Growing roses in the summer outdoors
Note! Roses are easy to care for, but when choosing a variety, you need to take into account that not all of them are frost-resistant, although there are some that tolerate severe winters well.
For seedlings, choose a suitable place and land. The soil is needed loose, fertile. Stagnation of moisture around the bush is unacceptable. This can lead to root rot.
Roses can multiply:
- seeds,
- cuttings,
- dividing the bush (transplanting, offspring, layering).
Plantings are planted mainly in spring and autumn. If there is a need to plant roses in the summer, seedlings are chosen with a closed root system (in a container) or grown by cuttings.
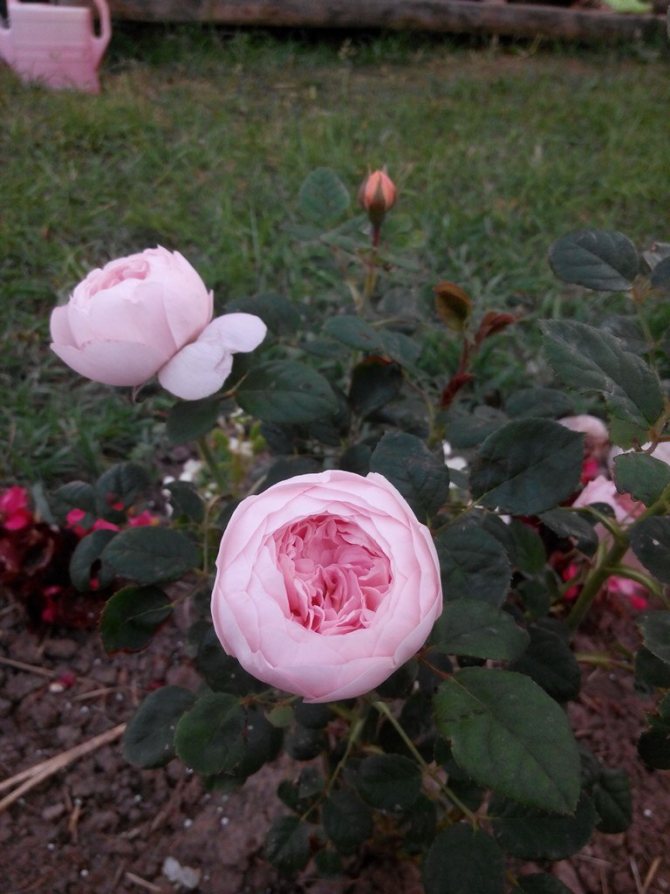

Growing roses in the summer outdoors
Plants will not take root with an open root system in hot summer. The purchased seedlings in the container may take root. When buying, it is advisable to choose a healthy seedling without damage and stains. Preference is given to a bush with several lignified shoots.
Important! When starting to plant a plant, you need to lower the container in liquid for a while, so that, when removing the seedling, you do not damage its roots.
Propagation of roses by seeds


Rosettes can be grown with any seeds: purchased and collected from their own plantings. You need to collect seeds as soon as the fruits of the rose begin to turn red (seeds from such boxes germinate better).
- Cut the fruit and remove the seeds.
- Rinse them with a solution of water (glass) and bleach (2 tsp).
- Wash the bleach off the seeds thoroughly.
- Soak them in a solution of 3% hydrogen peroxide for a day.
- Check the seeds periodically, those that have surfaced, select (they are unusable).
◊ Stratification (increased germination). Liberally dampen a cloth (or cotton pads) with hydrogen peroxide. Place the seeds inside. Put all this carefully in a plastic bag.
Place it in a place with a temperature of + 3-5 ° C. Such cooling helps to activate the seeds. Check them periodically, remove moldy ones.
- You can also make it easier: sow the seeds for the propagation of roses in a container. Place the closed container in the same cool conditions. Ideal soil: a mixture of vermiculite (perlite) and normal fertile soil.
◊ Sowing seeds. Seeds hatch after 1.5-2 months. We will transplant them into the soil. When placed in the holes, sprinkle the seeds with a root rot agent (Captan can be used).
Instead of Kaptan, you can regularly spray the crops with an aqueous solution of hydrogen peroxide, and then mulch with perlite.
- Seed containers should be kept out of sunlight at room temperature and watered regularly. Seedlings will appear after 3-4 weeks, and the first buds in two months.
Sowing seeds for propagating roses is best in April. But keep in mind that the germination rate is very low, so a lot of seed will be required.


Divide the resulting seedlings into strong and weak ones. Transplant the strong ones into separate pots, where they can bloom after a few months.
How to cut roses in summer: ways
Reproduction of phlox cuttings in summer
Cutting creates healthy young bushes, the plant retains varietal qualities.There are several methods of rooting roses by cuttings, they differ in the way the cuttings are immersed in a moist nutrient medium: soil, liquid, potatoes.
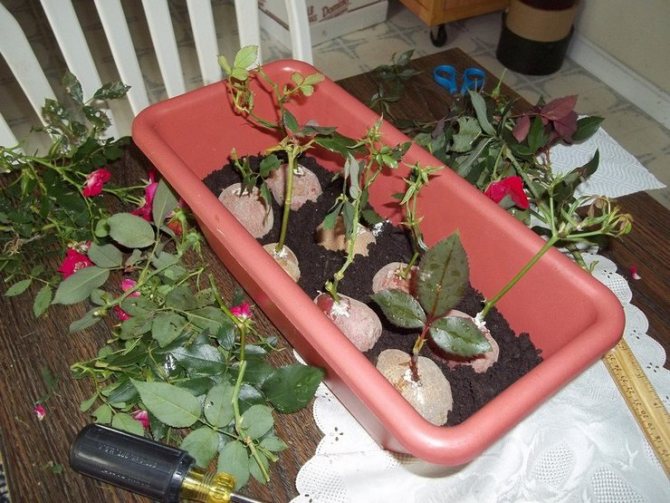
A medium-sized potato for germination of cuttings is selected and all eyes are removed from it so that it does not sprout. After making a depression and inserting a petiole into the tuber, you can plant it in a pot or in a prepared place on the land. Potatoes are poured into a trench, at a distance of 15 cm from each other, leaving a third of the petiole on top. Cover with cans on top. Thus, the seedlings will receive useful substances and a constant moist environment will be maintained around it.
The burrito method is a simple method recently invented by gardeners. Shoots for such germination are harvested longer, by 5-6 buds. The cut cuttings are tightly wrapped in damp paper or newspaper, they are placed in a dark bag and left to germinate in a moderately warm place. The scions are constantly checked to ensure they don't rot and mold. If the need arises, the paper is moistened.
After 2 weeks, the sprouts on which the callus has formed are planted in the soil, under the jar. Garden roses, especially climbing roses, are easy and convenient to grow in this way.


How to cut roses in summer
You can also use a glass of water, but this method is more time consuming, with the smallest yield of seedlings. The liquid is gained 2-3 cm, a growth stimulator is added to it and a sprout is placed. For the germination of roots, the container is placed in a bright place without direct sunlight. When the roots appear, they are planted in a pot.
Additional Information! You can cut cuttings from a bouquet of roses you like and want to extend their life and plant them in the soil. In healthy stems, places are chosen where there are 3 developed buds. Roses are easier to propagate from local varieties. Imported flowers on the market are treated with chemicals so that they last longer. This makes it difficult for the roots to germinate, but if everything is done correctly, using technology, then beautiful roses can be obtained from such cuttings. Growing dark colored roses is much easier than growing yellow and orange shades.
Growing a rose from cuttings under a jar
There is such a simple and affordable method for propagating roses by cuttings in the garden under a jar. Shoots are prepared as usual with two to three internodes, the lower leaves are removed completely, and the upper ones are shortened by half. Choose a location in the garden that is out of direct sunlight. Do not plant in the shade at all, as the rose will live there under the jar until next year, but for development it still needs light.


The simplest hiding place is a can or a five-liter plastic bottle.
A light, breathable soil is needed for successful rooting. If necessary, add sand to the ground and dig everything up well. Stick the cuttings into the ground at an angle, deepening the lower buds. Two or three cuttings of a rose can be placed under one jar. Water well and cover with a 3 liter jar.
Now it remains to water the ground around the bank, if there is no rain. The sprouts appear in about a month, sometimes earlier. They will be visible through transparent glass.
For the winter, the jar must be covered with fallen leaves or cut annuals. The shelter is removed only next year, when stable heat sets in, around the end of May.
As you can see, this method is very simple and inexpensive. All cuttings take little time, and care is reduced only to watering. If you plan to reproduce a large number of roses and you have a lot of cuttings, then it is more advisable to make a greenhouse and rooting a greenhouse.


You can use a greenhouse instead of cans.
Reproduction of roses by cuttings in summer: advantages and disadvantages
Cutting roses in summer is a natural way of rooting roses by cuttings in the garden. This breeding method has its advantages over grafted shrubs:
- plants grown in this way do not form root growth;
- planting material is easy to obtain, which allows you to propagate any variety you like;
- bushes made from cuttings are more durable than grafted ones.
Propagation of hydrangea paniculate cuttings in summer
The disadvantages include the poor tolerance of the first winter, since the plants do not have time to grow a large root system over the summer. We need to provide their shelter.
Important! Successful cuttings depend on the weather. The optimum temperature for seedlings is + 24 ... + 26 ° С.
Cutting roses in July, before and during flowering is a favorable period. Rooted sprouts will have time to develop during a warm period of time. In the southern regions, cuttings of roses into the soil can be carried out until mid-August.
Autumn breeding
In regions where summer is hot and dry, it is better to cut roses in autumn. When you prune your roses for the winter, prepare the cuttings and add them in your garden until spring. In early spring, plant them in a cuticle or permanent location as described above. It's even better if you stick the cuttings into the ground right away. Cover them with cut plastic bottles, and cover them with tops and leaves for the winter. In the spring, they will almost all take root.
A very interesting video about autumn cuttings of roses. One of the simplest, most affordable and effective ways:
Now look at what happened in the spring:
Basic rules for grafting
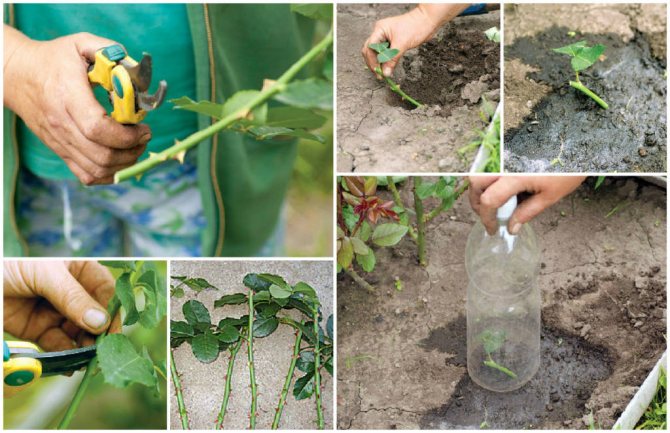
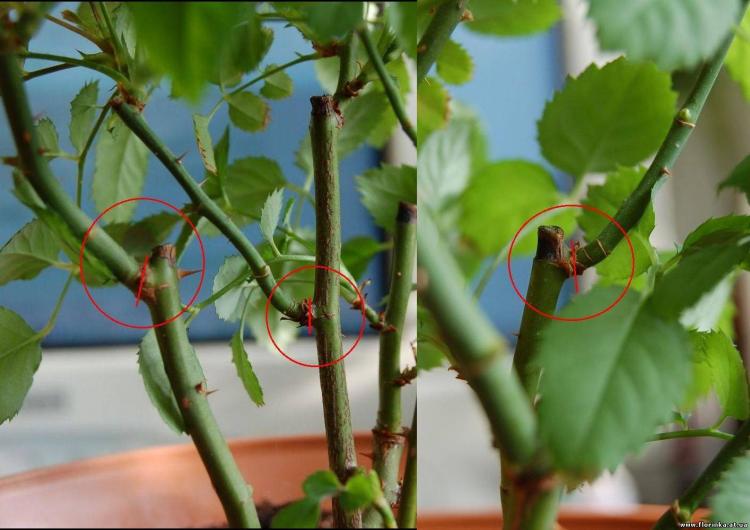
For the purpose of cuttings, shoots are chosen when they have expanding buds. The stems of roses with unblown buds are cut for cuttings, not young, but not old either. You can check by breaking off the thorns on the stems. If they break off easily, then the branches are suitable for cuttings.
How to propagate hydrangea by cuttings in summer
The best time to harvest the stalks is in the morning, when the bushes are filled with moisture. Sharp (so as not to cause injury to tissues) and treated with a disinfecting solution with a knife or pruning shears, cut pieces 12-15 cm long. Cut them from the middle of the stems, with three healthy intact kidneys. The lower cut is made obliquely right under the bud, the upper cut is 2 cm higher. The leaves are removed or cut by a third so that moisture evaporates less. When grafting in the light, the leaves must be left, and when germinating in a bag, the leaves are cut off. The thorns must also be carefully removed.
Important! Cuttings that are cut from fattening green shoots (stems that do not bloom) are not suitable for reproduction.
Having made a high-quality selection and cutting suitable cuttings, it is advisable to place them in a root growth stimulator for a day. Kornevin, Heteroauxin will accelerate the appearance of the root system, which will appear in 14-15 days, with the usual method it will take 30 days.
You can use folk remedies to stimulate root growth: dissolve 20 drops of aloe juice or a teaspoon of honey in 250 g of liquid.
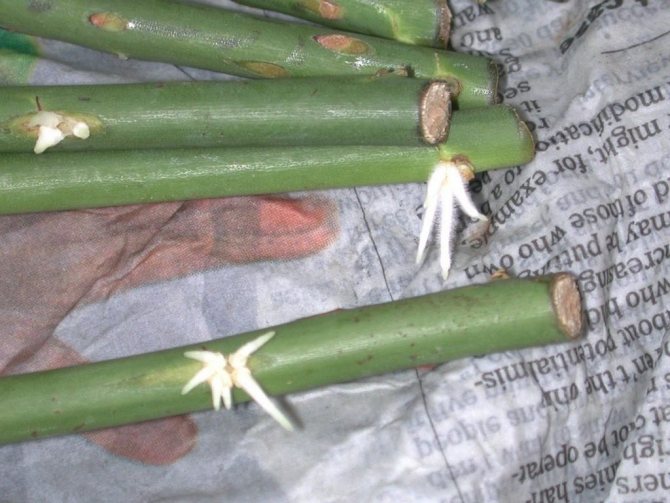


Burrito method
Cutting roses from a bouquet
This video shows how to cut roses from a bouquet in cups:
How the cuttings feel after two weeks:
Propagation of roses by cuttings from a bouquet can be done in two ways.
Method one: in this case, everything is done in almost the same way as described above.
- Cut the middle part of the stem of the rose from the bouquet into cuttings 12-15 cm long with two to three buds. Make the lower cut on the stem at an angle of 45 degrees 1 cm below the bud. The top cut should be straight and no more than half a centimeter above the kidney.
- Remove the bottom sheet, shorten the top to one third. Trim the thorns.
- Burn the upper cut with potassium permanganate or brilliant green.
- Hold the cuttings in aloe juice or growth preparations for 12 hours.
- Then dip the bottom cut into the powder of any of the preparations that promote the formation of roots.
- Plant the cutting in prepared soil. Before planting, sprinkle the soil surface with sand, a layer of 3 cm. Plant to a depth of one and a half to two centimeters.
- Drizzle, cover with plastic bottles with the bottom cut off, neck up. Watering through the neck of the bottle.
- If a bud appears, it must be removed immediately.


Reproduction of roses by cuttings from a bouquet.
Thus, you can try to propagate roses by cuttings from a bouquet. This option is somewhat simpler, but no more than three cuttings out of ten are rooted this way.
From this video you will learn how you can cut roses from a bouquet directly into the ground:
Method two: with this method of reproduction, the percentage of rooting is noticeably higher, but it will take much longer to tinker with it. First you need to wait until green shoots begin to grow from the stem of the donated rose, and only then these young shoots will try to root.
This is how Olga Rubtsova, a gardener from the Leningrad Region, does it.
I propagate by cuttings of roses, which are presented to me in bouquets for the holidays. Only this process is lengthy. If the donated flowers were in the store for a long time, and aspirin or other drugs were added to the water there so that the rose lasted a long time until it was bought, then such cuttings are not suitable for propagation, they die on the fifth day. The lower part of the plant turns black. It is better to throw out such a rose right away - there will be no sense from it.
And do not cut a rose with a slightly wrinkled stem - it will also die in the near future. The desired stalk should be dark green, smooth, buds visible in the leaf axils, and the leaves should be dark green in color. The easiest way is to propagate roses that are presented on March 8th. They did not have time to lie on the counter, and in spring the plants take root better.
I cut a flower from such a rose on a short "leg" and put it in the water separately. The remaining twig, which I will use for reproduction, for prevention from pests, is mine under warm water with laundry soap.
At the bottom, I make an oblique cut with a very sharp knife or razor. I put the handle in a glass. I put on a transparent plastic bag on top. I tie the bag so that there is a small hole for air and greenhouse conditions for the plant are not created. I put the handle under the fluorescent lamp.


Leaves on young sprouts are reddish at first.
It is normal for old leaves to fall off. The main thing is to remove them from the package in time. After a while, sprouts will appear from the dormant buds. The leaves on such sprouts are first reddish, then they turn light yellow, then light green. When the leaves on the shoot turn dark green (like the parent leaf), the shoot is ready for grafting.


Such a young shoot is already ready for grafting.
With a razor, I cut off such a shoot-cutting from the stem and put it in a dark-colored medicine bottle (in a dark container, the roots will appear faster). I tried to cut a stalk with a heel - a piece of the mother plant, but noticed that such shoots take longer to root. I put on a small plastic bag on top and do not tie it, but throw it on. I put the handle under the fluorescent lamp.
You can add a little ready-made solution of HB 101 to the water. As I said, the process of propagation of a rose by cuttings from a bouquet is very long, only after one and a half to two months a light-colored thickening is formed at the end of the shoot. This is a callus formed, on which roots will subsequently appear. When the roots appear (at least 1 cm), I plant the cutting in a pot. I put a plastic bag on top, but do not tie it. After 2-3 weeks I remove the package. Once a week I water the plant with HB 101 or Krezacin.


When the roots appear, the cutting is planted in a pot.
Roses with dark flowers - red, burgundy, dark pink - take root best. Roses with light-colored flowers - white, yellow, light orange - take root worst of all.
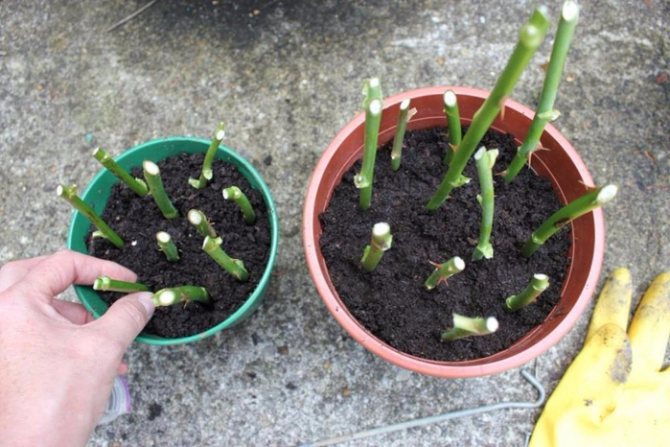
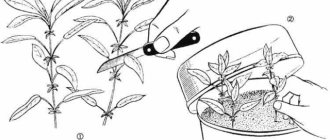
Summer planting of roses in July with cuttings step by step
Before planting cuttings on the site, it is necessary to prepare a place and fertile land with which the allotted territory is filled. The place is chosen darkened so that the sprouts do not get burned under the scorching sunlight. You can place them under trees so that the sun hits them at times.
The bed is covered with 8-10 cm of sod-humus soil, on top - a layer of 3-4 cm from a mixture of equal parts of sand and peat.
Attention! You cannot add manure or compost. Adult roses love this kind of dressing, and cuttings from such additives can rot.
The shoots are planted to a depth of about 2 cm; if they are planted deeper, the rooting process will slow down. Cover with glass jars or plastic bottles, creating a greenhouse effect. A plot of land with seedlings should be constantly slightly moistened. During the summer, plants are watered between the banks, they do not need to be removed and lifted.
The formed young pink bushes remain to winter in the beds, so a shelter from frost should be provided. In addition to cans, you can cover with leaves, grass.
Roses are planted in a permanent place next spring.
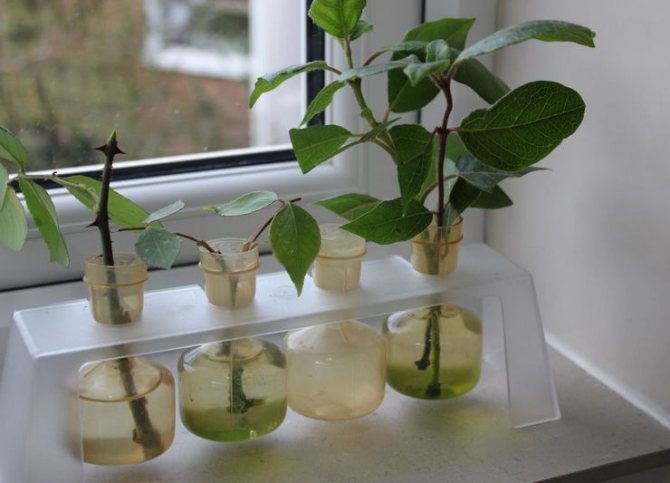
Rooting a home rose in vermiculite
Indoor roses are easily propagated by cuttings. It is very convenient to root the shoots of miniature roses in vermiculite, perlite or coconut fiber. Almost 100% of cuttings take root with minimal maintenance.
Make drainage holes in a plastic cup, fill it with perlite, moisten it well and stick the stalk into it to a depth of no more than 2 cm. Cover the cup with a bag and place it on the window. Moisten the perlite from time to time, but it usually stays wet for a long time. In the photo you see cuttings with regrown roots. They were put on rooting 3-4 weeks ago and now it is time to transplant them into a pot of soil.


Such roots were formed in 3 to 4 weeks.
It is even easier to propagate roses by cuttings. To save yourself the hassle of replanting rooted cuttings, immediately prepare a pot of soil. Make a depression in the soil with your finger and add vermiculite or coconut fiber there. Stick a cutting in there and after a while, the roots that appear will germinate through the vermiculite and penetrate into the soil. The young rose will not need to be transplanted anywhere, it will immediately begin to grow and develop.


Rooted homemade roses.
In addition to vermiculite and coconut fiber, roses can also be cut in water. Rooting in water has one interesting feature: the boiled water poured for the first time cannot be changed, you can only add the same boiled water as it decreases in a jar. Even if it turns green, never pour it out! The jar should be dark glass. Oddly enough, cuttings root perfectly in this way.
Further care for rooted roses
New rose bushes need to be looked after: water on time, regularly apply organic and mineral fertilizers.
Roses are moisture-loving plants, but watering should be moderate. Roses are watered once a week under a bush. It is necessary to ensure that the soil under the plants does not dry out. With a lack of moisture, the leaves will begin to turn yellow.


Further care for rooted roses2
Periodically, you need to feed it with organic and mineral fertilizers, but you cannot exceed the dose, carry out the procedure in the sun and apply top dressing to the unmoistened soil.
When caring for a rose in summer, you need to know how to prepare shrubs for winter. In summer-rooted roses, the root system does not have time to get stronger before winter and therefore they are not frost-resistant. They need to be covered in the first winter.
All activities for the care of the rose garden end in late summer or early autumn, so that the plants can prepare for winter and easily endure the cold. Watering and fertilization ceases, soil loosening. Top dressing provokes the appearance of new shoots, this is a waste of the plant's strength, reducing its frost resistance.In mid-October, dry, old and diseased branches are cut, inflorescences are removed.
Other ways of rooting cuttings
Not all growers are equally good at the traditional rooting method. Fortunately, there are different techniques for propagating roses by cuttings. If your experience has ended in failure before, try using a different technology. Maybe this time it will work out.
In water


Gardeners who need to observe the root formation process to make sure everything is going well, prefer rooting roses in water. Although experts are skeptical about this method. Practice shows that this method is quite troublesome and the percentage of successful rooting is lower than with traditional planting of cuttings in the ground.
This technology is more suitable for miniature and ground cover roses.
- In this case, cuttings cut in advance are not pre-soaked in Kornevin or Heteroauxin. The preparations are added directly to the water for rooting.
- The water level in the container should be 2.5 cm high. The cutting is covered with a transparent bag on top and placed in a well-lit place without direct sunlight.
- The water in the jar is not changed, but little by little it is added instead of the evaporated moisture, maintaining the same level of 2.5 cm. It will take 2-3 weeks for the callus to form.
After that, the adopted cutting can be planted in a pot and grown further without shelter.
In potatoes
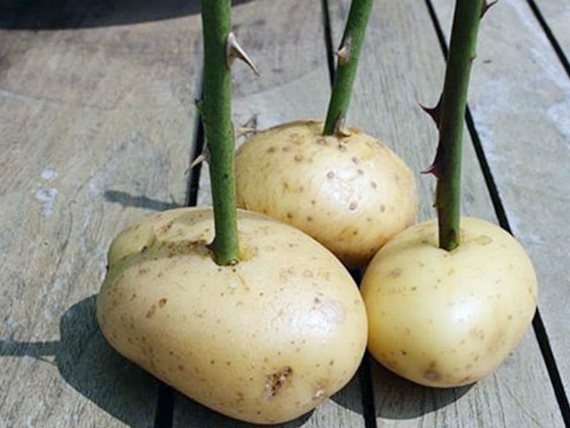


It is not known exactly who and when invented this method of rooting roses, but it has already become popular. This technology is suitable for the most inexperienced and lazy.
- The prepared cuttings are stuck with the lower end into large potato tubers by 2/3 of its height. If the potatoes have eyes, they are removed so that the germination process does not start.
- After that, the tubers are dropped in the open field to a depth of about 5 cm.
- You do not need to cover the cuttings on top. Potatoes will perfectly nourish them with moisture and nutrients. The planting process can be considered complete.
By the end of summer, the potato will completely rot and provide the plant with additional nutrition, and the rose itself will have time to grow full-fledged roots. Young bushes can be left in the winter right at this place and, if necessary, transplanted in the next season.
In the package
To root the roses in the bag, you will need the cuttings themselves, a plastic bag, some sterile earth and sphagnum moss.
- Beforehand, the moss is soaked in a solution of aloe juice (1 teaspoon per glass of water).
- The earth, sphagnum and cuttings are placed in a bag, tied hermetically and hung outside in the shade.
- In conditions of high humidity, after about 4 weeks, the roses will grow young roots.
- After that, they can be planted in a container or directly on the garden bed.
In a pot


It is convenient to root cuttings of roses at home using flower pots. If the containers have already been used, they must be thoroughly washed and dried. At the bottom, you need to pour a layer of drainage (medium-sized expanded clay is suitable), and then fill the pot with soil intended for growing roses. 1 cuttings are planted in each container.
The cuttings are buried in the soil, leaving 1-2 buds on the surface, and covered with polyethylene on top. In order not to remove the film every time, you can make small holes in it for air exchange. Now all that remains is to periodically moisten the soil and wait for the first leaves to appear.
In the future, such bushes painlessly transfer the transplant into open ground by the transshipment method.
In the newspaper


This method is also called "burrito". Prepared cuttings should be wrapped in regular newspaper. The result is a neat paper tube that looks like a Mexican burrito dish, consisting of a rolled flat cake with a filling inside.
The resulting bundle must be carefully moistened in water.It is impossible to keep the newspaper in a container with water for a long time, otherwise it will creep, but the paper must be sufficiently saturated with moisture. Several such convolutions can be made. Then the "burrito" is placed in a common plastic bag and stored at a temperature of 18 ° C.
Periodically, the convolutions need to be expanded and the condition of the cuttings should be checked. If the newspaper tubes are dry, they are re-moistened with a spray bottle. During the audit, spoiled cuttings are thrown away, leaving only those on which there are no traces of mold and decay. It is better to replace the newspaper in which the spoiled cuttings lay with a new one.
It takes an average of 2 to 4 weeks for callus to form. After the influx in the lower part of the cutting has formed, you can plant the rose in open ground, where further rooting will take place.
With this method of reproduction, the root system of plants will form faster and easier.
Read more in the article: How to process roses from aphids with folk remedies
Trannoy method
The propagation of roses by the Trannoy method consists in the special preparation of the shoots. Before you start cutting cuttings, a stem is selected in advance on the bush, which will be used for cuttings. On this shoot, cut off the top with a faded bud and several leaves and wait for the swelling of the lower buds, ready to release young twigs, to begin.
It is at this moment that you need to cut the cuttings, preventing the buds from developing. At this time, the wood accumulates the maximum amount of starch, which means that the cuttings will not be left without nutrition and will quickly grow roots. This method is used in June or July, after the first wave of flowering.
On the handle, cut off all the leaves, except for a pair of upper leaves and planted in a permanent place in open ground. It is desirable that this is an area illuminated by the sun. Several cuttings can be planted in one hole at once. At least one of them will definitely take root. Landing should be done at a 45 degree angle. From above, the cuttings are covered with a cropped five-liter bottle and slightly shaded with branches or cut grass.
How to propagate a climbing rose by cuttings in summer
A hedge of climbing roses can be seen near private houses and summer cottages. Summer residents decorate arches, gazebos, walls of houses with roses. Gardeners cultivate climbing roses by cuttings, layering, budding. Spring and summer is the best time to propagate such a rose. Climbing roses are not cultivated with seeds, because the new plant will no longer bear the parental characteristics. To get a bush that completely repeats all the qualities of the selected variety, the rose is propagated vegetatively - by layering, cuttings and grafting.
Cutting climbing varieties is a common method, and even a layman can propagate a rose by cuttings in the summer. This is done in mid-June. Almost all cuttings cut from young immature shoots take root. Cut segments of stems with 3-4 buds, 15-20 cm long. Make a cut from the bottom at an angle of 45 degrees, from above - 90 degrees. Then they act according to the same scheme as with other types of roses.
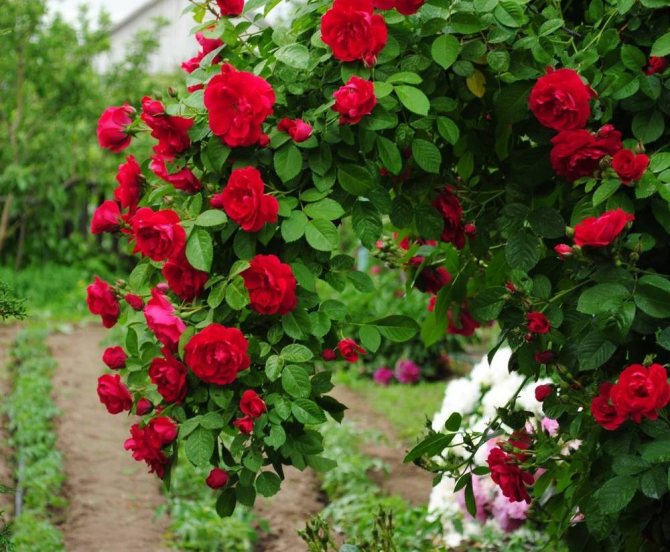


How to propagate a climbing rose by cuttings in summer
Caring for rooted cuttings of a climbing rose consists of watering, weeding and loosening the soil. When preparing plants for winter, they must be removed from the support and laid on the ground, covered with peat or loose earth.
Even if there is no experience in growing roses, it is worth trying any method of cutting flowers at home. This is not at all difficult to learn, no special knowledge is required for this.
Budding roses
Not only a common, but also a very popular way of propagating roses, which is most often used in nurseries. It all starts with a small, T-shaped cut in the bark on the trunk, closer to ground level. Further, a so-called peephole is inserted into the incision - a bud of a cultivar of roses.Thus, the grafted plant almost immediately begins to use the developed root system of the rootstock.
This method is widely used for propagating roses, but it is suitable only for experienced people, since everything needs to be done very accurately and skillfully. In addition, budding has a number of nuances in relation to different varieties of roses.
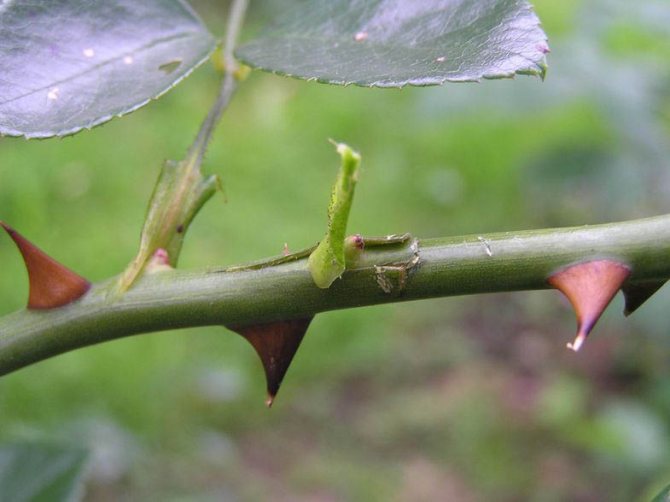


Preparing cuttings for propagation
How to root a rose? On the plant, a strong shoot is selected, which is ready for flowering, or a faded semi-freshened stem. It is not recommended to use thin, weak stems with dead leaves for propagation. If the thorns break off easily on the shoot, it means that it is ready for grafting.
Cut the stems with a sterile, sharp instrument. The propagation stalk should be 12 to 15 cm long and have two or three buds and at least two to three leaves. There should be no buds and flowers on it. After the cuttings are cut, they need to be processed. To do this, you should:
- Remove the lower thorns and leaves.
- Shorten the remaining leaves by two-thirds of the length. This is to prevent moisture from evaporating too quickly during rooting.
- Hold the segments in a solution of Kornevin or Heterooxin, which are diluted according to the instructions.
How to cover rooted roses for the winter
Own-rooted roses are hard to endure the first winter in their life due to the fact that the roots are still poorly developed. If possible, it is better to provide the plants with wintering in a cool basement or a heated greenhouse, and even on a windowsill. Under these conditions, until the end of January, roses are watered very sparsely - rarely and in small doses. In the case when the bushes began to grow actively before the arrival of spring, it is better to pinch the tops of the shoots.
On a note! Only those roses that have taken root no later than July can be left to winter in the ground.
For the first wintering in the open field, it is advisable to make a group shelter by building a strong frame and covering it with plastic wrap, leaving air vents for ventilation. You can combine roses during the winter with other crops. Due to the large volume of air in such a shelter, the plants tolerate frost well. Separately planted cuttings can be covered with a wooden box or a plastic bucket, having previously covered the bushes almost completely with peat or coniferous sawdust.
If the rose has managed to grow long shoots, they are bent to the ground and fixed with slats. The shelter should prevent moisture from getting inside, which can happen during an unexpected thaw, since this can also cause roses to die. In the spring, the shelter is removed gradually. By early May, the plants should be fully open.
Read more in the article: When and how to open roses after winter
Cutting rose bushes in the summer: methods and benefits
Summer cuttings use green cuttings, which appear in abundance on mother rose bushes, so choosing the right ones is not difficult.
Cuttings of roses planted for rooting in the warm season have time to take root until autumn, get stronger and do not give the grower any special difficulties during wintering.
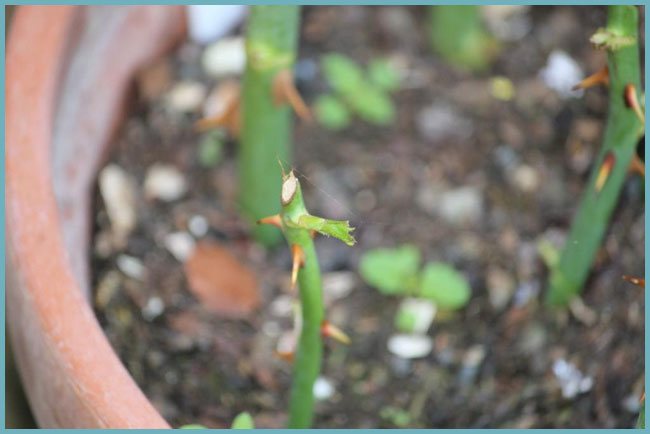


Cuttings of roses
Several methods of summer cuttings of rose bushes are practiced. Usually it is carried out 2 times during the spring-summer period:
- April-May (in the greenhouse);
- June-July (outdoors).
Soil preparation
Preparation for the procedure begins in mid-spring. The exact time depends on the climate zone. It is necessary to wait until severe frosts are no longer predicted, including at night. When the snow melts, you need to clear a landing site. It is necessary to remove small debris, last year's foliage, branches. This should be done carefully so as not to damage the mother bush. The size of the cut area is calculated taking into account the length of the stem that will be used for this purpose.
When the area next to the main plant has been cleared, it is recommended to prepare the soil. First of all, the earth must be loosened.If the area where the roses grow is poor in minerals, a small amount of fertilizer can be added. In addition, peat and some compost are poured onto the site prepared for layering. At a short distance from the main bush, a recess is dug, its length should be equal to the length of the stem, which is being prepared for layering. The width of this depression should be about 10-12 cm. The place for future plants can be left for several days so that the earth warms up under the sun.