Rose, as the true queen of the garden, requires special attention. Failure to comply with the rules of cultivation, adverse weather conditions on roses develop various diseases that cause fungi, bacteria, viruses. Treating rose diseases is always more difficult than preventing them from developing. Therefore, always try to carry out preventive measures to prevent diseases.

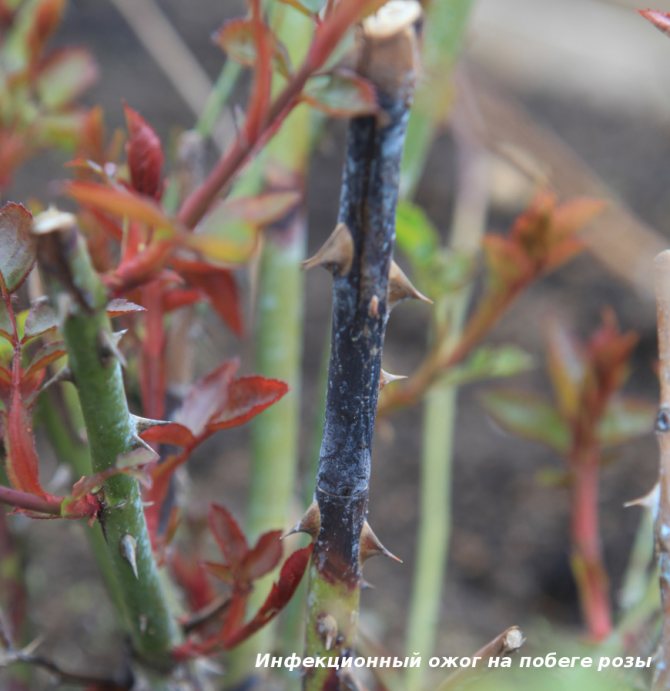
What is Rose Infection Burn?
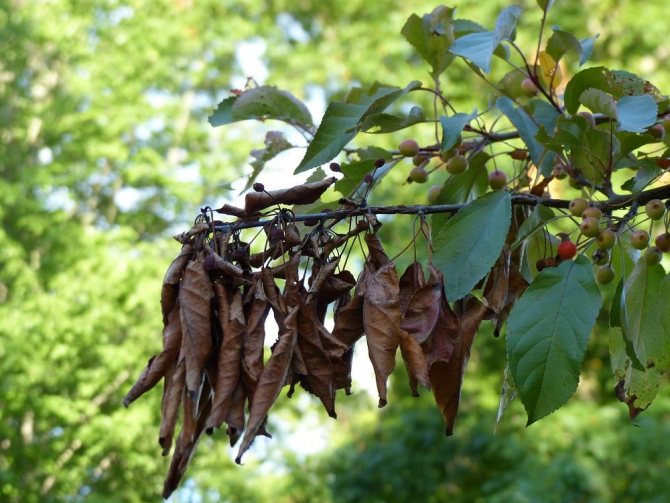
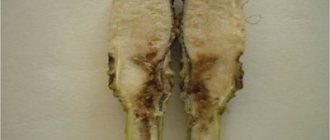
Infectious burn (stem cancer of roses) is very common in the climate of the middle zone and is easily transmitted from plant to plant. It is caused by the fungus Coniothyrium wernsdorffiae, which can grow at low positive temperatures.
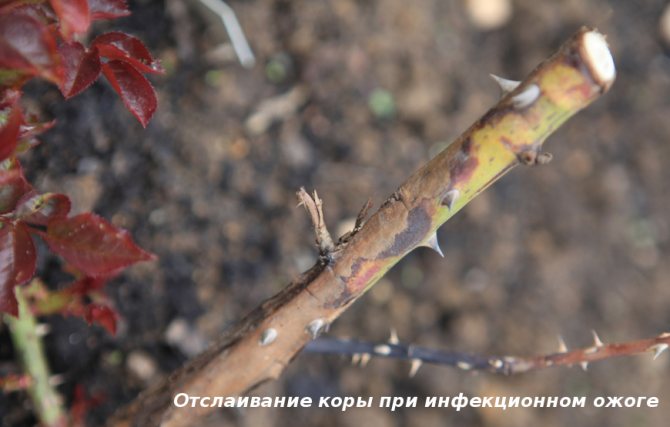
The main symptom of the disease is black necrotic spots with a red border, clearly visible on the shoots of roses. As the disease progresses, the bark dries up, cracks and flakes off, the affected shoot dies. There are no effective folk or industrial remedies for an infectious burn, prevention and timely radical action when signs of a disease appear.


Infectious burn: what to do to save roses?
Disinfect the pruning shears before moving from one bush to another. The causative agent of an infectious burn is often transmitted from diseased plants to healthy ones through gardening tools.
Be careful when trimming. Any accidental injury to the cortex can be the gateway to infection.
Wash the wounds on the bark with a 1% solution of copper sulfate (1 tbsp. L with a slide for 1 l of water), they can also be covered with tetracycline ointment, which is sold in pharmacies.
Remove unripe shoots. In severe frosts, they will die, and during a thaw, dead tissue will become a focus of infection.
Respect pruning times. Roses are pruned around the second half of October, when night temperatures drop below freezing.
Be sure to remove the leaves before hiding. Otherwise, under the shelter, evaporation from the leaves will continue, and high humidity creates conditions for the development of fungi.


Before the shelter of roses
Treat roses with a 3% solution of Bordeaux liquid (300 g of copper sulfate and 450 g of quicklime per 10 liters of water) to prevent fungal attack.
Hilling rose bushes with dry soil up to 30 cm high. Hilling helps preserve the buds and protect the base of the bush from freezing. In no case should the land for hilling be raked around the bush: you can bare the roots. Humus or compost can be used instead of soil, but it is categorically impossible to replace it with peat, sand or sawdust: these materials tend to accumulate moisture and can freeze over in winter, which will damage the bark of the shoots. The soil between the bushes is sometimes covered with crushed bark or old straw manure.
Remove all plant debris: it is unacceptable that they end up in the shelter together with the roses. It is recommended to incinerate the leftovers and not use them for compost.
How and when to cover roses?
Choose the right weather. Do not cover roses on a rainy day: the high humidity under the cover creates a favorable environment for the development of fungi. The weather should be dry, calm, moderately cold (up to - 7 ° С, with the exception of standard roses).
Work carefully. Your task is to prevent accidental damage. This is especially true for climbing and standard roses.Climbing roses are bent in several passes so as not to break the shoots. Stamp roses are covered at temperatures above zero, since in the cold the wood becomes fragile and there is a risk of damaging the trunk. It is impossible to lay bent roses directly on the ground: a layer of spruce branches must be laid between the shoots and the soil.
Consider airing the shelter during the winter. Warm weather and high humidity are precisely the conditions under which the causative agent of an infectious burn is most active.
Rules for caring for roses at home
A home rose is able not only to please the eye, but also to decorate the space of an apartment, only if it is healthy. This is evidenced by its dense, green foliage. If the leaves and buds turn yellow, fall off, then the plant needs to be treated urgently.


Home rose
The right place for a rose
The rose feels good on the southern or southeastern windowsill, only it should be shaded from direct rays. In winter, for regular flowering, it is worthwhile to supplement the plant with a tabletop or phytolamp.
Note! Dark-colored flowerpots heat up more and dry out the substrate, so it is better to plant a rose in a light pot.
Humidity and temperature
The optimum air humidity for a rose is 50-60%, the temperature is 16-22 ° C in summer and 8-15 ° C in winter. If the air becomes dry, then urgently spray the bush with warm water. It is advisable to put dishes with water next to the rose.
Watering and bathing
In the summer season, the bushes need to be watered every day. Watering is plentiful, but the rest of the water from the pan must be poured out. The water must be settled.
Regular bathing of roses helps a lot against the invasion of pests. So that the water does not erode the soil in the pot, it is worth covering the root zone with a film before the procedure.
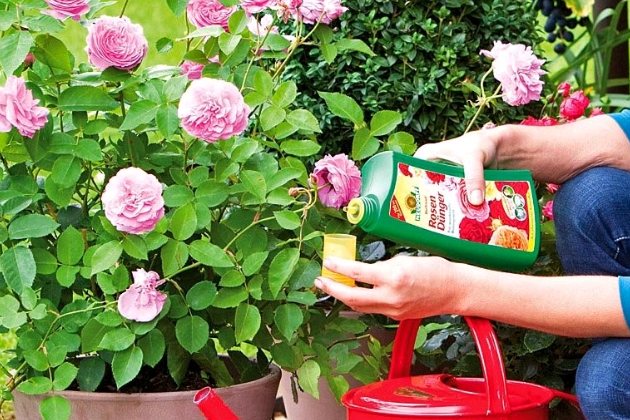
Top dressing of a room rose
Indoor roses need fertilization during the growing season. The plant responds well to organic matter (liquid mullein in a ratio of 1 tbsp. To 1 bucket of water). Can be fertilized with a ready-made compound, for example, fertika. For 10 liters of water, 1 tbsp is enough. spoons of fertilizer.


Top dressing of a room rose
Transfer
Young roses (up to 4 years old) are advised to replant every year. The procedure can be performed in early spring or late autumn.
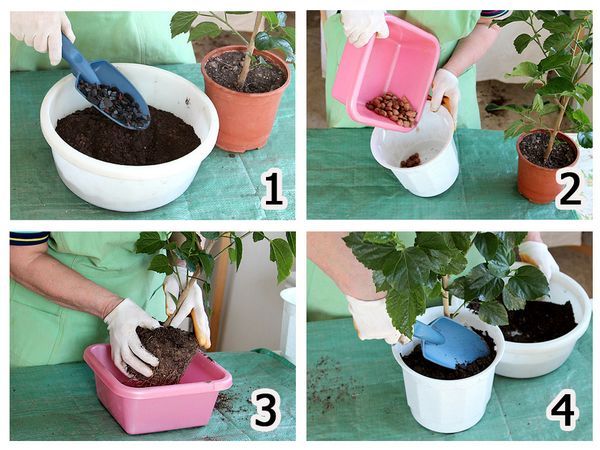
New dishes for the plant are chosen with a larger size (5 cm wider, 7-8 cm higher). The dishes must be washed with soap and dried. Then 5 cm of the drainage layer is poured onto the bottom of the flowerpot. It can be expanded clay, pebbles, crushed foam.
The soil can be used purchased. Suitable for universal or special for roses. You can also make the soil yourself from equal shares of turf soil, sand and humus. In order to avoid the development of pathogens, it is better to ignite the soil.
Then follows, in fact, the transplant. First, water the plant abundantly to soften the potting soil. This will make it easier to reach the root of the flower.
Next, the flower pot must be carefully placed on its side and the bush must be removed from the dishes with shaking movements.
If you are not sure of the good condition of the old soil, then you can quietly release the roots from it and transplant it into fresh soil. Otherwise, the rose is transplanted into a new flowerpot with a lump of earth.


Transplanting a room rose
The last stage of work is watering. Next, for about a week, the plant should not be disturbed (even watered). Top dressing can be started in 2-3 weeks.
Pruning a bush
Before going on a winter vacation, the bush is cut off. In addition to removing all damaged stems, the main branches are cut to a third of the length. Sections are immediately sprinkled with crushed coal (cinnamon powder, ash can be used).
Important! When shortening branches, remember about the correct formation of the crown.
Winter plant care
Although a room rose can bloom every 2 months, you should also arrange a seasonal vacation for it. This can be combined in time with the preparation of street roses, that is, when autumn comes. For the winter period, watering is reduced (you can just keep the pot in a damp pan), feeding stops and the temperature drops to 15 ° C.
Note! Dry hot air can lead to foliage falling, so places near radiators are excluded.
Reproduction of a home rose
Indoor flower propagates by cuttings. They are best cut during the warmer months from May to September. A partially lignified stem segment with 3-5 buds and several leaves is suitable for cuttings.
The cut stalk is dried for a couple of hours and placed in water with the addition of a stimulant in the proportion of 4 drops per 100 ml of water. Epin, root will do. It will take about a month for the roots to grow back. After their appearance, the seedling is transplanted into a pot.
At first, it is worth spraying with the same stimulant (0.1%). For good development of the bush, the first buds are recommended to be plucked.
Plant diseases
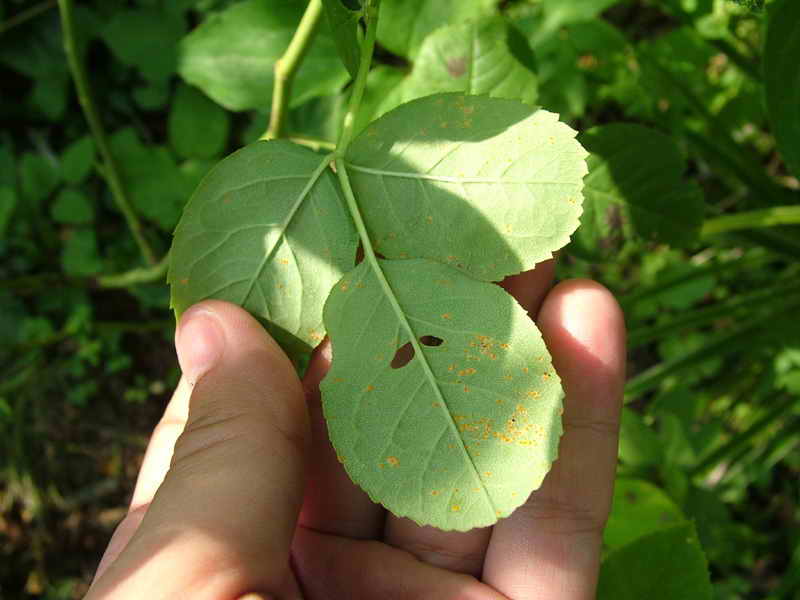
Why do roses have rusty buds? The reasons are high humidity and lack of ventilation. Under such conditions, a fungus develops on the plant, the vital activity of which leads to the formation of spots, and later the leaves and buds turn yellow, dry and fall off.
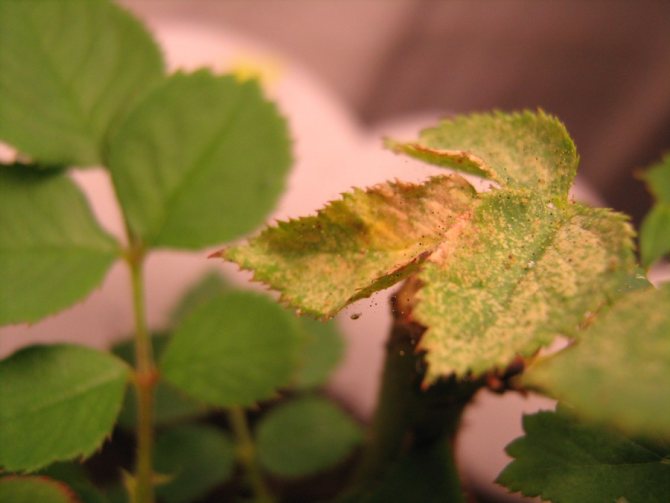


Diseases of the room rose
To get rid of the disease, the plant should be cleaned of the affected fragments and treated with an antifungal medicinal drug (topsin, foundation).
Powdery mildew is considered an equally dangerous ailment. Parts of the plant can be coated with "white flour". The disease arises from frequent temperature changes. To eliminate the disease, first remove all affected parts, and then treat the bush with a fungicide (fitoverm, actellik).
For your information! Leaf shedding can occur with prolonged cold indoors or excessive heat. To eliminate the cause, you just need to adjust the conditions of detention.
The roses still got sick. What to do?
In wet winters with frequent thaws, an infectious burn can develop despite all preventive measures, so check the condition of the roses as early as possible in the spring. If signs of disease are found, immediately trim the affected shoots to healthy tissue. If the lesion is strong, the shoot is cut out completely, then the roses are treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate. For the prevention of an infectious burn, it is recommended in the spring, for sleeping kidneys, to apply 3% iron vitriol or 5% Bordeaux liquid. Experienced rose growers recommend opening roses as early as possible - as soon as the weather permits.


The most common diseases of the leaves and stems of roses are powdery mildew, spotting, cancer, rust, cytosporosis and gray mold. If you do not fight diseases of roses, as practice shows, the bushes will bloom less, their leaves will lose their decorative effect, and soon the plants will die altogether. Check out the photo, description, methods of treating rose diseases with the best drugs and immediately start fighting ailments.
What else is good to know
In addition to powdery mildew, the rose can be susceptible to other diseases. The most common:
All the rest can be found in the reference book on diseases - there are quite a few of them. Also read the article on fungicides to know how to treat it all.


When beautiful flowers bloom in the garden, you must admit that it is pleasant, but if something happens to the flowers, the mood spoils. Often a white bloom appears on the leaves of a rose or buds and you do not always understand what to do, how to treat, how to treat it. And in this article I will try to answer in as much detail as possible all the exciting questions about this unpleasant matter.
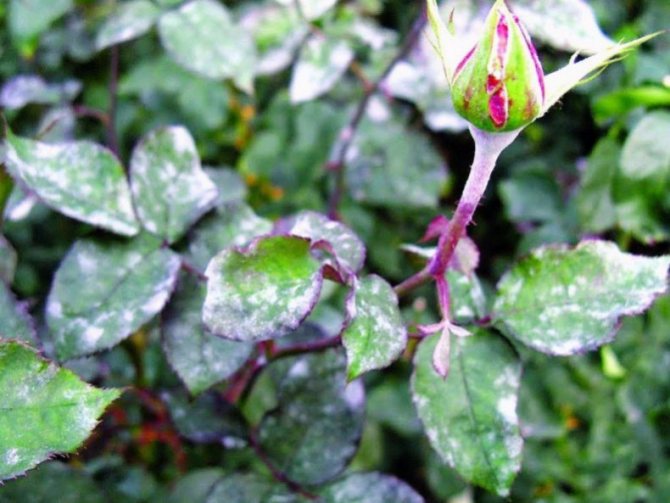
Fungal disease of roses powdery mildew: photo and treatment
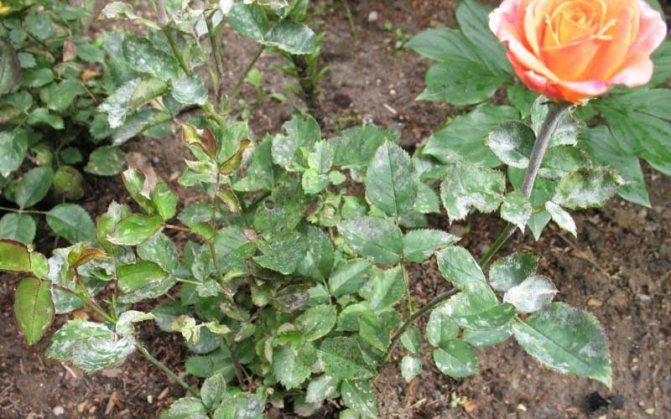


Fungal disease of roses powdery mildew in the photo
With a fungal disease of roses, powdery mildew appears on young leaves, shoots and buds; there is a thickening and curvature of them.
As you can see in the photo, powdery mildew on roses is manifested by a whitish bloom, which represents the mycelium and sporulation of the fungus:
The causative agent of the disease in the form of mycelium in the kidneys overwinters. The development of the disease is facilitated by excessive nitrogen fertilization, lack of calcium in the soil, drying out of the soil, too light sandy or, conversely, cold damp soils.
The disease develops especially strongly with insufficient lighting and high humidity. A sharp change in temperature, drafts, drying out of the earth and other conditions that disrupt the normal life of plants reduce their resistance to disease. Tea and hybrid tea roses with more delicate foliage are especially affected.
Resistant to powdery mildew are varieties of roses that have dense glossy leaves such as "Gloria Day".
For the treatment of powdery mildew on roses, when the first signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to spray the bushes with Topaz, Purest flowers, Fundazol or Skorom. At temperatures above 22 ° C, spraying with "Gray colloid" or "Tiovit Jet" is possible. If necessary, to combat this disease of roses, the treatments are repeated as young growth and powdery mildew spots appear on them.
Why does white bloom appear on the leaves and buds of roses
There may be several reasons for the appearance of white bloom on roses:
- Powdery mildew (downy mildew);
- Gray rot;
- Pests (spider mites, rosaceous scale insects, rosé leafhoppers, etc.)
Most often, roses are affected by powdery mildew. Powdery mildew can be real and false. Next, we will talk about how they differ, and what symptoms they have.
Powdery mildew
Powdery mildew loves to settle on young shoots, leaves and buds. Favorable time for her is late summer and early spring. The causative agent is parasitic fungi. The disease spreads very quickly, as doctors say, by airborne droplets. The disease can be brought into the garden with a diseased cuttings.
The reasons for the appearance of powdery mildew:
- Excess nitrogen fertilizers;
- High humidity;
- Dry soil around the roots;
- Dense planting of rose seedlings;
- High air temperature.
Powdery Mildew Symptoms
At the initial stage, a grayish (closer to white) bloom appears on the leaves in the form of spots on both sides of the leaf (below and above). Gradually, the leaves curl, dry up and fall off. Shoots acquire a curved shape, flowering stops, the plant begins to lag behind in growth. As a result, the rose loses its attractive appearance.
Unfortunately, powdery mildew is quite difficult to treat, therefore, it is better to carry out prevention and choose resistant varieties. Resistant varieties include roses with hard, shiny foliage, but roses with soft, matte leaves are more susceptible to this disease.
How to treat roses for powdery mildew
If a white bloom on the leaves of roses appeared due to this disease, then the sooner you start the fight, the more chances you have to save the plant. In the initial stages, you need to remove all diseased leaves, shoots, or buds and burn them.
Next, spray the plant with horsetail infusion: pour 1 kg. fresh herbs or 150 grams of dry bucket of water and let it brew for a day. After a day, the infusion must be boiled for 30 minutes, allowed to cool and filtered. Store the prepared solution in a plastic container. Before use, it is diluted with water 1: 5.
You can treat a diseased plant with nettle infusion. The infusion is prepared from 1 kg. fresh nettles (or 200 grams of dried) and 5 liters of water. Leave to infuse for 2 weeks, stirring the solution daily.When fermentation begins, some drill meal is added to the solution (to reduce odor). The finished infusion is filtered and diluted in water 1:10.
You can also prepare a solution of 2 parts of ground sulfur and 1 part of lime. Pollinate roses with this solution in warm, dry weather. Before processing, the rose is sprayed with warm, clean water.
Helps to cope with powdery mildew copper - soap solution, which is prepared from 300 grams of laundry soap (grate) and 9 liters of hot water. Dissolve the soap in water. Copper sulfate is diluted with water in a separate bowl (30 g of copper sulfate are taken for 9 liters of soap solution). When copper sulfate is diluted in a small amount of water, it is poured into a soapy solution in a thin stream, stirring constantly.
The prepared solution is allowed to cool and the roses are sprayed.
You can also treat the rose with colloidal sulfur (dilute 100 grams of sulfur in 10 liters of water).
Downy mildew
This disease is caused by parasitic fungi that appear in the winter on the remnants of rose leaves. Damp and hot weather or excessive watering contributes to the manifestation of this disease.
Downy mildew symptoms
Unlike powdery mildew, with this disease, a white bloom appears on the leaves of the rose from the lower part of the leaf. This plaque is more like mold. Over time, the white bloom changes color to brown, or red, the leaves are deformed.
What to do
It is important to see the disease at the initial stage, since at the beginning of the disease, the plant can still be saved by removing the affected parts of the plant and burning them.
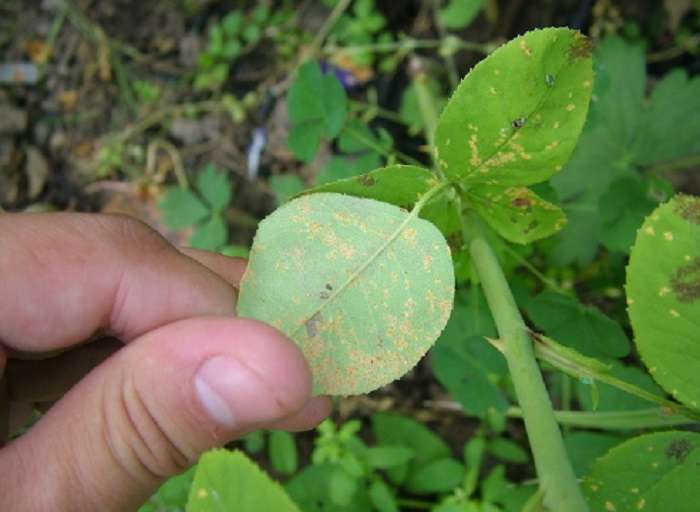
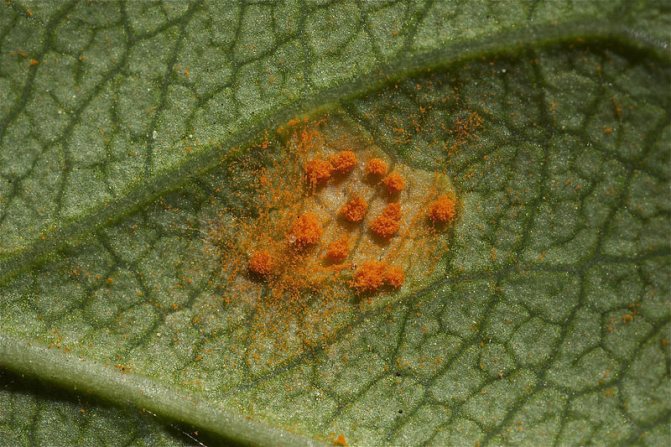
Rust of roses: photo and treatment in the fight against the disease
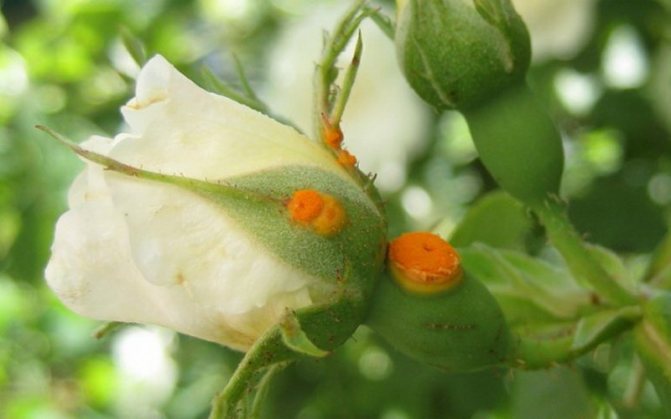


Rust of roses in the photo
With this disease of roses in flowers, the affected parts of the shoots are bent and thickened. In spring, orange dust appears on the stems at the opening buds and at the root collar. These are spring sporulation of the fungus - the causative agent of the stem form of rust. The fungus overwinters in plant tissues infected in previous years. The disease develops more intensely in years with warm and humid springs.
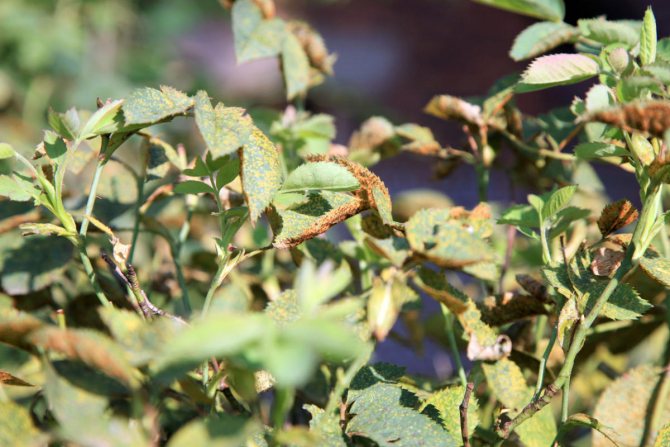
Rose leaf disease black spot: photo and how to treat
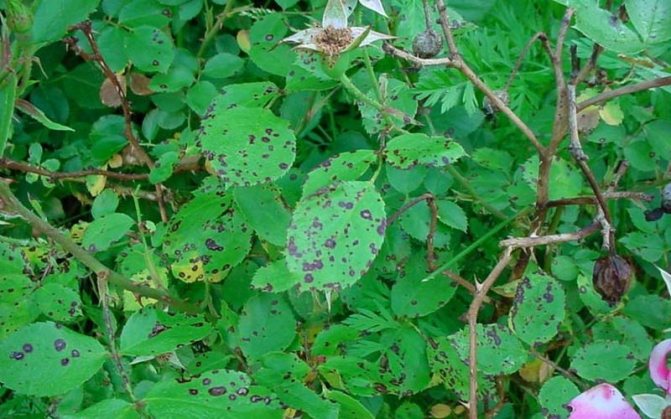


Rose leaf disease black spot in the photo
Disease of roses black spot is also called marsonina after the name of the fungus - the causative agent of the disease. In the second half of summer, dark brown, almost black, spots of various sizes are formed on the leaves. Leaves turn brown and often fall off prematurely. Spots can also appear on the green bark of annual shoots.
Plants with prematurely fallen leaves sometimes start to grow again, as a result of which they are greatly weakened and bloom poorly the next year.
Under the skin of the leaves, the mycelium of the fungus develops - the causative agent of the disease of roses, spotting, forming radiantly growing strands.
As you can see in the photo, with this disease of roses, the radiance is clearly visible at the edge of the spots:
This disease of rose leaves is more pronounced with a thickened planting, in shaded places, with poor ventilation of the site.
Measures to combat this disease include:
- correct agricultural practices that increase the resistance of plants;
- careful collection and in the fall of affected leaves and burning them;
- spraying plants during the growing season with preparations containing copper, which are used to combat rust.
- for the treatment of this disease of roses, it is recommended to use a special preparation (Skor to protect roses) for spraying, which is a systemic fungicide of preventive and curative action.
Treatments must be started when the first signs of the disease appear and repeated after each rain or abundant growth.
These photos show how to treat black spot rose disease:
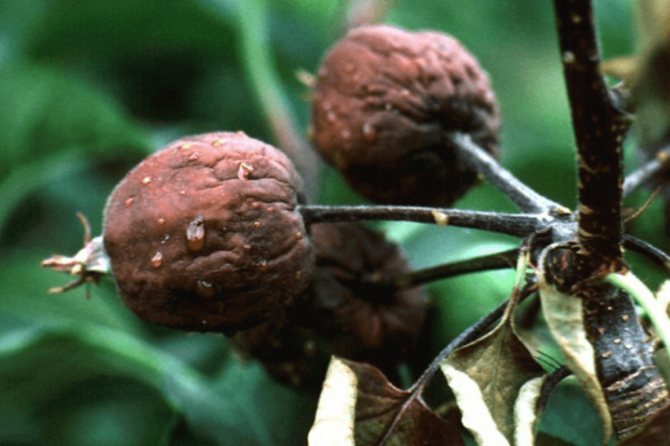
Rose bacterial cancer disease: photo and treatment of flowers
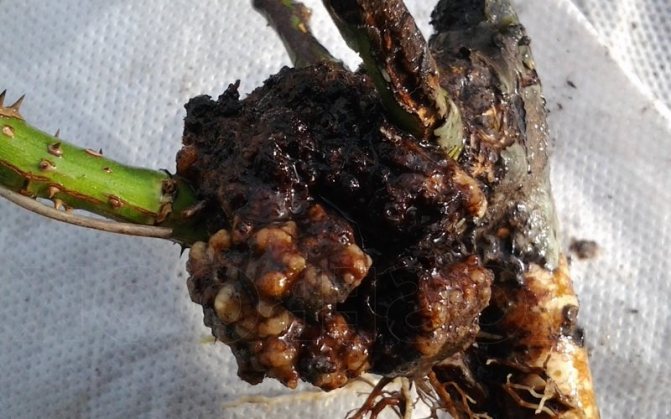


Disease bacterial cancer roses in the photo
With bacterial cancer of roses, growths of various sizes are formed on the root collar and roots of plants. Sometimes they are barely noticeable, but often reach several centimeters in diameter. The growths have an uneven tuberous surface. They consist of soft tissue, at first white, then brown, and in the soil are decomposed by bacteria.
There are also hard lignified growths that grow every year. Less often, the aboveground part is affected - trunks and branches, mainly in climbing and standard remontant roses. Here, lumpy nodules and tumors of various sizes are formed.
The cancer-causing bacteria infect many plants belonging to different families. Infection occurs through wounds on the roots of plants, from the soil, where bacteria can persist for a very long time.
The development of the disease is facilitated by high soil moisture, abundant manure fertilization, root damage, and an alkaline reaction of the soil.
When transplanting a plant with an affected root collar, it is necessary to destroy, and cut off the growths on the lateral roots. To treat this disease of roses, after pruning, the roots are immersed for 5 minutes in a 1% solution of copper sulfate, and then washed in water and dipped in a liquid mixture of clay and sand. Avoid excessive manure fertilization, destroy insects that damage the roots, do not dig up the soil near the bushes.
Look at the photo of rose cancer treatment:
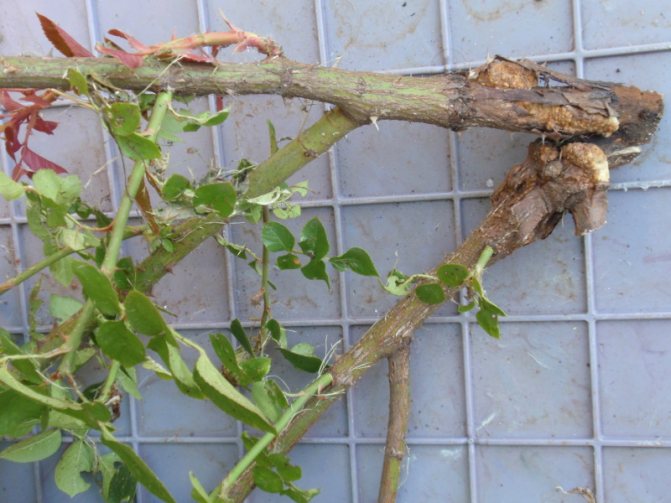
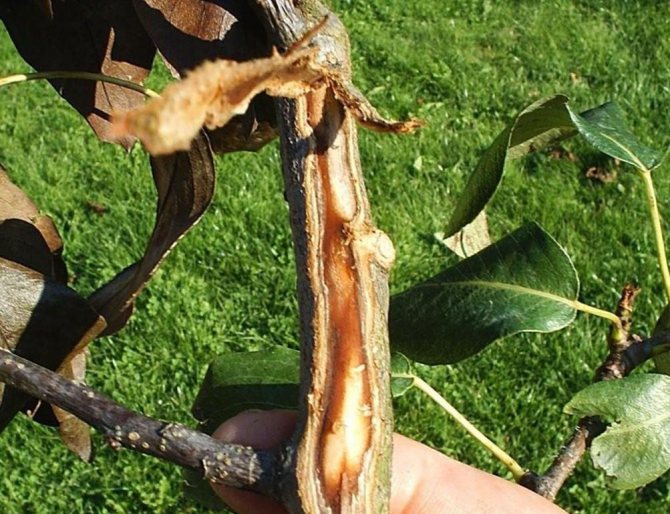
Stem cancer
Stem cancer
The reasons. Infection of a flower with cancer can occur as a result of rain, a contagious insect, poor soil and is often due to external damage from gardening tools. As a result, the bark begins to die off, and on the shoot the lesions become brown or yellow. The leaves dry up and curl, but stick to the stem.
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: Table salt in the country - unusual ways of using
Treatment. Infected shoots and stems should be cut immediately with disinfected garden shears. A solution of 3% zinc sulfate is usually used for processing. For the complete destruction of the disease, regular frequent treatment (2–4 years) is required.
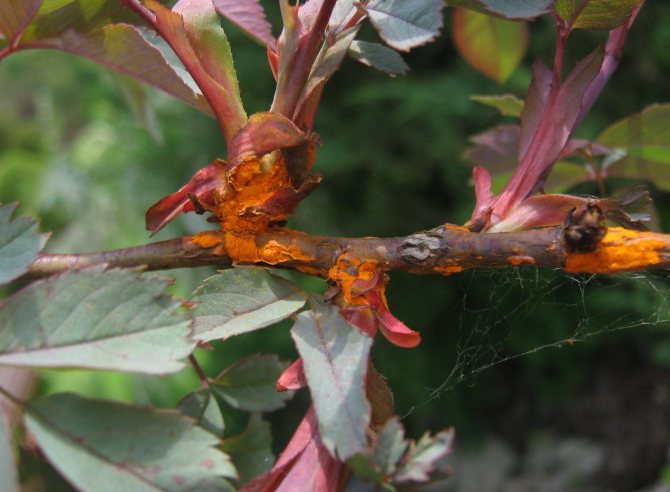
Fungal disease burn of rose branches: photos and control measures
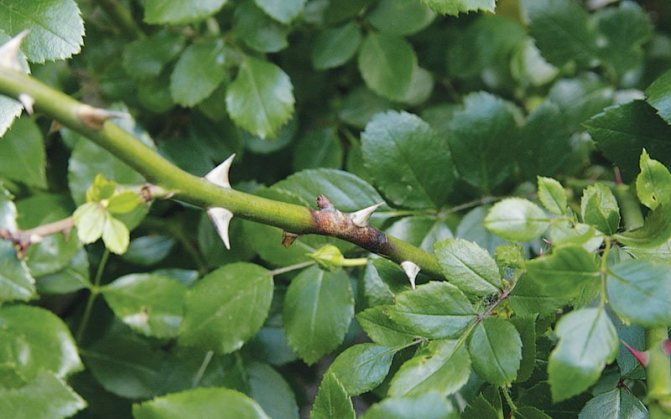


Fungal disease burn of the branches of roses in the photo
Branch burn is a fungal disease in which, on the branches, first reddish spots appear, later darkening in the middle; the reddish-brown edging persists for quite a long time. Growing up, the spots ring the branches. Above the affected area, tissue build-up may form. Diseased branches usually dry out at the end of summer.
Excess moisture under the winter shelter contributes to the development of the "burn".
To avoid severe damage to roses, you should remove the shelter earlier in the spring. Sick and frozen branches must be cut and burned in a timely manner.
As shown in the photo, when treating this disease of roses, plants need to be sprayed with preparations containing copper, as in the fight against rust:
Correct agricultural technology (timely fertilization, loosening and watering) helps to reduce the harmfulness of the disease. It is necessary to achieve good maturation of wood until the end of the growing season of plants.
For the winter, plants with already fallen leaves should be covered, if possible, in dry weather, so that high humidity is not created under the shelter. Before the shelter, unripe shoots with green leaves are removed, and the plants are sprayed with a 3% Bordeaux mixture or 1.5% ferrous sulfate solution.
Treatment of roses to protect against cytosporosis disease
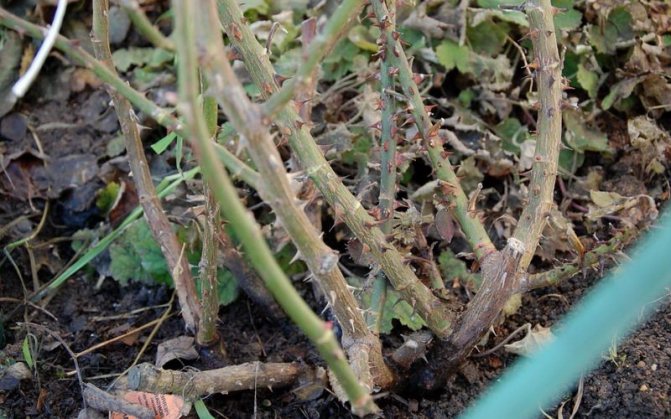


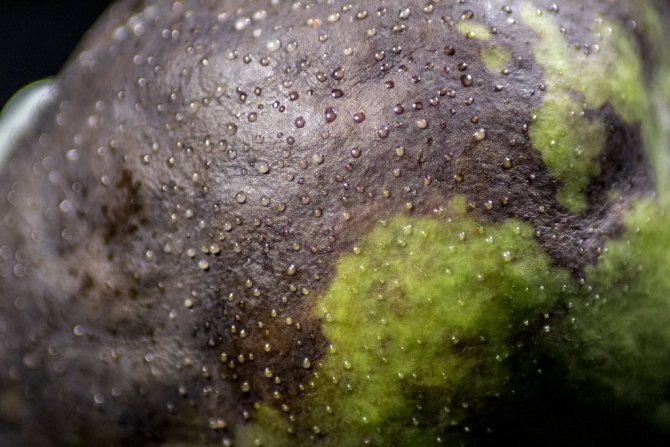
Cytosporosis is a fungal disease of roses in the photo
Cytosporosis is a fungal disease that is ubiquitous. Roses are struck by a number of ornamental shrubs, as well as pome and stone fruit trees, and nuts.
Cytosporosis is also called infectious desiccation. In some years, it leads not only to the drying out of individual branches, but also to the death of plants.Bushes that are weakened as a result of freezing, drought, sunburn, untimely pruning, etc. are especially susceptible to this disease.
Mosaic
Mosaic
The reasons. A virus that appears during the cultivation of roses. The disease begins to manifest itself clearly only in hot and dry weather. Represents yellow patterns on the leaves of the plant. The carrier of the infection is aphids or infected garden tools. The disease is so strong that it can easily be transmitted by contact of the roots.
Treatment. Rarely leads to the death of the plant. To avoid disease, it is necessary to carefully examine the seedlings. You can get rid of the infection only with the help of heat treatment in a specialized laboratory.
Gray rot on roses: how to deal with the disease
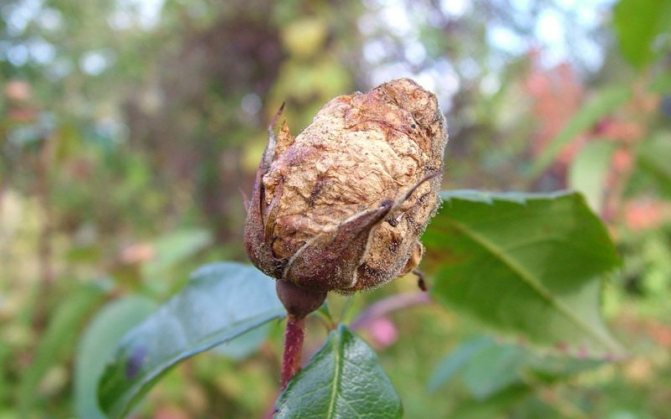


Gray rot on roses
Mainly buds with pedicels, tops of young stems and leaves suffer from gray rot of roses (botrytis) - in damp weather they are covered with a gray fluffy bloom.
First of all, this disease of garden roses attacks weakened plants, and most often - with white and light pink flowers. The buds on roses affected by Botrytis do not open, they rot and fall off. Small brown spots appear on the petals, the leaves turn yellow and also fall off.
The foci of infection remain in plant debris in the form of mycelium, which forms spores in spring. Then the spores of the fungi are carried by insects and the wind. Therefore, an undesirable "neighbor" for roses is, for example, garden strawberries, which are very susceptible to Botrytis.
Gray rot appears on roses with thickened plantings, or if the rose garden is irrigated late in the evening, when the leaves of the roses do not have time to dry before nightfall.
How to deal with gray mold of roses on a personal plot? Measures for the control and prevention of this disease of roses are the same as against other fungal diseases.
Interesting facts about rose diseases
Speaking about diseases of roses, there are several interesting facts:
- You can determine how resistant the roses are to diseases by the leaves: if they are dense and shiny, covered with a waxy bloom, the variety is resistant. The fact is that wax prevents the penetration of infection into the leaf, which means it prevents infection.
- There are no varieties that are absolutely resistant to disease. Even those varieties that are marked "disease-resistant" in the catalogs lose this valuable quality in 5-6 years, as diseases adapt to changing conditions and mutate like the flu. Therefore, old varieties of roses can be found only in the gardens of amateurs, but not in flower farms and on the streets of cities.
- Gray rot, for example, multiplies especially quickly in wet weather, and given that many gardeners plant roses densely, the soil under the plants does not dry out quickly enough after rain or watering.
- Foliage that does not dry out for a long time or cool nights, dew in the morning favor black spotting. Powdery mildew, and from pests - spider mites, on the contrary, love dry and hot weather. Therefore, roses growing near southern walls or fences are particularly affected by these pests.
- Florists can, to some extent, influence the development of diseases and the appearance of pests, as well as predict their appearance. Strong, well-groomed plants are less likely to get sick and are less likely to resist colonization by pests.
Watch the video "Diseases of roses", which shows all the main diseases of plants and methods of dealing with them:
Table of Disease Resistant Rose Varieties
By their appearance, roses are classified into the following categories:
- standard (grafted onto a rosehip support);
- shrubs (shrubs);
- ground cover and drooping;
- polyanty;
- climbing;
- patio;
- tea-hybrid, tea;
- repairing;
- floribunda.
Disease Resistant Garden Rose Varieties
| Variety name | Description of colors | Additional benefits |
| Garlands de Amour | Belongs to the group of ramblers and the category of climbing roses Small white flowers (average diameter - 3 cm) are collected in large clusters on thin stems Bush height - from 1.8 m to 3 m | Blooms several times a year, unpretentious to conditions Has a pleasant aroma, suitable for the formation of hedges |
| Prairie Joy | Is a park shrub rose The flowers are large, 6-7 cm in diameter, with a rich pink hue Terry border of petals No more than 5-6 buds are placed on the stem | Suitable for hedges, highly resistant to frost |
| Tequila | Refers to floribunda Roses are characterized by an oily yellow shade with a slight admixture of orange and pink. The size of the opened bud is 7-8 cm, there are up to 5-6 flowers on the stem Shrub height - 50-90 cm | Produces buds throughout the season Well tolerates any climate and rain |
| Angela | It belongs to the floribunda category and can be grown as a climbing rose Blooms in large clusters of several buds Flowers are deep pink with a raspberry tint in the middle, diameter - 5-6 cm The buds do not fully open Bush height - 1-1.5 m | Well suited for flower beds and parks Highly resistant to rain and low odor The bushes are distinguished by dense foliage. |
| Westerland | Scrub bush with bright buds and dark foliage It blooms in large buds (10-11 cm in diameter), which are collected in a brush of 5-10 pcs. The color scheme is a mixture of orange, yellow, scarlet and pink Wavy petals, soft, with semi-double edging Bush height - 1.5-2 m | Has a strong aromatic scent and medium rain resistance It tolerates frost well, blooms early and continues to bloom until late autumn |
| Sunny Rose | Refers to ground cover plants The buds are light yellow, after opening they fade to a creamy shade The average diameter of a rose is 3-4 cm, on the stem the buds are collected in brushes of 3-5 pieces Terry petals edge Shrubs are low (50-60 cm) | The variety is unpretentious and grows strongly on the ground Has a faint, delicate odor |
| Saremo | Refers to shrub varieties The buds have a delicate pink hue, and the flowers range from coral to light pink, depending on the time of dissolution The opened bud has a diameter of about 8 cm | Thick vertical scrub well suited for hedges |
| Siesta | Belongs to the category of scrubs Magenta flowers, average diameter 5-6 cm Up to 25-30 buds are collected in the inflorescence Bush height - 80-90 cm | Suitable for small hedges, massifs and ornamental parklands The scent is fresh, medium intensity, with a slight hint of violet |
| Perennial Blue | Is a climbing rambler Flowers purple-magenta, small diameter (3-4 cm), collected in large brushes Rose bush height - 2.5-3 m | Strong aroma Blooms early and releases new buds before the first frost |
| Pastella | Belongs to the floribunda category Blooms in large creamy cup-shaped buds (8-9 cm in diameter) The edges of the bud are colored pink, the intensity of the color depends on the weather conditions On the branches of the bush there are inflorescences of 3-8 buds The height of the bushes is 80-90 cm | Has a spicy aroma of medium intensity Blooms profusely, retains open flowers for a long time Handles rainy weather well |
Some varieties (for example, Jubilee of the Prince of Monaco) are susceptible to disease only in warm southern climates, but grow well in northern latitudes.
How to treat roses for diseases: effective remedies
Without exception, all flower growers are interested in how to treat roses from diseases. The most effective remedies for rose diseases include the following drugs.
"Alirin-B" - a biological preparation based on beneficial microorganisms isolated from natural sources. Effective against powdery mildew of ornamental and other plants.
"Glyocladin" - an analogue of the well-known drug "Trichodermin".It is effective against a wide range of fungal diseases such as fusarium, white and gray rot, late blight, root and stem rot, black leg and cabbage keel.
"Gamair" - a drug designed to protect against a wide range of bacterial diseases: bacterial leaf spots, fire blight, bacterial cancer.
"Topaz" - systemic fungicide to protect ornamental, pome, stone fruit, berry, vegetable crops and vines from powdery mildew. This preparation for the treatment of roses against diseases can be used as a protective, therapeutic and exterminating agent also against rust. The drug is available in the form of an emulsion concentrate.
As a destructive agent with a high degree of damage by powdery mildew, "Topaz" is used in increased concentrations (up to 10 ml), after 2 sprays with an interval of 7 days.
The drug provides reliable protection against powdery mildew, even against a high infectious background. Topaz is not phytotoxic, does not stain the treated leaves and fruits. As a prophylactic agent, it reduces the number of treatments, as it lasts for 40 days. The drug meets modern safety requirements for humans and the environment. It is quickly absorbed by plants, which reduces the risk of the preparation being washed off by rain
In order to avoid the appearance of resistance of pathogens of powdery mildew, "Topaz" is recommended to alternate with contact copper-containing preparations and colloidal gray and not to use on the same culture more than 4 times per season.
"Topaz" compatible with most of the drugs used in gardens for diseases and pests. The exposure rate is 2-3 hours after spraying.
And how else to treat roses from diseases and to prevent infections in the backyard?
Treatment with folk remedies
Until the fungus has grown into the internal tissues of the plant, you can try to fight it with folk methods. The main thing is not to miss the beginning. Examine the bush constantly. At the first sign, remove the affected area.
It's good if you can limit yourself only to folk methods. Still, in comparison with chemical ones, they do less harm to the environment. Less dangerous to yourself, bees and birds. They do not kill beneficial microorganisms in the soil and do not deprive it of fertility.
When spraying them, follow the general rules for preventive treatments:
Choose dry, calm weather for treatments.
If it rains immediately after spraying, repeat it when the leaves are dry.
Spray plants in the evening, but so that they have time to dry before night.
Prepare the solution as much as needed for one treatment. You don't need to store it.
Milk whey solution
- serum - 1 liter;
- water - 10 liters.
It is necessary to carry out three treatments every three days, observing the general rules for spraying.
Or prepare a solution of milk whey with the addition of iodine:
- serum - 1 liter;
- iodine - 10 drops;
- water - 10 liters.
The processing is carried out two times. The interval between procedures is a week.
Soap-soda solution
- soda ash - 25 grams;
- liquid soap - 5 grams;
- hot water - 5 liters.
Pour soda with water, add soap, mix everything well. The solution is cooled. Spray the plant and the ground under it with it. 2 treatments are carried out with an interval of 7 days.
Instead of soda ash, you can also use baking soda. Then the composition of the solution will be as follows:
- baking soda - 1 tablespoon;
- liquid soap - 0.5 teaspoon;
- water - 4 liters.
The rose is sprayed with this remedy three times, with an interval of seven days.
Mustard solution
- mustard powder - 2 tablespoons;
- water - 10 liters.
The mustard is stirred in water. The plant is watered with the solution twice every ten days.
Garlic infusion
- garlic - 50 grams;
- water - 2 liters.
The garlic is chopped and poured over with water. Insist during the day.After that, the infusion is filtered. Spray it undiluted.
Infusion of fresh manure
- fresh manure - one third of a bucket;
- water - 10 liters.
Insist for three days, stirring daily. Then drain the infused water. Dilute the resulting concentrate with water in a ratio of 1 liter of manure + 10 liters of water. And already spray the bushes with this solution.
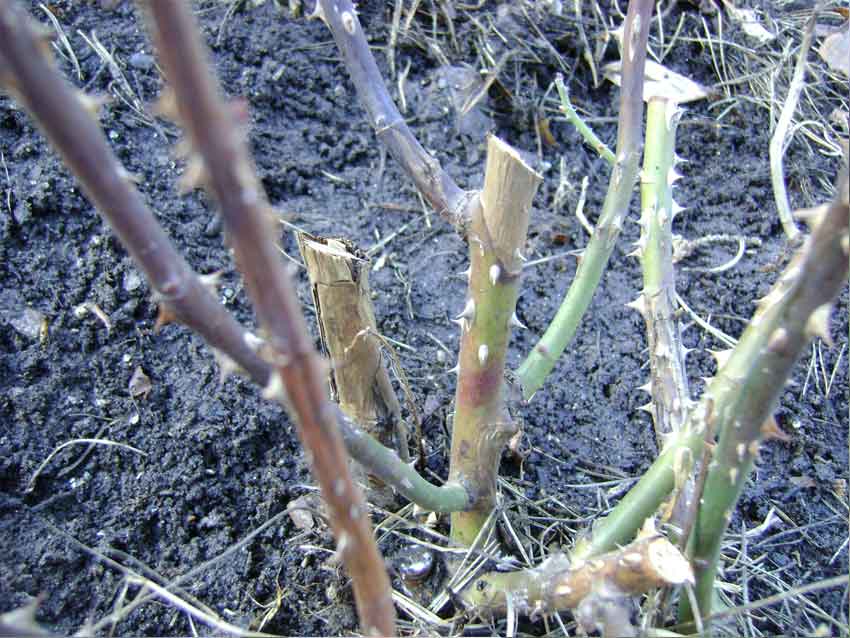
Signs of an infectious burn
Gardeners usually notice signs of illness in the spring after the protective shelters are removed from the plant. It is believed that park roses, hybrid tea and leafy varieties are more susceptible to this disease, while miniature plants and floribunda roses show some resistance to fungal pathogens of stem cancer. The most characteristic symptoms of rose damage are the following:
- reddish-brown spots that spread from the site of the primary lesion down the stem;
- black or dark brown areas of the stem, ringing the shoot;
- the appearance of small tubercles in places where the stem is affected, which represent spores of the fungus;
- clarification of the bark;
- the appearance of small ulcerative lesions;
- breaks and cracks in the bark, deep wounds in the stem;
- wilting of the stem.
All signs of an infectious burn are noted precisely on the stem of the plant, without affecting the leaves and flowers. Sufficiently strong stems that have a supply of nutrients can normally bloom all season, after which they wither and provoke the death of the entire plant.
If you cannot independently establish a diagnosis or doubt it, use the Rose Disease Identifier.
Cercosporosis, septoria, sphacelome
As already mentioned, they belong to the same group of diseases along with black spots. The difference between them is only in their manifestation:
- Cercosporosis is manifested by bright rusty-brown spots, up to 6 mm in diameter. The causative agent of the disease is Cercospora rasiola;
- Septoriosis looks like whitish "freckles" with a black rim on the leaves of the flower. It appears as a result of damage to the plant by the fungus Septoria rosae;
- The schaceloma appears due to the activity of Sphacelomarosarum and is small specks of crimson or black color. Cercosporiasis Septoria Sphaceloma
Prevention of treatment also requires handling and careful maintenance.
Causes of the disease
The main cause of stem cancer of roses is the fungal pathogens Coniothyrium cystotricha and Sacidium cystotricha, which live and reproduce under aerobic conditions at temperatures of +20 ° C and below. Quite often, such conditions are formed under the shelter of a plant, especially if polyethylene is used as a protective material. The fungus is very fond of high humidity and unventilated rooms, which also distinguishes the classic winter shelter for roses. Experts say that winter freezing of the soil slows down sporulation and prevents the development of rose disease.
The fungal agent can be transmitted to the plant from soil or water, but more often infection occurs during the pruning process, when the gardener neglects the rules of asepsis in relation to his own hands, pruning shears and other garden tools. One of the leading causative factors for the appearance of pathology is considered to be an excess of nitrogenous bases, which enter the soil along with fertilizers and accumulate by autumn.
How to prevent rust on flowers?
Roses are decorative flowering plants that are susceptible to infection by various fungi, in particular, rust. To prevent the development of rust in rose gardens, it is recommended:
- Growing varieties of roses with resistance to rust.
- The correct choice of place and soil for the flower bed.
- Preventive treatment of bushes with fungicides in early autumn and before the onset of winter.
- Sanitary pruning of roses.
- Control of the amount of application of nitrogenous fertilizers and fresh organic matter.
- Timely identification of the first signs of the disease.
- Maintaining the required level of soil moisture.
With the right choice of place and respect for flowers, growing thorny beauties will become a favorite business that does not bring hassle.
Blooming healthy roses will reward the gardener with their fragrance and neat appearance for the work invested.
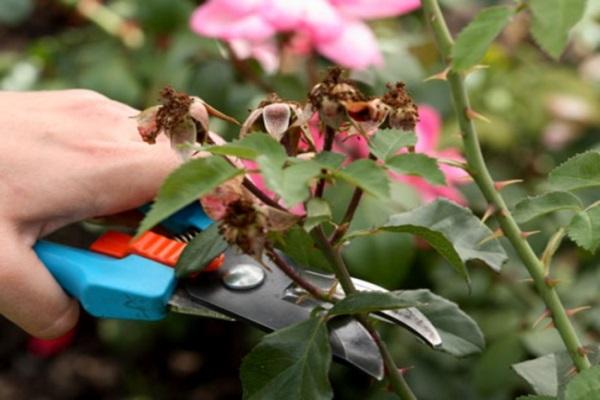


Treatment and prevention of an infectious burn
It is almost impossible to treat stem cancer, since most often the fungus, infecting the stem, ultimately causes its death. It is better, immediately noticing the first manifestations of the disease, to remove the entire affected area or to the border of healthy tissue, because even if the plant gives flowers, it will most likely die by autumn. In cases where there is only one stem, you can try to trim the spots of an infectious burn selectively using a sharp tool (razor blade or knife) and process the cut with garlic, sorrel or Rannet to slow down the development of the pathogen. Unfortunately, however, such treatment usually shows a low rate of effectiveness.
The best prevention of stem cancer will be proper care, focused primarily on the timely sheltering of the plant. Roses should not be covered in too warm and humid weather. It is ideal to perform this manipulation when the outside air temperature drops to 10 ̊С. In this case, it is imperative to pay attention to the fact that the earth and the plant itself are dry.
Root cancer
Root cancer
Cause. A hard growth at the point of contact between the ground and the stem of the rose - this is how root cancer manifests itself. The main factors in the occurrence of a bacterial disease are external damage to the flower or overdoing it when fertilizing it. Such hard compaction will in most cases lead to the death of the plant. It is also possible for the virus to appear at the grafting site of an oculated rose.
The infection can affect any variety of roses, but most of all, flowers that are grown on clay surfaces are subject to it.
Treatment. The first step is to remove the growth from the site of the flower's lesion. You need to cut carefully using a processed sharp knife. Anything cut from the plant must be removed from the garden and burned.
After that, the affected areas on the roses need to be treated with special preparations. There are many specialized disinfectants available to fight bacteria. But summer residents usually use a one percent solution of copper sulfate.
After processing, you need to wait 5-7 minutes and rinse the flower with water. In most cases, after providing such first aid, the flower survives.
But if the plant still died, it is recommended to dig it up and change the soil in the hole before planting another seedling.