Honey mushrooms is a word that unites a group of mushrooms from various families and genera. Why did these mushrooms get this name? In fact, everything is extremely simple, the word "honey mushroom" has a common root with the word "stump", and as you know, most honey mushrooms prefer to grow just on wood (stumps, dead woods, weakened living and dry trees). The only exceptions here are meadow mushrooms, they grow on the ground, and they got their name rather because of the external similarity with other representatives of this group.
As practice shows, many people speaking about mushrooms mean a specific type of mushrooms, namely "autumn mushrooms", since they are perhaps the most famous among amateur mushroom pickers. In fact, there are many other very tasty mushrooms included in the mushroom group, which are often bypassed by people new to the mushroom kingdom.
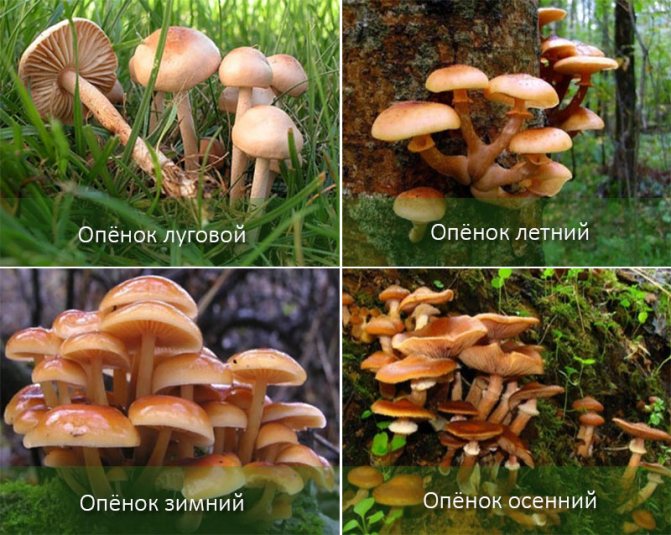
Next, I propose to get acquainted with the main mushrooms related to honey agarics. Some of them you may well have seen in parks or in the forest, and some may have even been seen by you in stores.
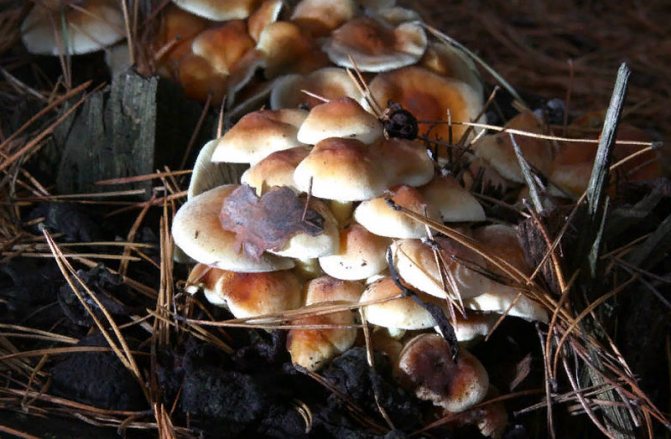
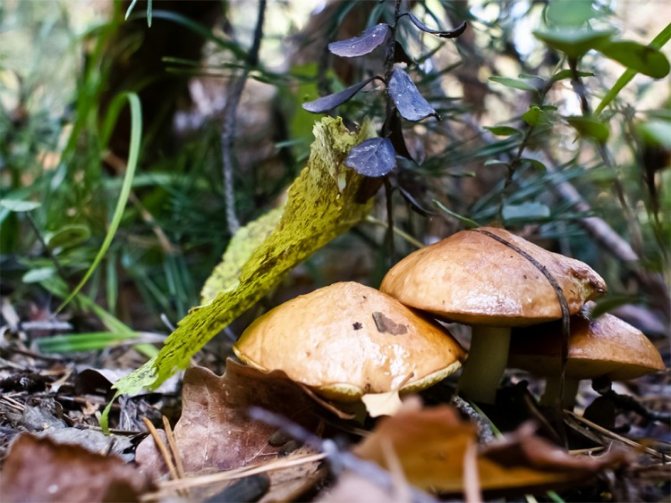
Description of summer mushroom
What do summer mushrooms look like?
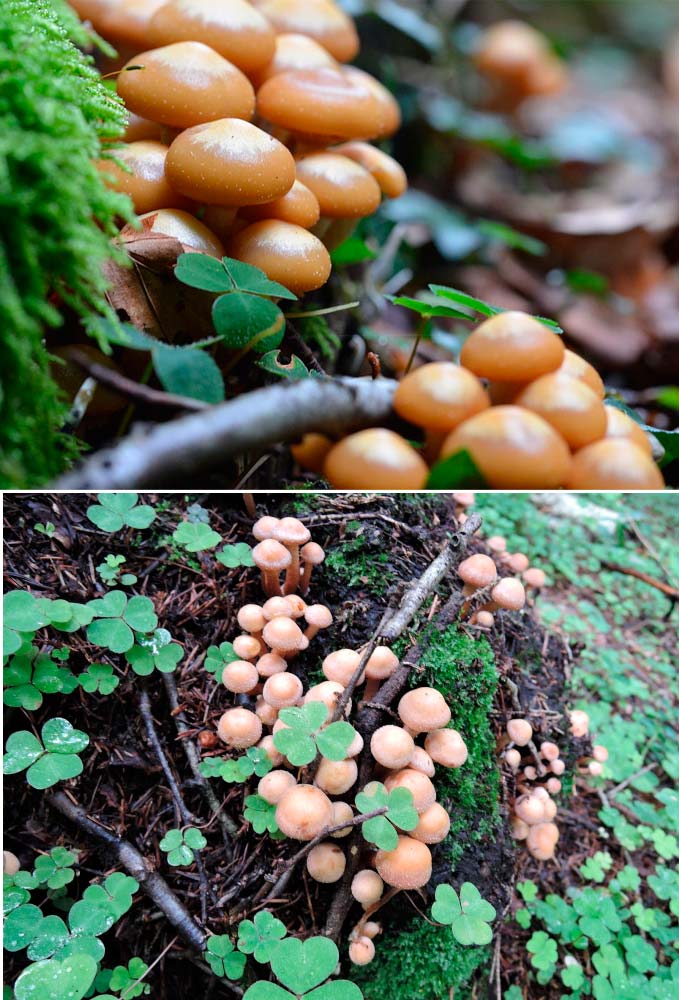

Two photos of summer honey agarics
- In young specimens, the cap has a convex shape; as it grows, it becomes flatter, and a characteristic tubercle remains in the middle. In diameter it reaches 3-6 cm. In dry weather, a yellow-brown tint prevails. In a period of high humidity, it becomes bright brown.
- The skin has a smooth texture and is covered with mucus.
- The leg is 7 cm high, 0.5 cm in diameter. It is quite dense, the color is light, it becomes darker towards the bottom.
- In the cap, the pulp is watery and very thin in structure, in the stem, on the contrary, it is dense.
- Young representatives have a thin ring. The plates grow very weakly to the stem, their color varies from light brown to brown, it depends on the age of the fungus.
Where and when do summer mushrooms meet
Most often, these mushrooms grow on hardwood trees. Favorite places are rotting wood, stumps and clearings by the river. Sometimes in mountainous areas, mushroom colonies can be found on spruce trees. A decent crop is harvested from one site. There are stumps completely covered with their colonies.
Another name is linden, as these mushrooms are often found on linden.
Do not look for these beauties only on stumps, they can grow near bushes and in various meadows.
Gathering summer mushrooms: If you live in an area with a warm climate, or go there, they can be found there all year round, in cold areas - from the second month of spring to mid-autumn. And then you ask: "Why are they called summer ones?" Because the peak of their growth season is in the middle of summer.
When collecting, you need to be as careful as possible. Cut gently with a sharp knife. It is not recommended to collect in places located near roads and landfills. These mushrooms, like sponges, absorb, in addition to useful elements, also harmful substances, and sometimes poisonous ones. All kinds of herbicides, heavy metals, radioactive isotopes and even mercury. It is also best not to pick mushrooms in the city park.
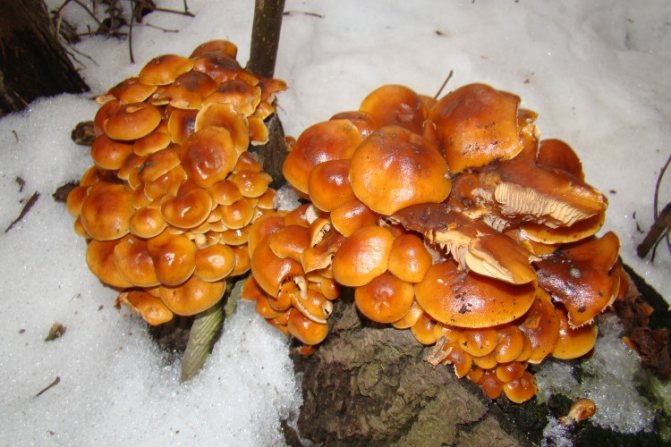
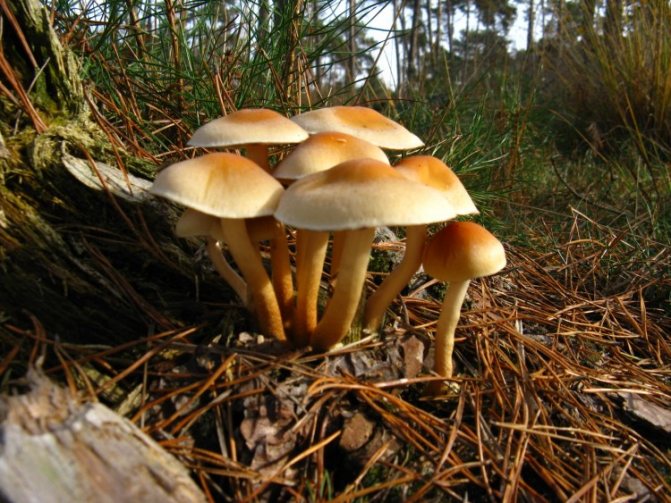
Winter honey fungus (Flammulina velutipes)
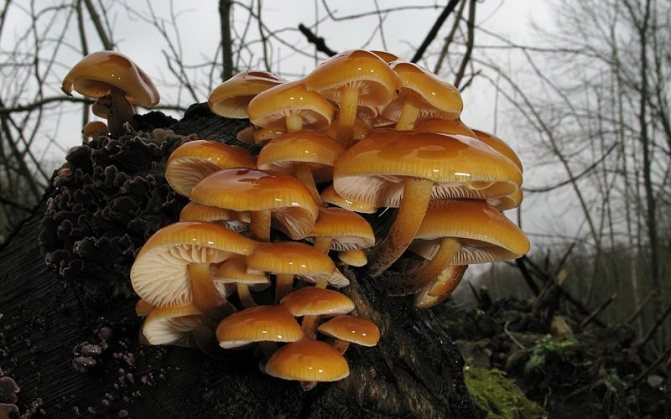


Winter mushroom in the photo
The mushroom is edible.Caps 2-8 cm, young - bell-shaped or convex, then prostrate, sticky, yellow-ocher or rusty-brown, underneath with frequent white-ocher or white plates. Legs are thin, velvety, without a ring, at first the color of the cap, not very hard, then they turn dark brown or almost black and hard. The main distinguishing feature of winter honeydew is a stiff, velvety leg. The aggregates of its fruiting bodies look like fiery spots against the background of snow. The mushroom has adapted to bear fruit during the thaws in winter. One can observe under a microscope how, when the temperature rises above zero, the cells of its mycelium that have burst during freezing grow together.
It grows on dead and living tree trunks, as well as on willow, poplar, birch and linden stumps. It can sometimes be found in conifers.
Fruiting from September to December. Sometimes it grows in spring.
It has no poisonous counterparts.
Soups are made from winter honey, salted in a hot way, marinated in jars.
The difference between summer agarics and false doubles
Summer honey agaric is often confused with mushrooms similar to it.
A mistake can become fatal: from an inedible dish to severe poisoning.
The most dangerous thing - instead of edible honey mushrooms, dial Galerina bordered. It is almost impossible to distinguish them: the same color, identical shape and even a ring on the leg. Only an experienced mushroom picker will understand that this is Galerina in the form of disputes.


Bordered gallerina is poisonous. As well as a pale grebe, it is fatal, if you do not help a person in time, a fatal outcome is possible. You can meet in coniferous forests, starting from May and until deep frosts. Usually grows from 1 to 3 mushrooms, in contrast to honey agarics growing in colonies.
You should be extremely careful, Galerina can sprout one among other honey agarics.
False mushroom is a poisonous mushroom that exists in two subtypes: gray and sulfur-yellow. A few hours after taking them, severe vomiting and dizziness appear.
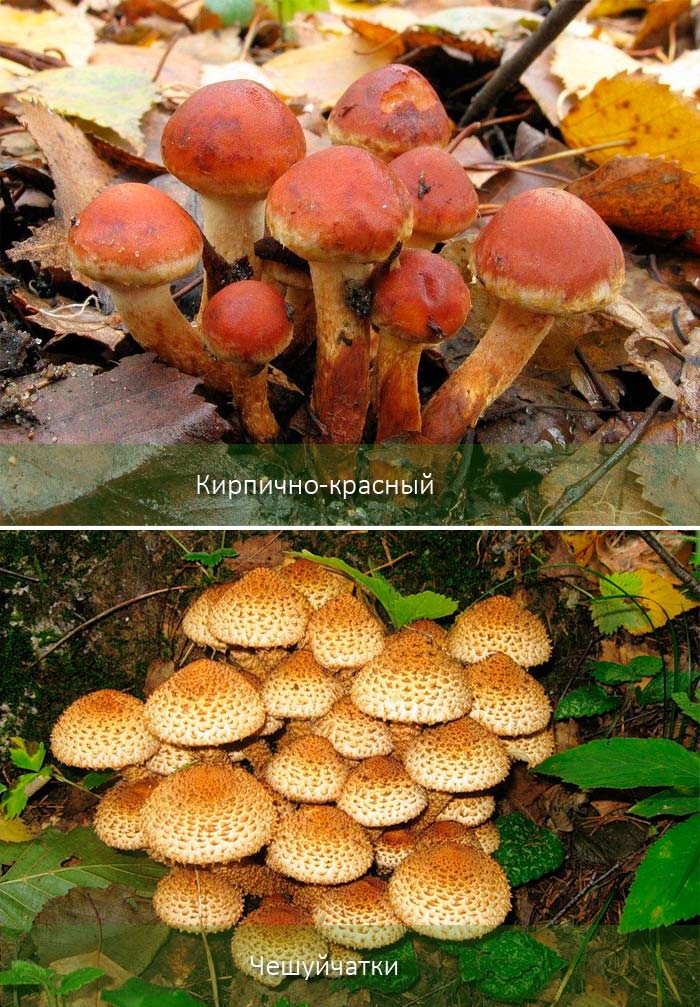


Less dangerous doubles include:
- brick red false honey, not poisonous;
- scales are inedible mushrooms.
When collecting, be extremely careful, carefully inspect each mushroom. If there are any suspicions, it is better not to frustrate.
One more tip by the way. Collect mushrooms in baskets, not in a bag, otherwise, under the influence of excess moisture, they will turn into a caked ball.
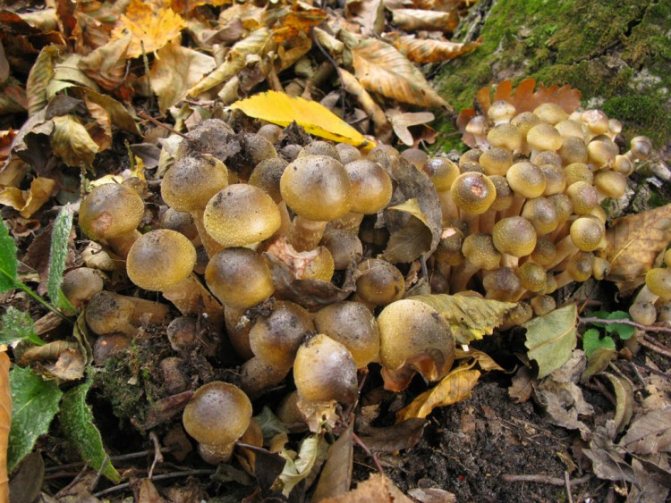
Autumn honeydew
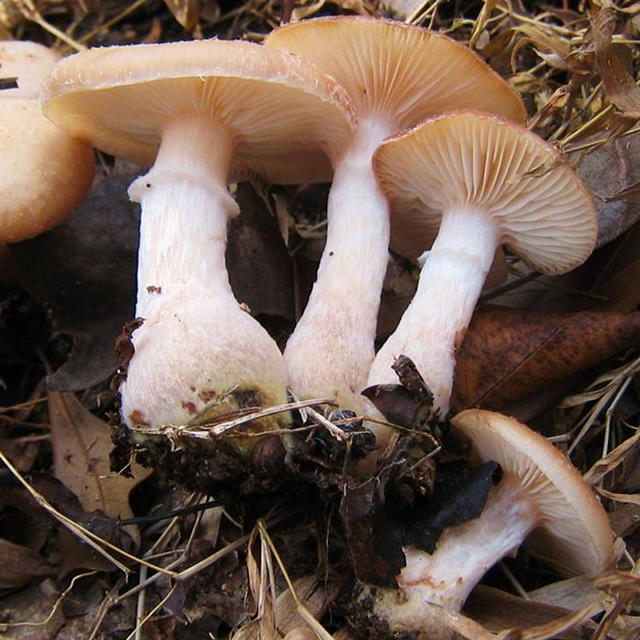


It differs from the usual autumn honeydew by a thicker leg at the base, the color is almost identical, but sometimes it is somewhat lighter and paler, and sometimes with light scales instead of dark ones. In addition, this mushroom looks stronger and does not grow in large clusters, but throws out fruiting bodies in groups of no more than a dozen. It is not seen on living trees, it feeds on rotting plant debris, therefore, it can more often be found on windbreaks and forest litter.
Bears fruit from August to October - evenly, without "layers". In especially warm years, fruiting bodies can appear as early as July. It is edible, in terms of taste it is not inferior to the usual autumn honeydew.
The composition of summer mushrooms and their calorie content
The energy value of these mushrooms is very small and amounts to 17-22 kcal per 100 g. If you are fasting or on a diet, then this dish is for you.
Nutritional value per 100 g of freshly cut summer mushrooms:
- water 90 g;
- carbohydrates 0.6 g;
- proteins 2.3 g;
- fat 1.1 g;
- dietary fiber 5.1 mg (25.5% DV).
Honey mushrooms contain vitamins B1, B2, C11 and PP. By eating 100 g, we get such minerals as: magnesium (5% of the daily value), potassium (16%), phosphorus (6%) and iron (4.3%). The content of trace elements will be: zinc (9.1% of the daily value), copper (16.1%), nickel (31.2%) and chromium (31.7%).
Medicinal properties
- All autumn mushrooms have healing properties:
- They are a storehouse of vitamins (A, C, E, PP, B vitamins), polysaccharides, trace elements.
- They have a bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effect.
- Helpful for hypertension, improve blood flow to the heart and brain.
- Improves vision.
- They have a positive effect on diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory diseases.
- To some extent, they protect from the effects of radiation.
- Show a sedative effect.
- According to research by scientists from China, the extract from these fungi inhibits the development of sarcoma-180 and Ehrlich's carcinoma. Also, the Chinese use them to combat neurological and mental diseases (neurasthenia, insomnia, photophobia, convulsions), ear diseases (tinnitus, inner ear disease), as well as to recover from a stroke.
- Reduces cholesterol levels.
- The substances of the fungus are the basis of the medicine against eclampsia (extremely high blood pressure in pregnant women and women in labor).
- There is information that an aqueous extract of mushrooms promotes immunomodulation.
- In the future, it can be used to combat the lack of oxygen in tissues.
- Honey mushroom tinctures are used as an analgesic for headaches and heartaches, even as a laxative.
- Mushroom ointment treats diseases of the legs and joints.
- Preparations from rhizomorphs (black cords of mycelium) are used for lumbar pain, as well as to support the body in diabetes mellitus.

The harm and benefits of using summer mushrooms
Eating honey agaric has a beneficial effect on the work of the heart. The pulp can be used to treat staphylococcus aureus.
It is contraindicated to use for acute gastritis, ulcers, colitis and cholecystitis. And also up to 7 years old.
Summer mushrooms are quite aromatic and pleasant to the taste.
Heat treatment is required. This is especially important if you are unsure of where the mushrooms have gathered.
After sorting out the mushrooms, throwing out all the suspicious and wormy ones, soak them in water for 30 minutes. When you start boiling, drain the first broth with the foam, add fresh water to it. Place the mushrooms in a colander and rinse with water. Use as you wish, adding to soup or salad, fry with potatoes, or put in a pie. You can also dry mushrooms for the winter, or pickle. Juicy and crunchy mushrooms are a delicious appetizer to the table.
Freezing is the best way to retain all the nutrients.
Summer mushrooms at their summer cottage
In order not to go to the forest for mushrooms, they began to grow on their own plots. Inoculation (planting of mycelium) occurs due to the transfer of a small area of wood with mycelium into previously prepared holes in the stumps.
The diameter should not be large, optimally 0.8 cm. The mycelium that you placed in the hole should be covered with moss. The infection process must be carried out in the fall or spring. Fruiting is on average 7 years.
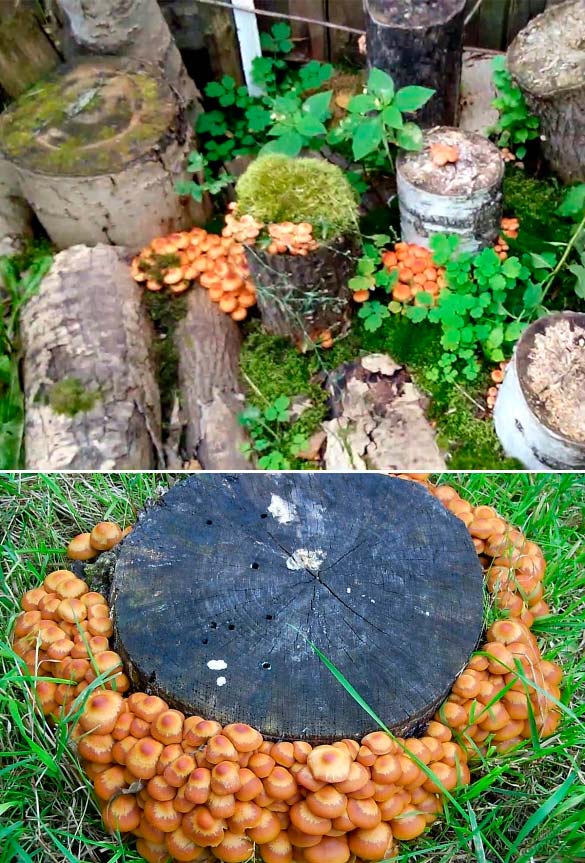


Alternatively, sprouting on wooden blocks is used anywhere in the summer cottage. To do this, prepare logs from any hardwood, freshly cut birch is best suited. Place the mycelium in them and leave for 4 months in a room with a temperature of + 15 ... + 20 ° C, and a humidity level of 85%. If you use the cellar or basement, then the chance that the mycelium will take root will increase significantly.
The care process is extremely simple - it is necessary to protect the mushrooms from direct sunlight, and to ensure a sufficient level of humidity. Keep in mind! Summer mushrooms instantly grow beyond the stump. The soil under the mushrooms is severely depleted. It is recommended to remove the topsoil every 3-4 years and replace it with a new nutritious one.


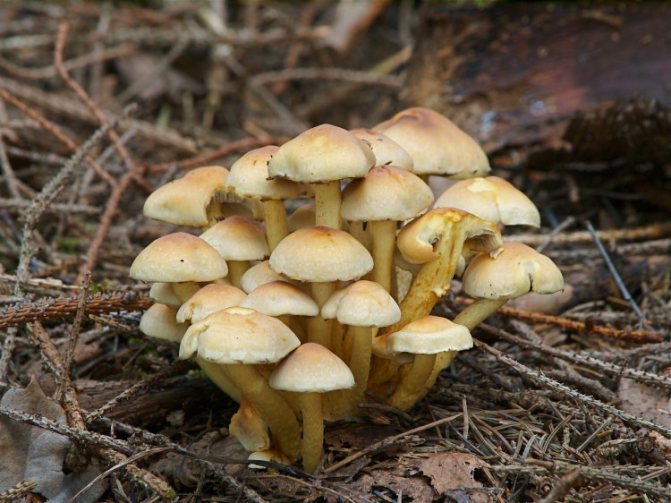
Shrinking honey fungus
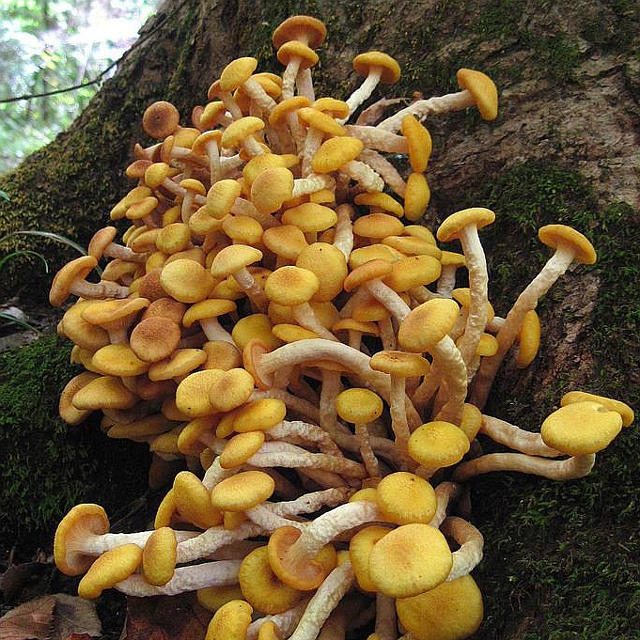


He is oak honey fungus, ringless honey fungus. Another species of the genus of real honey agarics, preferring broad-leaved species to other trees. More often it is harvested from oak trees, for which it received one of its alternative names.Beskoltsev is also called Beskoltsev for a reason - the fruiting bodies of the mushroom do not have a shrinking blanket, respectively, his leg is always without a ring, which greatly increases the chances of confusing this mushroom with false mushrooms, therefore only experienced mushroom pickers collect it.
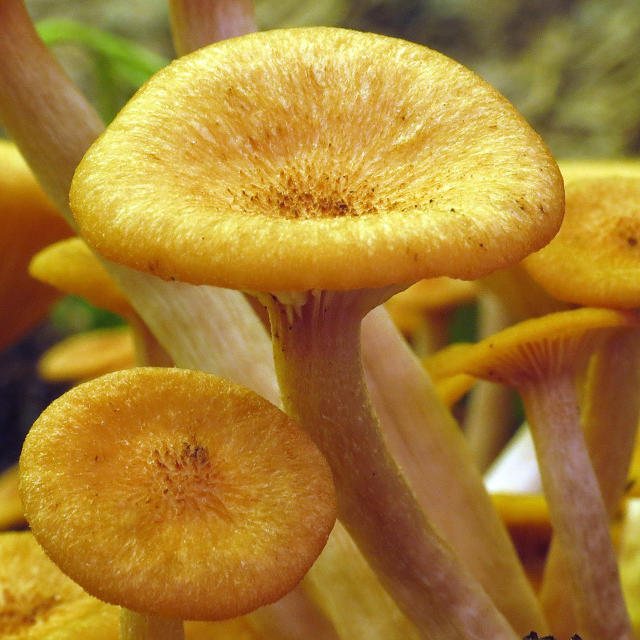


Photo 0. Fruiting bodies of a shrinking honey fungus close-up.
Nevertheless, the typical "hairy" hairiness of the fruiting body and the presence of scales on the cap are eloquent signs, by which it becomes clear that we are dealing with a representative of true mushrooms.
This mushroom bears fruit from July to October... In warm summers, fruiting bodies may appear earlier - already in June.
In terms of taste, the drying honey mushroom corresponds to other real mushrooms.

























