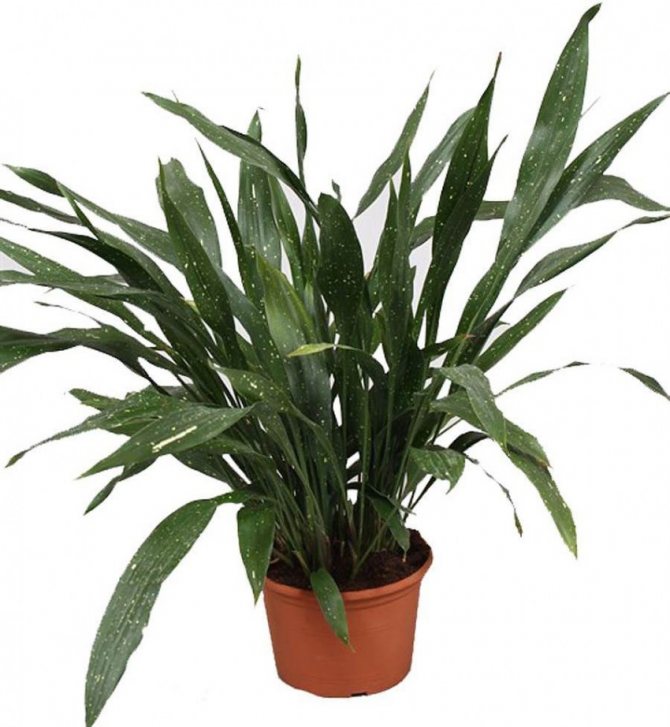
Aspidistra is a very beautiful herb with lush, basal leaves. A small genus belongs to the Asparagus family and includes only 8 species. Of these, only high aspidistra is used in home floriculture - a very hardy long-lived plant. The aspidistra flower spread throughout the world more than a century ago from East Asia (China, Japan, Taiwan). It will be a real boon for beginners who cannot devote a lot of time to indoor plants.

Description
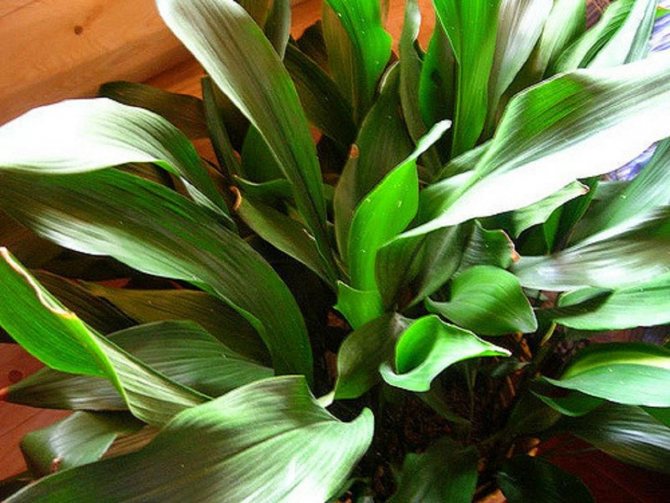
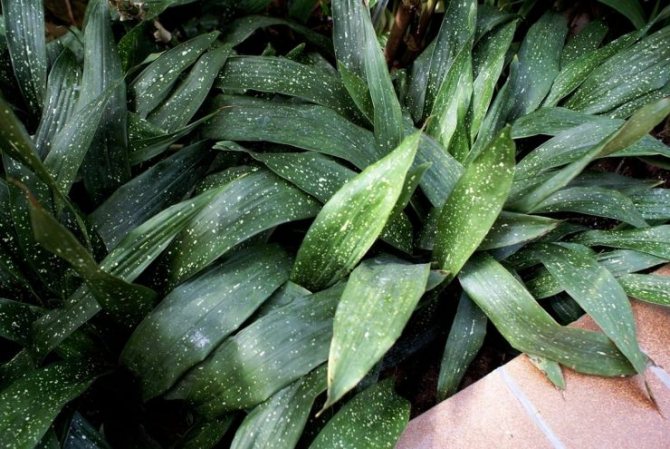
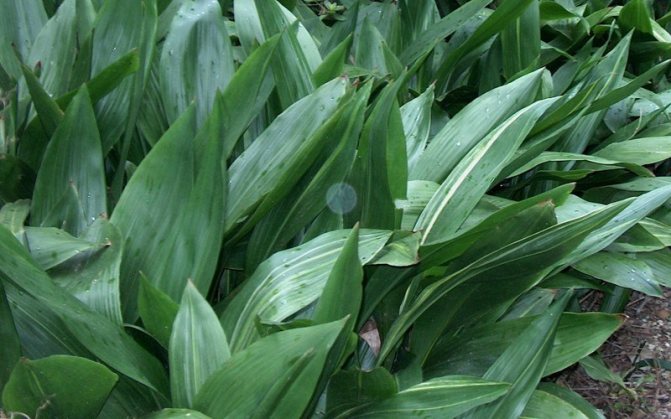
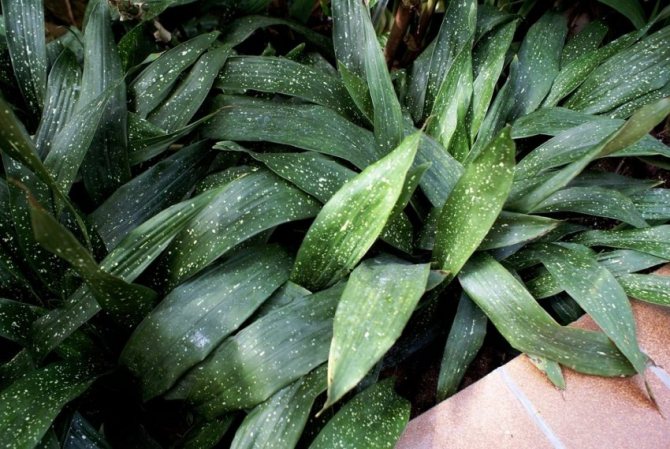
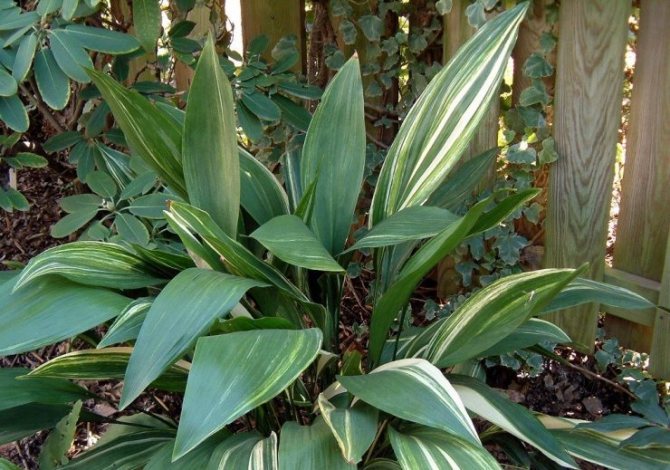
Aspidistra in the common people is called snake grass, because scaly curved rhizomes protruding from the ground are similar to the body of a snake. Basal leaves, devoid of stems, grow extremely densely and densely to each other.
Due to its visual similarity and lack of bulbs, this culture has long been considered a relative of lily of the valley and asparagus. The leaf blades of this flower are leathery dark green shiny, but larger and higher than the lily of the valley.
How does it bloom?
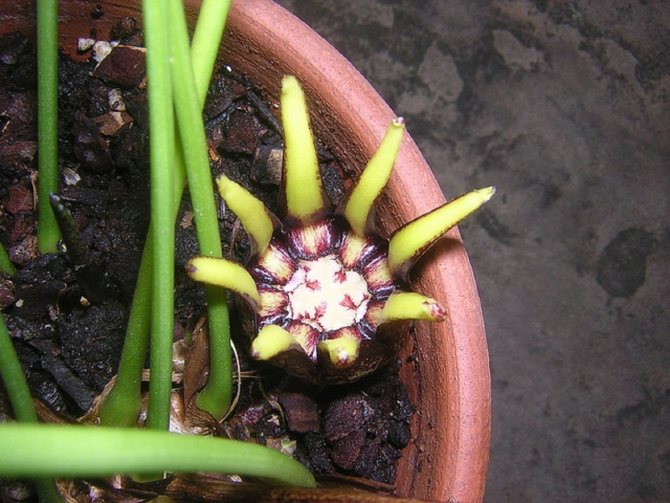
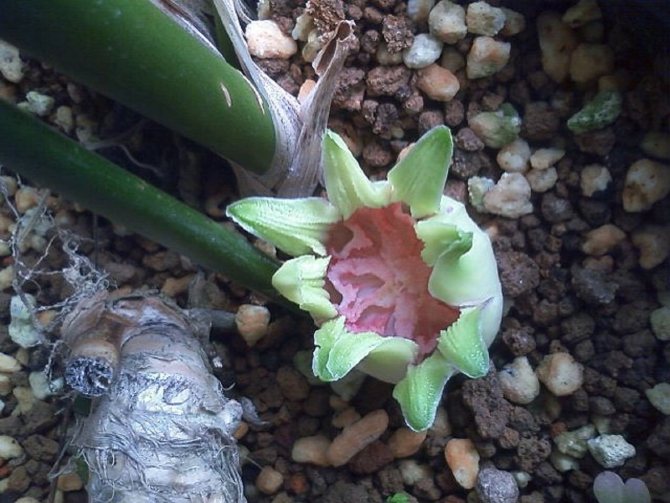
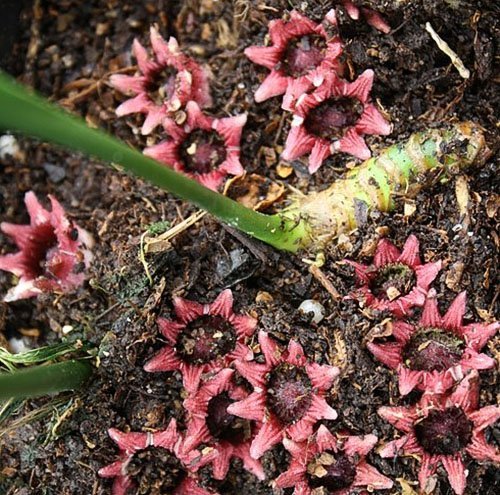
Aspidistra blooms rarely and sporadically. Indoors, this happens most often in winter or early spring. Stellate axillary small (up to 2.5 cm) sessile purple or lilac flowers appear between the scales directly from the rhizome.
After pollination, a pear-shaped or rounded fruit is formed with a single large seed inside.
Signs and superstitions
A number of signs and superstitions are associated with aspidistra. It is believed that the flower received as a gift strengthens character and strengthens willpower, as well as helps to overcome depression and heals depression. A bush growing in a house gives its owner stamina and endurance.
In addition to magical qualities, the beneficial properties of aspidistra are also used. All parts of the plant (rhizomes, flowers and leaves) have healing properties.


Decoctions of this herb are used for urolithiasis, cystitis, gastrointestinal pathologies, for muscle pain and cramps.
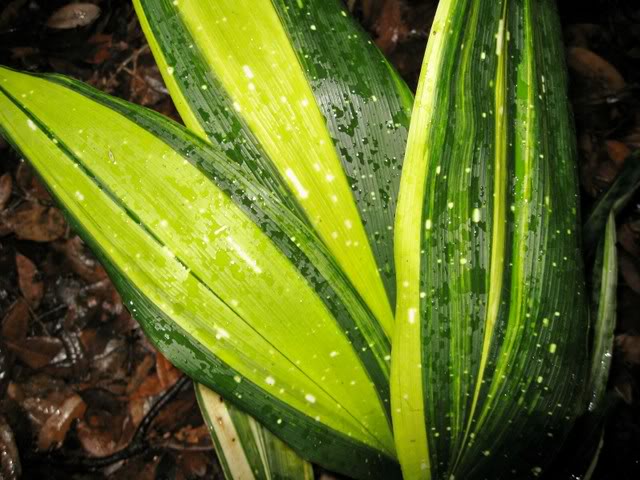
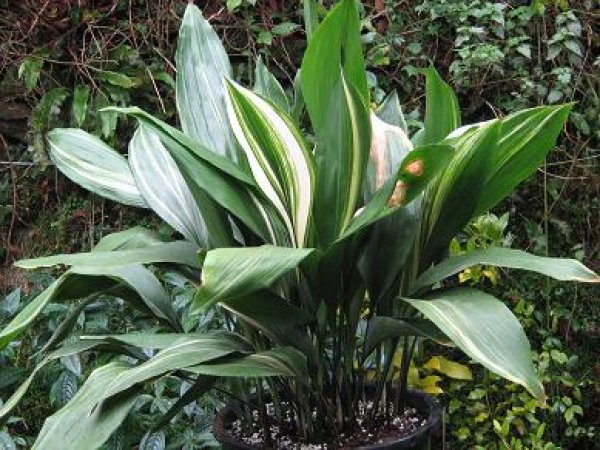
Aspidistra elatior Fuji-No-Mine


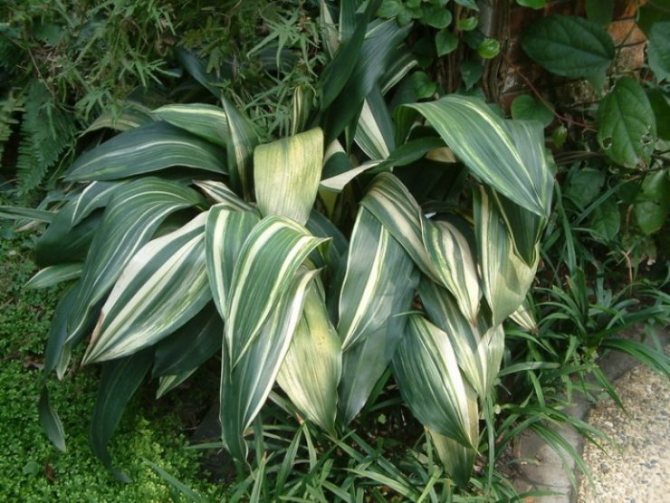
The broadleaf aspidistra shown in the photo also represents a large variety with striped foliage. On a dark green background of glossy leaf plates up to 40 cm long, light green stripes diverging from the base are clearly visible. The upper tip of the leaf is crowned with a light small cap, reminiscent of snow on Mount Fuji.
Types of aspidistra with photos and names
As an indoor flower, no more than 6-8 varieties are grown, differing in size, color and crown shape.
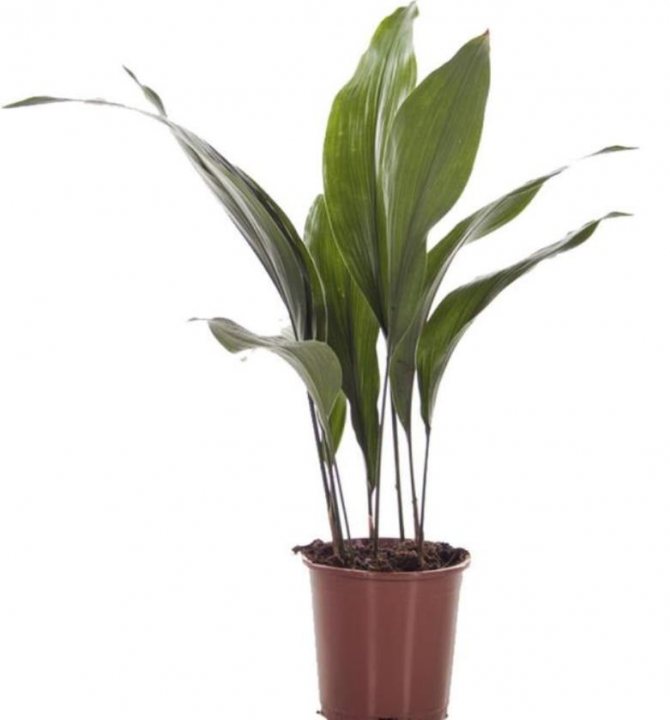
High (aspidistra elatior)
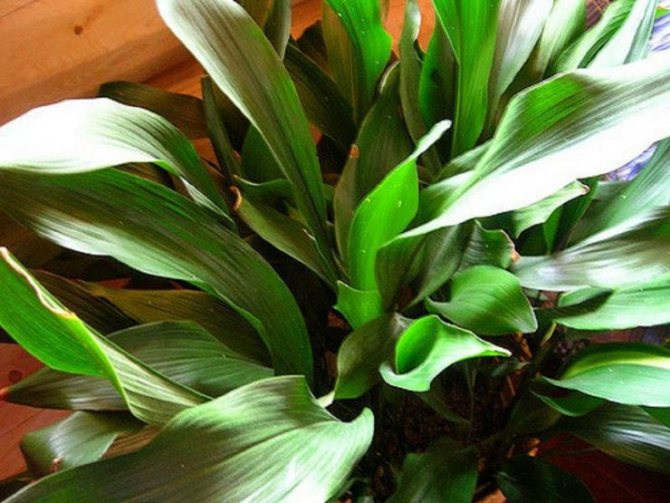
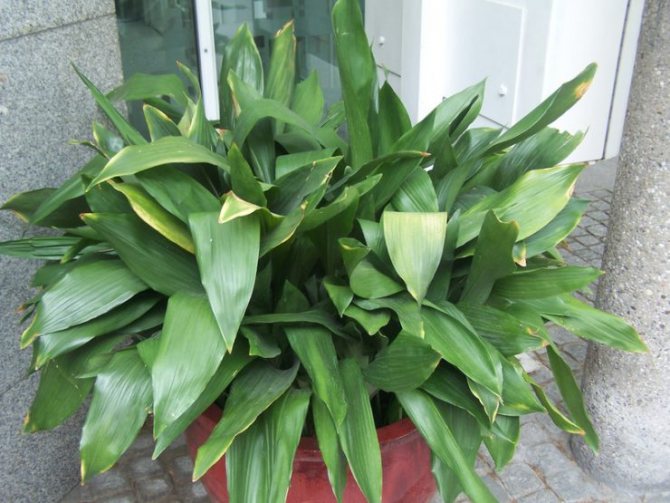
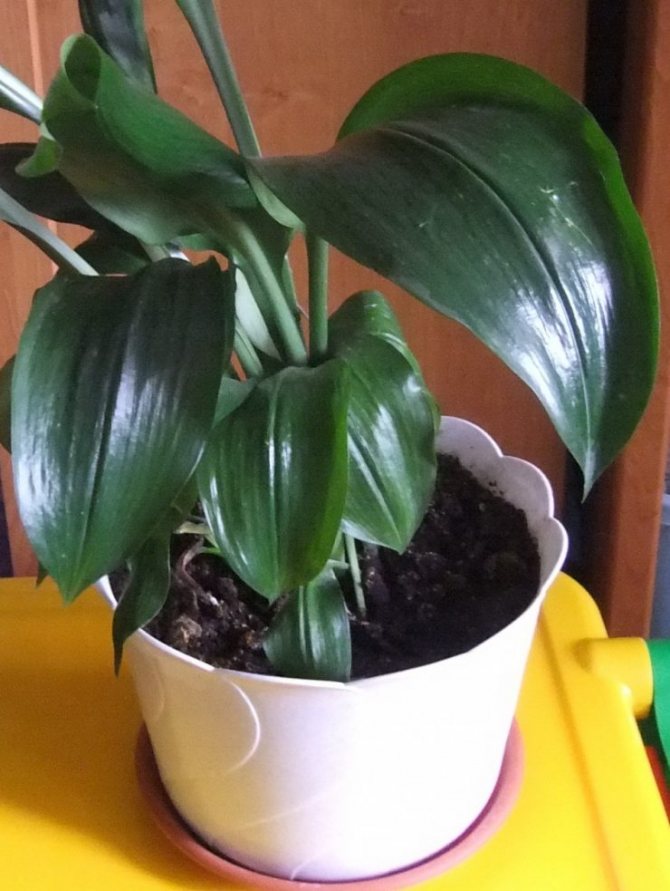
Most often in apartments and offices you can see the aspidistra elatior. The plant resembles a lily of the valley in shape, it is a dense bush 60-80 cm high, consisting of a large number of wide (6-10 cm) dark green leathery leaves.
Several decorative varieties of this variety are cultivated at home:
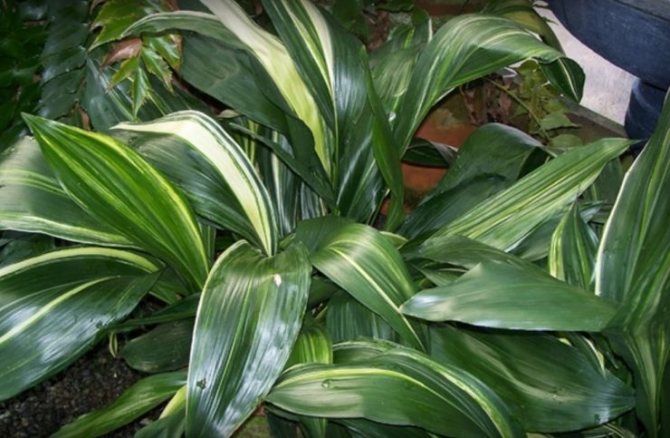
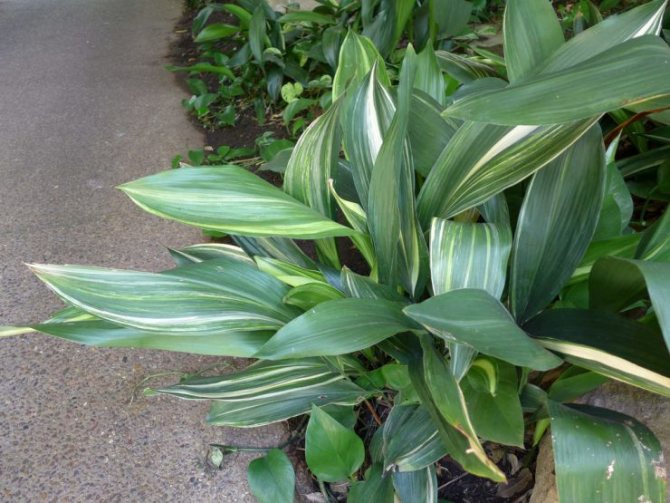
- Variegata. Lustrous juicy green leaf blades are dotted with longitudinal creamy white stripes of various widths.
- Blume. The plates are of a smaller size, of a single bright emerald hue. Flowers are yellowish or crimson-brown.
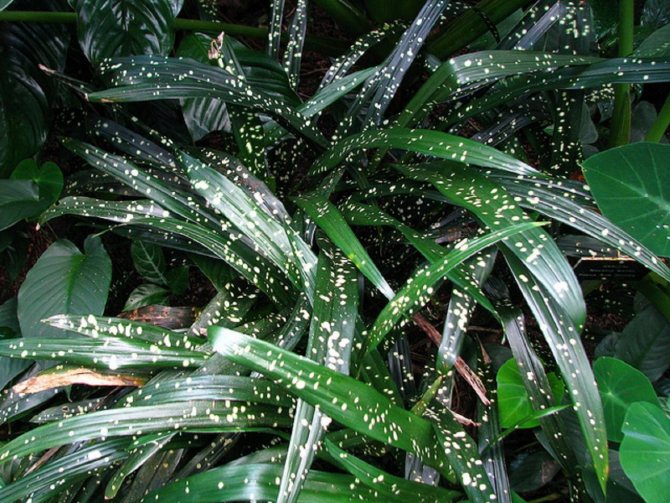
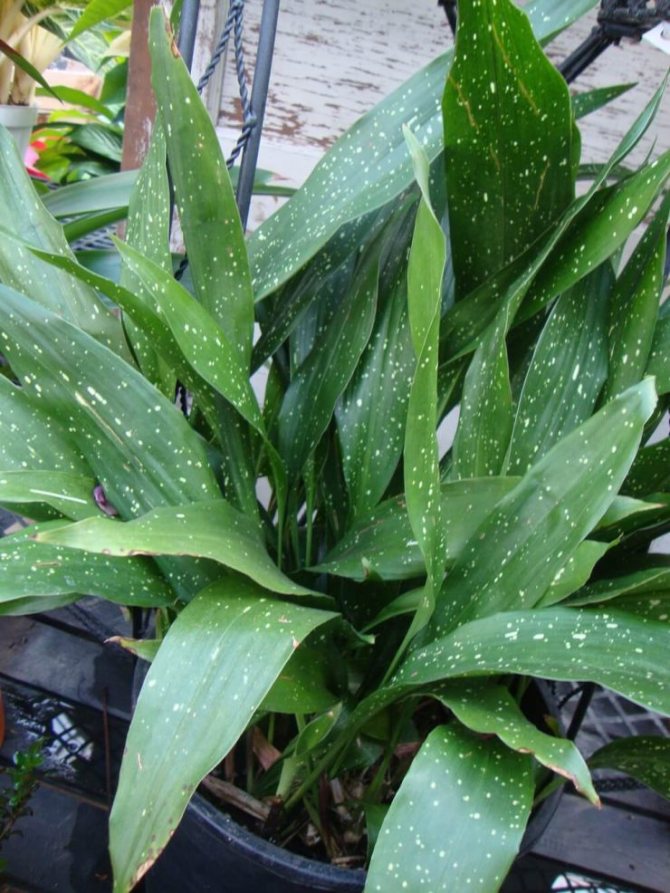
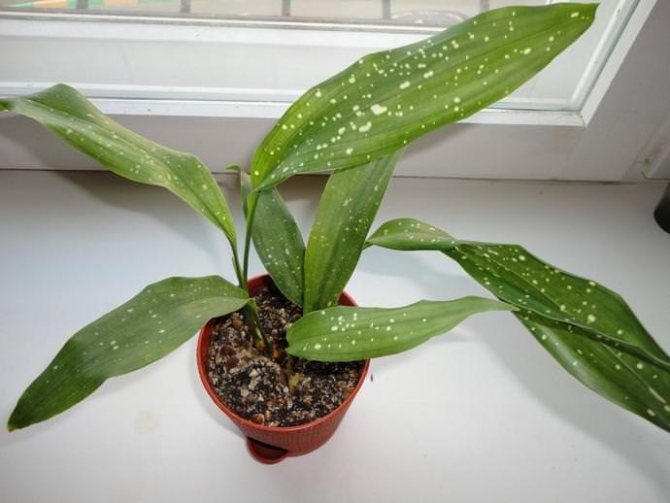
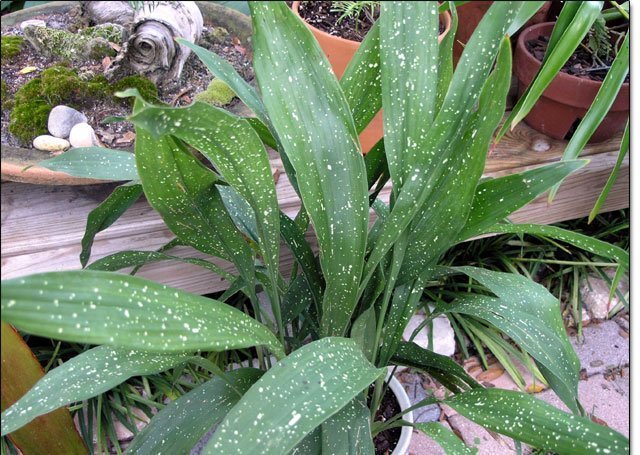
- Milky Way (Milky Way). A bush that does not exceed 40-60 cm in height, with elongated dark leaves, which are covered with many small creamy dots and irregular spots, reminiscent of stars in the sky.
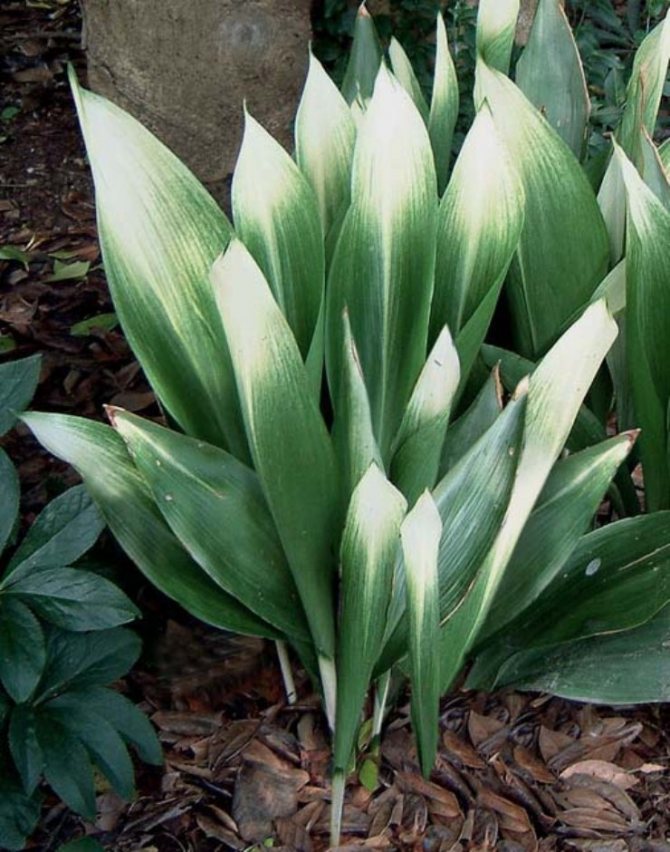
- Snow Cap.The wide leaf plates at the rhizome are green, gradually lighten and become almost white towards the ends.
Attenuata (a. Attenuata)
The species was first discovered in the wooded mountains of Taiwan. The variety belongs to indoor crops. Shrub 55-60 cm high with a powerful massive rhizome, forming dense clumps.
Leaves with small vague light spots 6-8 cm wide in a noble dark green shade are located on tall petioles. Single bell-shaped whitish or pale green flowers appear once a year at the very beginning of summer. The diameter of the bud is about 3 cm.
Oblancefolia (a. Oblanceifolia)
The variety differs from other varieties by the presence of narrow, no more than 3 cm wide leaf plates, the color of which varies from yellow to green (sometimes spotty). Small red star-shaped flowers open in early spring. The bush grows to a height of 60 cm.
Sichuan (a. Sichuanensis)
In the wild, it grows in dense bamboo thickets of China at an altitude of 650-1100 m. A plant with a powerful branched rhizome and single elliptical or lanceolate leaves, reaching 60-70 cm in height and up to 6-7 cm in width.
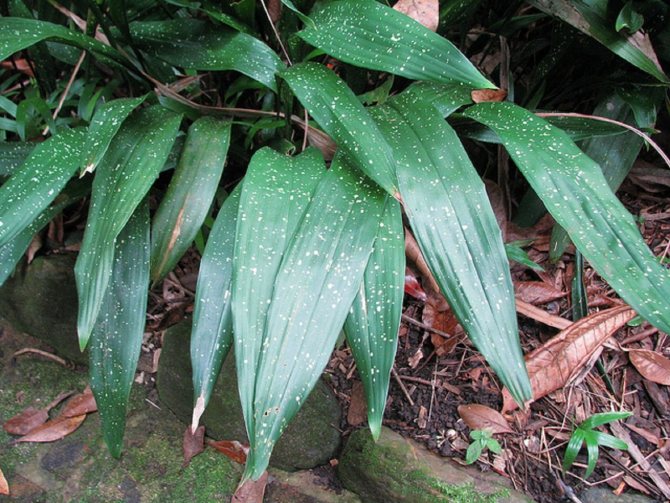
Dense green monochromatic or spotted plate has well-distinguishable whitish arcuate veins. A dark purple small bell flower blooms in winter.
Variety of types and structural features
With a wide variety of species, only a few have adapted to home conditions. Florists usually grow the following types of aspidistra:
- high aspidistra;
- graduate student Elatior;
- Aspidistra Variegata.
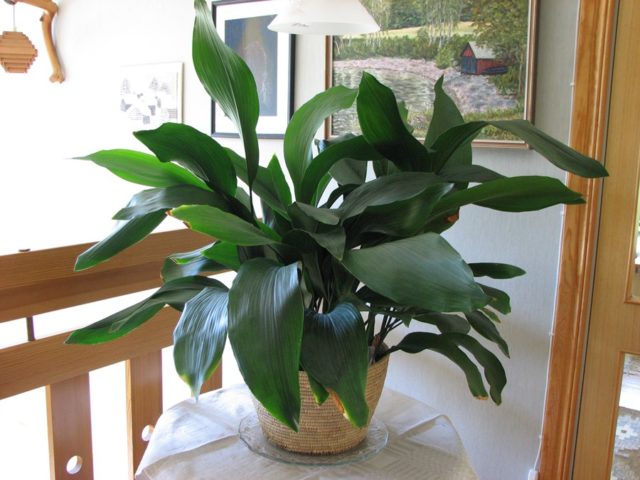


Aspidistra in the photo is presented in all its glory.
A feature of Aspidistra is the absence of a stem. Leaves emerge directly from the rhizome, which protrudes slightly above the ground. The color of the leaves is dark green, but it can change and become lighter when the amount of fertilizer in the ground changes.


Aspidistra Variegata
Aspidistra "Variegata" has a variegated color. The leaf blade is placed on a long petiole.
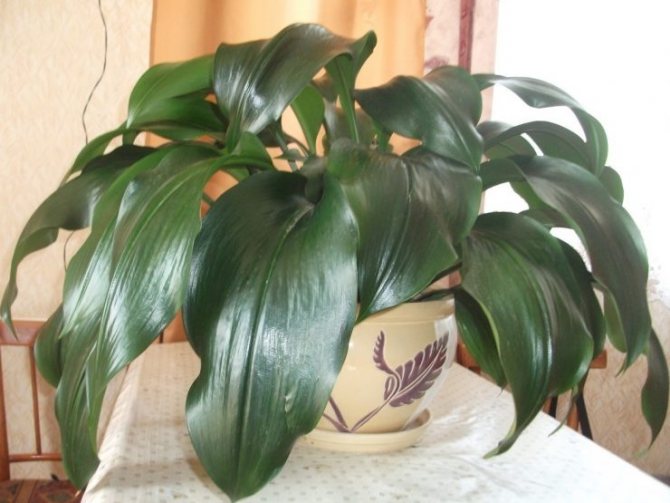
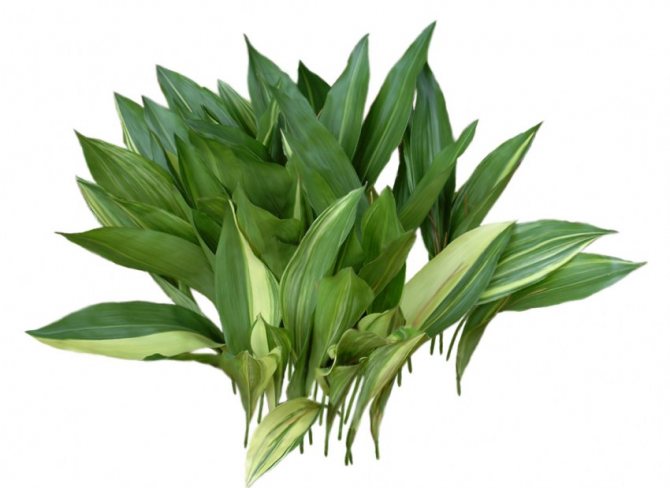
The leaf of Aspidistra is large enough. The length reaches 50 cm, and the width is 15-20 cm. Outwardly, they look like lily of the valley leaves. At the beginning of the petiole, several scaly leaves can be seen. A large number of leaves emerge from one stem. They are very close in the pot. It was this feature of growth that gave the plant the popular name "Friendly family". Up to five new leaves grow in a year.


Aspidistra flower
Flowering does not occur often. Flowers will allow you to admire yourself in the summer and just one day. The first time flowering may not be noticed. The flower is located at the surface of the earth, near the rhizome. What an unusual flower this is. The shape of the flower resembles an open box with carved edges or an extended bell. The color of the box has purple hues. After pollination, instead of a flower, a large fruit is formed, which has one seed.
Home care
Unlike most indoor plants, the aspidistra can be placed anywhere in the room. She is extremely unpretentious to care for and will feel good even in artificial light. The best place in the house for a flower will be windows of the north or east direction. Water the plant regularly, but in moderation. The next watering is carried out only after the top layer of the earth in the planting tank has dried out. During the period of active growth, the substrate is moistened 2-3 times a week, in winter 1 time in 7-10 days will be enough.
Transplanting a room aspidistra
The plant does not tolerate transplanting well and develops rather slowly, so the procedure is carried out only as needed. In the middle of spring, every 3-4 years, the bush is transferred into a stable pot one size larger than the previous one. A thick layer of drainage is poured onto the bottom of the container. It is not recommended to damage the earth lump.When planting, the upper part of the root collar should remain on the surface.
The soil for aspidistra is selected light and fertile with a slightly acidic or neutral reaction. Preference is given to deciduous substrates with a small addition of peat.


Characteristics of the species of aspidistra
At the beginning of the last century, a postgraduate student in many European countries was at the peak of its popularity. However, flower growers, although they value it for its attractiveness, undemanding care, have made little progress in plant breeding since then. Only a few types of "friendly family" are known... The most popular ones are presented below.
Aspidistra elatior or high (Aspidistra elatior)
It comes from China and Japan and enjoys well-deserved attention in greenhouse and home floriculture. The plant is supplied with creeping, close to the surface, extensive rhizomes. Its dark green, glossy and resilient leaves resemble lily of the valley leaves, but more of them (50 x 15 cm). Their petioles are long (up to 35 cm), and they themselves, closely adjacent to each other, abundantly emerge directly from the ground.
Flowers, similar to wide bells, yellow- or crimson-brown, squat. At home, they appear in January - April, during the rainy season. Then in place of the flower, dark, round fruits with seeds are formed.


Aspidistra elatior or high (Aspidistra elatior)
Aspidistra grandiflora (A. grandiflora)
This species is native to Vietnam. The tropical culture is interesting for its long, curved, ovoid, white-speckled leaves and unusual flowers. In the middle of summer, a couple of flower buds hatch on the roots of this plant, and then amazing flowers grow from them.
They are up to 4 cm in size, sit on creeping 5-cm stalks. Long and slender, widely spaced petals are lighter than the dark purple core.
This picture is surprisingly similar to a frozen tropical spider. But not every grower manages to see such a spectacle, because this aspidistra blooms only in conditions that are as close to natural as possible.
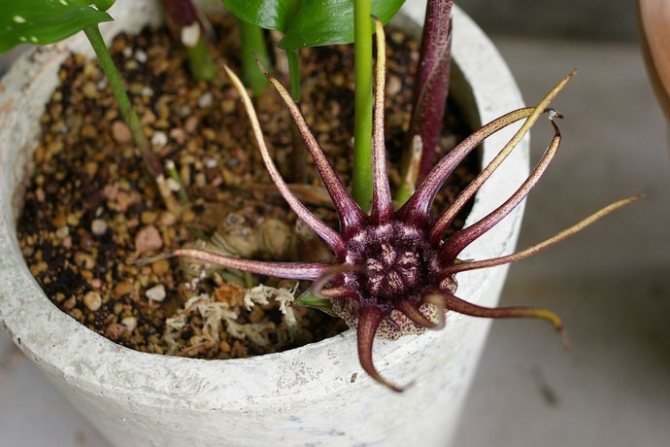


Aspidistra grandiflora (A. grandiflora)
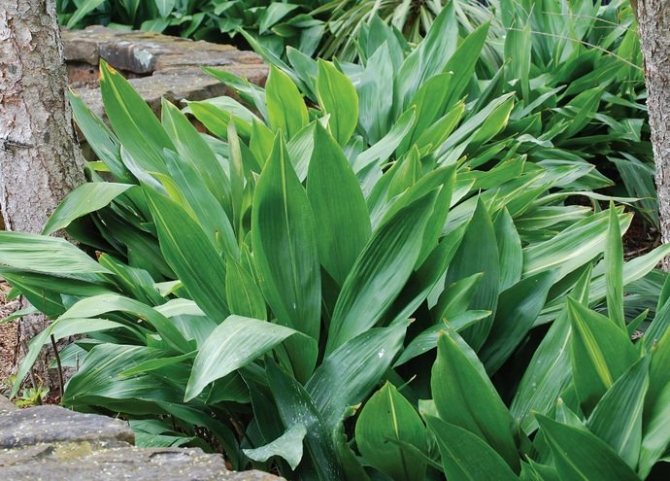
Aspidistra oblantsefolia (A. oblanceifolia)
The leaves of this Chinese woman are narrow and thin, solitary, lanceolate, slightly inverted. Their sizes are not as impressive as in other species, but they are interesting for the randomly located yellowish specks on them.
Flowers are small, lying almost on the ground. They have wide-open, moist red cabbage-colored cups. The inner side of their 8 petals is lighter.


Aspidistra oblantsefolia (A. oblanceifolia)
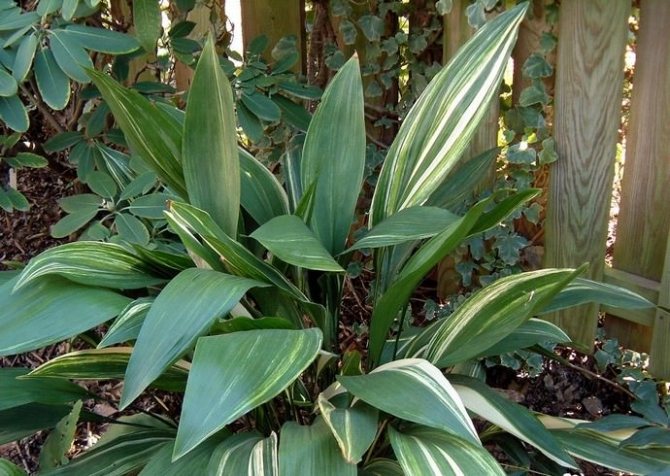
Aspidistra Attenuata (A. Attenuata)
Attenuata, a Taiwanese mountain beauty, looks like a tall or broad-leaved aspidistra. Its creeping rhizome, expanding widely on loose forest soil, creates whole groups of closely spaced plants. Light spots are visible on dark, large (up to half a meter) leaves.
Bell-shaped five-centimeter purple flowers with greenish or whitish petals. Plants bloom in June, after which they form a dense seed box.


Aspidistra Attenuata (A. Attenuata)
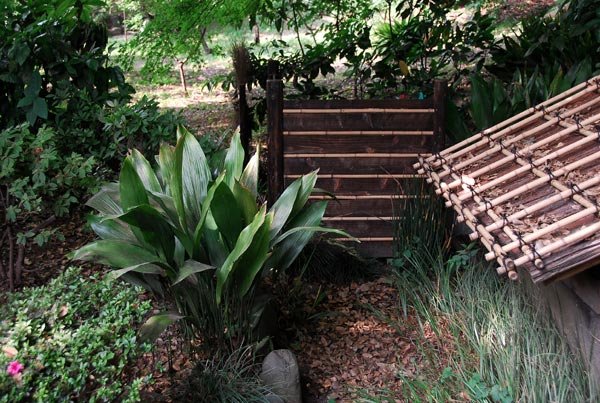
Aspidistra Sichuan (A. Sichuanensis)
In the bamboo forests of China, where it comes from, there are vast meadows with thickets of Sichuan aspidistra. The bright green of its medium-sized leaves (40x8 cm) is sprinkled with small, frequent specks. They are erect, single, elliptical.
At home, it blooms in the rainy season - January - March. Its six-petalled flowers are kept on a short stalk. They are small and very dark, almost black.


Aspidistra Sichuan (A. Sichuanensis)
Varieties
Aspidistra high (Aspidistra Elatior Blume)
This is the only type of aspirid that is grown in home gardening.
An additional name for this species is "friendly family".
It is associated with the presence of many root cuttings with leaves in the plant. Aspidistra has no erect root.
The rhizome is compacted, partially hidden in the soil. The leaves are elongated in shape, lanceolate, reaching a length of 60-80 centimeters and up to 13-15 centimeters in width.
Platinum plates are shiny, dark green in color. Some species have white and yellow lines along the leaves.
The flowers are unremarkable, planted in the perianths of a purple hue.
The fruits are large pear-shaped berries.


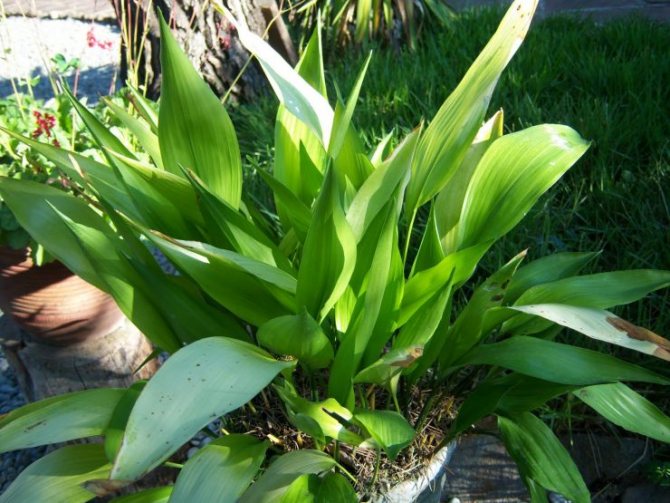
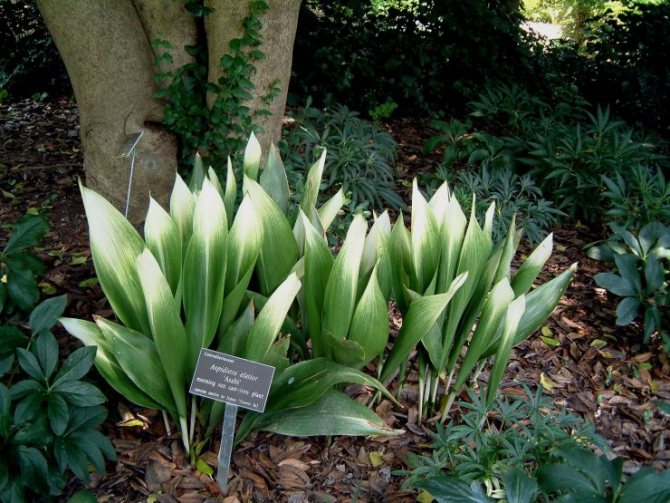
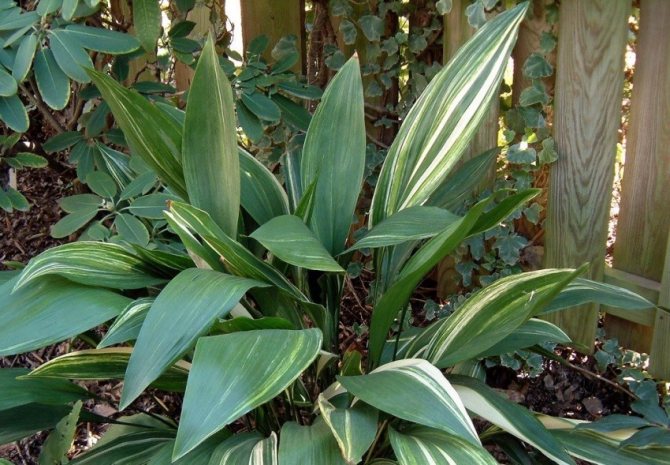
Aspidistra variegata (Aspidistra Variegata)
Grown in garden conditions. This plant has lighter leaves with cream-colored stripes. This species is more thermophilic than high aspidistra and requires an air temperature above 16 degrees Celsius for comfortable growth.


Video with interesting information about the plant:
The best varieties of apidistra for indoor cultivation
Of the hundreds of species of "snake pointer" only 5-6 are cultivated as indoor plants. The most popular of all of them is the type of aspidastra elator, which has several varieties. They differ in size, color and leaf shape. Here is some of them:
- Fuji-No-Mine. It is characterized by light stripes fan-shaped from bottom to top on dark glossy green foliage.
- Ginga Giant. A cold-resistant variety with leaves sprinkled with light, blurred spots, similar to drips.
- Okame. Its large (up to 70 cm) leaves are completely covered with wide light stripes. Therefore, it is difficult to say which color predominates on them dark or light.
- Asahi. Its graceful leaves are traced with thin dash-like lines.
- Snow Cap. It resembles the previous variety, but its variegation is more pronounced. The tips of the leaves are white and dark green at the base.
- Sekko Kan... The leaves are large, with white-green stripes.
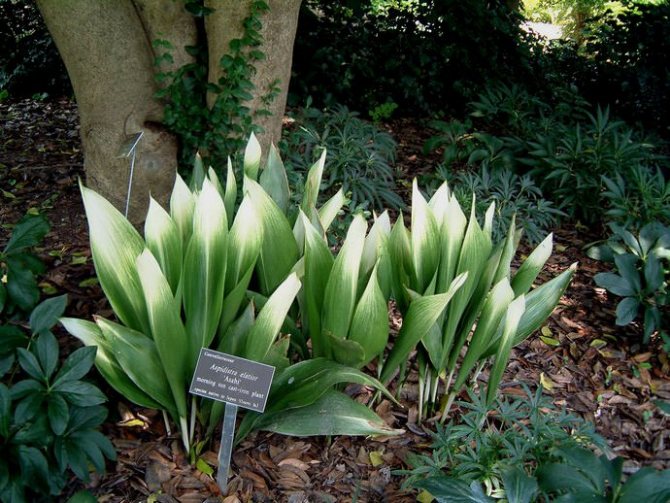


Aspidistra Asahi
Moreover potted varieties of other types of aspidastra are common:
- From the view variegata (A. Variegata), considered rather a garden variety, the Milky Way variety. Yellow-white strokes of stripes and specks on the bright green of the leaf from a distance resemble scattered stars.
- From the view attenuate, cultivar Alishan Giant Splatter. Very large leaves of a dark color with yellow-white spots.
- View large-flowered, cultivar Spiderman. Leaves are green, small in size, ovoid, on thin stems. They are complemented by tiny purple spider flowers.
- View oblantsefolia, cultivar Nagoya Stars. Its narrow spear-shaped green leaves with small yellow star-shaped specks, although extremely decorative,
- but they did not bring fame to the brand. Nagoya's stars are loved for their lavish bloom.
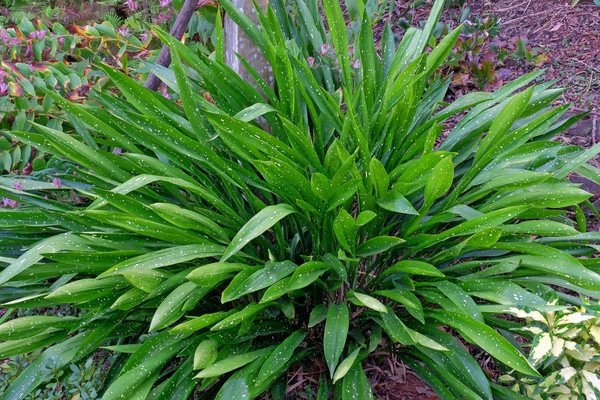


Aspidistra Nagoya Stars
Aspidistra in interior design and floristry
Taking care of Aspidistra is not so difficult. Such a plant is suitable for novice florists. It gives a lot of greenery and can be a decoration for any interior.
Modern florists began to use the leaves of adult specimens of Aspidistra for bouquets and flower arrangements. There are many decoration options. One of them is the formation of a green bow for the base of the bouquet.
Bouquets using aspidistra leaves
Such a flower is suitable for decorating general premises. Lobbies, banquet rooms can be refreshed with the greenery of Aspidistra.
Signs and superstitions associated with the plant
In addition to the aforementioned names, aspidistra has three more names - "iron plant" or "cast-iron flower" because the flower has excellent adaptability and adapts to any (even unfavorable) conditions. Last thing its popular name is "mother-in-law's language" it is believed to be associated with its positive energy and the ability to bring harmony, well-being and peace to the house. Perhaps, and "friendly family" he was nicknamed for this reason.
And the literal translation of the name from Latin - "index of snakes" is associated with the fact that snakes like to hide in thickets of wild plants. And when they crawl, the leaves warn of the presence of reptiles by swaying the leaves.
In old vaudeville, the plant was associated with something old-fashioned. But when the retro style came into fashion, the "cast-iron flower" was remembered again, and it became popular.
Aspidistra Elatior Amanogawa
On the basis of the Milky Way aspidistra, a plant was obtained, which had not only small spots on the foliage, but also yellowish stripes of a creamy hue. The variety of aspidistra shown in the photo was named Amanogawa, which means "Milky Way" in Japanese.
The dense, 40-centimeter-long, bright leaves will decorate any corner of the garden or home. Just like other variegated aspidistra, this plant should not be left outside if the temperature is below freezing. Having carefully transplanted into a suitable container, find a place for him among other indoor pets.
Secrets of proper care for apidistra at home
Aspidistra is unpretentious and shade-tolerant. But, in order to achieve complete decorativeness, she needs proper care:
- Lighting. The plant can be grown even on the north side and not near the window. But variegated forms are demanding on light, they need to be illuminated up to 16 hours a day. The direct sun, which causes burns, cannot stand aspidistra.
- Temperature. "Iron plant" is not demanding on the temperature regime. But in cold weather, it is advisable to keep it in a room with a temperature ten degrees below summer temperature.
- Watering. For it, settled and not cold water is used. Water it only when the top layer of the earth dries up. There is no need to humidify the air around. But dry air, especially in winter, is not desirable. It is good to periodically wipe the leaves from dust.
- Top dressing plants in the warm season with mineral and organic fertilizers, diluted twice, is carried out once a month. In winter, the "cast-iron flower" does not need feeding. And it is even harmful to fertilize variegated varieties. This leads to the loss of their decorative effect.


Aspidistra is unpretentious and shade-tolerant
Possible difficulties
Aspidistra is resistant to diseases and pests. With excessive watering and dampness in the soil, root rot can develop. Also, the fungus spreads to succulent petioles and foliage. In too dry air, the crown is damaged by spider mites and scale insects. You can try to wash off small parasites with soapy water and a hot shower, but it is much more effective to treat with an insecticide. To destroy the larvae, spraying is repeated twice at intervals of 5-7 days.
With poor water quality for irrigation, a disease such as chlorosis may develop. With it, the leaves retain their elasticity, but turn yellow and lose their rich color. Fertilization and the use of cleaner water will help to cope with the problem.
Reproduction and transplantation of a flower
The "mother-in-law's tongue" is propagated in three ways:
- By dividing the bush. This is the most reliable and common breeding method. They do everything in the spring. In order to avoid decay of the appendages, it is important that at this time the room is not cold and damp. The rhizome is cut with a sharp knife into pieces containing at least three leaves. After sprinkling the wounds with crushed coal, the new plants are distributed in separate pots.
- Reproduction by a sheet. The sheet is pruned near the base, slightly dried. It is then placed in a wide-necked bottle. A little root stimulant is added to the water, and the neck of the vessel is tightly closed and the cracks are covered, preventing air from entering. The container is placed in a warm and well-lit room. When roots appear, a young plant is planted in an impromptu greenhouse with loose and fertilized soil, covered with a glass jar on top.
- Seed propagation spend in the spring. At the same time, they are lightly sprinkled with loose earth and covered with glass, placed in a warm and unlit place. When shoots appear, the container is rearranged to the light. And after a couple of weeks, young seedlings are planted in separate containers and covered with transparent jars.
The "friendly family" gets along well in a cramped pot and does not like resettlement. When transplanting or dividing a bush, you need to prepare a nutrient mixture from turf, humus and sand (3: 3: 1) or with the addition of leafy soil (2: 2: 2: 1) with moderate acidity.It is important that it is fortified with nitrogen. To do this, you can pre-feed the soil with ready-made nitrogen fertilizer, which improves leaf growth.


Aspidistra gets along well in a cramped pot and does not like resettlement
Photo gallery
Now there are already about 100 varieties of this plant. Most of them are endemic, that is, they grow in a clearly limited area.
Useful properties of aspidistra (video)
Although the "mother-in-law's tongue" grows slowly, it is very hardy and unpretentious - it is not afraid of gas pollution, tobacco smoke, temperature changes and irregular watering, does not need special feeding. The plant is diverse in its decorativeness, it can be used to decorate shaded rooms. Aspedistra is a godsend for inexperienced flower growers and those who have no time to deal with plants.
In order not to lose the material, be sure to save it to your social network
Treatment and pest control
Aspidistra is quite unpretentious, but she can still get sick. We will indicate the main problems and ways to eliminate them:
- The leaves began to wither. This happens if there is too much moisture, or vice versa, the flower is dry. Dry air can cause this effect. You need to spray the plant regularly. The earth ball should be moderately moist.
- Slow growth. It is necessary to eliminate the lack of nitrogen.
- The leaves turned pale. Lack of light can contribute to discoloration of the leaves.
- The leaves turn yellow. Most likely there is an excess of moisture. You need to temporarily reduce watering.
- The leaves have brown spots. Perhaps a red spider mite has settled on the plant. It is worth treating the leaves with a special solution and humidifying the air.
- The leaves turned yellow rapidly and began to fall off. The flower can be attacked by the aspidistric scale insect. Visible pests need to be collected. The leaves are treated with a solution of soap and karbofos.
Ahimenes. Features and care.
- Homeland of the plant: Mexico, Brazil, Jamaica.
- Reproduction: cuttings, rhizomes, dividing with rhizomes (nodules).
- Temperature: in summer + 18-25 ° С, in winter not lower than + 15 ° С.
- Watering: abundant from spring to autumn, in winter - without watering.
- Air humidity: high.
- Lighting: bright, diffused light.
- The soil: fertile.
- Causes of the disease: aphids, spider mites, gray rot, thrips.
- Features: species and varietal diversity.
Ahimenes is a well-known herb with showy, abundant flowers. Being in close kinship with gloxinia and saintpaulia, achimenes is distinguished by its ease of cultivation and spectacular external data. Depending on the species, it can be an ampelous composition or an erect shrub with creeping shoots, which are decorated with numerous inflorescences. Shades: from pure white to purple-violet. The Ahimenes beautifully decorate open loggias and balconies. The species diversity of Achimenos is great. Almost every season new varieties appear in specialized stores. The older generation of today's plant lovers (their grandparents) is often referred to as Ahimenes: "a friendly family." The nickname is more than fair! To breed achimenes, you need shallow planters. Rhizomes (the so-called small nodules of plants) are planted to a depth of no more than 2 cm. The composition of the soil: leafy soil, peat and sand. The amount of drainage in such a mixture should be at least 1/5 of the total amount of soil. Ahimenez is very hygrophilous during the active period of his life, however, he does not tolerate stagnant water. Water for irrigation should be warm. I must say that achimenes, in principle, is a thermophilic plant. At temperatures below + 15 ° C, it stops developing. In addition to heat, the plant loves bright, diffused light. With all the species diversity of achimenes, the rules for caring for him are identical:
- As the shoots grow, it is recommended to pinch and prop them up;
- The plant is fed during the active period from spring to late autumn with mineral fertilizers;
- Moisturize by spraying air near the plant or with containers of water next to the pots.
An adult achimenes is capable of blooming twice a season. The first flowering, traditionally in May-June, is usually more abundant than the next.
The tubular flowers of the plant are similar to bells with bent edges. The lifespan of one such flower is not long. But, since flowering continues for a long time, and the number of flowers is large, this has little effect on the external data of the "friendly family". At the end of autumn, by the appearance of the leaves, it becomes clear that the plant is preparing for rest. To do this, you need to get rid of the entire ground part. The rhizomes remain in the ground. The surface of the soil is covered with sawdust or vermiculite, and the plant in this form is transferred to a cool shaded place. Instead of full watering during this period, he uses a spray bottle that slightly moistens the soil, preventing the rhizomes from drying out. Experts recommend doing this procedure no more than 1 time per month. At the end of February, the pots are returned to a warm and bright room and watering is gradually increased. Everything is ready for the awakening of Ahimenes! Due to the fact that seed propagation of achimenes is associated with mini-greenhouses and a special method of growing, and cuttings are an even less common option, the main method is dividing the rhizome. At the next transplant, the rhizome is cut, making sure that the fragment has at least one shoot. The cut site is treated with charcoal. To prevent decay of the rhizome, just before planting, it can be moistened with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. The most popular species, which gave numerous varieties: Achimenes ehrenbergii, which is easy to distinguish by the yellow-motley core of the flower; Erect Achimenes (Achimenes erecta), whose shoots are reddish; Long-flowered Achimenes (Achimenes longiflora) In addition to the elongated flower shape, this species is easily distinguished by the yellow throat. In the "friendly family" of Achimenos, there are about five dozen more species, the main difference of which is reduced to the configuration of leaves and flowers.
Use of automatic irrigation "Ol Gee"
For Ahimenes, we can recommend the use of an olGGol automatic irrigation device with a diameter of 12-19 cm. This makes it easier to maintain the conditions of constant soil moisture, its effective loosening, and to provide optimal care for Ahimenes, especially if you are going on vacation - the automatic irrigation tank will be enough for about 2 -4 weeks.
In preparing the materials, images from our own photo archive were used.
«>
Reproduction of aspidistra by dividing the bush
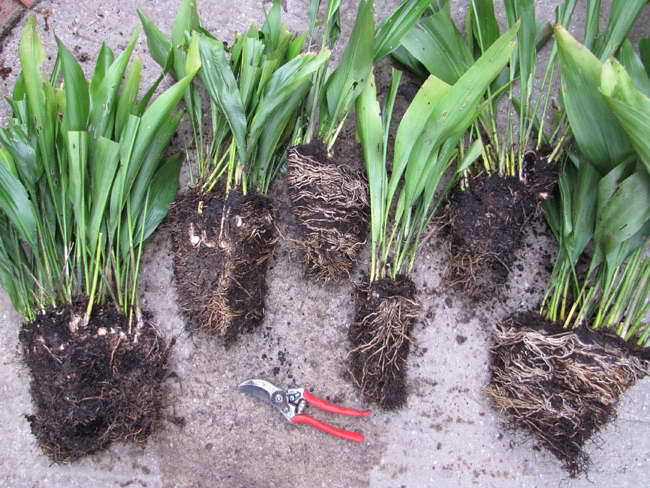


Reproduction of aspidistra by dividing the bush photo
It is most convenient to divide the rhizome: in March, free the plant from the pot, carefully cut the root into pieces with rosettes of 3-5 leaves at least. Sprinkle the cut with crushed charcoal to avoid rotting, immediately plant it in the soil. For new plants, select small pots, maintain an air temperature of 18-20 ° C for a week, water moderately
Varieties of aspidistra
The plant has about a hundred different species, which can be seen by looking at the photo of the aspidistra. However, there are only two varieties that have taken root in our country.


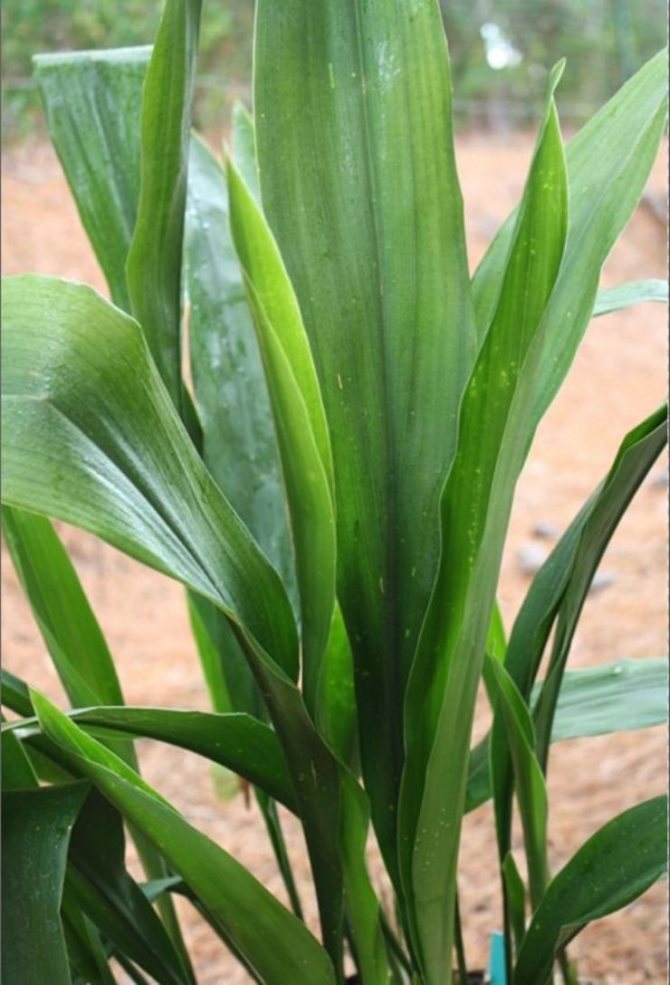
Aspidistra is tall, capable of growing in various rooms. It has large shiny oval leaves sitting on long, compacted petioles. The length of the leaves, together with cuttings, can reach up to half a meter, and the width is 13-15 cm.


Aspidistra garden - has a different color of leaves, filled with white or cream stripes. The rest of the parameters are the same as in the previous version.


Reproduction
The most common and effective breeding method is by dividing the rhizome. It is good to combine this action with the transplantation process. Separation of the roots should be done with a very sharp knife so that no chipping is left.It is advisable to cut so that each piece contains at least three leaf blades. Sections are required to be sprinkled with crushed charcoal, after which they are planted in prepared soil. It is recommended to observe the measure in watering, as excessive moisture can provoke rotting of the roots.
TRANSPLANTATION OF A POSTEDISTER
The conditions for caring for Aspidistra are such that the plant must be transplanted only if there are reasons for this, for example, the pot has become small, or there are already a lot of roots, as a rule, this happens every three to four years. Such a rare transplantation is due to the fact that the plant tolerates the transplanting process extremely negatively.
Watering the aspidistra
For a plant of this species, there are no clear watering rules that can be followed. Aspidistra needs moisture only when the topsoil begins to dry out. In spring and summer, it is recommended to water the flower two or three times a week. In autumn and winter, once every seven days.
Advice! Try not to allow the soil to dry out or waterlogged. Both of these factors are detrimental to the plant.


Aspidistra flowering
At home, the plant rarely blooms. This requires ideal conditions of detention. The uniqueness of flowering is that the buds of aspidistra are formed on the roots. These are very small flowers of a deep purple hue, reminiscent of a star.
Flowers delight with their beauty only for one day. Then a round fruit is formed in place of the flower. There is a seed inside.
In the wild in tropical Asia, the plant begins to bloom during the rainy season - January, February and March. At home, aspidistra can bloom in spring or summer.


Care errors, diseases, pests
| Problem | The reasons | Manifestations | Solutions |
| Root rot | Excess moisture, activation of the pathogen fungus. | Withering and yellowing of leaves. The appearance of dark brown spots and white fluffy bloom on the rhizome. | Removing diseased roots, treating "wounds" with ash, reducing the irrigation regime, using soil drainage. |
| Red spider mite | Lack of moisture, attack of insect pests. | Brown leaves, the appearance of pale spots and cobwebs on the back of the leaves. | Spraying weekly with soapy water or insecticides, the scabbards can be harvested by hand (adult scabbards have increased insecticide resistance). Increase the frequency of watering. |
| Palm scale insects | Yellowing and dropping of leaves, the appearance of small insects on them, as well as brown spots on the underside along the veins. | ||
| Non-infectious chlorosis (disease) | Watering with poor quality water. | The leaves begin to turn yellow. The green color loses its brightness and fades. The turgor of the leaves is preserved. | Top dressing with complex fertilizers and watering with clean water. |
| Infectious chlorosis | Damage to the plant with an infectious agent. | Rapid yellowing of leaves. | The disease is not cured. The plant is destroyed. |
| Sunburn | Exposure to direct sunlight. | The appearance of brown spots. | Transfer the plant to a shaded area. |
| Lack of development | Lack of nitrogen fertilizers. | Extremely slow growth. | Application of nitrogen fertilizers to the soil. |
| Water scarcity | Dry air amid high indoor temperatures. | Decreased trade, wilting and yellowing of leaves, drying out of their tips. | Spraying the plant, changing the frequency of watering. Move to a cooler room. |
| Loss of color by leaves | Lack of light. | Blanching of leaves, loss of their characteristic color. | Increase the intensity of diffused light illumination. |
| Excess fertilizer. | Selection of fertilizers and feeding frequency. | ||
| Excess moisture in the soil | Frequent watering | Leaves darken and become lethargic. | Removing excess water from the sump, reducing the frequency of watering. |
| Aphid attack | Insect pest activation. | Clusters of insects appear on young leaves. The leaves lose their shape and dry out. | Treatment of plants with insecticides, including preparations containing permethrin. |
| Leaf spot | Frequent watering, infection with a pathogenic fungus. | The appearance of brown spots on the leaves surrounded by a yellow halo. | Removing diseased leaves, reducing the frequency of watering, using fungicidal preparations. |
Pruning aspidistra
Over time, the plant loses its attractiveness. Damaged, withered or withered leaves are the cause. As a breeding ground for various pests and fungi, they can infect the rest of the leaves of the bush.
To return the flower to an attractive appearance and maintain health, you need to periodically cut off bad leaves. This should be done at the very root. This procedure not only improves the general condition of the plant, but also stimulates the growth of young leaves.


Fertilizers for aspidistra
You need to fertilize the plant every year in spring and summer. If the flower is in a shady place, feed it every three months. If the plant is in a sunny area, fertilize every month.
Use a water-soluble nitrogen-based flower dressing. Dilute the fertilizer half as much as indicated in the instructions. Try not to fill the young leaves that have appeared on the root with top dressing.
Advice! Do not feed plants with striped leaves. If you add fertilizers to them, the unique color will disappear.


Photo of aspidistra
Diseases and pests: how to identify and defeat - table
The causes of fungal diseases in aspidistra are constant waterlogging of the soil.
| Diseases and pests | Symptoms | Control measures | Prophylaxis |
| Root rot | Dark brown spots appear on the rhizome. The leaves turn yellow and die off. In advanced cases, the fungus covers the soil and affected plant tissues with a fluffy white coating. | Remove the yellowed leaves and cut the lesions on the rhizome until healthy tissue. Process with Maxim (according to the instructions). Transplant the aspidistra into disinfected soil. |
|
| Leaf spot | Initially, dropsy appears on the leaf, which, when dry, become a brown spot surrounded by a yellow halo. | Cut and destroy the affected leaves. Treat the plant with Fundazol or Skor, according to the instructions. Usually this is 4 - 5 applications with an interval of a week. |
|
| Red spider mite | The leaves covered with a thin cobweb turn brown and dry out. | In case of severe infection, treat the plant with Aktellik, Aktara or Fitoverm. Spray up to 3 times after 7 to 10 days. |
|
| Shield | Young pests spread quickly throughout the plant. Adults settle in one place, covered with a brown shell. Affected leaves turn yellow and fall off. |
Signs of diseases and pests in the photo


Root rot can kill a plant


It looks like a leaf affected by spotting


The spider mite braids the leaves with a cobweb, along which it deftly moves


An adult pest sits motionless in one place, covered with a strong shell
Aspidistra oblanceifolia Nagoya Stars
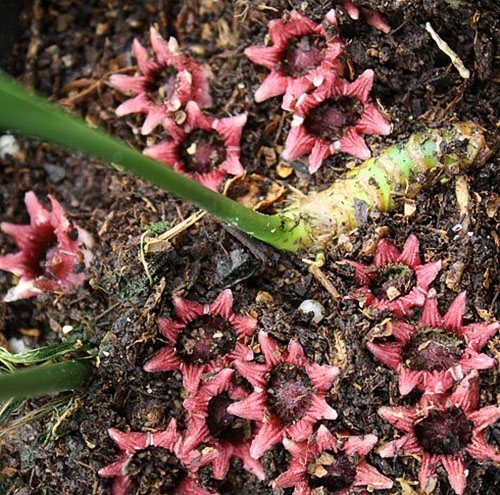


Those flower growers who are interested in the flowering of aspidistra can pay attention to the variety "Stars of Nagano", which reveals many small reddish flowers in early February.
The plant is the world champion in mass flowering and may well become the center of any collection. Having grown this variety at home, you can proudly show its bloom to your guests. The main condition is compliance with the rules of planting and care.The number of flowers and their appearance depends on the depth of the plant's root system.
Do not think that this species of aspidistra is invisible in other months. The variety of aspidistra Zvezda Nagano shown in the photo has tough narrow foliage also strewn with small yellow stars.
Medicinal properties, application
The benefits of using aspidistra preparations are determined by the presence of bioactive substances in its composition. Alkaloids have bactericidal properties, stimulate blood flow, promoting the resorption of hematomas.
Medicinal decoctions are used in the treatment of periodontitis, tonsillitis, cystitis, gastrointestinal diseases. The leaves of the plant are recommended to be chewed for bleeding gums. The juice is able to quickly stop bleeding. It is also used to treat bruising or open wounds.
The use of medicines based on it, in order to avoid harm to health, is recommended to be carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
Description of the plant
In the age of stove heating, when the air in the houses was heavy, aspidistra lived with every florist. Other natives of the tropics could not tolerate such an atmosphere. In the 20th century, with the advent of central heating, indoor plant lovers were so carried away by the cultivation of exotic flora that they forgot about the reliable aspidistra. And now this flower is returning to our homes and mastering offices. It is able to grow even in semi-dark rooms. Its harsh nature was appreciated by those who do not have time to carefully care for the plant.


Unpretentious aspidistra is becoming more and more popular
Aspidistra easily tolerates a break in watering, she does not need a backlight, and does not even like a flower transplant. At the same time, it gives a lot of greenery, large foliage is very decorative, you can choose varieties with white or yellow stripes, spots or specks.


The variegated variety of aspidistra is very picturesque.
This Spartan flower is native to the tropical South Asian forests. Aspidistra grows in the lower tier, which is why it is so calm about the shade. Rain does not often break through the upper plants, so the flower is used to economizing on moisture. Having moved to our homes, the beauty retained her harsh habits.
Aspidistra is respected by the planters of bouquets, although she cannot boast of her flowers. But bright flowers, devoid of their greenery, are wrapped in its wide emerald or variegated leaves.


Graceful aspidistra leaves accentuate the beauty of other flowers
The main charm of the aspidistra is its wonderful foliage, which looks like a lily of the valley sprout. This plant has no stem. Resilient and mobile, large (50 to 80 cm in length) and bright leaves grow on petioles directly from the creeping root. It is dark, long and winding, located at the very surface of the earth. Perhaps it was the serpentine form of the rhizome that gave the name to the plant.
The name "Aspidistra" translates as "snake index". It is believed that they called her that because of the ability to transmit the movement of creeping reptiles. The leaves of the aspidistra sway where the snake crawls. Other sources say that the name comes from the ancient Greek words "aspis" - a shield and "astron" - a star. The inflorescences of the aspidistra resemble an asterisk, and the leaves can be compared to a shield. Another nickname for the plant is also associated with its shape. For the fact that the leaves of aspidistra grow densely and consistently one after another, it was called a "friendly family". In Europe, this plant is popularly called the "shoemaker's palm", and in Great Britain - the "cast iron plant".


Aspidistra is a great option for landscaping an office
Aspidistra looks good next to other flowers. However, the adult specimen is often grown as a solitary floor plant. So all the charm of rich foliage is better revealed.
Description of varieties
About 90 species of this plant have been found in the wild. In home floriculture, only one species is bred - the tall aspidistra. It is a long-lived rainforest that can grow for almost a hundred years.
With indoor maintenance, such a long life has not been recorded, but the "cast-iron plant" will delight you for at least ten years.
Breeders have developed variegated (variegated) varieties of this variety. Flower growers from Japan have especially worked on the plant, so many varieties have received corresponding names.
- Aspidistra high (Elatior) comes from the southern forests of China and Japan. Above the serpentine root, bright green shiny leaves rise on petioles. Young shoots stand upright, dropping slightly with age. The size of an adult leaf reaches 0.5 m in length and about 15 cm in width. Platinum leaf is dense and elastic. Aspidistra high grows slowly, 5–6 leaves appear per year. It is a very hardy plant.
- The Milky Way is the most famous variety of variegated (variegated) aspidistra. Its leaves are vertical, dense in texture. On a green background, there are small creamy-white spots that look like clusters of stars. This aspidistra tolerates not only drought, but also low temperatures.
- Aspidistra Milky Way became the basis for the Amanogawa variety (which means Milky Way in Japanese). On leathery narrowish leaves, in addition to small white spots, there are pale yellow stripes.
- Aspidistra Fuji-No-Mine is the owner of wide striped foliage. Light green stains spread over the glossy dark greenery. The top of the leaf is decorated with a snow-white cap, the Japanese saw in it a resemblance to the top of Mount Fuji.
- Aspidistra Ginga Giant is the most shade-loving. Its large mottled leaves look brighter if they are not exposed to the rays of the sun. The plant can withstand frost down to -10 ° C.
- Aspidistra Okame is decorated with wide white stripes, which sometimes occupy half of the long and narrow (70:12) leaf blade. The plant is very delicate, does not tolerate temperature changes.
- In the Aspidistra Morning Sun (Asahi), the leaves are shaded along narrow whitish-cream rays. Their coloration becomes more intense at the top. The plant becomes decorative with age. It is grown in large containers.
- Aspidistra Snow White Crown (Sekko Kan) has long leaves, where narrow dark green stripes interspersed with wide white ones. But the beauty is fully revealed after three years - only adult plants have a characteristic color.
- Aspidistra Giant Splatter (Alishan Giant Splatter) is a variety with large greenish-yellow spots, bred in Taiwan.
- Aspidistra Spiderman is a special member of the beautiful-leaved family. It has no bright streaks or spots. But medium-sized leaves are located on strong, but thin spider webs, petioles, and purple flowers look like small spiders.
- Most aspidistra are raised for foliage, and the Nagano Star is prized for flowers. It blooms more abundantly than its relatives; in February, small reddish flowers open up massively right at the root. In addition, the narrow leaves are full of tiny yellow star-spots.
- Aspidistra Yellow Hammer is one of the most variegated varieties. Creamy yellow spots are located on the greenery of large leaves.
Photo gallery: aspidistra expansion


The leathery leaves of the Amanogawa aspidistra have white spots and yellow stripes.


Aspidistra Milky Way tolerates both drought and low temperatures The long narrow leaves of this variety are decorated with white stripes The beauty of the snow-white crown is most fully revealed in adults Purple flowers of Aspidistra Spiderman are similar to spiders Aspidistra Yellow Hammer is one of the most variegated varieties


Aspidistra tall - a species suitable for home breeding Aspidistra Giant spray - a variety with greenish-yellow spots The leaves of the aspidistra Star of Nagano are dotted with yellow spots that look like stars


Aspidistra Star of Nagano prized for its unusual flowers


The older the aspidistra Morning sun, the more intense the color of the leaves


The white tops of Fuji-No-Mine aspidistra leaves give its name.
Growing problems
- Decay of roots. Reason: excessive amount of moisture in the soil.Reduce moisture. Drying, spotting of leaves. Reason: penetration of straight, fine glimpses on the leaves. It is recommended to move the plant to partial shade;
- The appearance of cracks in the leaves. Reason: a lot of fertilizers. It is recommended to reduce the introduction of fertilizers;
- The leaves turn yellow. Reason: the flower is infected with scale insects. It is recommended to treat the damaged areas with soap or tobacco.
Flower propagation
Rhizome. This is the usual method used for an adult plant. Aspidistra should be approximately five years old. The huge disadvantage of this method is damage to the root system. The flower is weak enough to withstand such a procedure. The division of the bush is carried out in four stages:
- the rhizome is gently shaken off the soil;
- with a sharp knife, cut the root in the selected area so that there are at least 5 leaves on the new plant;
- sprinkle with ashes;
- the plants are planted in pots and moisturize the soil well.
Sheet. This is the best breeding option, since the roots are not injured. The leaf rooting procedure consists of five stages:
- a strong healthy leaf is carefully separated from the plant without touching the petiole;
- the leaf is dipped into a container with water. The bank is closely covered;
- the formed greenhouse is installed in a warm and clear area;
- when the first roots appear at the leaf, then you can start planting in the ground;
- the young plant is covered with a cap and another leaf is expected to appear.
Reviews of flower growers about a indoor flower
aspidistra is a leisurely lady. I have two variegated varieties only with peas growing faster on the leaf. A striped giant in comparison with her, gives out a leaf a year. This is where all her “whims” end. It grows on my balcony, it did not plant in open ground. Her pot, as expected, is the narrowest. This year it was at zero on the balcony, and at a slight minus (-2). Without any additional wraps. Alive and healthy! But I shade from the midday sun, spots have appeared, not yet a burn, but a piece of leaf has already burned out.
Karr
My aspidistra is over 50 years old. I also bought a sprout as a schoolgirl. I read about her in Verzilin's book. And since we lived in the basement, it was the only greenery that could survive in our house. Now it grows in a 12 liter pot. For the summer I take her out to the dacha, and spend the winter in the corridor. Perfectly problem-free plant. For half a year he lives almost in darkness, the light from the upper window is reflected, and feels great. For this I love.
Ivanovna
My aspidistra is 25 years old. And on the basis of more experience, I can say that she really does not like transplants ... if possible, only transshipments. can be propagated by a leaf, but with a part of the rhizome. She bloomed after 10 years of "sitting" in one pot without transplanting. Aspidistra in Egypt is called a dead flower because of its unpretentiousness. Indeed, it can grow in the darkest corners, tolerates bay and drought. No spraying required. But this does not apply to colored aspidistra.
bnv63
Aspidistra has a very persistent character and can grow in almost extreme conditions for other plants. But let's create an atmosphere of comfort for the noble aspidistra. And she, in turn, will answer you with the tenderness of lush green foliage, giving you a soothing and relaxing atmosphere after a hard day at work.
Errors in plant maintenance and their elimination - table
| Error | Cause | Elimination |
| Leaves turn pale | Lack of lighting | Move the plant to a more illuminated place or light it additionally. |
| Brown spots on the edges of the leaf blade |
| Provide a place protected from direct sunlight for the plant. Do not place near heating appliances. |
| Leaves turn black, become lethargic | Excess watering | Water the aspidistra according to the rules. |
| Leaves lose turgor | Overdried earthen lump | |
| Aspidistra slows down growth during the growing season | Lack of nutrients | Provide the plant with the correct fertilizer containing sufficient nitrogen. |
| Leaves turn yellow |
| If there is a gradual yellowing, the death of old leaves and at the same time the young foliage looks healthy, do not worry - this is natural aging. With excessive watering, root decay may begin. Let the soil dry before watering again. Try to find a cooler room for the aspidistra. |


Diseases and insect pests
Diseases in Aspidistra rarely appear, but it is worth knowing about the most common. Shield. Small insects are noticeable immediately. When you notice them, you need to remove all affected leaves. For processing, a substance of 30 grams of homemade or 10 grams of tar soap is often used per liter of water. For processing, use a cotton swab, which is used to wipe all the foliage. Next, the leaves are washed with water, wrapping the pot with cling film to exclude the penetration of the solution and excess moisture into the ground. You can treat the flower using an insecticide.
Popular: Branched ampelous Epipremnum from the Aroid family
Spider mite. The appearance of a thin sticky web on the underside of the leaves indicates the presence of infection. To cope with this problem, you need to prepare a cotton pad and soak it in vodka. Chemicals can also be used. Treatment of sick Aspidistra, in particular with a chemical, is performed in the fresh air. When processing substances, gloves and a mask are worn.


Problems and pests
If the leaves began to wilt or turn yellow, then this is possible either due to a lack of watering, or vice versa, due to overflow. If the leaves begin to dry out, it may be too hot in the room or the humidity is low. If the leaves grow poorly, this means that the soil has a low nitrogen content, the plant needs to be fed.
The appearance of brown spots on the leaves is a sunburn, you need to transfer the flower to a darker place. If white spots appeared on the surface of the leaves, this means that the plant was attacked by a red spider mite. You can get rid of it by washing the leaves with a solution of laundry soap.
Aspidistra is a beautiful, unpretentious and useful plant. There is a belief that she cleans the house of "evil spirits", heals depression, gives strength, destroys sadness and despondency in the house.
Soil for aspidistra
The flower feels great in ordinary land from the garden. But for a more accelerated development, it is better to use a universal, nutritious soil purchased from a store.
If you are not interested in using ready-made substrate options, you can make it yourself. The composition of the soil for aspidistra includes the following components: river sand, turf, leafy soil, manure humus. Mix these ingredients in a 1: 2: 2: 2 ratio.


Seasonal care
During the year, the aspidistra adapts to different conditions. The plant does not have a clearly defined dormant period. But in winter, life processes slow down a little. It is necessary to give the culture an opportunity to gain strength, to relax. The temperature can be lowered to + 15..17 degrees. Leave the lighting at the same level. Variegated varieties may require additional lighting to prevent the leaf plates from becoming uniform in color. Top dressing for the autumn-winter period is stopped, and at the beginning of spring the bush is abundantly fertilized. This gives him strength before the start of an active growing season.
Diseases of aspidistra
- Leaves wither - indicates that the soil is too dry or wet. Take steps to normalize soil conditions.
- Leaves turn yellow - a sign of flower aging or roots have begun to rot. To help the plant, stop watering, spray the leaves with a fungicidal preparation, treat the soil with a solution of potassium permanganate.
- Leaves dry - the reason may be too dry or warm air in the room.The problem can be solved by spraying the leaves more often and watering the roots.
- Color disappears - the plant does not have enough sunlight or there is a lot of fertilizers in the soil. It will be possible to return the decorative color if you rearrange the flower in a bright room and stop feeding.
- Pale leaves remind of the lack of lighting, gradually transfer the flower to a brighter place, if there is none, use fluorescent lamps.
- Leaves do not grow - the flower lacks nitrogen in the soil. To speed up growth, sprinkle the soil with urea. The solution is prepared in a proportion of one gram per liter of water.
- Brown spots appeared - they form on the surface and edges of the leaves. This happens when the plant is in direct sunlight, which causes a burn. Move the flower to a dark place.
- The appearance of dark spots could cause hypothermia and drafts. The plant is afraid of drafts, solve this problem faster.
- Infectious chlorosis, symptoms of which are yellow leaves, green petals on flowers and discoloration, immediately get rid of the diseased plant.


Aspidistra leaf propagation
The flower can be propagated using leaves cut from the main bush. This method is more time-consuming, but effective. To do this, cut off the leaf, leaving it with a petiole 7 cm long. Dry the cut area a little and place it in a bottle of water. The opening of the neck is wrapped with tape so that air does not penetrate.
The resulting stalk is placed in the light in a warm room. When the roots appear, the leaf is planted in a pot of soil and watered. To provide a weak plant with greenhouse conditions, it is covered with a transparent cap. After transplantation, the condition of the flower must be monitored.
Advice! You can speed up the emergence of roots by adding a growth stimulant to the water.


Bush cleaning
From hour to hour the bush needs pruning, old dried and withered leaves. You need to trim the leaves as close to the root as possible, with scissors. After such "trimming" the flower has a fresh, neat appearance, in addition, it causes the appearance of new young leaves.
Aspidistra Elatior Snow Cap
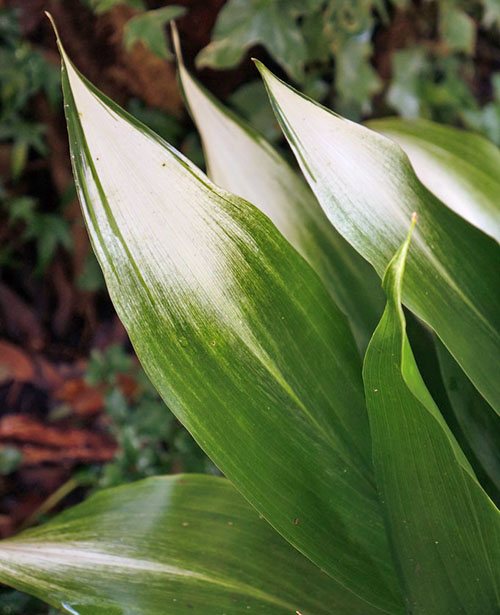


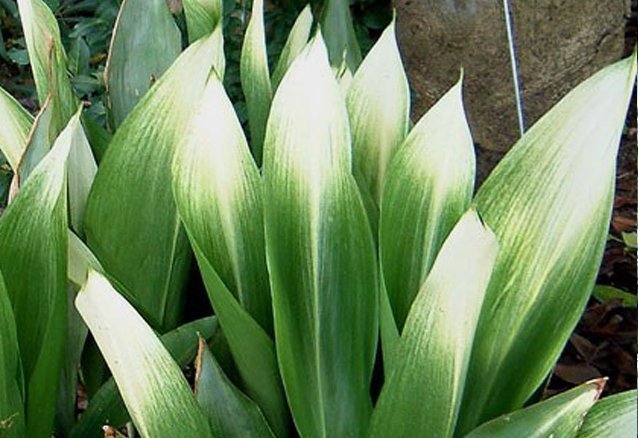
Sometimes the variety of aspidistra shown in the photo is called "improved Asahi". True, the plants are very similar, but in this variety, the white pattern is much broader and more noticeable, and it persists throughout the year.
As with the already described variety, in this case you will also have to wait until the plant is ripe in order to please the owner with non-melting, “snow caps”.