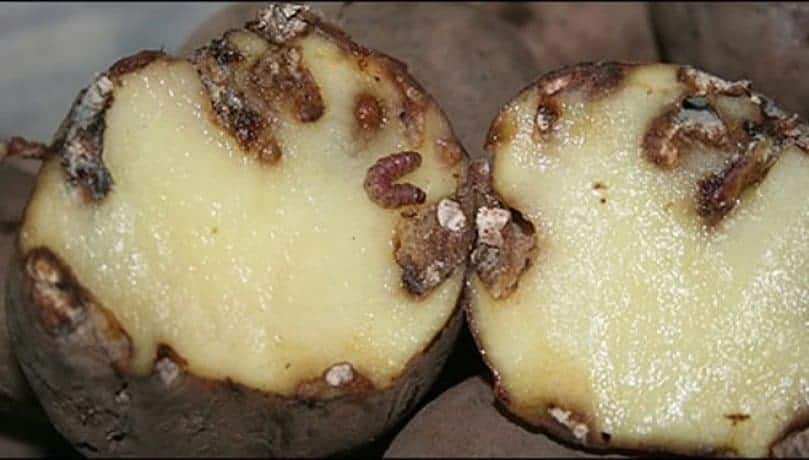
Late blight
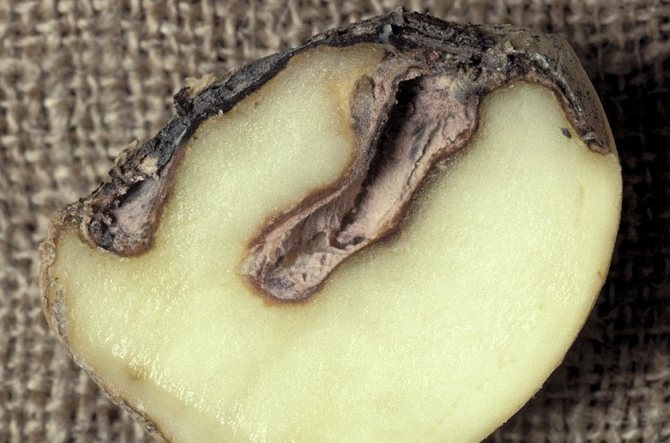
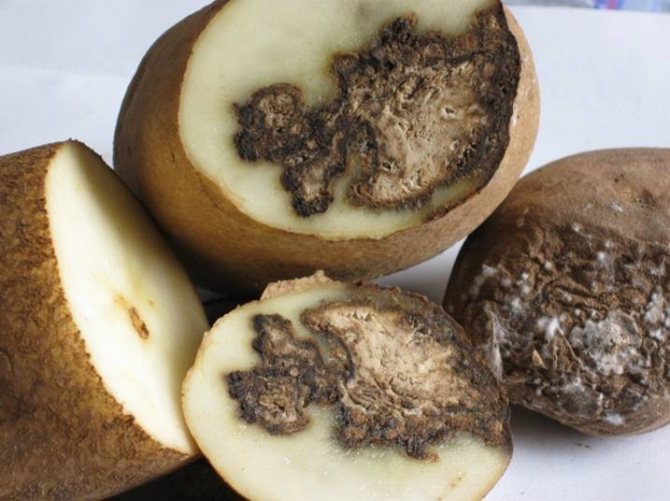
A very dangerous fungal disease that can destroy about 60-70% of the entire crop.
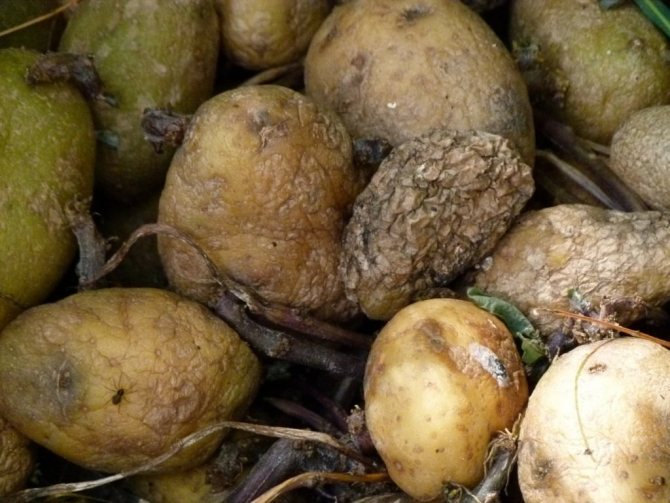
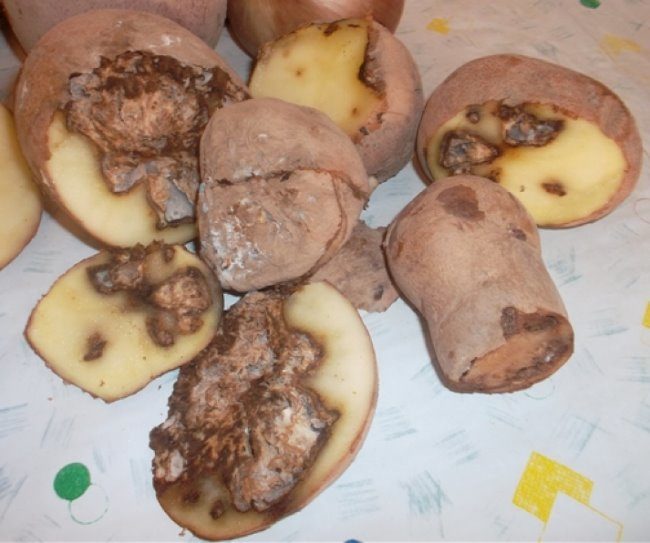
It is not difficult to calculate it: blurry gray, sometimes brown hard spots appear on the tubers, going deeper - if you cut the potato, they can be seen on the pulp.
The disease can develop during the growing season, as well as during harvesting: a fungal infection from the tops moves to the tubers and gradually destroys them. The development of the disease continues at the very beginning of storage at a sufficiently high air temperature in the cellar.
The fungal infection is not transmitted from tuber to tuber during storage.
How to deal with late blight?
- Dig up potatoes in dry, sunny weather. Dry the tubers for several weeks in a dry, dark place with good ventilation before storing. Then carefully sort the potatoes - if there are suspicious spots, rotten areas on the tubers, do not put the roots in the cellar.
- The air temperature in the room for storing potatoes should be about 2-3 ° C, humidity 80-91%; important factors are lack of light and good ventilation.
- Pour potatoes into piles or boxes with a layer of no more than 1 m. Storing tubers in bags is undesirable.
- During the winter period, do not touch the potatoes - this can damage the tubers and further infest them.
Phytophthora actively develops at high temperatures of about 20-24 ° C. Therefore, it is not recommended to store the crop in a residential building - the disease will destroy it very quickly.
Favorable conditions for breeding
Why does mold appear in some cellars and not in others? For the emergence of "life" certain conditions are necessary:
- the presence of spores in the air. They are transported and deposited in the cellar on people, food, animals;
- nutrient organic medium (paper, wood, soil, peat pots);
- favorable microclimate (high humidity, temperature about 20 degrees). Also, poorly working or not working ventilation at all negatively affects.
Some types of fungus have the ability to reproduce at temperatures of 0 degrees.
Pay special attention to the ventilation system. After all, it is designed for normal air circulation in the room. The movement of air prevents mold spores from adhering to any surface. In the corners, the movement of air is difficult, it is there that colonies of fungi often accumulate.
Ventilation helps to remove excess moisture from the room, which occurs against a background of high humidity outside or a large difference in temperature. If there are fungal spores on the walls, but there are no favorable conditions for reproduction, then they will not germinate. Based on this, we can conclude that poor ventilation is the main reason for the appearance of fungal colonies in the cellar.
How to get rid of food moths in the kitchen? Check out our selection of effective parasite control methods.
Read about how and how to remove mold from the wall in the apartment at this address.
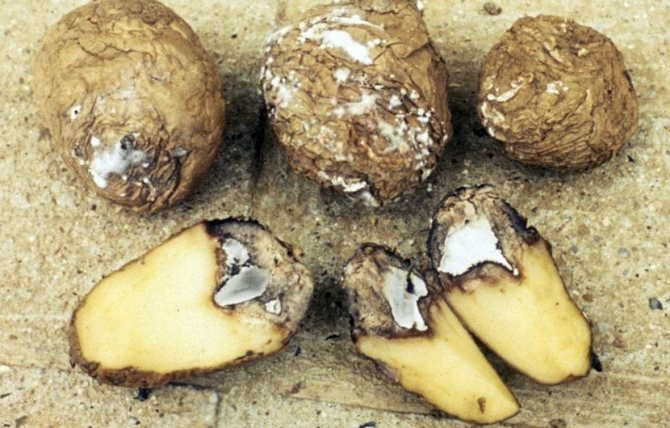
Fusarium dry rot
First, dull, depressed spots of gray-brown color appear on the tubers. After a while, the skin at the site of the spots wrinkles, the flesh becomes dry, in the affected parts of the tuber, voids with mycelium are often formed.
The infection penetrates along with lumps of moist soil - which is why it is recommended to harvest the crop in dry weather.
How to deal with Fusarium dry rot?
- Do not store potatoes with mechanical damage, for example, cracks or cuts, as well as tubers with signs of late blight or scab infection - such roots are very vulnerable to dry rot.
- Before laying, treat the tubers with the microbiological preparation Fitosporin-M (by spraying or dipping), follow the dosage indicated on the package. After that, dry them well in a dry room with good ventilation and send them to the cellar with a temperature of 2-3 ° C and a humidity of 80-91%.
- It is not necessary to sort the potatoes during the entire storage period - you can accidentally damage the tubers. But if you notice any affected potatoes, be sure to remove them from the cellar.
What to do if a problem occurs
When the problem has already arisen and some of the tubers of the newly dug crop are affected by rot, then all that remains is to reject the damaged potatoes. Before storing the remaining roots, they should be laid out to dry in a cool dry place and sprayed with biofungicides - Fitosporin, Fitodoctor, Antignil, etc.

Fitosporin-M Potatoes is effective against wet and dry rot of potatoes, as well as against fungal diseases
Table: processing potatoes before storage
| A drug | Application rules | Dosage |
| Fitosporin-M, Potatoes | Spray with a solution of the drug. Dry completely before storing. | For 10 kg of potatoes, dissolve 5 g of powder in 250 ml of water |
| Phytodoctor | Dissolve 150 g of the drug in 10 l of water. For 100 kg of potatoes, you will need 3 liters of solution. | |
| Anti-rot | Spray the preparation on the tubers with a spray bottle | One bottle with a capacity of 300 ml is enough for processing 300-400 kg of potatoes |
Rhizoctonia, or black scab
Rhizoctonia (black scab) is a fungal disease. A distinctive feature is flat black sclerotia that can be easily scraped off.
We have two news regarding this disease: good and bad.
Let's start with the good one: black scab does not spread in the cellar during storage, does not spread from diseased tubers to healthy ones, and does not spoil the taste of potatoes. Bad: it can greatly harm the plantings of the next year (for example, if you use seed potatoes affected by scab).
Remember: late harvesting, when it is already very cold and damp outside, contributes to the development of the disease.
How to deal with rhizoctoniasis?
- Go through the potato crop - discard the affected tubers.
- Treat the remaining "alive" tubers with the preparation Maxim Dachnik at the rate of 2 ml per 100 ml of water (10 kg of tubers can be treated with this amount of solution), dry and send for storage.
- The ideal air temperature in the cellar is 2-3 ° C, and the humidity is 80-91%.
Alternaria or macrosporiosis (dry spot)
A dangerous disease that can destroy the crop by a third. The fungus spreads with water droplets during watering or rain. High humidity also progresses the development of the disease.


External signs of alternaria (dry spot) of potatoes
Symptoms of the disease are diagnosed on the stems, tops and tubers of potatoes:
- there are large brown or brown spots on the leaves;
- elongated spots on the stems;
- leaves can curl;
- the tops turn yellow and die over time.
Protection measures - pre-planting treatment of seed material with disinfectants and immunostimulants. To contain the spread of the disease, fungicides Kuproksat, Ridomil, Quadris, Signum, Skor, Oksikhom, Raek, Abiga-Peak, Ridomil Gold, Ordan, etc. are used. . Preference should be given to biofungicides - "Fitosporin-M", "Alirin", "Gamair", "Trichodermin" and etc.
Wet bacterial rot
The source of the disease is putrefactive bacteria, which can turn beautiful tubers into gray porridge in a few months.
At first, the affected areas of the tubers darken, become covered with brown mucus, and become very soft. The end of such a potato is sad - it rots, exuding an unpleasant odor.
Related article: Classic American and German Potato Salad
The disease develops actively when storage conditions are violated (high temperature, humidity and poor ventilation) and when damaged potatoes are stored. It is through cracks and microtrauma that bacteria penetrate into the tuber, slowly destroying it.
How to deal with wet bacterial rot?
- Be sure to sort the potatoes before storing them: discard damaged tubers. Tubers that are being prepared for storage are treated with Kagatnik (25-40 ml per 1 liter of water). The resulting solution is sprayed with 100 kg of potatoes.
- Observe the storage regime for potatoes: the temperature in the cellar should be about 2-3 ° C (if the tubers freeze, they will be vulnerable to diseases) and humidity about 80-91% (to reduce moisture in the cellar, you can sprinkle ash on the floor, which perfectly absorbs moisture) ...
- If you notice signs of bacterial rot and even figured out a "sick" one, you need to continue to periodically review the potato bins, removing diseased tubers that are dangerous to healthy ones in time. Otherwise, the entire crop will be at risk - and instead of airy puree, you will get a gray rotting gruel. Not a pleasant prospect, is it?
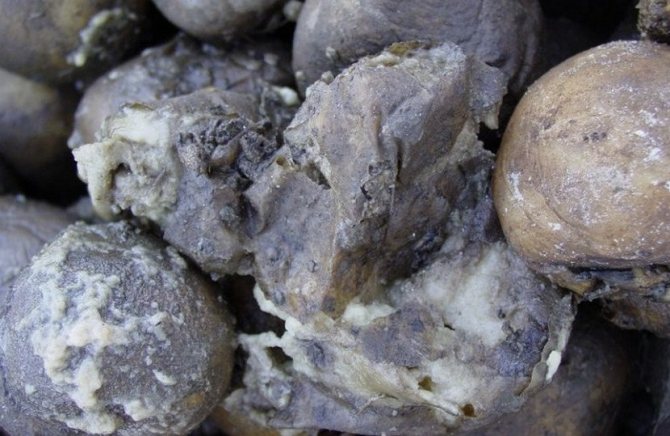
Mold on potatoes, what to do
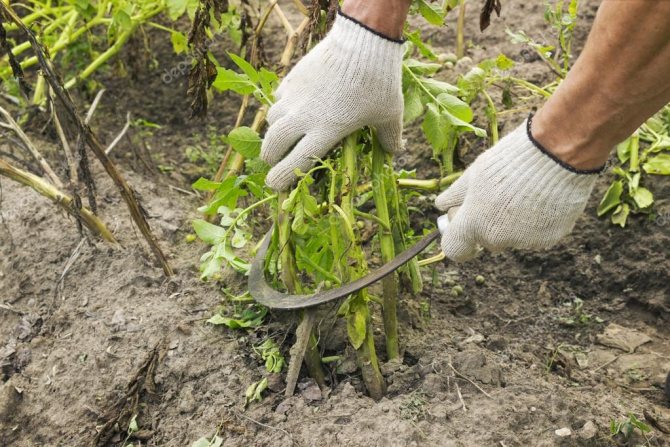
Start monitoring the safety of the crop while the tubers are still in the ground. Mow the potato tops a week before digging up the vegetable. This will prevent fungus from entering the tuber through the stem.
Before storing the potatoes, carefully treat the mold. A lime solution is perfect for this. Add a little 1% copper sulfate to it.
The storage area (basement, cellar) is also disinfected. For this, the smoke of dried herbs is used. You can use tansy or wormwood.
If, nevertheless, the potatoes are covered with mold, then use safe ways to remove the fungus from the vegetable storage area:
- Room processing. This "procedure" is performed using a quartz or ultraviolet lamp. Leave it turned on indoors for at least five hours.
- Removing mold from walls, floors and ceilings with a lime solution. At the same time, make sure that not a single drop falls on the potatoes during processing.
- Getting rid of infected tubers. Go through and inspect all the potatoes. We found the "infection" - safely throw it away.
- Decrease in humidity. Provide good ventilation in the potato storage room. Dampness is a causative agent of mold. In addition to equipping the room with ventilation, you can put a small container on the floor with the same lime (quicklime). It absorbs moisture very well. Sprinkle the tubers themselves with aspen chips or wood ash.
How many days does mold appear on potatoes?
For the growth of pathogenic microflora, four days are enough. Therefore, carefully sort the potatoes before storing them and discard the infected tubers.


Can you eat moldy potatoes?
A number of experts are sure that the vegetable can be consumed after removing the upper part from it. Remove at least a 3-millimeter layer from the potatoes. In this case, even a particle of fungus should not be allowed to get on the peeled part of the vegetable.
But not everyone agrees that contaminated potatoes can be eaten. There is a statement that the fungus gets inside the potato, and even heat treatment does not eliminate it.Recommended reading - At what temperature does mold die?
And the harm of mold for humans has been scientifically proven: ingestion of the body causes the manifestation of allergies, poisoning and even cancer.
Start caring for potatoes in the garden. If the potatoes were not grown independently, but were bought, then make sure that they are stored correctly.
Owners of private houses in the manufacture of conservation often encounter a very dangerous enemy in the cellar - mold, which looks like cotton wool. In most cases, such an unpleasant neighborhood causes many people to find it difficult to choose the appropriate method of fighting the fungus. This problem is solved quickly enough using the most popular disinfection methods, some of which will be discussed in detail below.
Before proceeding with the main stage of disinfection of the room, it is worth taking some time to prepare. In this case, we are talking about mechanical processing, which is carried out according to a certain sequence:
- 1. Initially, you need to take out of the underground all the workpieces, racks, barrels, boxes, boards and other items. If the fungus has penetrated canned foods, it is worth getting rid of them, since it is strictly forbidden to eat them.
- 2. Use a stiff metal brush to remove visible mold from walls and ceilings.
- 3. It is advisable to take the elements of furniture from the underground room outside for thorough drying in the absence of precipitation - this will help prevent the reappearance of the fungus in the cellar. It is best to disinfect in the summer, since during this period the process will be carried out much faster and better.
- 4. If the floor in the room is an earthen covering, you need to get rid of 20-30 cm of the topsoil, since the likelihood of contamination with mold spores is very high.
- 5. At the final stage it is imperative to dry the subfloor. This measure eliminates moisture - the preferred habitat of the harmful organism.
Read also 3D paper tree


Since invisible spores, penetrating into the human body, can cause a serious imbalance of the immune system, which entails dangerous chronic complications, it is worth using protective elements at the time of processing the cellar.
It is recommended to wear a special suit, gloves, goggles and a mask (respirator). At the end of the work, you need to start directly cleaning the space from the fungus.
At the moment, there are several developed disinfection methods that quite effectively save the cellars from the invasion of a fungus that is white as fluff. There are 2 main types of processing: chemical and folk, each of them is highly effective.


Having studied each of the methods, anyone will be able to choose the one that they like and the most suitable in a particular case.
A brief classification of fungal control chemicals in order from more popular and effective to less effective, so:
- Sulfur bomb: it must be used carefully according to the attached instructions, since the pores of the gas, spreading through the air, can have a negative effect on the human body. Before activating the drug, it is necessary to ensure absolute sealing of the corresponding room, covering the cracks in possible ways. At the end of the work, it is recommended to immediately leave the cellar, tightly closing the door behind you. When approximately 24-36 hours have passed, it is required to open all windows and doors, ventilating the dwelling until the specific smell of sulfur disappears completely.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| High level of efficiency | Increased fire hazard |
| Provided security | Toxicity to animals, pets |
| Convenient use | Oxidation of existing metal objects in the cellar |
| Instant action | Undesirable use with potential moisture, including in the presence of groundwater close to the cellar |
| The impossibility of eliminating mold that has eaten deep inside the woody parts of the underground |
- Dezactin: the wooden elements of the cellar are actively treated with a yellow-white powder. Further, acting chlorine-containing compounds penetrate deep into the wood and eradicate harmful mold cells.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| High efficiency | Chlorine pungent odor |
| Ease of use | Do not inhale the pores of the powder - it is very dangerous |
- Formalin, bleach and water are mixed in the proportion: 20g / 50g / 1 liter in a container of the required volume. With this mixture, cover the surface of the floor, ceiling and walls of the underground, then thoroughly dry the room.
| Benefits | disadvantages |
| Low cost | Do not heat lime, as this will provoke an explosive reaction. |
| Good efficiency | Formalin has a rather pungent unpleasant odor |
| Convenient application |
Some people, for various reasons, do not use the above antifungal drugs, but at the same time prefer non-traditional or folk remedies.
Such substances are not inferior in effectiveness to chemicals. Moreover, the considered antifungal mixtures and solutions are characterized not only by efficiency, but also by low cost, which is a big plus:
| Substance | Mode of application |
| Vodka | The substance is filled with a spray bottle (or a cleaned bottle of perfume), then problem surfaces should be carefully treated with vodka. Alcohol allows you to get rid of mycosis pretty quickly. |
| White or ammonia | It is necessary to moisten certain parts of the underground using one of the means, using any of the usual methods. |
| Ordinary vinegar, brown and boric acids | These components are connected according to the proportion: 3/2/1. The mixture is applied to areas infected with the fungus. |
| Copper sulfate, quicklime and water | The listed substances are mixed in the proportions: 100g / 1000g / 2L, then the room is processed. It is necessary to pay special attention to working with active substances, since copper sulfate is a toxic fungicide of the 3rd hazard class. |
| Acetic acid | You need to cover the surface of the cellar with vinegar and then check the room. |
| Baking soda and water | A spoon with soda is dropped into a glass of water, the resulting solution is thoroughly stirred until visible homogeneity. It is necessary to dip a sponge (cotton pad) into the mixture and moisten the moldy surface. |
| Citric acid, water | 200 grams of light powder is combined with 2 liters of slightly heated water, the resulting solution is treated with surfaces affected by the fungus. |
Read also How to eat celery recipes
After the final disinfection step, it is recommended to cover the ceiling and walls of the underground with a new layer of waterproofing plaster or primer. Such preventive actions will save the underground space from the reappearance of the harmful fungus. Only a careful attitude towards all the premises of your home can save the owner of the house from the negative effects of mold spores, and the workpieces from early spoilage.
To get a good harvest of potatoes, you need to spend a lot of time and effort. But even during storage, there are unpleasant surprises - the tubers in the basement begin to mold and rot, as a result of which some of the stocks have to be thrown away.
From potatoes, as well as from walls and ceilings, fungus can quickly spread to other foods, and this shortens their shelf life. To get rid of mold in a cellar with potatoes, you need to know what it looks like and what remedies are effective against it.
Common scab
There are several types of common scab with distinctive features:
- flat - brown "abrasions" are formed on the affected skin;
- mesh - the tuber is covered with small cracks, resembling a net;
- convex - the tuber is covered with growths that look like warts;
- deep - shallow, depressed brown ulcers appear on the tuber, which are surrounded by a torn peel.
The scab does not affect the taste, however it spoils the appearance of the potatoes. It is especially dangerous because it makes the tubers vulnerable to putrefactive bacteria and fungi.
These sores spoil the eyes, making the potatoes completely unsuitable for planting next year.
How to deal with common scab?
- Store exceptionally healthy, undamaged tubers.
- After harvesting, let the potatoes "lie down" in a dark, dry place with good ventilation for two weeks before sending the tubers to the cellar.
- Remember the optimal temperature (2-3 ° C) and humidity (80-91%) in the room.
The effect of fungal colonies on human health
Mold on the walls of the cellar has a devastating effect not only on the appearance of the building covering of the basement. She is capable of causing serious damage to human health. The fungus multiplies quickly and moves to neighboring objects and food, reducing their shelf life.
Fungal formations affect directly the human skin. When contaminated products are used, the circulatory and respiratory systems are affected. Contact with harmful microorganisms can lead to the following pathologies:
- the appearance of headaches;
- dermatological diseases;
- allergies;
- diseases associated with the upper respiratory tract;
- gastric disorders;
- general loss of strength and exhaustion.
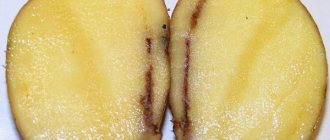
Mottling
Glandular spot (tuber rust) is a non-infectious disease, the main symptom of which is brown spots of various sizes and shapes in the pulp. Outwardly, a diseased tuber is no different from a healthy one.
The reason for the rusting of tubers is unfavorable soil and weather conditions. The disease develops in the field, not during storage.
Gray spots can affect tubers that have been hit during harvesting or transport. Outside, there are no traces of the disease, but inside, gray spots of different sizes appear on the tissues of the potato.
If the potatoes are boiled, the gray spots will change color - they will turn black.
How to deal with spotting?
- During harvesting, transportation and storage, be as careful as possible, do not throw potatoes - mechanical damage can provoke not only spotting, but also fungal and bacterial infections that will destroy a significant part of the crop.
- Observe the conditions recommended for storing potatoes in the cellar: temperature (2-3 ° C) and humidity (80-91%).
Before laying potatoes for storage, prepare the cellar in advance: dry it, clean it, close up the holes of rodents, disinfect the walls and ceiling by whitening them with lime. It is very good if the bins for storing crops are equipped with slatted floors and walls.
Products already stored in storage - potatoes, carrots, onions and beets - can be processed using the Whist bulk checker. Its active ingredient is safe for both humans and vegetables. Smoke for just one minute will protect tubers and root crops from fusarium, phomosis and various types of rot for a period of up to 8 months.
Potatoes are a very attractive crop for fungi, bacteria, and insect pests. They begin to attack him in the field. But even after harvesting, be on the lookout to repel the "enemy forces" that have encroached on your harvest during storage.
Fungal diseases
A large group of fungal infections. Most harmful in wet years or with excessive watering.
The fungus loves coolness, moisture, thickened crops, shading.
Late blight


Potatoes are susceptible to late blight, like a number of its relatives - nightshades (tomatoes, for example).
Susceptibility to widespread potato disease depends on varietal resistance, season weather, and growing conditions.
Late blight begins to appear externally on the leaves located near the ground.
If it warms up during the day, the weather is humid, and at night there is a temperature drop (cold), it is necessary to carefully observe the lower leaves.
Weather conditions are conducive to an outbreak of late blight.
If dark spots have formed on the leaves, late blight is likely to begin.
Wet cool weather is typical for the summer in the northwestern part of the country. Here late blight was prescribed thoroughly, preventive measures are important: you don't even need to expect signs.
The disease progresses rapidly, rapidly spreading upwards - along the leaves and downwards - to the tubers.


The translation of the word phytophthora is remarkable. Literally: killing plants. And it destroys. Leaves die, tubers rot.
Spore carriers can be found anywhere.
They are comfortable:
- The soil;
- Tops (vegetative or abandoned after harvesting on the site);
- Tubers remaining in the ground after digging;
- Container after infected potatoes;
- Storage walls and racks (other parts of them too).
Spores of a dangerous potato disease are spreading and by the wind, moreover, they are amazingly hardy, they can "doze" in the soil for years until a suitable food source appears - something from nightshade.
Spores become active, germinate, and attack plants.
Fight against late blight and other fungi
It is of a preventive (precautionary) nature:
- Compliance with crop rotation. Whether in the previous season there was late blight on the site or not, it is not necessary to plant potatoes there again. All nightshades do not plan to become predecessors, they can leave a pernicious disease infection in the soil.
- Weeds, especially nightshade, need to be destroyed in a timely manner, burning the remains. The nightshade is poisonous, but the plant is medicinal. Therefore, not everyone completely removes it from the site. The peculiarity of nightshade is to be a carrier. The plant looks healthy, but on its remains, berries, then - seedlings, phytophthora winters well. And it is transmitted simultaneously with the nightshade to emerging potatoes. Sometimes from such a neighbor, potato shoots are already affected, covered with spots. Potato disease transmitted by such a neighbor is developing rapidly.
- Seed potatoes (visual) are checked immediately during harvesting. Tubers should be dried in a place remote from cultivation.
- Dried potatoes are sorted out, carefully examining the tubers. With visible damage, signs of disease, they are discarded. Only healthy material is stored.
- The storage is prepared in advance, disinfected. It is advisable to treat it with a fungicide. Brick walls - whitewashed. Concrete - too. Over the summer, the storage (basement, cellar) must be dried.
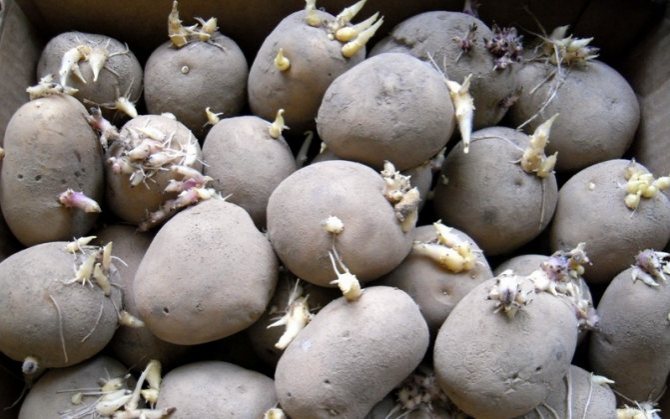
- In the spring, before planting, the tubers are cooked. Sorted out, etched with polycarbacin, nitrafen. Germination helps well: it both enhances growth and identifies infected tubers before planting.
- At least twice, and with prolonged humidity - three times a month, planting potatoes must be processed. Before the onset of potato fungal disease, prophylactically. They use traditionally Bordeaux liquid for this, any modern fungicides can be used.
- If potato late blight has already appeared, it is sprayed with azocene four times during the growing season. Three weeks before harvesting, planting must be sustained without chemical treatment. So that no chemicals remain in products.
- The fungus does not like copper: therefore, preparations with copper destroy it. Can be used against late blight, copper oxychloride, medex.
- But he loves fungus - liming. Lime acidic soils - in moderation, do not create a phytophthora resort.
- Planting should not be thickened. Productivity will not increase from a huge number of tubers in a small area.And shading and humidity - here they are - will rise. Which will please the fungus. Rarely planted plants are better illuminated and ventilated. And their food is better.
- Properly fertilized, the plants increase immunity. You cannot be zealous with nitrogen: its excess plays into the hands of the disease.
- Hilling protects potatoes from early attack by the phytophthora fungus. If the potato patch is small, and yellowing of the leaves near the soil is noticed, it is better to cut them off. After - carry out hilling.
- A good preventive measure is pre-harvest (in half a month) mowing the tops and burning them. Reception is good for protection against other potato diseases.
- When digging - a careful selection of tubers, even cut and very small ones. Any remaining is a potential apartment for the wintering of pathogenic microflora.
From improvised means come in handy:
- Harmless "chemistry" - spraying with a solution of potassium permanganate. The color of the solution is pink.
- Garlic is useful not only for human health, it will help the plant as well. Infusions from any parts of a hot vegetable are good. Phytoncides - burning substances, disinfect the leaf, kill the causative agent of the disease. Just one hundred grams of a leaf of garlic, arrows or its cloves are enough. Grinding the medicinal mass, pouring it with 300 g of ordinary raw water, keeping it for a day. Strain the infusion directly into a ten-liter bucket filled with water. This is a working solution. Stir and go. Spray twice a month. You can add a little soap - for adhesion. After the rains, this treatment procedure is repeated prophylactically.
- Ash and soap solution is a versatile person familiar to many gardeners. He is both feeding and protection. Pests cannot stand it, and diseases, too. You can just sprinkle it with ash, but it does not last long.
- Iodine with milk. It is not expensive as it might seem. Milk is taken in only a liter, iodine - up to 15 drops. The mixture is diluted with a bucket of water - the cure for fungal diseases of potatoes is ready. The frequency of treatments is 2 weeks.
- You can treat potatoes with trichopolum. Ten tablets, a bucket of water. Dissolve, leave for 24 hours and spray.
Alternaria


This disease affects the whole plant - all its parts. Visually it is found first on the leaves, before flowering.
The leaf is covered with large brown spots. The spots dry, have a characteristic pattern around the perimeter - a row of circles with a diameter tapering towards the center.
Stems and tubers are covered with spots. Sick leaves die off, turning yellow.
On tubers, the spots are depressed, with circular wrinkles. Inside the tuber is affected by dry dark rot.
Alternaria spreads, like late blight - the biology of fungi is similar.
The difference is that this potato disease begins to develop earlier. Plus two - and Alternaria gives a start. 25 ° is as comfortable for him as 2.
The range of acceptable temperatures allows Alternaria to cause significant damage to potatoes. One third of the harvest is lost.
Sprinkling, dew, rain are the conditions for spore germination. They manage to grab moisture and "wake up" in a couple of hours.
Fight against Alternaria in the same way as with late blight.
You can add biological products: integral, planriz - for pre-planting antifungal treatment of tubers.
Fusarium dry rot


Another fungus is a contender for a fifth of the potato crop. The losses are considerable.
Fungal diseases of the potato have adapted to nest wherever food is provided for them. The whole plant is affected.
Even healthy tubers in contaminated soil cannot protect themselves from Fusarium.
The spores are so small that they will find a crack to get into the tuber.
Mushrooms develop rapidly (remember the expression "grow like mushrooms"), capturing all parts of the potato bush.
The time comes to bloom, and the bush withers. This is fusarium wilting, there is such a term for the disease.
It is not difficult to diagnose an ailment by the whitish tips of the leaves.They turn white even before wilting, it is important to observe how the potato plant feels.
If this symptom appears, consider the stem. A pinkish bloom is another sign of potato fusarium.
The fungus is so harmful that it can even penetrate into a healthy tuber during transportation and storage. Or infect tubers in the field, but not be visible at first.
And in the store, where we left the potatoes to winter and do not visit often, the potatoes become spotty. Later, they simply dry out, at the same time rotting into dust.
Fusarium cannot be cured, so the emphasis is on prevention.
All preventive measures are similar to the prevention of late blight: mushrooms are different, but the conditions for their development are the same.
Rhizoctonia (black scab)


Before cleaning, the hostesses usually wash the tubers. Sometimes it is not possible to wash it - the tubers are covered with tough black spots.
These tubers are unsuitable for jacket potatoes, stains can be removed, but only with the skin.
This black scab is a fungal infection of the tuber. The view is unsightly, but the tubers are edible - black scab of potatoes (rhizoctonia) has partially affected them, it will be removed when peeling.
The peelings cannot be composted and the tubers are not suitable for planting.
Otherwise, a very unpleasant mushroom will settle on the site - rhizoctoniasis. It can hibernate both on tubers and in soil.
Rhizoctonia is harmful at all stages of a potato's life.
If the mushroom only hibernates in the storage, it wakes up on the site. After waiting for the planted tuber (or getting into the soil together with the already infected one), the scab begins to "work".
Spores germinate, the fungus infects all potato plants that have begun their growing season. The root system, stolons extending from the stem, young tubers - everything is affected by mycelium.
The temperature drop from warm to cold gives a violent start to rhizoctonia.
Potato sprouts have already begun to grow, a root system is being formed. And suddenly it got cold.
Five degrees in the soil is not dangerous, but uncomfortable for potatoes, it slows down growth.
And black scab tolerates this cold snap easily and actively feeds on the entire underground part of the potato.
If the bush has already risen, the scab will continue its dirty work in all its above-ground parts.
Check the leaf axils. If strange formations appeared there - nodules - the plant is affected by rhizoctonia.
The whole complex of symptoms:
- Rotting tubers and stolons;
- Ulceration of the plant neck;
- The formation of air nodules is typical for rhizoctonia, in the aerial part (leaf axils);
- Stem thickening at the bottom;
- Collapsing the upper leaves, changing their color;
- Lagging bushes in growth.
This disease also has a characteristic feature: "white leg". This is the base of the stem covered with a spore-bearing white shell.


It is formed in wet weather. White leg is a diagnostic sign of rhizoctonia.
Prevention - as with late blight. Difference: black scab does not like to settle on manured lands.
Specific preventive measures:
- Nitrogen or manure application;
- The tubers will be protected by the introduction of ash;
- Shallow fit;
- Landing on light soils is important;
- It is not too early to plant - by warmth;
- Do not be late with cleaning, you need to be in time before damp weather.
Common scab


The word "scab" itself - whether it is ordinary or not - does not a priori evoke pleasant associations.
Lousy, in a word, a disease, and the tubers look - accordingly. Common potato scab prefers its underground part.
Any kind of potato scab is also insidious due to its illegibility "on the menu".
You can't get off with one crop rotation - scab calmly parasitizes almost everything, even weeds. And goes to the cultivated neighbors on the site.
The harvest is declining, and may be lost altogether. The scab affects the eyes, they do not germinate. If the damage is insignificant, the yield shortfall will still be considerable.
The potato loses its taste, is poorly stored. It is impossible to plant an infected one, the soil is infected.
If the harvested potatoes are covered with a whitish coating, this is an ordinary scab.Later, it will manifest itself as ulceration of the peel.
For some reason, scab loves the red peel of potatoes more. Plaque on freshly dug tubers may have a different color. Greenish, grayish - any.
Potatoes are affected by radiant mushrooms, there are many varieties, the result is one: scab.
A feature that is important in diagnostics: plaque quickly disappears when it comes into contact with air. The fungus is hiding, the tuber looks healthy.
The common scab is actually extraordinary. Potato disease is fungal, and progresses - in heat, drought.
It is therefore important to distinguish between types of scab.
The insidiousness of this fungus is in the same relation to soil acidity - with cultivated plants.
Common scab thrives in alkaline soils and near neutral conditions. She doesn't like acidification, like most crops. Scab with potatoes live in conditions of the same acidity.
For the fight, general agrotechnical rules and techniques are observed.
In hot summer, after precipitation, plants are examined - ordinary scab may appear.
Moderate acidification of the soil (the introduction of fertilizers - sulfates) is permissible with ordinary scab.
If the acidity is slightly higher than comfortable for potatoes (this can be seen from weeds - wood lice, plantain), do not liming before planting.
Potatoes will tolerate slight soil acidification more easily than scab damage.
Macrosporiasis


Dry spotting (macrosporiosis) first appears on the potato leaf.
But the mycelium grows throughout the body of the plant, even if it is not immediately possible to distinguish it. Dark brown, sometimes gray, rounded spots with concentric stripes are visible on the leaves.
They are dry, they can crumble, forming a perforated leaf.
During the period of formation of spotting, a gray bloom of mycelium is visible on the bottom of the leaf.
The defeat coincides with budding, its early phase, the potatoes are not yet blooming.
Early varieties suffer more, the lower leaves turn yellow. Later, the stems are covered with spots. Dry spots are characteristic (hence - dry spotting). There is no decay, a dark coating is present.
Wind, rain, dew are helpers in the spread of the disease.
Mycelium overwinters in the soil, settling on the remains of tops and weeds. Moreover, it can take years for nutrition (a suitable nightshade plant).
Tubers are also an acceptable wintering substrate. A bush affected by macrosporiosis will not be able to have full growth.
It will not be possible to grow a high yield either - up to a third of the possible is lost.
Control measures:
- Compliance with agricultural techniques (the whole complex, as in late blight);
- Deep digging / plowing of the site in the fall - the pathogen hibernates shallowly and may partially freeze out;
- Optimal nutrition. The balance of basic elements (N, P, K - nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) strengthens plants, helps them resist the fungus;
- If necessary, treatment with antifungal drugs, as with late blight.
Early varieties are affected more and more often - the mushroom can withstand cold weather and develops at any temperature above zero, even if + 1 ° is not yet.
Potato cancer


A very harmful fungal disease. A newcomer from Germany since the war, but even in the USSR they hardly knew about such a potato disease.
Quarantine inspections were in place to stop the spread of the pathogen. Nowadays, potato cancer is common.
Cancer is called this fungal infection due to the formation of tissues unusual for healthy potatoes, growths.
Only the roots are not covered with growths, the rest of the parts visually give out the disease.
It starts with the tuber eyes. Growths near the eyes - a kind, like warts. There are many of them, they increase, sometimes they become larger than the tuber.
Stolons are infected too. The aerial part changes: you can see growths on the leaves, in their axils. The flowers are connected in an outgrowth, the inflorescence is not formed.
When digging, it is found: the tubers are rotten, there are few whole ones. Survivors rot during storage. It really is cancer, it destroys the plant.
In the country, there is no potato cancer where there is intense heat or freezing of the soil. This fungus is a sissy: it does not withstand such extreme conditions for it.
The rest of the regions are less fortunate - depositories of fungal spores, special formations - cysts - remain viable for three decades.
Cancer spreads in many ways:
- Through garden tools;
- Infected tubers planted;
- On the shoes of the grower;
- Spread by melt water;
- Even earthworms carry it.
Control measures are common to fungal. Agricultural engineering, search for resistant varieties.
Specific measures:
- Sick potatoes are forbidden to be given to animals and used as food. The plant - all parts - are burned.
- Cancer does not like manure - you need to apply it in areas where there was a painful mycelium.
- Sowing legumes or corn after diseased potatoes. The spores of the fungus are "deceived", they open up and germinate from the presence of these crops, but without the necessary nutrition (potatoes) they die. The same effect is from sowing rye.
Rubber rot
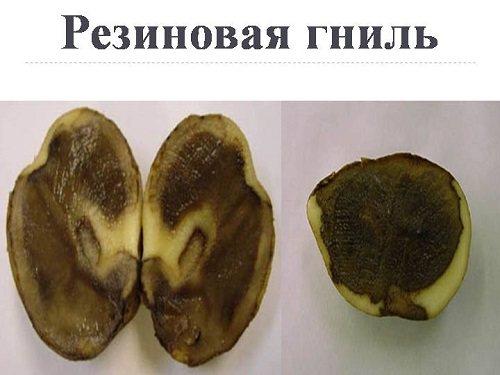

A disease with an interesting name, but disastrous consequences, spread in the country not so long ago, in the late 80s - the same age as perestroika.
England met with rubber rot - the first, back in the post-war years.
The fungus infects either sprouts or tubers. If sprouts, then they quickly rot, without even having time to sprout.
When infested, tubers become stained. The spots are brown with a dark border. Under the spots is a rubber-like tuber tissue. This gave the name to potato rot.
The tubers are unsuitable for food. If the infection has not entered a noticeable phase, and the tubers go to seeds, the soil is also infected.
Of the nightshade, pepper and tomato are susceptible; these crops should not be planted next to them.
Healthy potatoes are easily re-inoculated in storage if infested potatoes are added to them.
There are no varieties resistant to harmful rubber rot.
Control measures are agrotechnical, as with all fungi.
Specific:
- Do not overfeed the soil with nitrogen;
- Germinate tubers and reject the affected ones along the sprouts;
- Cultivate the soil: on heavy rubber rot progresses more strongly.
Potatoes are not our only food. But it firmly takes the place of the leading products on the menu.
Especially in winter, that's why they store it for a long time. For tubers to survive safely, they need health.
Fungal diseases love to attack our main food. Therefore, the gardener has to be careful.
Look closely at the plants - from seed tuber to harvest, throughout the growing season. And don't forget about him in the store, too. Then the losses will not be large even in meteorologically difficult years.


We got acquainted with fungal diseases. Now fully armed, but there is still a whole host of bacterial and viral diseases. But about them already in the next article.
See you soon, dear readers!
Reasons why potatoes rot
Picking vegetables in rainy or damp weather, inattention when examining the harvest, too early or late harvesting are the main causes of potato rot.
Important! To prevent decay, the room is periodically ventilated.
In the cellar, vegetables quickly rot at high humidity, inappropriate temperatures, poor ventilation, storage in bags with low air permeability.


Some dangerous diseases cause rotting: late blight, bacterial rot, black scab.
Late blight
Fungal disease manifests itself as dark spots on the tubers. When cut, it can be seen that the black rot goes inside the potato. Late blight occurs during the growing season, and is activated already in the cellar if the temperature exceeds the norm.
The main control measures:
- the potatoes are sorted out, the infected tubers are removed;
- normalize the room temperature;
- healthy vegetables are processed with biological products (for example, "Gamair").
Potatoes are dug out only in sunny dry weather, they are poured into boxes with a layer of about 1 m.
Wet bacterial rot
With this disease, tubers become covered with patches of gray mucus with a terrible smell in a couple of days. Temperatures above + 20 ° C and humidity more than 90% provoke the development of the disease.
To get rid of rot, do the following:
- the crop is sorted out and rotten tubers are thrown away;
- normalize humidity and temperature in the cellar;
- diseased areas on vegetables are cut off, the cut site is treated with alcohol;
- potatoes are periodically inspected.
Related article: Potato planting patterns - distance between rows and holes
Black scab
The fungal disease causes small black dots (sclerotia) and cracks on the tubers. Rhizoctonia disease does not affect the taste of vegetables, usually associated with late harvest.
Attention! The scab is passed on to the next generation of culture.
Disposal and prevention measures:
- the tubers are sorted out and the damaged ones are thrown away;
- the crop is treated with Ditan M-45 (200 g per 5 l of water, the solution is enough for 100 kg of potatoes);
- normalize storage conditions.
Causes contributing to the formation of fungus
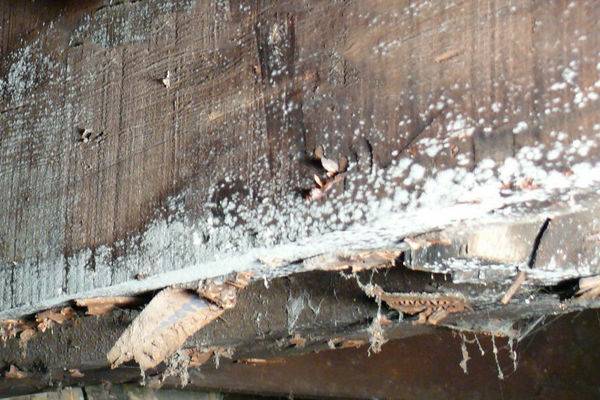


Mold on the walls of the cellar can appear if the following factors are present:
- there is no ventilation system in the room or does not work well;
- there is an excess amount of moisture in the air, condensation forms on the walls;
- poor natural circulation of air masses;
- the presence of rotten vegetables and other spoiled foods in the basement;
- the wooden surfaces are infected with fungal spores.
White mold in the cellar begins to multiply vigorously at high humidity and an increase in air temperature of more than 20 degrees. And, conversely, at negative temperatures, it loses its ability to reproduce. The forced ventilation system ensures the normal circulation of air masses. Spores cannot be fixed on the surface of walls and other objects.
How to store potatoes in the basement


In order for the crop to be stored in the cellar for a long time, the basic rules are observed:
- The room begins to be prepared about a month before the vegetables are laid: it is cleaned of debris, inspected for cracks and holes, washed with soapy water, treated with a 10% solution of copper sulfate, dried well, ventilated for several days. The cellar is additionally insulated from winter frosts, the floor is covered with lime to get rid of excess moisture.
- Potatoes are dried 5-15 days after clearing from the ground, sorted, infected, mechanically damaged and unusable specimens are removed.
- Make sure that the temperature in the basement is within + 2 ... + 4 ° C, the air humidity is about 90%.
The tubers are periodically inspected for suspicious spots and build-ups.
Important! Potatoes are sensitive to environmental changes, so they are kept in wooden boxes or bins with felt cloth on the bottom, sealed containers or bags. Plastic bags and tight, air-tight bags will not work.
Prophylaxis
In order to prevent the occurrence of potato rot, it is necessary to follow some simple techniques at all stages of growing - from planting to harvesting.
- For planting, only healthy tubers are selected without visible damage and signs of disease.
- If planting is carried out with cut potatoes, then this procedure is done 2-3 days before planting, so that the slices have time to tighten. This will prevent the penetration of pathogenic fungal flora into them.
- It is also advisable to spray the seed with fungicides before sowing.
- In the process of growing, the condition of the bushes should be monitored - if patients are identified, then they need to be dug up and destroyed.
- An overdose of nitrogen fertilizers often leads to the formation of rot, so it should not be allowed. It will be normal to add 1-2 kg of humus and 1/2 teaspoon of ammonium nitrate to each hole when planting potatoes.
- And also the lack of oxygen in the soil leads to potato diseases.It can be prevented by regular loosening and hilling.


In addition to creating conditions for additional growth of tubers, hilling contributes to the saturation of the soil with oxygen
The reasons for the appearance of potato rot immediately after the digging of tubers are rooted in violations of agricultural technology, admitted at any stage of cultivation. Compliance with the rules for planting and growing root crops, as well as the tips set out above, will allow you to grow a rich and healthy crop.
Potatoes in Russia are rightfully considered "the second bread". Dishes from it are prepared all year round, so it is very important that the harvested crop is preserved as long as possible. The following tips from experienced gardeners will help prevent potato rotting.
Why does potatoes rot immediately after harvesting
Immediately after harvest, the crop rots due to the influence of pathogenic fungi and bacteria. To prevent the problem, it is important not only to be attentive to the preparation of vegetables and storage rooms, but also to follow the agrotechnology of growing crops:
- plants are planted at a temperature not higher than + 15 ° C;
- the soil must be fertile (it will be hard for potatoes in clay soil);
- seed tubers are cultivated in whole or in slices, which are dried in advance and rolled in ash;
- the site is regularly weeded from weeds;
- monitor the level of soil moisture.
If the potato is already sick, proceed as follows:
- The crop is sorted out, getting rid of rotten and damaged tubers.
- Healthy specimens are treated with contact fungicide "Ditan M-45".
- Vegetables and cellar dry well.
- If new fungal or bacterial formations appear on the potatoes, the procedures are repeated.


Types of potato diseases


To defeat the enemy, you need to know him by sight.
Many potato diseases are manifested by rot, they are similar.
You can get confused and not take timely measures or, acting at random, not help the plant.
And potatoes are affected by diseases:
- Fungal - provoked by fungal microflora;
- Bacterial - caused by pathogenic bacteria;
- Viral.
There are also physiological, non-infectious diseases of the potato.
Why potatoes are covered with white mold
The appearance of mold is associated with improper storage conditions of vegetables.
Preventive measures:
- selection of varieties with strong immunity, high keeping quality;
- periodic ventilation of the cellar;
- humidity and temperature control;
- disinfection of tubers and premises;
- laying only ripe vegetables;
- isolation of the basement from groundwater;
- regular inspection of tubers for suspicious lesions.
If mold appears during storage, take the following measures:
- The crop is removed from the premises, kept under an ultraviolet lamp for 5-6 hours.
- Lime mortar is used to clean the walls, ceilings and the bottom of the cellar.
- Infected tubers are discarded.
- To reduce air humidity, place a container with slaked lime. The vegetables themselves are sprinkled with sawdust or wood ash.
Sometimes smoke bombs are used indoors.
Reasons for the appearance
Mold never appears just like that, this event is preceded by other unfavorable circumstances:
- absence or clogging of ventilation shafts. Lack of fresh air supply contributes to the growth of fungal colonies;
- high level of air humidity, accumulation of condensate. This aspect often depends on the first factor;
- insufficient air circulation in the cellar;
- storage of rotten fruits and vegetables. Spoiled products become sources of mold, spores actively spread throughout the room, settling on the walls, floor and ceiling;
- the use of wood products that are contaminated with fungal spores.
Tips & Tricks


When planting a crop, a variety suitable for long-term storage is chosen: Picasso, Asterix and others.
Potatoes are not kept with other vegetables, except beets: they are laid out in 1-2 layers on the tubers to remove excess moisture.
To reduce the temperature in the cellar during spring warming, several pre-frozen water bottles are placed.
How to prevent mold and build the perfect cellar
Mold on the potatoes, the surface of the walls and the ceiling of the basement are indicators of improper cellar equipment. In order for it to perform all the necessary functions and be operated for a long time, the following recommendations should be adhered to during its construction:
- it is better that the cellar is located in a dry and elevated place;
- stone, concrete or brick should be used for the construction of walls and floors;
- it is necessary to equip a high-quality ventilation system in the room;
- correct air exchange must be present in the cellar, which does not allow the occurrence of temperature drops and prevents the appearance of condensation;
- for plastering walls, you can use a concrete mixture.
At the stage of construction work, special attention should be paid to the waterproofing of the structure. It will prevent excess moisture from the external environment from entering the cellar. The outer slots of the basement are filled with concrete mixes. A drainage and sewerage system is being built. Thus, the outbuilding is protected from the effects of groundwater. All these measures will allow you not to think every year about measures to destroy fungal formations and use the cellar for a long time.
What is decay
From a chemical point of view, this is the process of decomposition of complex nitrogen-containing compounds due to the influence of putrefactive microorganisms. Another name for this phenomenon is ammonification.


Ammonification in plant tissues leads to increased evaporation of moisture, decomposition of nutrients - starch, sugar, proteins, etc. The causative agents of rot (fungi and bacteria) enter the tubers in various ways - they are brought in from the fields along with particles of soil, stored in storage from the previous harvest. Improper storage conditions of the vegetable contribute to the rapid progression of putrefactive processes.
Disease factors


Potato rot is the result of exposure to pathogenic bacteria or fungi that actively manifest themselves under favorable conditions for them.
Violations of agricultural practices lead to the emergence of many diseases. Major infections:
- late blight;
- alternaria;
- rhizoctonia;
- fusarium;
- phomosis;
- blackleg;
- ring rot;
- wet rot.
Late blight
If immediate measures are not taken to destroy the pathology, the infection rapidly spreads throughout the site, which is fraught with the death of the entire crop. The onset of late blight is expressed by putrefactive processes on the tops, then the tubers are infected.
Why potatoes rot and turn black during storage: an overview of the reasons
The following are typical phenomena that cause the onset of putrefactive decomposition of potatoes sent to the cellar.
Improper crop preparation
One of the first reasons is that the potatoes were poorly sorted out and did not dry out before laying them in the cellar. If among the entire crop there was at least one damaged or rotten tuber crop and it got into storage, then this will trigger the putrefactive processes of the entire crop.
Related article: Fertilizers for potatoes when planting in a hole - types and calculation
Other possible reasons:
- harvesting a vegetable in rainy, damp weather (the tubers are oversaturated with water, they will start to rot very quickly);
- potatoes are unevenly stored in storage;
- tubers were not laid out from the bags;
- harvesting unripe potatoes.
Storage violation
Rot appears due to the fact that the potatoes were laid in poorly prepared storage. Dampness and moisture, inappropriate temperature conditions, lack of high-quality ventilation - these factors provoke the onset of ammonification.
The list of the main diseases that are accompanied by rotting tubers is presented in the table.
What else does the vegetable rot
One of the other possible factors is storing the wrong potato varieties. It is recommended to store only mid-season or late varieties. Early maturing vegetables are intended to be consumed immediately after harvest. Their maximum keeping quality is no more than 2 months. Then the tubers either sprout, or wither, or rot.


The next reason is the wrong neighborhood of potatoes. Usually, all harvested crops are stored in a cramped cellar or on a balcony. In such conditions, vegetables have to be placed very close to each other, so during storage they can become infected with diseases and release hazardous substances.
It is recommended to store potatoes separately. If there is no free space for this, then the optimal neighbor for tubers is beets. This vegetable will not harm the potatoes, but, on the contrary, will help (drawing out excess moisture and preventing rot).
Prevention of decay when planting, growing and harvesting potatoes
To protect against mold, which covers potatoes during storage, it is necessary to carry out prevention. It is easier to prevent any disease than to struggle with its consequences for a long time. Preventive measures are as follows:
- It is necessary to select disease-resistant potato varieties. It is better to use local zoned varieties that are adapted to the given climatic conditions.
- Prepare planting material in advance; to solve this problem, the potatoes are carefully sorted out. Only healthy tubers are suitable for planting. White mold is especially carefully discarded.
- Pre-sowing processing of vegetables is carried out with special means (copper sulfate, Fitosporin-M, Prestige, Quadris, etc.).
- It is necessary to regularly treat planted plants from pests that carry infectious diseases.
- Compliance with crop rotation. Potatoes should be planted in one place no earlier than 3-4 years later.
- Cleaning work must be carried out in a timely manner. Unripe potatoes do not resist disease well due to their too thin peel. Too late harvesting of potatoes can provoke the development of fungal diseases on the tubers and their damage by insect pests.
- The harvest of potatoes must be dug in dry and clear weather, then cleaned of dirt and dried well.
- It is recommended to cut and destroy the tops approximately 10-14 days before harvest.
- Before laying the potatoes in the cellar, they are treated with special biological products (Gamair, Alirin-B).
- After harvesting, it is necessary to deeply dig up the soil on the site, since fungal spores are stored in the upper soil layer.
Compliance with these simple recommendations will help preserve the potato crop.


How to protect tubers from rotting
The following is a set of actions, the strict observance of which will help keep the harvest in full. All instructions must be followed.
Proper storage preparation
It is necessary to start preparing the storage (basement, cellar) from the summer months, since a lot of infection accumulates in it over the winter and spring, which can cause rapid rotting of any root crops immediately after a new bookmark. To destroy all bacteria and fungi, the following measures must be taken:


- Collect and remove all remnants of old tubers, sweep thoroughly.
- Leave the cellar open for 1-2 days to ventilate and dry.
- Pour sand on the floor. If it already was, be sure to completely replace it with a fresh one.
- Check the operation of the ventilation system.
- Disinfect the room with formalin solution (1%, 40 liters per 100-130 sq. M.) Or bleach (2%).
Compliance with conditions of detention
The recommendations below should be followed immediately after placing the potatoes for storage. Optimal performance and important rules:
- The air temperature should be constant, indicators - + 2 ... + 4 degrees.
- Particular attention is paid to humidity, it should not rise above 90% (for checking and monitoring, the storage can be equipped with special devices - a thermometer, psychrometer, hygrometer).
- Constant observance of the sanitary regime is important (immediate removal of the affected tubers).
- With a significant amount of infection (8-10% of the total crop and more), it is urgent to carry out a massive bulkhead of the crop.
How to treat potatoes from rot before storage
Particular attention should be paid to the harvest itself. Before adding to the repository, the following actions are required:
- Drying. If the collection takes place in dry weather, then the potatoes are dried in the field or in the garden, in rainy weather - in temporary piles under hay or straw. Drying time - 5-15 days, depending on the weather. Find out if potatoes are washed before storing.
- Bulkhead and rejection. Tubers must be carefully examined. If there is even the slightest damage on the potato (scratch, dark spots, cracks), it can no longer be put into the cellar. It is also forbidden to store tubers that have been damaged by pests. These potatoes are best used immediately.
- Before laying, vegetables can be “powdered” with wood ash or chalk. This will serve as additional prevention. You can also use more modern drugs, for example, the antifungal agent Fitosporin, Maxim or Antignil. Process only cleaned and dried tubers.


Potatoes are usually stored in wooden boxes. Such containers should have loose boards that will promote good air exchange. It is advisable to put 10-11 kg of potatoes in 1 box. The container should be placed at a distance of 25-30 cm from the wall, 15-20 cm from the floor and 50-60 cm from the ceiling. Between the boxes themselves, you need to leave a free space of 5-7 cm.
Other activities include monthly crop inspections or product quality checks. This will allow you to notice and prevent the beginning of massive potato rotting in time.
Effective control methods
How to treat the cellar from mold and mildew? Mold killing is hard work that requires a lot of effort and time. It is necessary to consider the causes of the trouble. An integrated approach will help get rid of mold, similar to cotton wool, prevent the re-growth of fungal spores in the cellar. The fight against fungal colonies is carried out in several stages, each of them is described in detail below.
Preparation for the elimination of dangerous microorganisms
Helpful hints:
- for the duration of the processing of the room, be sure to free it from all objects, fixtures and food. Thus, you will provide excellent access to possible places of localization of mold, protect the products that are in the cellar;
- remove all furniture, large objects from the room. They also need to be processed to avoid re-infesting the cellar with mold;
- do a general cleaning of the room. Clean off all the mold, if the spores of the fungus have penetrated deep into the finishing material, be sure to replace the damaged structures with new ones;
- the tree decays very quickly, if the floor is earthen, then about 20 centimeters of the soil layer must be removed (it is probably infected);
- after thoroughly processing the cellar, proceed to drying the room. Only then is it allowed to proceed to the direct fight against mold.
How to worry in advance so that the potatoes do not start to rot
In this section, we will share the secrets of professional gardeners:
- For planting, it is still safer to use the whole fruits of the vegetable.
- Potatoes left in the light turn green. It is undesirable to eat it. And for planting, this is the best option: such root crops are less sick and are better stored.
- About a month before planting, lift the potatoes out of the cellar or basement and place them in crates. Swap the boxes constantly so that all the potatoes receive the same amount of light.
- Sprinkle the planting material with wet sawdust a week before planting. Such sprouted tubers will produce a high and disease-resistant crop.
- Dig up the garden thoroughly in late autumn. With the onset of cold weather, pests living in the earth will die.
- Give preference to early potato varieties (Sineglazka, Rosa early). This is due to the fact that the bushes will get stronger and develop earlier than the pests and late blight are activated, which appears at the end of summer.
- Hand-pick grubs and beetles every day. Pour water and detergent into a bucket and shake insects from the bush into it.