawberry beds in the place of potatoes can grow no earlier than after 3 years.
It is strictly forbidden to grow potatoes in place of:
- sunflower,
- cucumbers,
- pumpkin,
- zucchini,
- squash,
- watermelons,
- melons,
- raspberries.
Soil care
In order to be able to plant any other plants on potato plantations, it is necessary not only to restore the nutrient balance of the soil, but also to disinfect the top layer. Digging is also an important post-harvest activity. You need to dig at least 10 cm deep, completely turning the layer over. This will help the ground freeze better, as a result of which all pests that have settled inside the soil will die, and the causative agents of diseases of the nightshade will be destroyed.
In the spring, the soil will begin to warm up, and then you will need to re-dig and start fertilizing it. During growth, potatoes take not only phosphorus and potassium from the soil, but also trace elements such as magnesium, manganese, copper, nitrogen, zinc and some others. Even a small lack of these elements can interfere with the normal growth of subsequent plants. Before planting them, it is necessary to fertilize the ground with compost under the dug layer or manure.
When using mineral fertilizers, it is better to pour them into the holes or furrows themselves, and not cover the entire ground with them. Ash will be a useful substance for potatoes, since the trace elements contained in it improve plant growth and help disinfect the soil. Siderata are planted in order to then bury them in the ground for humus.
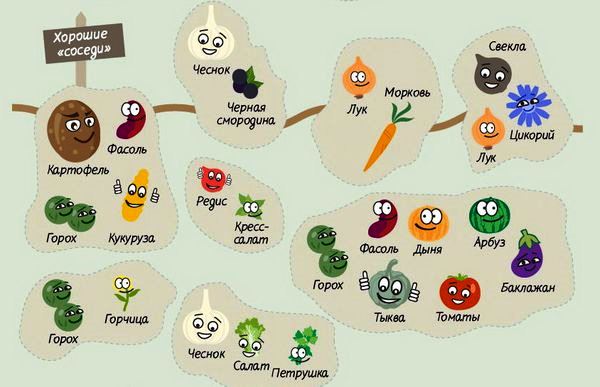
The best neighbors, what to plant nearby?


For the success of potato cultivation, you need to consider the principles of healthy neighborhood.
Potatoes go well with corn, cabbage, beans, horseradish, spinach, mint, garlic and onions. They have a beneficial effect on potato planting. Beans feed the potatoes with nitrogen, protect them from the Colorado potato beetle, and he, in turn, from the bruchus pest.
Neighborhood with potatoes for cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, tomatoes, squash, pepper, physalis, eggplant and cabbage are undesirable for each other.
Planting strawberries, strawberries close to the potato garden leads to the attraction of the wireworm. In rainy weather, the berries are affected by black and gray rot. The infection eventually spreads to potato tubers.
Potato and strawberry plantings should separate strips of spinach, carrots, beets, or radishes.
Potatoes also do not like the neighborhood with cherries, apple trees, raspberries, sea buckthorn, chokeberry and grapes.
To prevent the appearance of onion flies, weevils, cabbage whites, as well as damage to plants by fusarium, marigolds can be planted in the aisles.
- Calendula protects against the Colorado potato beetle.
- Nasturtium prevents the appearance of whiteflies and whiteflies.
- Chamomile feverfew keeps out aphids, cabbage scoop caterpillars, white beetles and rodents.
- Tansy - from many pests.
- Lavender - from aphids, ants.
With the right selection of neighboring crops, you can protect plants from diseases and pests, and increase the yield.

Soil and conditions for growing potatoes
This nightshade crop loves fertile, breathable, light soil, with a slightly acidic reaction, with a pH of 5-6.
Potatoes give a good harvest on sandy, sod-podzolic, chernozem, peat, gray forest soils.
Loose soil allows the root system to be saturated with oxygen and the tubers develop well. Normal access of oxygen to the roots guarantees good taste of the tubers.
Damp areas and beds with a close passage of groundwater are not suitable for planting potatoes.
Waterlogging of potatoes is highly undesirable. This leads to a slowdown in plant growth and contributes to the development of diseases. With a close passage of groundwater, a drainage system is required.
- Heavy sandy, clayey, podzolic soils require preliminary improvement.
- In dense soil, small, deformed and tasteless tubers are formed.
- A bucket of humus (, compost, peat) is introduced into heavy clayey, loamy soil per square meter. A bucket of clay soil is applied to a sandy or sandy loam area.
- In peat soil, you need to add a bucket of compost or humus, a bucket of clay, a bucket of coarse sand.
- With high acidity of the soil, slaked lime or ash is mixed in.
Top dressing, watering, weeding and hilling potatoes can compensate for the lack of oxygen and nutrients, which allows you to grow a good harvest.


Shaded areas are not suitable for growing potatoes. The beds should be light, fully warmed up by the sun's rays. Lack of light leads to stretching, lightening of the stems, poor flowering, poor and small yield.
Plowing or digging the soil for potatoes creates a loose, ventilated soil layer with sufficient moisture.
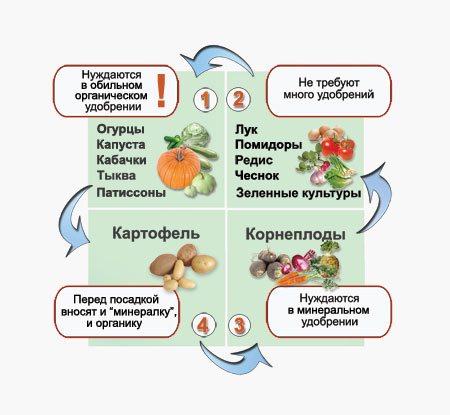
The potatoes are planted on a plot dug up in advance, since autumn, to a depth of 25-30 centimeters.
Before the start of digging, 5 kilograms of rotted manure or compost is applied per square meter of the plot. On sandy or depleted soils, the amount of organic matter increases to 9 kilograms. Fresh manure and unripe compost are not suitable for these purposes.
- Together with organic matter, 200 grams of wood ash or slaked lime, 25 grams of potassium sulfate and 25 grams of double granular superphosphate are introduced per square meter of beds.
- In the absence of organic matter, mineral fertilizers are buried in the soil. There are 50 grams of ammonium sulfate, 15 grams of urea or 50 grams of superphosphate per square meter of future plantings.
- Intensive potassium-phosphorus nutrition increases the resistance of potatoes to low temperatures and diseases, and helps to increase yields.


All fertilizers are buried 12-15 centimeters into the ground.
1/2 of the nitrogen fertilizer rate is applied in the spring, after plowing and covered with a rake. The second part of the dressing is applied before hilling the potatoes.
Potatoes are propagated vegetatively. For this, healthy large tubers are taken whole or cut in half. The future harvest depends on the size of the tubers and the number of eyes on them. It will not be possible to collect a large crop from small potatoes with a small number of eyes.
The tubers are prepared in autumn. They are selected and stored in a well-ventilated area. Tubers germinate 1-2 months before planting. To do this, they are distributed in a thin layer in boxes and placed in a bright room at an air temperature of + 15-20 degrees.


After germination, the filamentous tubers are removed.
Potatoes are best planted from north to south or from northwest to southeast. The optimum soil temperature for planting potatoes is + 7-8 ° C.
For early potatoes, a glass of humus, a tablespoon of ash and a teaspoon of superphosphate are added to each hole. The mixture is embedded in the soil to a depth of 10 centimeters. For mid-season varieties, the amount of dressing increases twice and deepens by 15 centimeters.
The potatoes are laid out in the holes and sprinkled with earth, tubercles are formed on top of the holes. If the air temperature has not reached the required standards, the landings are covered with a film or non-woven material. When shoots appear, arcs are established. When the weather is warm, the shelter is removed.




















