Description of the disease and pathogen
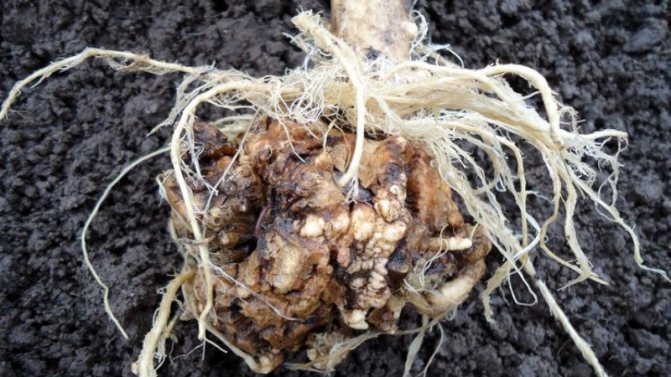
Keela of cabbage is a fungal disease that primarily affects the root system of the plant. Multiple putrefactive growths can be seen on the roots. Such cabbage is no longer able to receive moisture and nutrients from the soil, so it quickly stops growing, withers and dries up. The growths on the roots are capable of surpassing even the head of cabbage in size. Decayed roots are home to millions of new fungal spores.
The causative agent of the keel is the parasitic fungus Plasmodiophora brassicae Woronin. It is not able to grow and develop outside the plant, but its spores quickly spread throughout the site and have phenomenal vitality: they persist in the soil for up to 7 years.
Fungal spores are not airborne or seedborne.
Agrotechnical preventive measures
Agrotechnical preventive measures reduce the risk of fungal infection. To this end:
- provide the necessary content of calcium, zinc, potassium, boron and chlorine in the soil,
- increase the amount of humus, mullein and compost, rich in microflora and restraining the active vital activity of the fungal pathogen,
- observe proper watering,
- normalize acidity by introducing deoxidizing drugs, for example, by introducing colloidal sulfur,
- high spud cabbage plantings, which gives the active development of additional roots, which take on a compensating role in replenishing the nutrition and needs of plants in water.
When keela is found on most plantings, it is recommended to pay more attention to measures that prevent the spread of fungal infection:
- use disinfected technical equipment to avoid the transfer of fungal spores on the instruments,
- remove infected plants by checking the wells for residues of infected roots.
How to understand that the cabbage has hit the keel
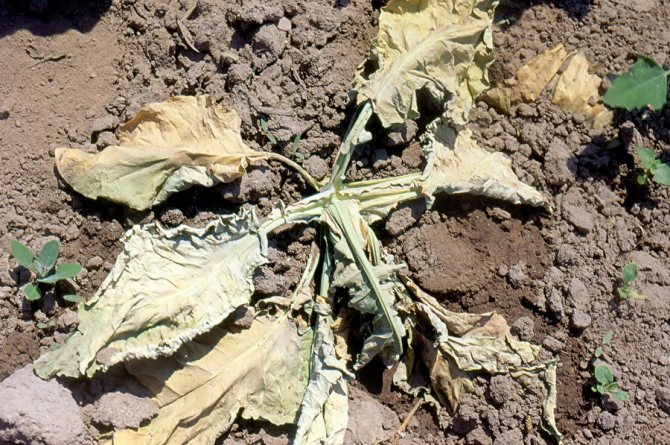
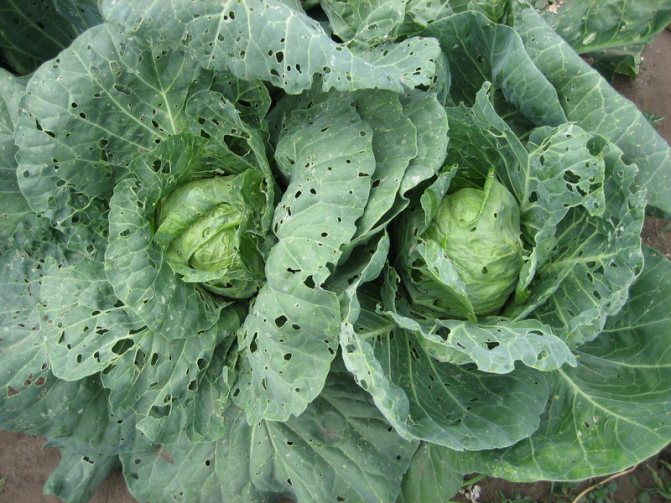
Most often, keela affects young plants or seedlings. It is very difficult to see the signs of the disease by eye: the growths on the roots of the seedlings resemble ordinary lumps of soil. You can only pay attention to the unnatural lethargy of the seedlings, despite all the feeding and regular watering.
Pronounced signs of keel appear already in grown cabbage:
- stopping or slowing growth;
- general wilting;
- yellowing and drying of the edge of the leaves;
- rolling the head of cabbage on its side.
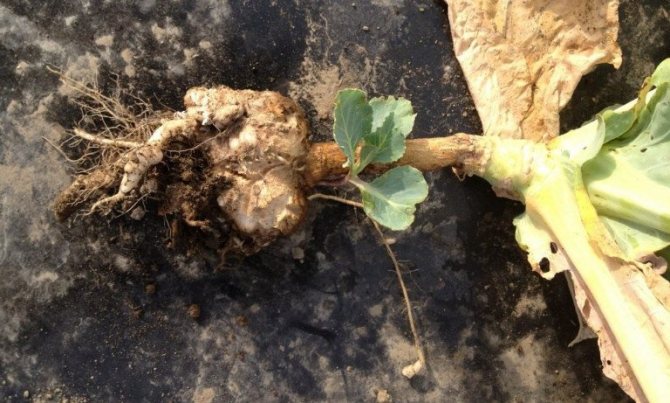
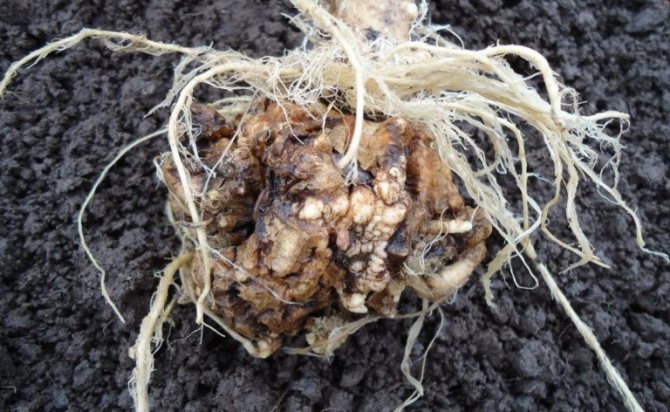
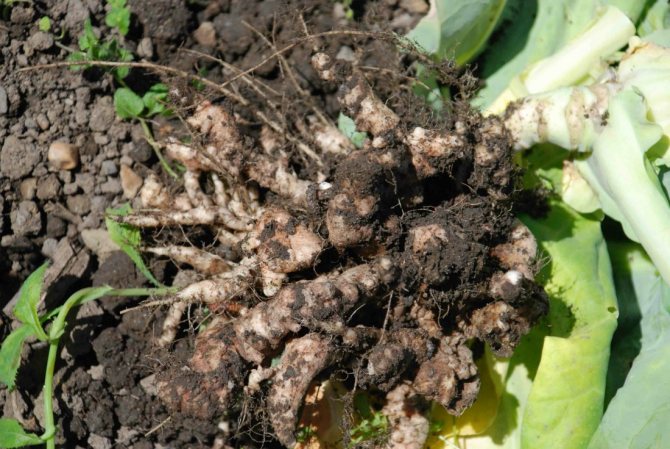
If you pull the head out of the ground, then instead of a thin root system, you can see spherical and oblong growths with open rotting wounds - this is a sign of the maturation of new spores.
Signs of defeat
The defeat of a cabbage with a keel begins from the roots, on which well-visible white thickenings or swellings are formed. They can be of different sizes and different shapes. When cabbage is infected even at the age of seedlings, these thickenings are located on the main roots and are large in size. If the infection occurred already during the growth of cabbage on the ridges, then the growths of the keel are on the peripheral roots and look like beads or icicles. By the end of the season, the thickenings acquire a brown color, begin to rot and collapse.
At the same time, many spores are released into the soil. They can be in the ground for years, and as soon as a cabbage plant is planted nearby, they begin to germinate, penetrate the roots through the root hairs. In their tissues, they multiply, fuse together and infect adjacent tissues.


Aerial parts of cabbage also suffer - due to malnutrition, the leaves wither, especially in hot weather and turn yellow, the heads of cabbage grow small and soft or do not tie at all. Young plants may die. Since lethargy and yellowing of the leaves can be a sign of other diseases or violations of agricultural technology, it is possible to determine the keel with accuracy only by its characteristic root thickenings.
Disease provocateurs
Infection can appear both from already infected soil and from diseased seedlings. Also, the fungus can get into the ground with rotten plants or weeds.
Fungal spores thrive in compost, in moist and acidic soil. Often starts up in heavy, damp ground. Overdried soil can also contribute to the appearance of microorganisms in it, although this happens much less often.
Suitable conditions for the rapid growth and development of the keel:
- temperature from 18 to 25 degrees;
- humidity from 75% to 90%;
- soil acidity from 5.6 to 6.5 pH.
During the frost period, fungal spores easily persist in the roots of many weeds, especially the cruciferous family. Among them, the shepherd's purse, rape, yarotka and field mustard are considered dangerous. It is worth getting rid of such herbs on the site immediately.


How to get rid of keels on cabbage
After identifying the disease, it is important to understand that it will not be possible to save the entire crop. Cabbage can no longer be cured, but the appearance and development of the disease in other areas can be prevented.
Crop rotation as protection against keel
To protect planting from fungal infection, you can plant other vegetable crops next to cabbage, which are not only resistant to this disease, but also accelerate the death of the fungus.
This will help:
- Nightshade: tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, peppers, allspice tobacco, petunias and others. The influence of these crops on the soil will help heal the soil from contamination in 3 years.
- Haze: beets, spinach, chard. They will heal the soil even faster - in 2 years.
- Liliaceae: onions, garlic, lilies, hyacinths and others. Planting tomato and spring garlic will be an excellent way to treat the soil.
Together they will heal the earth in just one season. After that, in order to be completely sure of the safety of the soil for the plants, it is advisable to plant disease-resistant varieties, hybrids or other vegetable crops for which the keela is not dangerous for the next season in these beds.


Folk remedies
If the disease manifests itself at an early stage, the crop can be saved using folk methods. However, this method cannot completely heal keila.
If the disease was detected in the last stages of development, no folk remedies will help. The crop must be destroyed immediately, and the land must be intensively treated.
Among the popular ways to combat the fungus are:
- Infusion of wood ash... To prepare it, 10 glasses of ash must be poured with 10 liters of water and infused for 2 days. All leaves affected by the disease must be torn off. Stir 1 liter of infusion in a bucket of clean water, then pour 500 ml under each diseased plant. Such treatment is necessary after each watering. After the procedure, it is necessary to huddle the stem higher in order to promote the growth of new, healthy roots.
- Organic fertilizers... Once a week, it is necessary to add mullein, vermicompost, compost and yeast under the plants. They will reduce the activity of the fungus and contain its spread. After fertilizing, the plants must be spud.
- Mortar... Dissolve 150 g of lime in 5 liters of water. Pour 500 ml of such a solution under each bush on infected beds. It will increase the alkalinity in the soil, and above 7.0 pH the fungus will die.


Chemical and biological products
Keela is dangerous because it is resistant to many drugs aimed at fighting the fungus.However, there are those that will help curb the growth and development of the fungus:
- Trichodermin.
- Previkur;
- Glyocladin;
- Topaz;
- Fitosporin-M.
- Alirin B.
- Fundazol.
These funds, for all their effectiveness, are not able to completely destroy the parasite and cure the crop.


Control measures
It is advisable to start treatment of the affected agricultural culture in the early stages of the development of the disease. If the fungal infection has spread, then the plant is almost impossible to save.
What to do if signs of keel appear?
- Effective measures to combat a pathogenic fungus are the timely digging up and destruction of the affected plant structures. If the cabbage root system is affected by the keel, then the plant is removed from the ground, the affected root structures are cut off. Diseased roots must be burned.
- Spores of the fungus can spread throughout the area, therefore, it is necessary to carry out the procedure for destroying the affected roots with rubber gloves. After burning, gloves, shoes and garden tools are disinfected.
- After harvesting, it is required to treat the ridge with disinfectants. An effective method is soil cultivation with a mixture of beet tops and the "Shining-1" preparation. Spray plant materials with a liquid agent, then spread on the surface of the ridge and dig up the soil.
- The next year, it is forbidden to plant cabbage, as well as other plants that are not resistant to fungal infections, in the ridge where the signs of the keel were replaced.
How to properly plant cabbage so that there is no keel
Fungal spores can eventually appear even in healthy soil, so you need to take care of the safety and health of the earth every year and carry out the following procedures:
- remove weeds;
- often and deeply dig up the earth, bringing into it finely chopped tops of potatoes, beets and quinoa;
- add limestone in the form of dolomite flour and wood ash to too acidic soil;
- a week before planting, the land should be treated with a solution that is prepared from 300 g of copper sulfate, 300 g of slaked lime and 8 liters of water. Instead, you can also use 0.1% Fundazole solution.
Immediately before sowing, seeds must be treated in either of two ways:
- soak in hot, not lower than 50 degrees, water for 20 minutes, then cool and dry thoroughly;
- leave in a 1.5% solution of mustard for exactly 6 hours.
If seedlings are used for planting, then its roots must be kept in a solution of Fitosporin-M for 2 hours, or treated in a suspension of preparations such as colloidal sulfur, Tiovit Jet and Cumulus DF.
Before planting on the site, the roots of the seedlings should be rolled in lime flour or dipped in a lime-clay mixture. In the second case, the effect will be better, since thanks to the clay, the lime is more strongly attached to the roots. Healthy plants that receive all the nutrients are much more resistant to disease. Therefore, together with organic fertilizing, one should not forget to add mineral additives to the soil: potassium, phosphorus, magnesium and zinc.


Keel-resistant cabbage varieties
Not all types of cabbage are equally affected by fungal attack. There are varieties and hybrids that do not succumb to this disease. After restoring the soil for the prevention of keels, it is advisable to plant the following hybrids:
- early maturing: Kilagreg;
- mid-season: Kilagerb F1, Nadezhda, Tequila F1;
- late ripening: Kilaton, Ramkila F1.
Keel-resistant cabbage varieties:
- Moscow late.
- Ladoga.
- Winter mushroom.
- Losinoostrovskaya.
- Present.
- Yielding.
- Taininskaya.
Peking cabbage also distinguished itself with hardy varieties. Among them, resistant to fungus are: Lateman, Clapton F1 and Clarithry.
All of these species will be excellent choices for planting in soil where an outbreak has already been detected.
It is impossible to ignore the keela after its occurrence. Fungal infection will not only destroy the crop, but also spread throughout the garden, affecting other plants as well. By observing all the rules of soil care, and carefully preparing the seeds and seedlings for planting, you can save the culture and reduce the risk of keel. If the keel has already spread, you should not spare the infected crop - it is better to lose it in one season than to quarantine the entire area.
How to prevent contamination of all soil


If a keel was found on plants already in the middle of the season, then it will be very difficult to do something serious in the current season. Remove all diseased plants, dry and burn the roots. Spud the remaining healthy seedlings higher and water more abundantly.
To localize the focus of infection, carefully clean the beds where the keel is found and the passages near them from weeds from the cabbage family. Where the keel was found only once, it remains for a long time. Therefore, all work on the care of an infected garden bed should be performed with specially designated equipment so that spores do not spread throughout the garden.
In the fall, when the cabbage roots are removed from the garden, dig up the soil with the beet tops. All plant residues from the soil must be selected very carefully - do not leave even minimal seedlings. Before you start fighting the keel, remove all affected plants from the beds and burn them.




















