What character and lifestyle
The water strider, or Gerridae (in Latin), belongs to the suborder of bugs from the Hemiptera family. Up to 700 species of insects are known on the planet, which are also capable of dissecting through water, as does the pond strider.
The water strider is a sociable insect, therefore, in one place you can find 5-6 insects at a time, which does not at all prevent them from arranging carnage around the food they find.
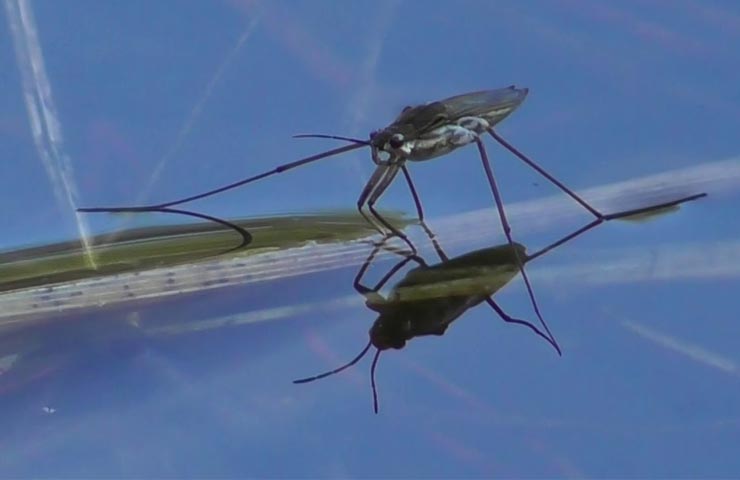
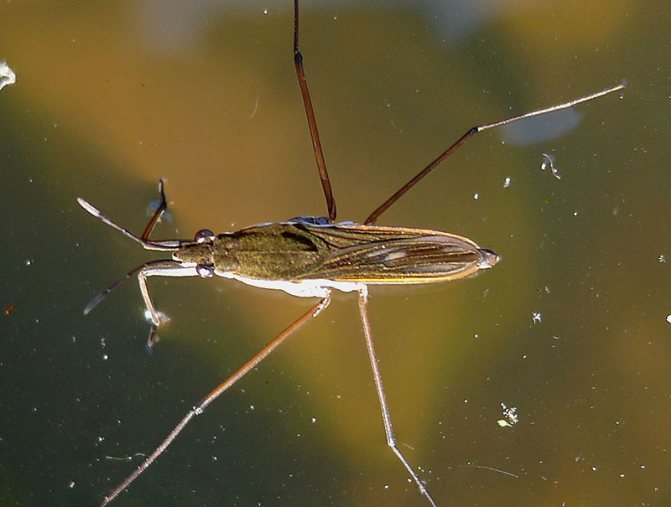
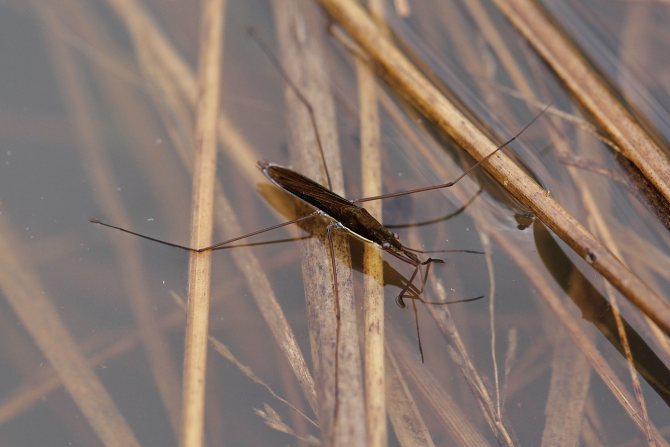
Although this insect belongs to bedbugs, the appearance of the water strider has nothing to do with these creepy insects, from which at one mention it makes you shiver. An enlarged photo of a water stripper bug shows that it has an elongated, boat-like body of brown, brown, almost black color, covered with hard hairs. The legs also have such hairs.
Gerridae has three pairs of legs. The front ones are short, they provide the speed and direction of movement of the water bug. The front legs are also used for communication between insects. With these paws, the bug captures prey, fights with other individuals that encroach on its property. The hind ones are elongated, strong.
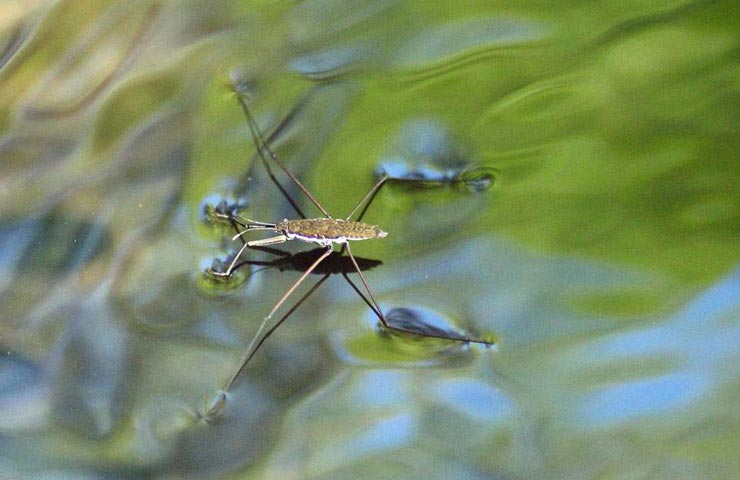

Water striders have very long legs.
Water strider bugs do not sink for several reasons:
- The shape of the legs encourages the insect to move through the water: the lower part of the foot completely rests on the water, thereby increasing the resistance of the water surface;
- Air accumulates inside the hairs. It forms a kind of air cushion.
- In addition to air, the legs have another remarkable property. They are lubricated with a special water-repellent fat, which is produced by the body of this amazing insect, and always remain dry.
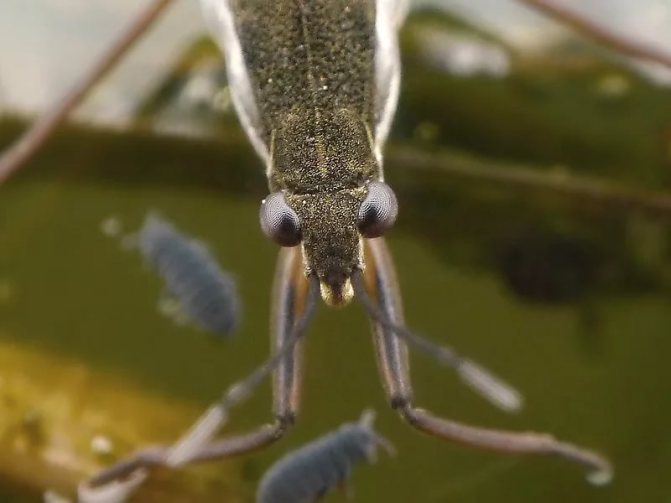
Gerridae has antennae on its head, which, like an antenna, perceive the slightest vibrations of water, which helps it to avoid danger and find food. Fluctuations in the water surface also help the male imago find the female for mating.
Life and reproduction
The mating process takes place in spring and summer. The male picks up a female suitable for breeding and climbs on it right on the water. The female lays eggs after 7 days. This process lasts all summer:
- Clutches of eggs can be found on the surface of aquatic plants. Each egg is held together by a special mucus that looks like a long cord. Insects of small species make clutches with eggs, without mucus. Sometimes they just stick them into the fabric of the sheet.
- The role of males is to protect the female and future offspring. They take care of her and protect her until she gives birth.
- The larvae (nymphs) emerging from the eggs are outwardly similar to adult insects, only of a smaller size. Their abdomens are convex. Just like adults, babies feed on small invertebrates. Growing up is fast. 30 days after birth, they turn into adult insects.
- In autumn, the activity of water striders gradually decreases. They leave reservoirs in search of hiding places for the winter. They hide among mosses, in fallen leaves, climb into the cracks of the bark of trees. Having decided on a shelter, the insect remains without light, food and goes into hibernation.
- With the arrival of spring, water striders wake up and begin to actively populate nearby water bodies. After waking up, they need good nutrition. They eat the remains of dead insects that have accumulated on the surface of the water.Thus, there is a massive purification of the reservoir.
A simple type of water strider that lives in water bodies, it prefers to be near the coast. So they can hide from fish in the coastal thickets. Rivers with weak currents and lakes are inhabited by freshwater insects. They also live in puddles and small streams. Freshwater water striders prefer tropical climates, but are able to survive in harsh, snowy conditions. On the coast of the Indian and Pacific Ocean, water striders are also found.
Food
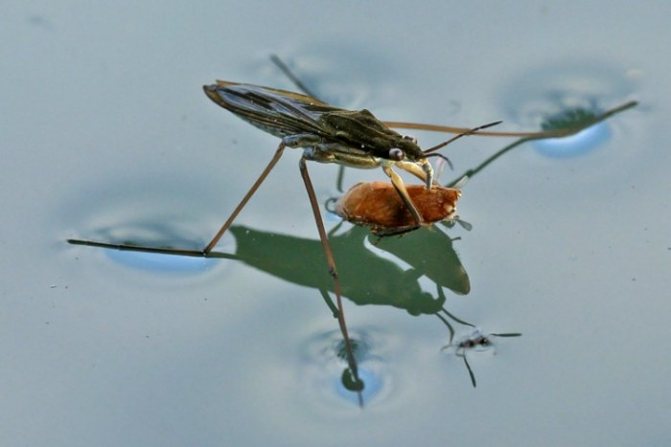
Water striders are predatorsalthough their size is quite small. They feed on various insects inhabiting the reservoir, regardless of the size of the prey. These can be their relatives, flies, mosquitoes or larger individuals. Power features:
- The organ of vision in spherical parasites. Thanks to this structure of the eyes, they see their prey from afar.
- They grab the victim with their front legs, on which the hooks are located.
- The insect sticks into the victim's body with a sharp proboscis and sucks out all the useful enzymes from it. So that the proboscis does not interfere with movement, after eating, it starts up under the chest.
- Food of sea water striders - jellyfish, physalia, caviar.
- Insect blood is drunk by parasitic species.
Natural enemies
All natural enemies of water striders live in reservoirs and rivers, since insects rarely come ashore and spend their entire life on the water. Main enemies:
- fish;
- frogs;
- water mite.
Water mite is the most dangerous enemy... Its larvae attack insects, bite through the body and suck blood. Water striders are able to move quickly through the water, they are agile and neat enough, they can jump, so they cannot be called easy prey. Tiny insects can run 1 meter in 1 second. Their movement receptors are so well developed that they can sense even the slightest movement on the water. With an impending threat, insects immediately leave the territory.


Rod-shaped water strider
Usefulness of water striders
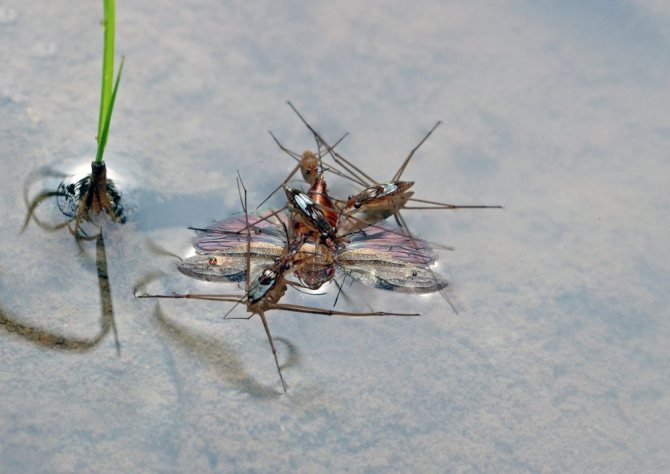
The use of water striders is that they regulate the number of insects such as horseflies... These blood-sucking parasites harm humans and animals. They lay eggs and larvae in water, where water striders destroy them. Bedbugs also exterminate adult horseflies, despite the fact that their size is much larger. They form a group, attack an adult parasite, then eat it. It takes about an hour to eat.
Danger to humans
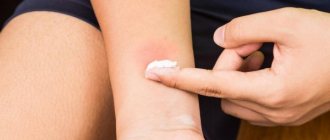
Water bugs are practically harmless to humans, but they can sting badly if disturbed. The sharp proboscis easily bites through the skin of a person. The bitten area turns red and itchy. Actions in case of a bite:
- Iodine will help relieve itching. It is enough to treat the affected skin area with a product.
- Usually, allergic reactions develop after being bitten by tropical water striders. Bite marks remain on the skin for up to 2 weeks. The victim should take antihistamines, and lubricate the wound with special drugs.
Water striders attack rare fish and feed on the contents of their bodies. This is the greatest damage caused by these insects.


How does it multiply
The male, sensing that somewhere near there is a female, hits the water with his paw, sending her a love signal. If the female accepts the "courtship" of the gentleman, she also responds to him and moves towards the male. Sometimes the male also begins to move towards the female. Sexual intercourse also takes place on the water.
Gerridae lays eggs on the leaves of plants that live in water. For one clutch, it manages to lay up to 50 eggs, which are located in one line and form a jelly-like lace. The eggs stick to the sheet and are held until the day when the larvae emerge from them.
Daddies-water striders participate in the reproduction process before offspring.
They jealously guard their territories, where their female laid the clutch.Seeing the enemy, they threaten the water with their paws, making it clear that they do not intend to tolerate a stranger on their territory. After two weeks, larvae emerge from the eggs, which go through all stages of maturation within a month and turn into adults.
In this video you can find many interesting facts about water striders:
Insect description
Larva
The larval insect differs from adults in its massive body and shorter limbs. The body is light brown or greenish in color.


Food consists of various insects living near the reservoir, their larvae and eggs. Despite its diminutive size, the larva is a real predator.
After hatching, the larvae develop for about a month, gradually increasing in size. At the same time, five stages of development go through. At the last stage, molting occurs. After molting, the abdomen is collected in folds, which straighten after eating.
Adults
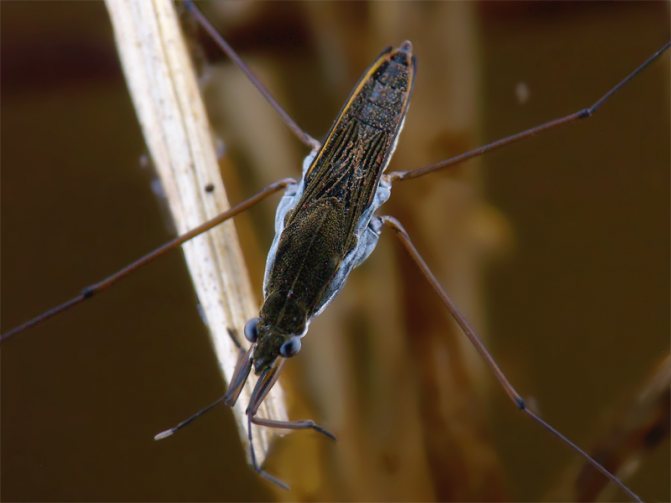
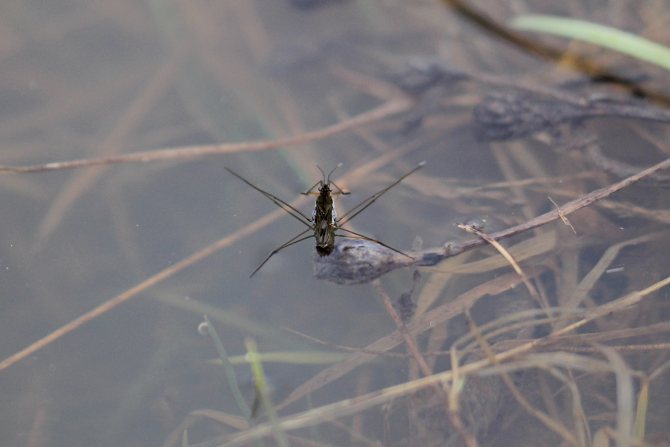
The size of an adult insect is from 1 to 30 millimeters. The body is elongated, with a narrow abdomen. The color is brown or brown. The head is small, with long antennae, equipped with a proboscis. The lower part of the body is covered with a wax coating. On the limbs there are small villi that prevent the insect from sinking. Due to the correct geometry, lightness of the body and special


equipment such as villi, the bug uses the surface tension of the water for high-speed movement.
Water bugs not only glide through the water, but also jump over small obstacles with ease, using the hind pair of limbs. The middle pair of legs is somewhat longer. The bug uses them instead of the steering wheel, changing the direction of movement. At the same time, the front pair is universal. With the help of it, the bug develops speed and slows down, grabs prey and holds it.
In most insects, membranous transparent wings are hidden under rigid elytra. If necessary, they can move between water bodies. For example, migrating in dry summers or migrating in search of prey. However, most spend their entire lives in one place. And some have no wings at all.
What are the biological features
Scientists have noticed that in times of danger, water striders always move south. The water strider is easily adaptable to the environment. Adapted to the cold, to the salt water of the seas.
The insect has wings that help fly from one body of water to another in cases of drought. When the water bug hibernates, the wings dissolve, turning into food for the entire winter.
The water strider itself serves as food for some fish and birds.
Is a water strider bug harmful?
The water strider bug does not pose any danger to humans. Only in rare cases, when the bug feels threatened or dangerous, it can bite. This bite is similar to a weak prick and does not even require special treatment, it does not itch or hurt.
It is also useful to read: Soldier bugs and the harm they cause
And one more thing: the bugs hid in all the cracks, and you can't find their nest in any way? And smoke bombs find bugs where even a needle cannot squeeze ...


The only damage that water striders can cause is eating fry of valuable fish species. The water strider bug very willingly attacks fry of early ages and kills them, sucking out the contents of the body. Sometimes it can devour clutches of fish eggs.
However, even for full saturation, the water strider needs very little food, and the fish living in the water column represent for the bug, rather, an addition to the usual diet, which is based on insects and mosquito larvae that have fallen to the surface of the water. This means that the bug does not pose a tangible threat to fish farms or the life of individual bodies of water.
It is interesting
Recently, scientists have discovered an interesting and useful feature of water strider bugs: it turns out that these insects play a large role in reducing the number of horseflies.Horsefly females lay their eggs in the water, and their larvae also develop here. Water striders attack both adult flies and larvae with equal eagerness. At the same time, an adult horsefly is a rather large prey for a water strider, and usually several bugs together attack it. Several bugs are able to suck the horsefly in a few minutes, while one individual usually spends from 40 minutes to 1 hour on this.
The water strider bug is not a parasite and does not cause any trouble to a person. This insect spends almost its entire active life on the surface of the water: there it reproduces, feeds and rests.
In the reservoir where these small bugs live, you can swim without fear, and in your free time you can watch the endless running of bugs on the water, reminiscent of a chaotic dance.
What do they eat
Gerridae feeds on small insects that happen to fall into the water. Although it belongs to the suborder of bedbugs, it does not attack people and is not a parasite. This insect is a typical predator. The water strider bug feeds not only on small insects. Proboscis are also available, such as, for example, dragonflies, butterflies. They eat fish caviar and even fry.
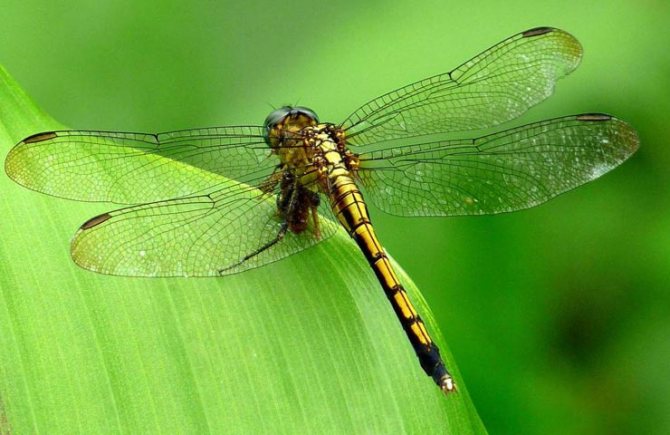


The water strider can even attack dragonflies.
With its proboscis, the insect injects digestive juices into the victim, and when it dissolves into the victim's body, the water striders suck out everything that is possible. The proboscis bends under the abdomen and thus does not interfere when insects fight for the right to possess prey, move along the water surface.
Gerridae fight each other when a small insect comes across. Large foods such as fish fry or large insects are eaten together. There is enough food for everyone.
Some interesting facts from the life of water striders
Scientists have studied water striders for a long time and came to the conclusion that these are unique insects. Some interesting facts about the life of water bugs:
- The flying muscles of water striders are absorbed during hibernation. When they wake up in the spring, their ability to fly is lost.
- Sea water striders have been found in the ocean, thousands of kilometers from the coast. Thanks to microscopy and other research experiments, it was found that the shell, which has a special structure, saves insects from salt water and ultraviolet radiation.
- There are 46 species of marine water striders, which are divided into oceanic representatives and individuals living near the coast. Of these, 41 species are coastal, which try to stay closer to land. They can be found on reefs or in mangrove thickets. Females lay eggs on algae, which protrude from the water at low tide, as well as on rocks and coral reefs. In the open oceans, 5 species of these representatives live. They have completely moved away from the shore, and lay their eggs on shells, bird feathers, pieces of wood and plastic and other objects floating on the surface of the water.
- Once in the Pacific Ocean, a 4-liter plastic canister was discovered, on which 70 thousand water strider eggs were fixed. The eggs were arranged in 15 layers. Since 1 female is capable of laying up to 10 eggs, it has been estimated that over 7,000 females used this item to give birth to their offspring.
- During the day, insects move towards sunset, at night - in the opposite direction.
- The high speed of movement of insects through the water is obtained thanks to a special technique: when the tips of the legs are immersed in water, miniature funnels are formed, from the walls of which the water strider pushes off, rushing sharply forward. From this it follows that an insect travels a distance 100 times larger than its body in a split second. Equating this ratio to a person, you can calculate that people could reach speeds of up to 650 km / h.
- Canadian researchers, from video recordings, observed how male water striders mate with females. To restrict movement of females, they use their hook-shaped antennas. This shape is ideal for the contour of the female's head.
- Individual representatives of the water striders Rheumatobates rileyi arrange whole warriors for the right to possess the female. The repeated mating process does not occur, since the female is able to store the sperm obtained after the first time in herself. In addition, this process is considered costly, since it does not allow her to eat normally and makes her vulnerable to enemies.
- Scientist Kiuchina Cho from Seoul, together with a group of robotics engineers, created miniature robotic water striders. Before creating them, they observed the behavior of insects for a long time and carefully studied their structure. According to the researchers, the robots turned out to be amazing. They slide and stay on the water like real insects.
- During the rain, water bugs can drown, so during such periods they leave the water bodies in search of shelter.
- To stand up for their food, water striders have to fight. In this they use their front legs. Without dividing food, 2-3 bugs disperse each other, interlock with their front legs, fall to the surface of the water and ride there until the most dexterous and cunning one grabs the prey and takes it to a secluded place. At this time, the rest of the insects continue to fight.
- The specific gravity of the insect is small, slightly more than one. Based on this, the water strider is heavier than water, but not to such an extent that it can cope with the force of the surface tension of the water.
Life on water is more difficult than on land. Water is a dense medium. In order for the insect to quickly swim and live in water conditions, its integument must be smooth, its body shape is streamlined, and its legs must be strong. With such data, nature has endowed the water strider bug.
What are the types
Up to 700 species of water striders are known on the planet. In Russia, the pond water strider mainly lives. In salty seas, there are sea water striders that have adapted to salty sea water. The size of their body is not more than 5 mm, which is much less than the pond. But they run perfectly and are able to move long distances at a speed of 3.5 km per hour. The appearance of water striders of different subfamilies and genera differs from each other.
- The pond strider has a body length of approximately 10 mm.
- The water strider is large and larger. Its body length is 17 mm.
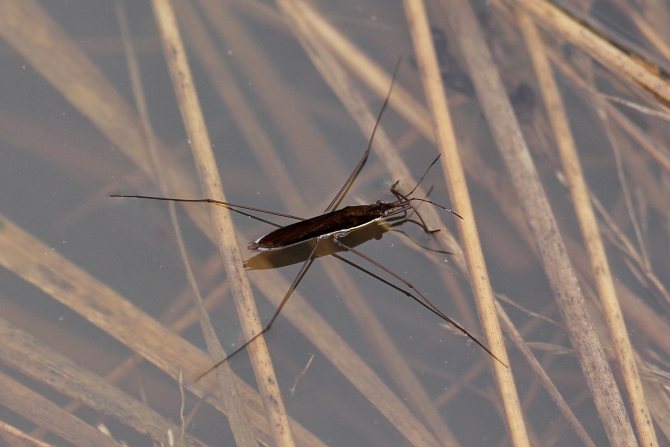
- The rod-shaped water strider lives in Siberia. They are slow, moving more slowly than the pond, it has a narrower body.
- Velia is the northernmost water strider. Feels great in cold water. She has no wings.
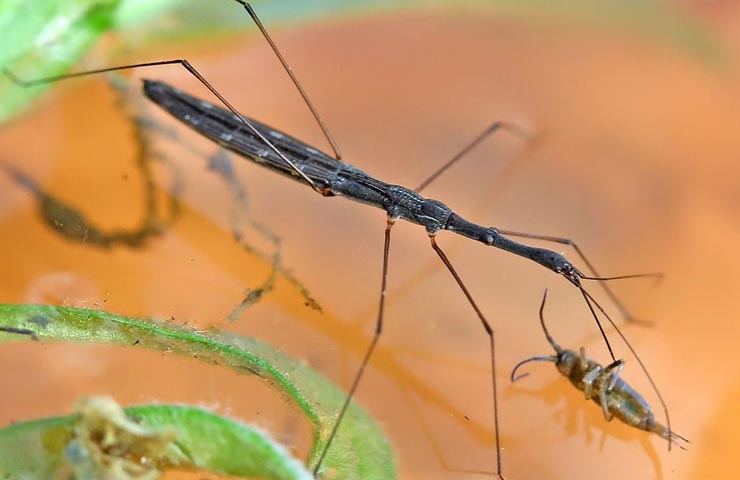


In Siberia, you can find a rod-shaped water strider
In the tropics, mostly sea water striders are found. Some of their types can be aggressive.
What does a water strider look like
There are a great variety of water striders - about 700. All of them differ from each other in appearance, color and lifestyle.
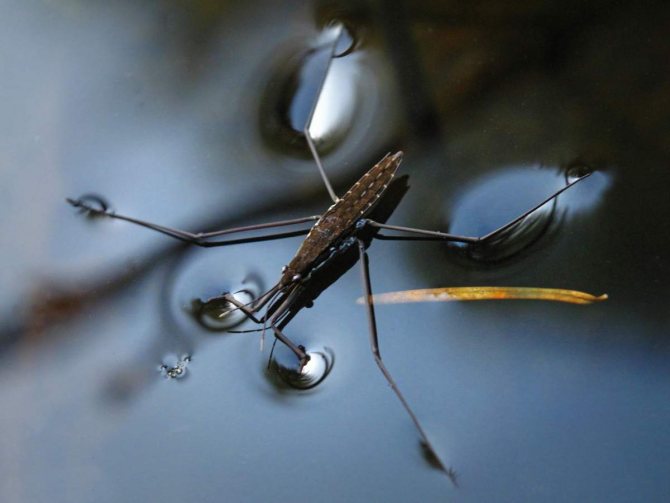
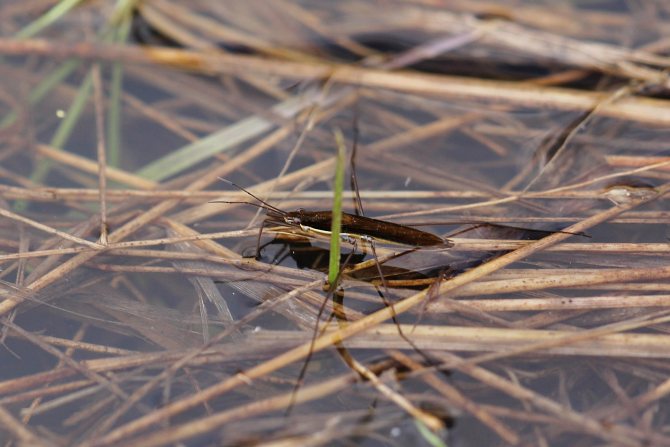
The narrow elongated body of the water strider bug (its size can vary from 1 mm to 3 cm) looks like a small stick, equipped with 3 pairs of legs of different lengths. The front legs are much shorter than the rest, they are used to capture prey and adjust the speed of movement on the water.


The middle and hind legs are one and a half to two times longer than the body length of the bug itself and are used as a reliable support and turning mechanism, as well as for jumping.


The bug is kept on the water due to the force of the surface tension of the latter, which creates a kind of film. The bug on its paws, like a person on skis, glides over the surface, never falling under the water.
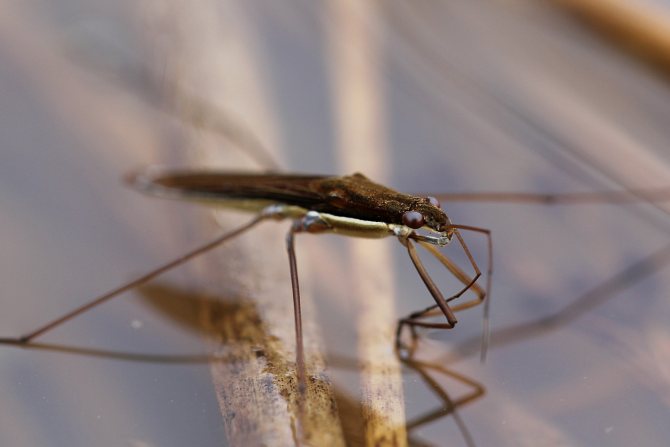
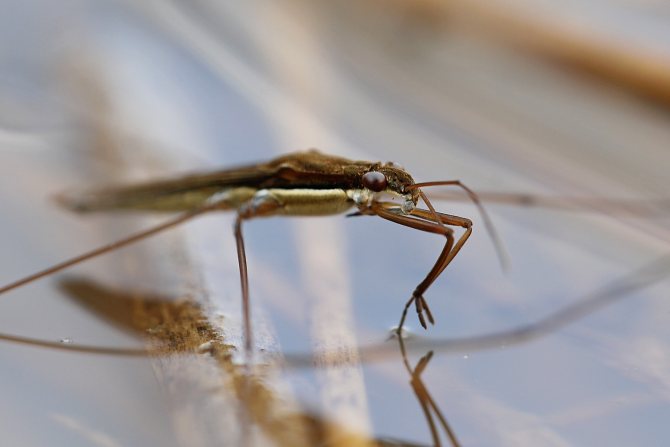
Sensitive antennae are located on the head of the water strider, which help the insect to catch sound vibrations of the water surface. Antennae also act as an organ of smell and touch.
The oral apparatus is represented by an articulated piercing-sucking proboscis, used by the bug to suck out the contents of the body of its victim.


Some water striders have wings that make it possible to move long distances in search of new bodies of water, temporarily populate puddles. However, bugs do not really like to fly and try to do it in exceptional cases. Wingless bugs have lived in the same pond all their lives.
The body color of different species of water striders can vary from light gray and greenish to dark brown. There is usually a speckled pattern on the underside of the backrest. You will not find any very noticeable or bright drawings on it. Exactly how an adult water strider looks like can be seen in the photo below:


Bedbugs lay their eggs on the leaves and stems of aquatic plants. Sometimes round, whitish eggs are located separately, next to each other, but more often they are held together by a mucous substance in the form of a ribbon of 40-50 pieces.
See also our experiments on bedbugs:
We catch bedbugs and test different agents on them - see the results ...
- We test the effect of Hector powder on bedbugs in two versions: simple processing and preparation of traps. See experiment results.
Experiment on bedbugs: at what temperature do they die and how it can be used in practiceWe put the bugs in a container that was treated with the Executioner a week ago - let's see if the parasites are poisoned with a long-dried remedy ...
- We tested Get Express on bedbugs - let's see what came of it ...
Bedbug Experiment: The Executioner Killed Them in 8 Minutes
We check the residual effect of the Executioner on the bugs (how quickly they are etched in contact with a previously treated, but already dried surface)
- Proven methods for killing bedbugs that have proven to be highly effective
The larva of this water bug is in many ways similar to the adult, the imago, but it has a more swollen and shorter body. She is called a nymph and eats the same food as an adult insect. In the photo, the larvae of the water strider are visible next to each other:
It is also useful to read: Details about domestic bugs
And one more thing: We catch bedbugs and put deadly experiments on them - this is a must see!
It is interesting
The long legs of the water stripper bug are covered with microscopic hairs that trap air and help the bug keep balance. The abdomen is also covered with whitish hairs and smeared with a wax-like liquid, which literally repels water. If you try to "drown" the water strider, nothing will come of it. In the water column, the insect will be surrounded by many air bubbles and will look silvery.
The most famous types of water striders are:
- The water strider is large, one of the largest representatives of this family in our country. Its body length can reach 17 mm.
- The water strider is a slow rod-shaped one, found in Siberia and having such a thin body that it really looks like a stick.
- The pond strider is remarkable in that it has a variegated color of its legs.
In the tropics, the largest species of water striders are found, which can hunt small fish and bite a person quite painfully.
Do I need to deal with a water strider
There is no need to fight against the Gerridae that lives on the territory of Russia. An insect that walks on water like on land does not harm people. Water striders can be considered useful insects necessary for nature:
- they eat horseflies, and thus, the number of these midges in nature is regulated;
- eat insects that have fallen into the water, thereby preventing their decomposition in water, and cleanse water bodies.
Thus, the insect reduces the population of horseflies, which are parasites of domestic animals, and contributes to the cleaning of water bodies.
Danger to humans
The water striders living in our area are quite harmless insects. Due to their small size, accidental bites are not dangerous for humans or pets. Naturally, these bugs do not chase warm-blooded animals in search of prey!
Contact with insects can occur accidentally, while swimming or on the shore, where they go in search of eggs and insect larvae. Hydrogen peroxide or brilliant green is suitable for treating the wound.
More aggressive representatives of the species live in the tropics. There, water bugs hunt small fish and bite people.
In Thailand, these insects, in addition to the proboscis, are equipped with a sting. The pain of a sting can be compared to that of a bee or a wasp sting. The bitten limb is numb. Painful sensations persist for up to an hour. Usually, such a meeting with an insect takes place for a person without consequences, but if an allergic reaction occurs, you will need to take antihistamines and anesthetic.
It remains only to advise tourists to be careful when swimming in the water or just being near water bodies in exotic countries.