Last updated 1 March 2020 at 01:25
Reading time: 5 min
Mushrooms belong to a separate kingdom, since they combine the properties of both plants and animals. They play an important role in the natural processes of the biosphere.
There are a huge number of species in the world. But the article will focus on parasitic ones. They cause harm to the body on which they settle, and then the owner dies due to a lack of nutrients.
We will find out which fungi are parasites, on which plants they can parasitize. What mushrooms look like, in general, it's all about mushrooms.
What is the biological description
All fungi belonging to the parasite group are completely dependent on their host. The affected individual is a means of subsistence. Infected plants and animals can survive for several years.
The life expectancy of the owner will directly depend on individual characteristics. There is also the likelihood of injury to a person. Diseases provoked by fungi are subject to urgent elimination. It is strictly forbidden to hesitate to see a doctor.
Mushrooms are able to feed only on living organics. The microorganism digests its food. A nutrient medium is essential for reproduction and distribution. In the absence of the necessary conditions, this is impossible.

There are many varieties of saprophytes
The common mycelium chooses plants, leaves, etc. for nutrition. Parasites also often affect living organics. Saprophytes are microorganisms that are able to live off representatives of flora, as well as animals and humans. This is a kind of parasitism on living matter.
There are varieties of fungi that are capable of digesting particles found on the skin, hair, and bones. This is the result of a mutation. Microorganisms were forced to adapt to the prevailing conditions and look for options for food.
Parasites include all saprophytes that feed on living organics. This nutritional feature was formed as a result of a kind of struggle for survival. Representatives are divided into several groups.
Parasites are capable of:
- live off the plant;
- be dangerous for insects, for example, destroy an anthill in a few days;
- to carry out livelihoods at the expense of the animal carrier;
- infect the human body and infect the skin, nail plate, hair and mucous membranes;
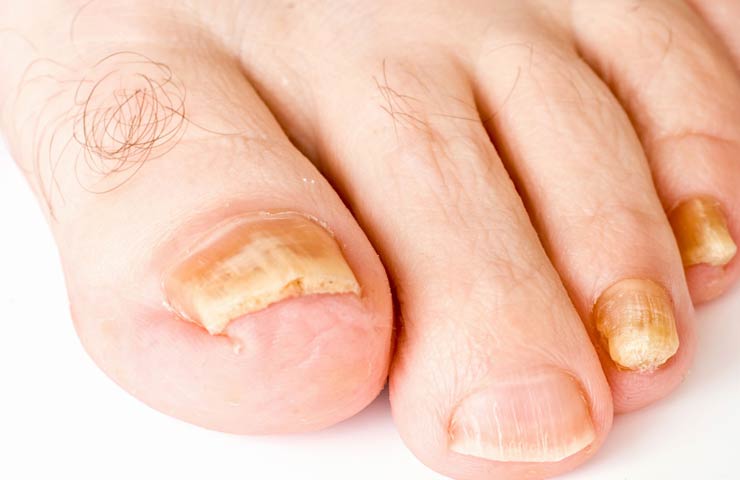

Fungal organisms can even infect nails
- live off other mushrooms;
- eat lichens.
Mushrooms are dangerous to their host, that is, plants and animals can die under the influence of a pest.
There are also representatives that feed exclusively on dead individuals. For this purpose, they have a special poison, which they release into their victim. This leads to instant death. These mushrooms are called aggressive.
Medical parasite cordyceps
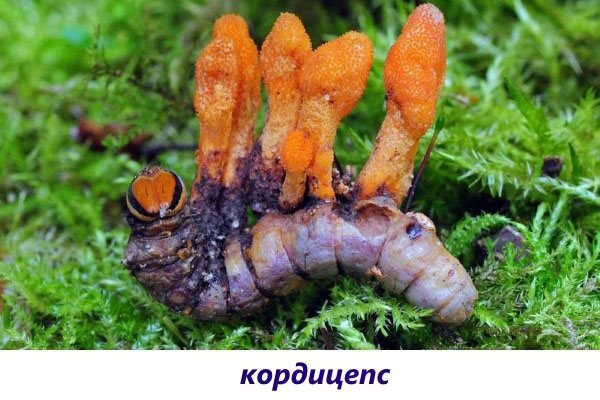


In addition to fungi that parasitize plants, there are also species that live organisms choose as the host. One of them is a unique creation of nature called cordyceps. The spores of the fungus begin their life cycle when they enter the caterpillar of certain species of moths. There they develop, feeding on a caterpillar and gradually turning it into a brownish-yellow mummy, until they completely kill, germinating through the body.
In oriental medicine, cordyceps is a valuable and very effective drug, with the help of which a large number of diseases are cured, in particular, heart, oncology, male problems, and so on.
It is possible to list and describe the varieties of parasitic fungi for a very long time. Although they have different owners, they all have the same nature: to survive at the expense of others, which is why mushrooms are called parasites. If you are fond of farming, horticulture, gardening or flowers, regularly inspect your property so as not to miss the appearance of these intruders and to destroy them in a timely manner. Be carefull! And watch your health!
What types are there
Mushrooms are divided into two subspecies. All types are described in the table.
| Obligate | These mushrooms carry out their vital functions directly in the body of their owner. The parasite's nutrition includes certain sets of elements. The microorganism fully adapts to the conditions, for example, before the cold, the parasite forms spores. |
| Optional | These organisms are attached to their host, and then begin to destroy it. After death, the parasites feed on the owner's remains. These microorganisms are harmful to agriculture. This is due to the fact that the parasite is able to destroy potatoes, peppers, etc. |
Mushrooms are resistant to environmental influences. Microorganisms adapt seamlessly to changing conditions.


Mushrooms can grow in a wide variety of conditions
What are examples of fungi parasites
There are many varieties of parasitic fungi. The group of these microorganisms includes Golovnevye. Pests attack plants and destroy tissues. Above, a representative of the flora is covered with bloom.
Smut is a parasite that lives only on certain plants. It is almost impossible to cope with a microorganism. The best option is soil and seed treatment.
Ergot is another type of mushroom. Formed on cereals instead of grains. Destroys crops. This parasite is also grown in vitro for medical purposes. Previously, this microorganism became the cause of death among people.
Rusty ones affect plants, namely their aboveground part. Fruit trees are often affected, which means they harm agriculture. Coping with the parasite is quite difficult. Reduces yield and deteriorates the quality of the fruit.
The parasite can infect several plants at once. Treatment consists of regular spraying.
Many fungi attack agricultural plants. They settle not only on annual plants, but also on perennials. To prevent infestation, regularly inspect plants and periodically apply chemicals.
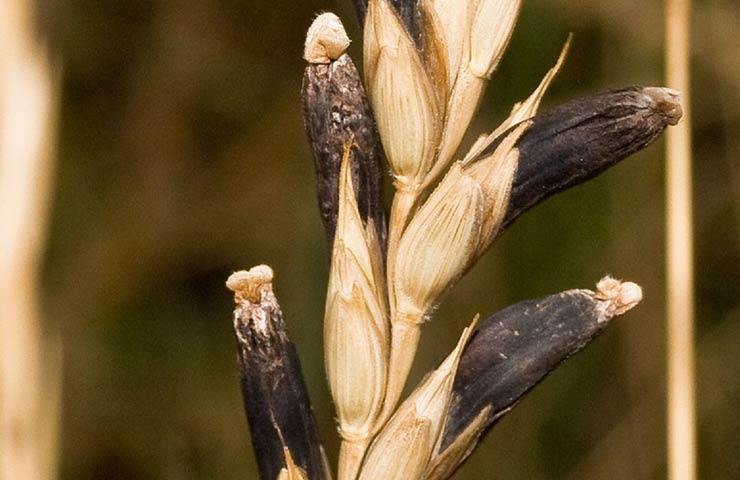


Ergot usually affects cereals
The value of mushrooms in nature
The nutrients decomposed by the mushrooms are further absorbed by other plants. Living creatures (animals and insects) feed on hat species. There are also such mushrooms that are specially grown artificially. These are champignons and oyster mushrooms. Moldy mushrooms (aspergillus, penicilli) are used to obtain antibiotics and even hard cheeses. Ergot (formed on cereals) is used to fight malignant tumors.
Many parasitic fungi harm living organisms and plants, causing disease. A lot of damage is done to wood. It is not recommended to use contaminated building material for wooden structures. Since the mushroom culture can cause fatal poisoning, experts advise that you be very careful when harvesting it.
Tinder mushrooms: who is it
Another type of parasite is tinder fungi. These pests destroy tree tissue. Harmful to forestry. Spores penetrate through lesions.
Germination occurs in the mycelium. The wood becomes rotten, and the tree loses its ability to grow and develop. The fruiting bodies of the fungus resemble hooves in appearance.
Often, fruiting bodies appear only a few years after direct infection. Perennial growths. Hollows appear in damaged trees. The plant is destroyed from the inside and is unsuitable not only for growth, but also for the further use of wood.
Way of eating
For the normal functioning of any living organism, proteins (proteins), carbohydrates and fats (lipids) are needed. Proteins are synthesized in cells from amino acids supplied to heterotrophs from the external environment. Fats are part of the cell walls and become an energy reserve in case of carbohydrate deficiency. Complex carbohydrates are derived from glucose and are energy materials. In plants, complex carbohydrates are synthesized from simple carbohydrates - starch and fiber. In animals, they turn into glycogen, here in fungi they are completely similar to fauna, and glycogen is also present in their bodies.
To get all these substances from the external environment, they must first decompose more complex compounds into simple ones. Indeed, neither peptides, nor starch, nor fiber enter the cell. For this, organisms release enzymes into the external environment. Some representatives of the kingdom, for example, yeast, do not have enzymes. Therefore, they live on a specific substrate of simple carbohydrates that penetrates the cell walls.
Complex multicellular higher fungi synthesize enzymes in the mycelium, and some species in the fruit bodies. Each variety has its own characteristics. Some produce enzymes that can dissolve a large number of substances. Others have only specific ones, for example, they only break down keratin. It depends on what medium they will grow on.
The body of multicellular species consists of special filaments - hyphae. It is through their cells that nutrients are absorbed. It is also where the synthesis of proteins takes place, the conversion of glucose into glycogen, simple lipids into complex fats. Hyphae are fixed on the substrate. Depending on what kind of environment and method of nutrition mushrooms choose, they are divided into:
- saprophytes or saprotrophs;
- parasites;
- symbiotics or symbionts.
Most of the representatives of the kingdom belong to saprophytes, which settle on decaying remains. But there are thousands of parasitic species. Some have chosen a special way of interacting with other organisms - mutually beneficial symbiosis. Such mushrooms do not feed only at the expense of another organism, but help it to receive chemical elements from the external environment. This is their main difference from parasites.
What a variety of parasites and what diseases cause
The parasites are included in a large group of 2000 species. Diseases caused by fungi can be divided into 2 groups. Mycoses develop under the influence of direct parasitism of microorganisms. Both external integuments and internal organs can be affected.
Mycoticosycosis - poisoning provoked by toxins formed as a result of the vital activity of fungi. Most often, the deviation is formed under the influence of the consumption of low-quality food products.
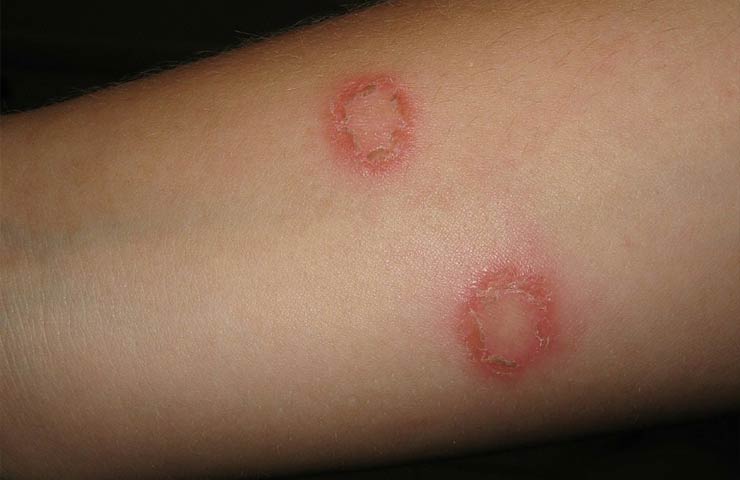

Ringworm is a common fungal infection.
By the way of reproduction, fungi can also be divided into 2 broad groups:
- microparasites that multiply inside their owner;
- macroparasites that live inside another individual, but reproduce in other ways.
The most common disease caused by fungi is ringworm. In this case, the parasite affects the outer covers of a person or animal.
Most often, the disease affects children who come into contact with street cats and dogs on the street.Microorganisms are also transmitted through the belongings of the owner of the parasite. The patient's skin is crusted and the hair breaks off.
Symbiosis
This method of interaction is quite common in nature, although it is specific. Two imperfect organisms exploit each other's characteristics and are mutually beneficial. Hat species often enter into symbiosis with trees in the forest. Their mycelium envelops the roots of the plant, penetrates the cells. Its area reaches 1-6 km² and even more.
The absorption of minerals passes through the hyphae and shares them with the tree. Thus, almost the entire periodic table is supplied to it. The suction surface of the roots increases, which stimulates the growth of oak, birch, aspen or other species. Some trees cannot even exist without their helpers, the villi of their roots atrophy.
The fungus receives organic substances from the tree in large doses, which it synthesizes in the light through photosynthesis. Often these compounds enter the mycelium in a simple form that is accessible to cells. As a result of these normalized relationships, species are more likely to survive in natural competition.
What mushrooms affect animals
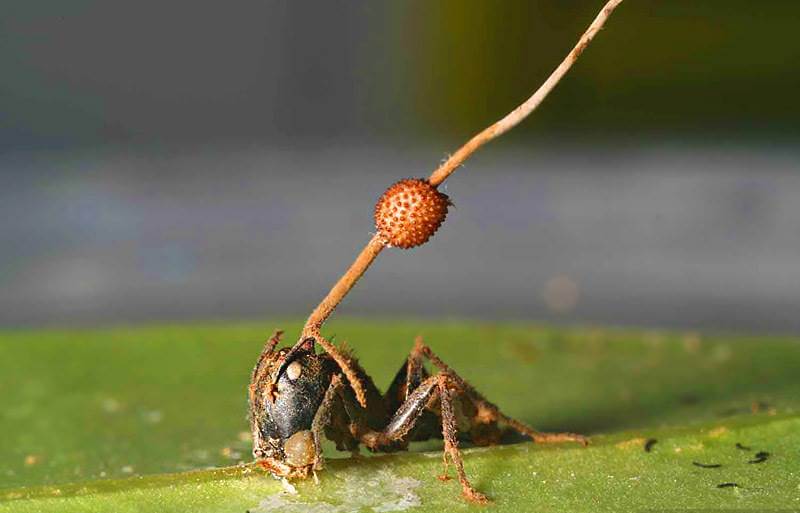
Cordyceps mushrooms are often infect animals. Parasites prefer warm climates. The microorganism settles on insects, namely ants.
After infection, the insect leaves its home and lives on the back of the leaves. The parasite completely fills the ant, and then grows through the host's head. Even after death, the owner remains a distributor of disputes.
Insects are also susceptible to attack by septobasidiums. The parasite takes away all the nutrients and contributes to the death of the owner.
Cats and dogs are susceptible to microsporia. The fungus settles on its owner. Over time, foci of damage to the wool cover appear. The coat is partially broken off. One gets the feeling that the animal was partially shaved.
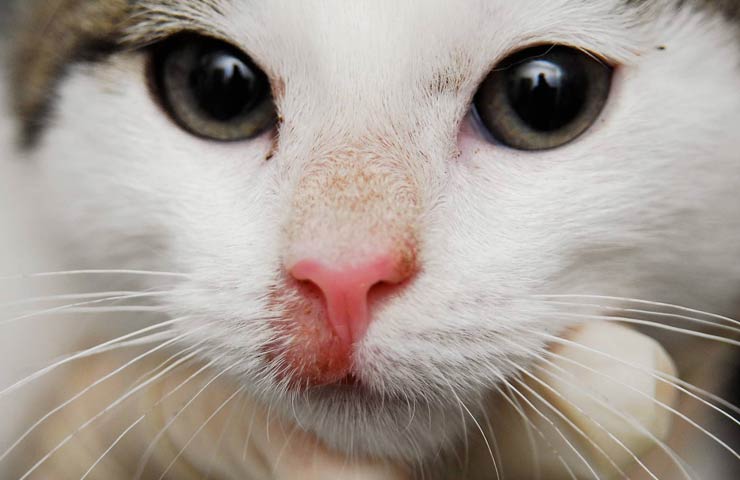


Cats also have fungal infections.
What mushrooms infect humans
The most common fungus in adults belongs to the genus Candida. The development of candidiasis or thrush occurs. Deviation develops with a decrease in immunity. It is often a consequence of the transfer of other pathologies and the use of antibacterial drugs.
The disease affects:
- nail plates;
- skin covering;
- mucous membranes.
There is a possibility of infection with Trichophytosis. The pathogen affects both humans and animals. The deviation extends to the nails and hair, as well as the skin.
Mr. Dachnik recommends: wood mushrooms - useful properties, use in cooking
The Chaga birch tree mushroom has become famous for its medicinal properties - teas, decoctions from it have a powerful immunostimulating and tonic effect.
Farm mushroom planting has become a lucrative business and now we often see delicious and nutritious oyster mushrooms on sale, which are also woody. In nature, they are yellow, greenish and other shades and grow in a large family. Forest species are much more fragrant than their artificially bred relatives. A big plus is that they do not have poisonous counterparts.
Tree ears, as mushrooms are called due to their resemblance to the auricle, are very popular in oriental dishes. However, they are rarely prepared as an independent dish, since they do not have a special aroma and pronounced taste. Mushrooms are good as a side dish paired with meat, giving it a subtle haze flavor. The crispy and dense texture is delicious and nutritious, especially well seasoned.
Undoubtedly, woody mushrooms have taken a worthy place in human nutrition: it is not for nothing that we have begun to meet them more and more often on supermarket shelves, thereby enriching the diet with healthy and nutritious protein products.
Parasitic fungi receive the necessary nutrients from living organisms on which they settle. They parasitize not only in forests and gardens, but also in fields, affecting agricultural crops. And some species pose a danger to human health.


The harm of fungi parasites









![Mice: [name, photo and description]](https://bgn.imadeself.com/wp-content/uploads/myshi-nazvanie-foto-i-opisanie-330x140.jpg)




