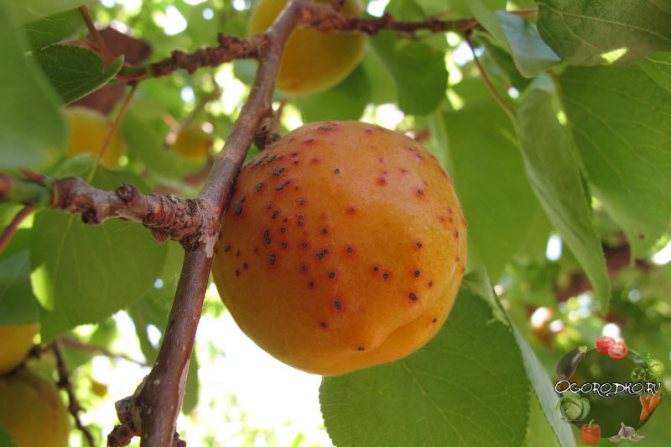
Natalya Popova Grows an apricot in the country
Any gardener living in regions with moderately cold winters inherent in middle latitudes, and in particular in the Moscow region, knows how difficult it is to grow apricots in such conditions. There are many fruit trees on my site, among them 4 apricots. Apricot Lel is an undoubted favorite in many ways. Its main advantage is easy adaptation to our climate. Of course, growing a southern tree in an environment far from its natural range requires certain skills and labor. But with strict adherence to agricultural technology and careful attention to the plant, good harvests of apricot will become the norm.
Description of apricot
Apricot is a fruit tree from the Pink family, genus Plum. Brought to Russia from warm regions. In the southern part of the country, it begins to bloom in mid-April, in the eastern part it blooms in early May.
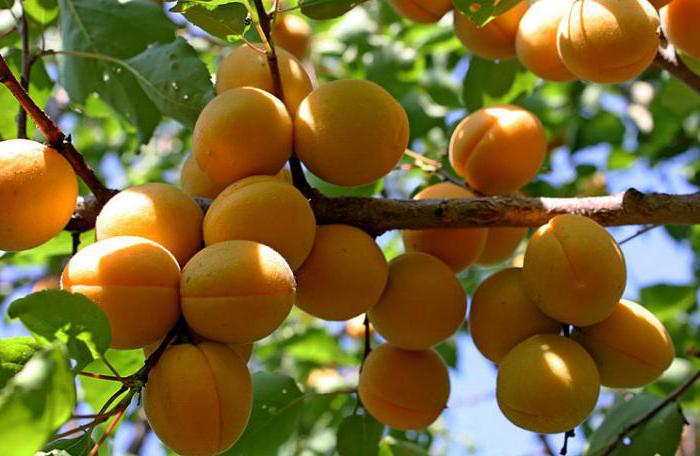

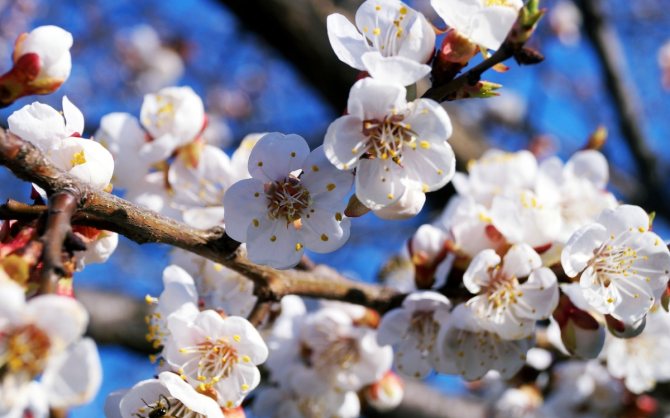
The tree blooms mainly with white, red and pink flowers, exuding a very delicate aroma, but the flowers shed quickly enough, on average in 8-10 days. The height of the apricot tree can reach up to 8 meters, the crown is densely branched. The leaves are light green or emerald green, oval, round or heart-shaped. With proper care and feeding, the lifespan of an apricot can reach 100 years. Fruiting begins after 3 years of life.
The history of the emergence of apricot in the north of Russia and description of the Lel variety
For the successful spread of apricot to the north, various measures were taken. And they sowed the seeds of the fruits they liked in more severe conditions, and crossed varieties of common apricot, common in the south and in the Transcaucasus, with wild species, but the best results were obtained when grafting common apricot on a plum or cherry-plum stock.
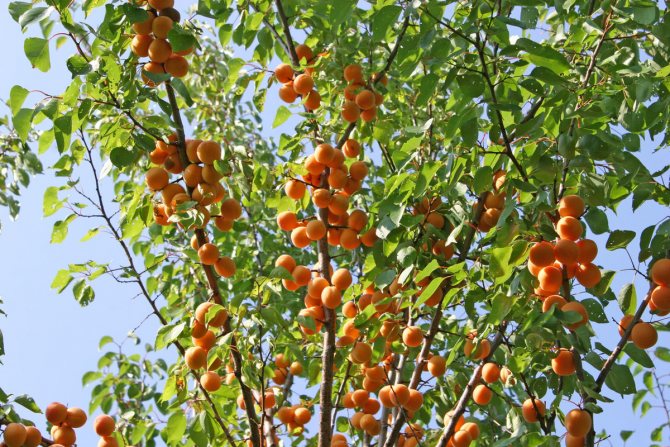
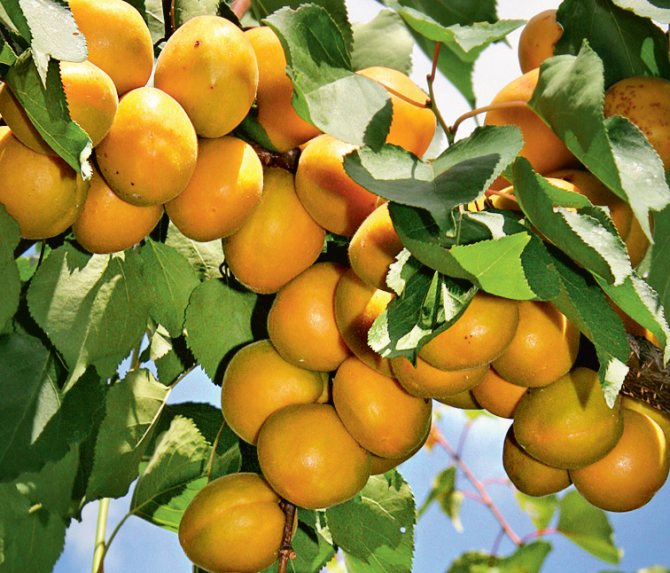
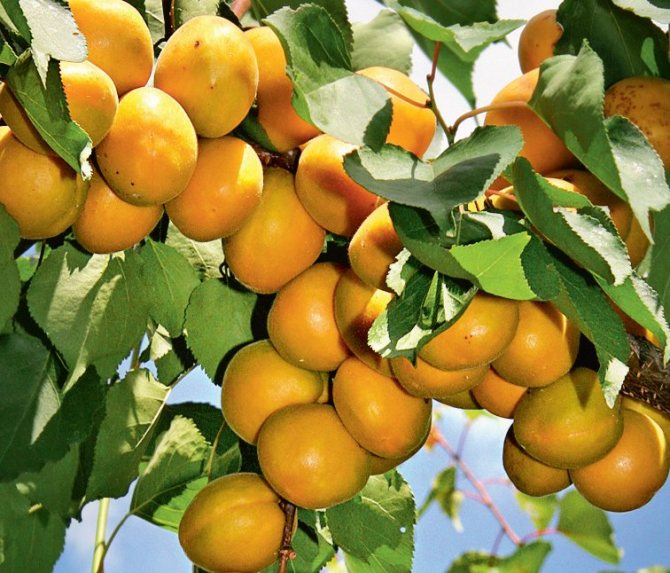
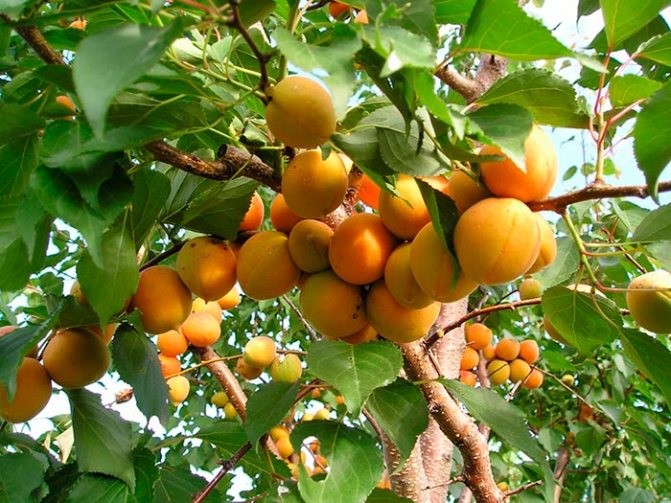
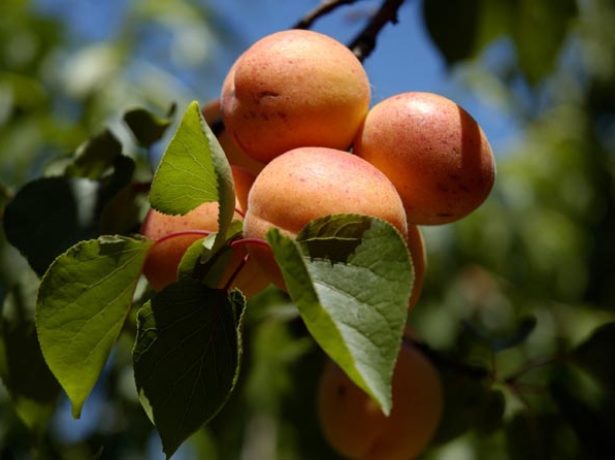
Apricot branch Lel strewn with golden fruits
The variety was created at the end of the twentieth century, and since 2004 has been included in the State Register. It is recommended to grow Lel apricot in the Central region. The tree does not grow large, has a not very dense, wide crown. The variety is early-growing, in the third year after planting it begins to yield a crop of a very early ripening period. However, gardeners note the frequency in fruiting.
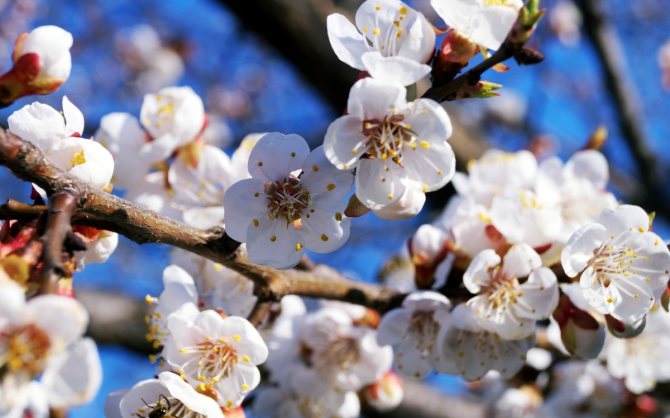
The skeleton of the tree is formed by smooth, straight, dark red shoots. The apricot begins to bloom before the leaves appear. The flowers are large, have five white-pink petals. There are five sepals, dark red. When blooming, a delicate sweetish aroma spreads around the trees.


Apricot flowers bloom before the leaves appear
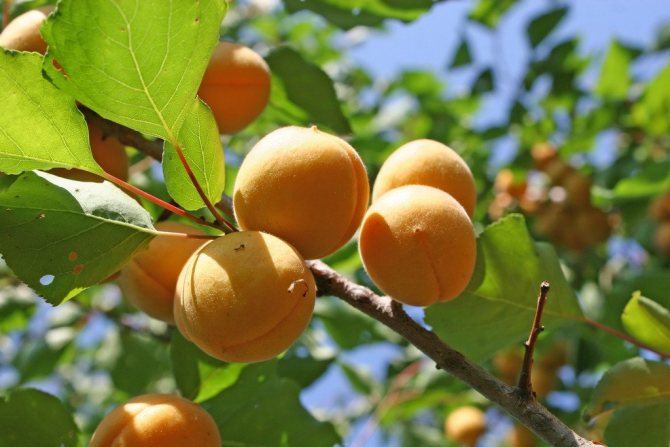
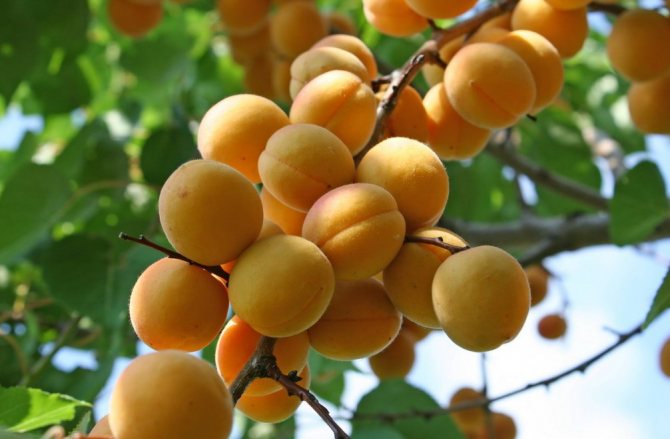
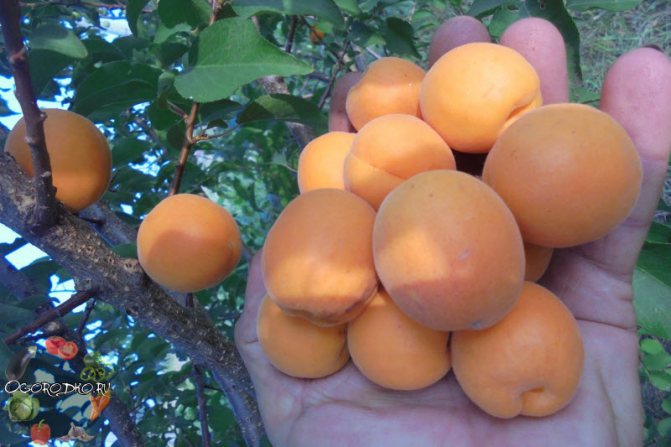
The leaves are dark green, round-ovate, with a pointed tip, smooth, shiny. The fruits are round, orange, but if allowed to ripen completely, they are filled with an intense red blush. Covered with soft, weak down. The average weight of fruits is 18 g. Orange pulp, juicy, very tender, sweet and sour taste, received the highest tasting score.
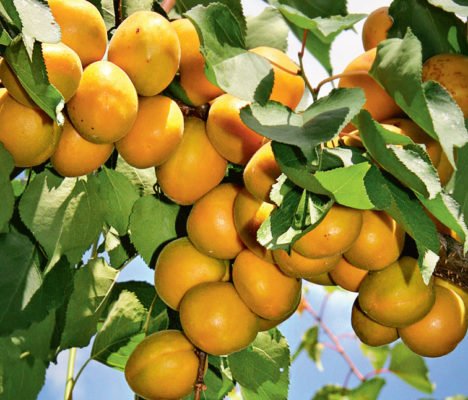


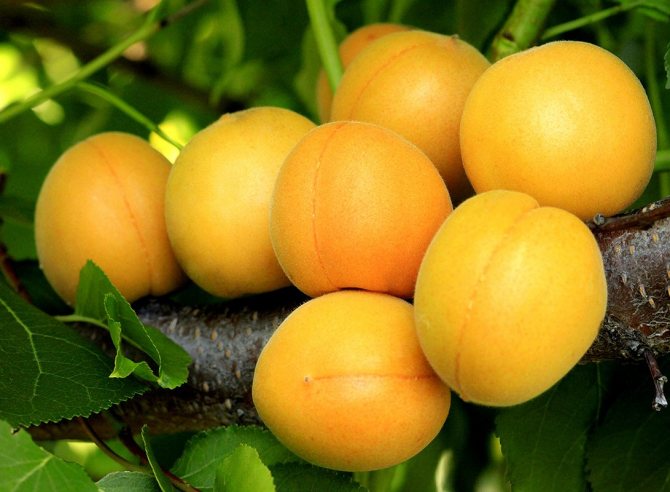
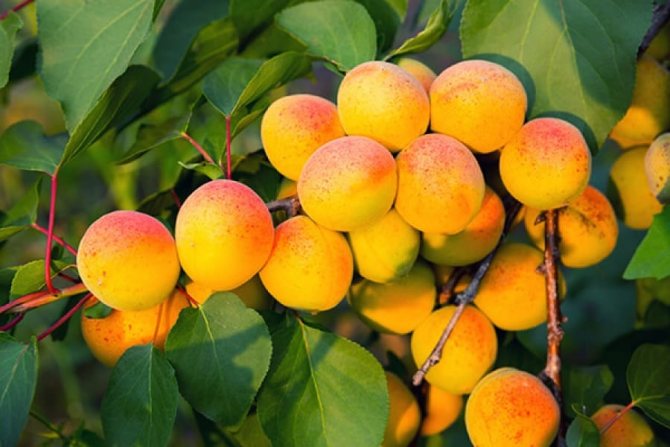
Apricot Lel - a productive variety with rounded fruits
Apricot Lel is winter-hardy, shows average resistance to klyasternosporiosis and practically does not suffer from aphid attacks, less than 1% is damaged.
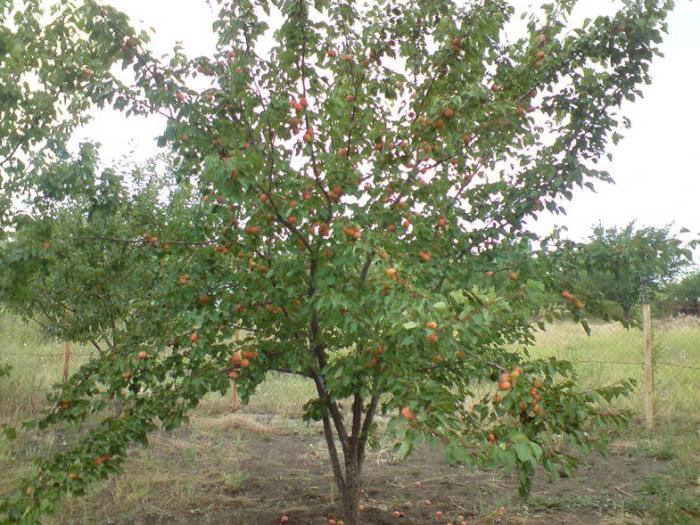
The apricot tree has a compact crown, reaches a height of three meters, and grows slowly.The appearance of the apricot is very beautiful: in the spring the tree attracts the eye with its bright, fragrant flowering, in the summer - with ripening fruits, in the fall - with red-orange dense foliage.
The variety was bred in 1986 by breeders Alexei Skvortsov and Larisa Kramarenko on the basis of the Main Botanical Garden in Moscow. In 2004, apricot Lel was included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements and recommended for zoning in the regions of the Central Federal District.
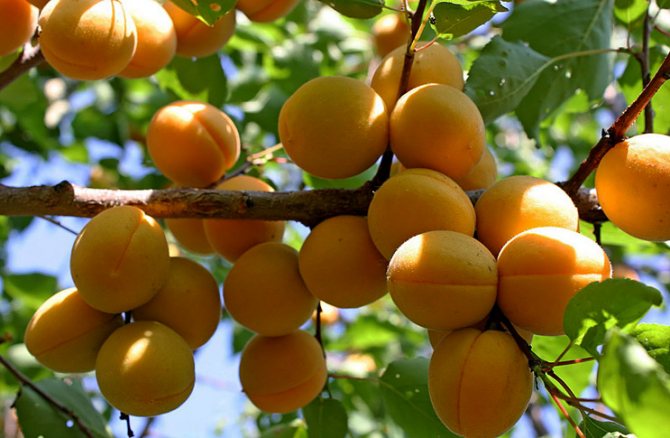


Apricot Lel
Ah, this apricot! Lel variety
This variety was bred in 1986 on the basis of the Moscow Botanical Garden. N. V. Tsitsin RAS by breeders A. K. Skvortsov and L. A. Kramarenko. In 2004, it was entered into the State Register of Plant Breeding Plants of the Russian Federation.
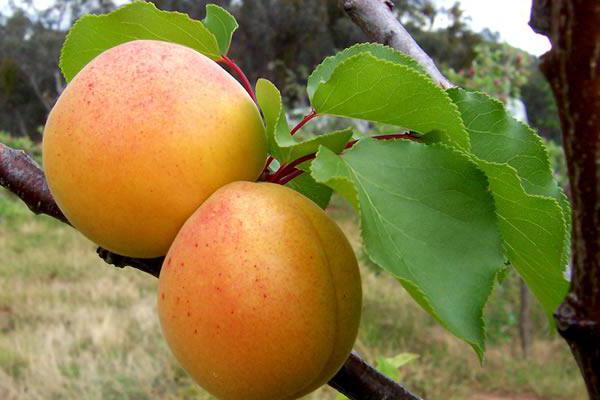


Despite the moderate productivity, apricot Lel, reviews of which are only the best, is successfully grown in collective gardens and in personal plots. The excellent appearance and sour-sweet taste of its fruits make up for this deficiency. Read on how to properly grow Lel apricot (a description of the variety is presented in the article).
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Considering all the above characteristics of the Lel apricot variety, it will not be difficult to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of this plant. True, despite all the disadvantages, the existing advantages of the Lel apricot variety fully compensate for them, which is why plants are so often found in personal plots.
- So, the list of indisputable advantages of culture includes:
- relatively high indicators of frost resistance of trees;
- self-fertility of plants;
- drought resistance of the culture;
- insignificant annual growth;
- early onset of fruiting (on average, 3-4 years after planting a seedling on the site or grafting a young plant to another variety);
- excellent indicators of the keeping quality of the crop;
- compact crown size and well-groomed appearance even with moderate care;
- low demands on the composition of the soil.
- As for the disadvantages of the variety, there are slightly fewer of them, but you cannot ignore them, because these are:
- weak resistance to common diseases and pests of fruit crops;
- relatively low yields;
- large fruit stone;
- small fruit sizes.
Appearance
The tree is medium-sized, reaching a height of 3 m, the crown is quite neat and compact. One-year shoots are weakly branched. This variety is distinguished by moderate, rather restrained growth.
The leaves are dark green, shiny, ovoid, with small teeth, smooth and soft to the touch. In autumn, they are colored in different shades of red.


White-pink single flowers of medium size, having five rounded petals, are able to withstand temperatures down to -1.5 degrees. The flowering period is from late April to early May.
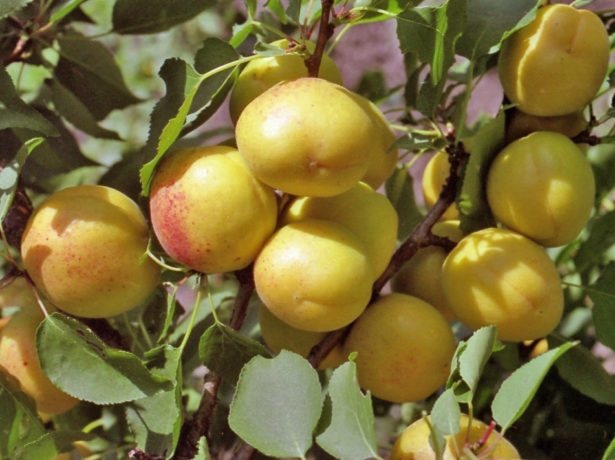
Apricot Lel: description of fruits
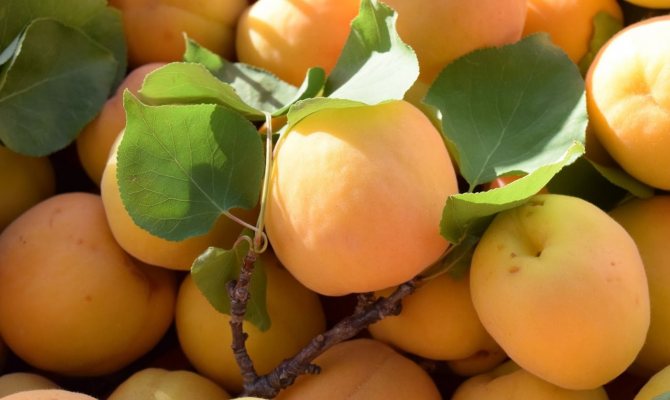
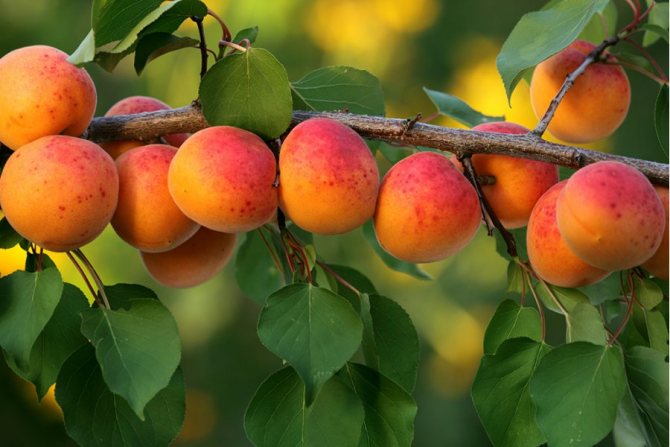
The fruits of this variety are very beautiful and shiny, rounded, slightly flattened from the sides, weight - about 20 g. The skin is orange, almost not pubescent, without blush. The flesh is orange in color, firm and very tender. The bone is perfectly separated. Early ripening. The yield is average, sometimes high. The fruits are delicious both fresh and preserved. Keeping quality is good.
The apricot fruit is tasty, nutritious and aromatic. They contain a significant amount of sugar, pectin substances, organic acids, carotene, as well as malic and citric acids. An important role is played by the mineral and vitamin composition - the presence of vitamins of group B, C, P, PP, H, E, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, iodine, iron, folic acid, etc.
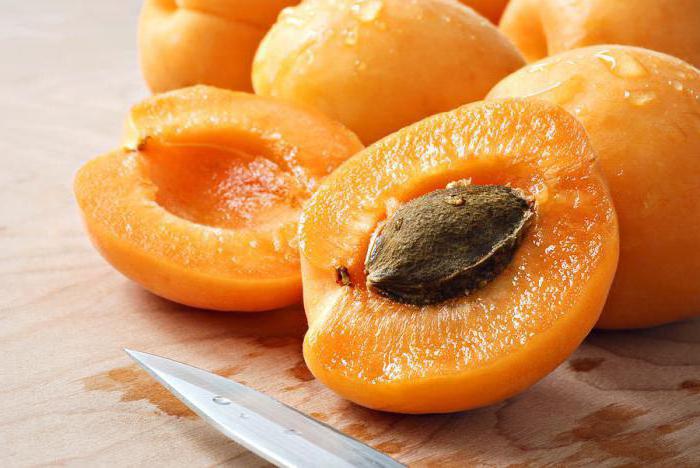


The consumption of apricots helps to maintain health and prevent the development of many diseases. The calorie content of 100 g of fruits is 44 kcal.
Harvesting
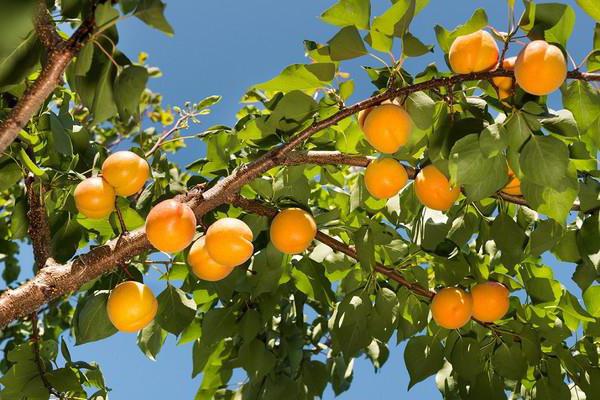
The ripening time of the first apricot fruits of the Lel variety is mid-July.
Apricots ripen gradually.For 30–40 days, the tree will delight its owners with juicy and sweet fruits.
Apricot Lel enters the fruiting period 3-4 years after planting. From a young tree in one season, you can collect 10-15 kg of fruits, from an adult (after 10-12 years of life) - 25-30 kg. With proper care, this yield will last for 18–20 years.
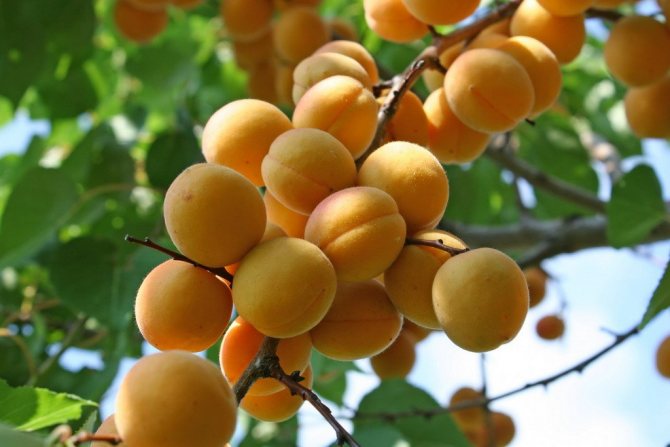


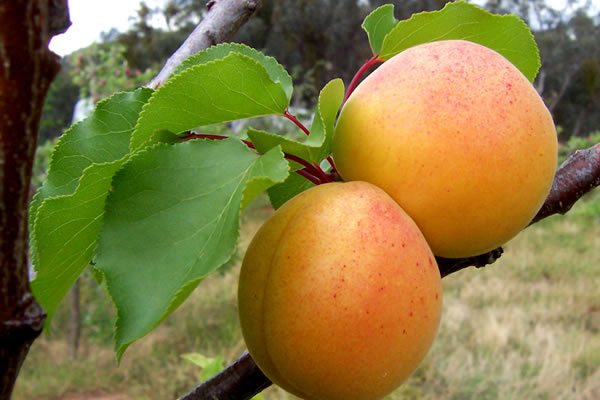
Ripe fruits harmoniously combine acidity and sweetness
Transport and storage of crops
Fresh apricots can be stored in the refrigerator or basement at 0-1 degrees and 85-90% relative humidity for 1-2 weeks. The harvested fruits are prone to rotting and softening of the pulp. With long periods of storage (3-4 weeks), losses can be up to 20%.
For transportation, as a rule, unripe apricots are removed (7-10 days before the full ripeness of the fruit). The removed fruits are laid out in layers in wooden or cardboard boxes. Elastic apricots ripen within a few days, completely retaining their taste and attractive appearance.
Harvest use
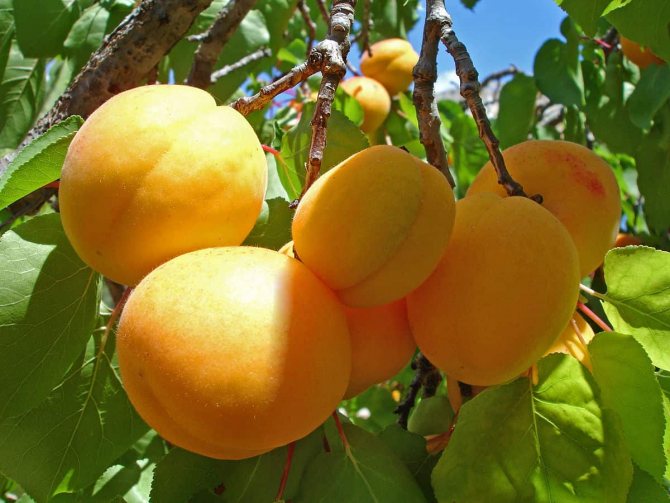
Apricot is a universal product. Most of the juicy and sweet harvest is eaten fresh. Due to the high content of dry matter (16.8%), apricots are dried in the fresh air, in an oven or in an electric dryer at a temperature of + 50-80 degrees. Fresh seedless halves can be quick-frozen.
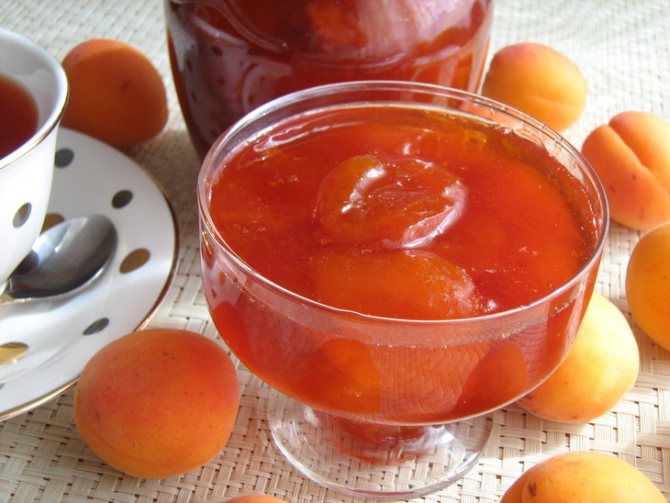
Fragrant jam and compotes are cooked from the fruits, canned in sugar syrup and marshmallow is prepared. Canned and fresh apricots are used to prepare fruit salads. Apricot pits taste like almonds and are used in the preparation of cakes, muffins, sweets.


Apricot variety Lel is suitable for the preparation of any kind of workpieces
The use of the fruit for medicinal purposes
The high potassium content (417 mg per 100 g of product) makes this fruit an essential component in the summer diet of elderly people suffering from cardiovascular or immune diseases. Iron-containing orange fruits are recommended for pregnant women. To maintain youthfulness, firmness and elasticity of the skin of the face, masks are made from juicy fruits.
Apricot varieties Lel are distinguished by high taste and excellent presentation of fruits. Elastic bright orange, as if covered with a layer of varnish, the fruits will decorate the dining table and will stand out among the variety of fruit products on the market counter.
Landing
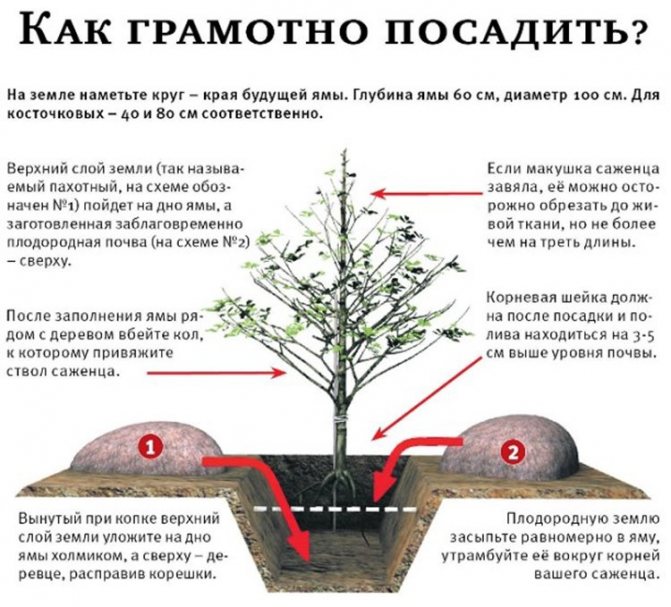
To plant apricot Lel, you need to choose a well-ventilated and well-lit area of the garden, preferably on the south side of fences or buildings. The culture loves fertile, potassium-rich soils with deep groundwater. Autumn and spring months are suitable for planting. In this case, you need to pay attention to the condition of the soil (it should be loose, crumbling) and the air temperature, which should not fall below +10 degrees at night.
Apricot Lel is undemanding to the soil, it can grow successfully even on rocky ground. The passage of groundwater should be no higher than 2-3 m.
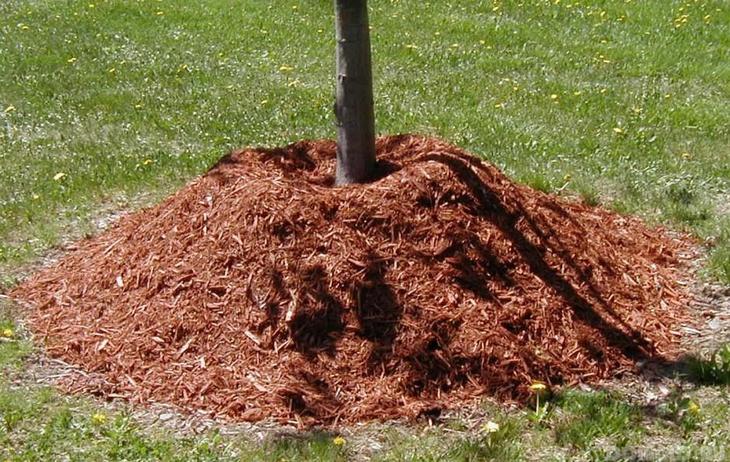
When planting a tree in spring, the pit for it is prepared in the fall. In size, it should be at least 1.5 m in terms of basic parameters. Drainage is poured into the bottom of the planting pit, and on top is soil mixed with humus, superphosphate, potassium salt and lime. At a distance of about 10-15 cm from the stem of the seedling, a wooden stake with a height of 1.7 m is inserted and a tree is tied to it. Pour 10 liters of water over the apricot. Mulch wet soil with dry grass or sawdust with a layer of 10-15 cm.
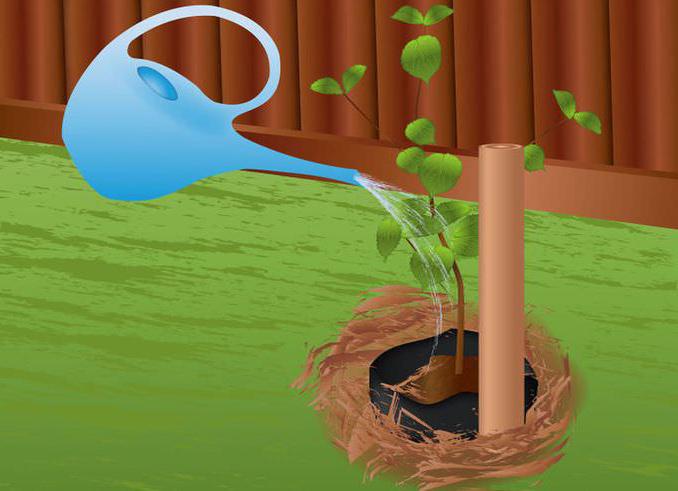


Growing recommendations
Before planting apricot Lel, they are determined with the timing, place, dig a planting hole in advance, prepare the soil. Productivity depends on the quality of the acquired seedling, neighbors and the implementation of the planting algorithm.
Landing dates
Since winter in the Central regions comes relatively early, it is preferable to plant the culture in the spring before the leaves bloom, but with already swollen buds. If the dates for planting a fruit tree are postponed to autumn, then the time is calculated so that at least two months remain before frost.
A suitable place for apricot Lel is an open, sunlit slope, protected from drafts. The plant does not develop well in cold northern winds. Planting trees in lowlands is unacceptable, as the root system begins to rot.
The culture prefers loose and fertile soil, sandy loam and loam. If there is no suitable soil on the site, an artificial embankment is created.
Common diseases, competition for light and nutrients lead to incompatibility of apricot with the following crops:
- cherries;
- peach;
- cherry;
- walnuts;
- apple tree;
- pear.
Apricot also does not like fruit bushes located in the neighborhood, he prefers to live separately. Primroses do not interfere with the tree - daffodils, primrose, tulips.
A suitable seedling for planting Apricot Lel is a two-year-old standard tree grafted at least 1.2 m from the root. Such plants tolerate winter better.
Before purchasing planting material, the root is examined, which should be branched and not shorter than 20 cm.If rot spots or dried bark are visible on the smooth trunk, the plant is discarded.
Planting process


When growing apricot Lel on an industrial scale, maintain the distance between seedlings in a row of 4 m, and in row spacing - 6 m. It is not recommended to plant more than 1-2 trees in a summer cottage, since the roots of the culture grow in diameter 2 times the crown, sucking moisture and nutrients from adjacent beds.
In the fall, a planting pit is prepared, measuring 70 x 70 cm. If the root ball of the tree is larger, the recess is expanded. The fertile soil layer is combined with two buckets of humus, 500 g of nitrophoska, 1 kg of ash are added.
Apricot seedling planting technology:
- a drainage layer is laid at the bottom of the planting pit if the soil is heavy and clay - with sandy;
- in the center, drive in a support that rises above the surface by at least 1 m;
- holding the trunk upright, straighten the roots;
- fall asleep with a prepared substrate;
- lightly tamp, watered abundantly.
The root collar should rise 4–5 cm above the surface.
A rich harvest and a healthy appearance of Lel apricot depend on a well-chosen place and adherence to planting rules, high-quality plant care. To do this, the gardener is advised to follow the following set of instructions:
- Choose or create your own gentle slope, accessible to the sun's rays and protected from the north wind. The diameter of the embankment should be 2 meters, the height - 70 cm. In September, a hole is dug on top of the hill and humus and ash are added to it;
- It is better to plant apricots in April and early May, but you can also in the autumn months. The main thing is that the soil is loose, crumbling, and the air temperature is 10-12 degrees above zero. Neighboring trees will help to choose the exact moment of planting - swollen, but not yet blossoming buds should appear on them by this time;
- Watering is carried out up to six times per season. To protect the soil from drying out, it should be mulched;
- In the first year, you need to form the crown. This should be done carefully, since the Lel variety grows for a long time.
Important! A wooden shield covered with whitewash, 2.5 to 3 meters high, installed on the north side of the tree, will help protect the tree from cold winds. This design will reflect sunlight towards the apricot, which will provide it with uniform illumination and heating. A wall of a house or utility room, a high fence, etc. can act as a wooden shield.
Any quality of soil is allowed - a tree is undemanding in this respect. Still, one important condition must be observed - the depth of groundwater should not exceed 2-3 meters.
A sign that the apricot will quickly take root and will actively grow is the presence of old trees with a developed root system on the site. It is recommended to buy seedlings in local fruit nurseries. It is important that they are all grafted at a height of 1.5 m.Thanks to this, the seedlings acquire such valuable qualities as:
- frost resistance and disease resistance;
- early onset of the fruiting period;
- high productivity.


Apricot
Some gardeners grow apricots using seeds. This is due to the fact that the seedlings are quite whimsical and can be subject to various diseases. It is important to keep in mind that sowing apricot tree seeds may seem like a simple process, but in practice everything happens differently. Planting seeds is very different from planting seeds of other plants. In addition, many qualities of the variety are completely lost in this case.
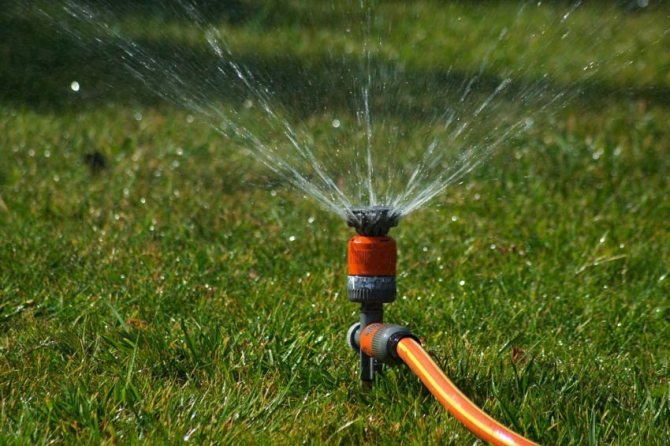
To ensure high-quality watering of the tree, you should dig a small groove in the area of the trunk circle. Water prepared for irrigation is poured into a ditch. Every year the diameter of the irrigated zone is expanded. The ditch should be at a distance of 30-40 cm from the trunk. During flowering, ovary formation and fruit ripening, abundant watering is required - up to 45-50 liters under one tree.
Important! You need to feed the tree in spring, summer and autumn. In the spring, before and after flowering, nitrogen-containing fertilizers (30-40 g per square meter) are added to the soil. At the same time (once every 2-3 years), fertilizing is carried out with organic fertilizers (manure, compost or bird droppings).
In the summer, foliar dressing is carried out containing useful trace elements (2-5 liters per tree). This is done when the leaves dry out, a mesh appears on ripe fruits, the tops of the shoots are exposed and in other problem cases. The preparations with which the apricot is sprayed must contain iron, a solution of boric acid or manganese sulfate. With gommosis or cracking of the fruit seed, root feeding with slaked lime is necessary.
In autumn, the tree is fed with wood ash and chalk (300-500 g per 1 square meter).
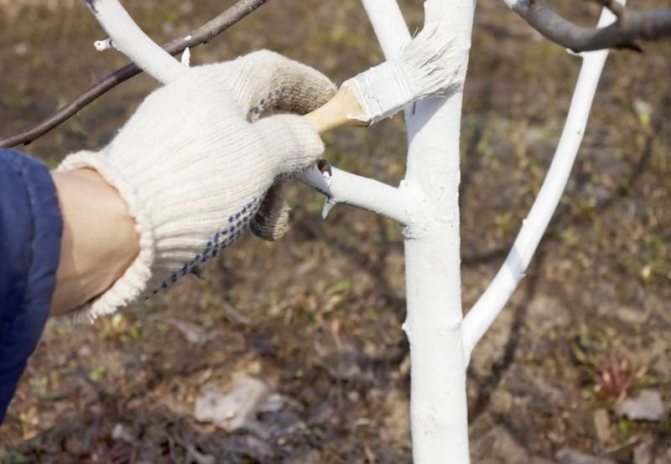
In the first days of spring, damaged, broken and infected branches are cut. In late autumn, the lower part of the apricot trunk is whitewashed. In this way, disinfection of the bark of the tree is achieved, larvae of pests and fungal spores are destroyed. In addition to the trunk, it is also recommended to whitewash the base of the skeletal branches.
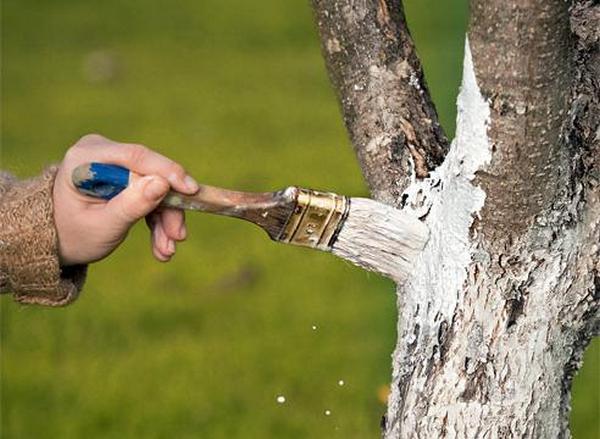


Whitewash
Care
For normal development, growth and a stable harvest, timely implementation of agricultural activities is necessary.
Apricot Lel is a drought-resistant tree that requires moderate watering. During the season, it is watered three times: in mid-spring, at the end of May, and a few weeks before the fruit ripens. In addition, one more watering is required - in the fall when preparing the apricot for wintering.
It is important to remember that the apricot tree is quite sensitive to waterlogging of the soil, its waterlogging can lead to decay of the roots.
Pruning
The compact crown of Lel apricot, as a rule, does not cause much trouble for gardeners. The tree is pruned annually. In the spring, branches frozen after winter are removed. It is in the spring time that pruning is considered the most effective. Summer pruning is done at the end of August. In autumn, trees are pruned in order to prepare them for the winter period and increase winter hardiness.

Gardeners reviews
Apricot variety Lel is wildly popular among summer residents, due to its excellent taste and appearance, as well as good winter hardiness.
Ivan, 55 years old
“Several years ago I decided to plant apricot trees on my site. I gave preference to the Lel variety. The hybrid turned out to be unpretentious in cultivation. It winters well, although winters in Kazan are quite harsh.This year the first fruits have grown, which turned out to be very tasty. "
Olga, 39 years old
“The Lel variety has been pleasing us for several years with excellent sweet fruits, which we eat fresh and preserve for the winter. The trees are compact and do not take up much space. They don't require much care. "
Preparing for winter
An adult apricot Lel is able to tolerate low air temperatures well. Its preparation for winter includes wrapping the trunk with burlap and covering the near-trunk zone with snow. Young seedlings need more care. A small structure is built from wooden pegs and covered with a film, sprinkled with earth on top.
The most dangerous time for apricot trees is the winter thaw, when warming is followed by a decrease in temperature. During this period, cracking of the stem or freezing of flower buds is possible. Most often this applies specifically to young trees that have not yet managed to grow a sufficient amount of wood.
Fertilization and feeding
During the first five years of the life of the apricot tree, fertilizers can be applied to the near-stem zone. Further, the coverage of the soil for fertilization should increase every year.
In the spring, the soil is fertilized by introducing 4 kg of humus mixed with 5 g of phosphorus, 6 g of nitrogen, 8 g of potassium per square meter.
Also, for a good yield, apricot trees need mineral fertilizing:
- 2-3 years after planting, it is necessary to add superphosphate (0.13 kg), ammonium nitrate (0.06 kg) and potassium chloride (0.04 kg);
- for the 4th-5th year, superphosphate (0.2 kg), potassium chloride (0.06 kg) and ammonium nitrate (0.1 kg) are introduced;
- for the 6th, 7th and 8th year - superphosphate (0.31 kg), ammonium nitrate (0.21 kg) and potassium chloride (0.14 kg).
Subsequently, superphosphate (0.88 kg), ammonium nitrate (0.37 kg) and potassium chloride (0.25 kg) are added annually.


Rules for the care of apricots
For successful cultivation and maximum fruiting of Lel apricot, the tree needs to be properly maintained, which will include timely watering, top dressing, crown pruning and soil care in the near-stem circle. Special attention should be paid to the prevention of diseases and pests of crops, because the described variety is not highly resistant to external adverse environmental factors.
Prevention and protection against pests and diseases
The main preventive measure in caring for Lel apricots is compliance with the requirements for watering plants, dosed use of nutrients during crop feeding and timely fight against already manifested diseases or pests. Bordeaux mixture is considered to be an effective chemical agent for the prevention and treatment of popular apricot ailments (for example, klyasterosporiosis), spraying of which is carried out before bud break and in the autumn, shortly after harvest.
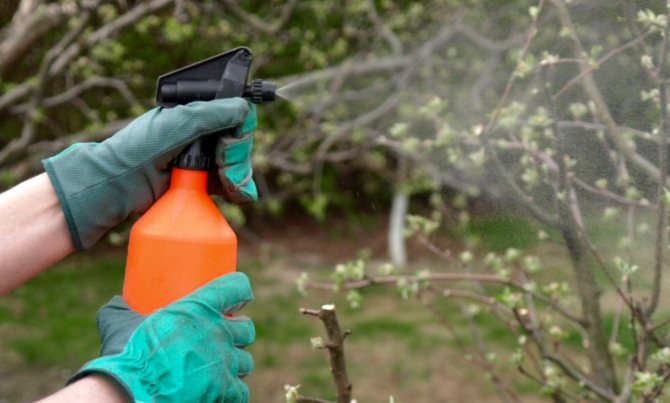


In addition, when preparing trees for the cold season, the trunks and bases of skeletal shoots are whitewashed, and the crown can be sprayed with copper sulphate (aphids, moths and moths do not tolerate it) Areas damaged by diseases or insects on trees should be removed in time and immediately burned. Places of cut branches must be treated with garden varnish, which will prevent damage to the deep layers of tissues by pathogens. In case of mass destruction of apricot trees, special chemical fungicidal or insecticidal preparations will be appropriate, the most popular of which are deservedly considered "Skor", "Aktara", "Fitosporin", "Aktelik".
Learn more about apricot tree diseases and their treatment.
Irrigation intensity
To provide the tree with high-quality watering, it is necessary to organize a small hole along the edge of the trunk circle, into which the irrigation liquid will be poured. The diameter of the circle will grow annually, which means that the deepening needs to be diverted further and further from the center of the stem.On average, at the initial stages of Lel apricot cultivation, the deepening is no closer than 30–40 cm from the trunk, and about 20–30 liters of water are consumed per tree at a time. With the age of the plant, the volumes of irrigation liquid increase, bringing the values to 45–50 liters per adult tree.
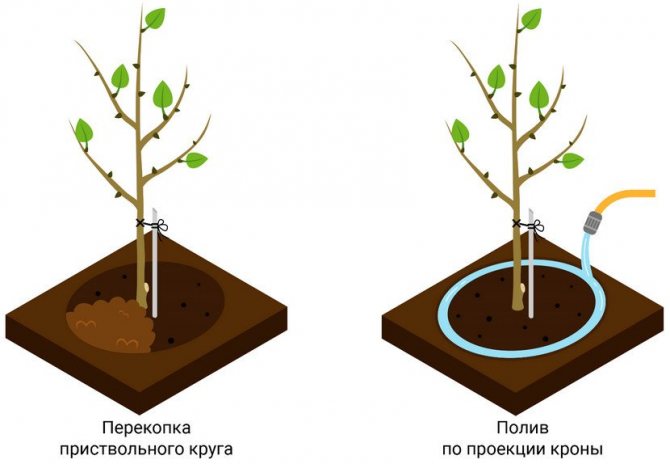

The apricot is watered in circular grooves located around the trunk so as not to expose the roots The same amount of water is required for plants during the period of ovary formation and fruit ripening, and the rest of the time the apricot can be left un-watered (provided that the summer is moderately hot and there is sufficient natural precipitation ). On average, adult plants are watered about 3-4 times a season, ending the active growing season with water-charging irrigation (performed in October and provides for the use of 50-60 liters of water per plant).
Feeding scheme
The choice of a suitable fertilizer and the peculiarities of performing the feeding procedure itself directly depend not only on the age of the plant, but also on the season: spring, summer or autumn. With the arrival of the first heat, before flowering and immediately after it, nitrogen-containing substances (for example, urea) are introduced under the apricot, at the rate of 30–40 g per 1 m² of the trunk circle. In the same period, once every 2-3 years, you can add rotted compost (5-6 kg per 1 m²), manure or bird droppings (300 g per 1 m²), previously dissolved in water in a ratio of 1:10.
You will be interested to know why the apricot tree does not bear fruit.
For the summer period, foliar dressings are more characteristic, which are applied by spraying the formulations (2–5 liters per plant). Usually, the preparations used for such treatments contain iron, a solution of boric acid and manganese sulfate, and in case of homoses or cracking of fruit seeds, root feeding with slaked lime (300-500 g per 1 m² of the trunk circle) will be appropriate. There is nothing complicated in such a fertilizer: you just need to mix the selected substance with the soil, evenly distributing it in the soil.
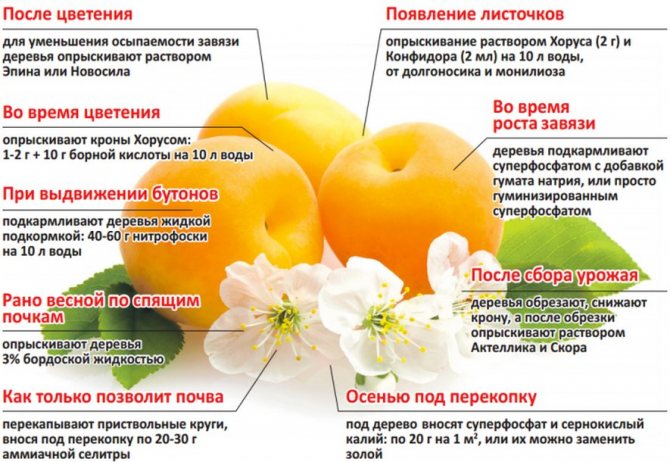

For feeding apricots in autumn, they usually use wood ash and chalk, at the rate of 300-500 g per 1 m² of the territory. As with lime, all you need to do is mix the substance evenly with the soil. It is most logical to perform the procedure while digging the soil in the aisles
Pruning and shaping the crown
Formative and sanitary pruning of apricot trees, like other plant maintenance activities, should be performed on a regular basis, which will guarantee the limitation of the spread of diseases and pests, as well as optimal ventilation and illumination of fruit trees with sunlight. In the first spring days, all damaged, broken and diseased branches are subject to cutting, and if necessary, this procedure can be repeated in the autumn.
Important! When pruning, always remember the principle of subordination of branches: on the first tier there should be the longest branches, on the second it is shorter and on the last one, even shorter ones.
As for the formative pruning, then all actions are performed according to a certain scheme:
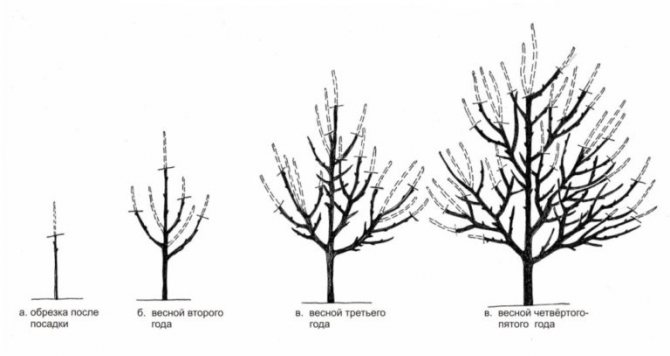
- In the first year after planting a young seedling, only the main, central shoot, the very top of the plant, are shortened, and then only by 3-4 buds (the remaining height should correspond to 80-100 cm so that the first tier of the apricot is well formed).
- In the second year a young plant has lateral branches that should be cut to 1/3 of their original length. In this case, only 2–3 of the strongest branches are left, located strictly horizontally, growing in different directions. The rest of the shoots are cut “on the ring”. The apical part of the main conductor is also subject to pruning, and the cut should be performed at a height of 60–80 cm from the branching of the first tier (from the lateral, uppermost shoot). This forms another tier, the distance to which should be no more than 50 cm.A distance of 10-15 cm is allowed between individual branches of the same tier, with a total stem height of 80-100 cm.
- In the third year cultivation, you will have to shorten the side branches again, and also cut off the young shoots of the second order by one bud (about 1/3 of the total length). In addition, do not forget to leave 2 shoots of the second tier, also having previously shortened them by 1/3 of the entire length. The top of the central trunk must also be trimmed again, necessarily at a distance of 30–50 cm from the second tier. During this period, the main central trunk should remain alone, and all competitive lateral shoots will have to be removed “on the ring”.
- The next, fourth year of growing a seedling - the last stage of crown formation, however, provided that only three tiers are planned. All actions are performed similarly to the previous activities, except that when forming in three tiers, it will be necessary to leave two main shoots, and cut the top "into a ring", transferring it to a side branch (third branch).
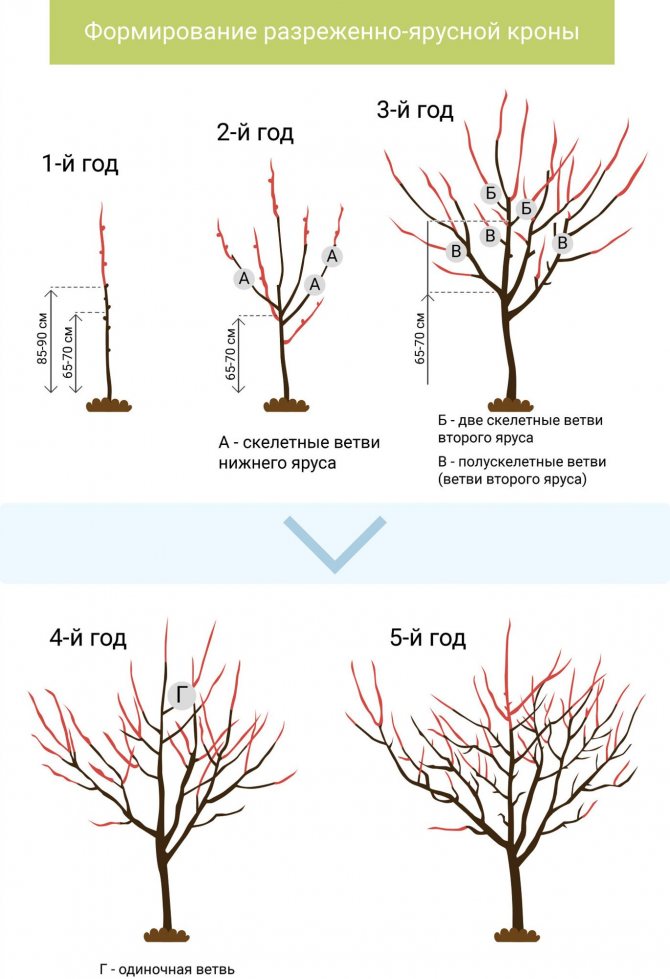

After five years of cultivation, rejuvenating and sanitary procedures are performed instead of formative pruning. The optimal height of an apricot tree for harvesting is 3.5–4 m, although, if possible, a two to three meter plant can be formed.
Preparing for winter
When growing apricot Lel in the southern territories of Russia, it is likely that even very young seedlings will survive the winter without their usual shelter, but in the central or northern regions this probability is not so high, therefore, if possible, it is advisable to play it safe using agrofibre or any other material for shelter organization. Preparation of apricot Lel for winter begins with harvesting fallen leaves, sanitary pruning of the crown and digging the soil in the trunk circle.
Read how to insulate apricot trees for the winter.
In the future, it is necessary to clean the bark, whitewash the trunks and the base of the skeletal branches, and only then proceed to the use of agrofibre or any other insulation material. Dried (not fresh) sawdust can be used from natural insulating materials, but then you have to take care of additional protection from rodents.
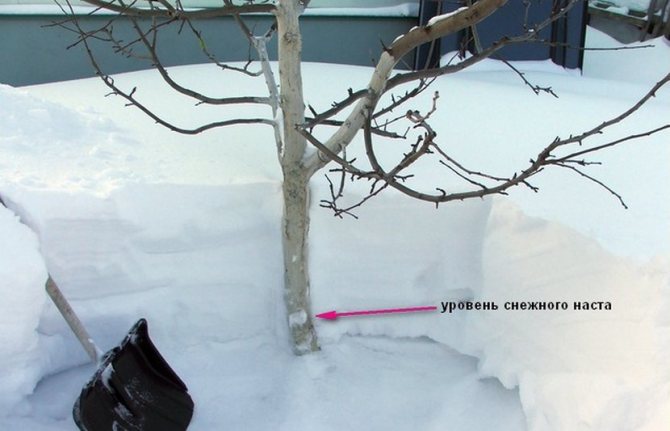


In addition, after the first snowfall, it is useful to heat the snow on the tree trunk, however, this recommendation, to a greater extent, applies to adult plants.Sometimes, to protect the branches of the crown from frost, a mixture of slaked lime, powder clay, copper sulfate and office glue is applied to them, and to protect apricots from rodents, their trunk is wrapped with pine or spruce branches. The soil in the near-trunk zone can be mulched with peat chips or humus, which must be laid on the surface of the earth in a ten-centimeter layer. At the very base of the trunk, a small embankment is made from such soil, up to 20-25 cm high.
Reproduction
Apricot Lel is propagated vegetatively (i.e. by grafting), by cuttings or grown from seeds.
The last of the options is used to obtain new varieties. Apricots, which are grown from stone, have a high survival rate and frost resistance. For planting, seeds are selected from the ripe fruits, then a test is carried out for their quality. The bones are immersed in a container of water. Those of them that float up are unsuitable for landing. Then a stratification procedure is carried out based on temperature differences. The seeds are planted in a pot and await germination. When the seedlings get stronger, they are planted in the ground, taking into account all the requirements for planting this tree.
Cutting is a highly ineffective way of propagating apricots. Cuttings, as a rule, do not take root, and green ones give very little results. In addition, the apricot grown in this way has a low viability.
Grafting is considered the most popular way to propagate apricots.It takes root well on seedlings of cherries, plums, peaches, etc. Good results can be achieved by grafting cuttings using the improved copulation method or under the bark, which gives the highest survival rate. The most favorable time for such manipulations is at the beginning of May.
Pollinators
Female and male flowers grow on apricot trees of the Lel variety. This allows the plant to be considered self-fertile. However, in some cases, for example, when some of the flowers are damaged by fungal diseases, insect attack or frost, experienced gardeners are advised to plant other varieties of apricot on the site. Trees of varieties Iceberg, Alyosha, Aquarius are good pollinators for Lel apricot, which can support and increase its yield.
Photo gallery: suitable pollinators for apricot cultivar Lel


Variety Aquarius annually pleases gardeners with bountiful harvests


The Alyosha variety is distinguished by good frost resistance.


The fruits of the Apricot Iceberg variety are distinguished by good keeping quality and transportability.
Diseases and pests
Among the diseases affecting the apricot Lel, one can distinguish the Vals mushroom, moniliosis, bacterial spotting, cytosporosis, verticillosis, gum lesions and perforated spotting. There are different ways to deal with them. It is imperative to remove the affected fruits and leaves. Treat the tree with Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate or other fungicidal agents.
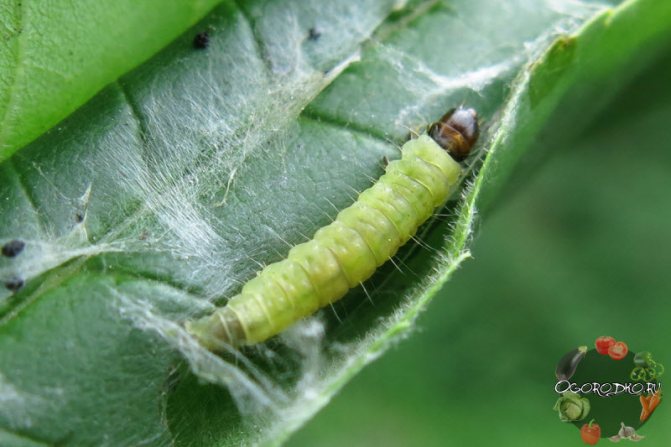
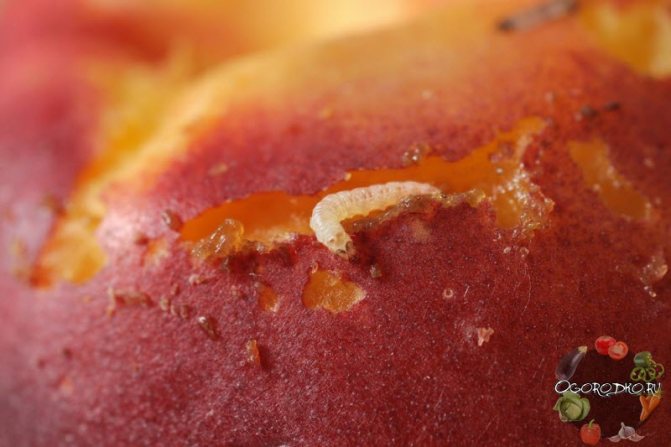
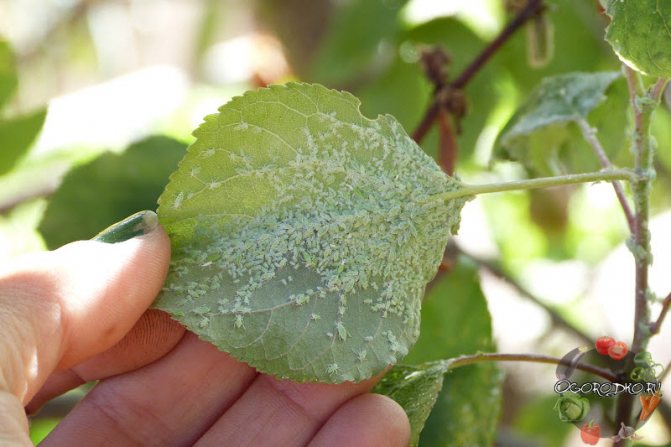
Among insects, aphid, leafworm and stalk are a threat to apricot, insecticides and herbal infusions will help get rid of them.


Self-fertility is a gift of nature to northerners
The apricot tree has a compact crown, reaches a height of three meters, and grows slowly. The appearance of the apricot is very beautiful: in the spring the tree attracts the eye with its bright, fragrant flowering, in the summer - with ripening fruits, in the fall - with red-orange dense foliage.
The variety was bred in 1986 by breeders Alexei Skvortsov and Larisa Kramarenko on the basis of the Main Botanical Garden in Moscow. In 2004, apricot Lel was included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements and recommended for zoning in the regions of the Central Federal District.
For the successful spread of apricot to the north, various measures were taken. And they sowed the seeds of the fruits they liked in more severe conditions, and crossed varieties of common apricot, common in the south and in the Caucasus, with wild species, but the best results were obtained by grafting common apricot on a plum or cherry-plum stock.
The variety was created at the end of the twentieth century, and since 2004 has been included in the State Register. It is recommended to grow Lel apricot in the Central region. The tree does not grow large, has a not very dense, wide crown. The variety is early-growing, in the third year after planting it begins to yield a crop of a very early ripening period. However, gardeners note the frequency of fruiting.
The skeleton of the tree is formed by smooth, straight, dark red shoots. The apricot begins to bloom before the leaves appear. The flowers are large, have five white-pink petals. There are five sepals, dark red in color. When blooming, a delicate sweetish aroma spreads around the trees.
Leaves are dark green, round-ovate, with a pointed tip, smooth, shiny. The fruits are round, orange, but if allowed to ripen completely, they are filled with an intense red blush. Covered with soft, weak down. The average weight of fruits is 18 g. Orange pulp, juicy, very tender, sweet and sour taste, received the highest tasting score.
Apricot Lel is winter-hardy, shows average resistance to clasterosporium disease and practically does not suffer from aphid attacks, less than 1% is damaged.
Few fruit trees have the ability to self-pollinate. It is imperative to have two varieties in order for an ovary to form in an apple tree, a pear tree, and in some varieties of apricots. You can find out whether the Lel apricot is self-fertile or not by looking at the structure of the flower.If there are stamens with pollen in a flower and an ovule is a pistil, then self-pollination is possible. It is these flowers that are present on the apricot, but not all. Some require cross-pollination. Therefore, the yield will be greater if more than one tree grows on the site. It is even better if there is a pollinator, for example, Aquarius.
Self-fertility is one of the methods of procreation. Apricot blooms early, there are no pollinating insects yet, or few. So nature has presented the possibility of self-pollination. By the way, to preserve the species, not all seeds from the batch will sprout in the first spring, they will remain dormant, as a reserve in case of seedlings death due to bad weather. They will rise in the years to come.
Apricot Lel was bred in 1986, and in 2004 it was entered in the state register. The authors of the variety are domestic scientists Larisa Kramarenko and Alexey Skvortsov. The productive period begins 3-4 years after planting. The tree bears fruit annually. The harvest ripens in mid-July. If there is a pollinator nearby, you can get about 20 kg of fruit from one adult tree.
Winter hardiness is high: both wood and buds can withstand frosts down to -30 ° C, and flowers up to -1 ° C, which makes it possible to grow this variety, including in the Moscow region. True, young trees can suffer during winter thaws with sudden temperature changes, which lead to cracking of the bark and freezing of buds. In this case, the frostbites should be cleaned up to living tissue and covered with garden varnish.
Claterosporium resistance is medium, and high resistance to aphids. Under unfavorable conditions, the tree can be affected by gum flow, Vals fungus, perforated and bacterial spotting, cytosporosis, verticillosis. Lel tolerates drought quite well.
The self-fertility rate is high, but the presence of other apricots nearby, blooming at the same time, helps to increase the yield. Good pollinators for apricot Lel are the varieties Aquarius, Iceberg, Alyosha. Pollinators are especially important when grown on an industrial scale. The soil should be fertile and loose, it should allow water and air to pass through well, and to a great depth. The variety reacts very badly to excess moisture: the depth of the groundwater must be at least 3-4 m.
A mature tree requires 3 to 6 waterings per season, depending on the weather. It is desirable that the soil is neutral - acidity provokes diseases of the root system.
The site must be well protected from the north wind and drafts. Good lighting is important, especially in the morning. When planting several seedlings, the distance between the rows should be 6 m, between the trees of the same row - 4 m.
This variety is most successfully propagated by grafting. Planting seeds is possible, but varietal qualities may suffer in this case. Reproduction by ordinary cuttings (without grafting) most often ends in failure. According to a number of experts, plum is the best stock, in particular such varieties as Tulskaya Chornaya, Eurasia 43, Skorospelka Krasnaya.
Testimonials
As a rule, the apricot (variety Lel) receives positive reviews from gardeners. The fruits, although not large, are quite juicy. The firm flesh has an excellent sweet taste with a slight sourness.
Many gardeners note that the planted seedlings take root well, grow normally and winter well. It is only necessary to carry out prophylaxis against pests and diseases in time.
Almost everyone, without exception, recommends protecting apricot trees from the cold wind, because they are afraid of them. Therefore, for planting, you must choose a sunny and quiet area of the garden.
Varietal features
Apricot Lel is distinguished by a number of varietal characteristics that must be taken into account when growing:
- resistant to various pests and diseases (aphids or clasterosporia);
- bears fruit early, only the varieties Alyosha and Iceberg are ahead of Lel in ripening rate;
- the presence of a rather large bone - up to 12% of the fruit volume;
- long life expectancy - with good care up to 100 years;
- low calorie content - only 44 kcal per 100 g.
- saturation with useful substances - vitamins B, C, P, H and microelements (phosphorus, iodine, folic acid).
The fragrant fruits of the tree are used for eating raw, they are used to prepare jams, compotes, fruit drinks, juices. The use of juices is recommended in the fight against anemia and in diseases of the liver and cardiovascular system. For newborns, it is recommended to use Lel apricot puree for the introduction of complementary foods, since it is hypoallergenic.


Nuances of cultivation
Planting apricots of the Lel variety on your own garden plot will be relevant if you follow the recommendations of agronomists. They relate to the requirements for terrain, soil and irrigation:
- plant crops in open, sunlit, elevated areas;
- control the composition of the soil. The plant does not take root on black soil, clay and sandy soils. Optimal soils are loam, sandy loam, light loamy soils with light acidity;
- planting in the spring with the obligatory introduction of 20-30 liters of water.
For planting, an ordering technique is used with a distance between rows of 6 m and a distance of seedlings of 4 m. Good yields with mutual pollination can be achieved by planting only 3-4 cuttings.