In the Voronezh region, where I live, not all crops can fully develop and give a rich harvest. In recent years, the summer in our area was not too warm, and in July the "rainy season" began. Therefore, the cultivation of even early-maturing varieties of watermelons and melons has become almost impossible. And last season I decided to experiment with such an interesting agricultural technique as grafting watermelons and melons onto bottle gourds - lagenaria. What came of this, I will tell you in my article.

Grafting watermelons and melons on lagenaria - a solution for cold climates
Why is watermelon inoculated on lagenaria
You can plant a watermelon with any pumpkin variety, but it has the perfect combination and full compatibility with the lagenaria variety. After grafting a watermelon on a bottle pumpkin, you can get:
- early harvest;
- larger fruits, improved palatability;
- a plant that is protected from specific diseases.
Watermelons, as heat-loving plants, need a well-warmed soil. At a soil temperature below + 16 ° C, the plant stops growing and developing, which negatively affects the quality and quantity of the crop. Grafting a watermelon on lagenaria allows you to get a plant with a watermelon root system. In such a culture, development continues at a sufficiently low ambient temperature. Thus, the yield of the crop is significantly increased, the taste is improved due to the increase in the amount of sugars, the fruits ripen 10 to 15 days ahead of schedule.


Grafting watermelon
Grafted watermelon plants are not susceptible to fusarium wilt, which can also affect cucumbers. For an early harvest, you can plant a pumpkin or squash.
Types of pumpkins
What varieties of pumpkins are not there today! They are striking in their variety, and it is difficult for a gardener to make a choice of a variety. There are 3 main types - hardy, large-fruited and nutmeg. Among which there are climbing pumpkins and growing in the form of a bush, having large and portioned fruits, with a sweet taste, many seeds, table and feed.
Hardcore is a type of vegetable crop in which the ripe skin is very dense to the touch. Such vegetables have an early ripening period - they can actually be harvested in late August - early September. They are characterized by small fruits with an excellent taste of seeds. Hard-bore crops received from nature a ribbed stalk, on which grooves are clearly visible. They also have a spiny and hairy stem and interestingly shaped leaves with five corners. The seeds of these vegetables have a delicate creamy shade. Among these plants, there are varieties that grow in the form of a bush.
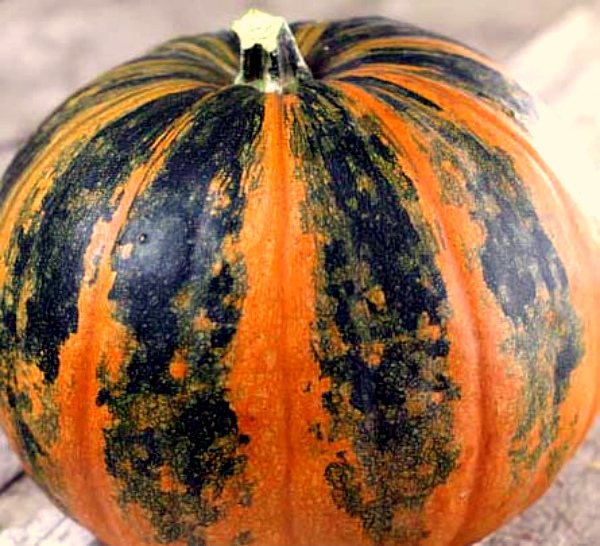


Large-fruited crops are striking in gigantic size. Moreover, the degree of their sugar content can be up to 15%. They have a rounded stem in the shape of a cylinder, the stem is completely devoid of grooves, the leaves of the plants are almost pentagonal. Seeds can be dyed brown or milky white. The advantages of this type of experts include the ability to tolerate very low temperature indicators and lie for a long time even in an apartment, while maintaining normal taste.
Nutmeg varieties are vitamins, they have excellent taste, whatever variety you choose. But at the same time, the disadvantages include their thermophilicity and late ripening of fruits. Therefore, they are advised to grow in the southern regions, so that delicious vegetables have time to ripen in a season. They are distinguished by a pentahedral peduncle, which is wider at the base. They have brown or dirty yellow seeds. You can grow such crops in the middle lane if you plant a culture in the form of seedlings. Moreover, it is permissible to harvest the crop unripe and leave it in the apartment so that the fruits “reach”.
Popular among gardeners are the following pumpkin varieties: "Zorka", "Rossiyanka", "Acorn", "Spaghetti", "Marble", "Freckles", "Sweetie", "Gribovskaya bush", "Almond", "Volzhskaya gray" and others.


Next, take a closer look at some of the varieties:
- pumpkin "Dawn" - is a large-fruited table variety. It has a medium-early ripening period. The fruits are dark gray with characteristic orange spots. The average weight of each is 5–6 kg. The variety has long, highly developed whips. It has a rich orange pulp, which contains up to 14% sugar. Revered by gardeners for the increased presence of carotene - in many ways it is not even inferior to all the well-known carrots.
- pumpkin "Rossiyanka" - a variety with large fruits and early ripening. Its lashes reach 1.5 m in length. The fruits are like a top and have a beautiful orange color. They usually weigh in the range of 2-4 kg. The flesh of the hybrid pleasantly surprises with delicate and delicious notes of melon. The variety is resistant to low temperatures and is considered a high-yielding variety.
- "Acorn", which is also called "acorn pumpkin" - a variety belonging to the hard-bore and quickly ripening crops. It can be climbing or bushy. Its fruits are somewhat similar in appearance to large acorns. The most common vegetables are green, although black, yellow and white vegetables are not uncommon. The flesh of the hybrid has a light yellow color and cannot boast of any special sweetness. This hybrid is great for both baking and stuffing.
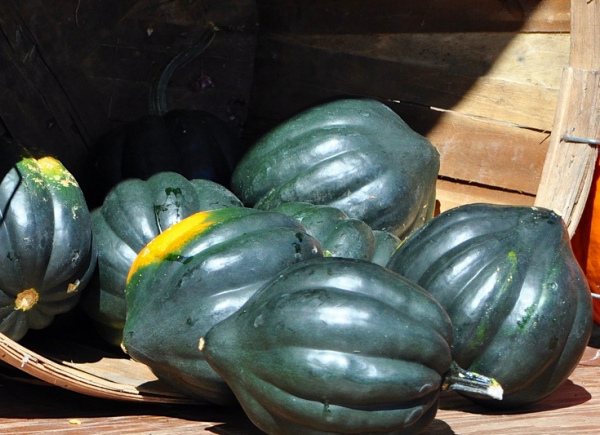


And this is a description of only some of the wonderful varieties. Which pumpkin variety to choose for growing on your own plot depends only on your desire.
When to vaccinate watermelons in the Moscow region
You can plant watermelon and pumpkin seeds for seedlings at the same time or watermelon 3-4 days earlier, in the 20th of April. Daylight hours by this time are already of sufficient duration, so the sprouts will not become thinner due to lack of light. There are several ways to properly plant a watermelon on resistant lagenaria. Such manipulations do not take too much time and do not require special skills.
Grafting a cucumber on a pumpkin
One of the most common methods of vaccination is the tongue method, which even novice summer residents can correctly perform:
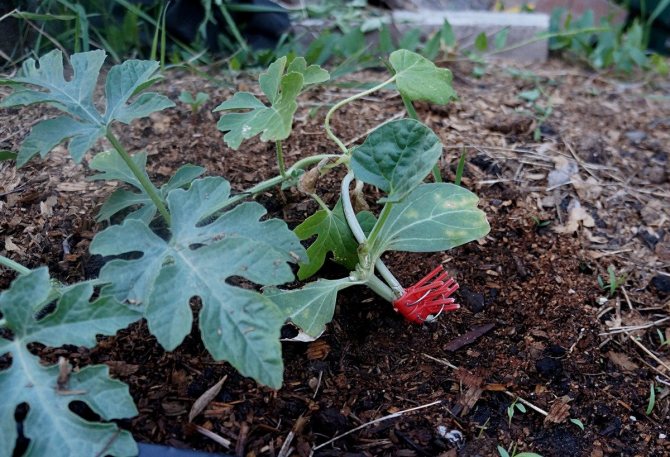
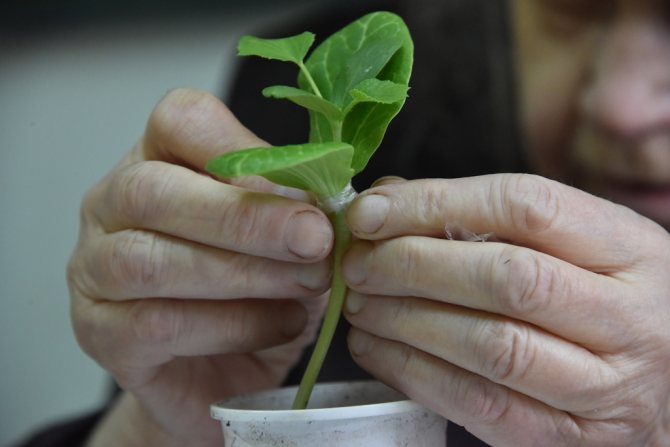
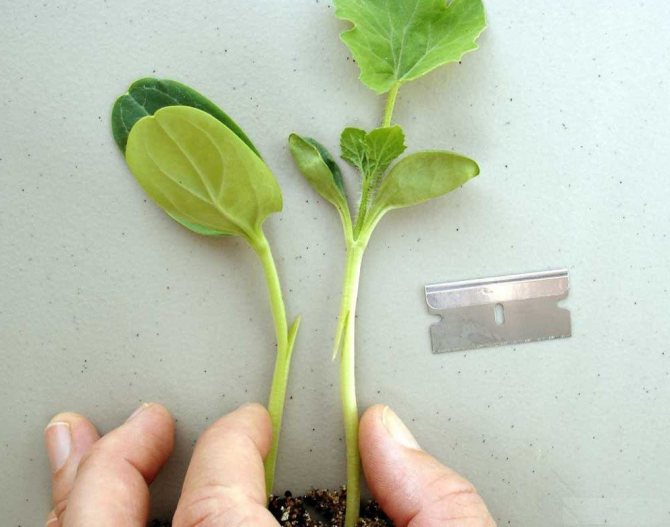
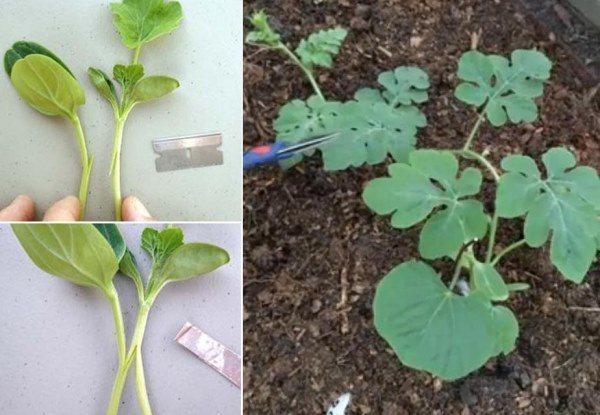
- When a sprout of a watermelon (scion) has 1 - 2 leaves, and a lagenaria (stock) has 1 real leaf, you can begin to vaccinate. To do this, with a very sharp knife or blade under the cotyledon leaves of the pumpkin, an oblique incision is made for 2/3 of the stem from top to bottom.
- In a similar place on the sprout of the watermelon, the same incision is made, from bottom to top.
- The incised stems of the sprouts are combined, superimposing the incised "tongues" on top of each other.
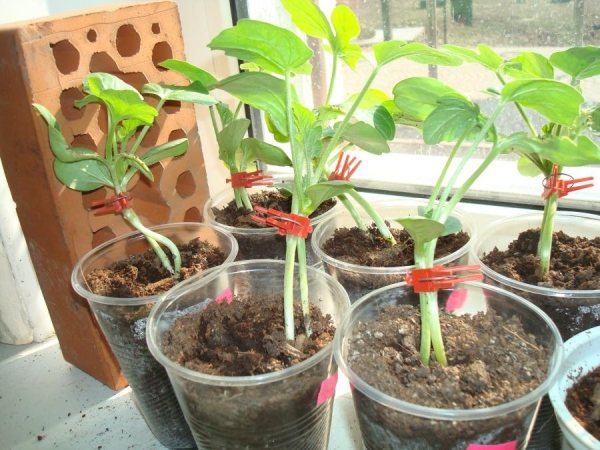
- The stalks are tightly fixed with a foil tape or a special clothespin.
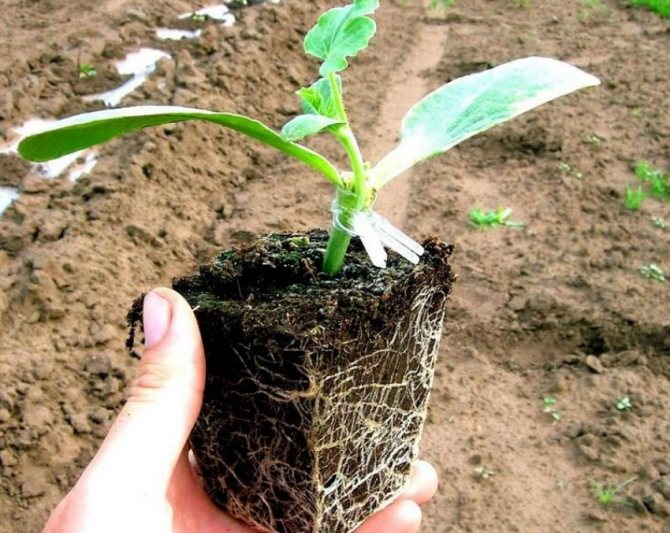
- Both sprouts are planted in one container with fertile soil and exposed in a sunny place.
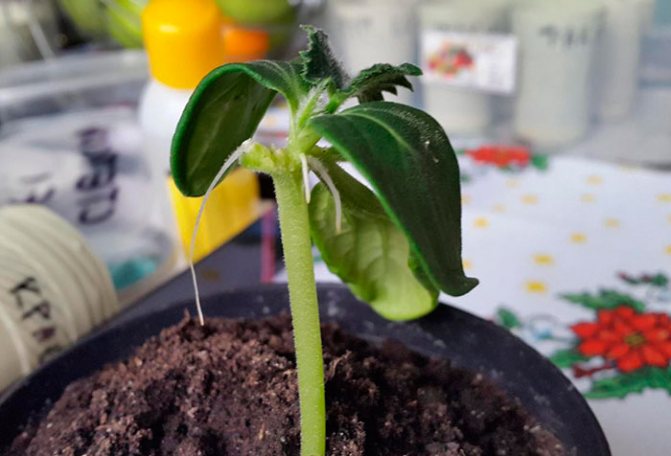
- After 4 days, the stem of the watermelon is pinched below the site of inoculation, because of this, the provision of the sprout with "native" roots is disrupted. Therefore, the grafted plant switches to full provision of a powerful pumpkin root system.
- After 8 - 9 days from the moment of inoculation, you need to completely cut the transferred stem of the watermelon and cut off the growing top of the lagenaria.
Thus, a new plant is obtained with a powerful pumpkin root system and watermelon foliage. By this method, melons, cucumbers, zucchini can be grafted.
Important! Use a very sharp, thin blade to make cuts in the scion and rootstock. It is with such a blade that you can make high-quality cuts that will quickly grow together.
Choosing a variety for grafting
Before you start grafting, you need to choose a stock for your melon. The following varieties of melons are considered the most suitable.
- Pumpkin. Pumpkin grafting is the most common and can be done in a variety of ways. A culture grafted onto a pumpkin gives fruits of good taste, but larger in size. Hardwood varieties are usually chosen for the stock.
- Lagenaria (Latin name Lagenaria). It bears fruit with elongated bottle-shaped pumpkins. Melon grafting on lagenaria is rarely practiced, the risk of death of the seedlings themselves is too high, and the taste of the fruit changes for the worse.
- Zucchini. In the northern regions, zucchini seedlings are often used as a rootstock - the resulting plants quickly form and give off a crop, the bushes themselves have increased resistance to changeable weather.


Melon grafting on pumpkin
There are also special Chinese rootstock systems. They are hybrids, so it is impossible to grow them on your own, you have to order seeds.
Crossing pumpkin and watermelon by the method of convergence
How to germinate watermelon seeds
A fairly simple method allows you to independently cross a watermelon for lagenaria:
- In one medium-sized container, filled with loose fertilized soil, one seed of kavuna and one pumpkin are sown at the same time. The seeds are placed very close to each other so that the sprouts germinate side by side.
- When both seedlings have 1 - 2 full-fledged leaves, on the stems from each other's side with a sharp blade, you need to make thin longitudinal slices of the skin at the same level.
- Gently connect the sprouts, the cut parts should be in close contact.
- You can fix the stems for several days using foil or a special clothespin.
- After the stems grow together, you will need to cut the trunk with the root system of the watermelon and the top of the harmelon.
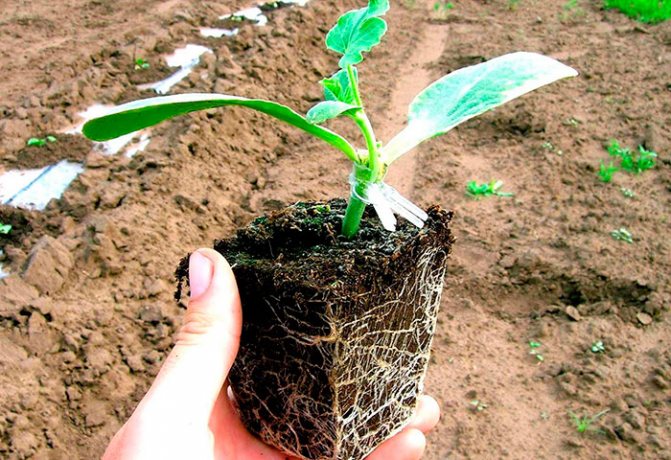
The grafted plant should be strong before planting in open ground.
Features of the procedure
To enhance the properties of the grafted plant, breeders traditionally use a younger stock. Accordingly, the scion must be older.
The graft must be older than the rootstock. This is due to the fact that a young plant changes individual qualities more easily. Thus, the quality of the scion will dominate in the grafted plant.
In our case watermelon seedlings should be planted at least three days earlier than lagenaria seedlings.
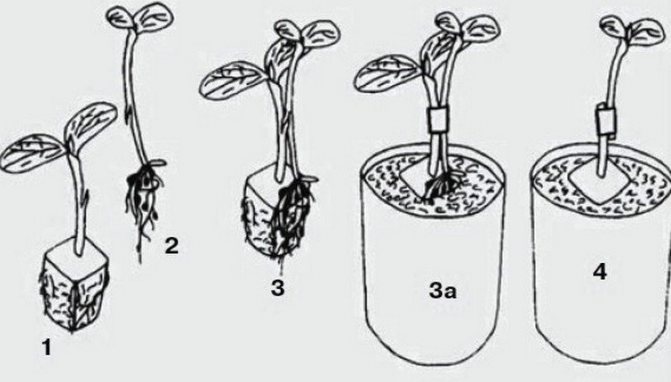
Before grafting, melon seedlings can be grown in small cups of 100-200 ml. After grafting, the plant will need a much larger volume of the nutrient mixture.
After grafting, the plant is immediately transplanted into a larger glass (0.5 - 0.8 l).
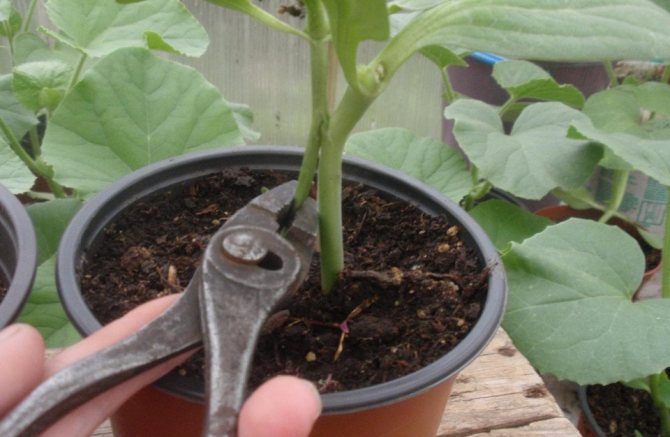
To increase the yield of grafted plants, all pumpkin leaves (stock) should be removed... This stimulates the metabolic processes of the combined plants, and the result is a good harvest.
Another feature of a grafted watermelon is the need for more territory.... When planting in open ground, each seedling is allocated up to 8 square meters. m of usable area.
Watermelon seedlings should be planted at least three days earlier than Lagenaria seedlings.
End-to-end grafting method
Watermelon seeds - how to prepare for sowing
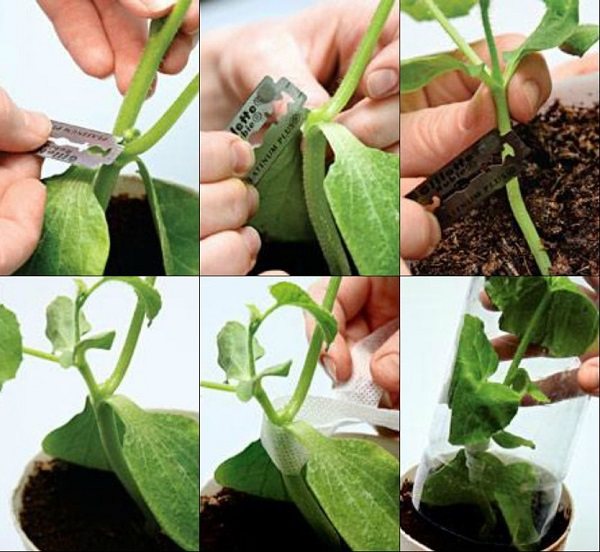
When the pumpkin seedling has 1 true leaf, and 1 - 2 leaves have grown on the sprout of the watermelon, you can graft with the butt method. With a blade, a very sharp knife or a surgical scalpel, an oblique cut of the stem is made on the lagenaria. At the same time, the growing point and one cotyledonous leaf are removed, the second must remain intact on the stem.


Butt
The top of the watermelon sprout is cut obliquely below the cotyledon leaves and connected to the pumpkin cut. Both stems are connected with a special clothespin or clip. The grafted plant needs to be provided with a warm and humid environment for faster and easier engraftment of cut surfaces. For this purpose, the pot with the plant can be covered with a plastic bottle cut off on one side or a plastic bag. The ambient temperature should be within the range from + 24 ° С to + 26 ° С. It will take several days for the sprouts to take root, after which the connecting clip is removed.
Tongue grafting technology
To carry out the procedure, you need:
- a bottle gourd seedling (lagenaria), which is in the phase of full disclosure of cotyledon leaves, and a watermelon seedling, which is 3-4 days older than the pumpkin seedling;
- a surgical instrument - a new double-sided razor blade, one edge of which is wrapped with electrical tape, or a small medical scalpel;
- dressing material - a strip of foil, a piece of bandage or a loose plastic clothespin with smooth lips;
- thin wooden peg;
- marker.


The grafted bushes are attached to each other
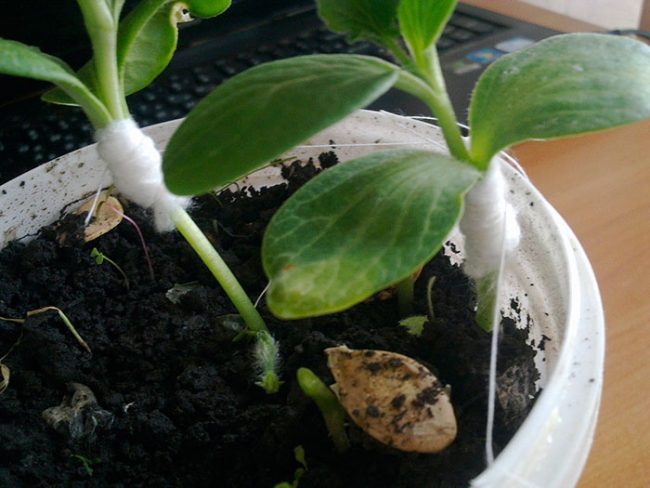
1. Lean the seedlings growing next to each other so that they connect just below the leaves, and mark the point of their contact on the stems with a marker.
2. Having retreated from the marked risks down by 1 cm, touch the razor to the watermelon stalk and from this place make a long, two-centimeter oblique cut upward.
Attention! Move the blade very carefully! The stem does not need to be cut, but only cut so that a triangular tongue "looking down" is formed on it.
3. On the lagenaria sprout, make a similar cut, but this time go up 1 cm from the mark and move the razor in the opposite direction.


You can plant a bush a month after vaccination
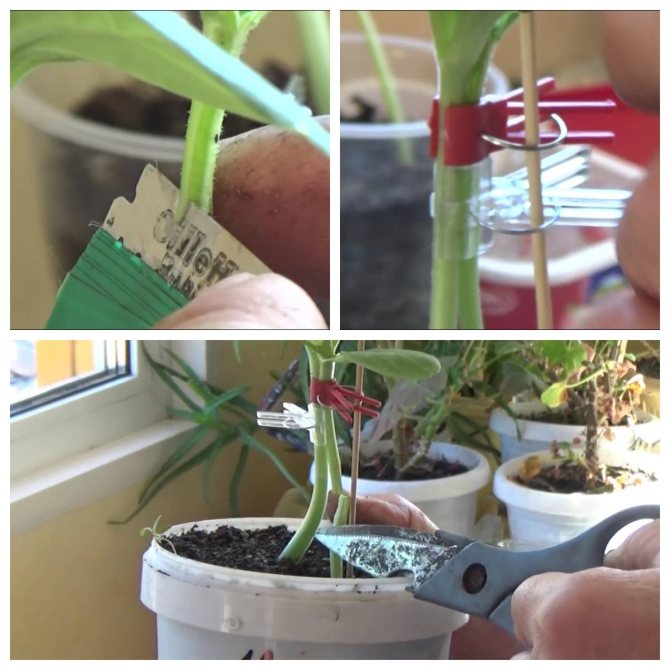
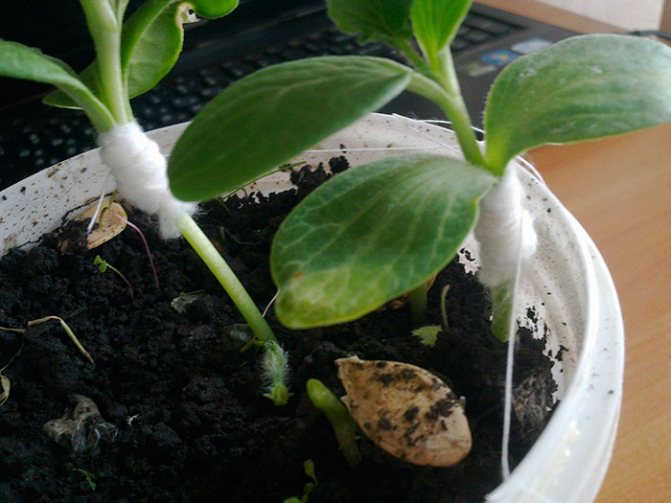
4. Clasp the sprouts with the resulting tongues (by winding them one after the other), ask the assistant to hold the seedlings in this position, tightly wrap the junction of the sprouts with foil, tie the bandage with gauze tape or fix it with a clothespin.
5. Next to the tied stems, stick a peg into the ground to keep them upright.
6. On the fifth day, squeeze the stalk of the watermelon located below the grafting site with your fingers. Such a crimping is done so that the sprout begins to feed on Lagenaria juices. Repeat this procedure a day later, and on the ninth day from the day of inoculation, completely cut the watermelon stem that has withered by this time, remove the leaves from the top of the lagenaria seedling and pinch the point of its growth.
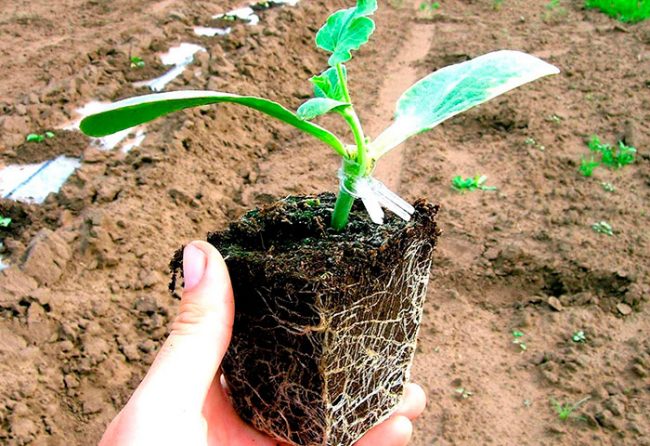
On melons, a watermelon grafted on a pumpkin stock can be planted when it reaches the age of one month.


When grafting by the method of convergence, only a little incision is made on the skin.
Lateral incision grafting method
You can easily graft a watermelon yourself into a side cut on the stem of a pumpkin. When there is already at least 1 real leaf on the Lagenaria sprout, and 1 - 2 leaves on the Kavuna seedling, you can graft the plants. With a sharp knife blade on the pumpkin stalk below the cotyledonous leaves, a vertical cut is made approximately 1.4 - 2.0 cm long. The same sharp blade is used to cut the watermelon top at an acute angle below the cotyledonous leaves.
The cut top of the watermelon is inserted into the vertical cut on the stalk of the harmelon, so that the cut surfaces of the two plants are in close contact. The vaccination site is fixed with a vaccine clip for several days.
Important! Do not remove the vaccine clip before the due date. This can lead to a violation of the fusion of the scion and rootstock.
A greenhouse effect is created for the plant using a plastic bottle or plastic bag cut off from one side for the period of overgrowing of the slices. Approximately 10 days after the successful inoculation, the top of the lagenaria is cut off, leaving an engrafted watermelon sprout.This is how a new plant is obtained with watermelon tops and a powerful pumpkin root system, capable of actively taking moisture and all the necessary nutrients from the soil even at low ambient temperatures. The roots of an ordinary watermelon, accustomed to growing in well-warmed light soils, do not have such features.
Tips & Tricks
Newly baked plants need special care.
Immediately after inoculation, the melons are covered with caps and removed to a warm place so that direct sunlight does not fall on them. High humidity is maintained inside the mini-greenhouse, but at the same time, one should not forget about short-term (1-2 minutes) ventilation.
Important! It is recommended to remove the caps only after a couple of days, after the melon begins to grow.
When watering, it is important to ensure that no drops of water fall on the vaccine.
Experiments on grafting melons and cucumbers have their own subtleties and their own terminology. The grafted plant is called the scion, and the self-rooted plant on which it is grafted is called the stock. Melon, watermelon and cucumber are used as a scion, and table pumpkins are used as stock. For example, from large-fruited pumpkins, it is advisable to take Gray Volzhskaya 92, Gribovskaya Winter, etc.; from hard pumpkins - Mozoleevskaya 49, Ukrainian multiparous, and from nutmeg - Vitamin and Interception local. In Holland, some practitioners, to avoid root rot in greenhouses, plant a cucumber on a Fig-leaved gourd that is resistant to fusarium wilt. The cultivation of melon, watermelon and cucumber by grafting on a pumpkin has its own characteristics.
Recommended varieties for grafting on pumpkin
The use of a gourd pumpkin as a rootstock significantly increases the cold resistance of grafted watermelon, melon, and cucumber. Back in the late 1950s, at the former Gribovskaya station (now VNIISSOK), double yields were obtained from watermelons grafted onto a gourd. The fruits from the grafted watermelons turned out to be larger and sugary in comparison with the watermelons grown on their own roots. Melon grafted onto a pumpkin also yielded good results (S.P. Lebedeva's experiments, set up at the All-Union Agricultural Exhibition before the war). For grafting on a gourd, scientists recommend taking high-sugar melons (Ich-Kzyl, Gulyabi, Kzyl-uruk, Ak-Kaun from Central Asia, the European variety Kolkhoznitsa, etc.). Watermelons for this purpose are suitable for the following varieties - Melitopolsky 143, Bykovsky 23, Marble and others. It is better to take heterotic hybrids from cucumbers (parthenocarpic and bee-pollinated).
Conditions for fusing grafted plants, tools and grafting process
For successful fusion of grafted plants, a warm (20-30 °), humid atmosphere (95-98%) and diffused light is needed, especially in the first days after grafting. The expert needs to make a film box, it can be placed in the kitchen near the window. The height of the box is 30 cm, the length is 0.5-1.5 m and the width is 0.3 m.Tighten the sides and lid of the box with a light film, and the bottom can be a wooden or metal tray, on which 2-3 cm of sawdust should be poured or sand, subsequently moistened. Whoever has a greenhouse or greenhouse, it is better to keep the vaccination box there. Pots with grafted watermelons and cucumbers grafted onto a gut can simply be placed in plastic bags, spreading them out with sticks and placing the pots in plates with a layer of sand or sawdust. To bandage the wound site in grafted plants, it is necessary to prepare a 20 cm long cotton wool flagellum, as well as a soft washcloth cut into ribbons 30 cm long and 0.5 cm wide.
To vaccinate, you need to stock up on an unused safety razor blade or a razor-sharp knife. The plant sowing time is set so that the grafted plants are planted in a permanent place at the age of 30-35 days. Sow rootstocks 2-3 days earlier than scions.
If the seedlings are prepared in greenhouses or a greenhouse, it is more convenient to sow the scions in seed boxes with a distance between rows 3-4 and in rows of 1.5 cm, and rootstocks in pots, preferably clay or film, 10-15 cm in size. 2-3 seeds in pots to the stock. Grafting is started when the plants are in the cotyledon phase or one true leaf.
The graft is inserted into the lateral incision of the stem, into the split (only for rootstock with a completed, incomplete stem) or by bringing it closer together. In the latter case, the plants sown side by side are interconnected without separation from the roots. In places of contact, the skin is removed from both plants along the stem to a length of 1.5-2 cm and tied. After accretion, the roots of the scion are cut off.
The best grafting is in the lateral incision of the stem. On the stem of the pumpkin, make a longitudinal cut on the hypocotyledonous knee, slightly receding from the cotyledon node (between the cotyledonous leaves) on the side opposite to the first true leaf. The length of the longitudinal cut on the pumpkin should not exceed 1.5-2 cm. The cut is made straight to the entire depth of the stem tissue up to the hollow space in the middle of the stem.
The graft (melon, watermelon, cucumber) is cut from the root and on the cotyledon knee on two opposite sides of the stem under the cotyledon leaves, the layer of the skin (epidermis) is cut straight off to the same length as the cut on the pumpkin stem. To open the cut on the stock, you need to slightly bend the stem of the pumpkin, press it from the bottom of the cut with the thumb of your left hand away from you and with your index finger on top of the cut towards yourself; the wound will open easily. The scion is inserted into the cut of the rootstock stalk in such a way that the bare-skinned scion stalk is exactly in contact with the cut walls of the rootstock. In this case, the end of the scion stem should come close to the end of the rootstock cut and not slip into the hollow part of the pumpkin stem, as well as not protrude beyond the outer surface.
After the stem of the scion is inserted into the rootstock incision, the site of inoculation is bandaged with a washcloth or a cotton wool flagellum. To prevent the melon stem from moving, it is held with the thumb and forefinger of the left hand, and bandaged with the right hand. It is important that the dressing material fits snugly around the stem of the plant, but does not press into it. After finishing bandaging, the plant is watered and placed in a moist warm atmosphere of a film box.
Caring for grafted plants
In the first days after grafting, the plants must be shaded from direct sunlight with paper to prevent wilting. The grafted plants should be watered daily and ventilated. On the 5-10th day after the vaccination, if it is successful, the grafts begin to grow. From this moment, the ventilation is intensified and the plants are gradually accustomed to normal conditions; after 2-3 days they can be taken out and the box. It is necessary to ensure that the bandage does not tighten the stem, which is why it has to be bandaged several times. The pumpkin leaves shading the scion should be cut off. However, leaves cannot be removed completely.
They are preserved throughout the growing season and are systematically cut off, preventing oppression and shading of the grafted plant - melon, watermelon or cucumber. In this respect, gourd as a stock has advantages over table pumpkins. Watermelons, melons and cucumbers grow on a gourd, with no true leaves in the gourd rootstock. Unlike potted table gourds, gourd can be sown in a box with 8-10 cm soil at a distance of 4-5 cm between rows. Before grafting, dig out the gourd, put it on the table, remove the growth points and the first real leaf, and through the hypocotal knee (between the cotyledonous leaves) make an incision 1.5-2 cm long, insert into this incision the scion removed by 1.5-2 cm from skin on both sides, bandage with a cotton wool flagellum and plant in a pot, without covering the grafting site with earth. Further care is the same as for pumpkin grafting.
When growing seedlings, so that the grafted plants do not break, they are tied to pegs or twigs 18-20 cm long.The grafted plants are fed 2-3 times with organic fertilizers (1 part per 10 parts of water) and urea (1 g per 1 l of water).
Planting seedlings of grafted plants
Plants are planted after the frost has passed. To get earlier production, seedlings can be planted 15-20 days before the end of frost on the soil mulched with a film or on steam (manure) heaps and cover them with caps made of translucent film. When covering with foil, it is necessary to provide ventilation in sunny weather. To do this, uncut or pierce the film over the plants. Melons, watermelons, cucumbers, grafted onto a gourd, are planted without filling up the grafting site. The feeding area in open ground is 1X1 m, in unheated greenhouses they are planted at the rate of 2 plants per 1 m 2, tying them to trellises, like ordinary cucumbers. During planting, 3 kg of rotted compost, 1.5 g of superphosphate, 5-8 g of potassium chloride and 10 g of wood ash are introduced into the hole. When planting melon, watermelon and cucumber, grafted onto different rootstocks of table pumpkins, the feeding area is left larger (2x1.5 m).
Before planting, the site is marked in two directions, so that there is 2 m between the rows going from east to west, and 1.5 m from north to south.A hole is made at the intersection and grafted plants are planted, no deeper than they were in pots, and so that the accretion remains above the surface. Before disembarking, you must loosen the bandage. After planting, the plants are watered abundantly with water, and then sprinkled with humus or peat. Pumpkin scourges are taken to the side (to the east or west) and lightly sprinkled with earth to prevent burns. For the same purpose, the stem of the scion is placed on the stem of the pumpkin - under the shade of the leaves of the pumpkin. The place of fusion with the pumpkin is covered with a thin layer of grass. After planting, it is necessary to ensure that the ground in the holes does not dry out, in dry weather, water at least one, and preferably twice a day, until the planted plants take root. The grafts are carefully taken to the side towards the south and fixed with twigs. To prevent the scions from shading, during the summer it is necessary to systematically limit the development of the stock (pumpkin) by pinching the tops of the main and lateral shoots. Pumpkin whips should not be longer than 1.5-2 m. They must be pinned to the ground with twigs and sprinkled with damp earth in order to cause the formation of additional roots and distribute the whips as evenly as possible on the soil surface.
Care for scions of melons, watermelons and cucumbers
Grafts are given the opportunity to develop freely and only late ovaries are removed (in the Moscow region from August 25). The frequency of fertilizing depends on the fertility of the soil. Before the formation of fruits, you can give top dressing in 10-15 days. For the first feeding, nitrogen fertilizers are taken, for the subsequent complete mineral fertilizers per 1 plant (in g): 20 - urea, 30 - superphosphate and 15 - potassium salt. It is best to use organic fertilizers, poultry manure and mullein are diluted 8-10 times with water, slurry - 4-5 times. 1-2 liters of such fertilizer are poured under each plant. For seeds for the next year harvest, fruits with high taste are selected from the most fruitful and early ripening plants: melons, watermelons and cucumbers grafted onto a pumpkin.
Based on materials from the magazine "Household economy", 1987 O. Yurina, doctor of agricultural science.
Many growers grow melons, but the results are not always as expected. Since melons are very often affected by various diseases. One of the most dangerous diseases is fusarium wilting... Today there are already many varieties resistant to this disease, but this does not solve the problem. If your site is infected with this fungus, then you need to wait more than five years for the soil to clear. The best way out of this situation is to graft the melon onto the bottle gourd (lagenaria). You can graft a melon onto a regular pumpkin, but the fruits will be too large and their taste will be worse than the real ones. Also, such a vaccine takes root very badly. Therefore, it is very important to know how to properly graft a melon onto a pumpkin.
Grafting into cleft
For grafting into the rootstock split, it is better to use Lagenarium seedlings sown 3 to 5 days later than watermelon. The grafting process goes very well when a full-fledged leaf is just beginning to form on the stock, and the scion already has 2 or even 3 leaves.
A thin sharp blade is cut off the growth point on the pumpkin stalk, while removing the forming leaves. At the site of the cut, an injection is made with a toothpick, extending the empty space literally by 1 - 2 mm. between the cotyledonous leaves. A watermelon top with leaves and a growth point, cut at an acute angle, is inserted into the resulting split. The cut surfaces of both plants are pressed tightly against each other using foil tape or grafting clothespin. This fixation is left for several days until the rootstock and scion are completely fused together.
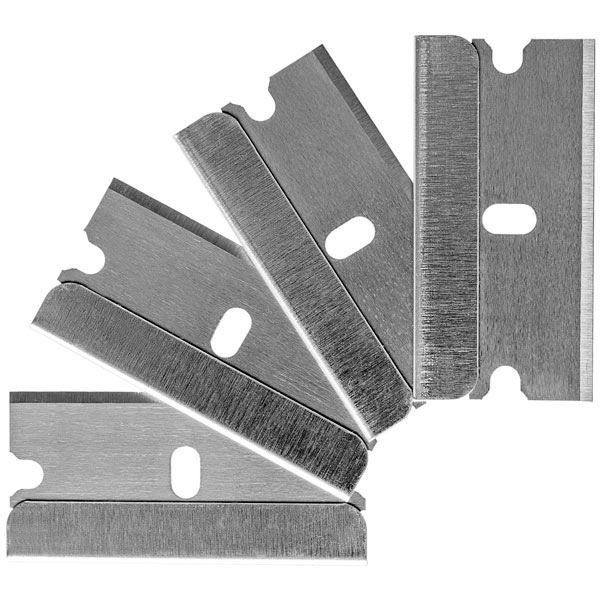


The blade is worth using
This method may confuse some gardeners, however, with patience and perseverance, you can quickly gain the skills of grafting watermelons and melons into clothespins and using the injection method.
Technology and ways to instill
For grafting you will need: a sharp safety blade, non-woven or polyethylene bands for tying, grafting clips. Before the procedure, the instrument is disinfected with alcohol, one side is wrapped with electrical tape.
There are three main methods of grafting besides the splitting method. Home procedures guarantee only 70% -80% survival rate.


Grafting in the center of the pumpkin
To the center of the pumpkin
Quite a complex procedure that requires some skill and knowledge of technology. If it is the first time, it is advisable to involve an assistant.
- at the rootstock, the upper part is cut perpendicularly with the first leaf above the cotyledons;
- between the cotyledons in the center of the stem, a puncture is made with an awl to a depth of 1.5 cm;
- the scion is cut off at the soil level, peel off the skin from the bottom by 1.5 cm;
- the stem of the scion is inserted into the puncture hole for its entire length;
The tissues of the grafted plants must be in close contact. After that, the joint is tied with a tape and fixed with a clamp.
By the convergence of plants
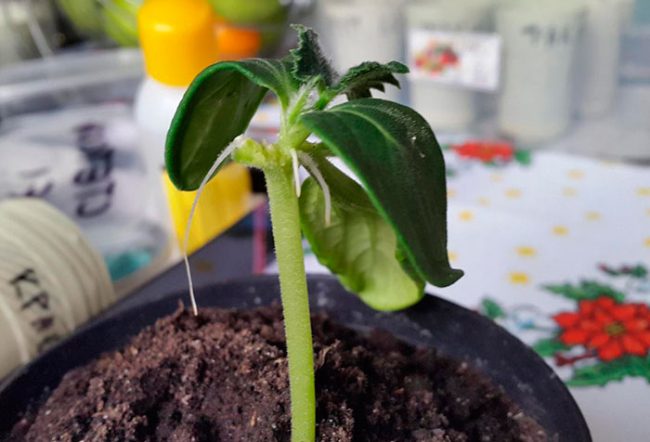
This is a relatively simple procedure that a beginner can do well.
- pumpkin and melon seeds are sown nearby;
- under the cotyledons, a thin skin (epidermis) of plant stems is removed by 15-20 mm;
- plant tissues are tightly pressed against each other;
- tie and fasten with a clip.
There is a second version of the procedure. On the rootstock and scion, cuts (tongues) of the same size (1.5 cm) are made in opposite directions. The tongues are inserted into each other with a "lock" and fixed.


Grafting by convergence of plants
After 5 days, the stem of the scion below the graft is slightly crushed with your fingers. This procedure is carried out daily until the stem of the melon is dry. After 6-8 days, the pumpkin stalk above the grafting is removed. The root of the scion is cut off during transplantation into the ground.
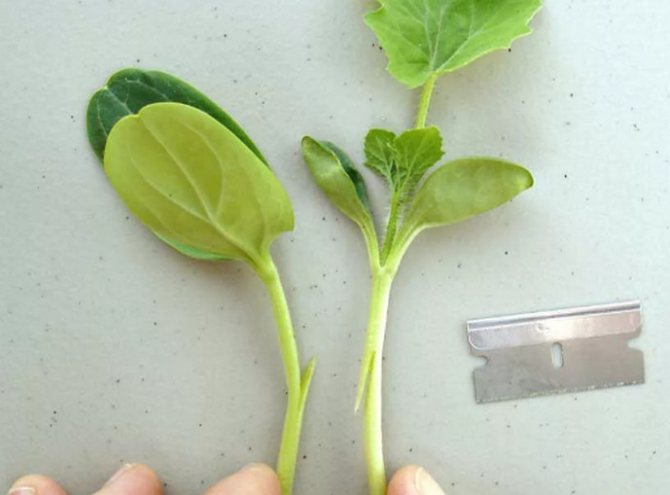
To the side of the stem
The growth point is removed from the rootstock so that only the first true leaf and cotyledon leaves remain. On its stem, a straight incision is made from top to bottom with a length of 1.5-2 cm. The depth of the cut should reach the middle of the stem.
The graft is cut from the soil. On both sides of the stem, from the side of the cotyledonous leaves, peel off the length of the rootstock cut. Slightly bending the stem of the rootstock, open the incision and insert the scion, achieving a snug fit of the tissues, tie it with a ribbon.


Grafted melon in the side of the stem
Care Tips for Grafted Watermelons
Gardeners cultivating land in regions with a short cool summer are unlikely to boast a good harvest of ordinary melons and gourds. That is why the inhabitants of the Penza region plant watermelons grafted on the lagenaria.
When the grafted seedlings reach the age of 1 month, they can already be planted in open ground. It is better to choose plots for sowing melons and gourds with good sunlight, if possible on a hill. All melon loves light, loose soil, but grafted kavunas, which have a powerful pumpkin root system, feel very comfortable on dense soils.
Important! Crop rotation must be observed. The ideal predecessors of watermelons are root crops, legumes, and cabbage.
For planting watermelons crossed with pumpkin, you do not need to use the standard scheme for planting melons and gourds, up to 7.5 - 8 m2 of free area should be allocated per plant. Many novice gardeners are wondering: why leave so much room for each small sprout? The answer is very simple: the powerful root system of the crossed plant supplies much more nutrients, which contributes to the active growth of the tops and the formation of fruits. A thicker planting may result in thickening.
Watermelons need abundant watering during the period of leaf and ovary growth, but by the beginning of fruit ripening, watering will have to be reduced to increase the sugar content of the crop.
https://youtu.be/6_xT5qpFGNA
Why vaccinate
The main reason that prompted vegetable growers to graft watermelon seedlings is their weak and very sensitive root system. The strong, taproot of the pumpkin, on which the watermelon will grow and ripen, is not only resistant to adverse conditions and temperature fluctuations, but also:
- not affected by soil pathogens that cause such watermelon-destroying diseases - fusarium, anthracnose, root fungal rot;
- allows you to plant a crop in open ground earlier than usual;
- significantly accelerates the growing season, the rate of development and maturation of the watermelon;
- increases the number of full-fledged, ripening ovary, the yield increases almost 2-fold.


Required tool


The success of the vaccination directly depends on the correct choice of the instrument. The main requirements for the tool: it must be sharp and clean. With insufficiently sharpened metal, you cannot cut the cambium, but only crush it. As a result, moisture will not be able to get into the tissues, the process of cell mitosis will slow down, and the scion itself will dry out. That is why many summer residents use a shaving blade for grafting, one half of which is wrapped in woven material.
It is also important to ensure full contact of the rootstock for the home watermelon with the scion. It is important that as many cells as possible are in contact with the membranes. For this, tying is usually used, which provides for a tight winding of the junction of the cultures with hemp thread. Instead of a thread, you can use a bandage, washcloth or cellophane strips. After tying, the material is tightly pressed with special clips.