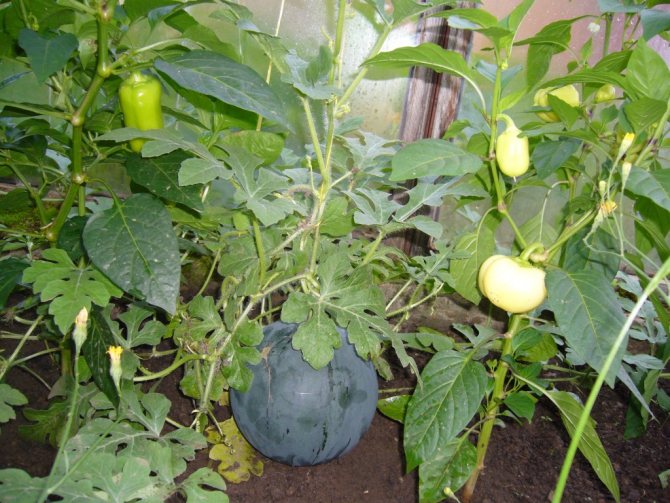
The cultivation of watermelon in a greenhouse has proven itself quite well. With the observance of competent agricultural technology, the correct choice of seed variety and several nuances of cultivation, you can achieve a good result. All the features of the cultivation of watermelon are described in the article.
Watermelon is a melon culture. It grows on land exclusively in hot southern climates. But this culture can also be grown in Siberia. How to properly grow a watermelon in a polycarbonate greenhouse, plant and care, correctly form a bush, and it will be discussed.
What varieties are suitable for growing in a greenhouse
For greenhouse conditions, early maturing varieties with a low weight at the output are considered the most suitable.
These include:
- "Skorik" - ripening period 60-65 days, weight up to 4 kg. The fruit is in the form of a ball, the rind with a strip, not thick, smooth. The pulp is juicy, fibrous, with a pronounced aroma;

- "Ogonyok" - ripens in 85 days, weight up to 2.5 kg. A globular fruit with a dark green skin and a sweet, juicy pulp. The variety is immune to diseases of melons and gourds;


- "Prince Albert F1" - ripening period up to 80 days, weight up to 3 kg. Thin-skinned, yellow fruit with sweet, sugary pulp. Disadvantage - not stored for a long time;
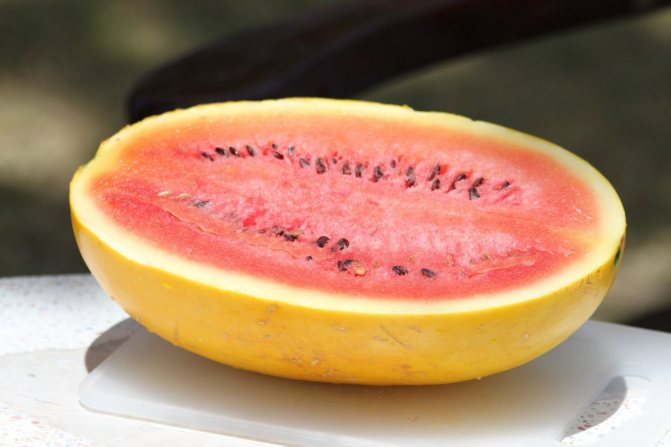


- "Prince Hamlet F1" - ripening period 75-80 days, weight up to 2 kg. Differs in strong immunity and resistance to temperature changes, popular in the Moscow region. It has a yellow flesh with few seeds and a thin striped skin.


Preparatory actions
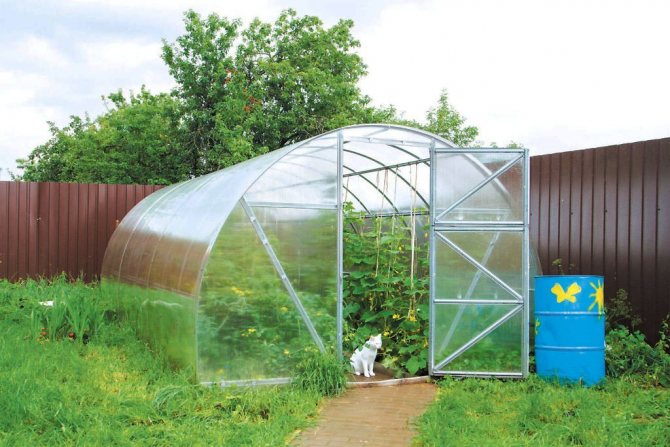
Since the watermelon bush develops, stretching along the support, the height of the greenhouse should be at least 1.7 m. There should be no gaps in the walls or window frames, the doorway: a draft is contraindicated for a thermophilic culture. The ideal option for melons would be a polycarbonate coating. The material has better transmission capacities than the film, it is easier to regulate the humidity in the room.
Greenhouse preparation
In autumn, a general cleaning is carried out in the greenhouse, preparing it for spring sowing. If you did not have time to wash the room in the fall, you need to do this before planting. It is imperative to spill the prepared soil with a disinfecting solution: copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid. In the room, you need to achieve a temperature of about + 30 ° C, humidity 60%.
Important! At high humidity, melons and gourds are affected by fungal spores.
Soil requirements
Plants need a loose soil that is perfectly permeable to moisture and air, with an acidity of 6-7 pH. Since autumn, the soil is dug up with humus 4 kg / m². In the spring, to provide warmth in the ground, heating is prepared: the top layer of the ridge is removed, a layer of humus mixed with hay is put. The mixture is thoroughly spilled with hot water and covered with a layer of soil. If it is possible to arrange water heating, pipes are laid under the ground through which hot water flows.
Selection and preparation of soil for watermelon
One of the important conditions for the successful cultivation of watermelons both in the open field and in greenhouse conditions is properly prepared soil. The ideal option would be to start preparing in the fall. The soil is fertilized by introducing rotted manure for digging (20 kg per 1 m²), grass is also used, for example, green manure.
Green manure crops or green manures are plants that are grown for the purpose of subsequent embedding in the soil, which allows improving the structure of the soil, enriching it with microelements and nitrogen.
In addition to organic fertilizers, you will need to add river sand (1 bucket per 1 m²), as well as mineral components such as nitrophoska and superphosphate, 10 g each, based on the same raincoat. In general, watermelons need light, sandy soils, in which stagnant water is excluded.
Video: preparing the soil for the new season
When preparing the soil for melon, do not forget about such an important indicator as acidity. For a watermelon, it should be in the pH range of 6-7. You can determine these values using a special device or probe strips. If the indicator deviates significantly from the norm, then for deoxidation it is necessary to add, for example, lime at the rate of 0.7 kg per 1 m². If the soil, on the contrary, is alkaline, then to increase the acidity by 1 ph, add 3 kg of manure or 9 kg of compost per 1 m².
Growing and caring for seedlings
Seedlings are sown in the month of April. Before sowing seedlings, the seeds are calibrated by placing them in clean water. Floated instances are discarded. The planting material is kept in a solution of potassium permanganate for half an hour for disinfection. For germination, dried up after processing, the seeds are wrapped in wet gauze. They are placed on a heating battery for several days. As soon as they hatch, sowing is carried out.


In the garden soil, mixed 1: 3 with humus, add 3 g of any potassium and nitrogen composition and 9 g of phosphorus per 10 liters of soil. In order not to disturb the root system of plants with dives, the seedlings are planted in peat pots up to 10 cm in diameter. The seed is buried 3 cm, laying it on its side. Cover the top of the cups with foil.
For the normal development of plants, containers with crops are placed in a special microclimate:
- temperature - + 22 ... + 25 ° С;
- humidity - 55-60%;
- lighting - bright, diffused.
Did you know? Watermelons are native to South Africa, there, in the Kalahari Desert, you can still find a wild specimen weighing up to 200 g.
Crop care is carried out as follows:
- watering - as the soil dries, water at room temperature, settled;
- top dressing - no earlier than 10 days after germination, using mineral formulations.


Feeding option for 2 liters of water:
- 4 g ammonium nitrate;
- 3 g of potassium sulphide;
- 10 g superphosphate.
Planting material


In order for the harvest to be sufficient, it is necessary to correctly approach the choice of seed.
Tip: Seeds taken from a purchased watermelon may not germinate at all. It is better to make the choice in favor of fast-maturing seeds.
Before starting the cultivation of watermelons in the country, you need to decide whether the local climate is suitable for this crop. At the same time, varieties are selected according to the conditions of the climatic situation. Before planting in the ground, the seeds are calibrated. Dry and empty are removed from the seed lot. To speed up the process, the seeds are placed in a bowl of salt water, in which the unusable specimens will float to the surface.
Seeds are selected large, with a pointed end. After the salty liquid, the seeds are rinsed. To prevent the early stages of seedling disease, the seeds are sprayed with a manganese solution.
How to care for watermelons in a greenhouse
Further care of the seedlings consists of standard procedures.
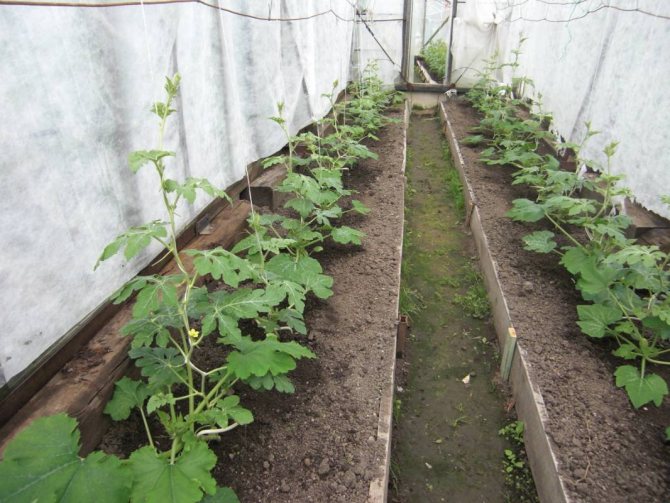


Humidity and watering
The temperature in the greenhouse must be monitored, the thermometer indicators should not rise above + 30 ° С, fall below + 20 ° С. Humidity must not be allowed to rise above 60%. To maintain the microclimate in the desired mode, the temperature and humidity are regulated by natural ventilation in the greenhouse. Watering the culture is carried out on the soil, the water is defended, heated in the sun to t + 20 ° C.In order not to flood the plants, the frequency of watering is determined by the state of the foliage: if the leaves are slightly wilted, it is time to water.
Important! When watering, you need to ensure that no drops of water fall on the foliage and stems, which can lead to decay.
Top dressing
At the beginning of the development of seedlings, the plants can be fed with an organic composition: the rotted manure is poured with water 1 to 10. The solution is infused for a day, then watered on the moistened soil under the root.
While tying flower buds, the plant is fertilized with a mineral mixture per 10 liters of water:
- 10 g of ammonium nitrate;
- 25 g of potassium sulphide;
- 30 g superphosphate.
During flowering and fruiting, 5 g of boric acid is added to the mixture described above.
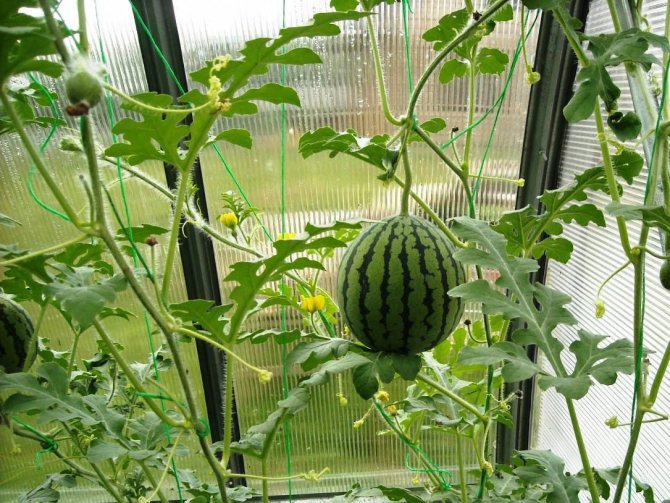


Pollination
It is impossible to guarantee 100% insect pollination in the greenhouse, so summer residents carry out this process manually.
The technology is as follows:
- The largest male flower is picked early in the morning.
- Tear off or bend back the petals.
- The stigmas of the female flower are touched with the male anther, thus pollen falls off.
Learn also about the benefits and dangers of watermelon peels.
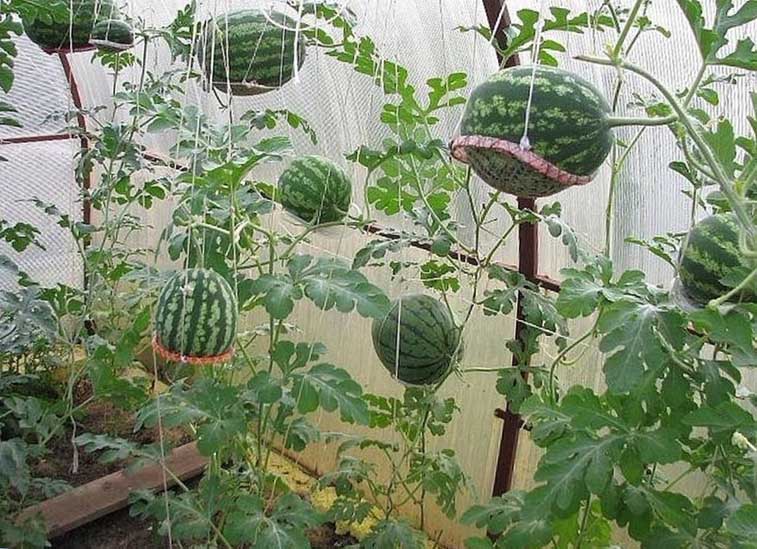
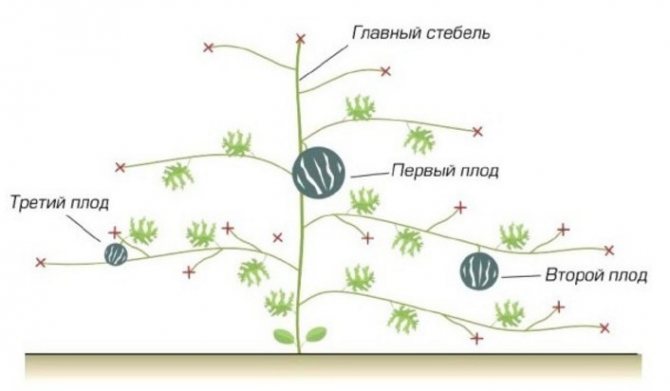
Garter and bush formation
When fruits appear the size of an average tomato, the bush must be properly formed:
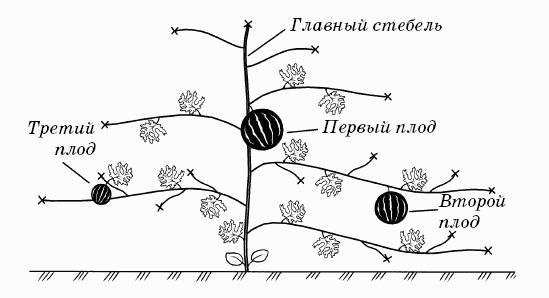

Bush formation scheme
- Above the fifth leaf, pinch the growth point.
- The lowest shoots and stems that do not have ovaries are removed.
- On the side lash, the third leaf is counted over the female flower and shortened.
- The same procedure is performed on the male flower, counting 7 sheets.
- For the normal development of fruits on one bush, it is not recommended to leave more than 2 fruits.
- Until the watermelons began to grow in width, new shoots are pinched.
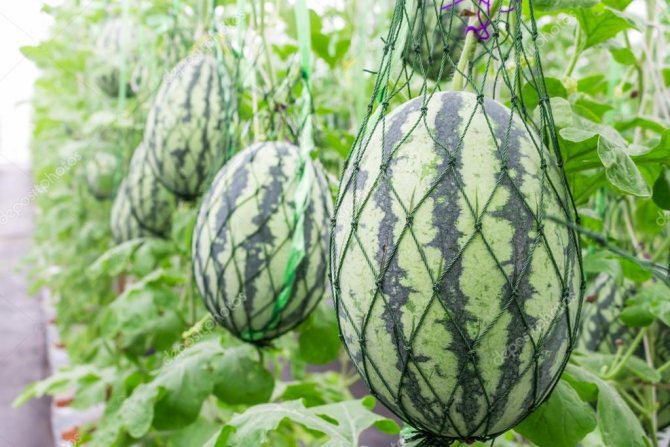
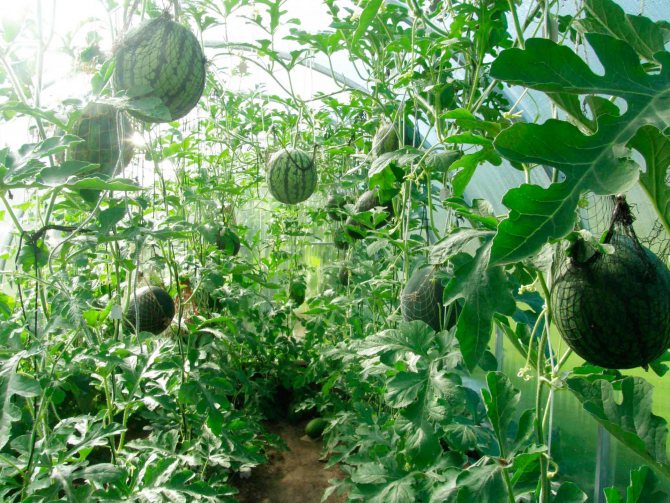
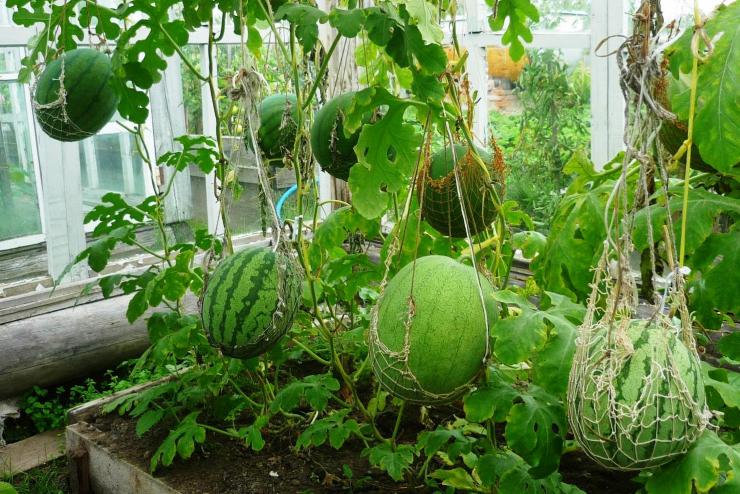
Along the perimeter of the room, a vertical type of trellis is installed, with a distance between the supports of 40-45 cm. The lashes are tied to the supports, on which the nets for the fruits are installed. Watermelons that have reached the size of a large apple are placed in nets and tied up so that it does not break off under the weight of the ripening fruit.
Video: growing watermelons in a greenhouse
Two ways for open and closed ground
Some Siberian gardeners grow large watermelons in a very simple way, which has already been mentioned. One whip is left in the bush and one watermelon, which was tied to it first. The stem is pinched after 5 sheets from it, and all lateral shoots, flowers and ovaries are also removed. They say it's easier to grow 30 bushes with one watermelon than to plant 10 and pinch them constantly to grow the same 30 berries. In addition, the third watermelon does not ripen in every locality, but one at a time on a bush ripens quickly.
Video: one bush - one watermelon, a greenhouse in Siberia
Other watermelon growers solve the problem of non-ripening of the third fruit in an alternative way. They ensure that three berries are tied, grow and ripen at the same time. To do this, leave the main whip and two stepsons emerging from the sinuses 3 and 4 from the ground of the sheet. All other shoots are removed. It turns out three whips. When the fruits are tied on each and begin to grow, they pinch over the fifth leaves from the fruits. But this technology should be subject to your criticism. After all, a lot depends on the size of future fruits, the place of cultivation and the weather.
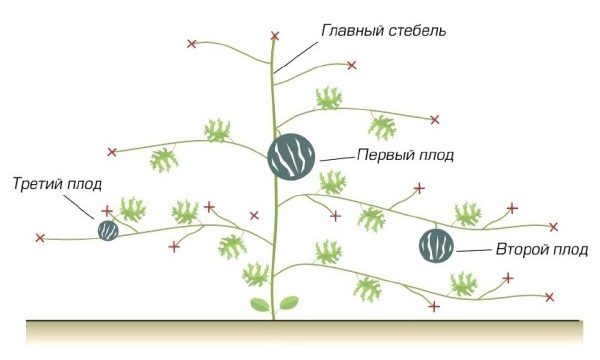

The scheme of the formation of a watermelon in three stalks - in order to get three fruits
There are many technologies for forming watermelons. There is no one universal for all varieties and regions. If this is your first time growing this thermophilic crop, then it is better to start with the simplest schemes. Another option is to arrange an experimental melon, test all known methods of formation and choose the most suitable one for specific varieties and climatic conditions.
The main ways of forming watermelons: how to get a decent harvest from yagodka.club.
Timing and basic rules for harvesting
The maturity of the watermelon is indicated by the darker color of the stripes, if the variety is striped.You need to knock on the fruit with your knuckles: a dull sound indicates ripeness. Watering of the crop is stopped 3-4 days before harvesting. The berries are harvested by cutting off the stem so that 3 cm of the root remains. The fruits are dried, during transportation and storage, they are shifted with paper. Fruit contact can lead to rot infestation.
Did you know? In the city of Kherson in Ukraine, a monument is erected in honor of the watermelon.
Possible mistakes when growing watermelons in a greenhouse
Newcomers to the cultivation of watermelons make some mistakes, because of which the culture is sick, the quality and quantity of the crop decreases.
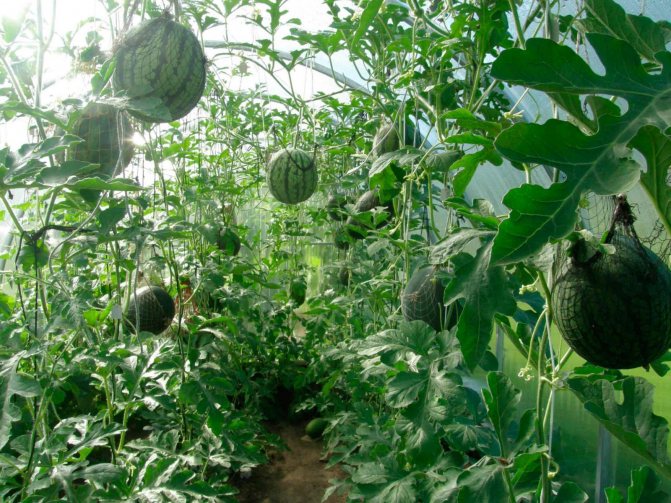


Helpful tips from experienced gardeners:
- Shading the greenhouse will not provide enough light for the development of the crop. If the situation cannot be changed, install lamps in the room for additional illumination.
- The most resistant to temperature changes and diseases are hybrid plant varieties.
- Seeds and soil must be disinfected, this will prevent diseases and the appearance of pests. The same goes for autumn greenhouse cleaning.
- The seeds must be germinated as the shell is too hard.
- When sowing, the seed is placed on its side, which accelerates the growth of the shoot.
- The root system of the seedlings is fragile, the sprouts do not tolerate the picking, so the ideal container is a peat cup.
- When planting on greenhouse beds, at least 70 cm of distance must be left between the seedlings, so that, while developing, the bush receives enough light and does not shade other bushes.
- If feeding the seedlings is missed, because of which the bushes are frail with yellowed leaves, you need to add fertilizing: 15 g of ammonium nitrate / 5 liters of water.
- Watering by irrigation or sprinkling is not suitable, and the method of applying top dressing on a leaf is not suitable. This increases the humidity in the room, which is fraught with fungal diseases.
Watermelon is a healthy and tasty fruit, loved by both adults and children. Growing a sunny berry on your site is not so difficult. It is important not to allow changes in the microclimate in the greenhouse and to carry out maintenance procedures on time.
Pollination
In good weather, bees and bumblebees fly into the open doors of the greenhouse and pollinate. But it is better not to rely on insects and to carry out pollination by hand.
- You need to find out which flowers are female and which are male. It is not difficult to distinguish them. In females, immediately after the inflorescence, there is a slight thickening, and in males, the petiole is even and thin. Male flowers appear earlier than female flowers.
- The male flower is plucked and the petals are carefully folded back.
- They bring it to the female flower, lean against the inside and lightly tap them against each other.
To consolidate the result, such a procedure with one female flower can be carried out several times. The best results are obtained when pollination is carried out in the morning.