Mushrooms
0
1467
Article rating
In the forest, you have to apply in practice all the theoretical knowledge gained, determining the edibility of the crop. If the mushroom turns blue on the cut, it is necessary to understand whether it can be harvested, is it safe?

Mushrooms with blue cut
Blue lump
This mushroom is widespread throughout our country, but prefers to grow in the forests of Siberia and the Urals. Many residents of foreign countries consider it inedible, but this is not the case. It's just that the cooking technology is a lot of trouble. This mushroom has many names: purple, blue, lilac, canine.
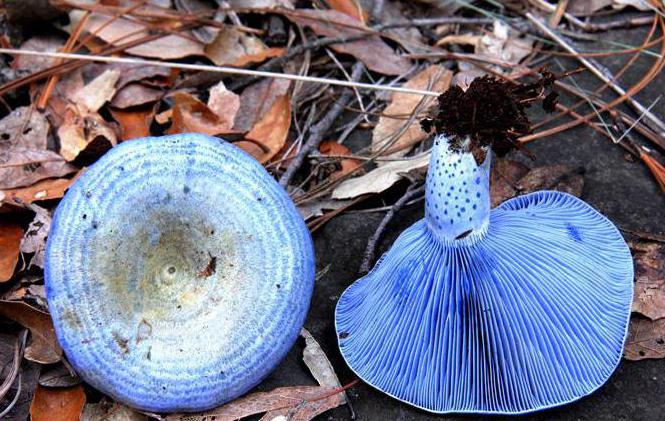


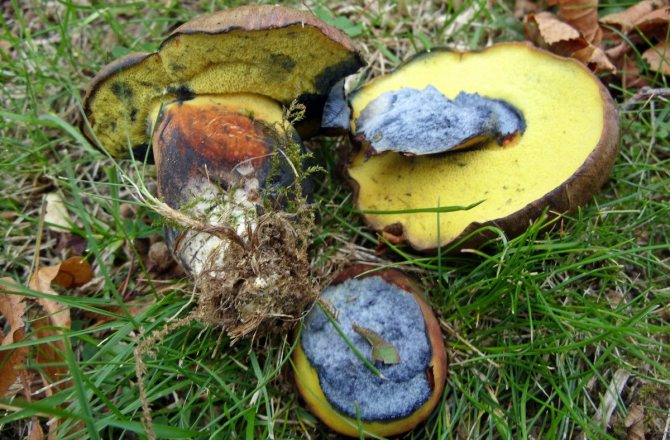
Many edible mushrooms turn blue when cut. A typical representative is a blue lump. Its cap reaches fifteen centimeters in diameter and is yellow. If the mushroom is cut or pressed on it, it turns blue. Hence the name. The cap of young milk mushrooms is slightly convex, but in the process of their growth and aging, it becomes prostrate or depressed. Blue mushrooms are mushrooms that turn blue when cut. The photo clearly demonstrates this. The mushroom is distinguished by dense and thick pulp, which is yellow, light brown or cream in color. Interacting with air, the white juice acquires a lilac color.


This mushroom has no counterparts. Mid August - early September is the best time to pick blue mushrooms, which are rich in mixed and coniferous forests. They hide under birches and spruces. These mushrooms are fried or boiled. They are not pickled, as both the mushrooms and the liquid turn blue.
Distribution and when to collect


Blue gyroporus is very rare. It can be found in the northern temperate zone of Russia in a mixed or deciduous forest. He prefers a humid climate. Forms mycorrhiza most often with birch, oak or chestnut, inhabits sandy soils. The first mushrooms can be found already in the middle of summer, the fruiting season for bruises lasts until October.
Mushroom - bruise
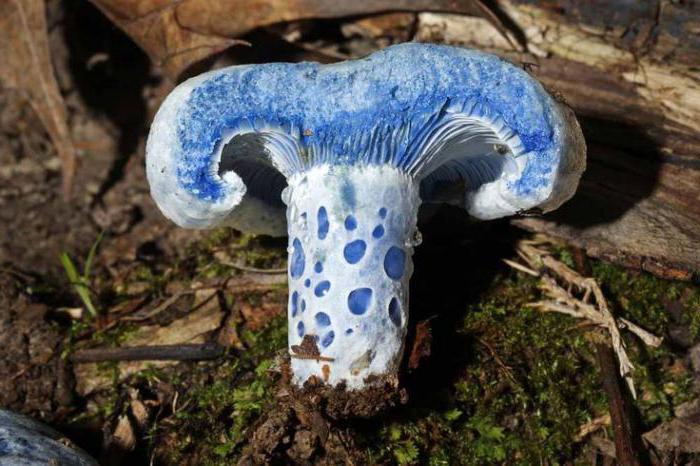
It got its name for a special property: its pulp on the cut changes color from white to bright blue. If the mushroom looks like white, it turns blue on the cut - this is a bruise. The appearance of the two varieties is very difficult to distinguish. The bruise mushroom is extremely rare, so information about it can be found in the Red Book.


The diameter of its cap reaches 15 cm. In a young mushroom, it is convex, and in an adult, it is prostrate. Subtle cracks can be seen on the brown or yellowish cap. Mushrooms on the cut turn blue when touched and pressed. Therefore, they cannot be confused with poisonous mushrooms, which are deprived of this ability. Under the cap are yellow spores and tubules, which instantly turn blue at the slightest impact on them. The leg is dense, tuberous in shape. Its structure is gradually deteriorating. In an aging mushroom, it is hollow.
The pulp does not have a special taste and smell. This kind is good stewed. The bruise mushroom is a lover of a humid warm climate; it can be found in oak and coniferous forests from mid-summer until its end. What kind of mushroom turns blue when cut? It may be a relative of the bruise - a chestnut mushroom, which is also rare and also found a place in the Red Book.
Edible species
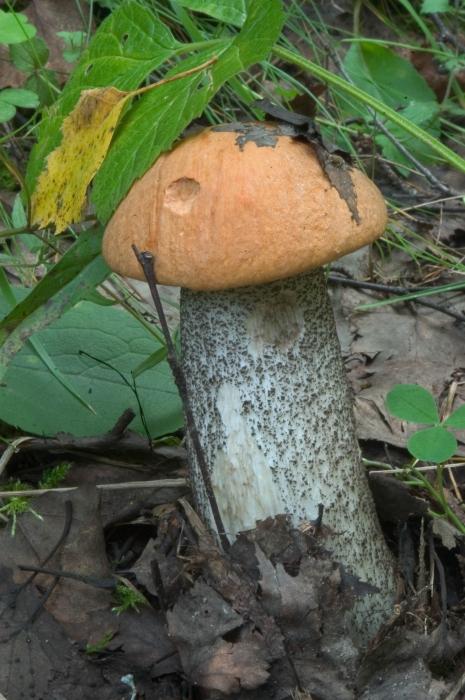


To find out which mushroom turns blue on the cut, you should also consider the edible species, which are quite common. These are varieties of tubular: boletus, boletus, Polish mushroom.
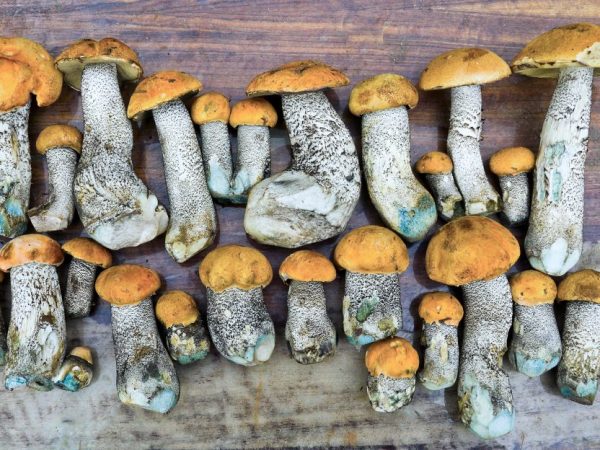
The fruiting body of the boletus instantly turns blue on the cut, and both the leg and the cap darken. Because of this, the boletus looks ugly in dishes, but it has an excellent taste and wonderful aroma. You can recognize him by his bright red hat and gray mesh leg.
In boletus boletuses, the leg turns blue, but not so clearly, and the cap remains white at all on the cut. The fruiting body consists of a long stem (1-1.5 cm in diameter) and a brown convex cap. The color can range from light (almost white) to dark chestnut. The leg is always gray, with barely noticeable scales.
Aspen boletus
These mushrooms have several varieties, one of which is the red boletus. It is also called krasyuk, aspen, red-headed. This is exactly the kind they say about: the mushroom leg turns blue on the cut. The boletus has a luxurious hat, the diameter of which can reach thirty centimeters. In young mushrooms, it is hemispherical in shape with edges tightly attached to the stem. Mature mushrooms are distinguished by a pillow-shaped hat that can be easily separated from the stem. The skin is red or terracotta, hence the name. The surface is velvety, smooth. The tubules under the cap are white with a yellowish or olive tint.
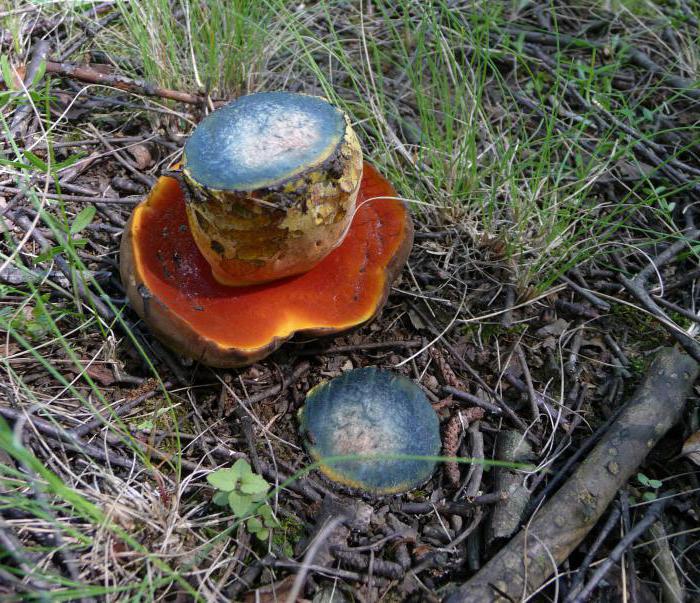


An adult mushroom is endowed with a high, thick stem. It is covered with small scales, the grayish-white color of which changes to dark in adult fungi. The hat is elastic, fleshy. The leg acquires a fibrous structure over time. At the fault, it first turns blue and then turns black. The smell of the mushroom is mild, but has a pleasant aroma.
Description
The bruise mushroom (Gyroporus cyanescens), blue gyroporus or birch gyroporus, is a tubular fungus and belongs to the genus Gyroporus, the Boletov family. It got its name due to the property of the pulp to quickly change its color at the cut or pressure point from white to bright blue.


- the cap of the mushroom changes its shape depending on age: in a young bruise, it is convex, then becomes flat as it grows. The skin color is matte whitish-cream or yellow-brown; with the slightest pressure, bright blue spots appear at the sites of damage. The hat is velvety-felt, dry to the touch. Diameter 5 to 8 cm, can reach 15 cm;
- the flesh is creamy or white, easily breaks down and quickly acquires a rich blue color with a cornflower blue tint at the site of damage. The characteristic mushroom smell is poorly felt, has a pleasant nutty taste;
- the tubular layer is almost free, also of a light cream or white shade, turns blue at the fracture, up to 10 mm thick. The pores are very fine. Pale yellow spore powder;
- the leg is smooth, from 5 to 10 cm in height and up to 3 cm in thickness, thick at the base, slightly pointed at the end. There is no ring. The inner part of young mushrooms is dense, in adults it is completely or partially hollow. The color of the leg is white or has a shade close to the color of the cap, when touched or at the cut point, it sharply turns blue.
Blue gyroporus is an edible mushroom belonging to the second category. It is not bitter and is considered more valuable than chestnut gyroporus.
Podduboviki
These mushrooms have another name - Polish. They are among the rarest blue specimens. They are found only in oak or deciduous forests. Poduboviks differ in that their pulp instantly turns blue on the cut or even becomes purple. But as soon as they are dried, the pigment disappears. Podduboviks are easy to confuse with boletus or porcini mushrooms. To prevent this from happening, just look closely, and you will see that the Polish mushroom always grows with an open hat.
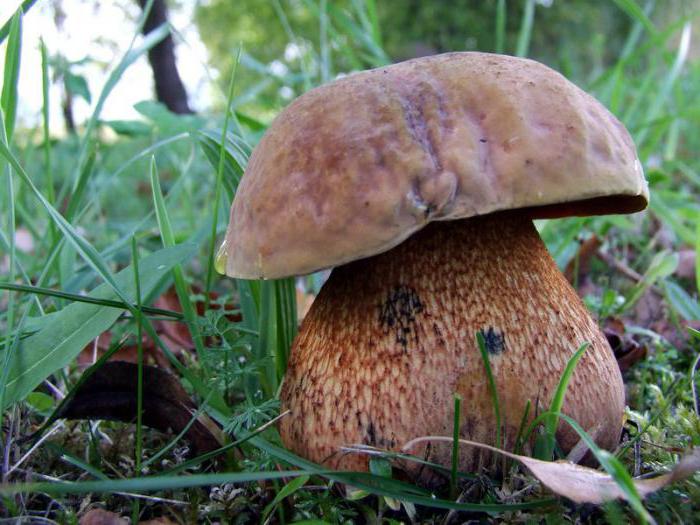


The pulp of the fruit tastes very good, which is often the cause of worm damage. The peel of a coffee or chestnut hat gleams, but does not stick to your hands.The tubule layer is yellow or greenish in color. These mushrooms turn blue when cut. But you don't need to throw them away. If you are not sure if a mushroom is edible or not, put it in another basket, and at home you will find information that will tell you what to do.
Warning: dangerous doubles
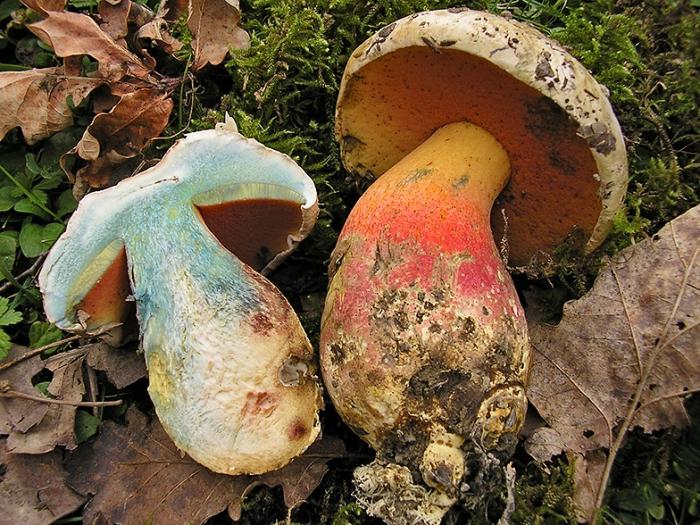


If you do not know which mushroom turns blue on the cut, but such a handsome man met on your way, be extremely careful. This is the so-called "satanic mushroom" or false white. Outwardly, he really resembles a boletus. The same dense fleshy leg, convex cap, but there are a number of differences! The white mushroom on the cut does not change color. The pulp of a poisonous double instantly turns blue or pink. In addition, the leg of the satanic mushroom is covered with a pronounced mesh, and the color is much brighter than that of the boletus.
Does the porcini mushroom turn blue on the cut or not?
This mushroom is often confused with the satanic double of the porcini mushroom. But the difference is that in a poisonous representative of this species, the breakdown first turns pink, and only then turns blue. The color of the edible white mushroom does not change on the cut, remember this! What kind of mushroom turns blue when cut? Satanic, which has a cap that resembles a porcini mushroom, but the spores under it are red or orange. Its leg is bright yellow with a red mesh pattern.
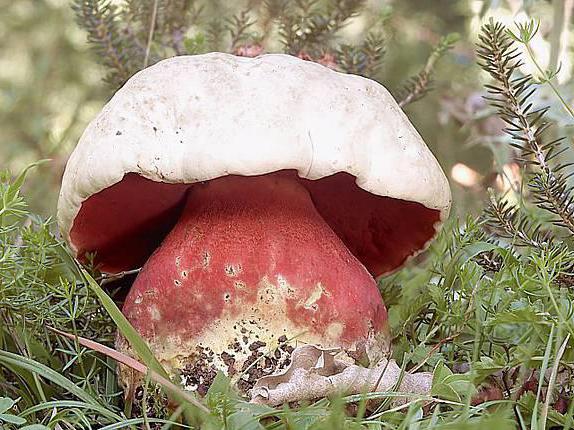


The shape of the cap of all poisonous mushrooms is slightly domed, and in white it is spherical with a whitish edge in young fungi. Growing up, they have a convex shape of a brown-red or brown cap. The tubules under the cap are at first white, but later they acquire a yellow or green tint. The leg is light, barrel-shaped with a mesh brown pattern. Does the porcini mushroom turn blue on the cut? The answer is unequivocal: the color on the cut of this mushroom never changes!
Blue in the face - an alarming signal, or a trifle, not worthy of attention?
The pulp can turn blue in ordinary boletus mushrooms and in the satanic mushroom in a matter of minutes, so this feature cannot be decisive in answering the question of whether it can be eaten. Some people mistakenly believe that blue is a characteristic sign of the presence of toxins, we repeat that this is a delusion. Why do mushrooms change color to blue? It turns out that the reason is that the pulp, under the influence of air, oxidizes, and its tissues turn blue. This happens even with very tasty and healthy mushrooms.
Beneficial features
- Mushrooms have a high amount of vitamin D, just like butter.
- In terms of vitamin B content, they are not inferior to cereals.
- Mushroom lecithin reduces blood cholesterol, which makes them useful for people with impaired metabolism, with vascular and heart diseases.
- Mushrooms are recommended to be included in the diet, as they are low in fatty acids that prevent arteriosclerosis.
- They are used as an anti-cancer and stimulating agent for the human body.


- Mushroom enzymes break down fats, so they should be consumed by people who want to lose weight.
- A large amount contains fiber, thanks to which the stomach is cleansed and digestion is improved.
Eating
Mushrooms are a healthy and nutritious natural product. They contain a large amount of vitamins, minerals and essential amino acids. As a low-calorie product, mushrooms are used in dietary and vegetarian diets. And their high protein content has made them popular in special sports diets. In addition, the nutrients and compounds contained in mushrooms are successfully used in folk and traditional medicine.
Fruit bodies that change the color of the flesh to blue are not always unusable and dangerous to eat.
Harmful properties
- Mushrooms contain a lot of plant fibers and chitin, which are difficult to digest, which is why nutrients are poorly absorbed.To eliminate this, the mushrooms are dried, thoroughly ground and sent for storage in hermetically sealed jars in a dark place. Important: edible salt is added to the mushroom powder. This drug is used as a seasoning.
- There are many toxic and radioactive substances in the atmosphere, which are absorbed by edible mushrooms. Therefore, collecting them along roads and in areas with industrial enterprises is associated with a danger to life. You should not buy mushrooms from the market, as it is not known where they were collected. Perhaps in an ecologically polluted area.
- Don't go mushrooming alone. Remember, if a poisonous mushroom gets into the basket, it can lead to the poisoning of all its relatives. Better get rid of the contents of the basket.
- Mushrooms are considered a heavy food, so they should not be consumed by babies, nursing and pregnant women and people with various diseases of the digestive tract.
Mushroom time is called a quiet hunt. Be careful that this silence does not make you worry. Collect only edible mushrooms!
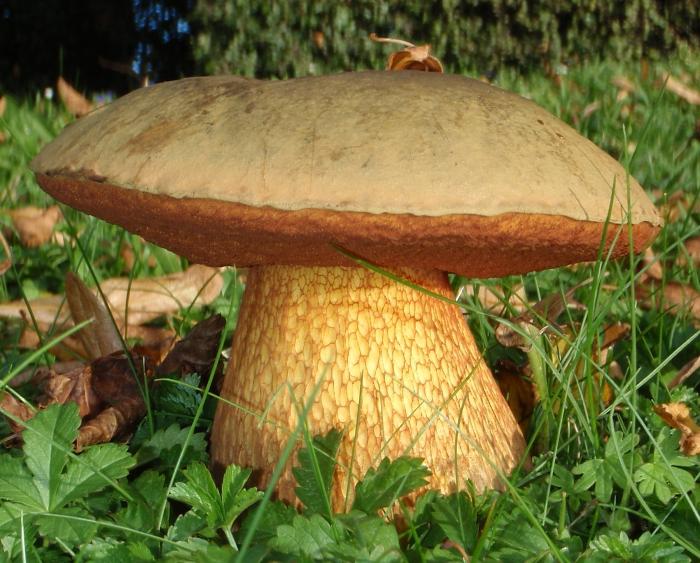
Gyroporus chestnut
Another representative of the gyroporus family. Belongs to the department of basidiomycetes, forged agaricomycetes. Genus: gyroporus.
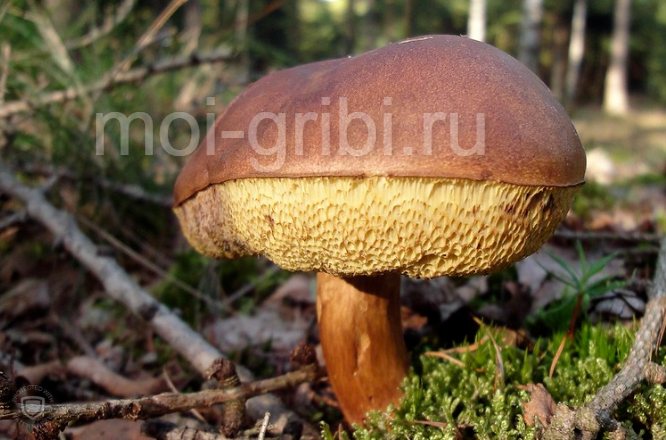
Hat
The cap of this mushroom has a characteristic rusty hue with brown spots. Less often it is red-brown. Even less often chestnut shade. The younger the mushroom, the lighter its cap, but with age it becomes darker. The diameter of the mushroom reaches 11 cm. The surface of this mushroom, if you run your hand over it, is quite velvety. Also a little fluffy. Less often, it is naked and without a single villi. If the sun's rays hit directly on the cap of the mushroom, it begins to crack. If you look under the cap, then the tubes inside are first white, then they acquire a yellow tint. As for the older age, the cap becomes less elastic and drier.


Pulp
Special attention is paid to the pulp. It is quite white, and at the same time tries not to change its color at the cut. At first, it is quite hard, while fleshy. However, it becomes more fragile with age. At the same time, her smell and taste are quite unpleasant, so many people prefer to bypass the chestnut side of gyroporus.
By the way, the spore powder of this mushroom has a pale yellow tint.
Leg
The leg is quite stable. It is unevenly cylindrical, but at the same time, it can bend at any angle. Clavate and fairly flattened. Dry, up to 30 mm in height. The thickness is the same. Inside, the leg is quite elastic, but with age, this elasticity is commensurately lost. Often the hat outweighs the leg and breaks it off.
Where to grow and when to go
If you are looking to find Chestnut Gyroporus, you are very lucky. This mushroom is especially widespread in the central territory of Russia. It grows immediately as a large brood, therefore, having spotted it in a clearing, know that there are probably many of its fellows around.
This mushroom grows from July to right until November, but on condition that the autumn is warm. If it is cold, then you need to go for the mushroom at the end of September and beginning of October.
Prefers coniferous and deciduous forests for growth. Also, predominantly prefers sandy soils, cut wet. Loves dry soils, settles away from swamps.
Fruiting bodies are somewhat widespread from each other, however, they are nevertheless grouped well. In one glade, you can find up to thirty mushrooms at a time.
Edible Gyroporus chestnut
Many people say that chestnut gyroporus is much worse in its taste characteristics, in contrast to blue gyroporus. This is indeed the case. Despite the fact that this mushroom is edible, it still has a very specific taste.
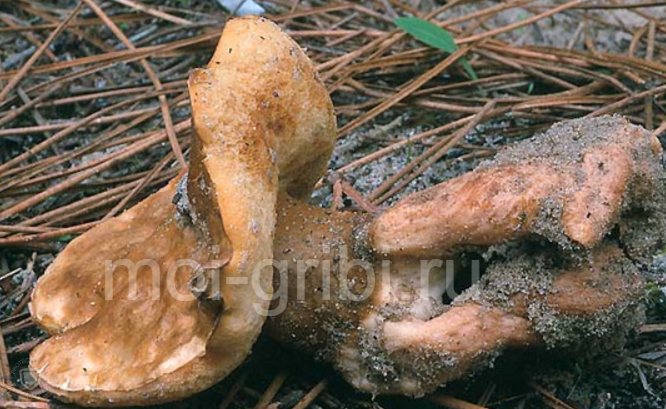


First, you smell the champignons, and then it takes on a bitter tint. Even after heat treatment, this mushroom cannot be eaten.At some point, it becomes so bitter that there is nothing to do but throw it away. Also, he can impregnate absolutely all the ingredients that were prepared with him with bitterness. For example, if a gyroporus is mistakenly baked with potatoes, the potatoes also become very bitter.
Therefore, it is predominantly better to use such a mushroom as a seasoning. Indeed, a slight bitterness will not hurt some people, and in general, this mushroom perfectly replaces pepper, it becomes more aromatic.
To prepare the seasoning, you must perform a number of the following steps.
Important! Gyroporus chestnut mushroom is quite toxic. If it grew not far from roadways, enterprises, industries, then it should not be taken in such.
To begin with, the mushroom is washed well under running water.
All rubbish is removed. The mushroom is dried well and cut into several pieces. Then boil in boiling water for about 10 minutes. The mushroom is salted again and then carefully placed on baking paper on a baking sheet. The temperature in the oven is set at 60 to 70 degrees. Mushrooms go there for one and a half to two hours.
However, check readiness periodically. To do this, you need to take a piece of the mushroom in your hands and try to break it. As soon as this happens with a crunch, it means that the drying cycle is over. Now you need to let the mushrooms cool down at room temperature. However, try not to get wet around. Once the mushroom has cooled down, we suggest grinding it in a coffee grinder. Done, delicious and bitter seasoning will decorate any of your dishes.
However, it is recommended to store it in a dry jar in a dark place.