Description of the variety
All cultivars of carrots belong to the sowing carrot subspecies. By selection, it has been removed from the wild carrot species belonging to the Carrot genus from the Umbrella family. The plant has been known for over four thousand years, although it was first grown for spicy seeds and herbs. The stem is branched at the top. Its height varies from 25 to 100 cm. The plant is biennial, the flowers are collected in the inflorescences of umbrellas, they appear in the second year. Flowering time falls in June - July.
Wild carrot root vegetable lacks sweet taste and juicy crunchy texture. It is bitter, rough and dryish. The color is white, white-gray or cream. It must be said that until the 16th century, only white or light cream carrots were used for food. It was such a carrot that the inhabitants of ancient and medieval Greece and Rome ate.
It appeared in these countries from Pakistan and Afghanistan, where it was widely grown for the consumption of terrestrial parts or grew wild. The emergence of orange varieties is associated with natural mutations. And, according to historians, with the patriotic feelings of Dutch breeders. At the beginning of the 17th century, the orange carrot appeared, which corresponded to the heraldic colors of the ruling dynasty of the Netherlands and is associated with the loyalty of the subjects of the Stadtholder, the revolutionary William of Orange.
Origin and development
White carrots (Latin name Daecus) belong to the Umbrella family. Along with red and yellow, it is the closest relative of wild carrots. This species has been known since the 3rd millennium BC. on the territory of modern Afghanistan, Iran, Pakistan. It was originally cultivated as a fodder plant and a spice. In the 17th century, Dutch breeders managed to give this vegetable a sweet taste, increase its resistance to temperature changes, even change the color to the corresponding flag of Holland.
Since then, white and orange carrots have become ubiquitous culinary uses. Today, these crops are among the top 10 most grown crops on the planet. In Russia alone, the annual harvest is more than 1.5 million tons.
Features of white carrots
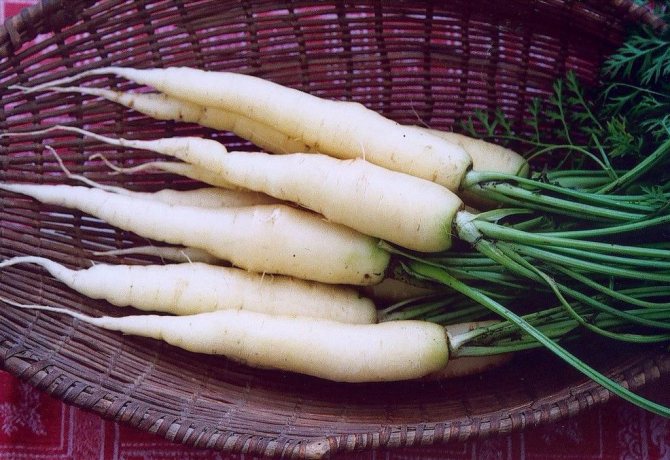
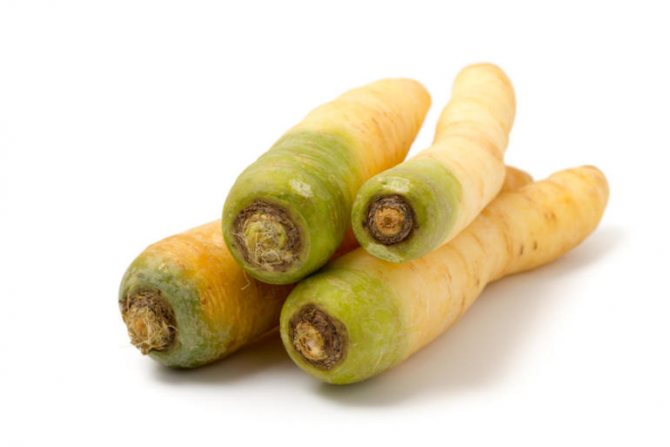
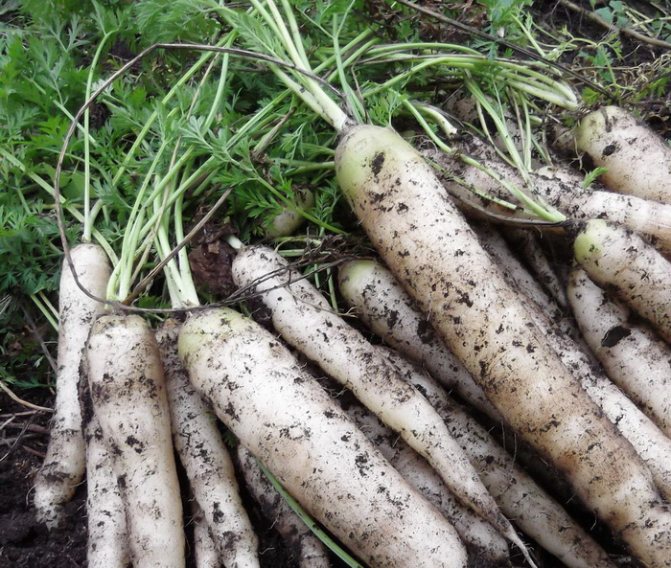
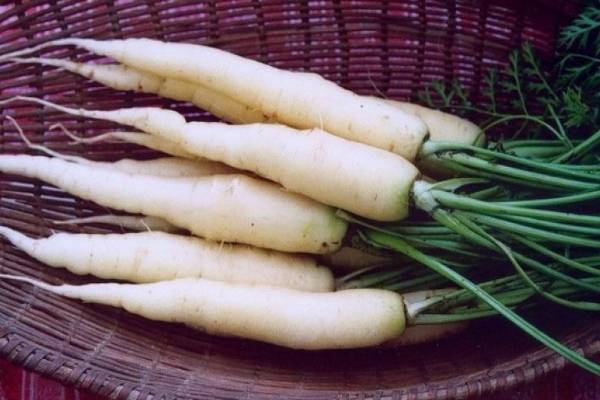
For a long time, white carrot varieties retained a slight bitterness, like their wild-growing ancestor. They were used mainly as fodder root crops. Later, varieties and hybrids were obtained that were devoid of bitter taste. A good variety of white carrots has a smooth, juicy root crop. Its leaves are petiolate and strongly dissected, pinnate. The white color is due to the low content or the complete absence of pigment substances.
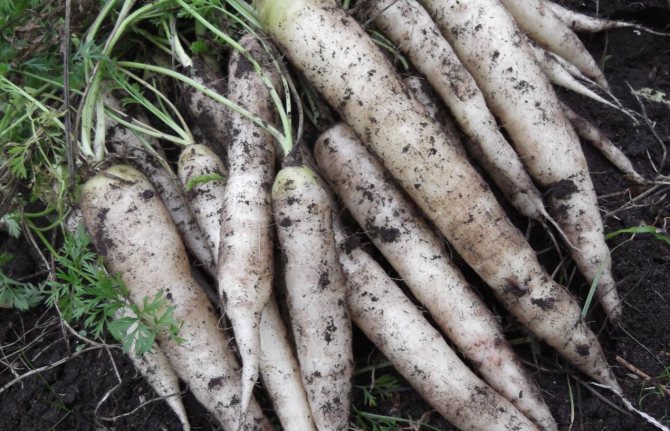
The table hybrid of white carrots Waite satin (white satin) is considered the best for taste. The root crops of the hybrid are smooth, with light creamy juicy pulp and a pleasant taste without bitterness. The shape is cylindrical, the tip is narrowed, sharp. The length is on average 25 - 30 cm, weight is about 100 g, the growing season from the moment of germination of seeds to harvest is 100 days.
Another variety Lunar wite (moon white) is also quite good, its roots are medium-sized, thin, up to 20 cm long. They are distinguished by tenderness, juiciness and sweet taste. Hybrid F1 "White Sugar" has snow-white juicy roots about 20 cm long, they are completely devoid of bitterness, have a light unobtrusive slightly sweet taste.
Despite the fact that white varieties do not contain beneficial pigments, they taste great and are indispensable in the diet of people prone to allergic reactions to orange and red plant pigments. A feature of white carrots is also a thin and delicate skin. You just need to wash young carrots.
Choosing carrots for storage
Good carrots at an optimum temperature of + 1 ° C to + 3 ° C and high humidity can be stored for up to 6-8 months. A solid time, huh? Let's go over the main traits of a good carrot.
By color and shape
Choose bright between bright orange and pale. A rich color indicates a higher carotene content. In the past, a pale color was considered a sign of feed carrots. Now there are solid varieties with good taste of light color. But, if there is a choice and there is no opportunity to try the carrots before buying, then I recommend opting for orange carrots.
Carrots should be smooth, firm, straight and blunt. Choose root vegetables without deformations and cracks. Don't buy washed carrots. She, of course, looks neater, but it is stored worse. Don't buy greasy to the touch.
Carrots inside
Ask the seller for permission to break one carrot and assess the condition of its inner core. In carrots, nitrates accumulate in the core. Therefore, if the core is very different from the rest of the color, density and stiffness, most likely it could not do without them. Don't take it.
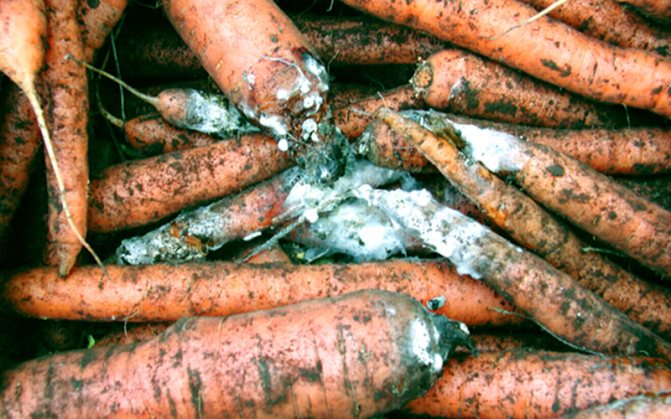
If possible, peel (wipe) one of the carrots. You should pay attention to the presence of black stripes going deep into the depths. Such stripes are a trace of a pest of a carrot fly. Such "moves" contribute to the rapid decay of carrots.
Pay attention to the "stump" of carrots. Ideally, the tops should be trimmed flush with the neck - then the vegetable will not germinate. The color of the neck will tell you about the degree of freshness - in fresh carrots, it is slightly greenish. A strongly green top is a sign of shallow growth of carrots. When cooking, this part is cut off. I do not recommend buying such fruits - there is a lot of waste.
These carrots should be avoided:
How to grow white carrots
Site selection and soil preparation
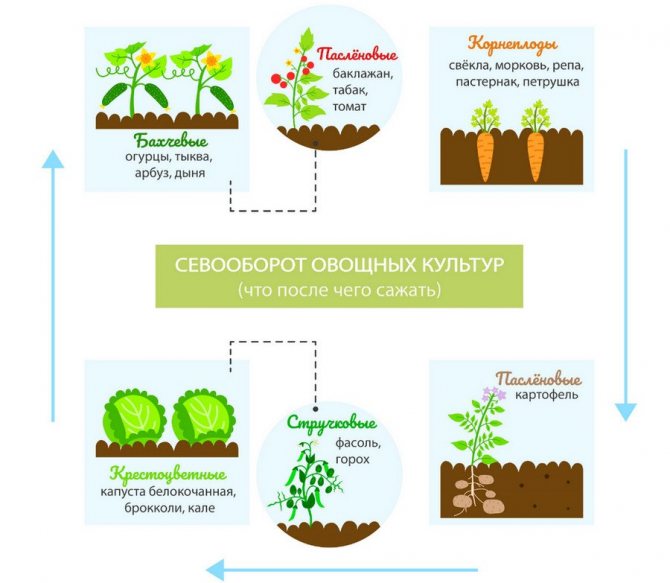
Carrots grow well on light, water- and air-permeable soils with a slightly acidic or neutral reaction. It is desirable that before that on the chosen place grow:
- cabbage
- onion
- tomato
- cucumbers
The worst predecessors for carrots will be parsley, dill. The bed is dug to the depth of the shovel with the obligatory introduction of well-rotted manure in the amount of 5 kg per 1 sq. m. You can also add 30 - 40 g of nitrogen, potash and phosphorus fertilizers.
Sowing carrots
For winter storage, carrots are sown in April-May, for summer use, sowing is done at the end of October. Furrows are made on the bed about 20 mm deep. The distance between the grooves is 30 cm. To distribute the seeds evenly, they can be mixed with sand.
Video about the correct planting of carrots:
One teaspoon of seeds is enough for a glass of sand. When sowing in spring, carrots emerge on the 18th - 20th day, they belong to tightly similar crops. Pre-soaking the seeds in water for a day will help accelerate germination.
Care
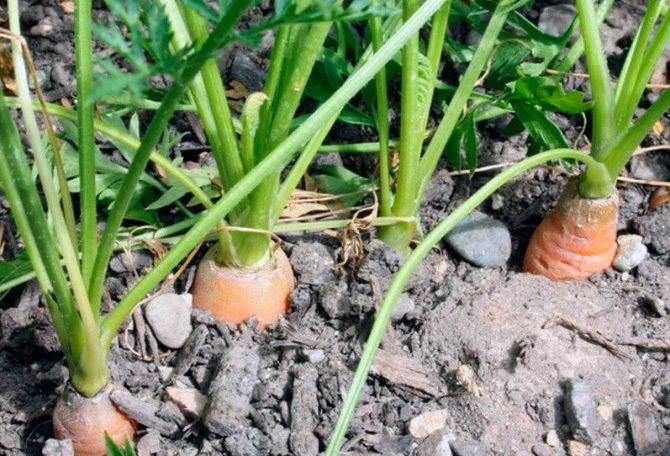
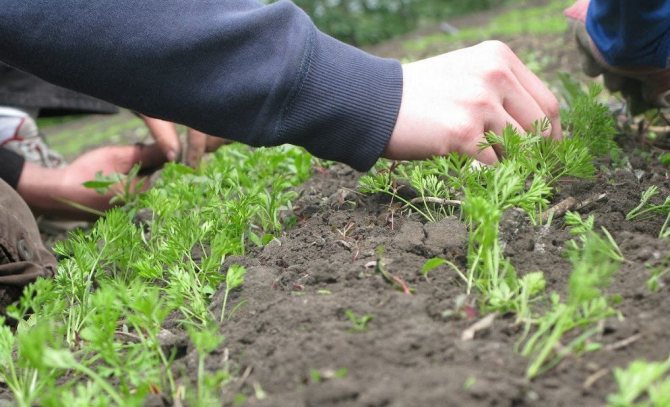
Before the seeds germinate, it is better not to water the bed so that a hard crust does not form. A special feature of carrot care is not only double thinning, but also regular hilling of plantings. After the second thinning, about 5 cm should remain between the plants. Timely hilling will prevent the appearance of green at the top of the root crop. There are no other features when growing white carrots.
What to do to avoid a bad harvest?
Although the list of problems that arise in the process of growing carrots is quite extensive, the ways to deal with them are basically the same:
- the right choice of carrot variety;
- preparation of seeds and soil for planting;
- compliance with the rules of crop rotation;
- fertilization of the soil both at the stage of preparation for planting carrots, and further application of dressings at different stages of growth of root crops;
- optimal watering;
- timely thinning and getting rid of weeds;
- prevention of pest and disease control at the stage of soil preparation, as well as the timely use of insecticides (both folk and industrial) in case of plant infection;
- timely harvest.
Carrots are considered a fairly unpretentious crop, however, there are a number of features that should be taken into account when growing it. Timely monitoring of the condition of the tops and growing root crops can help to quickly correct the problems that have arisen and take measures to solve them. In addition, preventive measures are also important for a high-quality harvest, which will often help to avoid problems in the future.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl + Enter.
Useful properties of carrots
The benefits of white carrot tops are high in vitamin C. The chlorophyll of the tops purifies the blood. The content of potassium and vitamin K affects the work of the heart, the state of blood vessels and blood. Vitamin K regulates blood clotting, helps with bleeding. Leaf tea relieves swelling, has a mild diuretic effect.
White root vegetables contain almost no vitamin A and beta-carotene. On the one hand, this is a disadvantage, on the other, it is an advantage. White carrots can be included in the diet of allergy sufferers. The content of vitamins E, K, H, group B makes white carrots irreplaceable in human nutrition. Potassium, zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium salts regulate metabolic processes,
Low calorie content, the presence of dietary fiber make white carrots indispensable in any diet. White carrots regulate the digestive tract. In a boiled form, it has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the liver and kidneys. With moderate consumption of food, there are practically no contraindications to the use of carrots with white roots. White carrots, sown even for the sake of curiosity, can be a pleasant addition to the assortment of this crop for the gardener.
Cooking methods
By resorting to additional literature or using the advice of friends, you can easily find cooking methods and the best carrot recipes that can perfectly diversify your lunch menu.

- The juice. When juicing, all the nutrients are completely retained. Before squeezing, you should select undamaged fruits, rinse them thoroughly and clean them. It is not recommended to add sugar and salt to the juice. And the daily use of freshly squeezed juice half an hour before lunch helps to normalize digestion.
- Grilled vegetables. The method of cooking carrots in combination with other grilled vegetables allows you to preserve all the nutritional and healing properties, while the taste becomes more pronounced.
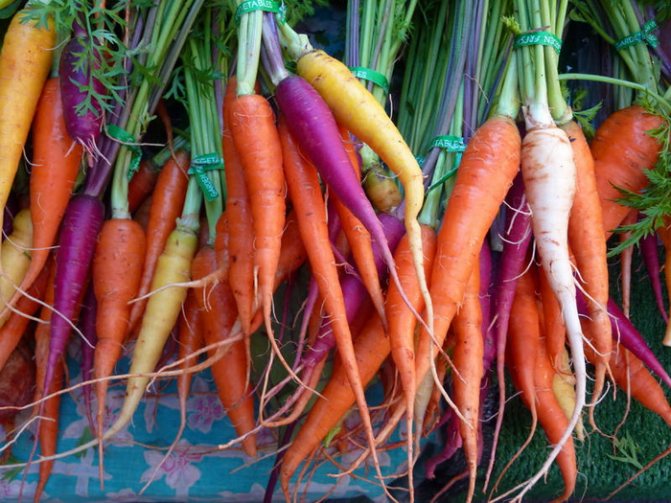
- Puree. Making carrot puree soups with some equally healthy vegetables is ideal even for very young children. And by resorting to imagination and adding purple to the usual orange carrots, you can get an original dish of amazing color that you will like not only in taste, but also in appearance.
- Bouillon. Cooking broth with the addition of different varieties of carrots, be it white, orange or purple, will turn out to be incredibly attractive and low in calories. Despite the fact that at high temperatures the percentage of vitamins decreases, the part necessary for the body in the cooked dish remains, which makes the culinary masterpiece not only beautiful, but also useful.
- Drying. Carrots are great for drying for future use. Before harvesting, carrots must be thoroughly washed and peeled, then either chopped or grated.An electric dryer helps to speed up the drying process, thanks to which the cooking time will be reduced several times, while all the vitamins contained in the carrots will be preserved as much as possible.
- Dessert. The purple carrot is so sweet that it can be used in a variety of desserts. For many years Europeans have preferred to make jam from carrots, which has an amazing taste.
- Table decoration. Even having mastered the carving technique a little, you can arrange a dining table and make it incredibly beautiful and unique. Using a thin knife, a vegetable dish can be turned into an exquisite culinary masterpiece, the appearance of which on the table will attract the attention of not only children, but also adults. A unique combination of white, orange and purple carrots, as well as the creation of compositions from them, will surprise every guest present, and cooked carrot recipes will not leave anyone indifferent.
Don't be afraid to experiment. Then an ordinary lunch will turn into a real meal.
What does it look like
The plant has feathery leaves, strongly dissected, petiolate, reminiscent of some varieties of parsley.
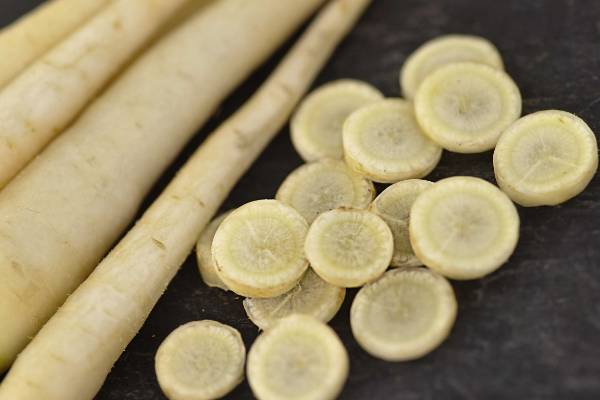
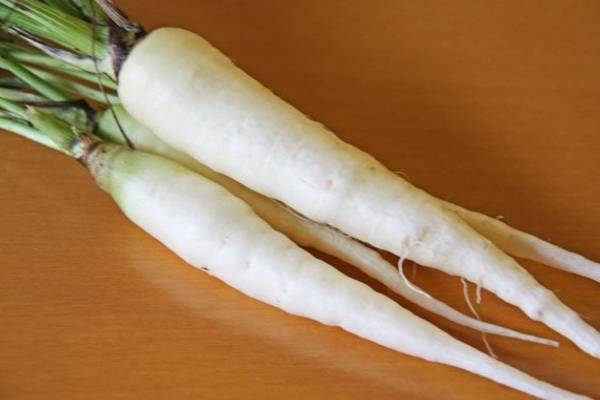
Root crops of good varieties have an even bright white or ivory color, without admixture of green shades, even and juicy, rarely "branch".
White carrot varieties lack the beta-carotene pigment, which colors the orange varieties. The species differ little in composition, however, white contains more vitamin E.


Varieties
Lunar White (Lunar white). Germination time - 1-2 weeks, ripening time - 60 days. Temperature range + 16-20 degrees. Root crops are tender, elongated, with a thin skin, about 20-30 cm long, have a sweetish taste without bitterness, vaguely resemble the taste of mango. The variety is bred for cooking. It can be stored for up to a year in bags with sawdust. The variety is whimsical: it needs chernozem and peat soils, planting seeds at regular intervals, and regular watering.


White Satin (White satin). Germination time - 1-2 weeks, ripening time - 70-100 days. Root vegetables have a creamy hue, the shape of a regular cylinder with a sharp tip, a length of about 20-30 cm, a weight of about 100 g, crispy, sweet. Quite unpretentious, requires moderate watering, medium-dry soil.
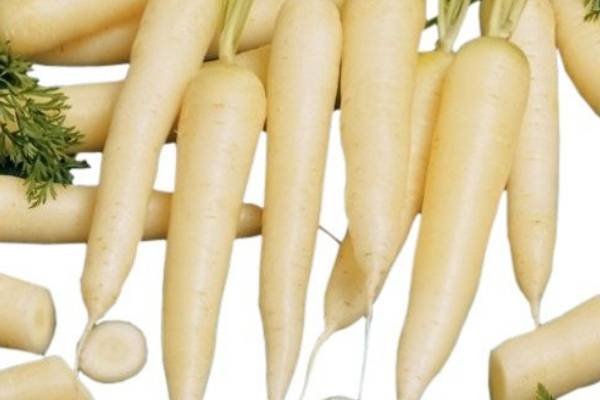


White Belgian (White Belgian or Blanche A Collet Vert). Germination time - 1-2 weeks, ripening time - 90-100 days. The pulp with a yellow tint, fruits up to 25 cm, large, have a green “cap” up to 1 cm. The variety was bred as a fodder, it got on the table by the end of the 19th century, as it has a dull taste and a mediocre aroma, requires heat treatment. Quite unpretentious, does not require fertilizers, grows in open ground. But, not resistant to frost even at -2 degrees, the minimum temperature is +10.


The chemical composition of root crops
The main difference between white and orange carrots is the almost complete absence of anthocyanin and beta-carotene, which is converted in the body into vitamin A (180 μg / 100 g of product).
The rest of the vitamins in 100 g of the root vegetable contains: B1 - 0.1 mg, B2 - 0.02 mg, B5 - 0.3 mg, B6 - 0.1 mg, B9 - 9 μg, E - 0.6 mg, H - 0.06 μg, PP - 1.2 mg, K - 13.2 μg.
Minerals are useful: phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chlorine, calcium, magnesium, sulfur - and trace elements: iron, zinc, copper, iodine, fluorine, chromium, manganese, selenium, boron, vanadium, nickel, aluminum, molybdenum, and even lithium and cobalt. Amino acids and bioflavonoids remove harmful substances, pectin promotes digestion.
Composition and calorie content
Like other varieties, yellow carrots have a rich chemical composition:
- magnesium, potassium and calcium;
- iron and zinc;
- fluorine, iodine, as well as sodium and phosphorus;
- vitamins of group B, A, C, E, H and PP, K.
Important! If you eat a lot of red, orange, or yellow carrots in a short amount of time, your face and hands can take on a noticeable yellow tint.
The nutritional value of the vegetable is as follows:
- 1.3 g protein;
- 0.1 g fat;
- 7.2 g of carbohydrates;
- the calorie content of the product is 33 kcal.
Research by scientists has shown that the quality and duration of human life is directly related to the proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.If the digestive tract works slowly and intermittently, then toxins are formed and retained in the body, which is a slow-acting poison for humans.
The solution to this problem lies in the regular supply of fruit and vegetable waters to the body. And in this, too, will help a person eat carrots, it contains a large amount of fruit water.
Important! Umbellifera seeds are rich in essential oils and daucarin. Biologists are convinced that the bulk of nutrients and most valuable vitamins are found in the skin of root vegetables, and they should be consumed together with the skin (rinsing well with a brush and water).
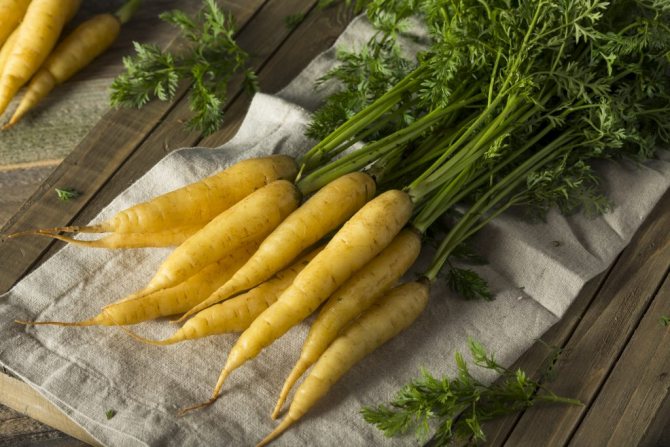


Yellow carrots are rich in the following minerals and vitamins:
- magnesium and potassium;
- fluorine and calcium;
- phosphorus and zinc;
- iron, iodine and sodium;
- B vitamins;
- vitamins A, C, E, H and PP, K.
This yellow root vegetable is very useful because, in addition to a large group of minerals and vitamins, it contains 70% carotene, 7% sugars, xanthophyll and lutein.
Carrots are a fairly satisfying product, their calorie content is 330 kcal per 1 kg. After eating carrots, the body undergoes a reaction that converts carotene into retinol. It should be borne in mind that such a beneficial reaction occurs only when at least a minimum dose of fat is present in the body simultaneously with carotene. Therefore, such dishes as stewed carrots with sour cream, butter or vegetable oil are so useful for humans.
Did you know? It turns out that the well-known myth about the benefits of carrots for vision is military disinformation. During World War II, the British Air Force began to use radars in combat operations, and in order to hide this information, counterintelligence launched a story to the masses that British pilots eat a lot of carrots and therefore hit the target so well. Disinformation is widespread in society and has lasted in the minds of mankind for over 70 years.
The color spectrum of the root crop depends on its chemical composition. Yellow carrots, together with the reddish-orange representatives of the varieties, are characterized by a predominance of carotene in the composition. Violet and light pink species are susceptible to the accumulation of substances such as anthocyanins. White carrots have small amounts of these ingredients, but are famous for their high amounts of glucose and dietary fiber.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: Grape Elegant: description of the variety
Yellow carrots, together with representatives of white varieties, first grew in Central and Central Asia, while orange and red types of root crops consider the Mediterranean countries their homeland.
The yellow vegetable has both a pale shade and a rich canary. Yellow carrots are used in the world more often than orange, traditional in Russia. It grows small: up to 4 cm in diameter and up to 25 cm in length.
Features that give carrots a yellow color:
- The presence of xanthophyll. This substance is similar in structure and characteristics to carotene. Its high amount gives the roots a yellow tint and a sweet taste. This substance is capable of limiting and stopping the growth of pathogenic cancer cells, for which it is revered by scientists around the world.
- The concentration of lutein in carrots also turns the vegetable bright and sunny. Lutein acts on the human body as a prophylactic agent against cardiovascular diseases. It also has a positive effect on the retina of the eye, protecting against the harmful effects of bright sunlight.
The yellow varieties of carrots contain many vitamins, micro- and macroelements, among which there are vitamins of groups A, B, E, K, PP, H, C, as well as potassium, phosphorus, iodine, iron, zinc, fluorine and magnesium.
Vegetable water inside the root crop is of great value. Its amount depends on the region: the hotter the climate, the drier the vegetable tastes.The sugar content in the composition of yellow carrots is average - up to 7% of the total mass, but it contains a lot of fiber and carotene compounds - up to 70%.
The benefits and harms of root crops
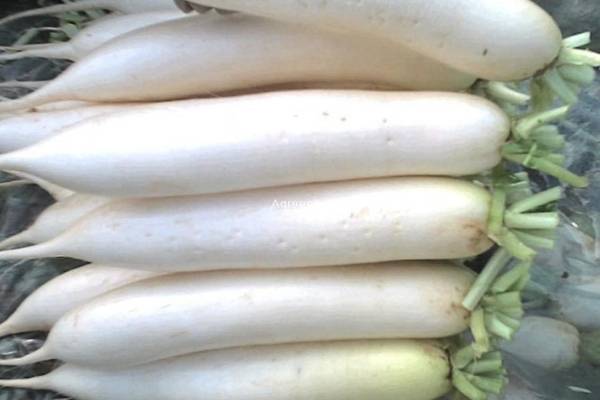
Let's talk about the benefits of white root vegetables:
- prevention of oncological diseases;
- improvement of the digestive tract due to fiber, reduction of pathogenic microflora after antibiotics;
- cleansing the blood and improving circulation, reducing the risk of stroke due to trace elements;
- strengthening general and local immunity due to vitamins;
- prevention of atherosclerosis and reduction of cholesterol accumulation;
- prevention of pathologies of the nervous system, including age-related;
- improved digestion, bile and diuretic effect;
- improvement of the liver, kidneys, prevention of nephritis (boiled);
- expectorant (in the form of a decoction);
- normalization of blood sugar levels;
- reduction of inflammation and acceleration of wound healing, increased blood clotting, help with bleeding due to vitamin K and potassium;
- reducing eye strain;
- prevention of tonsillitis and stomatitis;
- slowing down the aging of the skin;
- helping muscles after exertion (in the form of juice);
- pain reliever (in the form of a decoction);
- improved sleep and increased mood;
- useful broth cleanses the blood and improves overall immunity.


Cons of using:
- lack of carotene;
- individual intolerance;
- hypervitaminosis B, C, E;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- when consumed in very large quantities: exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases, headache and weakness, rash (due to essential oils), frequent urination (acceleration of metabolism).
How to grow
Preparing for landing
Inventory: during normal sowing of seeds, the shovel and the hoe must be clean, without fertilizer residues; when landing on the tape, the tape itself is prepared.
Soil: carrots grow well in neutral or slightly acidic soils, in black soil and light loam, before winter, carrots should be planted on peat or sandy soils; it is good if, a year before the carrots, cabbage, zucchini, tomatoes or cucumbers grew in the chosen place; in the fall, you can add potash and phosphate fertilizers (pour 25 g of ammonium nitrate, 50 g of superphosphate, 25 g of potassium salt into a bucket of water); before sowing and creating grooves, dig the bed to the depth of the shovel.
Seeds: soaked for a day in water or a light solution of fertilizers; for even distribution, they are glued onto a tape or mixed with sand (a teaspoon of seeds per glass of sand). Germination time - after 18 - 20 days.


Landing
Planting dates: from October - winter crops for consumption in summer, from April - spring crops for food in autumn and short storage, May-June - summer crops for long storage in winter.
Planting scheme: distance between rows 30 cm, between plants after thinning - 5-15 cm; sowing depth of seeds - up to 5 cm for the summer, 5 cm for the winter.
Care
Suitable microclimate: soil temperature 8-10 degrees; after sowing, cover the soil with a damp cloth to retain moisture and allow air to flow.
Watering: should not be too abundant throughout the growth; infrequent before germination, the first shoots can be watered more abundantly, during growth - 2 times a month to a depth of 30 cm, and at later stages, watering can be reduced; carrots are quite drought-resistant.
Top dressing: three times during the growth period; the first after the first shoots, the rest at monthly intervals; only mineral fertilizers are needed (for a bucket of water 20 g of potassium nitrate, 15 g of superphosphate, 15 g of urea, 1 tablespoon of nitrophoska, 2 glasses of ash); top dressing after watering.
Loosening: it is carried out after the emergence of sprouts, before thinning - only between rows, after - between plants; it is necessary to sprout sprouts to avoid the appearance of a green "cap".
Weeding: the main feature is two-fold thinning of carrots during growth.
Mulching: raw or dry weed without testicles, needles, compost (up to 8 cm layer), nettle, rotted manure, small leaves; film and covering material, cardboard and burlap are used. Mulching is done when the sprouts are more than 15 cm. Do not use newspapers, straw and peat.


Harvesting and storage of crops:
- time depends on the variety; early varieties are harvested in July, mid-season ones - in August, late ones - in mid-September; you need to choose a warm and dry day;
- you can take out the carrots by the tops, help with a pitchfork; after sorting, the carrots suitable for storage are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and dried for 2 weeks under a canopy at a temperature not higher than 15 degrees;
- then they are stored in a dry basement at temperatures from 0 to +4 in wooden boxes with sand, fine sawdust or onion husks: layers of sand and fruits alternate.
Priming
The absence of weeds in the early growing season is of fundamental importance. Therefore, the predecessors can only be early ripening (zucchini, cucumbers, early tomatoes, etc.), so that after harvesting them, you can prepare the soil. The crop rotation period for carrots in one plot is 4 years.
It is important to prepare the soil in the fall by adding phosphate and potassium fertilizers: add 25 g of ammonium nitrate, 25 g of potassium salt, 50 g of superphosphate to a bucket of water. Fertilizers must be applied to the previous crop, because application under carrots can provoke branching of the growing fruit.
Acceptable soil: black soil, light loam, sandy loam, sandy, peaty. Planting on heavy clay soils is not recommended, which has an extremely adverse effect on both the yield and the appearance of root crops.
List of mistakes when growing
- Trust seed producers with positive reviews and check the expiration date - 1-2 years.
- Carrots don't like acidic soils and acidifying fertilizers like fresh manure and sawdust.
- Do not tamp the mulching layer. Mold on the mulch should be avoided.
- Improper watering: insufficient with crusting or too much watering.
- The depth of sowing seeds is too large - no deeper than 5 cm is needed.
- Without hilling, a green “cap” and greenish hairs appear on white carrots - this indicates a deterioration in the quality of the product.
Diseases and pests, prevention
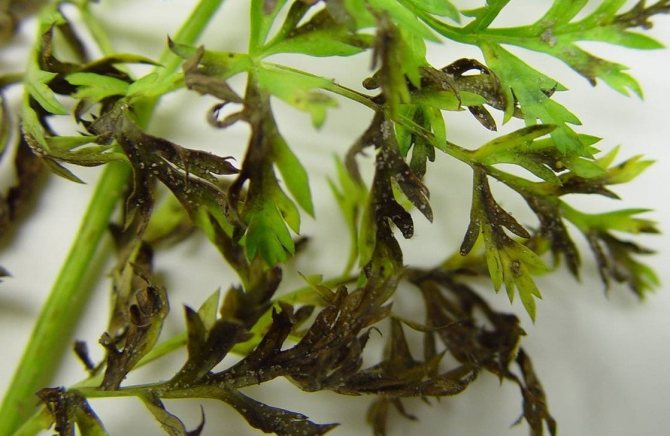
Diseases of white vegetables are similar to diseases of orange ones: spraying with the composition "Rovral" will help against black rot, spraying with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture for cercosporosis, fungicides will help against powdery mildew, felt rot should be sprayed with a solution of copper chloride, with brown spot - loosen the aisles bacteriosis is helped by spraying with a fungicide after the third week of germination; against gray rot, you need to feed it with nitrogen fertilizers.
Against carrot flies, flies, carrot moths, both chemical preparations (EDG, Decis Profi, etc.) and folk methods can help: spraying with soapy water, ash infusion, decoction of tomato tops. A solution of vinegar (1 glass in a bucket of water), poured into the holes, will help from the bear.
Clumsy
A chagrin for any gardener will be the growth of twisted carrots instead of even smooth root crops. Of course, there is nothing serious about this unevenness, but the taste of carrots may deteriorate, and the appearance of such squiggles will not please.
Those who want to grow carrots will be interested in information about such carrot varieties: Abaco, Chantanne, Nantes - 4, Samson, Canada F1. We also prepared information on carrot diseases and planting in open ground.
Reasons why root vegetables grow ugly
The reasons will be similar to the case of horned carrots, but options with improper weeding and insufficient moisture can be ruled out. Most often, these root vegetables grow if you planted carrots on heavy rocky soil, when feeding, they used organic matter or a bear or a carrot fly sneaked into the garden with an orange vegetable.
Attention! If pests are the cause of the clumsy carrots, then you need to pay attention to this, because they can lead to other problems. In order to prevent the bear and carrot fly from appearing on the carrot bed, try not to overfill the plantings, not thicken them and carry out weeding on time.
If the attack did appear, it can be fought with the help of such means as Aktellik and Fitoverm. You can sprinkle the aisles with wood ash or eggshells, it also repels pests well.


How to use
- raw - in salads;
- fresh juice;
- after heat treatment - cooking, frying, stewing (in this case, useful properties are partially lost);
- in the form of a decoction of root crops and tops - for medicinal purposes.


On our plots, the usual orange carrots are found, and colored carrots are very rare. But every gardener would be curious to sow and grow unusual varieties that will pleasantly surprise you with their appearance, benefits, and taste.
Yellow carrots: recipes


Yellow carrots are used in baking desserts. In dishes using meat and fish, vegetable stews. And also it is added to soups, borscht, and yellow carrots are also suitable for pilaf.
When cooking, the vegetable can be grated on a variety of graters, squeezed out the juice. And also cut carrots into rings. You can cook stews and all kinds of side dishes with the addition of vegetables, sauces of your own production.
Carrots fried in sunflower oil are added to dishes, which gives them a unique aroma and taste. The dish takes on a pleasant yellow tint.
Interesting fact. With all sorts of manipulations during cooking, the vegetable does not lose its beneficial properties and minerals. The dishes are delicious. And also have great benefits for the body. You can make an unusual filling. Fry the carrots in an oil pan for about half an hour. Add sugar as desired.
A whole young carrot or pieces of it are used during the preparation of preserves. You can prepare canned vegetable mixes, canned tomatoes or other pickles.
Common varieties of white carrots
There are now several varieties of white carrots. Their yield ranges from 100 to 500 kg per one hundred square meters. With intensive watering and fertilization, you can get 750-800 kg.
White Belgian
Root crops of this variety are spindle-shaped. Europeans know it as Blanche A Collet Vert, and we call it White Belgian carrot. It has white flesh with a creamy yellow tint, and the top has a greenish tone. The size of the root crop reaches up to 25 cm.
This vegetable is good to use in cooking, because when heat-treated, carrots give a pleasant smell. The ripening period is 75 days. The fleshy fruit is unpretentious to feeding. The disadvantages include weak frost resistance (withstands up to + 10 ° C), as well as the fact that the taste is revealed during heat treatment. The taste is weak when raw.
Lunar White
This variety reaches a length of up to 30 cm. The elongated root crop has a pure white color and a thin skin. Juicy and sweet root vegetables can be harvested 60–75 days after planting. Given the early maturity, carrots can be grown in the northern regions with short summers. It is ideal for human consumption. It is pleasant to eat it not only processed, but also raw.
The only drawback is the exactingness of the care. It is necessary to follow all the rules for growing this plant crop.
White Satin F1
This variety of white carrots has excellent taste. It is juicy and sweet. Root crops grow large in size, have a flat surface with a cream color. The shape of the vegetable is cylindrical with a pointed end. In length, the root crop reaches 20-30 cm.The vegetable ripens within 60 days with moderate moisture.
Breeding work
The first experiment on a root crop was carried out by Dutch scientists in the 18th century. The aim of the breeding was to get the carrots to produce larger and juicy fruits. During the events, the vegetable lost some of its essential oils, but acquired a lot of other useful properties.
Up to this point, history has known a red, yellow, purple, white variety, but not orange. According to one of the versions, the vegetable owes its roots to Orange Prince William, allegedly as an expression of gratitude for Holland's gaining independence during the war with Spain.


The first experiment on a root crop was carried out by Dutch scientists in the 18th century.
According to another hypothesis, the orange color of the root crop was obtained by crossing the red variety with the yellow one. It happened in the 18th century, when the vegetable was brought to the Netherlands from Iran. It is the orange blossom that is considered the symbol of the Dutch state.
Peter I brought carrots in the form in which we know them to Russia together with other vegetables. For a long time, the root crop was used only as a remedy for the treatment of diseases. Only 2 centuries later, carrots began to be widely used for food.
From the 70s of the twentieth century to the present day, breeders continue to work on the quality of carrots, improving its usefulness. The percentage of carotene in it has almost doubled: by the twentieth century, carrots have become the champion in its content.
The benefits and harms of root crops
It is useful to include white carrots in the menu for gastrointestinal diseases. The juice of this root vegetable normalizes the digestion process and improves appetite. A decoction of white carrots is a pain reliever and also removes excess fluid from the body. The tops of white carrots contain a lot of vitamin C, as well as chlorophyll, which purifies the blood. The infusion of foliage relieves swelling, as it has a diuretic effect. Due to the absence of pigments, this product is suitable for allergy sufferers. Useful elements (salts of potassium, zinc, magnesium, phosphorus, selenium) in the vegetable normalize the metabolism in the body, and the low calorie content allows it to be included in the menu of any diet.
- Consider the beneficial properties of white carrots:
- has a diuretic and choleretic effect;
- has a positive effect on kidney function, is the prevention of nephritis (boiled);
- good natural antioxidant;
- relieves inflammation;
- inhibits the reproduction of harmful bacteria, improves the intestinal microflora;
- a decoction of carrots has an expectorant effect;
- normalizes blood glucose levels, which is very useful in diabetes mellitus.
Carrots have no particular contraindications, but consuming a large amount of the product can be harmful. Excessive consumption of the vegetable raw may cause diarrhea or frequent urination. Such phenomena are extremely rare, since few people eat mainly carrots in large quantities, excluding other foods.
- There are very few contraindications:
- individual intolerance;
- exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases;
- exacerbation of thyroid diseases.
What is useful for the human body
A plant in which there are so many vitamins and nutrients cannot but be useful.
Beneficial features
The properties of colorless carrots are impressive in their scope:
- the vegetable prevents the development of malignant tumors;
- helps to improve the functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- removes cholesterol and toxins from the body;
- strengthens the immune system;
- helps to normalize glucose levels;
- improves vision;
- accelerates metabolic processes in the body;
- enhances blood clotting;
- reduces the risk of strokes, heart attacks and atherosclerosis;
- has a choleretic and diuretic effect;
- heals small wounds and cuts;
- prevents diseases of the nervous system;
- prevents kidney disease, nephritis;
- eliminates the effects of long-term antibiotic treatment;
- it is used as a remedy for eliminating helminths.
Features of growing white carrots
For white carrots, you need to choose the right place and prepare it, observe the crop rotation and plant according to the recommended scheme.
Site selection and soil preparation
The area for planting white carrots should be in a well-lit place. Shading will reduce yields and root quality. This plant culture prefers loose, fertile, air-permeable soils. This is black earth, medium loamy and sandy loam soil with a neutral reaction.
The site for planting should be prepared in the autumn. To do this, during digging, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied. For 1 bucket of water with a volume of 10 liters, take 25 g of ammonium nitrate and potassium salt, 50 g of superphosphate.
If the soil has a high acid level, then in the fall it must be calcified. For this, lime or chalk is added to the soil.
Crop rotation in the garden
When planting white carrots, it is imperative to follow the rules of crop rotation. You should not plant this root crop in an area where the following crops previously grew:
- parsley;
- dill;
- parsnip;
- celery.
In the place where the carrot itself used to grow, it is allowed to plant it again only after 3-4 years
Good predecessors are:
- tomatoes;
- cucumbers;
- zucchini;
- onion;
- garlic;
- potato;
- cabbage.
Planting scheme and depth
Sowing seeds is carried out in the spring when the soil warms up not less than + 8 ° С. This usually falls between late March and early April. For longer storage, carrots are sown from the second half of April. Sowing before winter is recommended only on peat or light sandy soil.
Planting is carried out at a depth of about 2 cm. The distance between the grooves is at least 30–40 cm, and in the row between the seeds 2 cm. After planting, the soil must be compacted. The first shoots should appear 10–12 days after sowing when the air warms up to + 15… + 18 ° С.
Planting and leaving
Spring planting should be started no earlier than the soil warms up to 8-10 * C. This will reduce the formation of flower shoots and increase the quality of the crop. Podwinter sowing is permissible only on peaty or light sandy soils.
Ridge landing is considered optimal fit to give long roots space to grow. The distance between the rows should be 30-40cm, between the plants - 5-15cm. The height of the comb is up to 20cm.
In order to avoid the green "shoulder", which is considered a virtue only in the White Belgian variety, the plants should be hilled regularly. The top of the root crop should not look out of the ground.


Carrot care
White carrots should be properly cared for to achieve high yields of good quality.
Watering and fertilizing
If you want to get juicy and sweet fruits of good size, you should take care of proper watering.
First, after sowing the seeds, the first two weeks are watered every day to improve germination. Then watering is enough to carry out 1 time in 7-10 days. Humidification is largely dependent on the weather. In the period of heavy rains, watering is stopped, but in extreme heat it is carried out more often - 2 times a week. Watering is stopped 14 days before harvesting.
During the entire growing season, it is necessary to carry out two dressings:
- the first feeding is carried out 21-28 days after the appearance of the first shoots;
- the second feeding is carried out after 60 days.
The following mixtures are used as fertilizers based on 10 liters of water:
- 1 table. spoon of nitrophoska;
- 0.5 l of wood ash;
- 20 g of potassium nitrate;
- 15 g of urea and double superphosphate.
Loosening
For a good and high-quality harvest carrots should be constantly loosened and weed removed, which pulls moisture and nutrients onto itself, preventing the plant from developing. It is also useful to huddle this crop in order to avoid the formation of green shoots.
It is necessary to ensure that there is no thickening of the planting. For this purpose during loosening, thinning is carried out... The first time they thin out the garden, when real leaves appear on the plants. The distance is maintained between the plants about 3 cm.When 2 pairs of leaves appear, the procedure is repeated, leaving about 6 cm between shoots.
Pest and disease control
Carrots can be susceptible to the appearance of various fungal and infectious diseases.
Consider them:
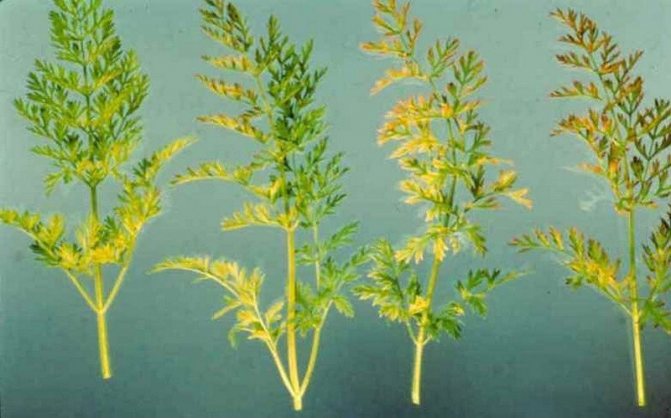
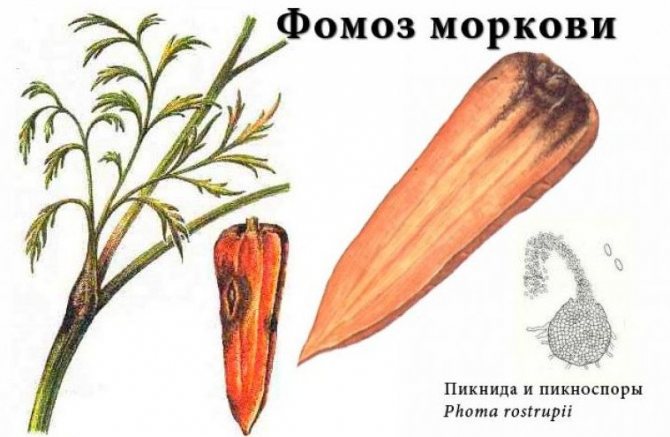
- Fomoz... The disease manifests itself at the end of the growing season in the form of dark spots on the tops and stalks, which gradually appear on the vegetable itself. To eliminate the disease, they are treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid.
- Alternaria... Signs of the disease are dark spots, curling of leaves. Carrots acquire a bitter taste. For the fight, treatments are carried out with the drug "Rovral".
- Cercosporosis... This fungal disease affects the leaves of the root vegetable. Dark areas appear on them, and after the tops begins to rot. Root crops are deformed and become small. To eliminate the disease, they are treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid.
- Brown spot... You can identify the disease in young shoots by the brown formations at the base of the plant. In an adult specimen, yellowed areas appear on the leaves, which then darken to brown. To eliminate the disease, loosening of the soil should be carried out, as well as spraying with a decoction of celandine, horsetail or nettle.
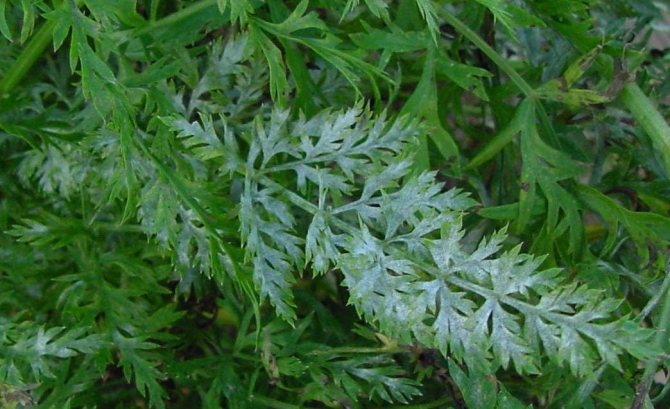
- Powdery mildew... It is detected in the appearance of flour plaque. Fungicidal preparations are used ("Trichodermin", "Glyocladin", "Fitosporin-M").
- Felt rot... A putrid bloom of a dark color appears on the fruits. Then it turns into a brown crust similar in structure to felt. With severe damage, black dots appear. Spraying with a solution of copper chloride is carried out.
- Bacteriosis... This disease is first found on the lower leaves. They become yellow in color. Then they turn brown and the whole plant is affected. The root crop is covered with small dark spots and sores. In this case, it is necessary to spray with the fungicidal preparation "Hom" in 21-28 days after the emergence of sprouts.
To prevent the appearance of diseases, loosening and removal of weeds should be carried out, crop rotation should be observed, disinfection of seed material before planting, as well as preventive treatments with Bordeaux liquid should be carried out.
Of insect pests, white carrots are affected carrot fly and moth, carrot flies... To fight, spraying with chemicals "Intavir", "Karatan", "Profis" is carried out. You can also carry out treatments with folk remedies - infusion of garlic, wood ash, tobacco-soap solution.
Another pest is bear... To combat it, a vinegar solution (250 g of vinegar per 10 liters of water) is poured into the passages dug by the pest, or Medvedox is used.
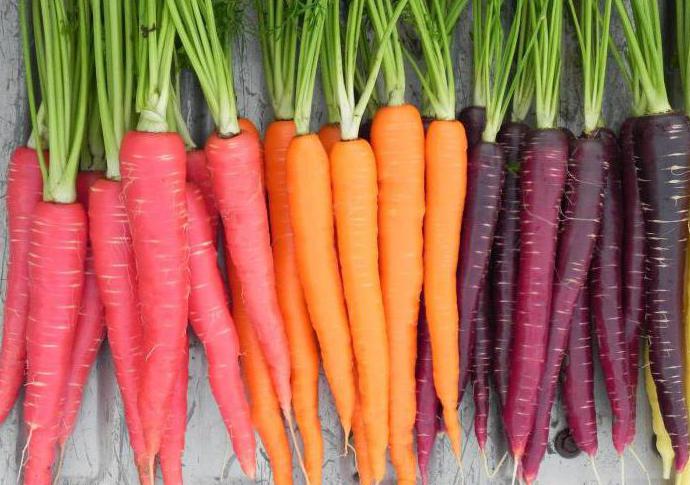
Why did the carrot turn orange? Until the 19th century, carrots were purple!
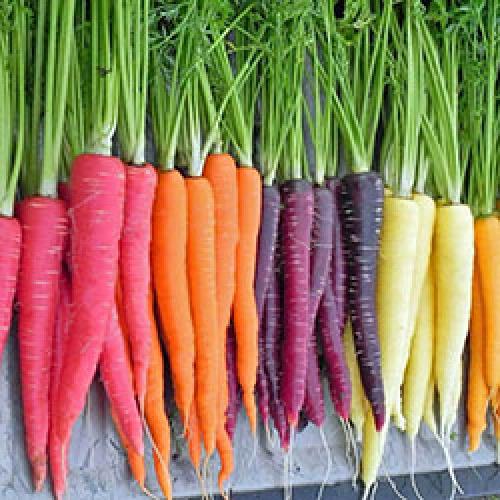




Today, no one is surprised with an elongated orange vegetable. Even toddlers know they are carrots. Today, its cultivation is commonplace, and once, back in the 16th century, Dutch farmers could observe yellow, white and even purple representatives of modern carrots in their fields. They decided to conduct an experiment, the result of which was the emergence of the well-known orange vegetable with a sweetish taste. This is a cultivated carrot. Her wild ancestor was tough, with a bitter taste and not meaty at all. It took several thousand years for the wild form of carrots to take on a modern look. The domestication process was lengthy. The first specimens grown in gardens were used as medicines. Today, you can still find wild representatives, only domestic and wild carrots are already different plants.


Only one nature could not so much modify the wild culture, here man made his own efforts. At the same time, a person without nature would also not be able to achieve the desired result.Growing carrots in his backyard from seeds that he collected in his beds, carrots will eventually lose all their good qualities, returning to the original, genetically inherent and inherited from wild ancestors. Therefore, the modern carrot is a product of modification. You probably often hear such a common abbreviation GMO (genetically modified organism) today. Additional genes are introduced into the product, which in the future will give it new useful properties, for example, the culture becomes resistant to various pathogens or harmful insects.


Afghanistan is considered the birthplace of carrots. Its color in those days was radically different from modern specimens, and was purple, occasionally yellow representatives were found. Mixing the traits of the two parents, leading to the formation of hybrids, in natural conditions is a common process. In the west, where the carrots were exported, producers tried to cross yellow and purple specimens. At the same time, orange representatives turned out, but they did not yet have the necessary sweetness, nor the necessary hardness. Experts tried to improve the new variety, they succeeded. This did not take a lot of effort. Good care and good climatic conditions have been enough for several generations. And here we have juicy, sweet and bright roots.


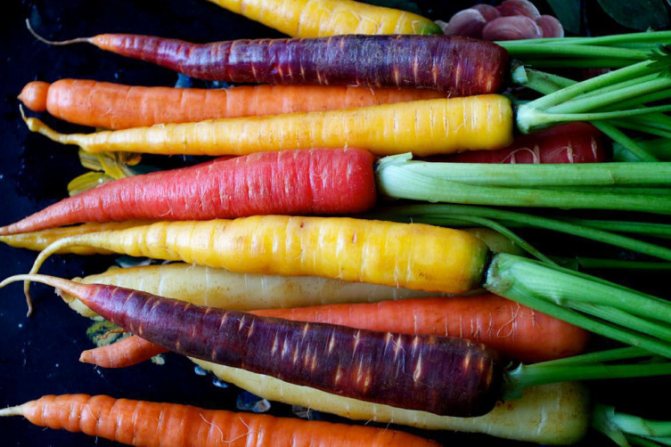
The cultivated culture is divided into two varieties: one that came from the East, the other from the West. In the first, during long-term storage, purple and yellow roots are formed. In the western variety, they can be yellow, orange, or white. These types, most likely, became the parents of the orange carrot we are used to. You probably also love crunching sweet carrots ?! Today carrots of all colors are grown: yellow, orange, purple and red. All representatives are large, juicy root, sweet taste, and the color of the root depends on the content of the corresponding pigments in it. Yellow and orange carrots are rich in carotenes, in white they are completely absent, in red there are a lot of xanthophylls and lycopene, and in purple there are carotenes and anthocyanins. A person, interacting with nature, can preserve and increase the beneficial properties of a plant, thereby increasing the taste of products, increasing their size, helping to acquire excellent immunity in order to become useful and useful products for people. Remember: juicy carrots contain a large amount of vitamin A.
Carrots are a common crop with beneficial properties.

Harvesting and storage
Carrots are harvested before frost. For this purpose, you need to choose a dry and sunny day. The fruits are dug up with a pitchfork, and then cleaned from the soil. It is also necessary to cut off the top to 1 cm, removing the tops. Then the vegetables are placed under the canopy to dry for 4-5 hours. After the carrot dries out, you need to sort it out, rejecting mechanically damaged and rotten specimens. It is also advisable to sort the fruits by size to ensure uniform ventilation. The selected vegetables are then transferred to a permanent storage location.
It is better to store carrots in a cellar at a temperature of 0 ... + 2 ° С with a humidity of 91–95%. The room should be preliminarily calcified to prevent the appearance of fungal infections. Take care of good ventilation as well.
For convenience, storage is best done in boxes filled with sand and slaked lime based on a ratio of 50 to 1. Vegetables are laid in them in layers, sprinkling each layer with a mixture so that the fruits do not touch.
Coniferous sawdust can be used instead of sand. The boxes are sometimes replaced with plastic bags, which are punctured for ventilation. Thus, the carrot can lie until a new harvest is obtained.
Video: White carrots
White carrots have a juicy sweet taste and are grown in the same way as regular carrots. It can be stored until next season and diversified with this root vegetable in your diet.
White carrot (lat.Daucus) - vegetable crop from the Umbrella family.
Description
It is no secret that the color of a carrot is determined mainly by the content of all kinds of natural dyes in it. Carrots owe their usual orange-red color to the carotene contained in it, and their unusual purple color to anthocyanin, which largely contributes to the protection of the human body from oncology. And white carrots are white for the simple reason that they do not contain any coloring pigments at all. But in its composition you can find a huge amount of substances that are most useful to humans!
Ripe root vegetables boast an unprecedented juiciness and a very sweet aftertaste. True, the ancient varieties of white carrots were distinguished by a slightly bitter aftertaste, and therefore they were often used as a forage crop. And now there is a great variety of white carrots called White Satin F1, completely devoid of the slightest bitterness. By the way, this variety was bred in Latvia.
It is impossible not to mention that white carrots are characterized by a tendency to the regular formation of tiny green shoots on the forming roots. In order to avoid their appearance, growing crops must be regularly hilled.
Fresh, high-quality root vegetables should be fairly straight, smooth and firm. In addition, all of them should be painted in bright white tones, and their heads are usually greenish. But soft, oily and overly branched specimens should be avoided. Root crops with broken tops should also be treated carefully: in this case, it will not hurt to look at the stems of the plant - the dark stems are direct evidence that the vegetable is not young for a long time. And all the remaining tops should ideally be airy, not withered and quite juicy.
Peeling a young white carrot is not necessary at all - as a rule, only older vegetables need to be peeled. And in order to refresh slightly limp roots, it is enough to put them in ice water for a short time.
Where grows
Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan are considered to be the homeland of white carrots.
It's time to return a tasty and healthy vegetable parsnip to Russian vegetable gardens
As you know, everyone grows carrots, but its close relative parsnips, which are sometimes called white carrots (they look very much like carrots, but have a yellowish-white root crop), are now found only in some gardeners. Moreover, even in the literature, it is often referred to as purely fodder crops.
At the same time, this root vegetable used to enjoy immense and well-deserved popularity. In particular, parsnips were appreciated even in Ancient Rome, honoring it not only as a vegetable, but also as a healing culture.
In pre-revolutionary Russia, light vegetable dishes were prepared from it, which were included in the most exquisite menus for ceremonial feasts and ceremonial receptions. And in Renaissance Europe, this plant was almost as popular as potatoes today, since it was parsnips (albeit until the time when potatoes gained universal recognition) that Europeans were widely used in salads and soups, fried and stewed with other vegetables. Moreover, the British even learned how to cook various desserts from parsnips (for example, jams) and homemade wine, which, according to connoisseurs, had a magnificent golden color and was distinguished by excellent taste.
Of course, today parsnips are not a competitor to everyone's favorite potatoes, but as one of the additional vegetables that diversify the diet, it will come in handy, as it goes well with other vegetables and is able to ennoble the taste of a wide variety of dishes. So getting a small bed with parsnips does not hurt at all, especially since every gardener is quite capable of growing it.
And taste and benefit
Root crops of parsnips are distinguished by a peculiar aroma and a unique sweetish taste, which is due to their high content of sugars and starch.Therefore, before they were widely used as a seasoning for vegetable and meat soups and dishes with boiled meat, they were used in stewed and fried form, in the preparation of vegetable caviar and sauces (once parsnip sauces were usually served with sturgeon and cauliflower). Dried and ground parsnip root vegetables were used to make coffee, and boiled root vegetables with hops were added to beer.
As for the benefits of this plant, in terms of the total content of easily digestible carbohydrates, parsnip holds the palm among other root vegetables. It stimulates the appetite and aids in digestion, and therefore is useful for stomach ailments. A large amount of vitamin B2, zinc and magnesium contained in root vegetables support the immune system, therefore parsnips are recommended for recuperation in recovering people. It also contains a fairly significant amount of other vitamins (primarily vitamins C, B1 and PP), minerals (sodium, potassium, calcium, iron and phosphorus), various enzymes and essential oils, which in turn causes diuretic and expectorant properties. Therefore, in folk medicine, the infusion and decoction of the roots are taken as a diuretic for dropsy and as an analgesic for renal, hepatic and gastric colic, and they also drink when coughing to soften and enhance the separation of phlegm. Water infusion of parsnips with sugar is used to improve appetite and as a tonic for general weakness of the body.
It should also be noted that parsnip is a valuable feed for animals and birds, since it significantly increases milk yield and the percentage of fat in milk and increases the productivity of keeping other animals.
Preferences
In comparison with many other garden crops, parsnips are very unpretentious, however, in order to obtain high yields of high-quality root crops, some of its features should be taken into account.
1. Among root crops, parsnip is one of the most cold-resistant - the minimum temperature for germination of its seeds is + 5 ... + 6 ° C, and the optimal temperature is + 16 ... + 18 ° C. Seedlings can easily withstand frosts down to -6… -8 ° C.
2. He loves sunlight and fertile soil, so this crop will grow well where cabbage or potatoes were grown last season. However, on soils where manure was introduced this year, parsnips (like other root crops) should not be planted, this plant does not tolerate acidic soils.
3. Parsnips need regular watering (especially during the formation of root crops). With a lack of moisture, the leaves of the plant turn pale, their growth slows down, while some of the plants are arrowed, and the resulting roots are strongly cracked and become dry and fibrous.
4. Parsnips do not tolerate excess moisture in the root zone - in the case of sowing in areas with a close occurrence of groundwater, the plants cannot fully develop and are strongly affected by fungal infections. Therefore, it is necessary to choose areas for parsnips where groundwater is deeper than 0.7-1m.
5. It requires a deep arable layer. If the arable layer is insignificant (less than 30 cm), then the root crops will not be large and even, because they will have to bend and branch out to fit into the existing thin layer of root soil.