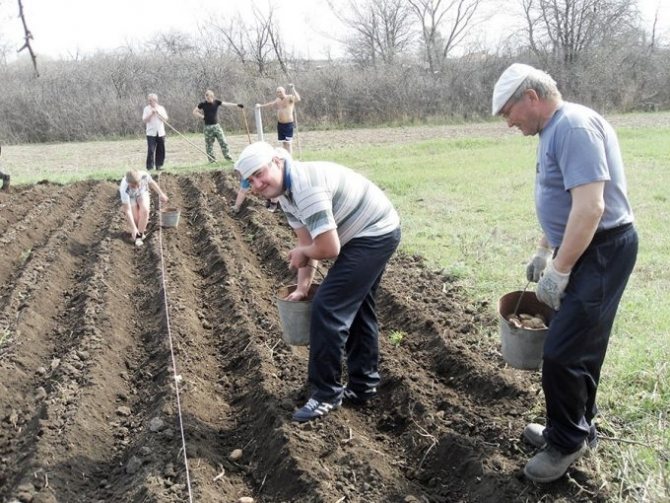
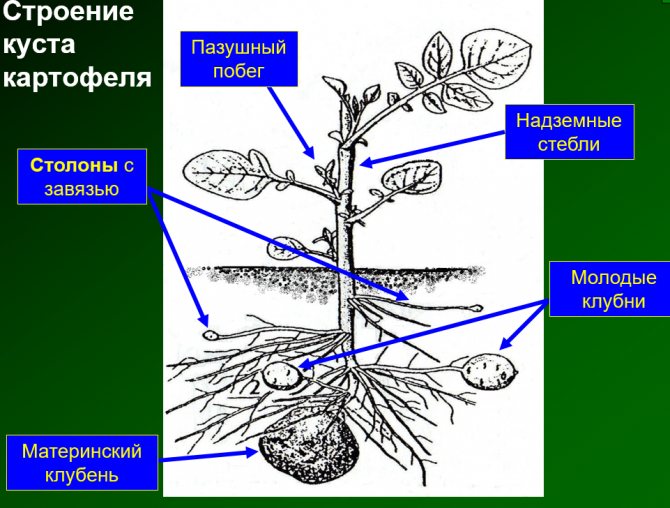
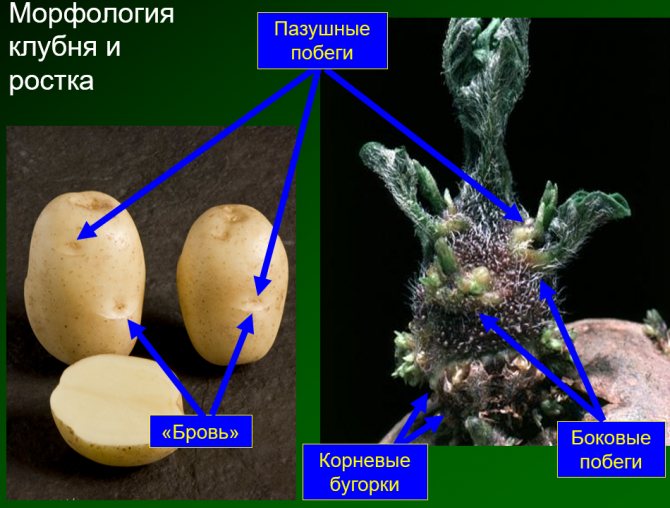
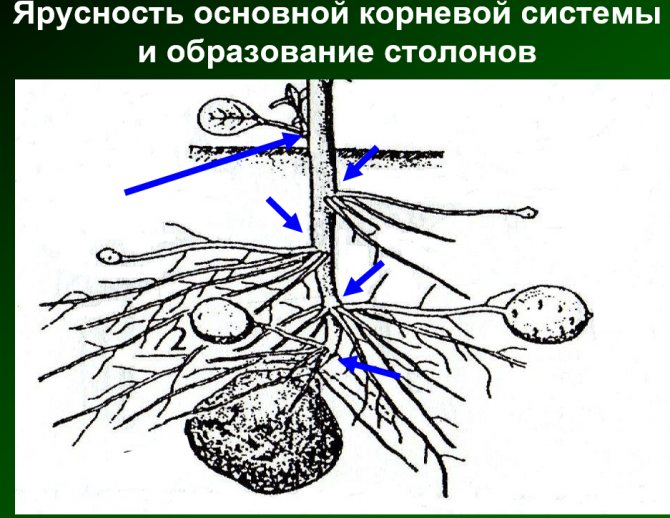
Gardeners know that potatoes forgotten in the autumn in the beds germinate in spring and sometimes even bear fruit no worse than those specially planted. NI Kurdyumov, a well-known popularizer of organic farming techniques, claims that tubers can easily tolerate temperatures down to -10 ° C at a depth of 10–15 cm. So planting potatoes before winter is scientifically justified.
Advantages of planting potatoes before winter:
- the possibility of getting early potatoes;
- high productivity;
- plant resistance to late blight;
- no need to weed mulched beds.
Disadvantages of planting potatoes before winter:
- high labor intensity;
- impossibility to apply mechanization;
- high probability of crop death due to the vagaries of the weather;
- the complexity of protecting landings from bears and rodents;
- the method is not suitable for northern regions.
Potato growing rules
There are crop farming rules that apply regardless of which variety the gardener plans to grow:
- The plant does not tolerate frost and extreme heat. These nuances should be taken into account when deciding on the place and date of planting potatoes.
- The need for watering depends on what stage of ripening the crop is. Young shoots, as well as faded crops, do not need a lot of water. The maximum amount of moisture the plant needs at the time of flowering. If during this period the potatoes are not sufficiently moisturized, this will negatively affect its quality.
- Crop beds should, if possible, be located from north to south. With such an arrangement, ultraviolet rays will fall on the potatoes for as long as possible.
- As for fertilizers, a prerequisite is the use of mineral fertilizers: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Gardeners often use manure or poultry droppings.
- Root crops in one place should be planted no more than two (three) times. The best precursors are: beets, cucumbers, cabbage, cereals. You should not plant potatoes where tomatoes, eggplants or peppers were previously grown.
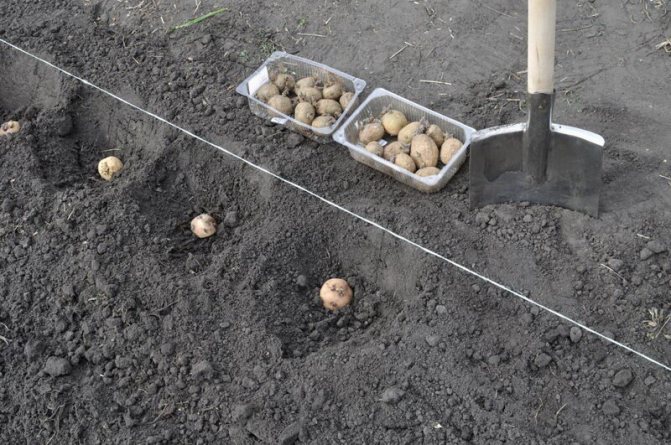
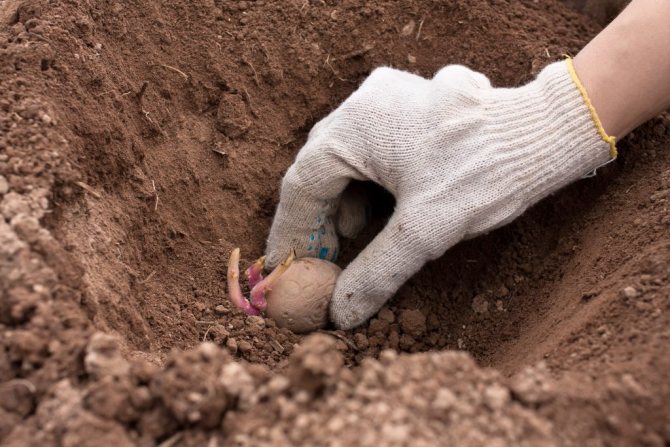
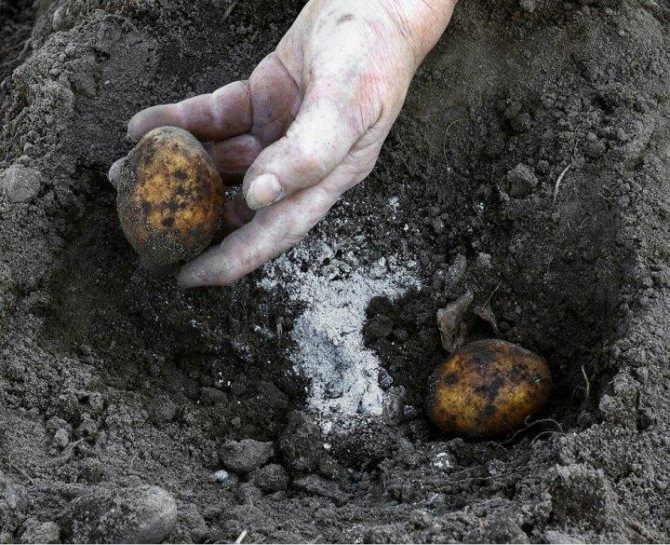
- The planting depth of a crop depends on the composition of the soil. If it is light, the roots are placed deep. With loamy soil, potatoes are dropped by 5-6 cm, sandstone - up to 15 cm.

Site selection and placement of potatoes in a crop rotation
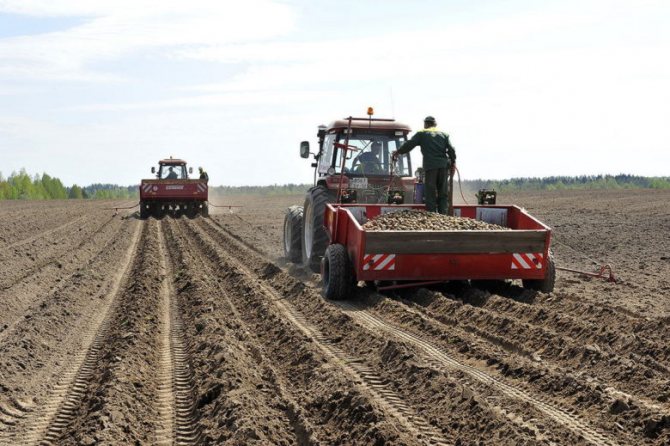
On a large scale, potatoes are grown in the field. The choice of sites for planting must be approached very seriously, since the future harvest depends on the quality of the soil. This plant has a rather weak root system, requiring a loose, light, air and moisture permeable soil. Sandy light, sandy loamy soils are best suited; loamy soils are also suitable.


Fields for planting potatoes
The soil should remain loose after rains and watering, and should not float and be compacted. Therefore, if the soil is clayey or heavy chernozem, to loosen it, you need to introduce quite a lot of organic matter and carefully process it with special equipment. Requires dry, level areas without slopes, flooding and waterlogging. Soil acidity at the level of 5.5 - 6.5 pH. Heavily weedy fields are also not a good choice, especially if there are many weeds such as wheatgrass.
Solanaceous crops have many diseases and pests, therefore, due to the risk of re-infection, potatoes are planted in the same place only after 3-4 years.Sometimes in open ground with good cultivation of the land in the fields and fertilization, you can plant this plant for 2 years in a row. But it is better not to do this, since bacteria of diseases and pests can remain in the soil.
In a crop rotation, the area of pure fallow should be no more than 50%. Pure fallow areas are land that is left unplanned, yet prepared for future planting.
Pure fallow is considered a good precursor for planting potatoes.
In order for the soil to bear fruit productively, crop rotation must be observed.
Planting methods
There are many ways to plant potatoes. When choosing a method, they are guided by a number of factors, one of which is the territory of the land plot.
In large areas
Large areas in the garden are mainly planted in traditional ways:
- the usual method;
- into the ridges;
- in the trenches.
These options allow you to plant a crop and grow a high yield of potatoes without any problems.
See also Features and varieties of purple potatoes
On a small plot
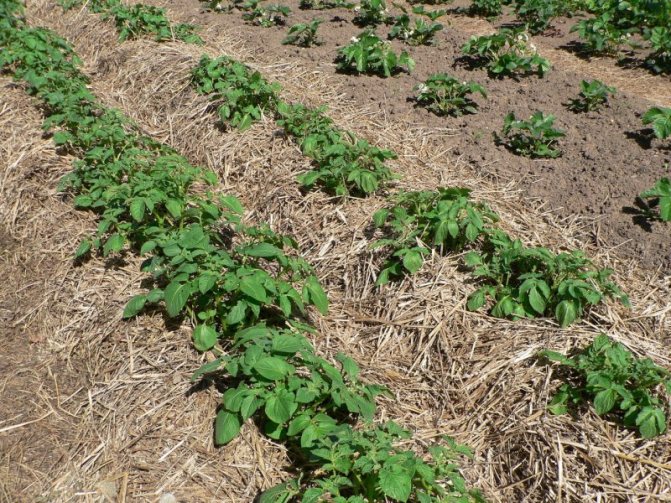
In small plots in the country, the culture should be planted, first of all, on suitable soil. So, before that, corn, pumpkin or sunflower should not be grown on the ground. Better to plant the vegetable after the legumes. As for the planting method, in general, those that do not require time are suitable: under straw or in barrels.


How to plant outdoors?
To date, summer residents and gardeners on a small area use three main types of planting potatoes in the ground.


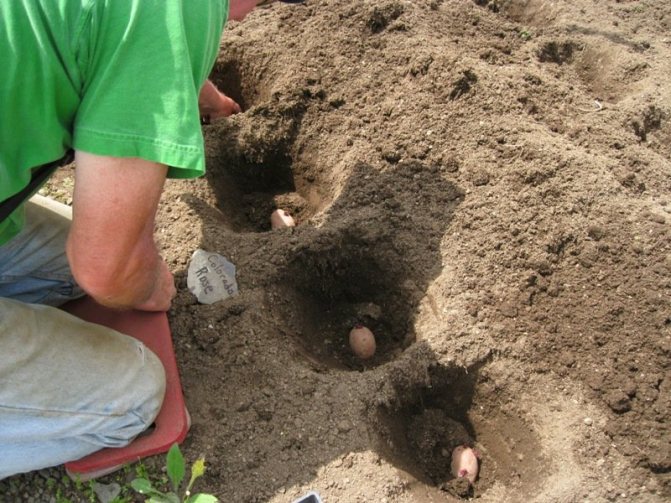
In the old fashioned way, shoveling in rows. This method is applicable for areas with flat terrain, where holes are clearly formed and visually even rows are obtained. 1-2 tubers are placed in each groove made with a shovel. Humus or ash is thrown there, and sprinkled with earth on top. The depth of the hole is about 10 cm, the distance between the tubers is 35-40 cm, and between the rows is 50-70 cm.- Ridge method. It uses it in waterlogged areas, areas with heavy clay soil. Ridges are formed along the entire length of the site using a tractor or walk-behind tractor. It is also possible to do the procedure by hand with a hoe. The distance between the ridges is maintained at about 70 cm, and 15-20 cm in height. Potatoes are planted on top of them. The root crop gives good results due to the warming up of the earth by the sun and good air exchange.
- Trench. It is considered ideal for sandy soils. If, with the ridge method, the potatoes are located on top, then in this, on the contrary, they sink to the bottom of the trench. This helps to protect them from overheating and drought. The trench is dug with a depth of 10-15 cm, and the distance between them is 50-70 cm.
Optimum temperature and humidity
The optimum climate for culture is moderately cool, without sudden changes. Potatoes are sensitive to frost and heat. In the warmest months, a suitable temperature should not be less than + 20 ° C.
Agronomists have bred a lot of potato species with tubers ripening from 60 to 170 days, so it is allowed to choose the right one for each region. Plants begin to germinate at a temperature of + 4 ° C. If it drops to -2 ° C, then there is a partial or complete loss of tubers and bushes.
If the average daily temperature rises to + 26 ° C, the tubers undergo necrosis, become lethargic and the development of the plant stops.
The optimum humidity is 70-80%. Lack of moisture leads to a decrease in yield and spoilage of tubers. Too much water can lead to loose skin.
How does a vegetable grow by day?
From planting potatoes in the ground to the first shoots, an average of 20 days pass. It all depends on weather conditions, the depth of planting the tuber, soil fertility and the degree of preparation of the planting material.
From the moment the sprouts appear until they are fully ripe, a certain time interval passes, which in turn depends on the variety:
- Super-early varieties are ready for fruit digging in 50-65 days.


Early potatoes - ripening period 70-90 days (see a separate article on how to grow early potatoes).- Mid-season variety - give a high-quality harvest in 100-125 days.
- Late ripen after 140-150 days.
However, the choice of a variety is a purely individual matter for each grower and region of growth. Also, the choice is determined by the following criteria:
- taste characteristics;
- the purpose of the species;
- ability for long-term storage;
- resistance to various diseases.
Proper care technique
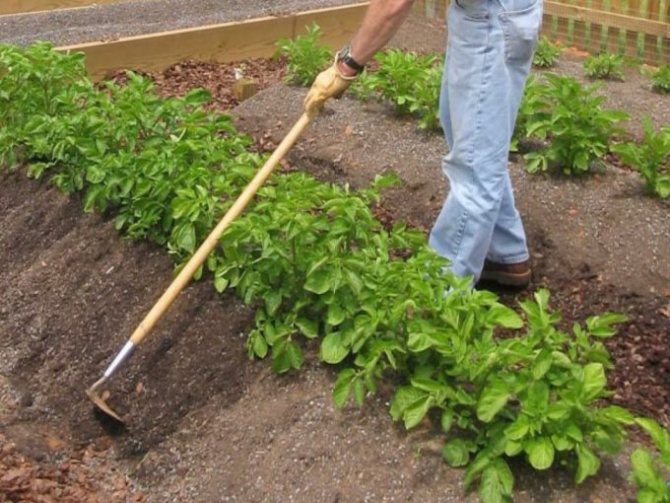
Correct agricultural technology is an important condition for obtaining a high yield. Crop care begins before the shoots appear. Growing tubers need air, which is achieved by loosening. You also need to monitor the condition of the soil. It must be free of weeds, which can be removed without problems at first with a rake or boric acid. Next, you need to loosen the ground between the rows and after watering (rain). No crust should form on the ground.
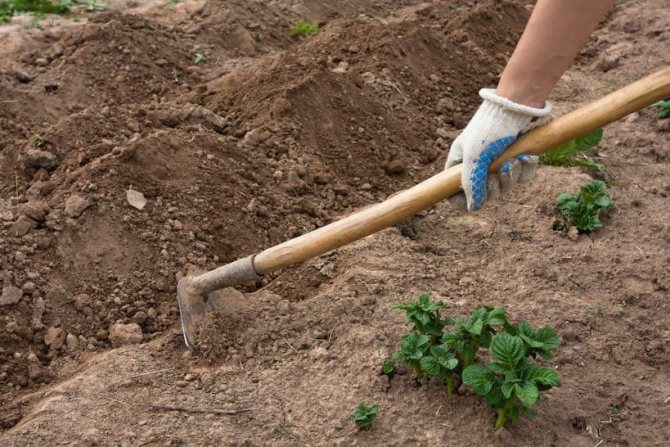


The hilling of the crop is carried out at the moment when the potato grows to 15-18 cm. In the southern regions of the country, where there is a lack of moisture, the plants do not need to be hilled. Loosening is carried out instead.
As a top dressing of potatoes, mineral fertilizers or ash are used, which is scattered near the bushes (15 cm from the stems).
To carry out liquid top dressing, furrows are dug between the rows, where fertilizer is sent. As a rule, potash, phosphorus and nitrogen fertilization is used. As for liquid organic fertilizers, manure or bird droppings are suitable for the crop. After the fertilizers are completely absorbed, the potatoes are spud and loosened.
At the budding stage, the soil should be moistened. If during dry weather the soil dries out to a depth of 5 cm, the culture must be watered.
Also, while growing potatoes, you need to regularly carry out prophylaxis against pests and diseases.
Harvest storage
Storage of the harvested crop is an important point in the entire chain of growing potatoes in large volumes. For long-term storage and preservation of the crop, vegetable stores are used, in which all the optimal conditions are created:
- Moisture so that the crop does not dry out and rot;
- Sorting allows you to separate healthy tubers from damaged ones;
- Creation of conditions for the healing of damage to the vegetable obtained during harvesting;
- Temperature regime so that the potato keeping quality is longer and it does not germinate;
There are two most common storage methods for potatoes:
- In bulk... The method is somewhat resource-saving - you can save on storage containers, but you need a good ventilation system.
- In containers... You can more flexibly sort vegetables according to various parameters, create a high-bay warehouse, and it is also easier to transport and monitor the safety. But an economically more expensive way of warehousing.
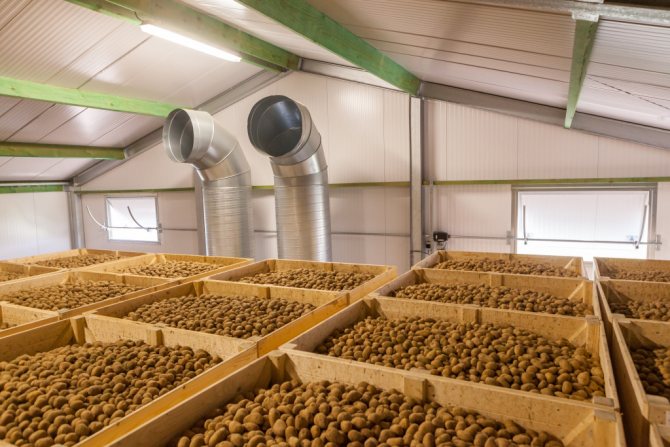


Storage in containers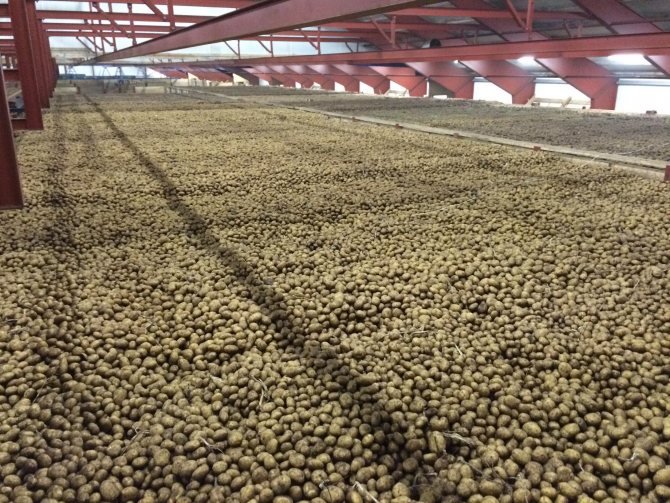

Bulk storage
Tips and tricks for growing potatoes
To get a high yield, it is worth resorting to some tricks.
Growing large potatoes
To get good potatoes at the end of the season, you need to select the appropriate planting material. The culture is prone to various diseases, both infectious and viral, so it is not worth growing your own crop from time to time.
See also How to properly apply Corado from the Colorado potato beetle on potatoes
When choosing root crops for planting, they pay attention to the variety, yield, color and taste.The size of the planting material also plays a role, since you can get a large vegetable from the same type and characteristics of potatoes.
Criteria for the selection of planting material:
- climatic conditions of the region;
- tubers with a lot of eyes;
- checking planting material for diseases;
- the size of the potato for planting should be larger than average;
- ripening period.
Ways to increase the yield
The method of planting a crop can increase the yield of potatoes. To get more than one bucket of vegetables, you can use the following techniques:
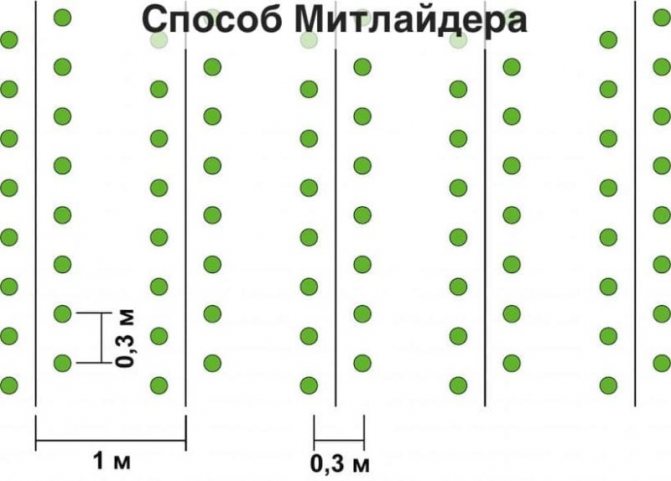
- Meatlider's method. The culture tubers are placed at a distant distance from each other (there should be 1 m between the potatoes) and in a checkerboard pattern.
- Dutch technique. Planting is carried out in high beds, the distance between the planting material should be 80 cm. The holes are additionally filled with fertilizers. The soil under the planted crop is constantly mulched, watered and fed.
- Gulikh's way. The garden is divided into squares (1 mx 1 m), in the center of each of which the earth is mulched and fertilized with humus. Next, the tubers are planted. After the potatoes sprout, cover the ground. As a result, small mounds should form.

Preparation of planting material
High-quality, healthy planting material is the key to an excellent harvest. Before planting, you need to prepare the tubers. This includes the following activities:
- unloading potatoes from storage sites;
- rejection of rotten, damaged, diseased tubers;
- dividing them into fractions;
- heating and germination of eyes for early varieties;
- pickling against fungal diseases with fungicides.
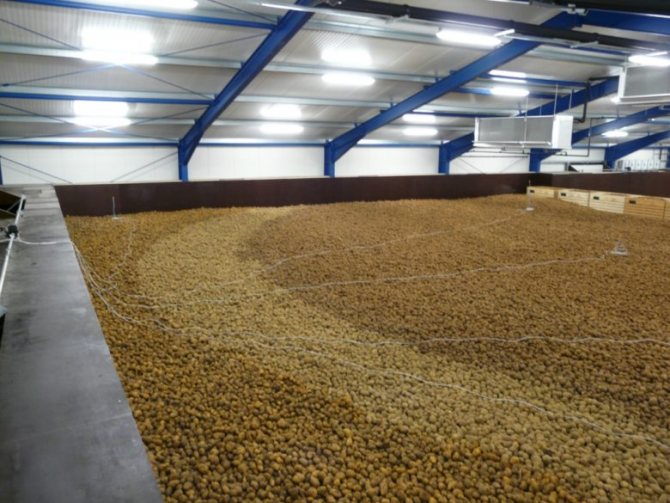


Planting material storage
For planting, you need to use healthy tubers that correspond to the variety and the requirements of the 1st and 2nd class. It is not allowed to use slightly frozen, rotten, irregularly shaped tubers.
Planting material begins to be prepared 2-3 weeks before planting in the ground. This improves the quality of tubers and increases yields.
The potatoes are divided into fractions using sorting rollers. There are the following factions:
- 25-50 g - small
- 50-80 g - medium,
- 80-120 g - large,
- more than 120 g - very large.
After sorting, the tubers are taken to closed areas, where they are laid out in a layer up to 20 cm thick and dried for 12 days at a temperature of 16-20 degrees Celsius. At this time, the germination of the eyes occurs. At the same time, potatoes are treated for diseases. And to accelerate germination, tubers are treated with various stimulants.