In addition to propagation by grafting and seed rearing, which have already been discussed earlier, plum can be propagated:
- cuttings;
- root shoots;
- layering.
Each of these methods has its pros and cons, which will be discussed in more detail.
Plum propagation by root shoots is only suitable for self-rooted plums. In those cases when it is necessary to preserve the varietal characteristics of the grafted tree, it is impossible to do without reproduction by layering or cuttings.
Plum breeding methods
Plum is grown vegetatively: by cuttings, root shoots, grafting.
Grafting is a method when grafts are grafted onto rootstocks to obtain a new variety. Buds and cuttings are taken as scions. Saplings quickly bear fruit.
The seed method is used to grow rootstocks. Sowing is carried out in early spring. Preparation begins in advance. Seeds are stratified up to 6 months. The hatched bones are planted in April. Young rootstocks grow over the season.
Cuttings
Experienced gardeners prefer to grow plums by cuttings. This breeding method is considered reliable. They have a high survival rate of plantings, retain varietal qualities.
Cuttings suitable for propagation are green and lignified. You can root twigs at home and greenhouse structures.
Green cuttings
Propagation by green cuttings was used in industry when large volumes of seedlings were required. Varieties with a developed root system are ready for this method. The principle of cultivation is constant irrigation of the leaves in the greenhouse. By autumn, the top watering is canceled, and they move on to preparing for the winter - hardening.
Root shoots
Propagation by root shoots is a simple method that does not require lengthy preparation, as is the case with cuttings. The correct approach guarantees the harvest of fruits for the next year.
Shoots are young plants that sit around the mother tree. They are united by the root system.
The specimens should be chosen further from the mother trunk. Closely growing shoots feed from the mother, therefore, the underground part of them is poorly developed, and the distant shoots feed autonomously.
The optimum length of the process is up to 50 centimeters.
Before starting work, examine the desired escape for integrity, signs of oppression. The optimal time for breeding is April, August.
Rules for planting and caring for plums in the open field


To get high yields, you must follow the rules for planting and growing plums. Growing a tree is not easy, it takes desire, patience and hard work.
Need to know:
- what timing is suitable for planting;
- how to prepare the ground to please the sink;
- what size should be the pit for planting;
- why it is important not to deepen the root collar;
- how to properly cultivate and care.
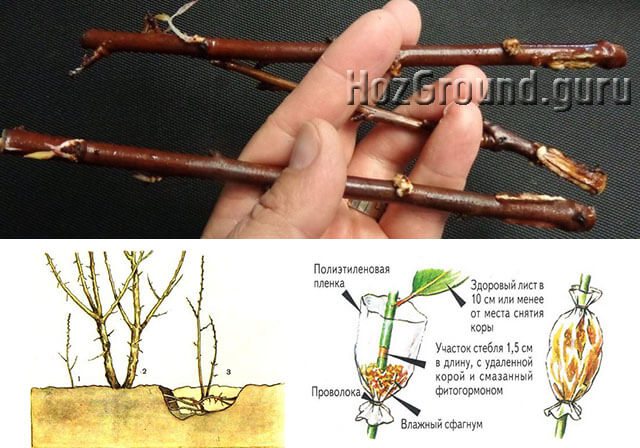
How is rooting of cuttings
Lignified cuttings are planted in the substrate in this way:
- the third kidney is not visible on the surface, but does not deepen far;
- that part of the branch that goes into the ground is processed with a growth stimulator - "Kornevin", "Heteroauxin";
- cuttings are planted at an angle of 45 degrees;
- the landing is covered with a film.
Roots are formed at the cut and along the length of the stem.Over time, they die off from the upper part, remain at the end of the stem, they are called basal. It is from them that the formation of the root system takes place.
There is another unique method of rooting outdoors. A lignified stalk is launched into raw potatoes. The main thing is that 3 buds should be outside and 3 inside the tuber. The vegetable will give off moisture until the roots appear.
Green cuttings are planted in steps - 3, in rows - 5, depth - 3 centimeters. The top leaf is on the surface. The plantings are covered with a film to create a favorable microclimate.
It is important to maintain the temperature in the greenhouse up to 29 ° C. The soil must be moist.
Rooting will take place in the interval of 18-30 days. The film is removed during the day for optimal oxygen access. After about a month, the cuttings are fed with mineral fertilizers. In autumn, the seedlings are prepared for wintering and covered with dry leaves.
Blossom, but do not bear fruit


And sometimes it happens so, plum trees bloom profusely, then ovaries appear, which massively fall off without bearing fruit. For this reason, growers even uproot healthy trees. What to do in this case?
Consider all the reasons for the poor harvest of plums: from the choice of varieties to agricultural technology and climatic conditions.
- Most varieties require pollination, as they are self-infertile. Each variety has its own "companion": they must grow close to each other. The symbiosis of two varieties - "Annushka" and "Skoroplodnaya" - will yield a high yield. When the “pair” is not identified by the breeders, you will have to plant a “clump” of several varieties of fruit trees. You can cooperate with neighboring trees by planting your own plums near the fence. Insect cross-pollination is reduced in cold or rainy weather - you can't wait to harvest.
- A phenomenon known to biologists as a physiological volunteer: the tree does not have enough nutrition for all the fruits that have set. Defects in the root system are considered a common cause. Alas, it is impossible to fix this, but due to the correct formation of the crown, amateur gardeners still increase the yield.
- Bacterial diseases of trees can often be observed in plums - this is the result of careless attitude towards them by gardeners. The carrion from under the crown and fallen leaves must not only be removed, but also taken out of the garden. The crown of trees must be regularly treated against gray rot and pathogenic fungi. One percent Bordeaux liquid, applied three times, with an interval of two weeks, successfully copes with infectious diseases of stone fruits.
- Insect pests can significantly reduce the yield. The most common are the plum sawfly, moth and moth caterpillar. Apply agrotechnical techniques (loosening, hilling), put trapping belts. This will protect your garden without chemicals.
- Weather and climatic conditions determine the future harvest. Traces of frost damage can be seen on young shoots after winter. Clean these places, process with garden pitch. But amateurs cannot fight the sterilization of pollen. It is caused by a strong cold wind during flowering. In the northern latitudes, the tree does not have enough warmth, in the south, the seedlings are threatened with drought, the middle strip is recognized as the best for growing plums.
- Failure to comply with the conditions and place of landing. Saplings love neutral soils, sunny areas of the garden not shaded by large trees, where there are no "foreign" roots.
Now that you know about the causes of plum crop failure, you can weigh your options and desire to choose several plum trees for a new garden, knowing their characteristics.
Finishing the article, I want to invite you to watch videos about planting plums and pruning them.
See you soon, dear readers!
Rules for harvesting cuttings
Green cuttings are taken from young trees. There must be growth buds.
Lignified cuttings of annual shoots are best cooked in the fall, since annual shoots freeze slightly. Pruning is carried out from the south side of the trunk (they take root better). Tools - only sharp (secateurs, knife).
Before grafting, make a rejuvenating pruning of the mother tree. The mother tree must be healthy and fruitful. Age - from 3 to 10 years old.
You can not take thin branches with undeveloped buds, damaged, crooked shoots, tops. The one-year growth is cut off on cuttings 40-50 centimeters long, the diameter is chosen 7 millimeters.
The planting material is stored at a temperature of 2-3 ° C.
Cuttings
The main advantages contributing to the spread of this method are the increased survival rate and accelerated reproduction. This is a very fast method for producing a large number of new plants. However, this does not apply to all plum varieties. Therefore, you should use those plants that form a lot of root growth. Also, the following factors can affect the results of cuttings:
- quality of cuttings;
- timing of cuttings;
- instruments;
- age and condition of mother trees;
- the use of fertilizers.
Harvesting plum cuttings
How to cut a plum? The simplest variation of the method under consideration is reproduction by lignified cuttings. A year before grafting, you need to cut the plant shortly, after which many shoots are formed on it, capable of forming a root system and fully developing.
Procurement terms
Green cuttings of plums are carried out in summer, in early to mid-July, when the plants are intensively growing. For lignified cuttings, a dormant period is suitable. In regions with frosty winters, they need to be cut in late November - early December, but only before the air temperature drops to -20-30 ° С.
Important! It is allowed to harvest cuttings in early spring, before the buds begin to swell. This can be done only when there were no severe frosts in winter.
Harvesting cuttings
In order to cut the cuttings, you need to pick up suitable annual stems of the appropriate size on the mother tree. Ideally, it should match the width of the pencil. Thinner specimens can dry out quickly. The length of the shoot used for propagation should be about half a meter.
Important! If the plum to be propagated has a very small and weak annual growth, spring shortening of the skeletal stems should be carried out.
Harvested cuttings are usually stored at 2-4 ° C. In regions with snowy winters, they practice storing planting material under a snow layer 50-70 cm high. If there is a risk of thaw, the cuttings are covered with moistened sawdust and left in the frost. Soon the sawdust will freeze sufficiently and form a dense and durable cocoon. After that, the cuttings are transferred to a room where the sun's rays do not penetrate, and covered with a layer of dry sawdust (30-40 cm). From above they are wrapped in plastic wrap. 2-3 days before the start of rooting, the cuttings are moved to a warm room, where they will gradually thaw.
Important!If there are not very many cuttings, then they can be kept in the refrigerator. The planting material is wrapped in plastic wrap and tied with twine. You should not put it in the freezer - there they risk being killed.
Care should be taken to keep the cuttings in a dry place, as excess moisture is detrimental to the planting material. If, during the preservation process, they begin to dry out, you need to update the sections, place them in a container with water and put them in a cool room.
Green cuttings usually do not last long. Cut in the morning, if possible in cloudy weather, and immediately cut into small cuttings.
Rooting cuttings
For better rooting, cuttings should be placed in a solution of root stimulants before planting.It is recommended to use them as:
Prepared cuttings about 15 cm long are usually planted in a greenhouse or greenhouse equipped with a drip irrigation system. In the absence of such an opportunity, you need to make a homemade greenhouse from wire frame arcs and plastic wrap. Cuttings need to be watered 2-3 times a day.
For full-fledged rooting, a normal soil saturated with nutrients is important. The sand is mixed with peat in equal proportions and the resulting mixture is scattered in a layer of 10-15 cm on the garden bed. A 2-3-centimeter layer of river coarse sand is poured over it. Immediately before planting, the soil mixture is treated with superphosphate, 1 teaspoon of which is diluted in a 10-liter container with water.
Read also: What can be grown in Siberia
Important! The bottom leaf is removed before planting in the ground, leaving only the petiole to avoid decay. The cuttings are buried in fertile soil to a depth of about 3 cm, so that the outermost leaf is above the ground. Planting material is planted at a distance of 5 cm from each other and between the rows. The optimum air temperature for fast rooting is 25-30 ° C.
Rooting of plum cuttings from easily rooted varieties is completed after 2-2.5 weeks after planting, and those that reproduce poorly by this method - within a month. With the onset of callus formation, it is necessary to periodically lift the film in order to remove accumulated moisture and increase the access of oxygen to the plants. A month after planting, mineral fertilizers are applied under the cuttings, and then watered abundantly.
Knowing how to propagate plums by cuttings, you can choose suitable varieties for this. These include:
- Tula black;
- Early ripening red;
- Memory of Timiryazev;
- Hungarian Moscow.
Tula black plum
Optimal timing
Lignified cuttings are harvested in advance and stored in the basement or refrigerator. If stored properly, they can be kept for up to 3 years.
In autumn, when the tree has accumulated the most useful substances, it is at rest, the material is being cut.
The preparation of the cuttings can be done in the spring. The main thing here is to have time to make a workpiece before the buds swell.
The green samples are cut exactly the opposite. The tree must develop intensively. In the summer, in July, you can start preparing.
The process of planting a young plant
The plum tree grows well on any soil, but does not tolerate stagnant water. Do not forget to determine the depth of the groundwater when choosing a location. The main condition for location is sunny space, without wind. The shade has a negative effect on the plum - it gives a lighter shade of leaves, small fruits.
The landing site is prepared in the fall, since the ground is frozen in spring, and the funnel should stand at least 2 weeks before planting. The depth of the pit is 0.5 meters. The diameter is chosen so that the root system is comfortably located, usually 0.7 meters. Reinforce the peg in the center. The land is used only fertile. Therefore, it is left around the seat. With a large number of young trees, it is worth maintaining a distance between the funnels of 3 meters.
A seedling is dug from its site before planting, preferably with a clod of earth. This is another secret of fast rooting in a new place.
A purchased copy, purchased in the fall, is buried in the ground. Cover with spruce branches, add snow in winter.
As soon as the buds were swollen, planting time came:
- The seedling is placed on the north side of the peg. Gently spread the roots along the bottom.
- They fall asleep with fertile soil.
- The neck is left 5 centimeters above the soil level.
- The earth is tamped.
- 4 buckets of water are slowly poured under each seedling.
- Peat or humus is laid on top.
A layer of mulch will maintain moisture, get rid of weeds.
What is plum sprout and the reasons for its appearance
Shoots are shoots that form in the root zone of a tree; in crops with a shallow root system, shoots can appear far from the main trunk. In most cases, full-fledged, fruit-bearing trees grow from a properly and timely transplanted shoot, in some cases, grafting is needed to obtain a crop. The growth of shoots from the root can be associated with the method of cultivation (more shoots are formed in self-rooted trees, grafted plums often grow without shoots), but there are other reasons for the appearance of offspring.
In a high-planted tree or when watering with a stream, the roots are exposed, due to which the stem is damaged. The offspring will grow continuously, the situation can be corrected by sprinkling the roots with a good layer of earth.
Pruning a significant portion of the branches
In the case when the tree has undergone critical pruning, the development balance is disturbed due to improper nutritional distribution. The root receives less substance from the photosynthesis of the crown, the tree tries to compensate for the losses by building up new shoots.
Mechanical damage to the trunk and root
Carefully monitor the health of the tree, treat the wounds with garden pitch, replace digging the soil with loosening. Remove foreign objects from the branches, such as a tag, a tied rope, or tight grafting tape. With the growth of the stems, the element will gradually cut into the bark, disrupt the process of sap flow, and in order to obtain normal nutrition, the root will release new shoots.
Incompatibility of rootstock with scion
If the scion and rootstock are incompatible, the appearance of root shoots is inevitable, due to metabolic disorders. The problem can be recognized by the thickening of the bark at the graft site, yellowing of the leaves on the branch, and sometimes on the tree. In addition to the appearance of abundant growth, immunity to frost and productivity will significantly decrease, if the stems growing from the root are not removed, the tree will die. The incompatible stock must be removed, the cut site must be treated with slaked lime.
Shoots are formed when there is a lack of moisture during dry periods, as well as if reliable protection has not been organized before wintering. The second reason is relevant for both young and adult trees. When a significant part of the branches and roots freezes, the plum tries to recover at the expense of the overgrowth. The mother tree dries up gradually, it is better to cut it down, and use the shoots for propagation.
The intensity of fruiting and the quality of the fruit depends on proper care in the spring. Basic procedures on the site ...
When can rooted plum cuttings be transplanted?
The time for planting cuttings in open ground is autumn or spring. There is only one regularity - the survival rate of trees is better in spring.
Spring starts at different times in different regions. The best guideline for planting is soil temperature. The earth should warm up to 8-12 ° C.
Home-grown cuttings should be hardened 2-3 weeks before planting. First, take out in the daytime to the terrace, balcony. Every day the time of "walks" is increased, up to disembarkation.
Cuttings grown in a greenhouse also require hardening. In the first decade of September, the film is slightly opened in the daytime. The duration of the walks is increasing every day. By the end of the week, open the ends of the greenhouse for the night.
After 2 weeks, the cover is removed completely. The starting point will be the first "walk".
In the spring, loose soil is prepared, where the seedlings will be planted. Throughout the season, plantings are looked after: watered, removed weeds, fed.
In the second spring, the young tree is transplanted to a permanent place.
Biological features
Skeletal and semi-skeletal branches are covered with numerous growth and fruit branches.
Escapes
Shoots grown in the current year can be pubescent (to varying degrees) or bare. The vegetative buds formed on them are relatively narrow, pointed, and the generative ones are more convex and large.
Leaves
medium to large, ovate, obovate or elliptical, with a pointed apex and wedge-shaped base, thick, wrinkled, pubescent on the underside. The flowers are predominantly white, 1-2 (rarely 3) from one bud.
Fruit
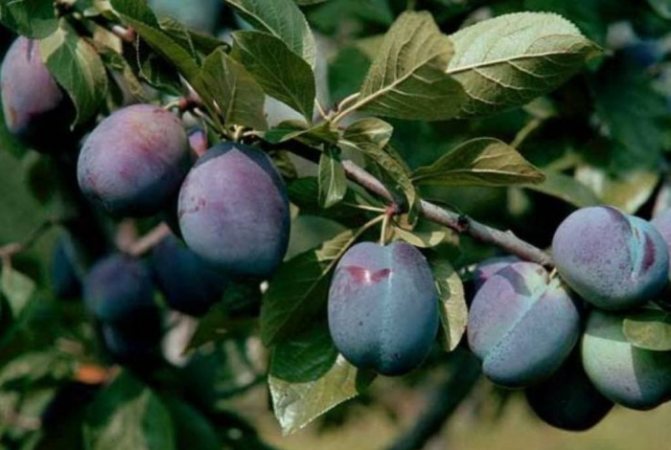
from small (6-10 g) to large (50-70 g), various shapes (from round to elongated ovate) and color (from yellow to dark blue), with a more or less strong waxy coating. The flesh of the fruit is often yellow or greenish, rather dense, juicy, sweet and sour. The stone is detached or fused with the pulp, of various shapes and sizes.
Root system
The root system of the plum consists of skeletal (0.3 to 5-8 cm or more thick) and overgrown (up to 0.3 cm thick) roots. Most of the roots often lie in the soil almost horizontally at a depth of 20-40 cm. Only individual roots penetrate quite deeply into the soil.
Closer to the root collar, the roots almost reach the soil surface. Some of them can grow under the root collar as pivots, penetrating to a depth of 60-80 cm.
Often the root system extends beyond the crown projection. Overgrowing roots are organs that ensure the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
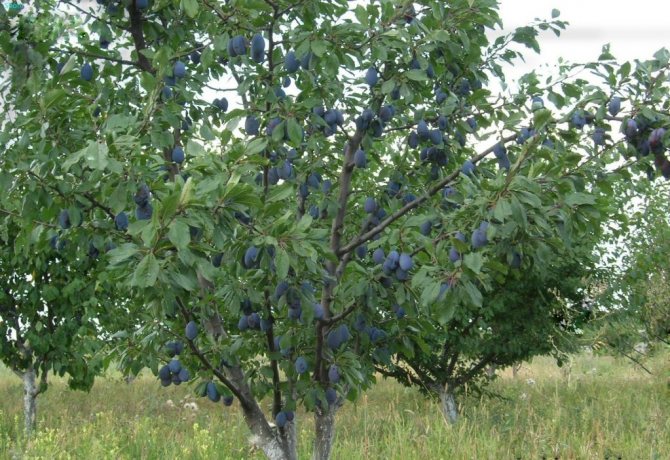
The better the overgrowing root system is, the more favorable the conditions for good growth of shoots, leaves and fruits.
The vital activity of plants is closely related to factors such as tempo.
Plum varieties cultivated in central Russia
Characteristics of plum varieties cultivated in central Russia.
Given the biological characteristics of the plum, its exactingness to the soil.
12 September, 2013
Plum is a culture that requires good care, the main thing in it is timely.
In this article, we will describe in detail the shape of the structure of the fruit tree on pr.
Caterpillars are yellowish-white with black b.
Planting work can be carried out in autumn and spring.
A source of plant nutrition and increased fertility.
In this article, we will describe in detail the shape of the structure of the square.
Powdery mildew, white and black spots, rusty.
Adding an article to a new collection
Modern plum varieties cannot be called unpretentious. They have certain requirements for planting, agricultural technology, fertilizers, and without meeting these conditions, trees may not bear fruit, or even die altogether.
We have repeatedly talked in detail about the various stages of plum care and the operations that need to be done with it, but in this article we want to collect all the main points for those who are just going to start this beautiful tree in their garden.
Rooting plum cuttings
What to do? And I propose to start rooting cuttings in March, in a city apartment! At the same time, optimal conditions for cuttings will be provided with minimal labor costs. How smart they will tell me. Have you tried it yourself? I tried it. And therefore I describe in detail what needs to be done.
I think many people have in store soil with the addition of compost since autumn. Personally, I always keep it dry. Therefore, for anyone interested, then leave a quarter of a bucket for rooting the cuttings and mix it with sand in a 1: 1 ratio. Then you can start making a greenhouse from a polyethylene five-liter bottle. With scissors, carefully cut off the lower part at a height of 15 cm, and leave the upper part as a greenhouse cover. Along its lower cut, at a distance of 2-3 cm, we make vertical two-centimeter cuts. We slightly bend the formed "petals" inward so that the cut perimeter decreases and the upper part of the bottle can be installed on the lower part (see Fig.).
A logical question arises: how many cuttings will fit there? The answer is: seven pieces. Few? And more is not necessary, because in order to update the old plum, in fact, two established cuttings are enough.
Now about the nutrient solution. I did it like this: in 1 liter of water I dissolved 3 tbsp. l.sifted ash and 1 tbsp. l. complex fertilizer (for example, nitrophosphate). Then he poured the prepared soil into the bottle in small portions, each of them watered with a solution, mixed and allowed to settle. As a result, at the bottom of the bottle there was 10-12 cm of soil with a moisture content of about 90%. Where does this accuracy come from? Yes, if it were 100%, then free water would appear at the bottom! And since it is not there, then the bottles and drainage holes are not needed (this I hasten to answer a possible question). At the same time, he did not compact the soil, leaving it loose and breathable.
For cutting cuttings, I chose branches 15-20 cm long from the lower part of the crown, which had well-formed buds. At a distance of 10-12 cm from the lower end of each branch, I chose a well-ripened main bud, above which I cut off a thin part and threw it away. The lower ends of the cuttings were cut obliquely.
By the way, only one selected kidney should be left on the cuttings (well, for insurance, you can “regret” the one that is still closest to it), and break the rest.
I stuck the cuttings into the moist soil vertically, to a depth of 5-6 cm.At the same time, I tried to place them in the bottle so that they did not touch the walls, leaving a gap of 2-3 cm.I know that some gardeners recommend treating the ends of the cuttings with a special solution , contributing to their rooting. But this is beneficial only in conditions of mass germination of cuttings. If there are such solutions in the stash, then you can use them. And if not, then buying such stimulants for an insignificant number of cuttings is a waste of money.
Crown formation and subsequent pruning
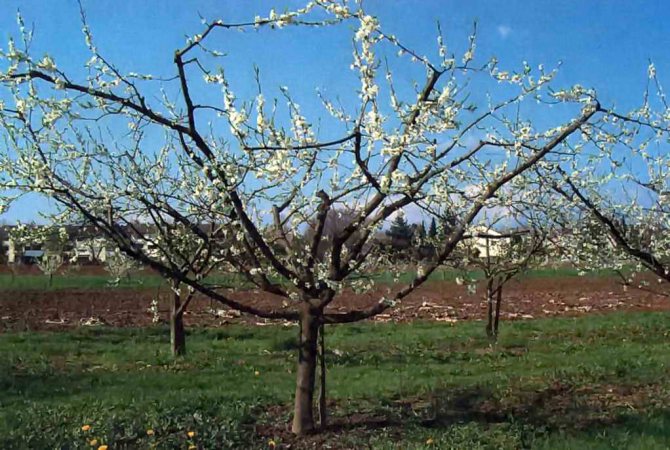
The plum is formed in the first 3-4 years. Usually the crown is given pyramidal shape. Such a crown consists of a central conductor, several skeletal branches, as well as semi-skeletal ones.
For plants that have been grafted onto medium or vigorous rootstocks, use poppet crown shape. Most of all, it is suitable for varieties with a horizontal arrangement of shoots. This crown shape is similar to a flattened pyramid. In the process of its formation, the main shoot is greatly shortened, while the lateral ones only delay. As a result, 6–8 skeletal branches should remain in the crown, while the leading shoot at the end of formation is transferred to a weak lateral one.
In areas where space is limited, you can apply fusiform crown shape. With this approach, the leading role is given to the central conductor, around which up to 12 semi-skeletal branches are located. The shape of such a tree resembles a spruce and takes up little space in space.