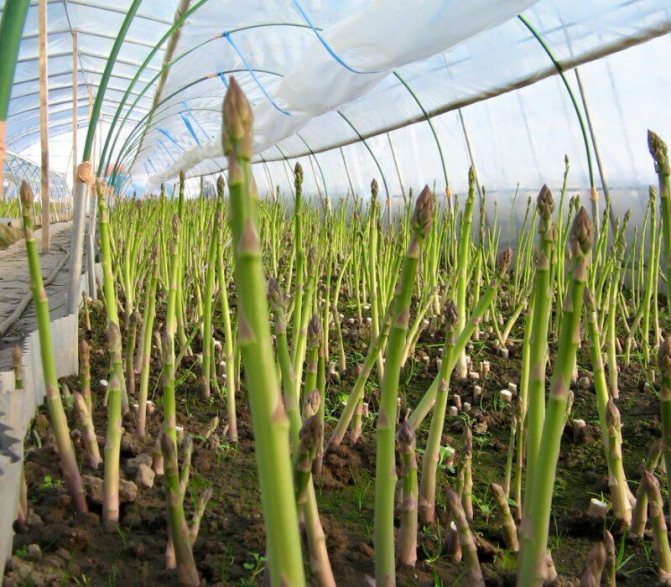
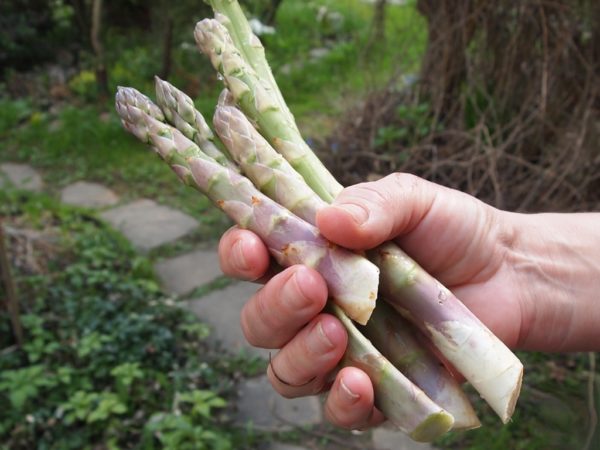
Description of culture
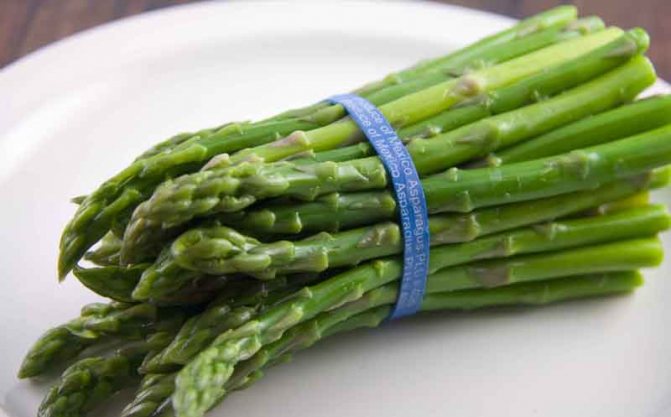
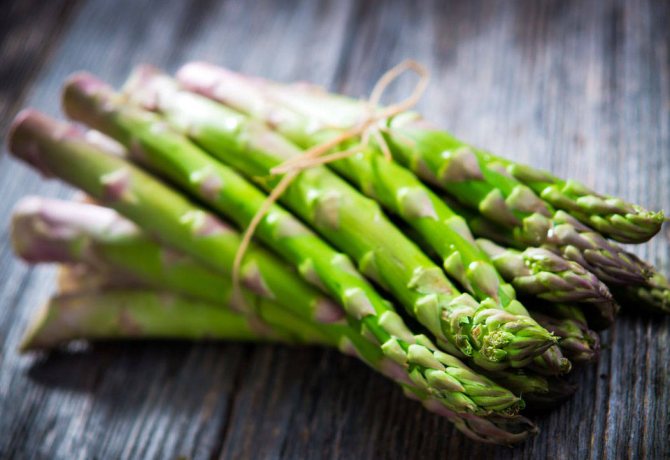
Today it is known about a hundred different types of asparagus, which, depending on their variety, can significantly differ in appearance and taste characteristics of the grown crop. The most widespread is common asparagus, which is successfully grown by gardeners and has an excellent delicate taste.
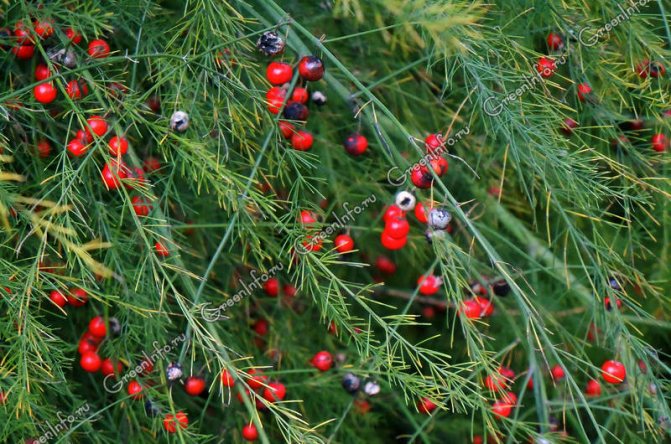
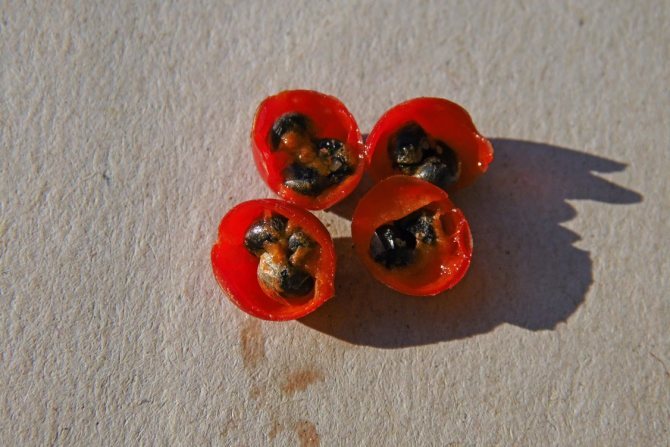
It is a perennial herb. can grow and bear fruit for 20 years, forming fifty or more edible shoots from one rhizome. The height of the plant in natural conditions reaches one and a half meters, and themselves plants are distinguished by excellent frost resistance... The bush of the plant has strongly branching green stems, on which there are thin twigs and small ovaries with inedible red berries. Asparagus has only young stems that are edible., which contain beta-carotene, calcium and iron, ascorbic acid, copper, phosphorus, sodium and other trace elements that are necessary for the human body to function properly.
Growing asparagus in the garden
Today, two methods of growing asparagus are most common: by planting seeds in open ground and pre-growing seedlings... For beginner gardeners, we can recommend growing asparagus by planting seeds in open ground. This will significantly simplify the care of this vegetable crop, while using high-quality planting material, you can get an excellent harvest. But the preliminary cultivation of seedlings is more laborious, but at the same time the gardener gets the opportunity to grow strong and viable plants that easily endure winter and subsequently bear fruit well.
When growing asparagus, remember that the first harvest can be obtained only in the 3rd year after planting... Caring for this plant culture is not difficult, which makes it extremely popular with gardeners. Let's talk in more detail about how to grow asparagus in the garden.
Asparagus properties
The properties of this vegetable crop are very valuable, since it is rich in a large number of useful substances, among which it should be noted:
- rutin;
- asparagine;
- coumarin;
- niacin;
- choline;
- inulin;
- purines;
- saponin;
- beta carotene;
- vitamin A, E, K;
- ascorbic, folic and pantothenic acids;
- iron, sodium, magnesium, manganese;
- dietary fiber and other microelements.
The product is low-calorie, dietary.
Thanks to this composition, the use of asparagus can benefit the body in many disorders and diseases.

Benefit
Asparagus has a beneficial effect on human health and has a positive effect on the functioning of its internal organs and systems.
- Her useful qualities:
- if necessary, adhere to a dietary diet in order to reduce weight, since it has a low calorie content, only 20 kcal per 100 g of product;
- strengthens the skeleton, prevents osteoporosis due to the content of vitamin K and improved absorption of calcium;
- normalizes the digestive system thanks to inulin, which is a natural probiotic, and a high content of coarse fibers;
- promotes the formation of connective tissue;
- normalizes the work of the heart muscle;
- strengthens blood vessels, promotes their expansion, thereby reducing pressure;
- coumarin helps to make the blood clearer, reduces the risk of blood clots;
- normalizes kidney function and tones up the urinary system, eliminating even inflammatory processes;
- helps to improve the condition of the liver;
- removes toxins, eliminates slagging;
- reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by lowering blood sugar levels;
- improves vision;
- used for diseases of the thyroid gland;
- enhances potency in men and libido in women due to the content of vitamins B6, E and folic acid;
- it is used for the prevention of oncological diseases due to the presence of substances that change the metabolic activity in cells and prevent their degeneration.
For pregnant women, asparagus is useful for the presence of folic acid, which is responsible for the correct formation of the skeletal system of the embryo and normal pregnancy. It helps to reduce swelling while carrying a baby and improves kidney function. In turn, magnesium normalizes sleep and improves the functioning of the nervous system.
In cosmetology, asparagus juice is used as:
- cleansing;
- emollient;
- nutrient.
It is used in folk medicine to remove corns and warts.
Important! Asparagus is recommended for people who have had a heart attack.
Harm
Due to the content of a large amount of active substances, the use of asparagus in food in some cases should be limited or excluded altogether:
- an excess of purines can lead to an increase in the concentration of uric acid, which can provoke the appearance of gout;
- a high concentration of substances that affect the functioning of the kidneys can negatively affect the well-being of a pregnant and lactating woman, therefore, asparagus should be consumed in limited quantities, despite its positive effect on other organs and systems;
- saponin can significantly irritate the lining of the stomach and intestines;
- can provoke the appearance of belching, flatulence in people suffering from problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor of urine and body is possible.
Asparagus should not be eaten by people with:
- kidney disease;
- gout;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- cystitis;
- prostatitis;
- urolithiasis;
- allergies to lily and onion crops.


Landing in open ground
Asparagus, which is easy to grow from seed, can be planted in late May and September. It is necessary pre-properly prepare the soil, for which the earth is dug up, cleaned of weeds and organic fertilizer is applied at the rate of 50 kilograms of humus per square meter of the garden.
Seeds are planted in rows with a row spacing of at least 25 centimeters. Immediately after planting, the bed must be watered abundantly and covered with a film, which is removed as soon as the first shoots appear.
Asparagus emerges and grows slowly, so the first shoots will appear no earlier than 20 days after planting. The appearance of seedlings can be somewhat accelerated by preliminary preparation of the seeds, which are soaked for a week in warm water. The water must be changed every day when soaking.
Transplanting seedlings to a permanent place
When growing asparagus from seeds in the country, you need to choose a place, taking into account some features:
- a light-loving plant does not like wind and drafts;
- the bush grows up to 1.5 m, so it is planted away from light-loving plants;
- optimal temperature regime for development: air - 20-25 ° С, soil - 12-15 ° С; the place is chosen where the snow melts earlier, the earth warms up faster;
- on acidic and infertile soils, development slows down.
It is better to plant the culture on a single-row bed, having previously prepared the soil:
- Spread mineral fertilizers (superphosphate, potassium chloride) over the surface.
- Dig up, mixing minerals with soil.
- Dig a furrow: depth - 0.35m, width - 0.45m, loosen the bottom.
- Lay out a layer of rotted manure (0.2m), then - humus (0.1m).
The next stage is the preparation of seedlings: poorly developed roots are removed, and the rest are reduced to 3-5 cm. Then they plant it:
- Bushes are laid out in the furrow every 0.3-0.35 m.
- Straighten the roots.
- Sprinkle with earth.
- They compact the soil and moisturize well.
If transplanted into beds in several rows, then the aisles are made at least 0.5 m, and 0.4 m is left between the bushes.
Proper planting care
Asparagus grows extremely slowly. Usually, by the end of the first year of life, the height of the ground part reaches 15 - 20 centimeters, only some hybrid varieties are distinguished by rapid growth rates and allow the first harvest to be obtained already in the second year after planting the seedlings.
Planting care is not difficult. The beds must be watered and weeded regularly. In June, fertilizing is performed using nitrogen fertilizers. We can recommend you to use the following mineral fertilizers:
- Urea.
- Ammonium nitrate.
- Wood ash.
Also excellent results are shown by feeding asparagus with slurry, which is diluted in water in proportions of 1 to 6... With proper care, the asparagus will have three to four shoots and a small well-developed rhizome by the end of August. The gardener will need to properly prepare the plants for winter. In late August or early September, plantings are fed with potassium and phosphorus. In October, the ground part of the plants dies off, after which the soil is mulched with peat or humus with a layer of no more than 3 centimeters. Additionally, you can cover the bed with fallen leaves or spruce branches.
Reproduction by dividing the bush
When growing asparagus outdoors, you can use another breeding method. It reproduces well by dividing the bush, and they can be transplanted even in the middle of summer, and not only in early spring and late autumn. You can divide asparagus bushes into as many parts as required, it is important that at least 1 shoot remains on each piece.
It is permissible to propagate asparagus and green shoots. To do this, in March-May, small cuttings are cut from last year's asparagus shoots. They are planted in moistened sand, covered with jars or halves of plastic bottles on top to create a greenhouse effect. The cuttings are regularly sprayed from a spray bottle, and ventilated every day, for which the shelters are removed. Rooting of cuttings takes about one to one and a half months. Then the asparagus is planted in suitable sized pots.
Caring for asparagus in the second year of cultivation
In the spring you will need additional feed the plantings with mineral fertilizers, which will allow in the future to accelerate the growth of asparagus, which quickly gains a green mass, and the roots in the ground will grow, and subsequently easily endure the winter. The soil along the rows of plants should be loosened, such work is done as carefully as possible, excluding damage to the roots.
Subsequently, planting care implies only regular watering and weeding of beds... In dry soil, the shoots of asparagus acquire a bitter taste and become fibrous. That is why plantings are watered at least once a week. It will also not be superfluous to feed the plantings, for which a solution of mineral fertilizers based on mullein nitrogen is used. Preparing plants for winter in the second year of growing is not particularly difficult. After the ground green part of the plants dies off, the beds are mulched with humus, peat or other organic matter.
Growing asparagus at home in the garden
The first thing to remember is that transplanting seedlings is carried out as carefully as possible, which will help to avoid problems with damage to the still extremely weak vegetative or root system of the plant. It is also highly recommended to comply with existing requirements and recommendations. Following the instructions will help you avoid serious problems in the future.
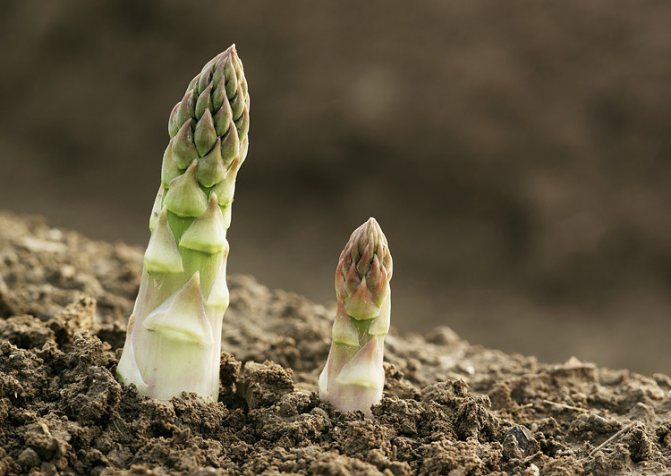


Transplanting seedlings is carried out as carefully as possible, which will help to avoid problems with damage to the still extremely weak vegetative or root system of the plant.
You must first dig out suitable holes. Their depth directly depends on the type of soil. If it is sandstone, then you will need to dig holes at a depth of 18 centimeters, and in the case of heavier soil - about 16 cm. The distance between the holes should not be less than 30-35 centimeters. As for the row spacing, it is recommended to observe an indicator of 80-100 cm.
Before planting asparagus, the pits are filled with high-quality organic fertilizer, for example, rotted manure or humus, after which they are covered with a thin layer of soil (about 5-8 cm).
Caring for this crop is a complex process that requires responsibility and proper understanding on the part of gardeners.
The prepared seedlings are placed in a hole in such a way that its root system is necessarily straightened out. A hole with an already planted bush is carefully covered with soil, after which it is watered abundantly (watering in this case is of decisive importance, since it depends on it how well the plant will take root). This procedure is repeated with each new seedling.
Harvesting and caring for asparagus
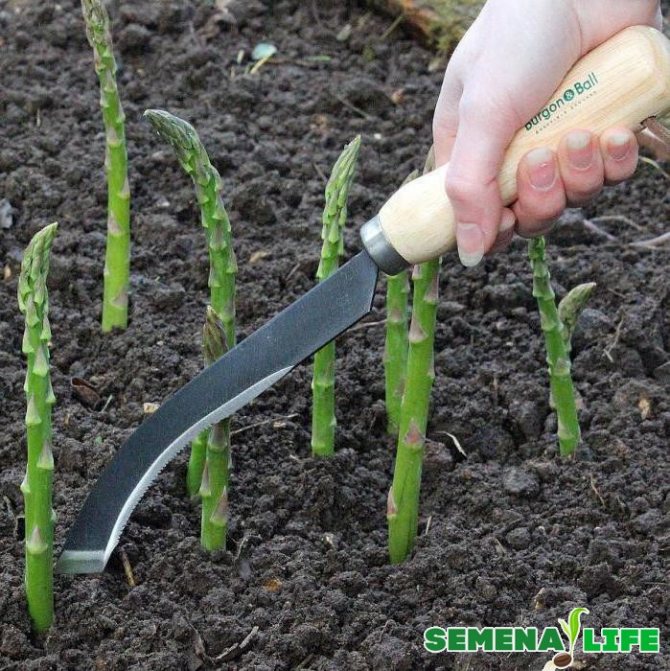
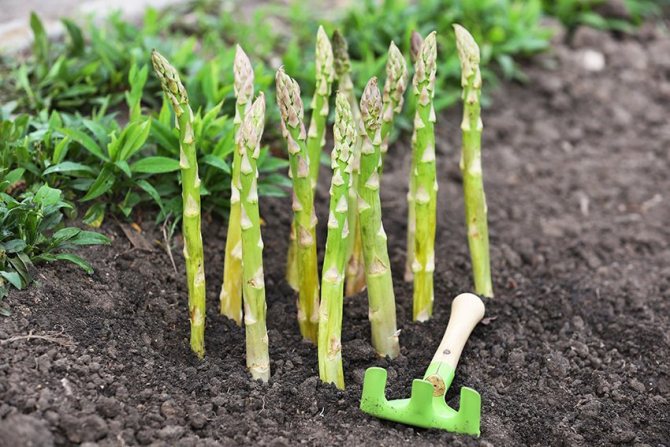
The first harvest is done in the third year after planting. By this time, the plants will become bushy and have a large-sized rhizome. Even before harvesting in early spring, the aisles must be deeply loosened, and the plants must be sprinkled high with humus and soil. Usually, in the third decade of April, young shoots appear under the soil, which after a few months reach marketable ripeness, after which you can start harvesting. Such shoots, which reach a length of 5-7 centimeters, can be cut every three days for a month..
5-7 shoots are usually cut from three-year-old bushes. In subsequent years, approximately 15 shoots can be cut from each such plant. After the end of the harvesting period, 3-5 shoots should be left on the asparagus, from which later powerful stems with branches of the second and third order are formed. In autumn, the green part dies off again and the gardener will only have to feed the beds and insulate the plantings with a small layer of mulch.
Care for asparagus in the post-harvest period should be given maximum attention. It was at this time that the foundation for the future harvest was laid. Humus, a small amount of wood ash should be poured into the aisles, and mineral nitrogen fertilizers should be embedded in the soil. In summer, after the end of the harvest period, the asparagus should be watered once a week. After such watering, the soil must be loosened, which prevents the formation of a surface crust.
In the future, caring for asparagus is not difficult. It will be necessary to perform the following work:
- Loosen the aisles;
- Remove weeds;
- Feed the plantings with a light mullein solution and nitrogen-based mineral fertilizers.
Reproduction
By dividing the bush
The method of reproduction by dividing the bush is quite simple to perform. You can use it in the autumn, spring or even summer period (when the berries appear). The plant must be completely dug up, it is worth being careful not to touch the roots, therefore it is necessary to dig as deep and wide as possible.
Then we divide the asparagus into several parts, leaving 2-3 shoots on each. Cut a small part of the roots.Before planting, for each new bush, we dig a deep hole so that the roots are placed freely.
Loosen the bottom and put 1 tbsp. superphosphate, a little humus and 1 tsp. potassium chloride. The distance between seedlings is at least 50-60 cm. Young plants should be replanted after a year, adults after 10 years.
Cuttings
For propagation by cuttings, green shoots are used. From an old seedling, from March to June, several shoots are separated, and cuttings are cut from them. Cuttings should be planted in wet sand for rooting to ensure good survival.
From above, this container must be covered with polyethylene or a cut-off neck of a plastic bottle. Regular airing and spraying will encourage shoot growth. After the seedlings reach 15 cm, we proceed in the same way as in the case of growing seedlings from seeds.
Asparagus is represented by over one hundred species. On our portal there is information about the beneficial properties of the plant, as well as about when it is better to refuse to use it.
Seedling growing
Growing seedlings at home is not particularly difficult. It is only necessary to use high-quality fertile soil, which will allow you to grow viable and strong seedlings as soon as possible, which quickly take root in a new place and subsequently easily endure cold winters.
Seeds should be planted in fertile soil, which is prepared from a mixture of sand, garden soil and peat... Having germinated and pre-soaked the seeds, you can get the first shoots within one to two weeks after planting. Subsequent care of the seedlings consists in regular watering and maintaining the temperature at 20-22 degrees. After one and a half to two months, the plants will get stronger and they can be easily transplanted into open ground.
How to grow asparagus from seeds
Growing asparagus in Russian conditions is carried out mainly by seedlings.
Growing seedlings in a nursery
Loose fertile soils are taken under the nursery. For digging for 1 m2, it is necessary to add 5-6 kg of organic matter, for example, humus or compost. Of the mineral nitrogen fertilizers, urea (1 tsp) is used. Potassium sulfate and superphosphate are embedded in the soil at the same dose. Then, grooves are made at a distance of 0.3-0.5 m and poured with a solution of the growth stimulator "Energen" (at the rate of 1 capsule per 5 liters of warm water).
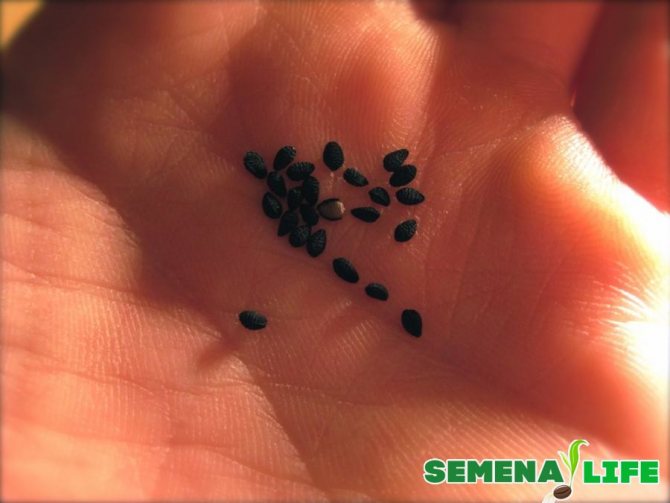
Seeds must be prepared before sowing so that they germinate better. To do this, they are kept in the preparation "Agricola Veta" (1 tbsp. L. Diluted in 0.5 l of water) in a tissue bag for 2-3 days. Swollen seeds are laid out on a damp cloth, wrapped in a roll and left in a warm place. Every day, it is moistened with liquid so that the seed does not dry out. The temperature at which germination should take place is approximately 23-25 ° C.
Naked asparagus seeds are planted in a nursery in late May or early next month - June. They are buried 3 cm into the soil at a distance of 8-10 cm from each other. Then mulching is carried out with rotted manure with a layer of 1 cm. To protect young seedlings from a possible spring cold snap, agrofibre is used, which is pulled over arcs installed on the beds.


Caring for the emerging asparagus seedlings is simple. This is watering and loosening the soil, which must be carried out regularly. You need to feed young plants for the first time a couple of weeks after the seedlings are formed. To do this, take organic fertilizers: potassium humate in the amount of 2 tbsp. l. diluted in 10 liters of water. After the same amount of time, they make the 2nd top dressing, this time with complex fertilizers.
In autumn, after cutting off the aboveground part of the plants, the ground is covered with peat, rotted manure or leaf. Asparagus is in the nursery until next spring.
Growing asparagus seedlings at home
There is a different approach to growing asparagus from seeds in the country.They can be sown not in the beds, but in boxes, shallow and wide pots and containers and grow seedlings indoors before planting on the beds. This method allows you to get seedlings earlier than with conventional sowing, so in this case, you can start sowing seeds as early as early April. The method of growing asparagus at home is also convenient in that it allows you to save space in the beds, where you can grow early vegetables at this time. Pots and containers are small, do not take up much space, so asparagus seedlings can be grown indoors even on a windowsill.
Before sowing in pots, the asparagus seeds are prepared as described previously. Then they are sown in a light substrate, which consists of 2 parts of land and 1 part of peat, manure and coarse sand, or use a universal soil for seedlings. Containers are filled with soil mixtures, seeds are sown, spilled and sprinkled on top with earth or soil. The containers are covered with a piece of film or glass and left indoors at t + 25 ... + 27 ° С. Asparagus takes a long time to germinate - about one and a half months, which is quite normal for it, so there is no need to worry. While the asparagus seedling is growing, it is watered, loosened, fertilized with complex fertilizers. It is transplanted to the beds in the second half of June.


Spring planting seedlings
In the spring, in the second year of growing, the asparagus seedlings are transplanted to a permanent growing site. It is planted in 1 or 2 rows. In the first case, you will need a site 1 m wide, in the second - 1.7 m. The length of the ridges is arbitrary and depends on the number of seedlings. It is planted in a row every 0.4 m, 0.7 m is left in the aisles. The soil on the ridges should be prepared in the fall. It is dug to a depth of at least 0.3-0.4 m, organic matter is introduced into it in the form of humus in a volume of up to 20 kg per m2 and phosphorus-potassium mixtures. Acidic soils are lime or chalk (0.2 kg per 1 m2). In the spring, the soil is again dug up and nitrophoska is scattered over it in the amount of 1 tbsp. l. or complex fertilizers, for example "Agricola" per 1 m2 of nursery.
They begin work in early spring, even before the buds begin to grow. Planting ridges are prepared: in their center or closer to the sides, 1 or 2 deep grooves are dug (depending on the method of forming the ridges). Their depth should be 0.4 m, width - 0.3 m. Compost is poured at the bottom with a layer of 25 cm and mounds of earth are poured on top.
Carefully dig out asparagus seedlings with a pitchfork, taking care not to damage them. Young plants should not have fibrous rhizomes - such specimens are removed. For the rest, the roots are straightened, immersed in the ground and directed downward. Plants are lowered into the furrows so that the asparagus buds are at a depth of 0.2 m. After all the seedlings are planted, the ridges are watered.
Planting seedlings in the fall
The agricultural technique of culture also allows for the autumn planting of seedlings. In this case, it is better to prepare the area for asparagus in advance. It needs to be well dug up and fertilized with 30 g of potassium sulfate, 20 g of ammonium sulfate and 60 g of superphosphate. The difference between the autumn planting of asparagus from the spring is that the plants are not buried in the soil, but a mound is poured over them. The layout is the same as in the spring.
Recommended to read
What does asparagus look like, where and how it grows
The benefits and harms of asparagus for the human body
How to grow Jerusalem artichoke outdoors
The benefits and harms of Jerusalem artichoke for the human body
Growing Arzhentelskaya asparagus
Popular with gardeners Arzhentelskaya asparagus, of the features of which we note low-fiber large shoots of white color. The cultivation of this variety is carried out according to standard technology, which allows the vegetable to be planted both by seeds directly on the garden bed, and with the help of seedlings, which are grown at home and subsequently transferred to the beds. The gardener will receive the first harvest of this variety in the third year of cultivation, and subsequently plants bear fruit well, allowing you to get up to 20 shoots from one adult rhizome.
Asparagus varieties for cultivation in the regions
There are very few varieties of vegetable asparagus. All varieties of this culture zoned for Russian conditions can be successfully grown everywhere: in Ukraine, in Belarus, throughout central Russia, in the Moscow region, the Leningrad region, in the Urals and in Siberia. It does not grow at all only in the regions of the Far North.


Vegetable asparagus has particularly thick shoots.
Table: the best varieties of asparagus
| Name | Ripening period | Coloring shoots | Characteristics of the variety | Zoning |
| Argentelskaya | Early | Green-violet | Old variety of the middle of the last century, still grown, very unpretentious | Zoned throughout Russia |
| Tsarskaya | Middle | Green | New high-yielding variety | |
| Mary Washington | Early | Green | New grade, resistant to rust | Not zoned in Russia |
| Snow head | Mid-early | Greenish cream | One of the most popular varieties of vegetable asparagus | Not zoned in Russia |
Photo gallery: asparagus varieties
Forcing asparagus in winter
Gardeners can easily cultivate this versatile vegetable crop in the summer in the garden and in the winter. in warm heated greenhouses... For such forcing, the rhizomes of adult five-year-old plants are used. In October, it is necessary to dig out the rhizomes of asparagus, which are removed to the basement until December, where the temperature is maintained at about zero degrees.
In early December, the dug up asparagus rhizomes are planted in a greenhouse in small containers. The containers themselves are tightly pressed against each other, which allows placing at least 20 boxes of asparagus on one square meter. Top of the rhizome should be covered with a 20 cm layer of humus. The containers are additionally covered with black plastic wrap.
Read about the construction and arrangement of a greenhouse in the article - "Do-it-yourself greenhouse"
In the first week in the greenhouse, the temperature should be maintained at 10 degrees, and as soon as the roots begin to grow, the temperature is gradually raised to 18 degrees for several days. This temperature regime is maintained for 2 months, that is, throughout the entire harvesting period. A similar original technology for forcing asparagus in winter can be used both in warm greenhouses and at home with the germination of rhizomes on a glazed balcony.
Pests and diseases of asparagus
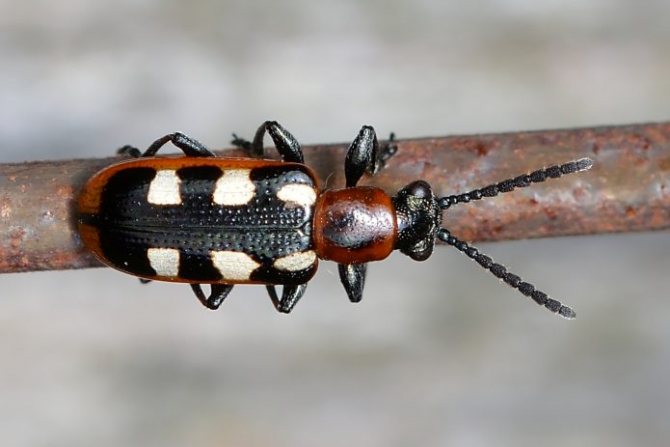
Of the common pests of this fruit crop, we note the asparagus leaf beetle. This insect can appear in the middle of summer, completely destroying the foliage. Once you noticed small black or yellow beetles and their black larvae, plantings should be treated with insecticides. We recommend using the following agrochemicals in your garden:
- Fufanon;
- Fitoverm;
- Actellic.
Can also damage asparagus wireworms, beetles, slugs and bears... As a prophylaxis against these insects, asparagus should be treated with insecticides and the beds should be weeded regularly, which will be an excellent prevention against the appearance of various insects and diseases of this culture.
Of the common diseases, we note red root rotwhich is caused by fungi. In diseased plants in the garden, the roots and root collar are affected. As soon as you notice small bald spots on the stem and in the area of the root collar, you should treat the asparagus with an agrochemical foundation. In case of serious infections, the plants should be destroyed, and a bed with a new plantation should be laid in a new place.
Asparagus
Diseases and pests of green bushes
Asparagus is a rarely sick plant.
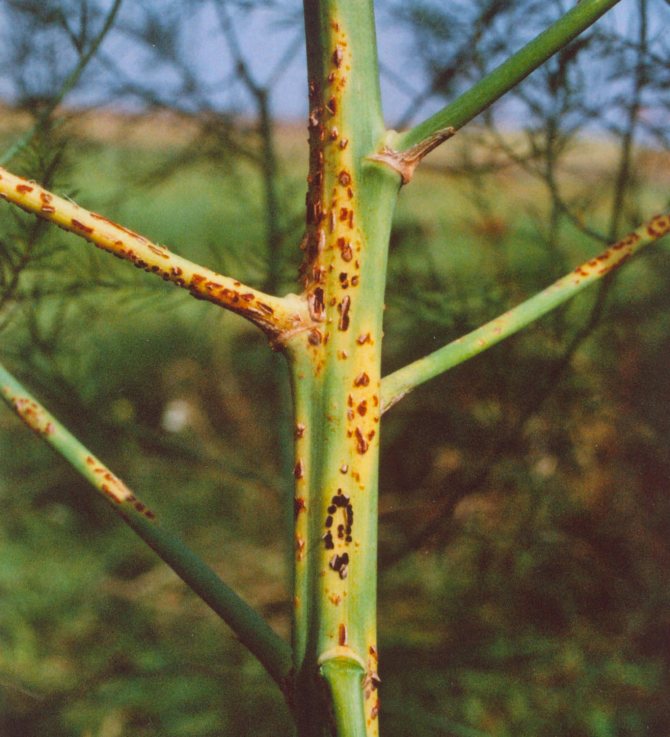


Sometimes it can be affected by a fungal infection.
The causes of the disease are improper care, high humidity of the soil and air.
The vegetable also does not tolerate the wind, protect the seedlings from strong gusts.
Asparagus has 2 pest enemies:
1 of 2
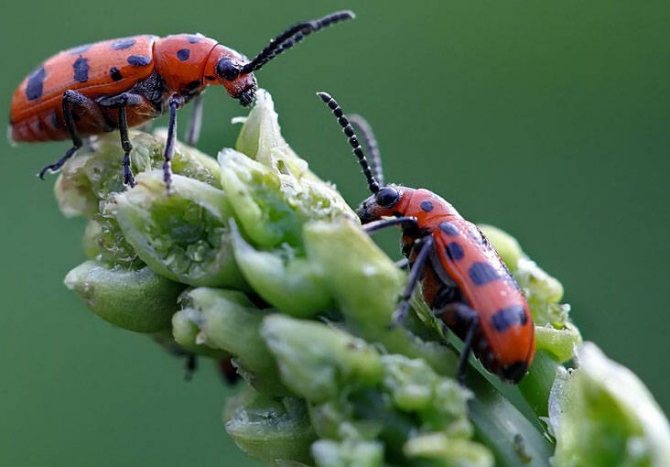


Asparagus leaf beetle - in the second half of summer, a beetle with blue wings can eat all parts of the vegetable.
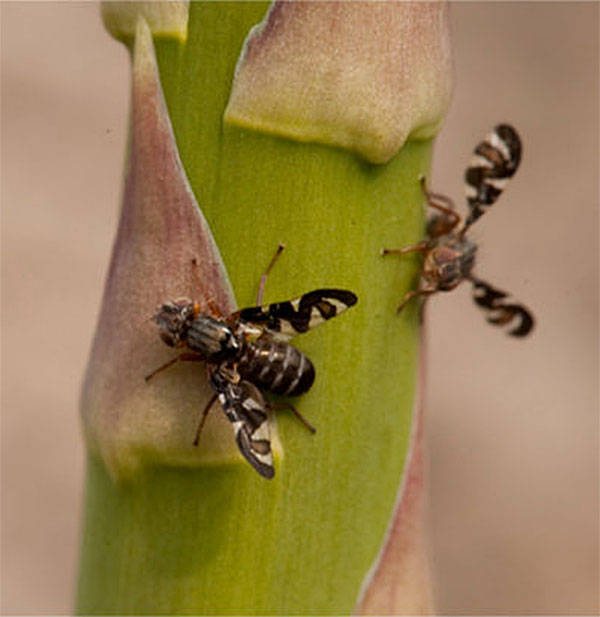


Asparagus fly - small midges with yellow heads.When a fly appears, the plant becomes lethargic, the stems bend.
Insecticides will help get rid of insects. The vegetable is sprayed regularly.
During watering, inspect for the presence of pest eggs. The damaged parts of the plants are burned.
To prevent the appearance of insect enemies, it is necessary to remove dried and damaged shoots in time. It is also important to get rid of weeds.