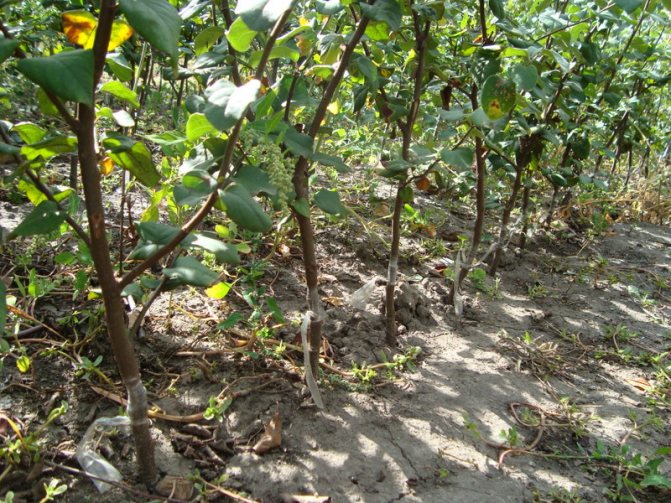
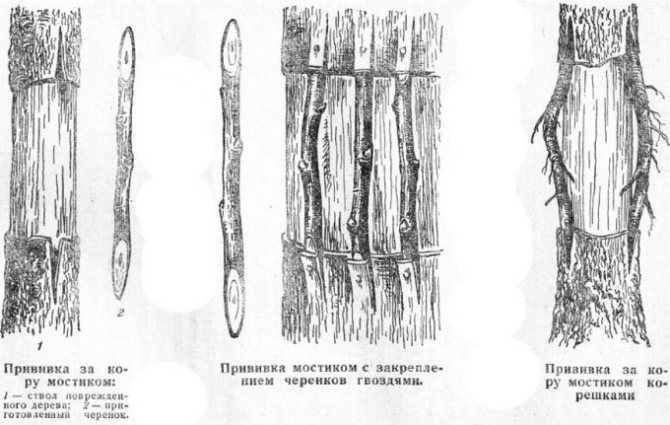
In what ways can cherries be grafted
There are many opportunities for grafting trees in horticulture, but three methods are recommended for stone fruit trees, especially cherries:
- grafting cherries with improved copulation;
- grafting cherries into the cleft;
- grafting for the bark of a tree;
- grafting with a kidney, budding.
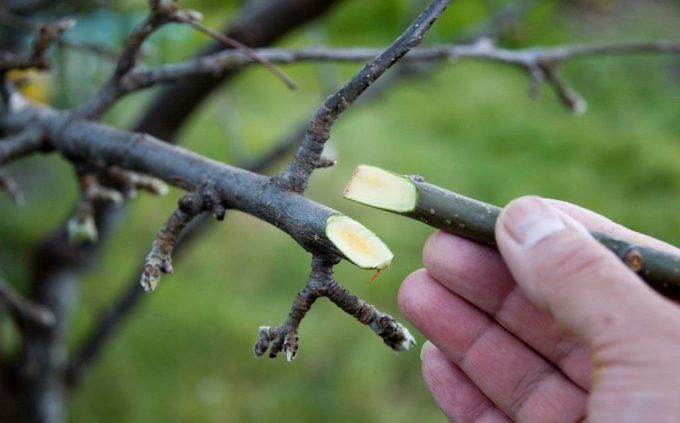
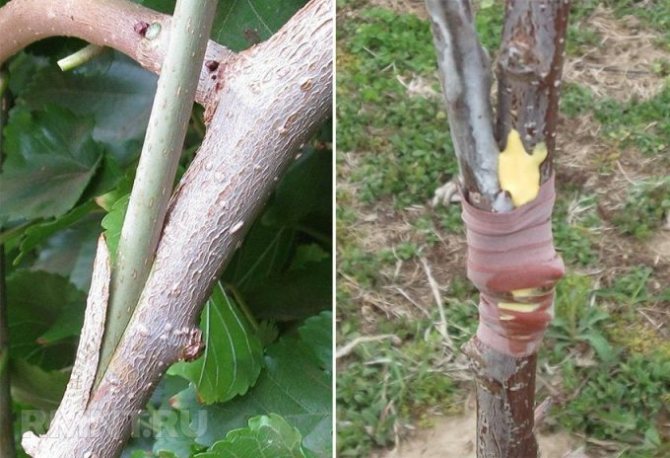
Let's make a reservation right away that it is better to carry out all the listed types of vaccinations in the spring. The improved copulation method is used when the grafted branch (scion) and the trunk (stock) have the same thickness. This happens when the cherry is still young, and the cut branches ready for grafting are also matched in thickness and size. In this method, the same cuts are made on the scion and on the rootstock, then the rootstock and the scion are joined, fastened with garden varnish (or oily paint), and then tied.

Grafting cherries in the cleft.
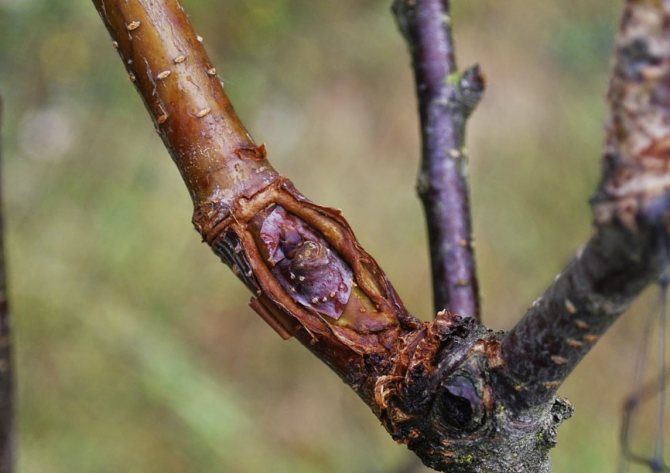
When carrying out this type of grafting, it is important that the exposed layers of the cambium on the rootstock and the scion are in contact with each other. The cuts on the rootstock and scion should be oblique, about 2.5 cm deep, and closer to the ends of the cuts, you need to make cuts about 1.5 cm deep.Remember that the knife, hands and all tools that are used in this process must be perfect clean. Otherwise, there is a risk of infection of the tree, and the infected plant can never be grafted, since all its strength will be spent on curing its own diseases.
Let us explain what cambium is. Cambium is a layer in the trunk of a tree that is responsible for the plant's ability to heal its own wounds. It is thanks to this property that vaccination became possible. Cambium is the third layer of the trunk from the outer edge, which comes after the bark of the tree, and the thin layer that follows the bark and is called bast in biology. Best and most of all this substance is released in the spring, hence the advice to start an inoculation in a nominal spring.
If the rootstock is much thicker than the grafted branch, the split grafting method is used. It is possible, if necessary and if there is enough space in the rootstock trunk, to prepare two cuttings for grafting. In this method, the stock is split in two, and cuttings are inserted into the cut site, which are then tied. In this type of grafting, the stem of the stock should be split to a depth of 2-3 cm.
In the bark grafting method, two grafts can also be used. This method is used when the trunk is much thicker than the cuttings and it is possible to place the cuttings under the bark of the trunk. In the bark, longitudinal cuts are made with a length of 2-3 cm and under the bark, in the places of the cut, cuttings are placed, previously cut 2 mm above the rootstock itself.


Cherry bud grafting
Not only in spring, but also in summer, you can plant a cherry with a bud. This method is also called budding. About a week before grafting, all shoots (lateral shoots) must be cut off on the rootstock. Cuttings can be cut right on the day of budding. When choosing cuttings, pay attention to the buds, they must be formed. On the day of budding, after collecting the cuttings, it is necessary to cut off the buds on them with a knife so that a small dent remains. Then the stock and the cutting in the place of such a cut are connected in a T-shaped way.
Pear - choice of rootstock and vaccination rules
| Friendship Tree in Sochi |
Vaccinations are not in vain considered the gardener's "golden key", they work wonders with plants. One of the unique trees is considered to be the Tree of Friendship, planted in Sochi: 45 species and varieties of citrus fruits - kinkans, lemons, tangerines and others - were grafted on it. Citrus fruits do not grow in our gardens, but you can still create your own unique tree by grafting new varieties into the crown of already existing adult trees.
Before starting vaccinations, you must objectively assess the condition of the trees in your garden. If the height of the apple tree exceeds 4-5 m, the crown is thickened and poorly lit, the growth is less than 30 cm per season - the tree needs rejuvenating pruning, reducing the crown to 2.5 m, intensive nutrition and care. And only after putting the tree in order can you be vaccinated.
It is important to take into account the compatibility of the rootstock and the scion according to the biological rhythms of their life: summer varieties get along well on the rootstock with the main summer variety or early autumn, autumn - with autumn, winter - with winter. Successful combinations of the groups of varieties that are closest in terms of development and ripening are possible: late autumn with winter, late summer with early autumn, but not "over the head" of the intermediate period. For example, winter and summer varieties will not feel comfortable on the same rootstock, some of them will be oppressed and soon, for sure, will die.
However, in your garden you can experiment as you like. If you do not set the goal of obtaining a large harvest, then it is quite possible to create a miraculous tree that blooms and bears fruit for all the periods existing in a given climate. At the same time, experienced gardeners recommend grafting summer varieties in the upper part of the crown, autumn varieties in the middle, winter varieties in the lower tier. The most delicate varieties are also grafted into the upper part of the crown or trunk, since the air temperature there in winter is much higher than above the snow surface. Often low-value varieties are re-grafted with good preservation of the boles.
Grafting with a bridge over the ring of damaged bark saves the life of young trees after winter damage by rodents. Additional grafting in the crown restores the lost branches of the ornamental tree and restores its beauty. Often, double grafting is used, including a stem former between the scion and the successful rootstock, if their compatibility is insufficient or completely absent. Inserts from clonal rootstocks, which slow down the growth of the scion, are often used as a strainer.
The mutual influence of the rootstock and the scion has been studied for a long time, some patterns have already been identified, and it is useful to know them so as not to waste time and money in vain. So, grafting plums on blackthorn or Altai Siberian spruce makes it possible to get undersized and very decorative trees. Shrub cherry, or steppe, serves as a stock for obtaining dwarf forms of cherry and sweet cherry. It is convenient and economical to graft a male branch of sea buckthorn into the crown of female plants - this will save space for purely male specimens of this wonderful culture. Weak pear trees can be obtained by grafting it on common quince, cotoneaster, black chokeberry (chokeberry), irga. But the risk of incomplete compatibility of these atypical combinations is great, and after a few years the tree may die (especially in the version with irga, which grows much slower than the grafted pear). A compromise option is to inoculate trees with an intermediate insert from plants of those species and varieties that are well compatible with both the scion and the stock.
Vaccination methods: 1 - into cleavage; 2 - in the side cut; 3 - for the bark |
Fruit growers have long noticed that a pear grafted onto a quince produces sweeter fruits than a wild pear. Reverse grafting of quince on a pear fails. A pear, grafted onto a mountain ash, accumulates a lot of tannic acids in the fruits and becomes little or inedible. Pear grafting on varietal mountain ash is often successful.Aronia on mountain ash becomes almost a dwarf and begins to bear fruit earlier (like most dwarf forms).
If you plant it on a bole about 1.5 m high from the ground, you can get an elegant tree. On the other hand, a mountain ash grafted onto a hawthorn grows taller than usual.
The incomplete compatibility of the scion and the rootstock is indicated by the noticeable influx of the scion, the oppressed state of the tree, the abundance of growth on the rootstock.
The methods of grafting are classic and well-known to everyone: butt, for the bark, copulation, improved copulation, less often - budding (it is usually used in nurseries on seedlings). Grafting by cutting gives a faster result in relation to the ultimate goal - fruiting. The main thing in the grafting technique is the purity of the material, quick smooth cuts without drying, the combination of the cambial layers of the scion and rootstock on at least one side (with a large difference in their size).
It is possible to graft new varieties both on young seedlings and in the crown of adult trees. The grafting time is spring, before and during sap flow, when the bark is well separated, but before flowering. Summer vaccinations are also practiced - at the beginning of July. For each type of vaccination, a certain amount of warm time is required before the autumn frosts, therefore, in our conditions, vaccinations are not done at the end of summer and in the fall.
When choosing a place for grafting, take into account the presence of space where a new variety of scion will grow, or deliberately thin out the crown so that the grafted stalk is well lit and well located.
In the first year after grafting, the scion is not allowed to bloom and bear fruit in order to direct all resources to development, strengthening the grafted shoot, therefore, the buds and fruits are promptly removed. At this time, they closely monitor the appearance of wild growth, remove it immediately, digging up the ground to the very roots of the rootstock. Otherwise, it can quickly drown out the grafted form and even completely replace it.
April-early May is the best time for grafting trees.
Many owners of summer cottages and household plots believe that the pear is a southern tree, and therefore do not want to experiment with its cultivation. And completely in vain. A pear, unlike an apple tree, does not have a periodicity in fruiting, it gives a harvest annually. As for its advancement to the north, modern breeders have done a good job: winter-hardy varieties of pears have been bred, suitable for growing in the northern regions. This progress is hindered by a lack of awareness, as well as a small number of quality tested varietal seedlings on the market.
The inability to buy a seedling for a gardener is not the main reason. If desired, seedlings can be grown by yourself. What do you need to know for this?
It is widely believed that in our zone the best pear stock is the wild Ussuri pear. I cannot agree with this. The best rootstocks for pears seem to me to be seedlings of cultivated pears (Tyoma, Vnuchka, Tonkovotka Uralskaya, etc.). many modern large-fruited Ural varieties are poorly compatible with seedlings of the Ussuri pear. Pears work well on a cotoneaster.
| Common quince |
I am currently researching the common quince (Cydonia oblonga) as a dwarf pear stock.
The Latin name comes from the city of Cydon (now Kanea) on the island of Crete. This genus includes only 1 species - oblong quince (ordinary) or Cydonia.
It grows wild in the Caucasus, Central and Asia Minor.
Deciduous shrub or small tree up to 8 m tall. Branches without thorns, young shoots are pubescent, olive-green to red-brown. The leaves are round, oval or ovoid, dark green above, tomentose, grayish below, entire, up to 10-15 cm long. The petiole is pubescent, the stipules persist for a long time.Single flowers (up to 5 cm in diameter) are very effective, white or slightly pinkish, abundantly covering the crown in spring for 10-13 days. Quince is decorative at the time of fruiting, when it is decorated with pear-shaped or apple-shaped, large, fragrant, yellow fruits, covered with thick felt.
It grows slowly, not frost-hardy enough, light-requiring, drought-resistant, undemanding to soils, tolerates even slight salinity, tolerates city conditions and shearing well. Propagated by fresh seeds, cuttings, layering, grafting. It is a good stock for pears (get dwarf forms), Japanese medlar, Japanese quince. Can be used in single and small-group plantings on lawns and forest edges, in hedges, taking into account its winter hardiness. In culture for a very long time.
As a weak rootstock for pears in the southern zone of fruit growing, a clonal rootstock of common quince - quince A (Anzherskaya), which is propagated vegetatively, is used. These rootstocks are well compatible with the vast majority of pear varieties, but they are recommended for use where snow falls before the onset of severe frosts.
T. D. Kilmakaev, landscape design workshop "Svetovid",
newspaper "Ural gardener", No. 21, May, 2010
What is the best way to plant cherries
Experienced gardeners say that you can plant anything and with anything. Indeed, there have been cases of grafting cherries with currants. The result of such an original crossing is a currant tree with large fruits of a strange taste. Therefore, it is nevertheless necessary to correctly combine cultures when inoculating.
A simple rule of compatibility is to combine better species and varieties in one breed. Cherry belongs to stone fruit trees, and that is why it will not go well with currants or apple trees, and things will be better with apricots. Although, this does not exclude experiments to combine seemingly incompatible cultures. But within the same breed, there are inconsistencies. For example, it is generally accepted that cherry plum is suitable for all stone fruit crops, but this rule does not apply to cherries and cherries.
The ideal combination for cherries and cherries is grafting to the very same cherries and cherries, and also to the bird cherry. But what about grafting cherries on cherries, you ask, because the question of combining cherries with cherries is also often of interest to many gardeners, and not only because these crops are so similar. Our answer is simple - you can combine! You will get tasty large berries that are well suited not only for juices and jams, but as a dessert, in their natural form too.


Cherry grafting for the bark
When is the best time to plant cherries
Grafting cherry cuttings (rootstock), promising to yield good yields of tasty berries, onto a stable young base (scion) allows you to get a strong tree with high fruiting rates. The process of connecting the lower and upper parts of the plant is not very difficult, but it requires quick confident actions from the gardener, knowledge of some basics. The effectiveness of the procedure will depend on the timing of the vaccination.


The most correct, giving the maximum percentage of rootstock survival, is considered the period of early spring, when the tree comes out of hibernation, the movement of sap in the trunks is activated. If spring grafting has not been carried out or has been unsuccessful, it is allowed to carry out in the summer, around mid-July. It is better to choose calm, windless, dry days, without strong night frosts, the optimal time is early morning or evening.
Currant grafting rules
Grafting is the transfer of one part of a plant to another plant for further fusion. The peculiarity of the combination lies in the possibility of obtaining a hybrid, which would optimally combine resistance to weather conditions, excellent taste, and high yield.As a result of grafting, the new organism has a powerful root system of one plant and good varietal qualities of the second.
The advantages of this procedure.
- Reduced waiting times. After planting, the young plant begins to bear fruit only after 5-6 years, and the grafted specimen - after 2-3 years.
- Thanks to grafting, you can multiply your favorite or scarce variety without buying a seedling.
- It makes it possible to quickly replace an unsuitable view with a new one with improved characteristics.
- Save the variety if the plant is threatened with death.
- Several varieties can grow on one tree, which will significantly save the territory of the garden.
- It will allow you to grow standard currants.
- Grafting helps to obtain a variety adapted to certain local conditions.
Plant grafting as it is
Not all plants reproduce successfully by seeds, cuttings, division. To obtain certain forms, improve species characteristics, adaptability to environmental conditions, grafting is used.
To graft means to combine two different species into a single whole by fusing their vegetative elements. The grafted specimen is called a scion, and the rootstock serves as the basis for it.
Self-vaccination will require practical experience and basic rules.
What to vaccinate on and how to choose a graft
For grafting currants, both individual currant varieties and other fruit plants are chosen.
Golden currant
This scion has been tested by numerous gardeners' experiments, in particular, Michurin. It is also suitable as a rootstock for various varieties of currants, as it increases productivity, gives crops resistance to adverse weather conditions. The compatibility is excellent.
Cherry
Crossing was tested by foreign gardeners, and the result met expectations. The stock was a cherry, and the scion was a currant. The fruit on the tree was large, but the taste was somewhat odd.
It is believed that cherries and currants are not the best combination.
On our territory, experiments were carried out, but with numerous rejections. Average compatibility.
Rowan
If there is no suitable rootstock, then the vaccination is justified. However, grafted cuttings do not hold well, the overall survival rate is small. Average compatibility.
Gooseberry
These two plants are of the same subspecies, therefore they are physiologically suitable. As a rule, gooseberry grafts are carried out on currants, and not vice versa. Compatibility is good.
Video
This video will tell you in detail about the copulation of pears with a cuttings in spring.
Our distant ancestors called the fruit of the quince “the golden apple”. They have many useful properties, contain a large amount of minerals and are distinguished by their peculiar taste. All varieties have a beneficial effect on the human psyche: they cheer up and invigorate. Also, the healing properties of fruits are widely used in medicine. Fruit juice has antiseptic and tonic properties.
Like any fruit tree, quince can be grafted and use its cuttings for scion.
Experienced gardeners have long noticed the many features of grafting this plant. Increasingly popular grafting pears on quince... In this case, you can achieve a special sweetness and enhance the taste of the fruit. What is not always possible to achieve when vaccinated in the wild. We have repeatedly mentioned that it is desirable to graft like on like. That is, the best vaccination will succeed when two different varieties of quince are combined. Grafting a quince on a pear succeeds extremely rarely. To do this, you need to have a certain amount of knowledge and skills in this area.
It is also rare that there is a case when it is carried out grafting quince on an apple tree. As mentioned earlier, quince is most often used as a rootstock, not a scion.Cuttings grafted to the quince tree are more quickly accepted and produce fruits that are better in taste. Grafting of quince on hawthorn also almost never produced. Most often, the cuttings do not take root at all and the taste of the fruit does not improve.
Grafting Japanese quince most often made for pear or urga.
Thus, if you want to plant a tree and do not know where to start, contact the specialists of our website. We will always help and advise you.
TO CONTACT US
Preparing cuttings
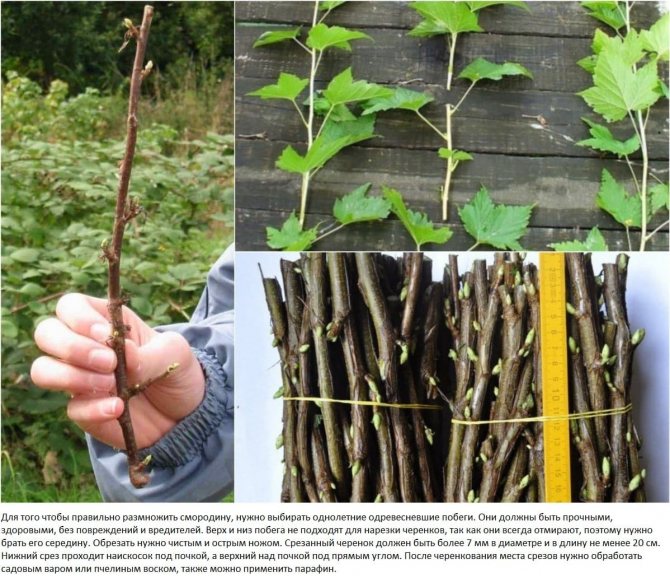
The graft will be responsible for building up the top of a bush or tree, as well as varietal characteristics. The quality and quantity of fruits depends on the cuttings, so only proven varieties should be chosen. The graft is a 10-15 cm long shoot with 2-3 buds.
Blank
For cuttings, fully matured annual shoots are chosen, which are cut from the southern side of the plant. It is there that internodes and eyes in leaf axils are optimally developed.
Usually cuttings are harvested in the fall after leaf fall, before the arrival of frost. But preserving them is not an easy task, since it is important to ensure the correct temperature and humidity conditions.
If it was not possible to procure natural material in the fall, then there is an option to collect it at the end of winter or early spring.
In severe frosts, it is worth checking the condition of the shoots first.
Storage
Comfortable conditions of detention will eliminate traces of rotting, drying out, mold, signs of frostbite. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the buds do not bloom ahead of time, to prevent access to rodents. Before sending for storage, cuttings should be signed by attaching a label to each variety.
Petioles are recommended to be packed in burlap or thick film. They are stored in the basement, cellar, in unheated rooms, in the refrigerator. It is desirable to maintain the optimum temperature for storage at the level of 0 .. + 2 ° С, humidity 65-70%. Regardless of the location, the condition of the natural material should be checked every 3 weeks. If necessary, disinfect, remove mold, adjust temperature indicators. Renew the section immediately before inoculation.
Harvesting and storage of cuttings
Graft cuttings (for winter and spring grafting) are harvested in the fall, when the leaves have already fallen, but frosts have not yet been established. At this time, they already "fall asleep". They are cut into 30-40 cm from woody shoots with a diameter of 4-5 mm, "sealed" with hot paraffin on both sides. Store in bundles in sawdust or sand in a cellar at a temperature of 0 +2 degrees and a humidity of 65-70%. The material can be wrapped in damp flannel and placed in the refrigerator. For summer grafting, cuttings are used freshly cut.
Short cuttings (1-3 buds) give good growth the next year, long cuttings begin to bear fruit earlier.
The rootstock, already rooted, cuttings 7 mm thick are shortened to 25-30 cm, dug in the fall before frost, stored in a cold cellar (0 +2 degrees) in boxes with peat or sand.


The graft and rootstock can be stored in bags in the snow or buried in the ground, but there is a possibility that they will be damaged by mice. They are protected from freezing with a layer of peat. Regardless of where they are stored, cuttings should be checked every three weeks.
To avoid soaking the bark, you can put the cuttings not in bags, but in plastic bottles.
Methods
Garden grafting is done in several ways. Knowing the features and techniques for performing each method, the owner of the garden has the right to choose the most convenient option in a particular case.
Copulation
There are two variations of this method: simple copulation and improved copulation. Their difference consists in additional oblique cuts of the scion and rootstock, due to which their accretion is improved.
For an improved method, you need: cuttings 20 cm long with two buds on each. An incision on the trunk is made at a distance of 20 cm from the surface of the earth, 4 cm in size.Graft carefully and wrap with foil.
For simple copulation, you need a 30 cm stalk with 3-4 buds.
- Make a cut at the base of the scion at an angle of 45 °.
- A similar cut should be made on the rootstock.
- Fasten the stalk to the rootstock, after cutting out the “tongues”.
- Secure with elastic material.
- Remove the winding after a month.
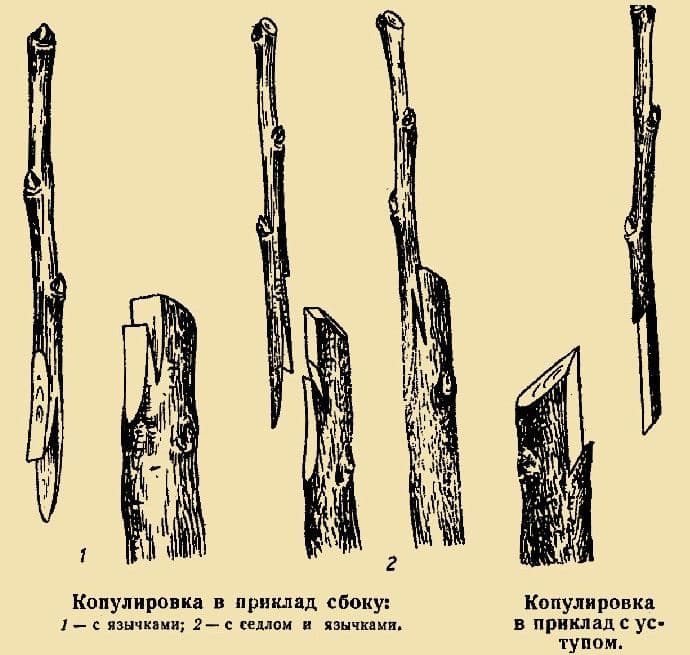

Picture. Copulation methods.
Below the site of inoculation, it is imperative to remove all growths.
Budding
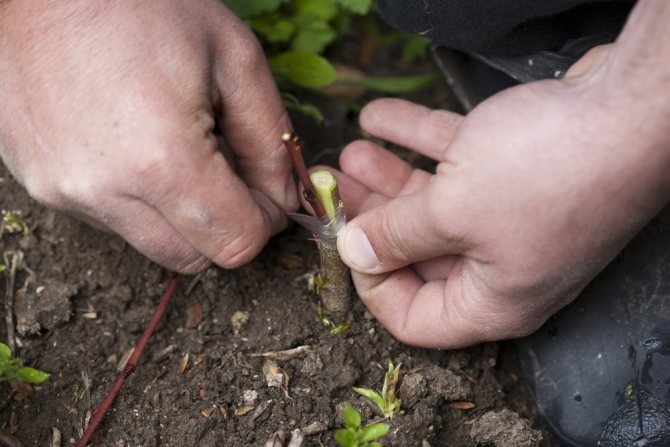
The essence of the method is to transfer the axillary bud to the stock. The grafting material is called a peephole. The method is simple, however, it is important to adhere to technology. For the procedure, you will need a sharp knife and strapping material.
- Choose a healthy kidney on the handle. Cut it off together with a part of the bark with a diameter of 2 cm.
- A T-shaped incision is made on the pre-selected stock.
- The flaps are opened and a kidney is inserted into the hole. It should be visible to the outside.
- Above the vaccination site is wrapped with a special material.


Picture. The method of grafting budding.
Many gardeners build a greenhouse around the grafting in order to create optimal conditions.
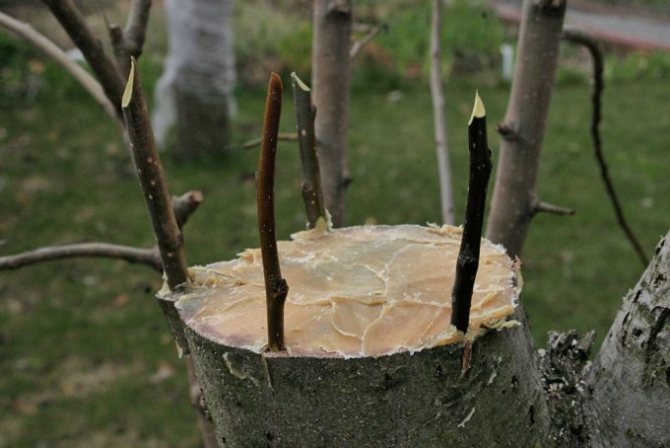
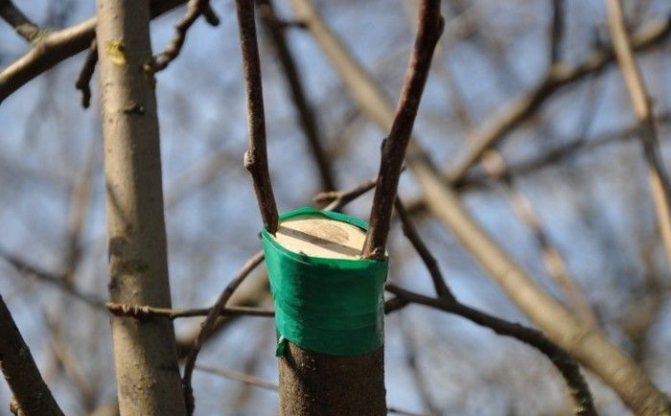
Into the cleft
This method is the oldest and therefore imperfect. Usually it is carried out in the spring. Used to restore old trees or broken thick branches. The disadvantage of this method is that when splitting, tissues are severely damaged, wounds heal slowly, and decay processes can develop.
The technology for performing the grafting consists in making a split on the cut of the rootstock, where the cuttings are inserted. On the scion, an oblique cut is preliminarily made on both sides. The bark on the stump and on the handle must match. The butt end of the cutting and the sides of the rootstock are smeared with garden pitch. If the handle is held firmly, then no strapping is needed.
For the bark
The simplest method for mature trees. Perform a month after bud break. The closer to this moment the vaccination is made, the better the result.
- The stock is cut into a stump and the ends are cleaned.
- An oblique cut is made in the lower part of the cutting.
- On the foam below the butt, the bark is removed with a grafting knife 3 cm. Raise it slightly and turn it away.
- A scion is inserted behind the bark of the stock. The oblique cut should not completely go deep, 3-4 cm are left on top.
- They are connected with strapping material, and the exposed fabric is treated with garden putty.
Cloudy weather contributes to optimal fusion.
Into the lateral incision
The method is most often used when the vaccinations done by means of budding have not taken root. As a rule, it is performed during the spring sap flow.
- The shank on the lower side is shaped like a double-sided blade.
- The stock is shortened to a size of 15-20 cm.
- A longitudinal cut is made with a copulation knife, which should have one side 1.5-2 times shorter than the other.
- The end of the scion is adjusted under the scion.
- The stalk is inserted in such a way that its bark and rootstock bark coincide.
- The inoculation is tightly connected and coated with garden varnish.
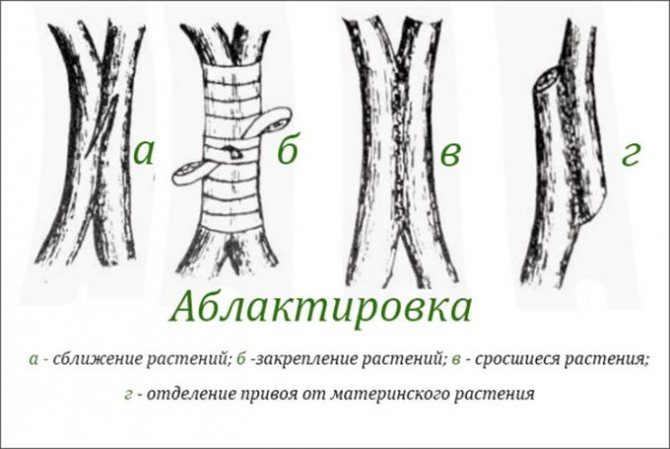
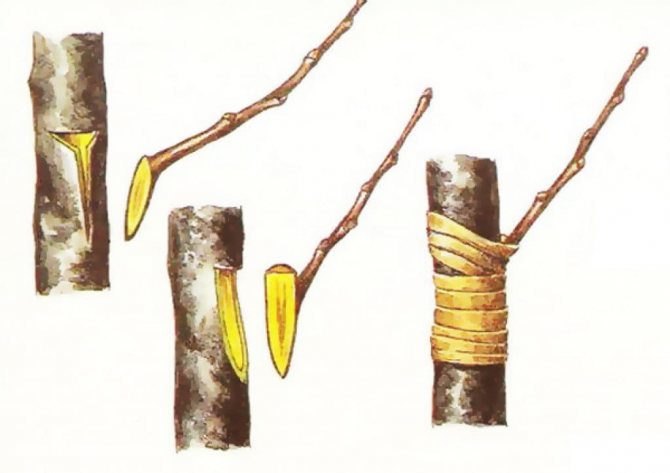
Ablactation
Or inoculation by intimacy. By its nature, it can be compared with self-grafting, the natural fusion of plant parts. The favorable period for the procedure is the beginning of March or August. The method involves splicing the branches without separating them from the mother plant. It is used to restore missing branches, compounds difficult to grow together plants.
- The bark is removed from the branch or trunk chosen for the stock. The exposed part is 4-5cm.
- It is also worth doing with the scion.
- For quick fusion, it is important that there is a kidney on the opposite side of the exposed area.
- Plants are combined with cuts and wrapped with elastic material.
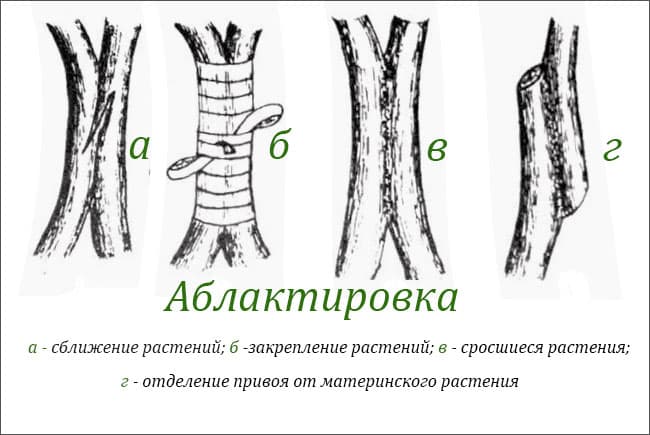

Picture. The method of grafting is ablation.
It is necessary to ensure that the bark cut fits snugly against each other.
Caring for a grafted tree
Vaccination will help not only achieve a good harvest, tasty fruits and save the tree, but also renew the old one. No expensive equipment is required, it is enough to carefully perform all operations, carefully fasten the parts to be joined, and control the condition of the tree after grafting.
Garden pitch will help to avoid contamination of exposed parts of the tree and better hold them together. It is imperative to control the vaccination site, you need to remove the mount in time, otherwise it will grow into a tree, it is better to remove it carefully with a knife.
As soon as the first leaves appear on the scion, it means that the film can be removed, all shoots that appear below the scion should be removed so that they do not take on the sap and strength of the tree. After budding on the scion, growth should be monitored and the following procedures should be performed:
- overgrowth below the vaccination must be removed;
- drying out of the roots is unacceptable;
- regular age-specific feeding is carried out according to the schedule;
- preventive and therapeutic spraying is performed regularly;
- branch formation will begin next year.
Whether the pear graft has taken root or not will be clear in 20 days, if the bud is green on the graft, then everything worked out. If you take proper care of the tree, the harvest will not be long in coming, and the result will be no worse than that of a purchased seedling.
Gardener mistakes
When performing the grafting procedure, even the slightest mistakes should not be made, every little thing is important, and therefore here are some tips that will help you avoid annoying misunderstandings and get a good result:
- Budding is carried out from the north side of the tree, this will help the cuttings to take root better;
- On the day of the vaccination, the weather should be dry and calm;
- Poor performance of the procedure, insufficient care, ignoring important procedures will lead to the rejection of the cutting;
- Any growth below the graft leads to poor nutrition of the cuttings, they must be cut off in time;
- After the stalk has taken root, the bud remains green, it is necessary to remove the bandage for better circulation of the juices, so the growth of the scion will be much better.
By planting pears on your site, you can achieve an extraordinary and surprising garden.
Now read:
- Choosing cucumbers for open ground according to your preferences
- Exquisite junkus (sitnik) spiral in the interior
- Ways to store carrots in winter so they don't rot
- Confidentiality
About
Agronomist of the state agricultural enterprise "Garovskoye" of the Khabarovsk region of the Khabarovsk region.
Step-by-step instructions for vaccination
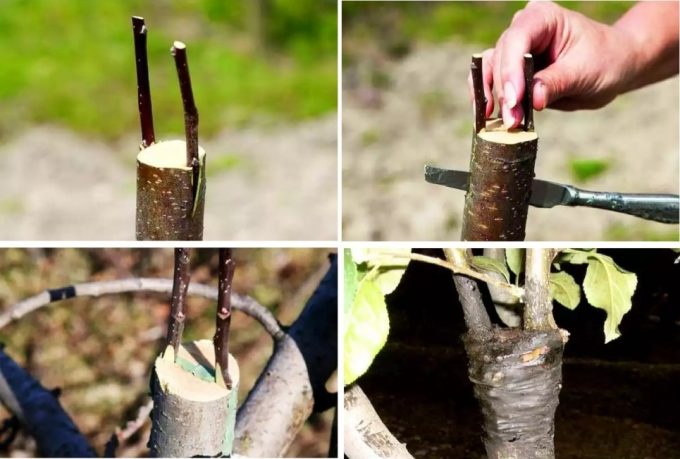
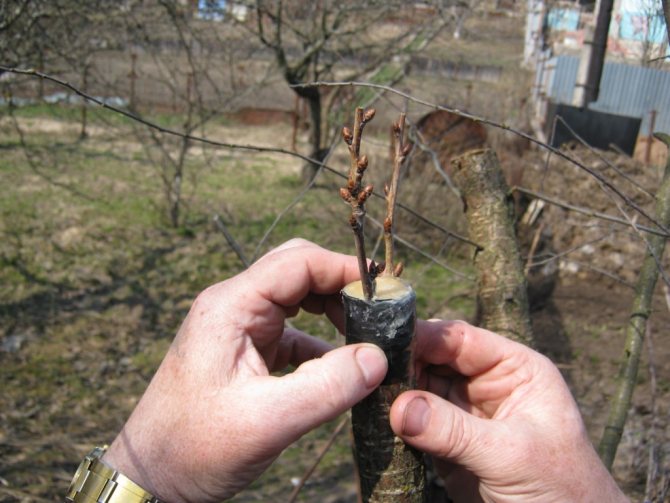
Usually cherries are grafted with a handle or eye. Both methods can be performed in a lateral incision, behind the bark, in the butt. However, for gardeners who do not have much experience in the processes of grafting, it will be easier to apply the method to splitting. Thus, gross mistakes can be avoided.
- An even cut with a diameter of 5 cm should be made on the stock and carefully cleaned.
- Split 10 cm deep in the middle of the branch with a small hatchet or sharp knife.
- If the resulting depression is dense enough, then you need to move the hatchet in different directions. Otherwise, it will not be possible to insert the grafted cuttings.
- Make two cuts on the handle to make a blade. The length of the cut and the split must match.
- Take your time to get the tool, and in this place determine the support so that the chips do not close.
- Insert the handle into the split so that the cambial layers touch.
- Gradually remove the support without moving the scion.
- If the rootstock is much wider than the scion, several cuttings can be inserted into the split.
- Tie the rootstock, starting from the upper side, with foil or special material along the entire length of the split.
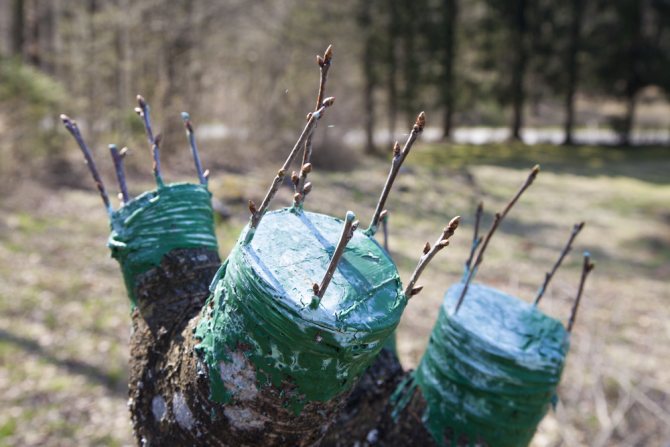
- Treat the grafting site and the upper cut with garden varnish.
- On top, make a greenhouse made of transparent polyethylene to maintain the required level of humidity and temperature.
- The bag can be removed after two weeks.This time is enough for successful grafting.
Recommendations
Pears should be grafted in early spring, before the buds have blossomed. Before the active movement of the juice begins, one can hope for 100% of the results of this scion.
In the southern regions, the procedure is carried out in early spring, in the north at the end of April or even later.
To determine the optimal timing for the scion, you need to monitor the air temperature. When night fluctuations become insignificant, you can start the procedure.
If you decide to carry out work in the summer, the best month is July, but you can make it before August. At the end of August, the difference between night and daytime air temperatures is significant, which negatively affects the survival rate of plants. Another important point is the correct choice of the scion:
- To grow a hybrid large fruit, take Yakovlev's Favorite, Bere-Clergeau, Bere-Gardi, Susov's Large-fruited. To plant these varieties correctly, you will need to separate a branch containing several buds.
- When performing a scion of branches equal in diameter, you need to choose one that is equal in thickness to the scion. If you decide to use the splitting technique, use a couple of branches of a small diameter for the scion - much smaller than the trunk of the tree used for transplanting.
A few weeks after the procedure, inspect the area where the shield and the main shaft meet. If the bud is green, everything went well. It is recommended to graft a couple of new branches into the split to minimize the risks of scion material death.
25px "/> This method can be used to work with any branch of the main tree, but manipulations performed on the north side are considered the most effective - the survival rate in this case will be maximum if you use a garden var.
Inoculation height
Rake the soil from the rootstock trunk so that the root collar is clearly visible. Gently remove twigs 10 cm from the ground and wipe this part of the trunk with a damp cloth. On the root collar, make a 3 cm long T-cut with a sharp knife.
What can the currant be vaccinated on?
Golden currant
Most often, ordinary currants are grafted onto golden currants. It has a larger bush size, a different leaf / fruit shape and a distinct taste. The tallness of this crop can be used to form a stem (currant tree), and its resistance to drought, frost and disease can be used to improve the qualities of a variety.
Currant
- Grafting of red currants onto black currants improves the palatability and size of the fruit. They become sweeter and larger. At the same time, the plant itself turns out to be more developed and strong due to the powerful root system of black currant.
- Some gardeners plant black currants on red or white currants (on the roots), thereby increasing yields and disease resistance. Abundantly fruiting red and white currants convey these properties to black ones, so that its flowers do not fall off, and the berries that have set become larger and more uniform in size.
- On any currant available on the site, more valuable varieties can be grafted, thereby either propagating them or updating the bush. Reproduction allows you to get new seedlings, and renewal - to restore damaged and old bushes.
Additional Tips
Whether a new plant has taken root or not becomes clear after about a few weeks. This is evidenced by the buds of the scion, which increase in growth in case of a positive result. Remains of tape or grafting tape can be removed after a while, but it is better to leave it until next year.
Having chosen summer time for grafting, thorough watering of the trunk is carried out in advance in order to accelerate the flow of internal juice. Particular attention is paid to the cleanliness of the sections and the instruments used.To protect the future tree from infection, antibacterial solutions must be used to treat fresh "wounds".
Planting cherries is not a difficult and interesting process, allowing you to experiment with new varieties. Adhering to accuracy, choosing a convenient technology, you can avoid many mistakes and achieve your goal the first time.
When can currant be vaccinated?
- In the spring. The best time for grafting currants is early spring. As soon as the flow of sap has begun, you can immediately start this event. For this, one-year-old cuttings are used, harvested since autumn and stored in a cellar (in wet sand). In different regions, the beginning of sap flow is noted at different times, so there is no exact date here. In the more southern regions, the vaccination can be done already at the end of March, and in the northern regions - in the 2-3 decade of April and even at the beginning of May.
- In summer. Currants can also be grafted in summer, when sap flow is activated. In the middle lane, this happens from about the second half of July to the beginning of August (later to the north). At this time, budding or grafting with freshly cut cuttings can be carried out. Shortly before such a procedure, you need to water the stock bush well, so that the movement of the juice increases, and the bark is easily separated from the wood.
- In winter. At this time, the vaccination is done in a warm room "on the table" (approximately in the second half of February). For this, cuttings are harvested in the fall and stored in a cellar. After inoculation, they are placed in wet sawdust or sand with peat, leaving them warm for two weeks (18-20 degrees). Then they are taken to the cellar, and with the onset of stable heat, they are planted in open ground.
Berry bushes on a trunk
Such unusual berry trees attract the eyes of even those people who are indifferent to any plants. Most often in the gardens you can find standard chokeberry (up to 3 m high), but standard forms of gooseberries and currants look more exotic. This effect can be achieved only with the help of grafting, since the formation does not bring the desired results due to the abundant growth and fragility of the branches.
These small trees not only bear fruit well, but also look very decorative. Large, clean and juicy berries ripen on them.
It is recommended to plant gooseberries and currants on a 2-3-year-old golden currant seedling. You can buy it in a specialized nursery or grow it yourself from seeds that are sown in the fall. The grafting should be carried out in the spring with cuttings harvested from the fall and the method of improved copulation should be used for this.
Currant grafting methods
- Budding. This method allows the variety to be propagated using eyes, which is very economical and relatively easy.
- Copulation. One of the best options for currants is improved copulation. In this case, the reliability of grafting and the survival rate of cuttings are high.
- Cleft inoculation. Very often this method is used to inoculate currants. It is quite simple in execution, effective and gives a high survival rate.
- Vaccination in the butt. This grafting method is used when the stock is noticeably thicker than the scion. When done correctly, it gives good results. It is best to vaccinate with a tongue butt - this increases the contact area and survival rate.
- Side cut grafting. This method is quite simple and accessible even to a beginner. It is used on thicker rootstocks.
- Grafting for the bark. It is used for the renewal of age bushes, including for grafting red and white currants onto black currants.
The grafting process is greatly facilitated by the grafting secateurs. This is an ingenious invention that is actively used by both professionals and beginners. This tool allows you to make perfectly compatible cuts, so even inexperienced gardeners can cope with this operation.The main thing is to carefully read the instructions in order to fully use all its capabilities. The use of a grafting secateurs not only facilitates and simplifies, but also significantly speeds up the vaccination process (which is especially important for mass vaccinations).
How to bind correctly - technology
There are basic rules for the procedure:
- Before the procedure, the places of future cuts should be cleaned with a damp cloth.
- Wash hands and tools for grafting trees, disinfect and only then cut the rootstock and scion according to the chosen method.
- Place the cuttings or buds on the places prepared for them, combining the cambial layers of the rootstock and scion; in these places they will grow together, forming a single vascular system.
- Wrap the grafting site with elastic material with overlapping turns, additionally fixing the stock.
- Protect open sections from drying out with pitch, garden putty or plasticine, otherwise one or two upper buds will not germinate on the scion, and pathogenic microorganisms will penetrate through the unprotected rootstock stump.
- Build a greenhouse from the package at the vaccination site for two weeks.
Vaccination by any of the methods is best done in dry, cloudy weather. Rain or heat will reduce the survival rate. The exception is winter vaccination: it does not depend on the weather. All stages must be passed quickly, without giving the material the opportunity to wind up and dry. Read about the best varieties of currants for the middle lane here.
Post-vaccination care
After the operation, you need to take care of both the vaccination site and the entire plant. Splice area:
- protect from the outflow of juice and infection, covering open sections with pitch;
- covered with a bag or cap, creating a humid microclimate inside;
- in the cold it is insulated, and with the establishment of positive temperatures, the insulation is removed;
- if the winding does not stretch, check if it has cut into the bark, loosen it if necessary.
Grafted plant:
- loosen or mulch, watered more often than usual;
- they are fed two weeks later with nitrogen fertilizer, then top dressing with a full set of macronutrients;
- cut off the growing shoots and pince the branches below the grafting site.


Currant care.
Errors of inexperienced gardeners
Vaccination at the wrong time
If you are vaccinated before the start of sap flow, the scion may simply disappear without receiving nutrition. If you delay with this case, then the probability of accretion will greatly drop and the scion will be rejected.
Incorrectly selected stock
If you take a stock, the compatibility of which is not very high or questionable, then the probability of success of the vaccination will tend to zero. And even if at first the scion takes root, after a while it may disappear or, at least, not yield a harvest.
Non-compliance with requirements
The success of vaccinations depends on how they are done correctly. If even one requirement is not met properly, the vaccine may not take root. When grafting plants, it is imperative:
- use a sharp knife;
- do everything quickly and clearly;
- do not allow the grafting material to dry out;
- after vaccination, cover and cover open areas, protecting them from infections and moisture loss;
- protect the grafted plant from overheating or frostbite;
- tightly connect and tightly wrap the vaccination site;
- vaccinate only with cleaned instruments and washed hands.
What tools are needed
The tools needed to graft trees and shrubs can be compared to a set of surgical instruments.
- Copulation knife. It has a straight blade and one-sided sharpening.
- Oculus knife. On the handle of such a device there is a special bone for bending the bark.
- Strapping material. Garden stores sell a variety of strapping materials. They fit snugly and do not squeeze the bark. There is no need to shoot such material, it disintegrates over time.If nothing like this is at hand, cling film, scotch tape or electrical tape will do.
- Pruner. This tool is required for cutting cuttings for scion.
In addition, a jar of garden varnish or other garden putty of a plastic consistency is prepared.
Standard forms of currant
The advantages of standard currant forms
- Decorativeness. Such trees, hung with bunches of currants, look very beautiful on the site. They are used not only for harvesting, but also for decoration, planting along the paths or even on the lawn.
- Convenience of harvesting. Since the standard forms are taller, it is much easier to pick berries from them. In this case, you do not need to bend down to the ground.
- Increased yield. Such plants have larger berries. This is explained by two reasons: the properties of the stock of golden currant and the good illumination of all branches.
- Improving the taste of berries.
- Such currants are sweeter and tastier. This is due to the same factors.
How to create a standard currant shape?
To create a standard tree, a one-year-old stock of golden currant is used, onto which a one-year-old scion stalk is grafted. The best methods of grafting are splitting (preferably with a grafting secateurs) and improved copulation. Vaccination should be done at a height of 0.8-1 m from the ground. Due to the tallness of the golden currant, which stands out as the stock, a rather powerful trunk is formed, which is beautifully framed by the hanging branches of the grafted bush.
It is better not to take the wild form of golden currant as a rootstock, since it gives a lot of root growth. But today you can buy specially bred clones of this culture, which do not give it. If you cannot find such a rootstock, use a regular one. It's just that in the future you will have to remove the growth in time. The grafted plant must be tied to a peg so that the man-made tree does not fall. This is a mandatory requirement for standard forms obtained from shrubs.
Not all gardeners are engaged in grafting currants. Therefore, you can become one of the "chosen ones", having successfully mastered such an exciting and useful business. This will allow you not only to update existing bushes or get valuable seedlings, but also to decorate your site with standard forms. By the way, in the form of a tree, you can also form a gooseberry. You can read about this ...
Grafting currants on cherries
Cultures for grafting on quince
As a rootstock, quince is used for pears, chaenomeles (Japanese quince), apple trees.
Chaenomeles. In its usual form, it is a bush. In the grafted state, it forms a standard tree (common quince serves as a stem builder).
In the first case, the grafting is carried out on a ready-made quince stem using a branch of the selected varietal specimen by the "split" method in the month of May.
At the end of the process, the docking place is wrapped in tight electrical tape, cling film or other similar material, open areas (butt and side slits on the quince, the upper cut on the grafted branch) are processed, carefully smearing with garden varnish. This method stands out for its simplicity, versatility and good survival rate.
The second method is used to carry out budding closer to the end of summer (July or August).
An interesting opportunity to graft simultaneously on different branches of quince stock, one bud from different varieties. The engrafted kidney remains outside, the adjacent space is fixed by tight wrapping with fixing tape. After half a month, the first results of engraftment can be observed. The following spring, the elongated quince shoot above the graft site is removed, giving the grafted kidney an opportunity to grow.
Grafting several different varieties on one plant as a result will create a unique specimen in the natural environment, surprising with its diversity.
Pear.Cultivation of a seedling of the selected pear variety on a quince lasts for two years in case of incompatibility of the desired variety.
For the first year, quince and a known compatible pear graft are inoculated. It is better to spend in the spring (there is time to repeat the attempt in case of failure, the grafted material grows from the buds laid in the last season).
For the next season, the successfully grafted material serves as the basis for the selected pear species. The intercalation insert serves as a gasket between the two components.
A one-season variant of this method is the connection of plants that do not fit each other when a thin piece of wood from a compatible object is inserted between them in the "behind the bark" method, cut to size.
Grafting on quince allows you to achieve early appearance and ripening of fruits, to grow a stunted version on a semi-dwarf quince rootstock or dwarf.
Apple tree. Grafting on a seedling and in a quince crown does not take root well, and, as a rule, is not durable. After three to five years, the vaccinated part most often dies.