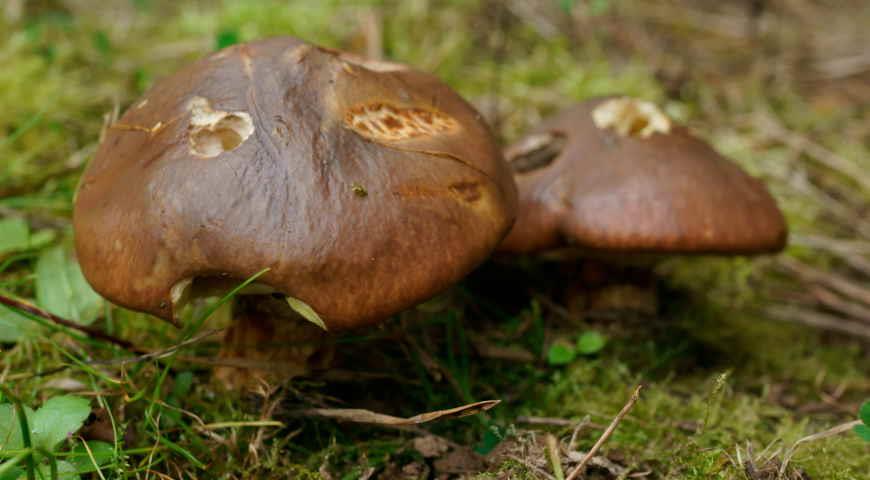
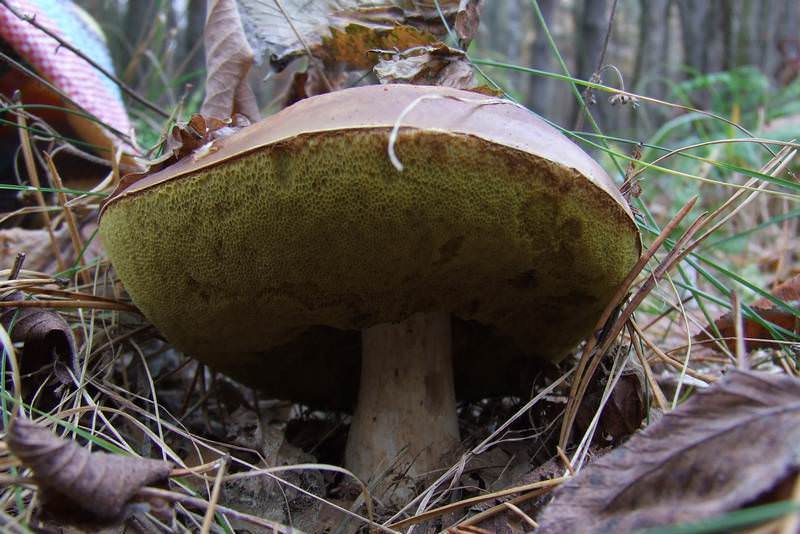
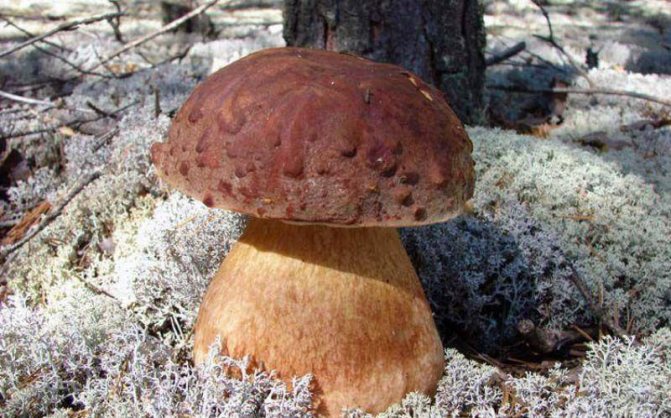
The number of mushroom pickers is growing every year, as are accidents associated with the consumption of poisonous and inedible mushrooms. They are quite capable of significantly replacing meat in the diet, it is a vegetable protein enriched with a large amount of vitamins and microelements. Self-picked mushrooms are tasty, healthy and economical. But it is useful only if they are edible and collected according to all the rules.
Edible, inedible and poisonous
The classification into edible, inedible and poisonous categories of fungal organisms is periodically undergoing amendments. With poisonous, everything is clear, their list is more stable, but the line between edible and inedible is very fragile. Some species that are not eaten in some areas are considered almost a delicacy in others. As they say: "You just need to be able to cook them." These include waves, russula, valui and some types of rowers.
You can get poisoned even with absolutely edible mushrooms if you neglect the rules of collection.
Preventive measures
As you know, parasites can settle in the body of absolutely any person. If you do not give them a chance to get inside the gastrointestinal tract, then complications can be avoided without much effort.
To do this, sometimes it is enough just to systematically observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Also, doctors provide the following list of recommendations:
- Wash your hands before eating and after coming from the street with soap,
- Do not consume water from unknown sources,
- Always cook fish and meat,
- Wash mushrooms and other plant products thoroughly and remove parasites,
- Do not eat lightly salted and raw fish (especially for river catch),
- Swimming in open water should be performed only if they are not in doubt,
- Do not kiss pets, check them regularly with a veterinarian,
- When visiting exotic countries, pay attention to protecting exposed areas of the body from blood-sucking insects.
Where you can't pick edible mushrooms
It is known that in no case should you pick mushrooms near highways and near industrial enterprises. But at what distance from the factory chimney or poisonous drains they can be torn apart is not very clear. What is under the layer of moss and soil is also unknown. And is it possible to collect overgrown and wormy mushrooms? Therefore, in this ancient and fascinating craft, there is always a share of risk. Experienced mushroom pickers are often more careful and attentive than beginners who have just entered the forest.
Answers to common questions
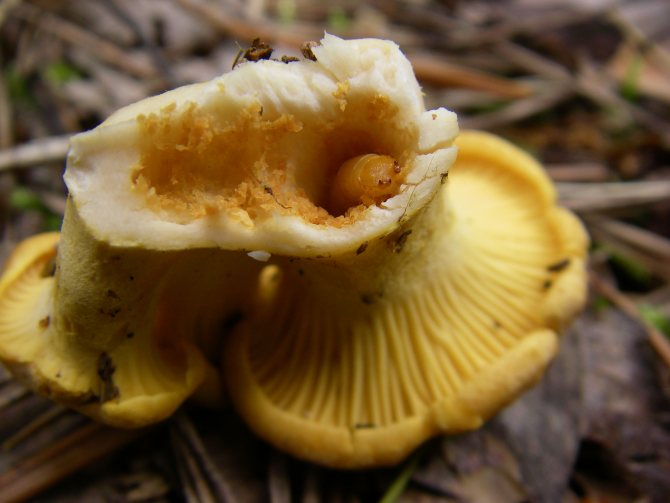
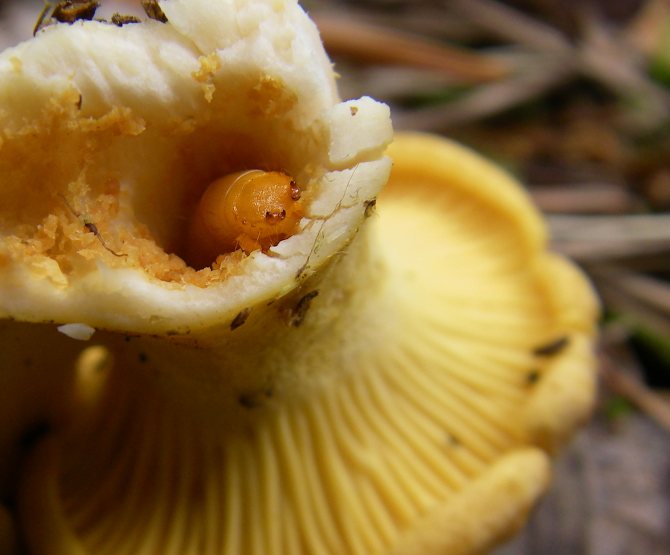
Parasites quite often infect fungi, regardless of whether they are edible to humans or not. The presence of worms in mushrooms does not make them dangerous for humans, and does not affect their digestion in any way.
Mushrooms are a unique and healthy product that not only people like to eat, but also all forest dwellers, including worms. It is rather unpleasant to stumble upon a wormy fruit, it is a pity to throw away the "harvest", but is it possible to eat it? Professional mushroom pickers believe that it is possible to eat wormy mushrooms, the main thing is to properly clean the product from the larvae so that they do not get into the dish.
What mushrooms are wormy
Worms in fungal organisms are the larvae of any forest midge.Insects love to lay their eggs on the bodies of forest beauties, because moisture, food and shade are ideal conditions for their reproduction. Moreover, their relationship is mutually beneficial. The worms help spread the spores in the soil, thereby increasing the mycelium and helping to increase the yield in the future.
Many people wonder if poisonous mushrooms are wormy. There is an opinion that no. This is partly true. So, for example, worms are not found in pale toadstool or fly agaric. However, the toxicity of venomous individuals is different, and therefore the likelihood of their being affected by fungal worms exists.
There are also edible, tasty and very healthy species that are never actually wormy. These are chanterelles, they are fried even without preliminary heat treatment, they have a rich vitamin and mineral composition, they are a natural antibiotic and, despite this, flies and mosquitoes bypass them.
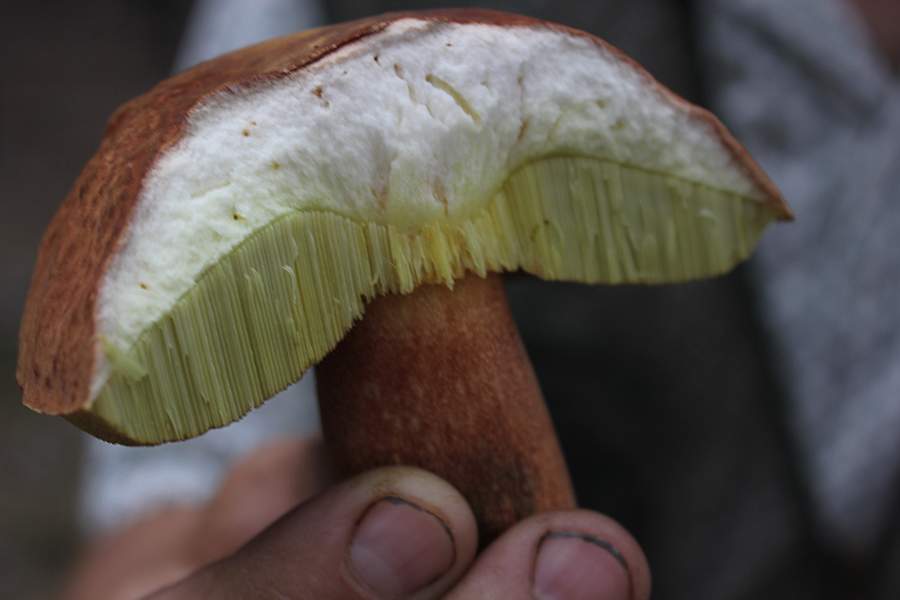
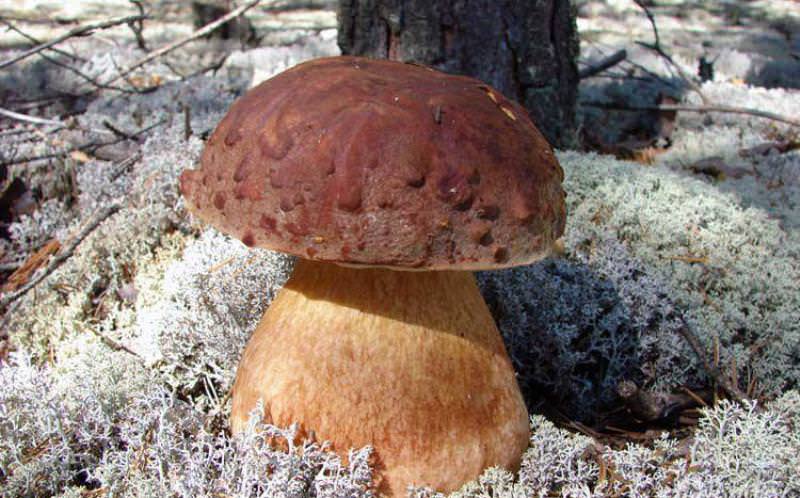
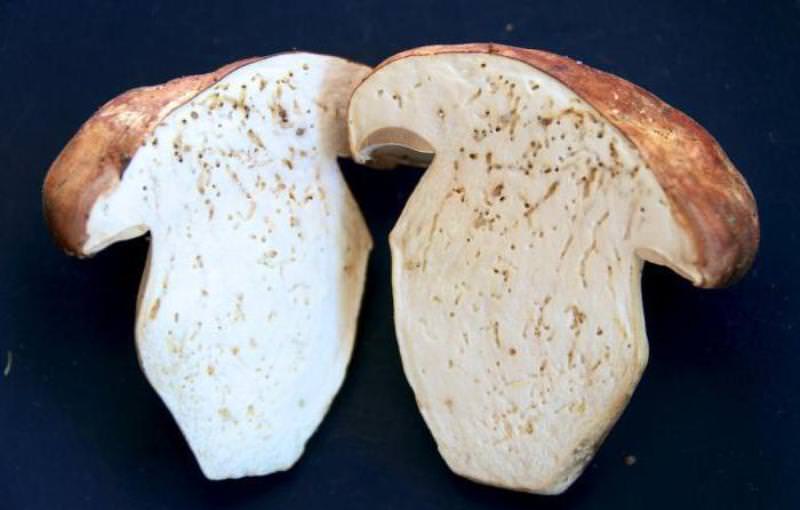
Worms most often affect white, boletus, mushrooms, russula, boletus, milk mushrooms. Worms are much less common in mushrooms, aspen mushrooms, gray and purple rows, oyster mushrooms. There is only one conclusion: there are fewer of them in autumn mushrooms than in summer ones. The cool temperature appears to be uncomfortable for flies and mosquitoes to reproduce.
Treatment
If the doctor determines that the patient has parasites, therapy with specific agents should be started immediately. Preference is given to complex treatment in order to combine the positive properties of several drugs.
So, first, medications are used that weaken worms, these can be funds based on Levamisole (Dekaris). A few days later, another anthelmintic is prescribed to the person, it can be Nemozole or Vermox.
Parasites in the body are paralyzed after using special means. This effect eventually leads to the death of the worms. The doctor prescribes drugs at his own discretion, based on the existing clinical picture. The list of medicines that are most often used for the treatment of helminthiasis looks like this:
- Biltricide with the active substance praziquantel. The remedy causes stiffness of the muscles and parasites are paralyzed,
- Vormil and Nemozol stimulate irreversible biochemical processes in helminths,
- Decaris or Levamisole - the agent disrupts the processes of energy exchange of parasites,
- Helmintox and Nemocid have a paralyzing effect,
- Vermox or Mebendazole eliminates cell synthesis and energy exchange of worms.
Ancillary treatment is also used:
- Sorbents: Enterosgel, activated carbon. Medicines remove toxic waste products of worms that are in the body,
- Symptomatic agents: pain relievers and antiallergic. Necessary to eliminate concomitant symptoms,
- The use of probiotics is indicated for the restoration of intestinal microflora.
These funds are normally tolerated by people of any age. They are also advised for prevention purposes. Lactation and pregnancy are special indications for therapy exclusively under medical supervision.
Attention should be paid to exclude the likelihood of re-infection. In the human body, the worms and eggs that exist will constantly come out, therefore, underwear and bedding must be constantly changed.
Currently, medicine offers some belekarsten methods of treatment, for example, therapy based on bioresonance vibrations of organisms.
Is it possible to eat wormy mushrooms
As for the wormy gifts of the forest, the opinions of experts differ. Some people, purely for psychological reasons, simply cannot afford to put a mushroom with worms in a basket. But those for whom gathering is a business do not disdain to be wormy, especially if you dry them, nothing will be noticeable at all.
In some cases, wormy mushrooms should not be eaten:
- as a rule, worms more infect old and overgrown organisms, which are doubly dangerous to collect;
- inedible does not mean poisonous. They can be bitter, tasteless to humans, but not to a worm. Therefore, it is categorically impossible to collect unfamiliar wormy mushrooms;
- worm to worm - discord, large wireworms, larvae of click beetles can damage the leg without affecting the cap. Many small worms make the fruiting body unusable.
The presence of worms in fungi does not make them inedible. We can say that everything depends on their number. It is difficult to refuse and leave handsome men in the forest - white or boletus - just because they have small wormholes on their legs. Usually mushroom pickers immediately in the forest check the trophy for worminess. Something needs to be thrown away, something should be cut off. If the infected specimens are kept for several hours in the same basket with the clean ones, the worms will quickly crawl onto them, and there will be no good ones left.
Collection and processing rules
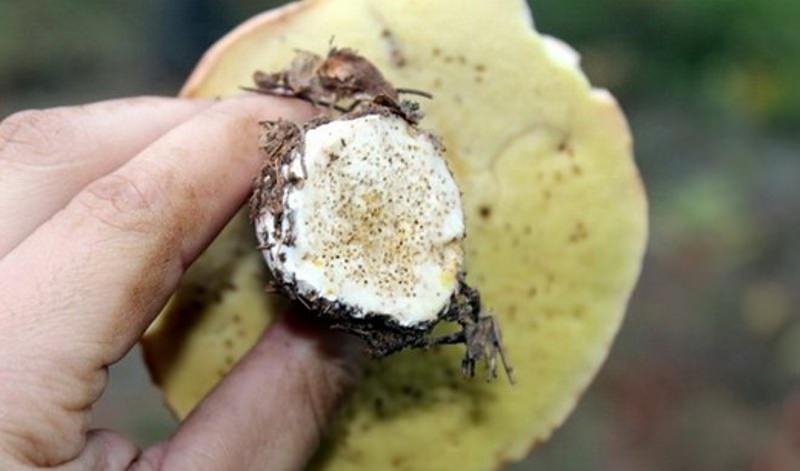
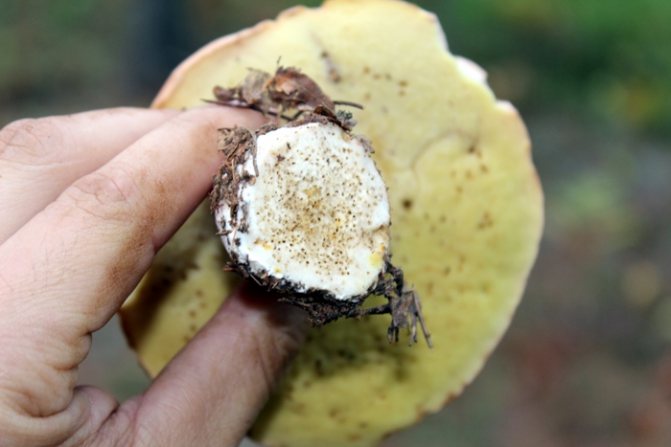
The larvae can be found in any part of the fruiting body, therefore, even if there are no passages or holes in the stem, they can be in the mushroom cap. Parasites very quickly eat the pulp of the fruit, therefore, it is better to cut off the parts affected by the larvae directly in the forest.
A sharp knife is perfect for this. It is also recommended to lay the wormy fruit separately from the "clean" specimens, otherwise the number of parasitized fruits will become much larger than it was at the time of collection.


You may be interested in:
Growing porcini mushrooms on a windowsill at home (15 photos) Mushrooms are a common product that housewives use to prepare various dishes. Most often ... Read more ...
A deeply affected fetus is not only not recommended to be taken home, but also thrown away. Better to prick it on the nearest twig, so it dries up and becomes a delicacy for squirrels and other forest dwellers in the cold season.
Advice!
In order to remove parasites from the fetus, it must be soaked in highly salty water. It is enough to keep them in the solution for 3-4 hours. Under the influence of salt, the larvae will hastily begin to leave the pulp. However, for a more effective treatment against parasites, it is recommended to cut the mushrooms into large pieces. After the "harvest" is cleared of unpleasant creatures and thoroughly washed, you can proceed to heat treatment and cooking.
You can also dry the "harvest", because under the influence of heat, parasites successfully leave the pulp of the fruit. Before cooking, dried mushrooms must also be thoroughly rinsed.
How to cook wormy mushrooms
If small wormholes do not cause disgust or spoil your appetite, they can be eaten. There are several proven methods for cleansing fungi from parasites:
- upon arrival home, the mushrooms should be sorted out, cut off, cleaned of debris, large ones should be cut into four parts and filled with saline (1 liter of water - a tablespoon of salt). Soak in this brine for 2 hours, then rinse well and boil;
- mushrooms to be dried should not be laid out on a baking sheet, but on a wire shelf. As they dry up, all the larvae will spill out of them;
- in the first minutes of boiling of the mushroom broth, the remaining worms rise upward along with the foam. Reduce the heat and carefully remove this foam.
In a separate category of worms, it is worth highlighting the larvae of the moth, which adores dried mushrooms and starts already at home if stored incorrectly. A proven method of dealing with it is to sprinkle dry fungi with bitter black pepper. Before cooking, they will still be rinsed, but the moth will not touch them.
There is an unspoken rule in the forest during harvesting: if by some parameters (maybe too old, rotten or wormy) the mushroom does not suit you, you do not need to throw it away. The hat should be carefully placed with the spores down.Perhaps this will be the formation of a new mycelium, and you will do your bit to increase the population of edible mushrooms. For the same reasons, you should never kick fly agarics and pale toadstools, contributing to their reproduction.
Published on 03/16/2018 by samsonmain and was posted under Edible. Bookmark the permalink.
Where to look for the Psilocybe semi-lanceolate mushroom: places of growth
Recipes for cooking and pickling honey agarics for the winter
Mushrooms, or the History of Poisoning
Each year in the Czech Republic, about 350-400 people suffer from mushroom poisoning. To prevent this from happening with ins, you should be guided by the following information.
Popular rumor
Mushrooms are mysterious creatures that have not yet been fully explored by scientists. Suffice it to say that the poison contained in them most often affects only humans, remaining harmless to insects and animals. In addition, it has not yet been established what is associated with the ability of fungi to produce toxins. The mainstream opinion of experts is simply a side effect of mushroom metabolism.
Nevertheless, mushrooms remain one of the leaders in the world of poisons. For example, the notorious pale toadstool contains amatin poison. “A pinch of this poison (literally on the tip of a knife - 0.5 g) would be enough to poison 100,000 mice. If we put them in one chain, then its length would be 18 km, which is about 4.5 hours at a military pace ”, - this quote from the play of Yara Tsimerman's theater is not fiction, but pure truth. At the same time, a dangerous mushroom "lady" in her youth looks like a champignon.


Mushrooms
Ignorance of the exact information about poisonous and edible mushrooms gave rise to a number of popular beliefs. So, there are several "rules" with the help of which it is supposedly possible to determine whether a mushroom is poisonous in front of you or not. Mycologists - scientists who study the world of mushrooms - argue that all these laws are absolutely wrong.
Poisonous mushrooms are not wormy or bitten by insects. Not true! Worms and insects have a different metabolism than humans, and therefore are more often completely insensitive to mushroom poisons.
By thermally treating the mushroom, i.e. having prepared it, you can neutralize the poison contained in it. The rule works only for some types of slightly poisonous mushrooms: lilac-footed ryadovka, olive-brown oak, pink-gray amanita, etc. The rest of the poisonous mushrooms contain toxins that are resistant to high temperatures, and therefore they cannot be “neutralized” by boiling.
Poisonous mushrooms are brightly colored. The same can be said about the almost harmless red fly agaric, while the deadly smelly fly agaric is of the usual white color.
Silver turns black upon contact with a poisonous mushroom. None of the known mushroom poisons cause such a chemical reaction.
In addition, killer mushrooms cannot be distinguished by taste. Some of the poisoned admitted that the specimens that crippled their stomach and kidneys were just an amazing culinary experience. The mushroom pickers who survived the meeting with the pale toadstool said that it was the best dish in their life. Therefore, you should not try an unknown mushroom!
Experienced tips
Czech mycologists give some basic tips to follow when picking mushrooms. They are based not on folk legends, but on logic and science.
FROMtake only what you know. You can, of course, take an atlas of mushrooms with you to the forest. But this will not relieve you of doubts, because sometimes mushrooms are in a different stage of growth than in the photographs in the book, or may just be similar to what you read about. It is better not to take the mushroom if you are not sure of its suitability.
Bonly young specimens should be fed. More "mature" mushrooms may look good, but inside they have already begun to decompose.
IN put in a basket only those mushrooms that have not been tested by insects or worms and are not saturated with water.It is worth remembering that rotting is already taking place in mushrooms bitten by insects or filled with water.
EIf suddenly you nevertheless violated rule number 1 and decided to bring home a dubious mushroom, do not cut it, but carefully remove it from the ground. Often it is at the very root that you can see a "skirt" or other characteristic signs of poisonous mushrooms.
ABOUTclean mushrooms right in the forest. It is about removing leaves, mucus, etc.
LIt is best to put the mushrooms in a basket. There they will not wrinkle or suffocate.
HDo not cook the mushrooms twice. Unlike other foods, heating or re-cooking mushrooms can lead to stomach problems or even poisoning.
HDo not pick mushrooms from roads, factories and mines. There they may be full of toxins from the outside. Radioactive elements are also not excluded.
EIf you are not well versed in mushrooms, it is better to buy them at the market or in the store. Now on the shelves you can find not only champignons, but also chanterelles, white, honey mushrooms. By the way, there you are more likely to find environmentally friendly mushrooms than if you follow them into the forest.
Deceiving mushrooms
In the forests of the Czech Republic, there are many mushrooms that are not familiar to the Russian people. Some of them are poisonous and disguise themselves as harmless and even popular mushrooms. Here are a couple of these "spies".
Row sulfur (?ir? vka s? ro? lut ?, Tricholoma sulphureum)... A family of such mushrooms, picturesquely spread out on moss, is easy to confuse with chanterelles. The cap near the row of sulfur is 3-8 cm in diameter, first convex, then prostrate, slightly lumpy, thin-fleshy, sulfur-yellow, buffy or brownish in the middle, sometimes fine-scaled.
The leg is 5-10 cm long and about 1 cm in diameter, cylindrical or widened towards the base, solid, made, sometimes hollow, sulfur-yellow, brown-fibrous. The plates are rare, thick, sulfur-yellow, green-yellow. It can be distinguished from a chanterelle by its smell: the ryadovka has an unpleasant, sharp hydrogen sulfide "aroma".
Burning russula (Holubinka vrhavka, Russula emetica). The cap is first convex, then flat, sometimes funnel-shaped in the center, 5-9 cm in diameter, with a peeling skin, reddish, light red or red. The edge of the cap is ribbed, dull, the flesh is white, pinkish under the skin, brittle, with a very pungent and bitter taste and fruity odor.
The plates are always white, adherent to the stem, yellowish in old mushrooms. The stem is white, in places pink, cylindrical. Forms mycorrhiza with coniferous and deciduous trees. You can recognize it by its spongy structure. Cut off a piece of the leg, and if it does not separate into fibers, you have a burning russula in front of you.
Galerina bordered (? Epi? Atka jehli? Nanov ?, Galerina marginata)... It belongs to the deadly poisonous mushroom and contains a poison similar to that of the pale toadstool. The diameter of the cap reaches a size of 1.7 to 4 cm. The cap begins convex and sometimes conical, with edges curved inward against the plates. As the cap grows and expands, it becomes more flattened, and sometimes a small umbo appears in the middle, which can protrude noticeably from the cap surface.
As a rule, a well-defined membrane ring is visible on the legs of young specimens, but this often disappears with age. In old fruiting bodies, the caps are flatter, and the plates and legs are brownish. Galerina is a typical "small brown mushroom" - a category that includes all small, hard-to-spot brownish mushrooms that can be confused with edible mushrooms (eg butter mushrooms or honey mushrooms). Often grows on fallen tree trunks.
Gall mushroom (H? Ib? Lu? N? K, Tylopilus felleus)... It is also called false white. The hat is 4-10 (15) cm in diameter, convex, cushion-shaped, dry, slightly pubescent, later - smooth, yellow-brownish, gray-ocher, less often chestnut-brown.The leg is 3-7 cm long and 1-3 cm in diameter, swollen, clavate, widened towards the base, yellowish-ocher, darker at the bottom, with a brownish-brown mesh pattern or simply with brown fibrous scales.
The pulp is fleshy, firm or soft, white, odorless, with a bitter taste or pungent aftertaste, slightly pink when cut, almost never worms. It is surprising that this mushroom, which, when consumed, can cause mild poisoning, in dried form can be the basis for gastric medicine.
Olga Ovcharenko
Published in the newspaper "Prague Telegraph" No. 36
How to provide first aid in case of poisoning?
If poisoning occurs, then you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. Before the ambulance arrives, it is recommended to drink more liquid, milk, water with a small amount of potassium permanganate or salted will do. You can wash the stomach and induce artificial vomiting several times. Better to take a horizontal position. You can put a bandage soaked in cold water on your forehead, but you can warm your legs and stomach with a heating pad or blanket. There must be someone who has not eaten mushrooms near the victim, so that if the patient loses consciousness, give him a sniff of ammonia. In a state of poisoning, the victim cannot be unconscious for a long time, otherwise he may fall into a coma.
You should not go to the forest for mushrooms without knowing their classification and what edible and poisonous specimens look like. In no case should you take children with you on a quiet hunt, because they can not only pick up a poisonous mushroom, but also have time to lick it or bite off a little. Edible mushrooms have counterparts, toadstools, which have small differences, without knowing which, you can easily make a mistake in your choice.
Answers to common questions
Parasites quite often infect fungi, regardless of whether they are edible to humans or not. The presence of worms in mushrooms does not make them dangerous for humans, and does not affect their digestion in any way.
The number of mushroom pickers is growing every year, as are accidents associated with the consumption of poisonous and inedible mushrooms. They are quite capable of significantly replacing meat in the diet, it is a vegetable protein, enriched with a large amount of vitamins and microelements. Self-picked mushrooms are tasty, healthy and economical. But it is useful only if they are edible and collected according to all the rules.
Eating
A wormy mushroom does not cause poisoning, unlike a poisonous or inedible fruit body. Usually old, overgrown specimens are affected by these pests. But these lose their taste, the pulp is tough or too loose with an unpleasant aroma. If you eat such a specimen, it will lead to indigestion and intoxication of the body.
If a mushroom picker has a spoiled boletus, boletus, oil can in the hands of a mushroom picker, it is worth making a little effort and preparing it for use. For this, the fruit body is cut into large pieces and poured with a solution of salt water. After 2 - 3 hours, when the pests emerge, the mushrooms are taken out of the solution. In this case, the water is not drained so as not to leave pests at the bottom of the dishes. Then they are washed, dried and prepared for use in the chosen way.
Wormy mushrooms
Helpful advice on what to do with wormy porcini mushrooms
The worms run like rats from a ship. White mushroom.
How to remove by soaking
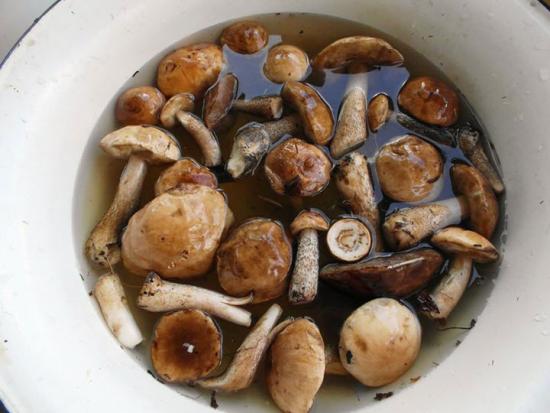
It is worth getting rid of worms in mushrooms immediately after they have been collected. To do this, they need to be cut into large pieces. First, a leg is cut off from the body, the tubular layer at the cap is removed, the leg is divided in half. The parts are placed in cool, salted water for several hours. For 5 liters of water, you need to take 1 glass of salt.


We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Is it possible to get a fungus from another person
The main thing when soaking is not to oversalt the water. If the water is too salty, the worms will die, remaining inside.
It should be borne in mind that different types of mushrooms have different densities. The peculiarity of preparing porcini mushrooms for use is that they should be kept in water longer than the rest - 3-4 hours. Milk mushrooms must lie in water for at least 24 hours. Russula and pigs can be kept for a couple of hours.
If the worms eat only a small part of the body, you can simply cut off the damaged part with a knife. The main thing is that the fetus has no signs of decomposition. The peeled mushroom can be fried, pickled, boiled, salted.