Vegetable growing »Potatoes
0
1106
Article rating
The Impala potato is the result of the work of Dutch breeders. It is distinguished by its productivity, high taste of tubers and ease of care.

Characteristics of Impala potatoes
Due to its unpretentiousness, the Impala potato variety is grown all over the world. In order to get good yields from a minimum piece of land, you need to know the rules of agricultural technology of the variety, as well as the peculiarities of preparing planting material in the spring.
The history of the origin of the Impala potato variety
This variety was bred by employees of the Dutch company Agrico (Emmeloord). It was included in the State Register of Russia in 1995. Four regions in the Russian Federation admitted to cultivation: Central, Volgo-Vyatka, North-West and Nizhnevolzhsky. This variety has another name - "Kubanka" or "Krymchanka".
The table shows data on the mass of marketable tubers (grams) of different varieties:
| Name | Variety | Weight |
| Nikulinsky | Late maturing | 70 to 120 |
| Cardinal | Late maturing | 65-110 |
| Rocco | Late maturing | 100-120 |
| Picasso | Late maturing | 80-140 |
| Borovichok | Early ripe | 120-200 |
| Elmundo | Early ripe | 120 |
| Felox | Early ripe | 100 to 120 |
| Bellarosa | Early ripe | 120 to 210 |
| Karatop | Superearly | 58 to 100 |
| Zhukovsky early | Superearly | 100 to 120 |
| Farmer | Superearly | 90 to 110 |
| Minerva | Superearly | 120 to 245 |
| Sorcerer | Mid late | 75 to 120 |
| Mozart | Mid late | 100 to 150 |
| Grenada | Mid late | 800 to 100 |
| Melody | Mid late | 95 to 180 |
| Giant | Mid-early | 100-140 |
| Tuscany | Mid-early | 90 to 125 |
| Purple Haze | Mid-early | 90 to 160 |
| Openwork | Mid-early | 90-120 |
Characteristic
- General characteristics: Very early table variety, well adapted to various climatic conditions and soil types, drought tolerant;
- Ripening period: 60-70 days after full germination;
- Productivity: Up to 360-450 c / ha;
- Marketability: 89-94% of the total harvest;
- Keeping quality: Up to 90%;
- Starch content: 10-14.6%;
- Cooking class / group: Type B (slightly crumbly after cooking);
- Flesh color: Light yellow;
- Skin color: Yellow;
- The mass of commercial tubers: 88-150 g;
- The number of tubers in the bush: On average, 7-11 pieces;
- Consumer qualities: The taste is excellent, the tasting score is 3-4 points (out of 5).
- Culinary Purpose: Universal
- Growing regions: North-West, Central, Volgo-Vyatka and Nizhnevolzhsky, in more southern regions it is possible to get two harvests in one season
- Disease resistance: High: potato cancer (D1), golden nematode (Ro1, Ro4), rhizoctonia, viruses Y, A, X, common scab. Medium: late blight of tubers, powdery scab. Susceptible to late blight by tops, rhizoctonia;
- Corolla color: White;
- Features of cultivation: It is recommended to preheat and germinate seed potatoes, the amount of nitrogen fertilizers is less than for other varieties. It is obligatory to trim the tops 2 weeks before harvesting the main crop;
- Year of inclusion in the Federal State Budgetary Institution "State Sort Commission": 1995;
- Originator: Agrico (Netherlands);
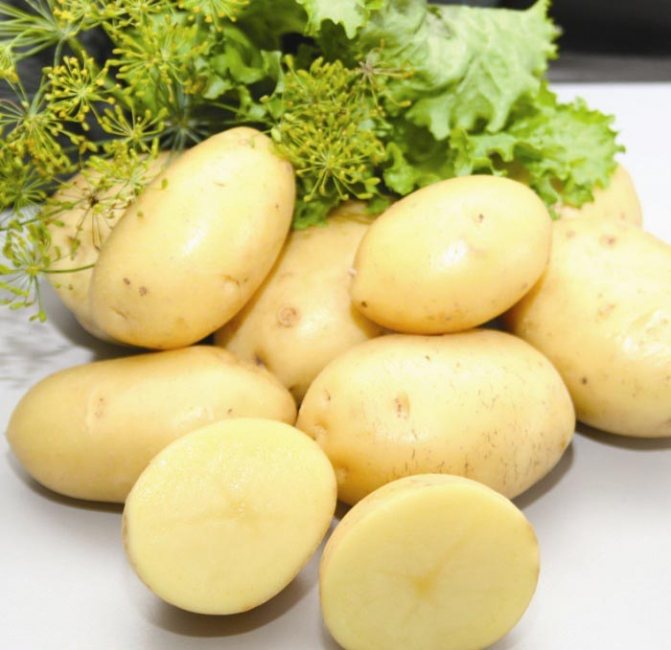
Root crops of Impala potatoes are oval in shape, with small eyes, covered with a smooth yellow skin. The pulp of the fruit is light yellow, contains no more than 14.6% starch. The average dry matter in the pulp is 17.7%.The average weight of a root vegetable varies from 88 to 150 g.
The number of tubers on one bush can be from 16 to 21, the yield of marketable tubers is 89-94%. The keeping quality of root crops is very high.
Under favorable conditions in the southern regions, it is possible to obtain two harvests of this variety in one season. Potatoes "Impala" have average resistance to scab and late blight of tubers.
Description of the variety
Roots:
- Oval tubers;
- Small eyes with shallow bedding;
- Root crops are smooth, light yellow;
- Average tuber weight is from 120 to 160 grams;
- The flesh on the cut is yellowish.


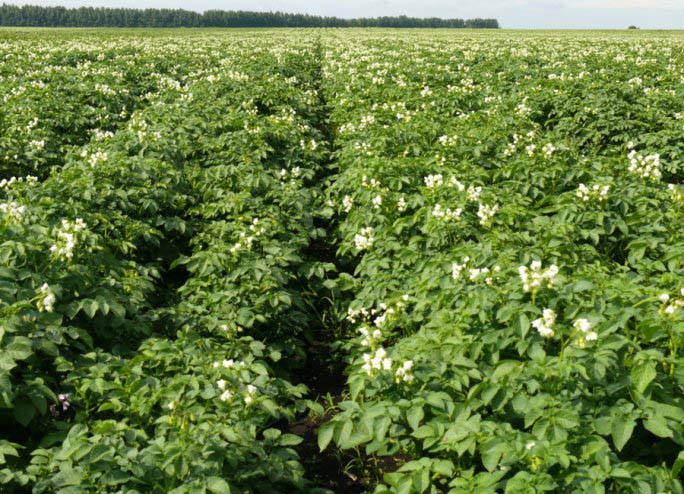
Shoots:
- The bush reaches 75 cm;
- Quite dense, formed by 4-5 stems;
- Saturated green medium leaves, with slightly wavy edges;
- The flowers are white, yellow in the middle.
disadvantages
The Impala variety also has some disadvantages:
- shoots are very tall and lush, so it is recommended to mow them 3-4 days before harvesting;
- tops are a favorite delicacy of Colorado beetles, so the bush must be sprayed regularly;
- does not bloom amicably, therefore there may be problems with pollination and collection of seed;
- susceptible to cancer of nightshades, bronzing of leaves and phomosis.
Due to the high starch content in the tubers, potatoes do not boil well and are not friable, but they are ideal for frying and preparing salads. It is also worth noting the fact that the pale yellow color of the tuber core does not change during heat treatment, which cannot be said about other varieties with a starch content of 15-17%.
Advantages, disadvantages and taste
This variety has a lot of advantages, because of which it is highly valued by gardeners:
- Resistant to dry periods and diseases. Potatoes are highly adaptable to different weather conditions. He is not afraid of drought;
- Tolerant to a number of diseases. It is not affected by potato cancer, hookworm, viruses A and Yn;
REFERENCE: The soil should be enriched with humus and have a fairly deep arable layer.
- Gives a high yield. With proper agricultural technology, more than 17 tubers can be harvested from each bush, from 37 to 60 tons per hectare can be harvested per season, and in the south, two harvests are possible;
- Early maturity. The main characteristic of the Impala is early ripening, the first crop is harvested as early as 45 days after planting. Potatoes fully ripen on 60-75 days, this factor depends on climatic conditions;
- Taste qualities. During heat treatment, the tubers retain their shape and do not crumble;
- Resistance to mechanical damage. During harvest, up to 97% of root crops are able to retain their original appearance;
- Unpretentious to the type of soil. You can grow Impala potatoes on any soil.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with potato varieties with different ripening periods:
| Late ripening | Early ripe | Superearly | Mid late | Medium early |
| Nikulinsky | Borovichok | Forty days | Crane | Yanka |
| Cardinal | Elmundo | Karatop | Sorcerer | Giant |
| Rocco | Felox | Riviera | Mozart | Tuscany |
| Kiwi | Bellarosa | Zhukovsky early | Grenada | Purple Haze |
| Ivan da Marya | Natasha | Farmer | Melody | Openwork |
| Picasso | Ariel | Minerva | Margarita | Santana |
| Asterix | Queen anne | Veneta | Ramona | Desiree |
| Slav | Arosa | Kiranda | Dolphin | Lady Claire |
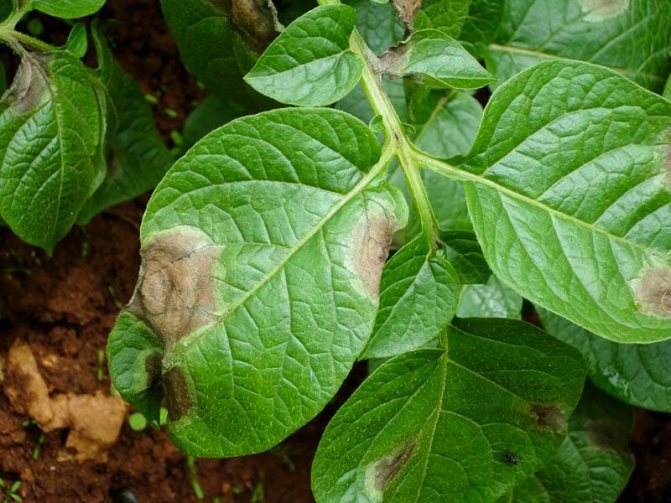
The disadvantages of the variety include susceptibility to the following diseases:
- Late blight;
- Common scab;
- Rhizoctonia.
Planting Impala potatoes, 1st reproduction, under agrospan:
Features of caring for potatoes after planting
Impala is drought tolerant but should be watered during dry summers. This is done 2-3 times during the growth of the bushes - 40 liters of water are used per 1 m² of plantings. Watering is carried out in the aisles and under the base of the plant so that drops do not fall on the leaves and flowers.
Weeding is recommended for potatoes. Between the beds, this is done with a hoe, and weeds that have grown close to the stems must be removed manually. Loosening and hilling affect the development of the aboveground and underground parts of the plant. As determined by potato growers, the correct implementation of agrotechnical measures can increase the yield by 25%.


Features of the
Thanks to many years of experience in growing the Impala variety, some features are distinguished that have a beneficial effect on its yield and the quality of root crops:
- This variety grows well on all types of soil, but only previously well fertilized, loose and sufficiently moist;
- Seedlings develop rapidly and appear at temperatures ranging from +18 to +25 ° C, and bloom and form root crops at +17 to +20 ° C;
- A high yield allows to achieve a loss of about 250-300 ml of atmospheric precipitation during the growing season, uniformly moist soil contributes to the full growth and development of potatoes;
- To obtain two potato crops, the first early harvest is harvested in cloudy weather, it is necessary to collect all the roots, and then re-plant the bush, not forgetting to water the hole abundantly with water. This will allow the second crop to be formed by the time of the main harvest.
How to get a higher potato yield?
The Impala variety is becoming more and more popular among gardeners. Recommendations have already appeared on how to improve the yield, increase the resistance of plants to adverse conditions. The following features will help you grow a high-quality and tasty harvest:
- Maintain loose and moist soil;
- When planting, pour humus and a tablespoon of ash into each hole;
- Mineral fertilizers are effective: a tablespoon of nitrophoska or a teaspoon of potato Kemira. They should be applied three times during the growing season. When leaves appear, when hilling, add a teaspoon of ammonium nitrate and humus. In the period of bud formation, add potassium and ash. During the formation of tubers, add superphosphate when hilling and water with a mullein solution.
- Position your potato beds from north to south for maximum light and warmth.


Correct fit
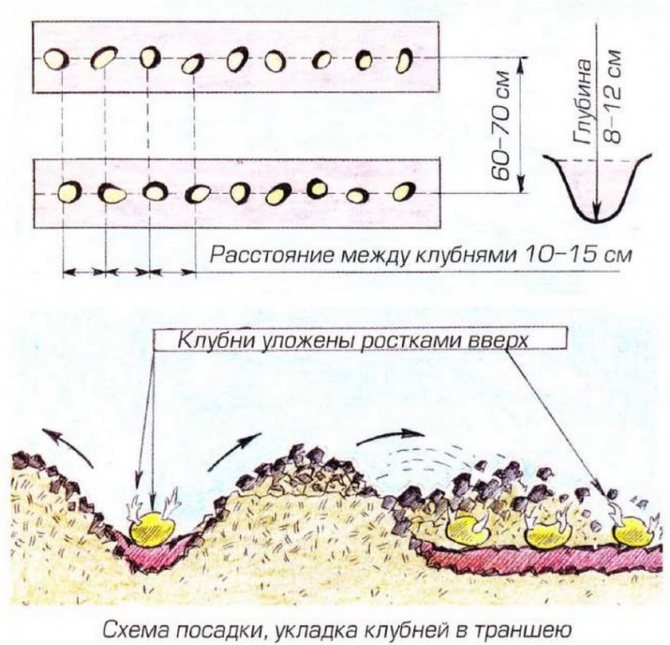
To get a good harvest, certain rules must be followed:
- Planting tubers in open ground is carried out no earlier than mid-April, in well-warmed soil. Planting times vary depending on the region's climate and weather conditions;
- The seed is medium-sized tubers with a sufficient number of eyes and no damage;
- Before planting, the tubers are kept for 30 minutes in a solution of potassium permanganate or boric acid, after which they are powdered with ash;
- Avoid injuring the tuber shoots. Due to broken off shoots, bushes develop slowly and yield decreases;
- When growing this variety, it is necessary to observe crop rotation. You should not plant Impala potatoes for two seasons in a row in the same area, as well as in the garden after peppers, tomatoes and eggplant. Plots after cereals (wheat, oats), legumes (peas, lupine, sweet clover), cruciferous plants (white mustard, rapeseed, rapeseed) are perfect;
- The tubers are deepened to a depth of 6 to 8 cm in a heated, moist and loose soil;
- Potatoes should be planted sparsely, the distance between the plants should be - 30 cm, in the aisle - 50 cm.
REFERENCE: The decontamination process will reduce the risk of developing diseases. Boric acid can stimulate growth.
Growing tips
When growing, you need to follow certain rules of care and cultivation. Correctly chosen timing of planting, watering, location and preparation of planting material will avoid many problems.


Optimal timing and location selection
You need to plant potatoes in mid-April-early May.At this time, the earth has already completely warmed up, there is practically no fear that the cold will return.
The best place is a well-lit place, protected from drafts and excessive waterlogging. The soil for planting should be warm, loose and with enough fertilizer.
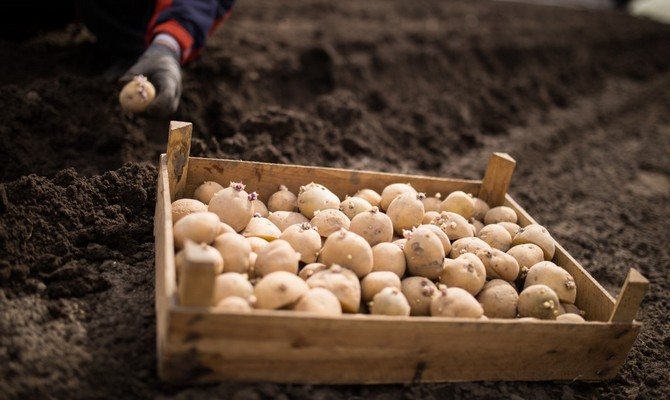
Tuber preparation
Pre-planting material preparation implies:
- Careful selection of healthy and whole tubers;
- Disinfection with boric acid, ash or potassium permanganate. The potatoes are immersed in the solution and kept for about half an hour. Dried tubers are planted;
- Pre-heating and germination of eyes. To do this, the seeds are kept in a warm place for 30-40 days at a temperature not lower than +18 degrees. It is important not to break the shoots when planting, so that the plants do not get sick and quickly grow.


Fertilization
Fertilizers need to be applied in advance, preferably in the fall. Rotted manure is scattered over the entire area, dug up and left until spring.
The introduction of nitrogen fertilizers is not recommended, since they enhance the vegetation of potato bushes and reduce the process of tuber formation, that is, the shoots will be strong, green with leaves, but the roots will turn out to be small or not form at all.
It is best to feed Impala potatoes with complex fertilizers with boron, iron, zinc, molybdenum, manganese.
You can find out which fertilizer works best in the article on choosing fertilizer for potatoes.
Care
How to care:
- A week after planting and after rains, carefully harrow the ridges with a rake. This contributes to the destruction of filamentous weeds and the destruction of the earthen surface crust, which impedes soil aeration. If necessary, it is possible to introduce humus, mullein or bird droppings, covering them with a hoe directly into the soil;
- Rare but abundant watering is recommended. So the soil will be soaked to a depth of at least 40 cm;
- Carry out regular weeding and loosening of the soil in the aisle;
- If pests appear, treat the bushes with Aktara, Actellik, Colorado preparations. To significantly increase the immunity of plants and prevent the development of late blight, spray potatoes with Fitosporin several times a season.
IMPORTANT: It is worth applying fertilizers only after heavy watering or rains.
Protection against diseases and pests
The main protection against fungi and pests is prevention. Conduct a competent crop rotation. Alternate Impala with:
- legumes: peas, lupins, beans, beans;
- perennials, like clover, sweet clover, alfalfa;
- spring and winter crops: rye, barley, oats, wheat.
But it is impossible to plant potatoes in place after nightshades, they have many common diseases and pests.
Before planting, it is also recommended to treat the wells with fungicides and insecticides. Re-processing is carried out during flowering, since many pests like to feast on flowers. For example, Aktara helps.
Rotted manure and chicken droppings repel pests. Water the wells before planting the tubers.
Also, the drug Bazudin is effective from the larvae of the click beetle. The granules are poured into the ground before planting and dug up.
The instillation of onion and garlic husks into the soil helps with the Colorado potato beetle. We already wrote earlier how to get rid of the Colorado potato beetle, we advise you to read.
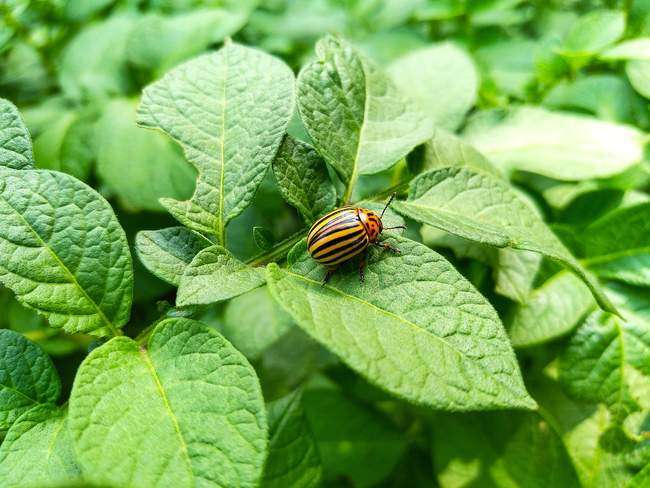


Colorado potato beetle
Medvetox helps from the bear, which is used in early July, when the larvae hatch begins.
If you find infected bushes with fungal diseases, immediately remove and burn them. Diseases spread quickly, so inspect plants as often as possible. Effective fungicides are Infinito, Consento, Penncoceb.
Be sure to carry out manual weeding, as they are the breeding ground for infection.
Variety reviews
Because of their excellent taste, Impala potatoes are highly valued by consumers.The content of a small amount of starch does not allow the tubers to darken after heat treatment, and only slightly crack. Potatoes can be fried, stewed, added to salads, soups, casseroles.
ATTENTION: Before picking, you need to pay attention to the general condition of the bushes: if the tops began to fall, and the lower leaves turned yellow, the potatoes are ripe.
Choosing the Impala variety, as a result, you can get a high-quality, consistently high yield, with the most preserved root crops. This excellent potato variety is suitable for growing subsidiary farms, as well as small and medium-sized businesses.
Harvesting and storage
Experienced gardeners advise against digging the tubers before full ripening, as they still taste mediocre. Harvest time is determined by the following criteria:
- three weeks after the end of flowering, the stems should begin to wilt, and the lower leaves should turn yellow;
- whether it is worth digging up all the bushes can be determined one by one; if the tubers are ripe, then you can start a large-scale harvesting;
- before storing potatoes, the crop is dried in a dark, dry and ventilated room;
- do not allow direct sunlight;
- you need to store potatoes in a well-ventilated area, spread out in one layer and periodically check the condition. Remove tubers that have begun to deteriorate and sprout immediately. You can read about other features of storing the crop of potatoes here.