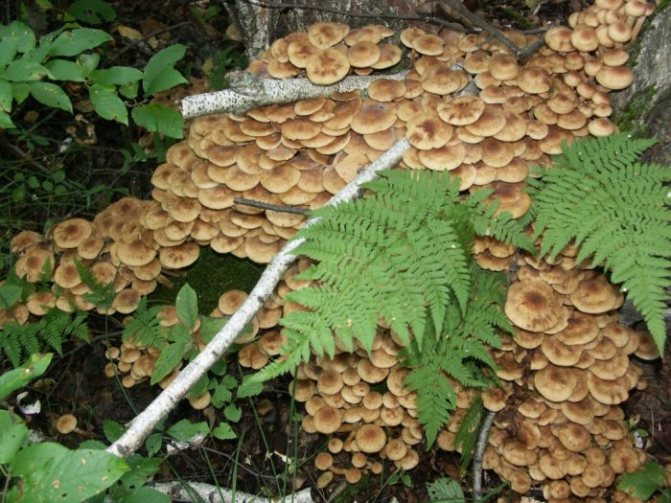
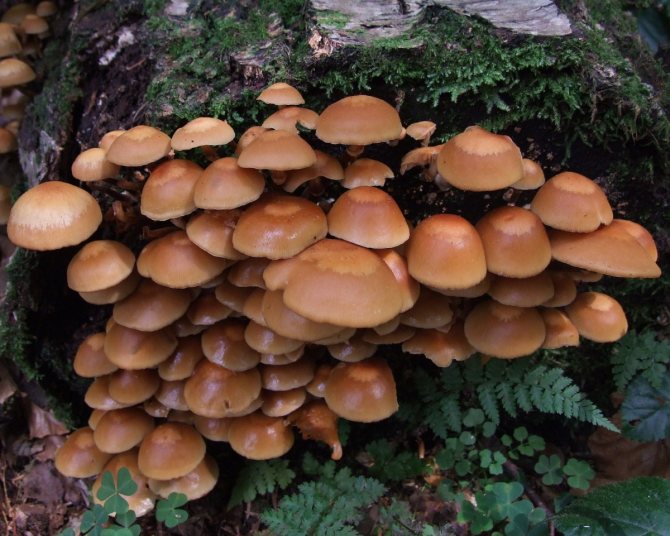
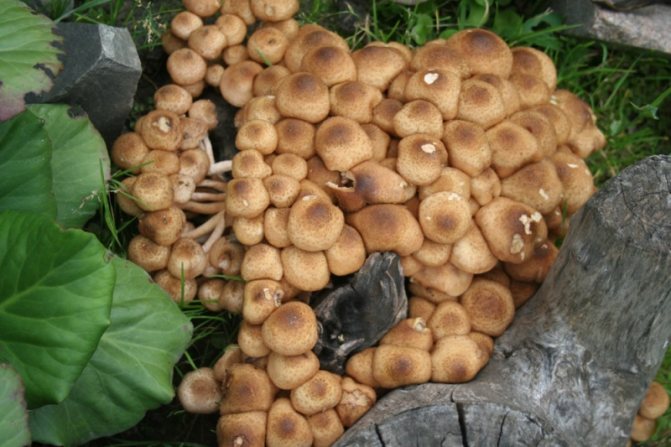
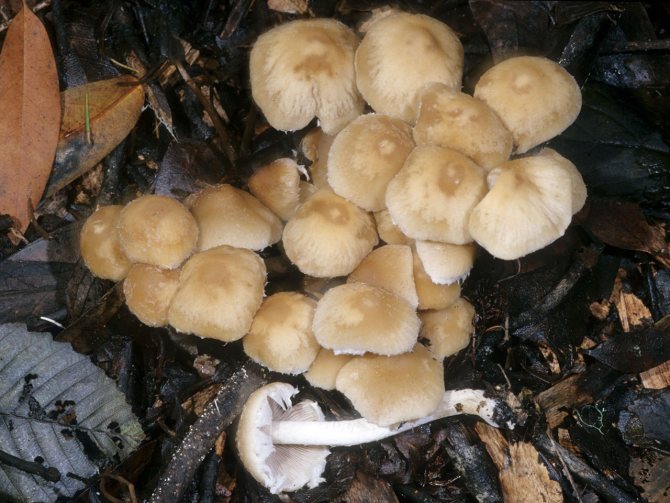
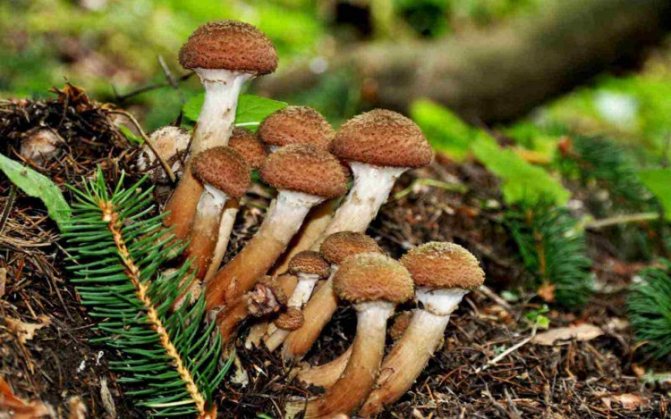
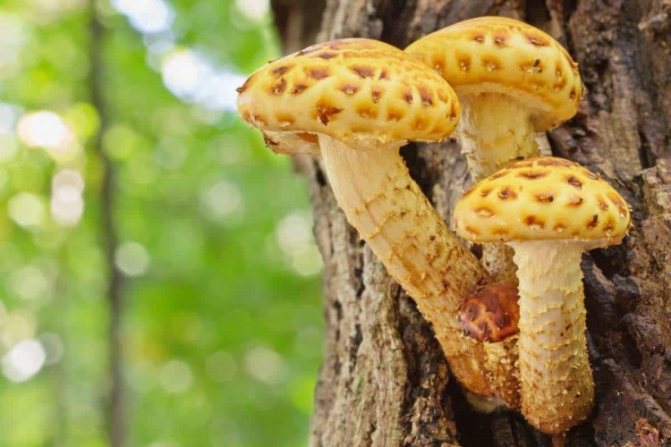
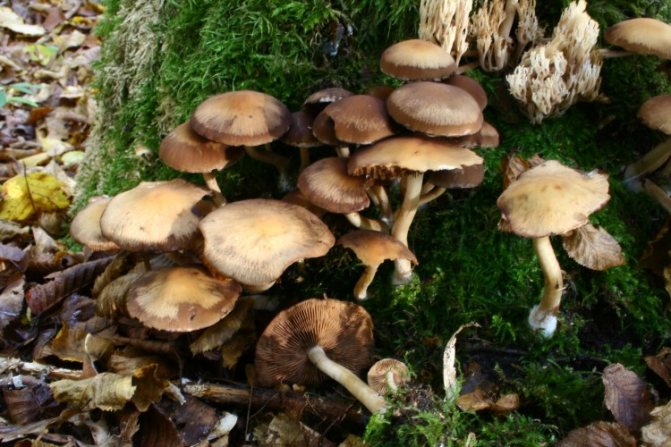
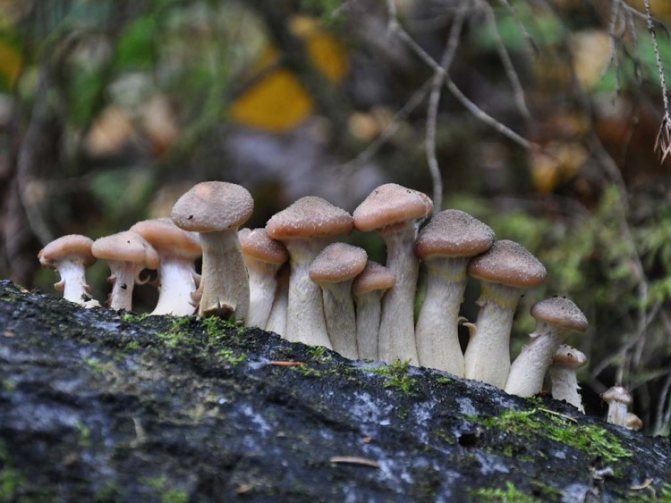
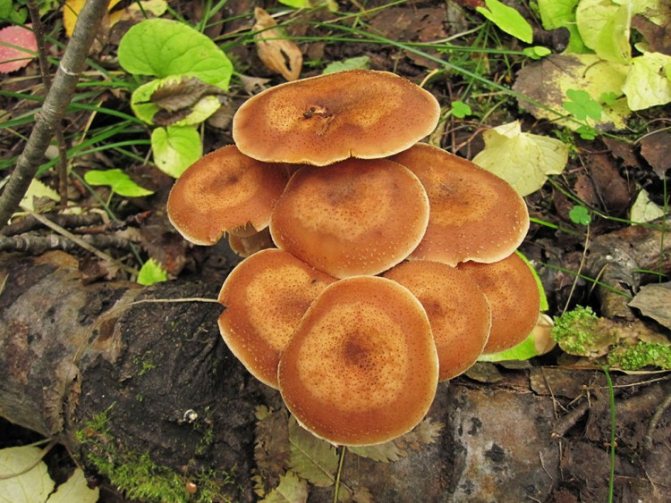
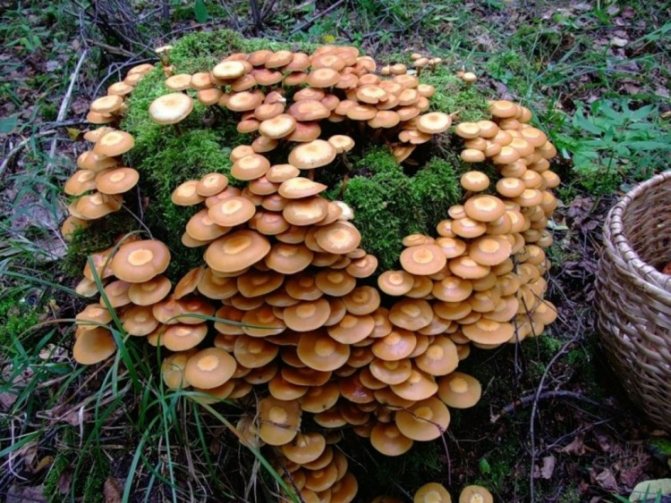
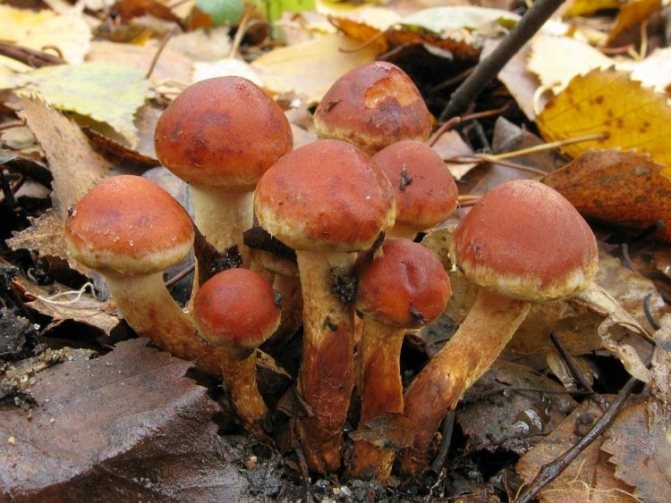
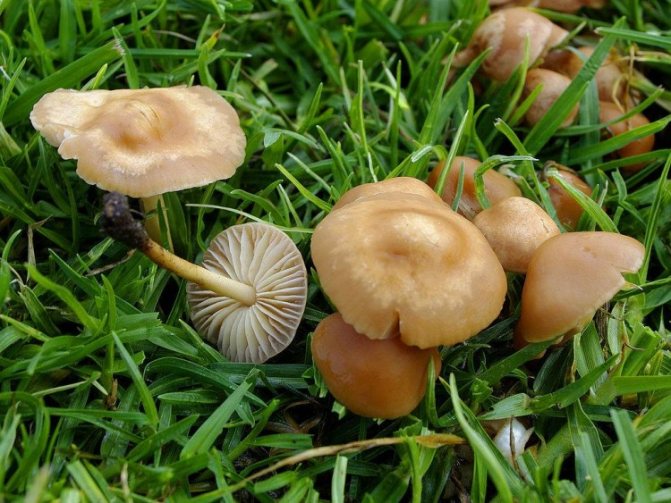
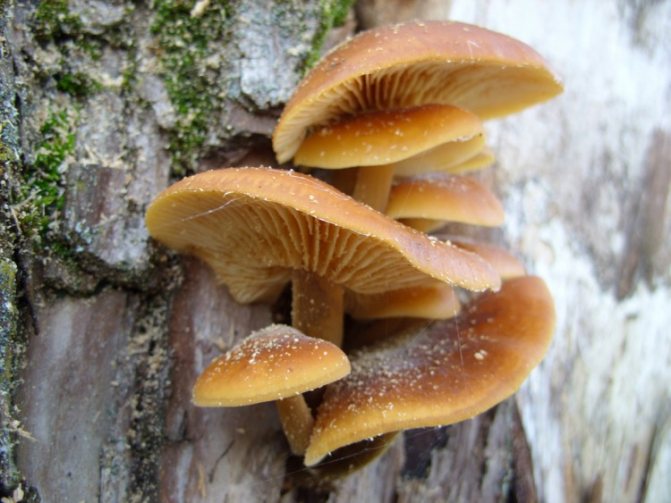
Today, more and more summer residents are thinking about growing mushrooms on their backyard plots. The easiest to breed mushrooms. All edible species can be artificially cultivated. But most often they stop at summer and winter ones.
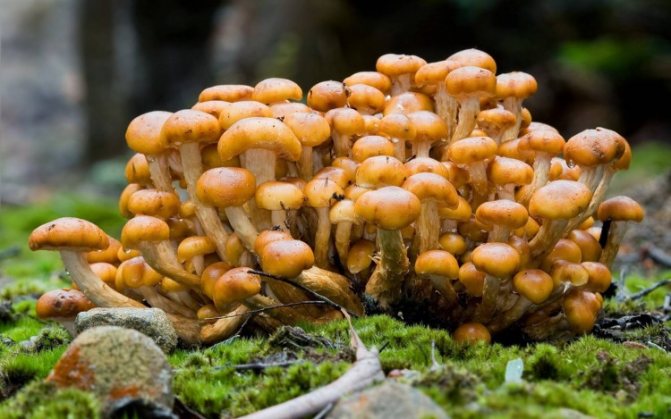

How to grow honey mushrooms at home? About this and not only in this review.


How to grow mushrooms at home
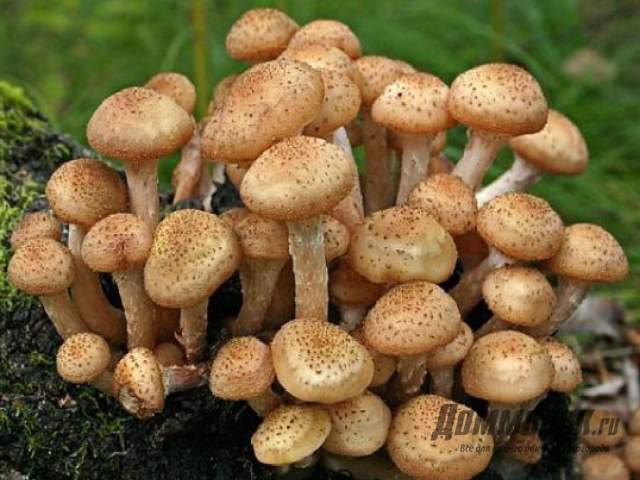
Honey mushrooms are considered one of the most popular types of mushrooms adapted for growing at home. Their attractiveness lies not only in their excellent taste, but also in their rapid growth rates, which allow them to obtain high yields in a small area. This article will tell you how to organize your own mushroom garden.
Among all types of honey agarics, winter and summer are called the most suitable for growing in artificial conditions. The first of them is appreciated not only for its good taste, but also for its medicinal properties, because this mushroom contains substances that increase the body's resistance to cancer. As you know, only a hat is taken from forest mushrooms for cooking, since the leg is too stiff. But with domestic mushrooms, both the cap and the leg are successfully used for food.
Growing conditions
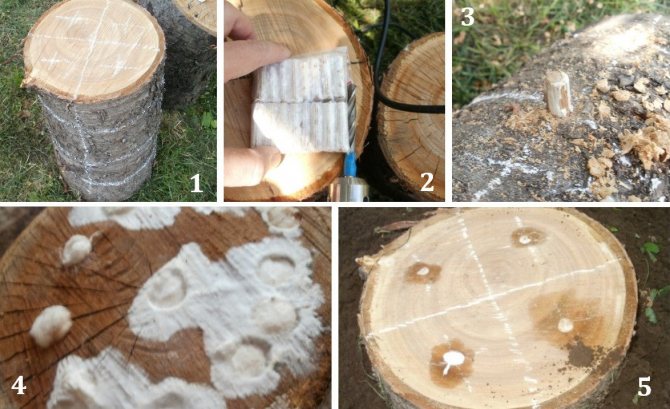
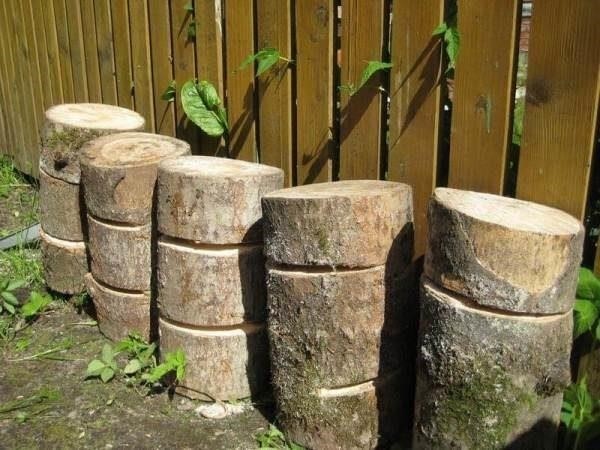
Winter species can be grown both in an apartment and in a basement, as well as in a greenhouse or just in a summer cottage or in a garden. The main thing is to ensure the proper conditions under which the mycelium will grow and multiply (Figure 1):
- A constant temperature of 10 to 15 degrees above zero.
- High air humidity (70% -80%).
- Adequate lighting level.
- Heating the room in which the mushrooms are grown in the cold season and cooling it in the summer.
- Well-established ventilation.


Figure 1. Growing options at home
It is also necessary to ensure optimal phytosanitary standards so that fungi are not exposed to pests and diseases.
Growing methods
Growing honey agarics at home for beginners can be done in several ways (Figure 2):
- On stumps (felled logs);
- In banks;
- In the greenhouse.
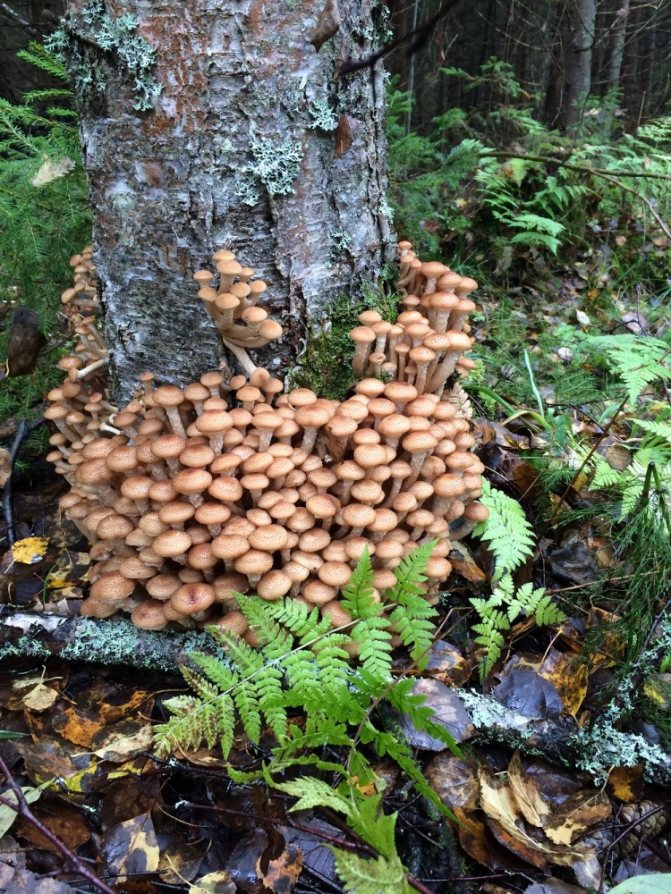
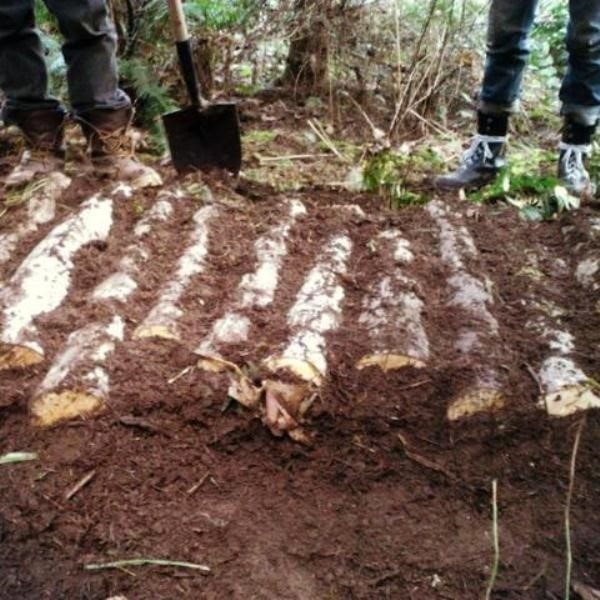
Consider the features of the technology of each of the methods. The most minimal cost is the method of growing on stumps. The essence of this method is that the mycelium of the mushrooms is introduced into small (1-2 cm) holes made in the wood, which are covered with moss.
Note: If the mycelium has been inhabited in growing stumps, then the ground around them must be watered periodically. If felled logs are used as a "container", then they must first be soaked in water for several days and only after that the mycelium should be populated.
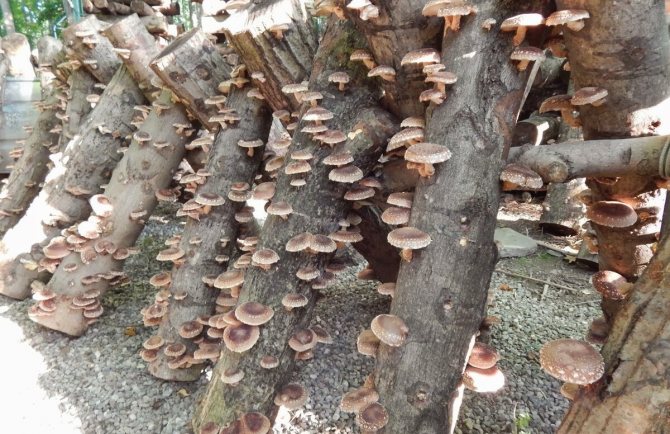
To stimulate the growth of mycelium, the logs are placed in a basement with a constant temperature (+ 15-20 C) and covered with straw. Since mushroom cultivation requires a high level of humidity, it is recommended to wipe the floors and walls of the room where the logs are located at least once a day. As soon as they become overgrown with mycelium, they must be taken out to the site and dug in. The next year you will be able to get the first harvest of honey agarics, while the mushrooms will bear fruit until the stump (log) falls apart.
If the plot itself is not there, then there is a way of growing in banks in an apartment. The main task here is to properly prepare the nutrient substrate.
You will need small sawdust (seed husks) and the same small chips in a 2: 1 ratio. This chip-sawdust mixture must be boiled in water, then allowed to drain. After cooling, nutrients are added to the resulting gruel: starch, oatmeal and corn flour at the rate of 8 g of starch and 25 g of each of the two types of flour per 1 kg of sawdust.


Figure 2. Methods of home cultivation: in a jar, on stumps and in a greenhouse
The resulting substrate is placed in jars (1-3 l) for two-thirds of the volume and compacted. Then the containers with the nutrient substrate are sterilized for 2 hours, and after it has cooled to room temperature, the mycelium is introduced into the hole 5-7 cm deep. Containers with mycelium are stored in a dark, humid room at a constant temperature of +24, and after germination of the mycelium, they are transferred to a cooler place or the temperature is reduced to + 14 + 16. For the convenience of harvesting, paper cuffs are put on the neck of the cans.
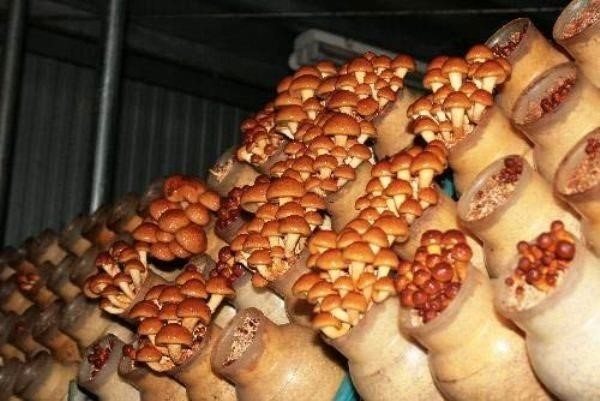
Owners of indoor facilities can use the greenhouse cultivation method. To do this, you will need special substrate blocks, which you can purchase or make yourself. Each block consists of hardwood sawdust (except oak), oats (barley) and chalk (limestone). 200 g of dry sawdust is boiled in 2 liters of water for 2 hours. After the gruel has cooled to +25, the remaining components are added: 70 g of oats (or its substitute) and 1 tsp. chalk. All components are mixed and placed in bags. Then, 20 g of mycelium is added to each such bag (block), gently kneading it.
Before tying the bag, it is necessary to put a sterile cotton plug so that the substrate inside does not dry out. The blocks are stored in a room with a constant temperature of +20 degrees. With the appearance of bumps on the surface of the substrate (this occurs within 30 days), the package is removed, and the temperature in the room is lowered to + 12 + 14 degrees. At the same time, high humidity (85%) should be maintained in the greenhouse and the room should be regularly ventilated.
Growing technology
The cultivation technology in the country and in the garden depends not only on the way they will be grown, but also on the method of obtaining raw materials for reproduction.
The most popular technologies for obtaining planting material are considered:
- The fruiting body of the fungus: for this, it is necessary to select the caps of overripe mushrooms, the reverse side of which is painted dark brown, and the diameter of the cap itself is at least 8 cm.The selected caps are kept in water for a day, then, without removing them from the aqueous medium, knead until a slurry is obtained, which filtered through several layers of gauze. Stumps (logs) are watered with the resulting talker from the spores. The wood must be pre-prepared by making small indentations on it, into which the liquid will fall. After settling the stumps, all the depressions are closed with wet sawdust or moss, and the ends of the stumps remain open.
- From the mycelium: this method is used mainly in the fall. A piece of the stump on which the mycelium grew in the forest is divided into small pieces 2x2 cm in size. These pieces of grafting wood are laid in the holes previously made on the sides of the hemp intended for cultivation. After that, the grooves are closed with sawdust or moss, and the end of the stump is covered with a dense plastic wrap, which will help maintain the desired level of moisture inside the stump. With the onset of a cold snap, hemp is additionally covered with spruce paws. In the spring, it is necessary to ensure that during the melting of snow, water does not fall on the ends of the stumps, since it can cause significant damage to the mycelium developing inside them.For this reason, it is necessary to regularly shake off the snow from the spruce branches so as not to damage the infected stump in case of a thaw. You can finally remove the branches immediately before the start of fruiting, that is, at the end of July, if we are talking about autumn mushrooms.
Remember that this type of fungus is a parasite, and therefore settles not only on dead wood, but also on living trees, shrubs and even herbaceous plants. Therefore, when growing autumn mushrooms on your site, take precautionary measures so that fungal spores do not infect fruiting crops. To do this, the stump infected with the mycelium of the fungus must be dug in a ditch 30 cm deep and 10 cm wide at a distance of 2 m.
Honey mushrooms are also well suited for growing indoors, where the required moisture level is always maintained. Therefore, the technology of growing in a greenhouse is so widely used. It involves populating half-rotted logs or stumps in bags with spore talkers. Infected logs remain in the greenhouse until the mushrooms germinate. At the same time, they must be periodically given to the sprinkling procedure. It is best to irrigate every hour from 12 to 5 pm. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. If this technology is followed, the first crop can be harvested in mid-June.
How to grow mushrooms step by step at home
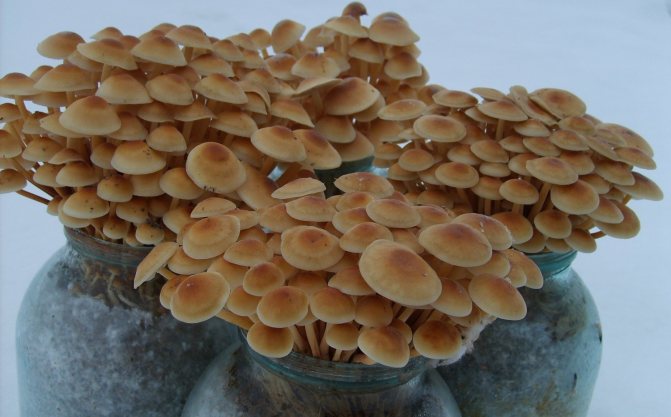
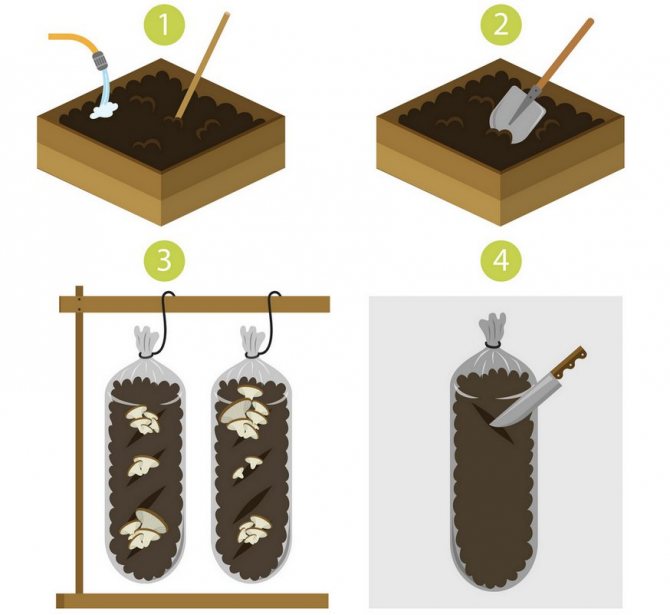
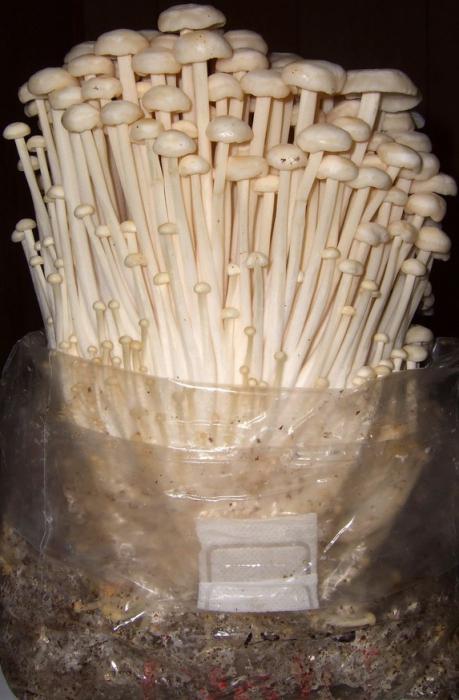
Honey mushrooms are so popular among mushroom lovers that a method was invented to grow them not just at home, but in an apartment, even if it is in a multi-storey building. You will be able to harvest home-grown honey agarics after only a month and a half from the moment the mycelium is introduced into the substrate. At the same time, in one can, with a capacity of 3 liters, you can grow up to one and a half kilograms of mushrooms. The only drawback of this method is that only winter mushrooms can be grown in this way, the size of which is ideal for breeding on the windowsill (Figure 3).
So, how to grow mushrooms in the country or in an apartment, step-by-step instructions will tell you:
- Prepare a nutrient medium from bran and hardwood sawdust in a 1: 3 ratio.
- Soak the resulting mixture for a day in water, then squeeze and put in three-liter jars, filling them half the volume.
- Use a thin, long stick to make depressions in the substrate that reach the bottom.
- Sterilize the substrate jars over low heat for an hour. After the cans have cooled, repeat the procedure again. This procedure will kill all pathogens inside the containers and prevent mold from developing.
- After the second boil, let the jars cool to room temperature, then close them with plastic lids with holes up to 2 mm in diameter.
- Introduce the mycelium through the holes made using a medical syringe.
- Banks populated with mycelium must be kept in a room with a constant ambient temperature (not lower than +20) for about 30 days.
- As soon as the mushrooms sprout, you need to move the jar to a cooler place. This can be, for example, a window sill located on the north side, or a balcony, provided that the air temperature there does not drop below +13.
- After the mushrooms reach the neck of the jar, the lid is removed, and a paper cuff is put on the neck of the vessel, which will limit the place where the mushrooms grow.
- Spray the mushroom caps periodically to maintain optimal moisture levels.

Figure 3. Features of growing honey agaric in a bank
Observing the above rules, you will be able to harvest the first harvest of winter agarics 2 weeks after germination. Mushrooms can be cut, or you can simply pull out, because in a few weeks a new wave of honey agarics will appear.
The video shows how to properly sow mycelium honey agaric when growing mushrooms in a jar.
Growing difficulties
The main difficulty in growing honey agaric is that their spores spread quickly and can settle on only rotten stumps, but also on healthy wood.
To prevent this from happening, you need to very carefully approach the procedure for sowing mycelium and cultivate mushrooms only in specially designated areas. In addition, honey mushrooms are very sensitive to temperature and humidity conditions, therefore, at all stages of growing, certain indicators must be maintained.
Required conditions for breeding
The very name of the mushroom "mushroom" speaks of a suitable habitat - stumps, large branches, logs. It belongs to the category of parasitic fungi that attack wood and gradually destroy it. Under natural conditions, honey mushrooms are found not only on living and dead trees, but also near some shrub plants, as well as in meadows and forest edges. They grow in large groups, the fruiting period begins in the fall and lasts until the onset of frost.
In artificial conditions, it is not enough just to place stumps sown with mycelium and wait for rich harvests. A number of basic rules must be followed:
- to organize a place for growing mushrooms with a free area of 15–20 sq. m;
- achieve high air humidity (70–80%);
- maintain the temperature within 10-15 degrees in the winter season and 20-25 in the summer;
- provide uniform illumination and protection from direct sunlight;
- eliminate air stagnation by arranging a high-quality ventilation system (due to carbon dioxide, the mycelium will not be able to fully develop).
At a stable temperature and high humidity, mushrooms will be able to quickly adapt to new conditions and begin to grow.
How to grow mushrooms in the country
To grow winter mushrooms in the country, you need a greenhouse or any basement in which you can provide a constant high level of humidity. In addition, you will need to purchase a special nutritious substrate for growing mushrooms or prepare it yourself, as well as stock up on granular mycelium of mushrooms.
We will describe in more detail the features of growing at a summer cottage.
Features of the
It is easy to prepare a mixture for growing mushrooms on your own using dry sawdust (200 g), oats (70 g) and slaked lime (1 tsp). All of these components are mixed, then soaked for 5 minutes, then boiled for another 45 minutes. After that, the water must be drained, and the resulting mixture must be dried for 20 minutes over low heat.
The finished substrate is cooled to a temperature of +25 degrees, then laid out in prepared containers (jars, bags). 20 g of mycelium are poured into the same containers, the containers are hermetically sealed, after inserting a plug of sterile cotton wool. In this state, the substrate with mycelium is stored at a temperature of + 15 + 20 degrees for a month. After germination of the mycelium, the bags are transferred to the material where fruiting will take place.
Sowing mycelium
Inoculation (seeding) of the mycelium. Oyster mushroom mycelium (mostly shock-free strains are used) is taken out of the refrigerator 3-4 hours before sowing and kept at room temperature. Before the start of inoculation, the container for the mycelium, instruments (tweezers) are disinfected (with alcohol).

Immediately before seeding the mycelium, the substrate can be sprayed with a liquid stimulant. The mycelium is applied with tweezers at the rate of 4-5% (45-50 g per can) of the mass of the moistened substrate. Sowing is carried out by two people. One holds a container with the seed mycelium: and brings the mycelium into the jars with tweezers, the other opens and closes the lids, ramps, feeds the jars for seeding and rearranges the already seeded jars. After sowing, the jars are marked, noting the date and month of sowing, the mycelium strain. Then the jars are transferred to the incubation room.
After three days, holes about 5-6 cm long are cut in the bags. After 14-20 days, the mushrooms will sprout and become noticeable.
They can be used to grow mushrooms both on the street and in the house at temperatures from +10 to + 25 ° С. The larch log should not be rotten, but moist and barked. Length 300-500 mm, diameter 200-500 mm. If it is dry, then it is soaked in water for two or three days. Then they are pulled out and allowed to drain off the water.
One- and two-liter jars or durable plastic bags with a volume of at least 2 liters are suitable for growing honey mushrooms. The resulting mixture is filled into a container by 2/3 of its volume.
With a disinfected stick, holes are made in the substrate 5 cm deep, no more than 1 in diameter. It is not difficult to calculate the required amount of mycelium - it should be 2-7% of the mixture mass.


The holes made are filled with mycelium. The temperature of the mixture at this moment should be 25 °.
Another way is when the substrate has cooled to 25 °, the mycelium is added to it and gently mixed with a sterilized wooden spatula. After that, the containers are filled.
Incubation (germination) of mycelium. The incubation period lasts 18-20 days. Incubation proceeds well at a temperature of 22-24 ° C. Based on this, they are looking for a suitable room (basement, cellar, etc.). To do this, if necessary, the jar is insulated so that the neck (lid) is free (since gas exchange takes place through the lid).
You can grow mushrooms on logs in three ways:


Greenhouses and greenhouses are well suited for temperature and humidity levels for growing mushrooms. Logs, stumps, logs are moistened and placed in a greenhouse. After that, holes are made in the wood and myceliums of honey agarics are laid, or they can be poured with a solution containing fungal spores. The planting is watered regularly to maintain moisture, and also monitor the air temperature. It is also possible to grow mushrooms in greenhouses in jars, bags or on substrate blocks.
Banks are closed with polyethylene lids, in which a hole with a diameter of 1 cm is pre-made. Gases released by the spores of the fungus will escape through the hole. In order to prevent moisture evaporation, the hole is covered with a cotton plug.
The cotton plug should not fit very tightly into the hole or be tight. It should be slightly fluffed up.
When growing flammulina in bags, they must be tied, leaving a small hole. It is also closed with a stopper.
How to grow honey mushrooms in the country from mycelium
Summer mushrooms can be grown from mycelium at their summer cottage. The optimal substrate for growing them will be old stumps of deciduous trees such as maple, birch, aspen or damp boards, or trimming logs (Figure 4). Moreover, they are much easier to grow than mushrooms or oyster mushrooms.
Features of the
It is important to know that when growing honey agaric on stumps that are on the territory of the garden plot, there is a risk of infection with the mycelium of fruit trees, which leads to the destruction of their wood and, as a result, to the death of the tree itself.
Therefore, try to choose those stumps that are far from living plants, or grow mushrooms indoors.
The ways
In early May, when the optimum level of humidity and temperature is observed, it is necessary to irrigate the surface of the stump with sowing mycelium. It is recommended to pre-make small indentations in the hemp to better fill it with mycelium. After populating the holes, they must be sealed with moss. Experienced mushroom pickers also practice breeding summer honeydew by grafting small pieces of wood infected with mycelium. They are inserted into pre-prepared holes on the surface of the hemp.


Figure 4. Preparation of mycelium for growing honey agaric
No matter how the mycelium is colonized in the stump, they must be covered with a dense film in order to create an optimal microclimate for the rapid development of the mycelium.One such mycelium allows you to harvest honey agarics for 3-6 years, while the first time you can remove the mushrooms in a year after the introduction of the spores.
You can also infect with fungal spores from trimming logs or even damp boards. For this, the spores of the fungus are added to a bottle of water, shaken thoroughly and poured over the material for growing with this solution. It is desirable that there are more gaps on the material in which the mycelium of the fungus can settle. Subsequent care consists in regular irrigation of the wood to maintain the required moisture level.
Features, nuances and secrets when growing
Experienced mushroom pickers claim that no matter how simple the growing method is chosen, certain rules must be followed.


Basically, the recommendations boil down to the following tips:
- The room should be equipped so that it is possible to regulate the temperature indicators at each stage of the growing season. For this, a ventilation, heating and humidification system is built. The lack of fresh air is fraught with low growth of mushrooms.
- You can choose different soil. The main rule: it should not contain signs of mold or decay.
- It is better to place containers with grown mushrooms on racks. The main condition is that they must be metal, wooden ones quickly rot.
- It is better to purchase ready-made mycelium from trusted suppliers. Only in this case can there be a guarantee that it is not infected with pathogenic bacteria.
- Before harvesting the mycelium, it should be disinfected: treated with boiling water or steam.
- Storage and handling of crops should be carried out in isolated areas. It is also desirable to provide a place for processing the spent substrate. It must be at a distance from the mushroom plantation.
The main difficulty in cultivating honey agaric is the rapid spread of spores. If the growing place is a summer cottage, and the plantation is located on the street, it is enough to dig a trench. A special room is allocated in the room.
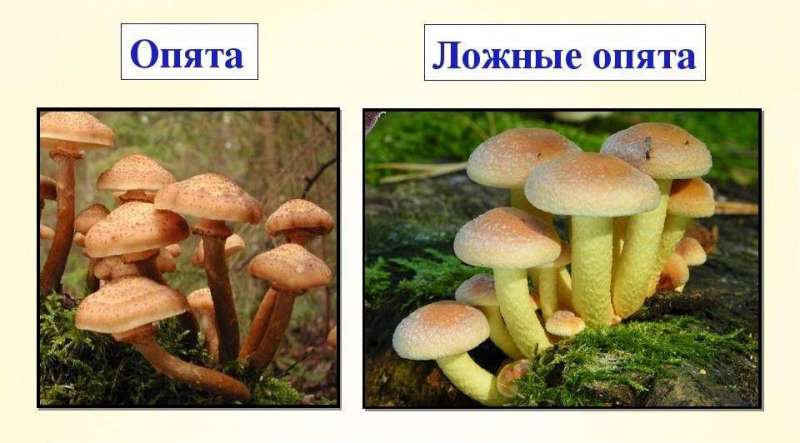
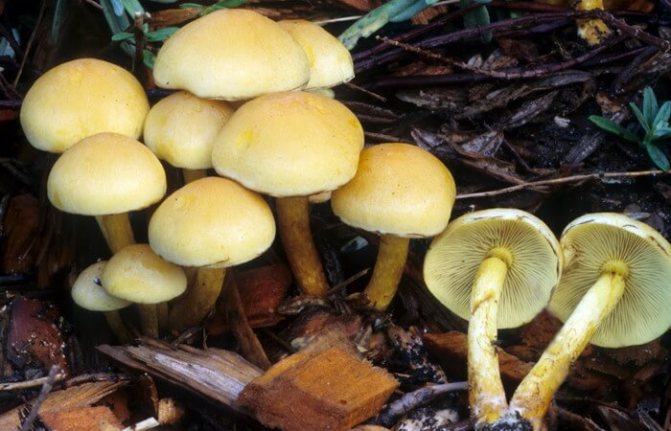
We recommend that you study what is the difference between edible and false mushrooms.
As you can see, cultivation of honey agarics on your own cannot be called light production. As in any business, certain rules must be followed. But the advice of experienced mushroom pickers will help in this activity, which over time can develop into an exciting business. The resulting harvest will delight you and your loved ones, and, possibly, will grow into a profitable business.
Growing honey agarics at home on stumps
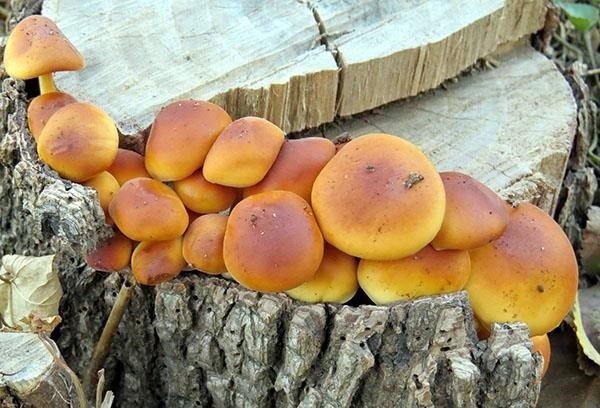
In your own garden or in your summer cottage, you can grow mushrooms on the stumps of deciduous trees: birch, poplar, aspen, apple, pear. The main thing is that the stump chosen for breeding is not affected by rot or tinder fungi. 2-3 days before the introduction of the mycelium, it is necessary to periodically moisten the stumps with water.
You can use both purchased mycelium and self-collected forest material. To do this, you need 10-12 mushroom caps, which must be poured with a bucket of rain (river, lake) water and kept like that for a day.
Note: It is important to know that water from stagnant bodies of water (pond, quarry, ravine) is not suitable for these purposes, since it can be contaminated with pathogens.
The present hats are kneaded with hands into a gruel, which is filtered through several layers of gauze. The end and side parts of the selected and prepared stump are poured with the resulting spore solution. To increase the likelihood of stump infestation with mycelium, it is recommended to make small holes with a diameter of 2 cm in the wood at a distance of 4 cm from each other. It will be much more convenient if the holes made are staggered. These recesses are additionally filled with spore gruel and covered with moss or sawdust. In this case, the end of the hemp is left open. Growing mushrooms in this way, you can get the first harvest of honey agarics in 2 years (Figure 5).
It is necessary to know that the mycelium of the fungus can infect other healthy trees in the immediate vicinity of an infested tree stump. Therefore, you need to take protective measures by digging in the infected stump with a ditch 30 cm deep and 10-15 cm wide at a distance of 2 m around it.


Figure 5. Features of growing honey agaric on stumps
The cultivation of honey agarics can also be carried out using wood sticks infected with mycelium, which are inserted into the prepared holes on the stumps. This procedure is carried out in April-May, when the sun is already active enough and can dry the mycelium. Therefore, it is recommended to cover the inhabited stump with a layer of straw or dry grass. For the winter, the stump must be covered with spruce branches. In snowy weather, regularly shake off the snow accumulated on the branches, and with the arrival of spring, make sure that melt water does not fall on the end of the stump, since this greatly inhibits the development of the mycelium, which means that you will get the harvest much later.
Mycelium germination conditions


Fruiting mushrooms. A room is allocated for fruiting, where the air temperature does not exceed 20-22 ° C (cellar, basement, etc.). During fruiting, if possible, maintain an air temperature of + 18-20 ° C. Lighting for 8 hours a day. The room is ventilated 3-4 hours a day, making small drafts.
This method of growing mushrooms allows you to do without personal plots. The jar can be placed on the balcony or on the windowsill.
A substrate is made for the growth of the mycelium - a mixture of sawdust (preferably larch species) and bran in a ratio of 3: 1. For one day, it is poured with water, then squeezed out and not strongly compacted.
After the mixture has cooled, a depression is made in it with a clean stick to the bottom of the jar and the mushroom mycelium is placed. The container is closed with a lid with holes and covered with wet cotton wool to maintain moisture. The jar is removed to a dark and warm place. As it dries, the cotton wool is moistened.
The mycelium will sprout in a month, and after 15-20 days the first mushrooms will appear. As soon as the mushrooms rise, the container is placed on the windowsill on the north side, or darkened from the sun. When they grow to the lid, it is removed and the neck of the can is wrapped with a wide strip of cardboard. This will help the mushrooms to hold on during growth. To maintain moisture, the mushrooms are sprayed with water. As it grows, the crop is cut off, and the remaining legs are pulled out. In 14-20 days, new mushrooms will grow.


The container is placed in a dark place where the temperature is maintained at about 25 °. After 2-3 weeks, the mycelium will germinate and fruit bodies will form on it.
The jar is transferred to a brighter place, the air temperature should be about 15 °. It can be a window on the north side, a glazed loggia.
The lid is removed from the can, the package is untied. Moisture is maintained by regularly spraying the caps and the substrate. If honey-colored drops appear on the caps, then the watering is excessive. The presence of a white coating indicates that there is not enough moisture.
If it is planned to grow winter mushrooms in a basement or garage, their walls are preliminarily whitewashed with lime or treated with formalin for disinfection. The room must be equipped with forced ventilation and an air heater.
To maintain optimal humidity (90%), the nozzle is watered. During watering, remove the nozzle and moisten it from the inside so that water droplets remain on the nozzle (Fig. 11). Wetting of the nozzle is carried out 5-6 times a day. You cannot water the banks directly. The crop is harvested 16-18 days after the end of the incubation period.


Planting mycelium on a stump is done in a warm, but not hot season. In the forest, on old stumps or tree trunks, they find mycelium and separate its part along with a piece of wood. For planting, recesses are cut out in the hemp, and pieces of mycelium 1-2 cm in size are laid. Then cover with wet moss or sawdust. The soil around it is watered, preventing it from drying out.
When the caps appear above the container, a ring of thick paper is put on the neck. This prevents the mushrooms from decaying and allows them to grow up as high as possible.
The ripening period of mushrooms is 45 days from the moment of sowing the mycelium. Cut off the mushrooms at the neck of the jar. The legs remaining inside are carefully removed, and the substrate is moistened and again covered with a lid. New mushrooms will grow in 3 weeks.
In one container, you can harvest 3-4 times, in the future the mixture is depleted, and it should be replaced.
For continuous harvesting, the mycelium should be populated in separate containers at intervals of 10 days. Then the mushrooms can be cut much more often.


Oyster mushroom harvesting. The crop is harvested on 16-18 days from the end of the incubation period. Harvested by cutting all fruit bodies from the cans at the same time. After harvesting the mushrooms, the top layer of the substrate, no deeper than 1 cm, is removed from the jar. Pour 200-300 g of water (it is necessary that the water does not stagnate), put on (previously well washed in water) nozzle and put it in its original place. After 16-18 days, a second crop is obtained. Thus, several crops are harvested from one can. The highest yields are obtained from the 1st and 2nd waves (harvesting), and subsequent yields are low. The collected mushrooms are stored in a refrigerator at a temperature of + 2-4 ° C, and for long-term storage, the mushrooms are processed or frozen.
Overripe mushroom caps with a dark brown color underneath are selected. They are placed in a container and filled with clean water for 24 hours. Then, without getting them out of the water, rub them with your hands. The resulting mass is filtered. A solution containing spores is poured over stumps or logs with notches made in them. Thanks to them, the wood is better impregnated. Then they are covered with wet moss or sawdust. Spores germinate for a long time, mushrooms will grow only after 1-2 years. After the mycelium has grown on wood or hemp, it can be propagated. For this, a part of it is carefully separated and transplanted to a new place.
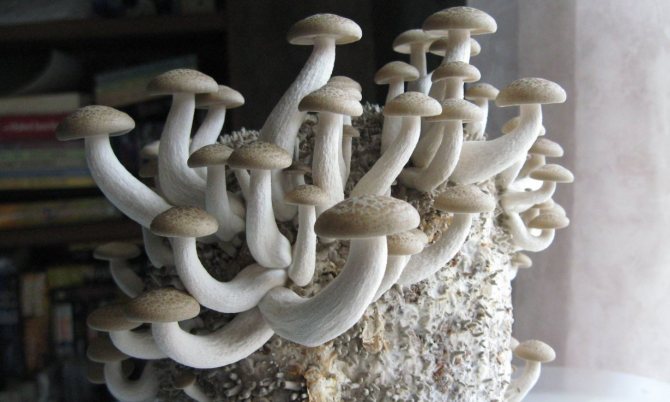
Winter honey agaric: growing at home
Among the edible species of honey agarics, it is easiest to grow winter mushrooms at home (Figure 6). Their small size allows them to be bred even in a three-liter jar on the windowsill. Various materials are used as a growing substrate: straw, buckwheat husks, sunflower husks, dry sawdust of deciduous trees. To give the substrate the necessary fertility, various additives are mixed into it, for example, bran, brewer's grains, corn cobs.
Then this nutrient medium is kept in water for 24 hours and squeezed out. Glass jars are filled with the prepared substrate to half their volume and closed with lids with holes made with a diameter of 2 cm. For these purposes, you can also use cotton-gauze plugs. The sealed cans are pasteurized for one and a half to two hours on low heat several times, after waiting for the cans to cool.


Figure 6. Methods of growing winter mushrooms at home
After the last pasteurization, when the jars with the substrate have cooled to +24 degrees, they begin to plant the mushrooms. To do this, with clean hands, pre-mashed pieces of mycelium planting material are placed in each jar. Closed jars are stored in a room with a temperature of + 20 + 24 degrees until the mycelium sprouts. After germination of mushrooms, the jar is placed in a cooler place: on the windowsill, loggias facing the north. When the mushroom caps reach the neck of the jar, it is necessary to put on it a paper cuff 5-10 cm high so that the mushrooms grow upward in the form of a bouquet. At this stage, it is very important to ensure high air humidity, therefore, it is necessary to spray the mushroom caps with water and moisten the cuffs. After the mushrooms have completely emerged from the jar, they must be cut off, and the jar must be closed again and taken out to a warm place. In a week or two, the second batch of mushrooms will ripen.
Possible difficulties
One of the most common difficulties when growing mushrooms at home is the rapid spread of spores and their infection of healthy wood. In street conditions, this problem is solved by organizing a trench. If cultivation is carried out indoors, then a special place must be allocated for the mushrooms.
If you plan to breed mushrooms on a large scale, then a separate room (plot, greenhouse) should be allocated for them. With the right organization of the necessary conditions, growing mushrooms can be a good business.
The difficulty in growing honey agaric is also the need to maintain a certain temperature and humidity. The easiest way to organize such conditions is in greenhouses. In an apartment, the need to comply with technology can cause some difficulties.
Honey mushrooms are valued for their taste. The simplicity of these mushrooms allows you to grow them at home. This can be done in different ways. To get a good harvest, you must follow the rules of cultivation.
0
Poplar honey agaric: growing
Poplar honey is highly prized for its pleasant nutty flavor and crunchy texture along with porcini mushroom and truffle. The main disadvantage of this mushroom is its short shelf life: raw poplar mushrooms are stored for about 20 hours, and frozen - no more than 6 days. For this reason, they cannot be purchased in the retail network. But poplar honey fungus can be easily grown at home, just in a flower pot (Figure 7).
First of all, you need a wet poplar or maple log from a healthy tree, free of branches. The height of the log should be about 30 cm, and its diameter should be 15 cm. It is necessary to make (drill) 2-3 holes with a diameter corresponding to the diameter of the sticks with mycelium. With clean hands, sticks with mycelium are inserted into the holes made, then they are sealed with wax, and the log is tightly wrapped in polyethylene, making several holes for ventilation. This kind of "container" with mycelium is stored in a dark and humid room until the mycelium sprouts (3-4 months). This can be determined by the white mycelium threads clearly visible in the holes. After that, the logs are placed vertically in flower pots measuring 70x15x15 cm, filled with earth (mulch, poplar sawdust). In this case, the logs should be deepened into the pot by 8-10 cm. Thus, you can get 2-3 harvests of mushrooms per year, and the mycelium will grow within 5-6 years.


Figure 7. Features of growing poplar mushrooms at home
You can also grow poplar mushrooms in your own garden or in your vegetable garden. A piece of loose fertile land near trees is ideal. In the spring, in this area, a recess of 10-12 cm is dug, at the bottom of which corrugated cardboard is laid, then a centimeter layer of sawdust. All this must be spilled with water, and when it is absorbed, the mycelium is placed on the substrate on the sawdust. The mycelium is covered with a layer of sawdust mulch or wood chips and watered again. Level the edge of the recess to the general level of the site using a slightly mulched soil layer. So that the substrate in the hole does not dry out, it must be additionally covered with straw or tree bark and watered abundantly again. Subsequent care consists in maintaining the soil moisture level by watering it when it dries up to a depth of 3-4 cm.
During the fruiting of poplar mushrooms, it is recommended to collect mature mushrooms every day so that the mycelium does not get sick, and in the cold season, take care of additional shelter for it.
Similar species
Several varieties of honey agarics grow in nature, but only two can grow in artificial conditions without loss of taste:
- summer;
- winter (so-called flammulina).


The winter look itself attracts with its delicate, unique taste.
They are consumed fresh and dried, and both caps and legs are taken for processing (unlike wild-growing relatives). Flammulina caps are reddish-yellow in color, grow up to 9 cm in diameter. The pulp is yellowish, with a pleasant mushroom taste. Under natural conditions, mushrooms ripen in autumn and can stand until December, and with frequent thaws - until February.
Important! Winter mushrooms contain light toxic substances that are destroyed 20 minutes after cooking.
Summer the variety is slightly smaller - the cap is up to 6 cm. Their flesh is watery, and the taste is soft, not pronounced. Mushroom pickers claim that they can be eaten raw by simply picking them off the hemp. In its natural environment, this species grows in colonies on rotten wood.


If the climate is mild, then you can pick such mushrooms all year round.
A rare species - poplar honey... The place of growth can be not only a poplar stump, but also a maple log. This variety differs in a nutty flavor and a crumbly structure.


But poplar honey has a big drawback: it is stored for no more than a day, and in frozen form - no longer than a week.
Perhaps the rarest form is the marble honeydew... Such mushrooms are considered delicacies. They taste sweet, nutty, crunchy. This variety is also prized for its lack of fat and high concentration of nutrients. In the cold they are stored no longer than 1-1.5 weeks.


Any housewife, even a beginner, knows that mushrooms need to be soaked in water. But not marble - they absorb moisture and become brittle.
Marble honey mushroom: growing at home
Marble honey fungus belongs to delicious mushrooms. When cooked, it has a sweet smell, a pleasant nutty flavor, and a slightly crunchy texture. In its raw form, this type of mushroom is stored in a cold place for up to 10 days.
Note: The difference between marble honey agarics and all the others is the fact that this species cannot be soaked in water, because, gaining moisture, they become brittle. In addition, marble honeydew contains a large amount of nutrients, with a complete absence of fat, which makes it possible to use dishes from it in diets aimed at weight loss, to stabilize metabolism. A positive effect is known in the treatment of anemia, asthma, diabetes, organs of the cardiovascular system and many other diseases using marble honey agarics.
For the cultivation of marble honey agarics, a substrate consisting of cotton waste (85%), rice or wheat bran (10%), sugar and gypsum powder (1% each), lime (3%) is used. Cotton waste is filled with water with lime dissolved in it. The resulting mixture is wrapped in a film for a day, then rice bran and gypsum are added to it, the acidity level is checked (it should be 6.5 - 7.5 pH).
The compost is placed in plastic bags or jars with a wide mouth, hermetically sealed and sterilized for 3 hours. The mycelium is populated into a sterile substrate, the bags are transferred to a storage room, in which the air temperature is + 18 + 26 degrees. After 40 days, the mycelium sprouts and ripens for another 30 days. Bags with ripe mycelium are placed on special racks in a cool room (+ 13 + 15). They must be opened, the substrate must be moistened, the bags must be covered with damp paper or cloth. After the appearance of mushroom caps, the damp cloth must be removed, further maintaining the necessary humidity by spraying air at the same temperature. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure the proper level of lighting in the room. If mushrooms are grown without the sun, they must be illuminated with a fluorescent lamp for 10-15 hours.
For harvesting, you need to gently cut off the bunches of mushrooms while pressing on the substrate around the root with your other hand. For the next mushroom wave, it is necessary to clean the substrate from the legs of dead mushrooms and add water to it. A new crop will appear in 2 weeks.In total, one such bag (package) gives 4-5 harvests of marble honey agarics.
In glass jars
This technology is the perfect choice for an apartment. You will need bran and sawdust. They should be mixed in proportions of 1 to 3 and boiled. Then you can add the nutrient mass. It is a mixture of oatmeal and corn flour and starch.


The composition is distributed in jars and sterilized for 2 hours. Then it is cooled, depressions are made and the mycelium is planted. After the container, it is necessary to transfer it to a dark place with high air humidity.


As soon as the mycelium sprouts, the room temperature is reduced to 16 ° C.


Seed material and technology for its production
Honey mushrooms are grown in two ways (depending on the seed), it is either a fruiting body, i.e. old mushrooms or mycelium.
The first technology step by step:
- remove the hats (usually they have a circumference of about 8 cm, with a dark brown tone from the inside);
- the material is placed in a container with water and soaked for a day (without rinsing and draining);
- the caps are crushed to a state of gruel;
- the resultant is passed through a gauze cloth;
- the liquid is poured into a glass vessel and used for inoculation;
- grooves are made on the wood of a stump or log, the resulting slurry is poured into them;
- the grooves are covered with sawdust.
The planting method from such seed is used at any time of the year in a closed building.
Mycelium is the mycelium from which honey agarics, champignons and other mushrooms are grown. You can find it in the forest in autumn:
- the mycelium is divided into pieces 2 * 2 cm;
- holes are made on the sides of the hemp;
- pieces of mycelium are placed in the connectors and covered with moss;
- from above, the holes are wrapped with polyethylene to create greenhouse conditions;
- at the onset of frost, the mycelium is covered with coniferous branches;
- if the planting stump is located in an open area, it is protected from excess moisture: it is cleared of a snow embankment;
- spruce branches, polyethylene and moss are harvested in June for summer ones, at the end of September for winter ones.
The advantage of growing from this material is that it can be kept outdoors.
Preparation and landing
How to grow mushrooms in the country? First you need to infect the old tree stump with the spores of the fungus. It's not hard. This will require the caps of already adult mushrooms. They must be laid out with the plates down on a blank sheet of paper. Spores should spill out of the caps. They look like dark dust. It is recommended to pour spores into a bottle of water and shake well.
It is also worth preparing the stump itself in advance. It is worth sawing off round timber from it, the thickness of which should be from 3 to 5 centimeters. After that, the upper part of the stump must be cut crosswise. This can be done with an ax. The more cracks are formed, the better.
Now it remains to infect the stump with spores. This is done quite simply. It is necessary to water the prepared wood with water, which contains honey agaric spores. After that, it is worth nailing the round timber from above, which was sawn off from the stump.
conclusions
- Before you start growing mushrooms at home, you should decide on the technology. It depends on living conditions, available funds and the type of cultivated honey agaric. Most often, honey mushrooms are bred on wood (stumps) or in banks.


- Having chosen the cultivation technology, you need to purchase the mycelium of the fungus. They buy it or find it in the forest. Also applicable for planting spores of mature mature mushrooms.


- Observing the conditions for planting and caring for mushrooms, it will soon be possible to harvest honey agarics.


Description
Honey mushrooms can be found in deciduous and mixed forests of Russia. They grow on dead wood, stumps, rotting wood, diseased, old or dry trees, under bushes. Most often, you can see mushrooms on birches, poplars, lindens, and in mountainous areas - on pine and spruce trunks. Stropharia can also grow on the ground (wet meadows, forest clearings near lakes and streams). In this case, they occupy large areas.
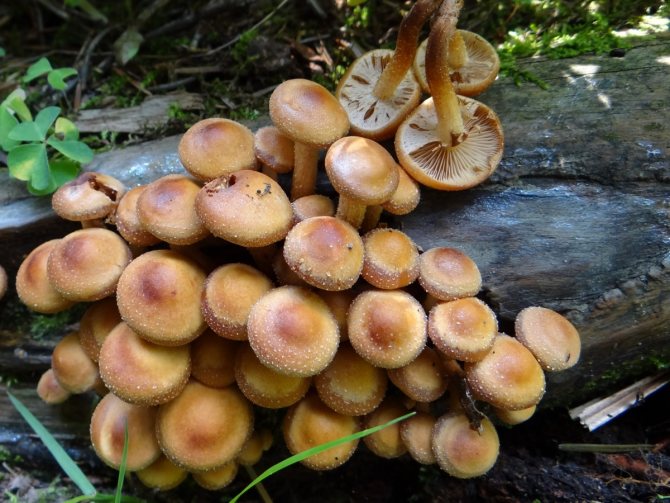


Summer honey mushroom.
Colonies of honey agarics growing on trunks and stumps seem to gird them like a ring, therefore, translated from Latin, the name of the mushroom means "bracelet".


The young summer honey agaric has a convex cap, the old one has a flat one, with a tubercle in the center. Its diameter varies from 3 to 6 cm, and its color depends on the weather. On clear days without precipitation, its surface is matte, honey, creamy beige, after rains or in the morning it becomes wet, light brown, translucent through.
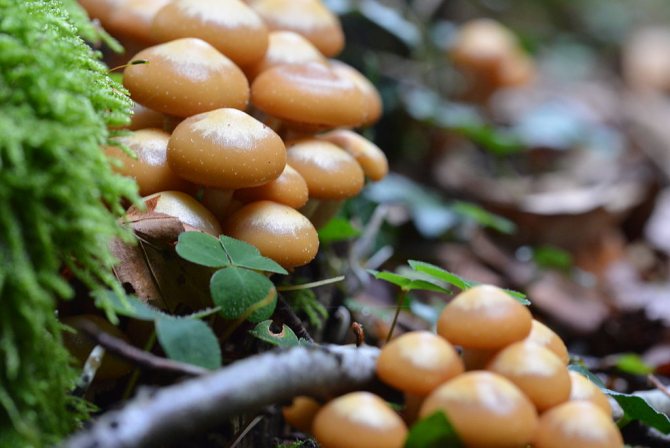


Young summer honey agaric.
Hymenophore - the lamellar layer of the body has a brown-beige color (the older the mushroom, the darker the color). The plates are of an adherent type (grow to the stem).
The diameter of the thin leg is up to 1 cm, and the height is up to 7 cm. The flesh of the leg is denser than the cap body, tinged with a reddish brown color, and covered with small dark scales on top. In very young specimens, the hymenophore is covered with a light film. Soon it breaks and becomes a ring encircling the leg from above. Then the ring collapses and disappears. Old copies no longer have it.
The choice of material for planting
Growing honey agaric on stumps is a simple process, but a long one. The main thing is to choose the right type of wood. They grow best on birch stumps. This material retains a large amount of moisture even after felling. At the same time, the dense bark protects the wood from drying out.
If mushrooms are planted in the garden, then it is worth using stumps of old pears and apple trees for these purposes. Honey mushrooms also grow well on alder, aspen and poplar chocks. It is worth considering that mushrooms are capable of destroying any stump in 6 years.
Do not use pine and spruce for growing this type of mushroom.
Interesting Facts
- Very often you can see such a phenomenon as the glow of stumps. This happens when the stump is covered with autumn mushrooms. The mushrooms themselves do not glow, but due to the fact that there is a contrast between the wood and the mushroom, the effect of a light bulb burning is created.
- The mycelium of the honey fungus, which is located in the ground, can reach a meter in size, and the fruit that we see can barely rise above ground level.
- Scientists have proven that all types of honey agarics appeared 400 million years ago, when dinosaurs walked the Earth. In the course of evolution, they almost did not change their structure, only broke into edible and inedible.
- Honey mushrooms, like people, know how to sunbathe. This happens with any changes in temperature and weather. Some species become darker when it rains and some when the sun is strong.
- Honey mushrooms grow very quickly. On average, each mushroom can grow 5 millimeters per minute. The growth rate is the same for bamboo. Only honey mushrooms stop growing, but bamboo does not ..
Germination in bags
Since not everyone is able to grow mushrooms in the country in the first way, you should think about their germination in a greenhouse. To do this, half-rotted pieces of wood should be placed in the corner of the structure. They also need to be watered with water, which contains honey agaric spores. After some time, the wood should be transferred to bags and placed in a dark place in a woodpile. In the spring, the ends, as well as those places where the bark has been damaged, should be covered with mycelium. The material is ready for planting.
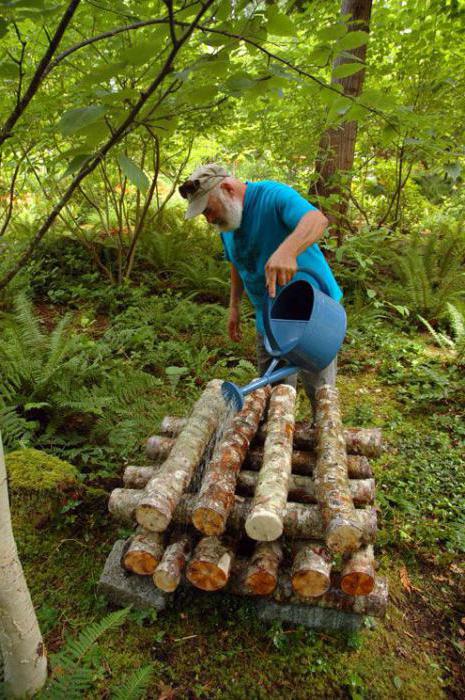


Method three
To grow mushrooms on the site, it is necessary to collect mature mushroom caps. It is recommended to place them in a container and fill with water. The hats should stand for a few days. After that, the water from the container should be drained and filtered. The resulting infusion must be impregnated with pre-prepared pieces of wood or stumps. In addition, ripe mushroom caps can be laid out on the surface of the material. They can be removed after two days.
It should be noted that this method is not suitable for everyone, since the germination process is very slow. The first harvest of honey agarics planted with a similar method can be obtained only by the end of the next season.
Primary requirements
Honey mushrooms are unpretentious representatives of the mushroom kingdom.
They are able to actively grow both in the basement and in a heated greenhouse, in an open garden plot, or right in the garden, under the trees.
The necessary conditions:
- maintaining the temperature regime at the level of 10 - 15 ° С;
- humidity about 70-80%;
- good constant lighting;
- creation of additional heating in the cold season and regular ventilation of the enclosed space during the hot season;
- taking preventive measures to protect against insects and infections.
Before planting, the substrate should be sterilized by pouring boiling water for at least 12 hours. This helps to get rid of the spore powder of parasites, weed seeds and pathogenic bacteria.
Usually, the first fruiting bodies appear 2-3 weeks after sowing.
The term may increase in the open air, where the temperature drops significantly at night.
Special cultivation technology
The technology itself depends not only on the method of growing, but also on the method of obtaining the material.
The most famous and used methods:
- from the fruiting body of the fungus;
- with the help of mycelium.


For the first option, it is necessary to select overripe mushroom caps. Then place in water and leave there for a few days. At the end of the required period, without pulling the mushrooms out of the water mass, knead them until a certain porridge is obtained, which should later be filtered with a layer of gauze. The resulting material is poured into wood, which is specially prepared in advance. To do this, you need to make small cuts into which water will flow. Then they are covered with moss and wet sawdust, and the ends of the stumps are left open.
The second method is relevant only in the autumn season. A piece of the stump is needed, on which the mycelium used to grow. It is divided into several parts, approximately the same in size. After that, these pieces are laid in prepared stumps, which are intended for growing. Further, the actions are similar, but in this case the end does not remain open, but is covered with plastic wrap, which retains the desired humidity. With the arrival of cold weather, the stumps are covered with pine branches.
And with the onset of early spring and warming, you should carefully monitor so that water does not fall on the stumps, because this way you can cause great harm to a growing body. To do this, it is enough just to regularly shake off snow from the surface of the hemp. It will be possible to finally get rid of the branches only at the end of July, just before the fruiting stage.
Keep in mind that fungi are a parasitic culture, and therefore measures must be taken to avoid contamination of other fruiting species.
Honey mushrooms are very well suited for growing indoors, namely in a greenhouse. To do this, rotten logs should be populated into bags with material. These logs are left in the greenhouse until the mushrooms germinate, constantly irrigating them.
Basement, package, sawdust
For growing in a basement, garage, hangar, cellar - any closed cool room, the most suitable method of planting in bags filled with sawdust mixture.
- To fill one two-liter bag, you will need 200 g of dry sawdust. You can take pine and all deciduous ones, you should not only use oak.
- Fillers such as barley, barley oats, buckwheat or sunflower husks should be 30% of the substrate. A teaspoon of chalk is also added to the mixture.
- Everything is dry mixed and soaked in water for an hour.
- Then, in the same water, the substrate must be sterilized for ¾ hour by boiling.
- After draining the excess water, the mixture is spread on a baking sheet and dried in the oven for about 20 minutes (low heat).
- Then the substrate, which should remain moist, is cooled and packaged in two-liter thick plastic bags.
- The mycelium, which must first be divided into small fragments with clean hands, is poured into a bag on the surface of the sawdust, about 20 g each.
- The mycelium is covered with cotton wool, the bag is tied.
All this economy is transferred to the basement or cellar. The temperature must be between + 12 ° C and + 20 ° C. You don't need to touch the packages for a month. Then, bumps should form on the surface, in places where the fruiting bodies of future mushrooms are formed.


At this time, the packages are untied, the cotton wool is removed. The mushrooms will grow in the direction from which the air stream comes. Additional lighting will be needed to keep the legs short.
If you make holes in the bag in those places where the fruit bodies have formed, honey mushrooms will grow from there, but the bag will resemble a hedgehog, whose needles stick out in all directions, so it will be inconvenient to collect them.
Growing honey agarics at home or in the country is an interesting and rewarding activity. These mushrooms do not require complex care steps and special conditions. They grow on their own, actively and abundantly bear fruit, and the quality and taste are not inferior, even surpass the taste of forest mushrooms. Many mushrooms can be grown at home. Champignons, oyster mushrooms, chanterelles, even white ones. But honey mushrooms are the most productive of forest species in artificial cultivation.
Varieties
Other types of these mushrooms grow in Russia:
- Meadow honey fungus, or meadow marasmius. Its colonies can be seen in open areas: meadows, ditches, forest edges, near dachas and country houses. Signs of this species are a thin stem, a small creamy cap.


Meadow honey fungus. - Udemanciella is mucous. A feature of this variety is the flat-convex olive-gray cap, covered with whitish or yellowish mucus. The pulp is tasteless, odorless. Udemansiella's favorite habitat is the trunk of a sick or fallen beech.


Udemanciella is mucous. - Thick-legged honey agaric grows on fallen leaves, rotten stumps of ash, fir, beech. It can be recognized by its thick and dense leg. She, like the brown hat, is covered with brown scales. The taste of the mushroom is cheesy, slightly astringent.


Thick-legged honey fungus.
In addition to summer, there are autumn and winter mushrooms. The former can be found in the forests of Russia in August - November, the latter - in November - April.
Preparing seedlings with your own hands
Regardless of whether you want to plant mushrooms in the summer or in the winter, the seedlings can be bought in the store or prepared by hand. It is the last method that we will consider.
The most convenient material thanks to which you can plant mushrooms is mycelium, growing in this way is not at all laborious.
You can get mycelium like this:
- Find old myceliums on wood that have already fruited in the forest. They are easy to spot by their characteristic white or yellowish bloom; on some, mycelium filaments (hyphae) are clearly visible. If you smell such wood, then you will smell a pronounced mushroom smell.
- Break off pieces from the stump, if it is not possible by hand, use a knife or other tool.
- Dry pieces need to be crushed, they will serve as seedlings.
Sowing material from fruit bodies
Collect ripe mushroom hats, preferably the largest ones. They should be intact, without any damage. The dark brown inner side of the cap will indicate the maturity of the mushroom.
Soak the caps in clean, non-chlorinated water for 24 hours. Then take out the mushrooms and mash them into gruel - this is your seed from the fruit bodies of the mushroom.