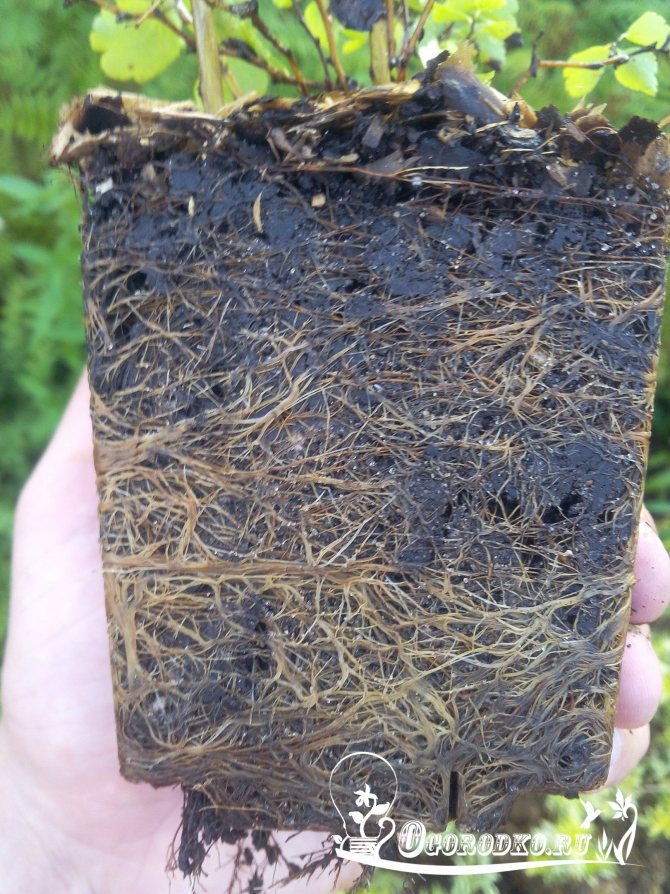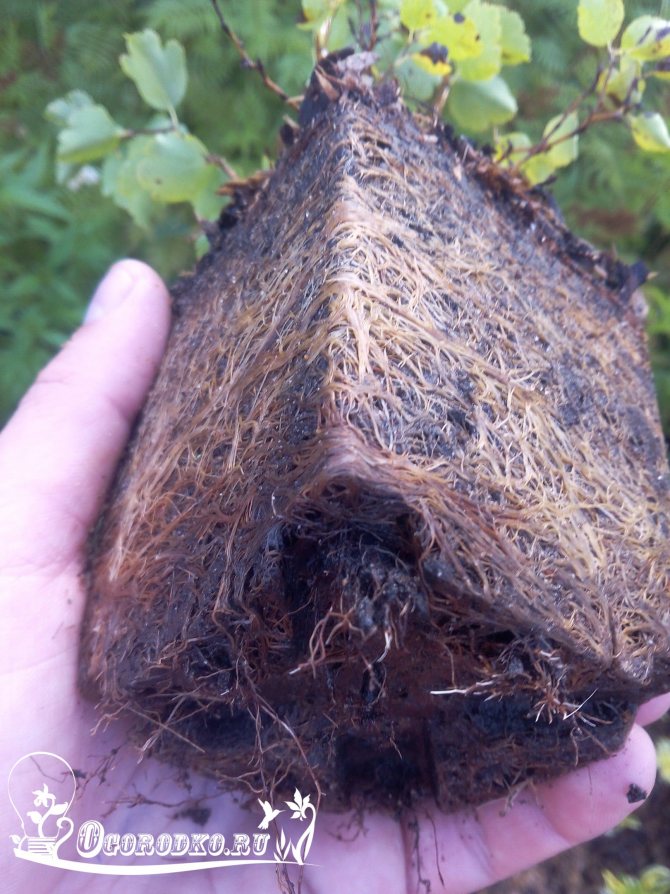
Spirea (Spiraea) is a flowering deciduous shrub plant from the Pink family, which has a high decorative effect, frost resistance, a long flowering period and unpretentious cultivation and care. Spirea or meadowsweet is common in areas with different climatic conditions, it feels great in the steppe and forest-steppe areas, in semi-deserts and on wet lands near meadows. In the genus of these crops, there are about a hundred different species and varieties. Among them, you can find miniature dwarf varieties about 15 cm in height and tall specimens with a growth of more than 2 m.
Description of the spirea bush
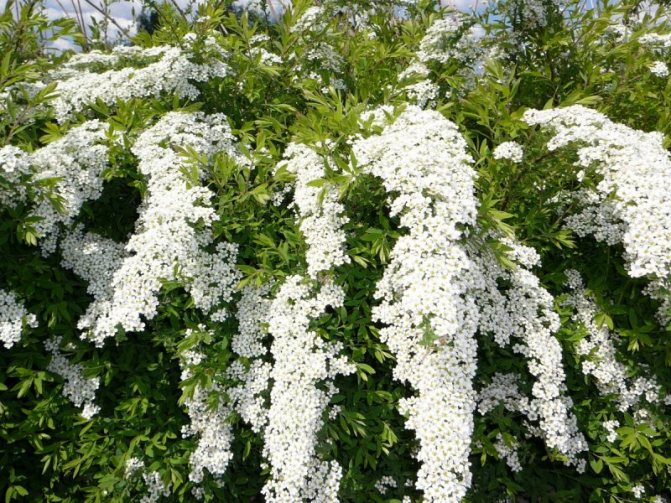
The shrub culture consists of a fibrous root located shallow from the surface of the earth, and numerous branches covered with peeling bark of a light or dark brown shade. Depending on the variety, the branches can be straight, recumbent, creeping or outstretched. Spirea blooms with a variety of inflorescences (ears, panicles, shields, brushes), consisting of a large number of small flowers and a variety of colors - white, pastel, light pink and bright raspberry, lilac and yellow. Reproduction takes place in several ways - with the help of seeds, cuttings, cuttings and root division. The plant can be planted as a hedge or "carpet", in compositions and as a solo crop. Professionals and ordinary flower lovers use meadowsweet for landscaping their backyards, in rocky gardens and rockeries, undersized species can be planted on alpine slides.
Features of growing spirea
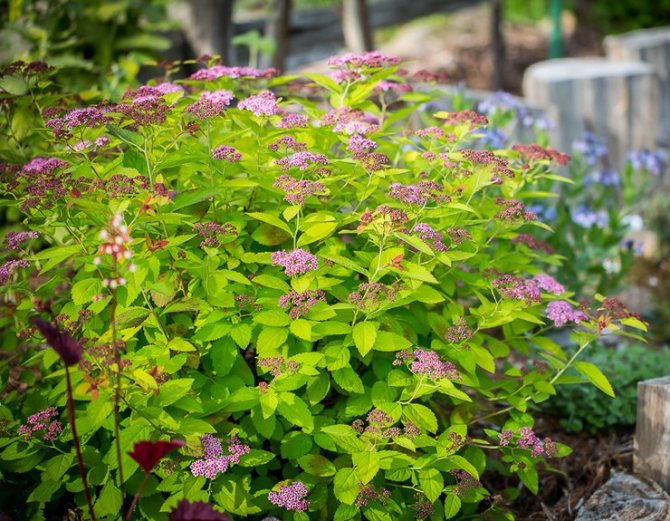


- For planting a bush, it is recommended to use sod or leafy soil, as well as a soil mixture, which contains garden soil (two parts), river coarse sand and peat (one part).
- For the full development of the bush on the site, a high-quality drainage layer is required (for example, from broken red brick).
- The planting hole should be approximately thirty percent larger than the volume of the root part with a clod of earth.
- The seedling is buried 45-50 cm so that the root collar remains at the soil level.
- A favorable time for planting a bush is September, it is advisable to choose a rainy day or when the sun is hidden behind clouds.
- It is recommended to take into account when planting future neighbors of the spirea. She gets along well with such plants as thuja, juniper, spruce.
Plant propagation technology
Spirea is one of the few shrubs that reproduces not only by cuttings and layering, but also by seeds. The only exceptions are hybrid varieties, which can be propagated only by dividing the bush (they do not form seeds). Breeding recommendations depend on the method:
- It is better to sow seeds in early spring in a mixture of peat, earth and last year's fallen leaves. Seeds sprout at least half of the time (often 70-80%). It is better to pick seedlings at the height of summer (2 months after the first shoots), since by this time the plants are sufficiently strong and their transplant will not be so painful.
- A more efficient breeding method is cuttings. To root the cuttings, a soil is used with a mixture of sand and peat in equal proportions.It is best to carry out these works in the middle of summer. Cuttings should not be planted perpendicularly, but with a strong inclination (45 degrees). This will allow the roots to grow as the top shoot grows more slowly.
- With the help of layering, the spirea is propagated only in the spring. Either the lower branches or root shoots are taken as a starting material.


Planting spirea in open ground


Planting spirea in spring
It is very important to plant seedlings in early spring before the first leaves appear on them. When purchasing planting material, it is necessary to carefully inspect the root part so that there are no damaged or dried roots on young plants. Shoots should be flexible, with good growth buds. Strongly overgrown roots can be shortened a little, dried up cut off, and slightly dried during storage - soak in a large container of water for several hours so that they are saturated with the necessary moisture. Having put the seedlings in full order, you can proceed to the planting process.
Spirea, unpretentious in growing, can delight with lush and long flowering only under certain conditions that must be observed:
- Only summer flowering seedlings can be used;
- The landing site should be open and sunny;
- The soil on the site is nutritious and fertile;
- It is necessary to observe the distance between plantings, taking into account the rapid growth of root growth on the bushes, due to which the territory occupied by the plant increases significantly;
- The landing pit should have sheer walls;
- The volume of the planting pit should be one third larger than the diameter of the root system of the seedling;
- At the bottom of the pit, for planting the spirea, a thick drainage layer with a thickness of at least fifteen centimeters of crushed red brick is required;
- The weather on the day of planting should be rainy or at least cloudy;
- After drainage, a special prepared substrate is poured, consisting of turf and leafy soil (in two parts) and coarse sand and peat (in one part), about one third of the height of the pit;
- The seedling is placed on the soil mixture, the roots are carefully spread, sprinkled with earth to the surface of the earth and compacted;
- The root collar must remain at ground level;
- The first watering is carried out immediately, each seedling requires 10-20 liters of water;
- After watering, the trunks should be mulched with peat.
Planting spirea in the fall
During this period, not only planting of seedlings is carried out, but it is also recommended to plant cuttings obtained as a result of the separation of adult bushes at the age of 3-4 years. Older crops are already more difficult to extract from the ground. The most suitable time for these procedures is from mid-October to mid-November.
It is recommended to observe the following conditions during autumn planting:
- Only spring-flowering and late-flowering species and varieties can be used;
- In a dug out bush, you need to rinse the root part well, this can be done in two ways - lower it into a bucket of water for acidification, or immediately wash it off under a strong pressure of water;
- It is necessary to divide the bush so that each division has a strong root and three strong shoots; 2-3 seedlings are obtained from one bush;
- Long thin roots need to be shortened slightly;
- The seedlings are placed on a small mound in the planting hole, covered with earth, tamped down and watered abundantly.
Features of landing in the Urals
Growing spirea in the Urals is not particularly difficult. The main thing is to comply with several conditions:
- choose the right planting time depending on the flowering time of the variety;
- qualitatively prepare the territory, taking into account the positive and negative neighborhood with other plants;
- to carry out the landing according to the technology.
When to plant
Planting of the plant in question can be carried out in spring or autumn.... All varieties that bloom in summer are planted in spring, before foliage appears on the plants. The rest of the varieties are placed in an open area - in the fall, after leaf fall.Given that the Nippon Spirea begins to bloom in June, it should be planted in the spring.
Video: Spirea Nipponskaya
Preparing a place for a bush
When starting to grow the culture in question, it should be borne in mind that this is a perennial shrub. Such plants live from 30 to 50 years. Accordingly, during this time, a certain area will be occupied by bushes. Plants need a fairly large amount of light (light partial shade is acceptable), so it is better to choose the territory on the southern or southeastern side. From the north, the bushes should be protected from drafts.
- Favorable neighbors for the culture in question:
- thuja;
- juniper;
- dwarf spruce.
Important! In the shade, the spirea will form a very small number of flowers and develop poorly.
Given that over time, spirea begins to give a large amount of root growth, it should not be planted next to large trees... Also, this plant is distinguished by a high vigor of rhizome growth, which, growing, can destroy the foundation of buildings or a fence. Given this, a distance of 5 m should be maintained from the plant to the nearest structure of a similar plan.
The site for planting begins to be prepared in the fall.... At this stage, all plant residues, stones and other debris are removed. Then deep cultivation is carried out (30–40 cm). After that, the area is disinfected with a 3% solution of copper sulfate. Add 300 g of the substance to 10 l of water. For each m², 1 liter of working fluid is consumed. After a week, the site is cultivated again to a depth of half that of the first time. For digging, manure, sod-leaf soil, peat (10 kg / m²) are preliminarily introduced.


Landing rules
A week before planting, the site is dug to a depth of 20 cm. For each m², 5 kg of sand and peat are applied. 2 days before planting, they begin to prepare the holes. If there are several plants, then a distance of 3.5 m is maintained between the pits. A similar step is taken in the aisles. The depth of the hole should be oriented to the size of the root system of the seedlings, that is, 2.5–3 times more.
At the bottom of the pit, a layer of pebbles is laid out (you can take expanded clay, broken brick or other drainage material) 15 cm high.After that, 5 cm of soil is laid out from the pit, mixed with compost in a 1: 1 ratio.
We advise you to learn about the varieties of rose spire shrubs.
Step-by-step planting process:
- Examine the dried-up roots. Then immerse the rhizome in a solution of "Kornevin" (1 teaspoon of powder per 1 liter of water) for 10 hours.
- Place the seedling vertically in the hole.
- Distribute the rhizome evenly over the entire area of the pit.
- Fill the hole with soil, periodically compacting it.
- Water the plant with 20 liters of water.
- After absorbing the liquid, cover the trunk circle with straw or sawdust (layer 10 cm high).

Spirea care


Watering and mulching
Watering spirea is recommended 2 times a month. Each bush will require 15 liters of water. It is important to have a mulch layer of peat with a thickness of at least 7 cm around each crop.
Loosening, weeding and fertilizing the soil
In order for the soil to be maintained in a loose state, it is necessary to regularly free the area from weeds, loosen the soil and apply fertilizers. In the middle of the summer season, the plants are fed with a mixture of liquid mullein and superphosphate (5 g per 5 l of solution), and after pruning - with mineral dressings.
Early flowering varieties undergo a minimal shearing once a year before budding. The tips of frozen or damaged shoots are cut off for 7-10 years, after which almost all old branches are subject to pruning to a stump. First, 5-6 of the strongest specimens are left to form young shoots, and then they are cut off. A sanitary haircut is carried out in the spring and summer months.
In summer flowering bushes, every year in early spring, the shoots are cut to large buds or removed completely if they are very small and weakened.
Spirea after flowering
Frost-resistant spirea will only need to be covered in regions with snowless and very harsh winters. Fallen leaves with a thickness of about 15 cm, which cover plantings in the second half of November, are perfect as a "heater".
Watering and feeding spirea in the Urals
The cultivated plant needs regular watering, especially on hot and sunny days.Abundant watering is carried out (1.5 buckets of water each) twice a month. If the soil around the plants is mulched, then the frequency of watering is slightly reduced.
Spirea grows well without feeding. But it will not be superfluous to apply fertilizers before flowering and after pruning. Apply nitrogenous fertilizers for each bush in the spring (for example, mullein). In the fall, they are fed only with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers.


We advise you to read
Reproduction of spirea


Seed propagation
This method of reproduction is not in demand among gardeners, since it does not preserve varietal qualities. Seed material can be planted directly into open ground or sown in planting containers for seedlings.
Propagation by cuttings
Cutting is a more effective method in which more than seventy percent of the cuttings root well and adapt in a new place. Depending on the variety, green cuttings are rooted in early or mid-summer, and lignified ones - in mid-autumn.
For cutting cuttings, direct shoots are chosen - one-year-olds, 5-6 leaves should remain on each segment, after which they are placed in a vessel with Epin's solution (for 3 liters of water - 1.5 ml of Epin) for 3-4 hours. Before deepening into the ground, the lower cut is treated with Kornevin or another stimulant and planted at an angle of 45 degrees. The plantings are covered with plastic wrap. Care consists in regular spraying - 2-3 times a day. In late autumn, rooted cuttings are planted in open ground, sprinkled with fallen leaves for the winter. Cuttings can be planted in a permanent place only for the next season, when new shoots are formed on them.
Reproduction by layering
The branch lower to the soil surface is tilted and fixed in the prepared groove with a wire pin, then sprinkled with earth and abundantly moistened. From spring to autumn, the cuttings form their own root system. Around September, they are separated from the main bush and planted in a selected area.
Types and varieties of spirea


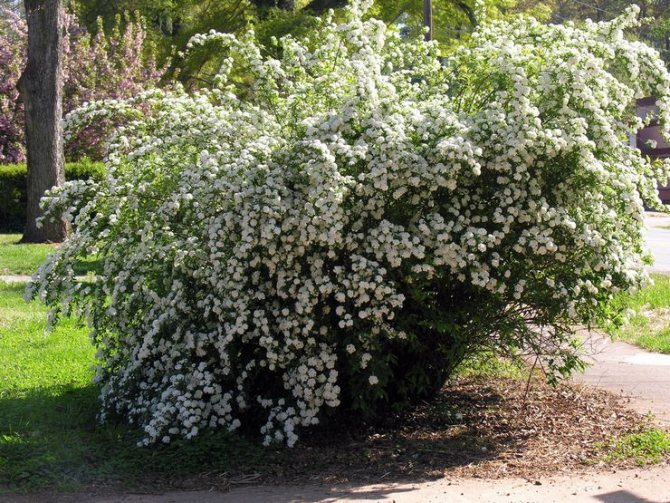
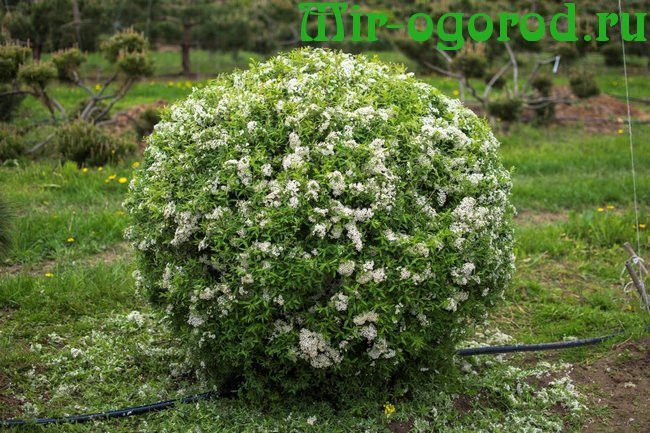
Spireas blooming in spring are distinguished by white flowers during flowering and strong tillering. The most popular are the "Gray" spirea and its varieties "Grefsheim", "Vangutta", "Nipponskaya", "Arguta".
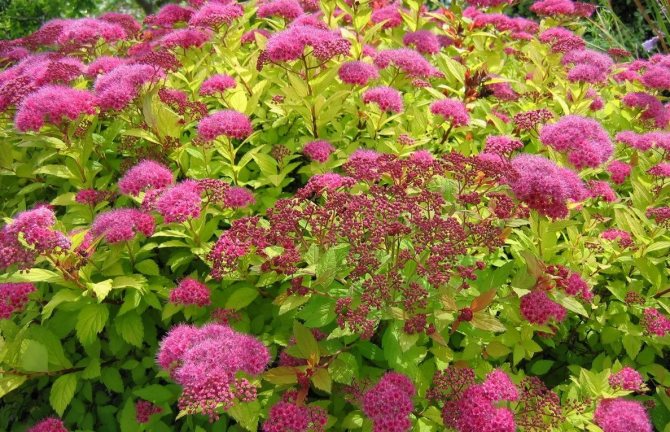
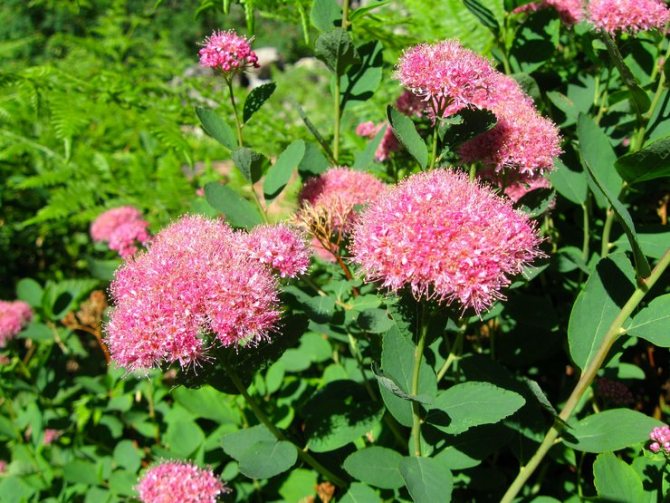
Summer-flowering spireas attract the eye with red-pink hues during flowering. This spiraea "Japanese" and its varieties "Little princesses", "Golden princesses", "Shirobana", "Goldflame", "Crispa", as well as spirea "Bumalda" and its variety "Goldflame", spirea "Ivolistnaya", "Douglas ", Billard".
All species, varieties and hybrid varieties are not similar to each other and have their own individual differences - the shape, splendor and volume of the crown, the height of the bush, the shape and shades of inflorescences, the duration of flowering and the rate of growth, the popularity of cultivation in culture.
The nuances of growing in Siberia, in the Urals, in the Moscow region
Almost all varieties and types of spirea are suitable for growing in central Russia. Shrubs such as Japanese Spirea and Nippon Spirea need additional winter shelter.
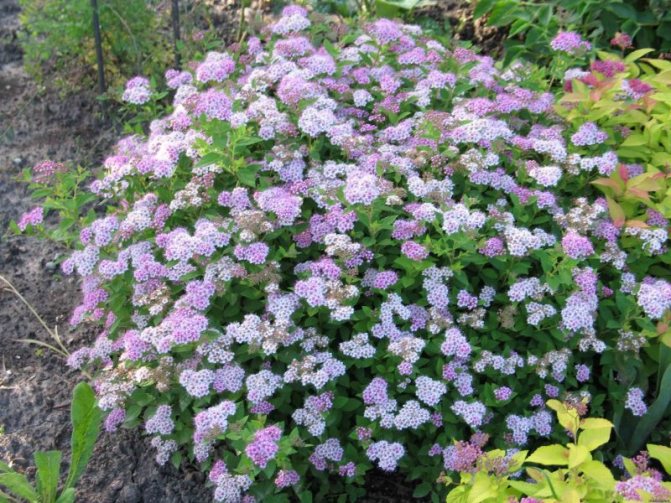


In the Urals, the climate is more severe. In its southern part, almost all types of spirits will grow well. In the middle lane and, especially in the north, frost-resistant shrubs should be preferred. The same can be said for spirea in Siberia. Only undersized varieties are able to overwinter under the snow without much loss. If medium and tall plants are not covered, then constant frosting in winter is guaranteed to them, decorativeness and abundant flowering cannot be achieved in such conditions.
Correctly selected varieties of spirea are able to create a flowering conveyor throughout the growing season and will be a real decoration of any garden.
Post Views: 1
Description of the plant
Spirea is not a novelty in floriculture and has been familiar to many for a long time. However, earlier she had the name meadowsweet or bride.
In its structure, it is more similar to a shrub.In nature, it can be found in most areas of the northern hemisphere: forest-steppes and semi-deserts. It is also found in the Urals and Siberia. It belongs to the perennial shrubs of the deciduous type, and there are a huge number of its species. Experts identify about ninety copies. The plant can be found in various forms:
- weeping;
- spherical;
- upright;
- cascading;
- pyramidal;
- creeping.
It is also diverse in size. Some shrubs only grow up to half a meter in size, while others can reach two and a half meters in height.
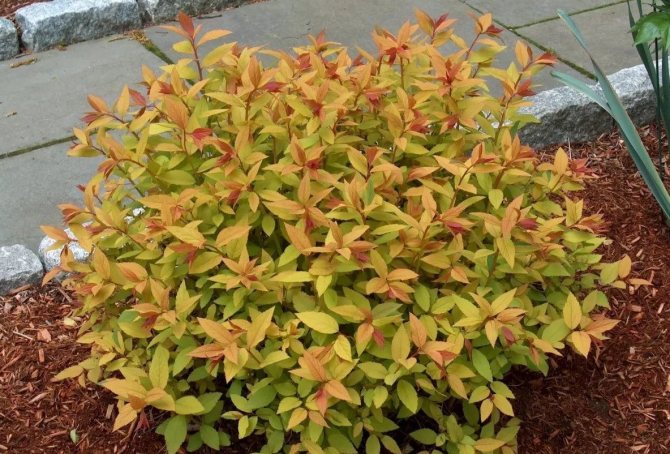
Spirea foliage may also differ depending on the type of shrub. Their size can be small or large, and the shape is round or lanceolate. The color palette ranges from golden yellow to dark green. By autumn, the shade of the leaves changes to orange or purple.
The color and shape of the inflorescences also depends on the plant variety. Shades can be white and red, but the shape of the inflorescences is as follows:
- pyramidal;
- paniculate;
- spicate;
- corymbose.
On the shoot, they can be located along its entire length or only on the crown.
Spirea is a rather unpretentious plant that does not require special care and looks very beautiful, so many flower growers and gardeners opt for it. Planting and caring for her is not difficult at all.
Varieties of spirea, varieties and hybrids
Spirea (lat. Spiraea) includes up to 100 species, each of which has its own name. Rarely, but you can hear or read another name - meadowsweet, whose origins stretch from ancient Russia. Spirea varieties are very diverse in shape, color and even leaf shape.


The shrub is a perennial plant, so every year you can observe how the spirea grows and becomes more lush.
Spirea is unpretentious to care for, sometimes due to weather conditions due to a lack of light and heat it grows with fewer flowers, but it invariably remains beautiful. There are spring-flowering and summer-flowering spireas. In spring flowers, flowers are predominantly white, formed on the shoots of the second year, in the month of May the bush becomes covered with beautiful inflorescences:
oak-leaved spirea is a weeping bush, can grow up to two meters and bloom earlier than other varieties, after May 10-15. The shrub is completely covered with flowers;
spirea Arguta (sharp-serrated) begins to bloom in the last days of May. The shrub has narrow leaves, drooping branches, grows up to 1.5-2 m in height;
spirea gray (ashy), often referred to as the bride. It is distinguished by its splendor, pubescent leaves of a grayish-green hue, small and white flowers. The abundance and splendor of flowers is simply mesmerizing.
A fairly large number of shrubs belong to spring flowering, among them the Nipponskaya spirea stands out. It is a small shrub (up to 1 m), in the shape of a ball, blooms closer to June. Another representative of the spirea Wangutta is a vigorous plant (2.3-2.5 m) with long flexible shoots, gray green leaves. Flowering begins in the second half of June.
Summer spirea is mostly pink in color and blooms in June or July, depending on the characteristics of the variety. This group includes Japanese spirea, which has many subspecies and varieties. The most common and famous are Nana, Little Princesses, Darts Red, Shirobana, and others.
White-flowered spirea is one of the representatives of the summer-flowering species, characterized by white flowers with a pronounced pleasant aroma, 0.6-0.7 m high. Billard's spirea is a hybrid, very frost-resistant. The leaves are wide, flowers of a delicate pink hue, bloom in July and bloom for quite a long time.Bumald's spirea, which belongs to hybrids, is well-known. The bushes have a height of 0.6-1.2 m, depending on the variety planted. Average winter hardiness, sometimes requires additional shelter (when grown in the northern regions, in the Urals and Siberia).
Plant varieties
Spirea varieties it is customary to subdivide into two large groups. These are shrubs that bloom in spring and shrubs that bloom in summer. By the way, the care of the plant depends on this, and the time of its planting.
Spring varieties bloom on last year's shoots. They grow strongly and they have a large number of young basal shoots.
Flowers in summer varieties are formed only on young branches. Flowering can be long and sometimes multiple. Old branches are replaced with young growth over time. Their life expectancy is about seven years. Flowers for the next year are formed on shoots that branches on last year's branches.
Of the shrubs blooming in spring, the following varieties can be distinguished:
- Spirea gray is a hybrid bred for a long time. It has gray-green foliage and white flowers, which are located throughout the branch and are collected in corymbose inflorescences. It can reach a height of up to two meters, but the falling type of shoots makes it compact and neat. Flowering begins in May and ends in late June.
- Spirea Vangutta - it is distinguished by abundant flowering from the end of May to June. Grows up to two meters. It has an unusual shade of foliage - bluish-green. The shade of the flowers is white, they are collected in umbrella-type inflorescences.
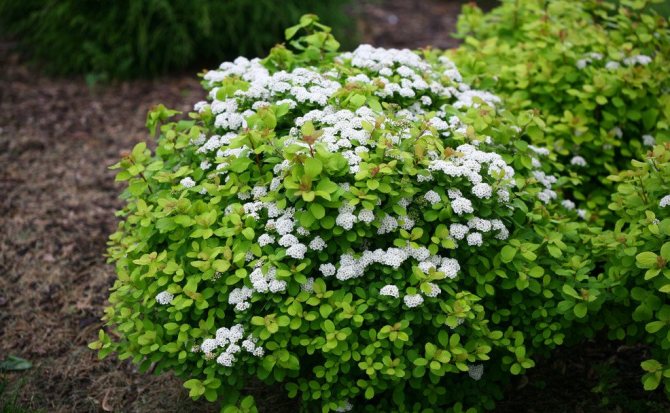
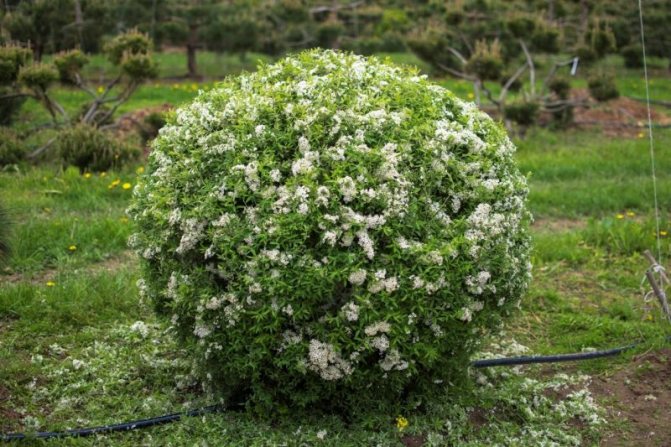
- Spirea Nipponskaya is a spherical shrub that grows in height up to one and a half meters. The foliage has a rounded shape, the flowers are white and stick around the shoot. They continue to bloom for an average of three weeks. It should be noted that this species is frost-resistant and unpretentious to the type of soil.
Summer flowering shrubs include the following types:
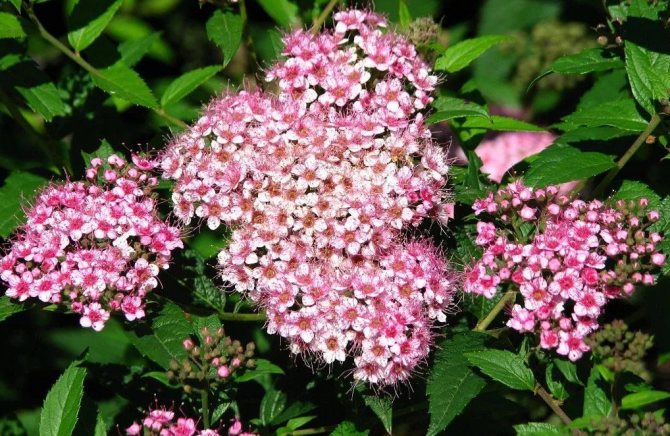
- Spirea Shiroban is a relatively small bush that does not exceed a meter in height. It is showered with small leaves of rich green color. Flowers can vary in shades. There are white and pink and even pink-red varieties. Blooms from July to August.
- Billard's spirea is a hybrid of Douglas spirea and willow spirea. The shrub is rather small, with spreading branches. It has wide foliage and pink flowers that gather in pyramidal-type inflorescences. It is capable of blooming throughout the summer.
- Spirea willow. A fairly tall shrub that grows up to two meters in height. Has shoots with a reddish tint and long narrow foliage. Flowers come in white and yellow shades and are collected in pyramidal paniculate inflorescences. It is a frost-resistant species.
Varietal variety
The variety of forms of spirea allows you to distinguish:
- tall (up to 2.5 m) and undersized (0.5 m) species;
- with a spherical, cascade, erect crown shape;
- white-flowered and with inflorescences of pink tones.
It is generally accepted to divide into two large groups, depending on the timing of flowering: spring and summer flowering.
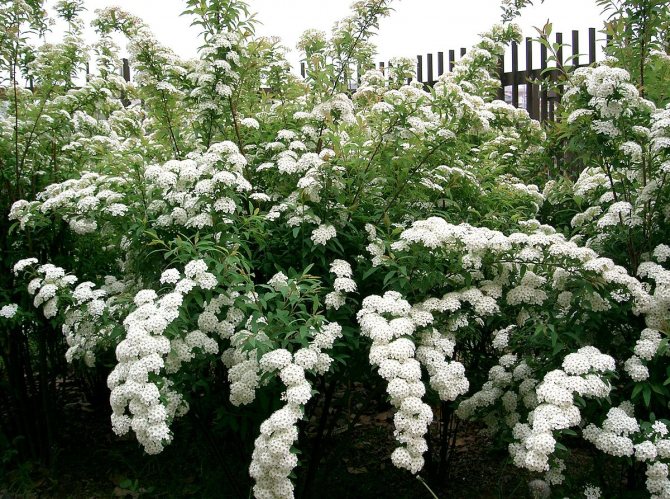


Spring blooming spirea
Spring blooming
In May, shrubs of predominantly white tones release buds. Cascades of inflorescences from all sides along spreading branches extend to the ground itself, forming a spectacle of incredible beauty. Flowering occurs in plants of the second year of life, buds are formed on last year's shoots.
Spirea arguta (sharp-serrated)... The plant with the earliest flowering among other representatives of the group. White inflorescences appear in early May, abundantly cover thin branches descending to the ground. The bush is high, spreading.
Spirea gray - the most popular representative of this group, has proven itself well even in the cold climate of Siberia. Grows up to 2 m in height. Snow-white inflorescences appear in May.


Spring flowering varieties of spirea
Spirea wangutta forms arched flower shoots from late May - early June. An adult bush grows up to 2 m. Umbellate inflorescences are often white, although hybrids with a pink color have been bred.
Spirea nippon... Erect branches in the center and drooping at the outer edge of the bush delight with the appearance of flowers from May to early July. Purple buds, opening, become white with a yellow-green tint. The height of the bush varies from 1.3 m to 2.5 m.


Spring flowering varieties of spirea
Summer blooming
From July to August it is time for this group to beautify the world. Pink, red or burgundy shades are characteristic of the inflorescences that form at the ends of young shoots.
Japanese spirea Is the most common representative of summer meadowsweet and has many wonderful varieties that can be grown in Siberia. All of them are considered undersized (no higher than 1.5 m), great for rock gardens and rockeries.
Spirea Japanese "goldflame"... The golden flame of the leaves by autumn further enhances the intensity of the color. The flowers are pink-red. The plant reaches a height of 0.8 m.
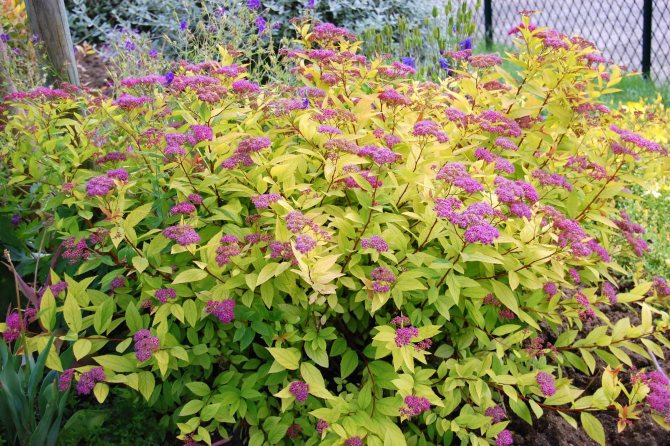


Spirea Japanese "goldflame"
Little princesses... A small bush 0.6 m high and 1.5 m in diameter forms inflorescence scutes of 3 cm pink flowers.
Spirea "crispa"... Erect shoots of this variety of Japanese spirea form a spherical crown, strewn with flat umbrellas of lilac-pink inflorescences since July. One of the lowest shrubs - no higher than 0.5 m.
Other known varieties of summer-flowering spirits are Willow and Boomalda... However, in the latter, in Siberia, annual shoots can freeze out during wintering.
"Anthony Vaterer"... Spreading-oval bush 0.8 m high. Blooms from July to early September. Shield inflorescences are large, up to 15 cm, deep pink with a purple tint.


Varieties of Japanese spirea
All of the above varieties belong to the Japanese spirea variety.
To create a hedge, spirea "willow" is often used. These are tall bushes (1.5–2 m) with erect shoots. Light leaves are similar in shape to willow leaves. At the end of June, elongated light pink inflorescences appear.
Planting a spirea: basic rules
It is during landing that you need to pay attention to the fact that what type of shrub does the seedling belong to?... That is, whether it blooms in the summer or in the spring. The landing time also depends on this. Therefore, when purchasing a seedling, this point should be clarified with the seller. Spirea blooming in summer is planted in spring. And the one that blooms in spring should be planted in the fall, so that by spring it has time to take root.
In the fall, the spirea shrub is planted after the autumn leaf fall, and in the spring - before the buds begin to bloom.
The seedling itself should be prepared depending on how it was purchased. That is, did he have open roots or were in an earthen coma. When buying a plant, special attention should be paid to root system... You need to carefully examine the roots and make sure they are healthy and not dry.
Before planting a shrub, too long roots are cut, if there are dry ends somewhere, then they must be removed, as well as weak ones. The aboveground part should be shortened by one third. In the case when the root system is not visible and it is in an earthen coma, it should be slightly moistened, for which you can place the seedling in a bucket of water and then plant it in a hole. If the earthy ball is too dry, then the plant can be left in water for a couple of hours. Do not worry if the soil is washed off a little from the roots.
When choosing a place to plant a shrub, some rules should be followed:
- the place should be bright and sunny;
- it should not be in a low place, it is better that it be a hillock;
- despite the fact that the plant is not picky about the soil, it is better that the soil is light and fertile.
Of course, the soil does not always meet the necessary requirements, but this is easy to fix.Spirea loves when the soil has good moisture permeability, so it is imperative to take care of drainage. And even if the land on the site is very fertile, then a little top dressing of the spirea shrub will not hurt. The planting pit is prepared as follows:
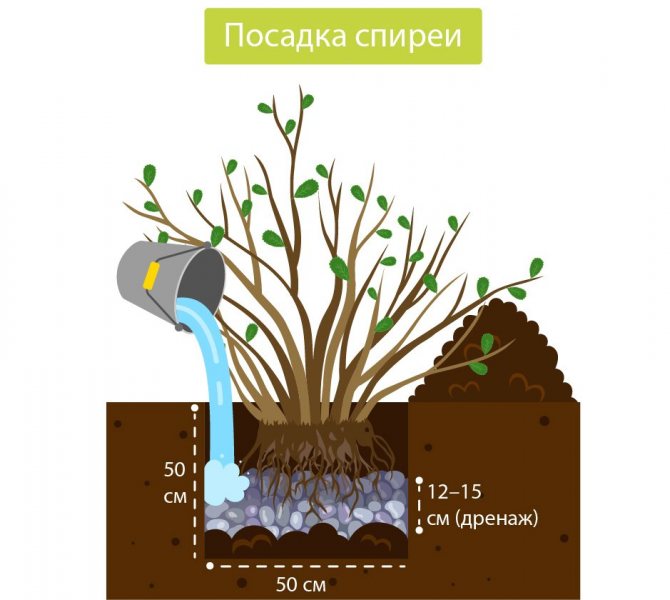
- soil is removed in accordance with the size of the pit, which on average should be fifty centimeters deep and wide.
- at the bottom, drainage is made, which can be brick chips or expanded clay. The drainage layer should be between ten and fifteen centimeters high.
- the soil that was taken out is mixed with sand and peat in a ratio of 2: 1: 1. That is, 2 parts of land and one part of peat and sand.
- a small part of the prepared soil is poured into the drainage with a slide.
On this, the pit for planting the spirea is ready. If you plan to plant several bushes, then it is imperative to keep a distance between them. It should be at least half a meter. More is better. If the spirea is planted as a hedge, then this gap can be reduced.
Final stage of planting Is the placement of a seedling in a pit. It is placed on the soil poured out with a slide, after having straightened the roots. Then the hole must be covered with the remaining soil and tamped tightly. Immediately after planting, the bushes require abundant watering. One bush consumes 10-15 liters of water. After that, it is better to mulch the soil surface near the bush with sawdust, peat or compost.
Plant care
The process of caring for a plant in the open field is simple, but in order for the shrub to grow well and please the eye, you should treat it with attention.
Spirea is good for moisture and therefore needs frequent watering. Especially those bushes that have only recently been planted and those that begin flowering in summer. Seedlings are watered abundantly for a speedy rooting process and rapid growth. And so that moisture does not evaporate too quickly, it is better to mulch the soil next to them. Spirea species blooming in spring require moderate watering.
In order for the plant to bloom abundantly and for a long time, it should be fed from time to time. This can be done using special mineral fertilizers or organic additives. If organic is used, it is better to take cow dung or bird droppings. From them you need to make infusions. For mullein infusion, you need to take one part of the manure and add six parts of water to it. Such a solution should be infused for at least ten days. Then one liter of fermented slurry is taken and ten liters of water are added to it. You can add 10 grams of superphosphate to the infusion, but it is better to do this before flowering.
The first time feeding is carried out in early springafter pruning the shrub. Then in mid-June. Young bushes begin to feed, two years after planting.
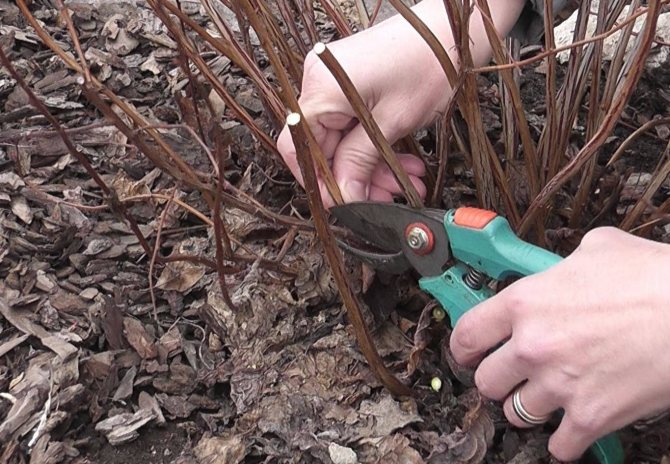
Spirea pruning
Pruning this shrub is a must. Firstly, it is able to give the plant a neat look, and secondly, it rejuvenates the plant. Pruning depends on which group the planted bush belongs to.
As the plant grows, its branches become thinner and begin to produce few flowers. When such branches appear in summer flowering bushes, they should be cut... In this case, only those shoots should be left on which well-developed buds have already tied. To form a beautiful and well-groomed bush, you should cut off all dried shoots, as well as weak and damaged ones.
As for the spirea blooming in spring, given that its buds are laid on young shoots, they should not be cut off. Sanitary pruning can be done in early spring and damaged and dry branches can be removed. You should not shorten healthy shoots, otherwise they will begin to branch strongly, and this will deteriorate the shape of the bush.
It is customary to cut off species blooming in spring after they have faded. Sometimes they resort to a radical form of pruning.This is done in order to rejuvenate the bush.
Reproduction of spirea: useful information
Like most plants, spirea can be propagated in several ways... Usually they use:
- reproduction by layering;
- cuttings;
- seed reproduction.
Reproduction using layering is considered the easiest way. With this method, in the spring, as soon as the first leaves begin to appear, the lower shoot is buried in the ground. It is watered regularly along with the entire plant. By the fall or next spring, this cutting should give roots and it will be possible to plant it.
By cuttings, the plant also reproduces well.but this is more troublesome. Cuttings are cut in summer - in July-June. It is better to cut off young green or slightly woody ones. They are planted in a mixture of peat and sand and covered with a cap to make it look like a greenhouse. They need to be watered quite often. Rooting can take a long time, and they can be planted in open ground no earlier than next spring.
Seed breeding method the longest and most laborious, and also ineffective, but if necessary, you can use it. The seeds are planted in peat in early spring. They must be covered with foil and watered frequently. From time to time, the film needs to be removed and ventilated. As soon as the first shoots appear, the film can be removed, but they are not planted until the end of summer. And by September they need to be transplanted into open ground. For the winter, such plants should be well covered, and the first flowers in a shrub grown in this way will appear no earlier than 3-4 years later.
How to plant a spirea correctly, landing pattern
Before planting spirea, inspect the seedlings. The roots should not be dry, a good seedling has a flexible root system, buds are present and there is no mechanical damage. If the roots are too long, they must be shortened before planting, if the roots have dried out during storage, lower them in a bucket of water.
A hole for planting a plant is dug 50 cm deep and wide. Drainage must be laid on the bottom: expanded clay, brick fragments, pebbles. Drainage layer - at least 15 cm. If several plants are planted, the distance between them should be up to half a meter. For planting, a substrate is prepared in advance, with which the seedling in the pit will be poured: leaf earth, peat and sand in proportions of 2: 1: 1. The plant is placed vertically, the roots are straightened so that they do not bend, sprinkled with earth, leaving the root collar at surface level. After planting, watering and mulching are carried out.
Read also: Miracle shovel - Mole: features of this ripper and the average price of inventory
Spirea - planting and care
Spirea a shrub that stands out clearly from other representatives of ornamental shrubs. It's not just about her beauty, the spirea perfectly adapts to almost any conditions and does not require special care. Inexperienced, novice gardeners can easily cope with the cultivation of spirea. The abundance of species, forms, varieties allows you to choose exactly the plant that is best suited for your purposes.
The content of the article
Spirea got its name from the Greek word "speira", which means "bend" in the native language. This name perfectly characterizes this plant, which is distinguished by the extraordinary flexibility of the branches. According to botanical taxonomy, spirea belongs to the Rosaceae family. In nature, there are species from dwarf, whose height does not exceed 15 centimeters, to tall, 2 meters high. In total, there are about 70 species of this shrub. Spirea bloom usually begins in May, but it mainly depends on the type of plant. The color of spirea flowers also depends on the type and timing of flowering. Bushes, which bloom in early spring, bloom with white flowers collected in inflorescences. Crimson flowers bloom on plants that bloom in summer.Most species of spirea bloom with flowers collected in inflorescences, but there are also spireas that bloom in single flowers. Usually this shrub is planted in a group, in the form of a hedge, but a single plant looks quite impressive.


Appearance and biological features
Plants of this genus can grow both small (up to 15 cm) and tall (up to 2.5 m). The branches of the shrub are erect or creeping. The color ranges from light to dark brown. The roots are shallow, fibrous. During flowering, the spirea is covered with numerous small flowers in inflorescences of various shapes. The color of the petals is from snow-white to crimson. Spirea inflorescences can be located both along the entire shoot, and on its upper part or at the end of a branch. The plant propagates by seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush, layering.
Spirea does not need pruning. It is carried out exclusively for decorative purposes in order to give the bushes a more aesthetic appearance. The crown of a plant can be dense and dense or slightly "sparse", but it always looks attractive. The branches bloom right down to the ground, so there is no unsightly "bare feet" effect.
The shrub is hardy, adapts well to various climatic conditions, so it can be grown not only in the south or in the middle lane, but also in the northern regions. If the spirea freezes under severe frosts, then after pruning it is completely restored and blooms in the same year. For the normal development of the plant, a few hours a day of direct sun, top dressing, and good soil are enough. You don't need to cover it for the winter.


Spirea blooms on shoots that grow during the same year, so pruning does not spoil its appearance
Growing spirea from seeds
This method of growing and reproducing spirea is not particularly popular among amateurs. It is used mainly by professionals in nurseries. Amateur gardeners use simpler breeding methods. But at the same time, there are cases when it is necessary to use this method of reproduction of spirea.
It is not particularly difficult. The similarity of seeds of an ordinary, non-hybrid spirea is quite high, up to 80%.
Sowing seeds is carried out in the spring. Basically, it practically does not differ from growing seedlings. But it will take a long time to wait for the appearance of the first shoots, 2 - 3 months. After the appearance of a couple of true leaves, the seedlings dive and grow in separate containers until the beginning of autumn. Planting seedlings directly into open ground in a seedling bed is also practiced. For the winter, young bushes take cover, and with the onset of spring they are planted in a permanent place. Spirea grown from seeds blooms in 3 - 4 years.
Preparing spirea for winter in Siberia
Before sheltering young seedlings for the winter, experienced gardeners recommend preventive treatment against dangerous pests, which include blue meadowsweet sawfly, beet aphid, and kidney gall midge. Treatment with chlorophos helps to get rid of the sawfly, from beet aphids - infusion of capsicum, from gall midge - metophos, chlorophos.
Young plants planted in autumn should be immediately protected from frost by building a shelter over them. Low-growing varieties successfully overwinter under snow, but taller bushes may need the help of a gardener. If the variety does not differ in hardiness (for example, Japanese spirea) or is planted in a cold region, it must be prepared for wintering annually. You will have to tie the branches, bend them to the ground and fix them with pegs, then cover them with dry leaves.
Planting spirea on the site is a groundwork for many years. An ornamental shrub will provide protection from prying eyes, wind and dust, and graceful white, pink or red blooms will transform the site every year.
Growing spirea from a cutting
This is the simplest and most common way to reproduce spirea. Moreover, all varietal characteristics of the bush are preserved with this method.
Cut the cuttings in early summer.
Annual, semi-lignified shoots are suitable for cuttings. The stalk should have about 5 - 6 leaves, from which the lower pair is removed. The rest of the leaves are shortened by half (as in the propagation of lemon). Before planting the cuttings of the spirea, it is advisable to hold for 10 - 12 hours in a solution of a root formation stimulator or dip the lower cut into root powder.
Cuttings can be planted both in a separate container with light soil, and in open ground on a specially prepared bed. It is advisable to plant the cutting with a slight slope to improve root formation. Cover the top of the handle with a transparent cap. This can be a glass jar or a wire-framed plastic bag. In the process of rooting the cuttings, keep an eye on the moisture content of the earth, not overdrying it, but not overmoistening it either. Ventilate and spray the cutting periodically. Protect from direct sunlight. For the rooting period, it is better to place the spirea stalk in a light partial shade. Protect the young plant well from frost and damage for the winter. With the onset of spring, when the spirea begins to give new shoots, transplant it to a permanent place.


Spirea propagation by layering
This is the easiest way. It is used for many garden shrubs (gooseberries, currants, climbing roses, etc.). Well-developed, but not old, bushes, about 3-4 years of age, are best suited for this. With the onset of spring, when leaves appear on the shoots of the spirea, select the extreme shoot and bend it to the ground, fixing it with a wire bracket at the point of contact with the ground. Loosen and water the earth in this place. You can also lightly scratch the bark of the shoot with a knife in the place where it will come into contact with the ground. Sprinkle with a layer of earth on top. Usually, by the fall, the shoot acquires its own root system. If desired, it can be separated from the mother plant and planted separately. Or you can take your time, let the roots grow and grow stronger until spring, and only after that they can be planted.
Types of spirea (varieties with photos and descriptions)
The following types and varieties of plants have gained popularity among gardeners:
Spirea gray "Grefsheim" is a hybrid, it is characterized by lush flowering. The bush is high, up to 2 meters, has a compact crown shape. Shoots are brown, leaves are gray with a green tint up to 4 centimeters long.


Spirea Wangutta was obtained by French breeders. Shrub up to 2 meters in height with a rounded crown. The leaves of the culture are of a standard green color, the inflorescences are white, made in the shape of an umbrella.


Spirea Bumald grows up to a meter tall, has pink inflorescences. Her leaves are red with a green tint. In some forms of hybrids, the color of the flower petals changes from white to pink. The flowering culture is observed from the first days of June to the last decade of September.


Spirea Berezolistnaya is a relatively small plant, the bush reaches 60 centimeters in height. The culture got its name from the similarity of leaves with birch leaves. The plates are green with small veins at the bottom. The crown of the culture is dense, spherical, shoots resemble zigzags. The leaves are small, up to 1 centimeter in length, elliptical in shape. Flowering culture is observed from 4 years of age. The inflorescences are dense, pink.


Spirea Billard grows up to 2.5 meters tall. The bush has erect shoots, a rounded crown. The bark on the branches is red, the leaves are bright green, lanceolate, with a well-visible central vein. The lower part of the leaf blade is glaucous. Inflorescences are pyramidal, bright pink. The flowering culture continues from the last decade of June until the very frosts.


Spirea Goldflame is a low ornamental shrub with a crown size of 60 to 80 centimeters. A feature of this plant is the change in leaf color throughout the year.The greens are homogeneous, lush, so the culture can become the color of any garden, it is widely used in landscape design. Leaves with jagged edges of light green color, pink inflorescences.


Spirea Ivolistnaya is a shrub up to 2 meters high. Leaves with sharp tips, reaching 10 centimeters in length, and the upper surface of the plate is much darker than the lower. The branches are erect, the bush grows rapidly through a huge number of root suckers. The inflorescences of this type of spirea can be burgundy, purple, pink or pomegranate.


Spirea "Golden Princess" is a relatively low plant, no more than 1 meter in height. The color of the shrub changes throughout the year from green to red. The inflorescences are pink, their diameter does not exceed 4 centimeters. The flowering culture lasts from June to July.


Spiraea nipponica Snowmound (Spiraea nipponica Snowmound) differs from other varieties in the early flowering period and decorative color of the leaves. The bush is up to 2 meters in height with a crown diameter of up to 4 meters. The branches are directed horizontally, the bark is brown in color. The leaves are rounded, bright green in color, up to 5 centimeters in length.


All the described types of spirea are used in landscape design for hedging, they are also used to decorate alpine slides.
Planting spirea


The choice of planting material
If you have grown a young plant in one of the ways described above, then you can skip this point. But if you decide to purchase an already grown sapling, then you should carefully approach the choice. First of all, you should decide in what quality and where you will grow spirea. If it is a hedge, then it is better to select plants of the same variety or of the same type. Usually these are tall species of spirea. To avoid misbehaving, purchase all the seedlings from one vendor. When choosing a spirea for a single planting, a variety with a long flowering period is best suited. For flower beds, flower beds, alpine slides, it is better to give preference to undersized species. When buying, be sure to inspect the roots of the seedling. A good spirea seedling should have at least three taproots with a developed lobe. The roots must not be dry or damaged. Do not take a seedling if it is dry, not flexible and does not have large buds. Saplings with open leaves are also not suitable.
Choosing a place for planting a spirea
With a lack of lighting, the spirea will bloom badly, this must be taken into account when choosing a place for planting it. Otherwise, this shrub has no special preferences. The composition of the soil in the selected area is not particularly critical. But it is desirable that the earth is not too heavy, clayey. Such soil must be lightened with sand or peat. If the earth, on the contrary, is too light, sandy, then add a little clay to it.
The size of the planting holes for planting is determined by the size of the seedling root system. In this case, the depth of the fossa should be made more, taking into account the fact that a third of the depth should be occupied by drainage.
Broken bricks, pebbles, gravel, etc. can be used as drainage. A layer of earth is poured onto the drainage layer, on which the seedling is installed. The roots spread out along the slopes of the mound.
Then the rest of the earth is filled up. After planting, the seedling is watered abundantly. On average, one bush takes 2 - 3 buckets of water. If the earth has settled, add it. To retain moisture, the ground around the trunk of the spirea must be mulched.
Planting spirea in the fall
At this time, mainly early flowering species are planted so that the bushes bloom next spring. Planting technique is the same as for spring planting. There are also nuances. So planting should be carried out no later than a month before frost. At the same time, the seedlings should no longer have leaves after leaf fall.
Diseases and pests and their control
All types of spiraea are not often attacked by various pests, but sometimes it happens.Let's take a look at some of them.
Spider mite
Perhaps the most formidable among them is the spider mite, since during one growing season, from 8 to 10 generations of this pest can appear. Whitish paniculate spots appear on the surface of the leaves on which the spider mite has settled. Then the leaves turn yellow, dry out and fall off. The number of spider mites increases especially noticeably from July to August (in hot and dry summers).
To combat this pest, arex (0.2 percent solution), metaphos, fosalon, celtan and phosphamide are used.
Also, aphids, which feed on the sap of leaves, pedicels and tender young shoots, do quite a lot of harm. It is especially dangerous from June to mid-August.
This pest can be destroyed with solutions of pyrimor, actellik, kronefos, fosalon. With a small lesion, folk remedies will also help, such as tincture of tobacco, capsicum, onion, garlic, and soap solution.
Spirea care


Spirea is considered a drought-resistant plant. But one should not rely too much on this ability of her. In this bush, the roots are located close to the ground, and moisture from the top layer of the soil leaves quickly. Therefore, if the summer does not indulge in rains, watering will be needed. Usually 2 - 3 waterings per month are enough for spirea. But they must be abundant. On average, at least 2 buckets of water should go to an adult bush.
In between watering, you should loosen the soil around the bushes.
For the successful growth and flowering of spirea, three dressings per season will be enough:
- In the spring, after pruning, mineral or organic fertilizers with a high nitrogen content are applied. If the variety is early flowering, then a complete balanced mineral fertilizer is applied.
- At the beginning of summer, spiraea (especially late flowering) is fed with a complete mineral fertilizer with an emphasis on the content of phosphorus and potassium.
- The last feeding is carried out at the end of summer. Fertilizer for this top dressing should not contain nitrogen, which will stimulate the development of new shoots on the bush. Potash or phosphorus-potassium fertilizers should be preferred.
Spirea pruning
In the spring, the first image is held. Its main purpose is to remove dry and damaged branches during the winter.
The second pruning is formative. It is carried out mainly for late-flowering species of spirea and is usually combined with sanitary pruning in early spring.
Bushes form well and can be shaped to the desired shape, but should not be limited to cutting off the tips of the shoots. This will negatively affect their development. On average, the shoots are shortened to a level of 25 centimeters above the ground, or a third of the length.
Early flowering spirea is cut and formed after flowering.
For old bushes (7 years or more), rejuvenating pruning is carried out. With this pruning, old shoots are removed, leaving several young, viable shoots. But you should not immediately radically cut out all the old shoots, this can significantly weaken the bush. It is better to carry out anti-aging pruning of spirea gradually, in several stages.
Spirea pruning in Siberia
Pruning is a mandatory procedure in caring for flowering shrubs, as it grows quickly and sometimes unevenly. The manipulation is carried out in the spring. In early flowering varieties, only the tops of the shoots are subject to removal at the end of flowering. In other species, the branches are cut by a third, while the large bud is left in place. Weak shoots are best removed completely. The larger the pruning, the more the bush grows.


Fresh articles about garden and vegetable garden
Tomato "Djalo Santa": variety description photo reviews
Fertilizers for orchids at home
Unabi: landing and care in the middle lane

































