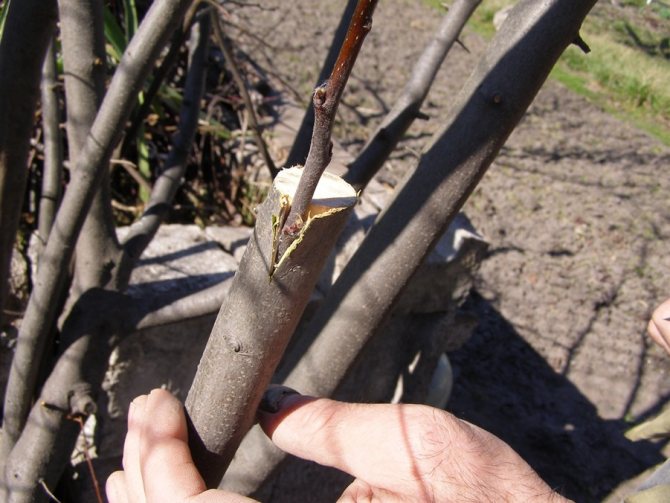
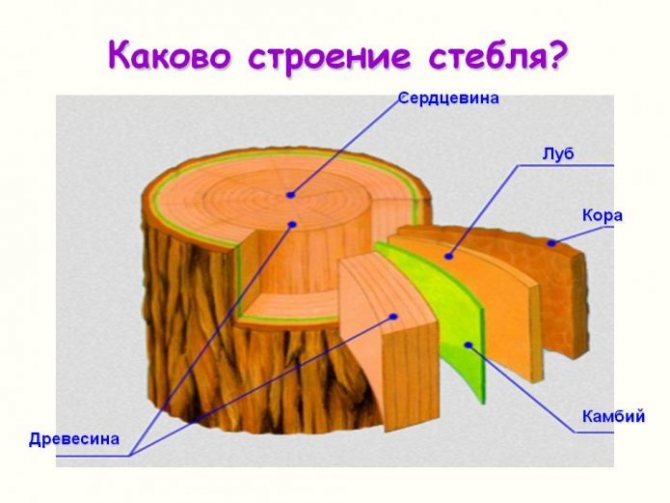
Good health, dear summer residents! Today the first snow fell, I went out into the garden to admire the winter landscapes. I also checked how my guinea pigs were doing. This is what I call the old thorns. In March, she grafted shoots from delicious varieties on them. The trees are doing great. Just in case, I shook off the snow from the branches, and once again admired the results of the work. While there is time, I will tell you how to properly plant a plum, why it is better to do it in spring and which trees are better to choose for this.
Why grafting a plum: the benefits and objectives of grafting
As a rule, the main goal of grafting is to get a tree that is more resistant to negative factors.
However, the benefits of plum grafting do not end there. Here are the purposes for which it can be produced:
- You want to cultivate the wild and plant a varietal plum on it (in other words, multiply it).
- Not satisfied with the planted variety, and you want to re-graft it to a more suitable one.
- You have a compact (small) area, and you want to have several varieties on one tree at once.
- Accelerate fruiting.
- Save the tree (in case of damage to the bark by hares or mice).
- Propagate or save a favorite or just a rare variety.
When to plant plums in spring and summer: optimal timing
Spring grafting of plums can be done as in early spring before the start of sap flowwhen the buds are in a dormant state, and already during the growing season (active sap flow).
Note! Terms of vaccination depend on which one method you are about to plant a plum.
When to plant plums in spring?
Depending on your region and its climate, the vaccination is usually carried out from March in the southern regions to early May (in the Middle Lane). However, first of all, you should rely on the weather conditions of the current season and the condition of the tree.
In this case, the air temperature should already be positive, regardless of the time of day, since prolonged subzero temperatures often lead to the rejection of the scion.
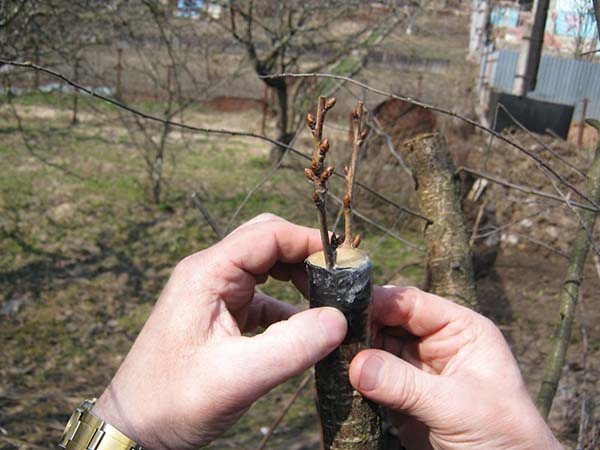

Note! And here is the plum grafting method budding (with an eye) is completely performed in the summer. More precisely, it needs to be carried out late July-early August
, when the buds on the growths of this year are already ripe, and the growth of shoots will practically stop.
As for whether when is the best time to harvest grafting material, is it possible to do this in the spring (immediately before vaccination) - we will analyze these and other issues in more detail later in a separate paragraph.
Short answer! Cuttings (rootstocks) can also be cut in the spring, before the buds begin to bloom, but there is always the possibility of freezing. Therefore, it is better to harvest cuttings in autumn or early winter, before the onset of severe frosts, and store them until spring.
How to choose the time for manipulation
Professional breeders and summer residents recommend grafting stone fruit plants in the spring. At this time of the year, it is already warm enough for the full development of the plant, but not too hot either. In general, the procedure is easiest to perform in the spring - it is warm, humid and there is no threat of night frosts. When choosing the time for manipulations, it is necessary to ensure that there is no rain for several days. Dry weather in spring is not conducive to the development of infections and rot.In the spring, the trees begin to actively move the sap, which increases the percentage of plant survival.


The vaccination is carried out in the middle of spring, when the threat of spring frosts goes away. It is worth noting that cherry plum grafting can be carried out not only in spring, but also in summer. Summer grafting on cherry plum can also take root and winter well. And the active growth of the cuttings will begin in the next growing season. In the fall, grafting of stone fruits on cherry plum is also possible. During this period, the procedure is performed only in the southern regions of the country. Light frosts in these parts will not be able to damage delicate cuttings. If the autumn grafting is performed in the northern regions, it is recommended to cover the place of manipulation with insulation. It is recommended for beginners to graft stone fruit plants in the spring, since this procedure allows the cuttings to grow stronger and grow by the onset of frost.
What trees can be grafted with a plum: suitable grafts
The best option for crossing a fruit tree is to graft a plum on a plum or on its wild.
In the case when there is no suitable stock of one species (genus), the plum is grafted onto others. stone fruits the cultures that are best suited for this:
- cherry plum;
- turn;
- felt cherry;
- apricot (although, as a rule, they do the opposite).
Video: grafting plum on cherry plum in the split
Good stock parameters
As rootstock ideally it is better to use young 1-2-3 year old seedlings, it is considered the best option for grafting plums.
Important! Grafting of young seedlings, as a rule, is carried out at a height of 3 to 25 cm from the surface of the earth, it is even possible almost above the root collar itself. The lower the graft, the better the accretion, the closer the roots, and the more powerful the seedling will grow.


But older trees are also suitable (in this case, as a rule, they are grafted onto their skeletal branches, but there are exceptions), while preferably not older than 10 years.
However, it should be borne in mind that the survival rate of cuttings (grafts) on a very old bark (rootstock) has very low rates.
Naturally, in the same Middle zone (Moscow region) and other cold regions for rootstock use the most winter hardy varieties.
Of course, the rootstock tree must be in good condition: be healthy, have no damage or disease, have increased endurance both to weather conditions and to various diseases.
As for the choice of a specific branch, it is better to graft at the base of the skeletal branches, at a distance of 20-40 cm from the trunk. In this case, the stock should be directed upwards or strive for a vertical position. It is these branches that grow much better, which means that the success of the survival of the cutting is significantly increased.
As a rule, annual cuttings (grafts) are grafted onto annual shoots (rootstocks), because they are of the same diameter.
Vaccination requirements
Best time to vaccinate
Best time to vaccinate
Spring grafting is most popular with gardeners. This is not surprising, because this season is the most active sap flow. If the procedure is performed correctly, the scion and rootstock are very tightly connected, the fusion between the two parts is ensured.
Important! If, for some reason, engraftment did not occur in the spring, the grafting process can be repeated again in the same season.
The summer period can be safely used to conduct experiments in your garden, but the likelihood of failure in this case is great.
Autumn grafting is a very undesirable procedure, because frost can hit at any moment. Weak cuttings will not be able to survive in extreme cold.
Preparatory stage
It is best to prepare cuttings in the fall.
Preparatory stage of grafting
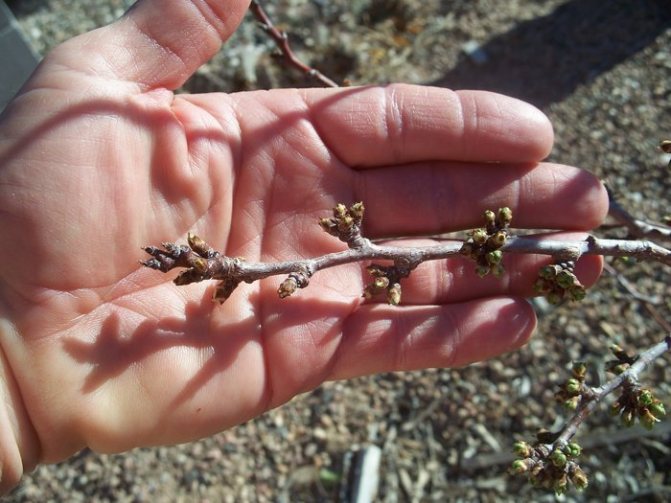
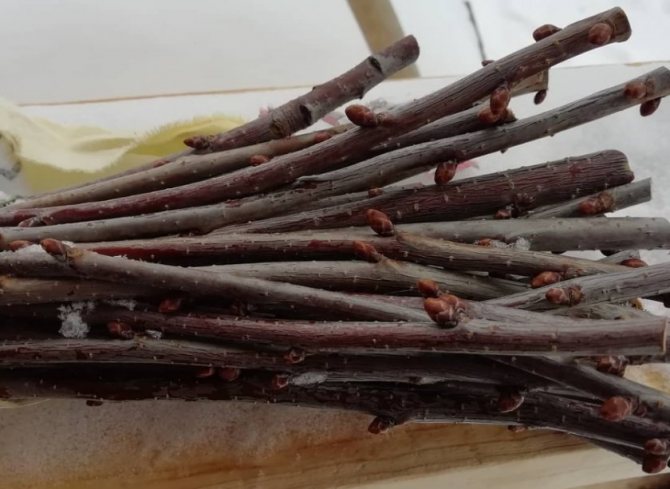
Twigs with the following characteristics are ideal:
- the optimal length is 30-35 cm;
- thickness - 7 mm (about the same as a standard pencil);
- pronounced kidneys - 4-5 pieces;
- internodes are short.
Important! Cuttings should be taken from a young tree (4-5 years old), which has already begun to bear fruit.
It is better to take those branches that are from the outer part of the crown (ideally from the south).
Cuts are made with an exceptionally clean pruning shears. The place of the cut must be treated with a garden pitch.
The cut cuttings can be wrapped in paper and kept in a cool place such as a cellar, snow, cold pit, refrigerator.
Cultural compatibility
According to experts, the same type of plant remains the best stock.
Grafting compatibility
The most successful experiments will be those in which botanically close plants should grow together.
According to the degree of kinship between the two plants, the following types of grafting can be distinguished:
- intraspecific - such a situation occurs when, for example, the gardener has to combine the cultivated plum and the wild plum;
- interspecific - when cherries are grafted onto cherries, cherry plums, for example, on plums;
- intergeneric - an example of this would be the grafting of a plum on an apricot, a peach on a plum tree.
Important! It is easier to succeed if you plant plants within the same species, the most difficult - between separate genera.
Many years of experience of many breeders allows us to draw the following conclusions:
- the best stock for stone fruit crops is cherry plum;
- on felt cherries, you can graft: blackthorn, cherry plum, Ussuri plum, apricot;
- a pear can be grafted onto an apple tree, chokeberry, mountain ash; the pear itself rarely accepts other trees;
- peach as a stock is ready to accept: cherry plum, plum, almond, felt cherry, blackthorn, apricot;
- plum accepts cherry plum better, you can use peach, blackthorn, thorny seedlings;
- for apricots, the best option for scion will be seedlings of other varieties of apricots, cuttings of sandy cherries, cherry plums, blackthorns can also be used;
- seedlings of such varieties can become ideal rootstocks for an apple tree: Anis, Antonovka, as well as M9, A2 MM 106.
You can view a list of fruit crops that are compatible with each other, as well as those that are not recommended to be grafted, and those that have no chance of successful grafting, in the table below.
Crop compatibility chart
| Well compatible | Poorly compatible | Incompatible |
| Quince + quince | Cherry plum + pear | Cherry plum + quince |
| Quince + pear | Cherry plum + walnut | Cherry plum + barberry |
| Quince + apple tree | Cherry plum + cherry | Cherry plum + |
| Chokeberry + chokeberry | Cherry plum + apple tree | Cherry plum + viburnum |
| Aronia + pear | Apricot + cherry | Cherry plum + peach |
| Cherry plum + cherry plum | Apricot + cherry | Cherry plum + plum |
| Cherry plum + plum | Cherry + apricot | Apricot + cherry plum |
| Cherry plum + peach | Cherry + pear | Apricot + pear |
| Cherry plum + apricot | Cherry + walnut | Apricot + barberry |
| Cherry plum + mountain ash | Pear + cherry plum | Apricot + viburnum |
| Apricot + apricot | Pear + barberry | Apricot + dogwood |
| Apricot + almonds | Pear + cherry | Apricot + apple tree |
| Apricot + peach | Pear + viburnum | Apricot + plum |
| Hawthorn + hawthorn | Pear + plum | Cherry + quince |
| Hawthorn + pear | Pear + cherry | Cherry + barberry |
| Hawthorn + apple tree | Apple + apricot | Cherry + cherry plum |
| Hawthorn + quince | Apple tree + barberry | Cherry + peach |
| Hawthorn + cotoneaster | Apple + cherry | Cherry + plum |
| Cherry + cherry | Apple + cherry | Pear + apple |
| Cherry + cherry | Apple tree + viburnum | Pear + quince |
| Cherry + apricot | Peach + cherry | Pear + dogwood |
| Cherry + peach | Peach + pear | Pear + sea buckthorn |
| Cherry + plum | Peach + apple tree | Pear + peach |
| Pear + pear | Peach + cherry | Apple + cherry plum |
| Pear + apple tree | Peach + walnut | Apple + dogwood |
| Ceparadus + cherry | Plum + cherry | Apple + peach |
| Apple tree + apple tree | Plum + pear | Apple + sea buckthorn |
| Apple + quince | Plum + cherry | Apple + walnut |
| Apple + pear | Plum + walnut | Peach + quince |
| Apple tree + cotoneaster | Peach + barberry | |
| Apple tree + chokeberry | Peach + viburnum | |
| Peach + peach | Peach + dogwood | |
| Peach + almonds | Plum + barberry | |
| Cotoneaster + pear | Plum + quince | |
| Plum + plum | Plum + dogwood | |
| Plum + cherry plum | ||
| Plum + peach | ||
| Irga + Irga | ||
| Irga + pear | ||
| Sweet cherry + sweet cherry | ||
| Sweet cherry + cherry |
Rules for the selection and storage of scion for grafting plums
Next, we will consider how to properly prepare the scion in the fall and save it until the spring grafting of the plum.
What should be a quality scion
A high-quality graft is the key to a successful vaccination!
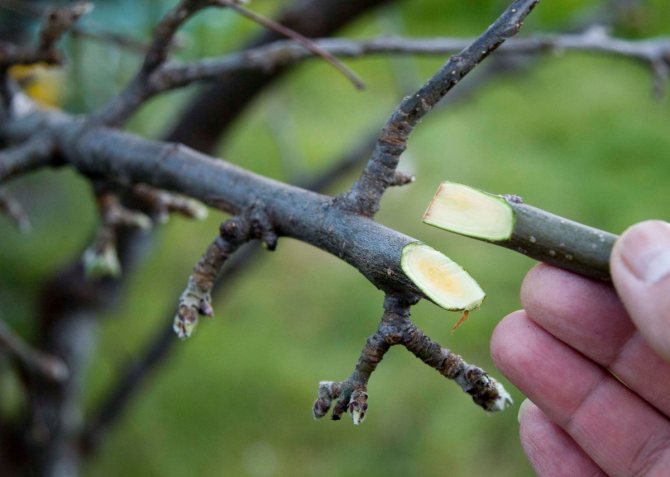
For grafting plums, you should prepare scion cuttings that need to be cut from annual (in rare cases, two-year) branches, at the top of the crown with south or west side, and it is from the middle part of the shoot. The cut itself is carried out on the annual ring between the growth of the last and this year. As for their quantitative characteristics, quality grafts should be with a diameter of 5-8 mm (with a pencil) and length 20-40 cm (already directly during vaccination, cut to the recommended number of kidneys - 2-3).
Cuttings should have exactly vegetative buds, rootstocks with fruit buds cannot be used.
The grafting material should look fresh, free of frost and damage. Therefore, before vaccination, it is recommended to make sure of its quality without fail. It is very simple to check this - on the cut, the cuttings should be as light (green) as possible.
Important! One of the popular ways to determine the viability of the cuttings for grafting is to bend it. If this was done easily, then the stock (cutting) is quite suitable for the procedure.
Directly during the vaccination procedure prepare the stalk (cut), leaving 2, maximum - 3 buds on it (optimally - still 2).
When to harvest and how to store cuttings (rootstocks)
Despite the fact that pruning of trees in the autumn period is undesirable, it is most convenient to harvest cuttings at this time. Therefore about scions (cuttings) it is worth taking care in advance and preparing them in the fall, before the onset of stable frosts.
However, this can also be done shortly before the vaccination procedure itself, during the annual spring pruning plum.
But in this case, you need to be sure to have time before the start of sap flow (swelling and even more blooming buds), while the tree is still in the dormant stage.
Video: grafting cuttings - how, where and when to cut
Storage
After the autumn harvesting of cuttings, they must be kept in good condition until spring and prevent premature start of the growing season.
The best way to store cuttings is wrap them in a damp material (cloth), and even better in moss or sawdust and put in a perforated bag.
In addition, they can be stored outdoors, digging in the yard (if you live in a private house), under the snow.
The main thing - keep the temperature low... Therefore, for storage will go basement, cellar or refrigerator, in other words, a place where the temperature is kept in the region of 0 .. + 4 degrees.
Advice! It is imperative (at least once a month) to periodically take out and inspect the cuttings (future grafts) for damage by mold or fungi.
Cherry plum
An unmistakable option is crossing two varieties of this variety of plum. But as a result of numerous experiments, botanists have proven that cherry plum is the best stock for most stone fruit crops.
The reasons for the popularity of cherry plum stock are:
- high survival rate of cuttings;
- increased yield of future scion;
- improved taste and large fruit sizes;
- increased drought and frost resistance of the scion;
- the presence of a smaller amount of root growth.


Experienced gardeners speak well of grafted on cherry plums, cherries, plums and peaches. At the same time, the effectiveness of the latter combination is noted only in warm regions where there are no harsh winters.
And it is also advised to use semi-wild varieties of cherry plum for inoculation.
Rules and recommendations for carrying out the plum grafting procedure
- It is imperative to observe the compatibility of trees (rootstocks and scions) with each other.
- Perform the operation (vaccination) at the correct time and under favorable weather conditions.
If you are planting in early spring, the weather should already be warm, but not dry and hot. There should be no rain a few days before the day of the vaccination.
- The vaccination procedure itself is best done in the morning.
- It is better to choose a place for grafting (on the rootstock) from the north side, in order to subsequently avoid direct sunlight (then you will not have to shade).
Important! It is undesirable to vaccinate from the south side of the tree, since the scorching sun rays will dry out the graft site, and the graft may not take root.
- Before carrying out the operation, be sure to wipe the graft site (rootstock branch) with a cloth.
- The success of the grafting largely depends on how smoothly you cut the cuttings (scions). They should be perfectly smooth, without any bends or roughness.
By the way! As a rule, the length of the bevel cut should be 3 times the diameter of the cutting (scion).
- The diameter at the grafting site at the rootstock and the scion should ideally be the same. However, if the stock is thicker than the scion, then in this case you need to move the scion to one of the edges, thereby aligning the cambial layers.
Note! It makes no sense to use a scion of a larger diameter than the stock, as well as to put a smaller scion in the middle of the stock. in this case, there will be no contact of the cambium, which means that the vaccine simply will not take root.
- It is necessary to carry out the operation quickly so that the cut surfaces do not have time to oxidize and dry out.
- During the vaccination procedure, in no case should you touch the slices with your hands, so as not to accidentally introduce an infection.
- The same applies to the instruments used: they must be not only sharp, but clean (disinfected), otherwise an infection may get on the cut.
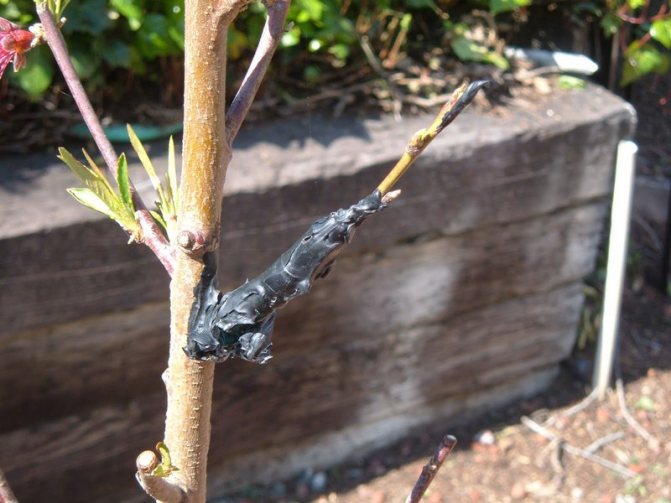
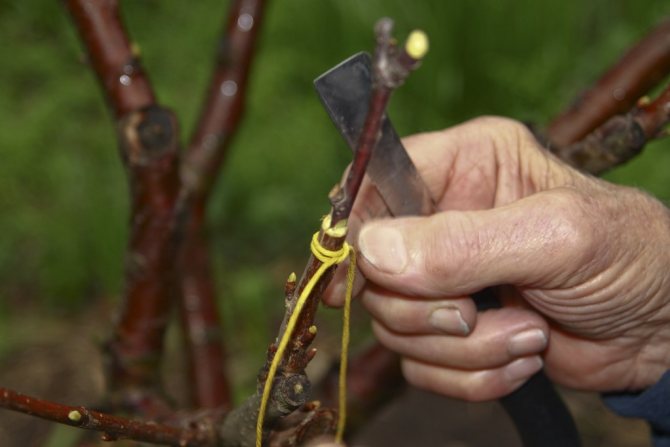
- The vaccination site must be wrapped as much as possible (optimally with a polymer film, but you can also use electrical tape or special tape) and cover the open parts of the graft and the cut off top of the cutting (scion) with garden varnish.
This measure is necessary to protect the vaccination site from drying out, as well as to isolate it from the ingress of air and moisture.
Some gardeners, for better adhesion, put a plastic bag (bag) on top of the graft, but this is not necessary at all, because it is much more important to tightly fix the vaccination site with tape.
- Do not ignore the rules of caring for a grafted tree, otherwise it may reject the cutting.
- Remember that any grafting is a risk of not too strong fusion, especially in the early years, so it is advisable to drive a peg next to a tree and tie it to it.
Read also: Pot for anthurium which is better
Vaccination tools
- grafting knife (also called budding knife);
Of course, you can use the usual pocket or clerical knife, but it must be very well sharpened.
- plastic tape or electrical tape;
Ideally, this is a special film, which itself is destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet rays (i.e. it does not have to be removed).
Answers to popular questions
Several answers to popular vaccine questions.
In the future, the paragraph will be supplemented.
Is it possible immediately (on the day of vaccination) to cut the cuttings and graft in the spring?
It is undesirable, since in spring, in warm weather, the stalk will quickly grow, not having time to take root. The kidneys will draw out all the juices from him, because of which he may die. In other words, if the buds begin to bloom before the graft takes root, then the stalk may simply dry out, since the buds will take all the nutrition from it.
Alternative opinion! However, many gardeners successfully plant cuttings that are cut right on the day of grafting. Of course, subject to access to the donor tree.
The main thing is that the kidneys do not wake up yet.
Moreover, the survival rate of such grafts can be much higher than from cuttings that have passed through storage (due to improper storage conditions, their quality could deteriorate).
When can you cut the cuttings right away?
Always with summer vaccination, namely budding (peephole vaccination).
Why is it best to harvest cuttings in the fall?
The fact is that the cuttings that you prepared in the fall and stored in the cold will definitely be in a dormant state during vaccination. Thus, tissue fusion will occur before the kidneys begin to wake up.
In addition, in a harsh winter, there is a possibility of freezing of the donor's kidneys, which will worsen the result of the vaccination. In addition, in winter, and especially in early spring, nutrients are consumed, which also affects the result.
Best time to get vaccinated
Mostly they do spring or summer vaccinations. Although recently, surprisingly, it is a fact that cultivars began to practice winter. It is difficult to say how effective it is or not, since there are still few reliable results.
But for a long time, breeders have mainly used the grafting technique in the spring. How do you catch the best time for your procedure? The most important thing is not to miss the sap water. Pay attention, it begins even when the snow has thawed, but the earth has already appeared, and the buds on the trees and shrubs have noticeably swollen.
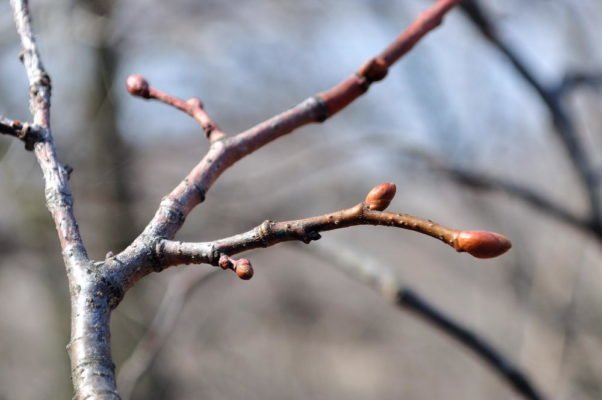


The first thawed patches appeared, and the buds on the trees swelled - you can vaccinate
Plum grafting methods
Plum, like other fruit trees, can be planted using various methods. The gardener makes the optimal choice based on his personal experience and preferences.
Advice! To begin with, choose the easiest one for yourself (in your opinion), and then be sure to practice making cuts, fixing the vaccination site. In short, fill your hand.
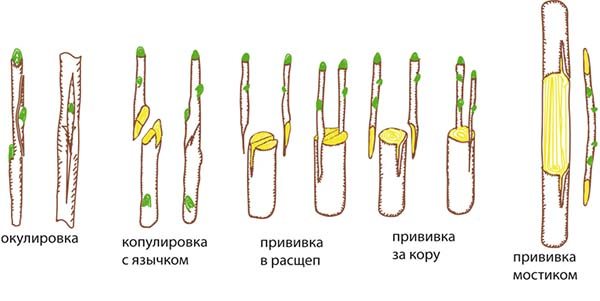

By the way! The vaccination process in any way consists of 3 main stages:
- preparation of stock and scion;
- their combination;
- protection of the vaccination site (wrapping with tape and covering with garden pitch).
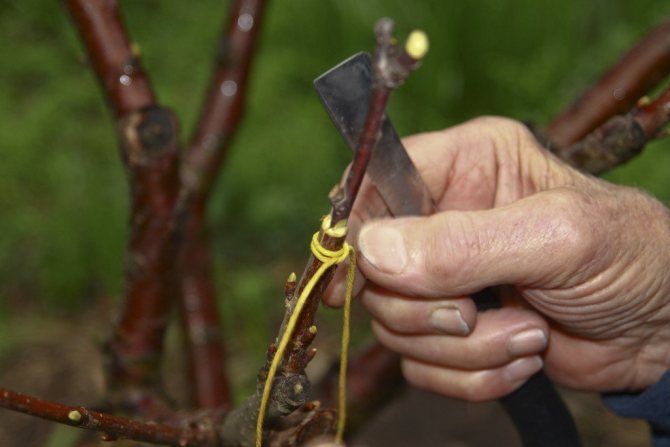
Copulation
Plum grafting by copulation is carried out in early spring, when the tree is at rest, i.e. before the start of sap flow.
The diameter of the scion, as well as the rootstock, must be the same. Or the stock may be slightly thicker than the scion (cutting), but in this case, you need to be sure to combine their cambial layers.
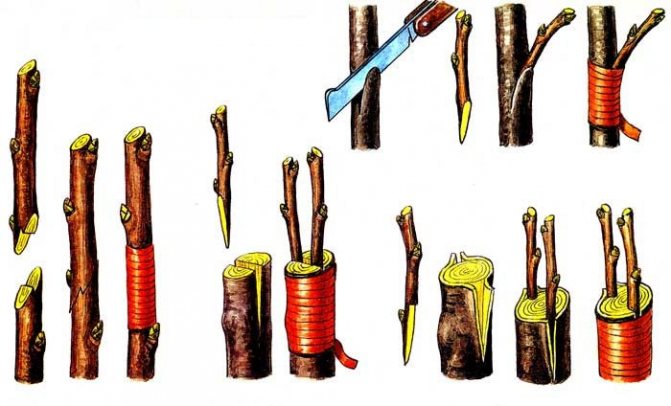
There are two types of copulation: simple (a) and improved (b).
Naturally, the second method is more popular, since thanks to a more reliable contact, the vaccine takes root better than with simple copulation.
Simple copulation
Stages of simple copulation of plums in spring:
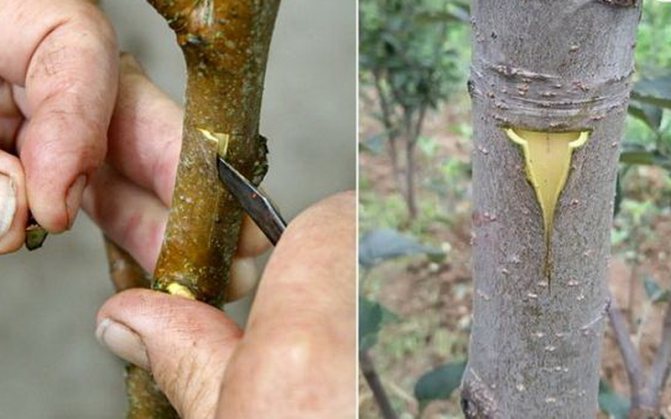
- Make an oblique cut (at an acute angle to yourself) on the rootstock and an identical cut on the scion (cuttings) under the lower bud in the same direction.
The cut on the rootstock and the scion should be made of the same length, at the same angle and preferably in one motion (but it's okay if 2-3 times).
- Attach the scion to the stock so that their cambial layers coincide.
- Wrap the vaccination site tightly with foil or electrical tape.
- Cut off the top of the cutting (scion), leaving 2-3 buds (above the upper bud) and cover the cut with garden var.
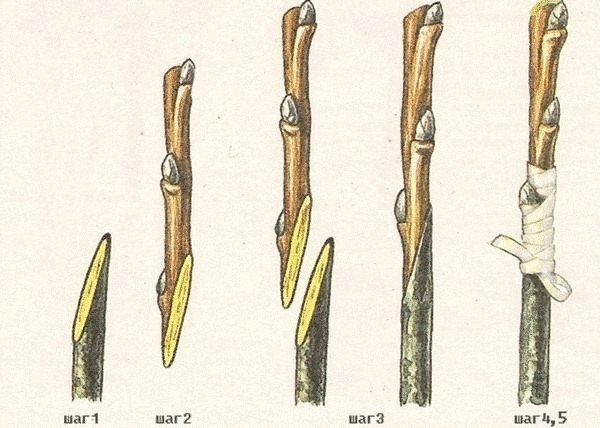

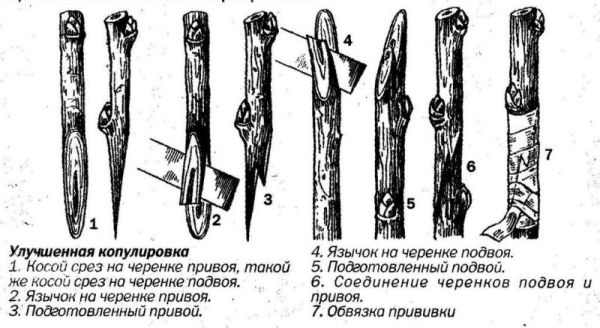
Improved copulation
Spring grafting of plums using the improved copulation method:
- Similar to simple copulation, oblique cuts must be made on the rootstock and scion.
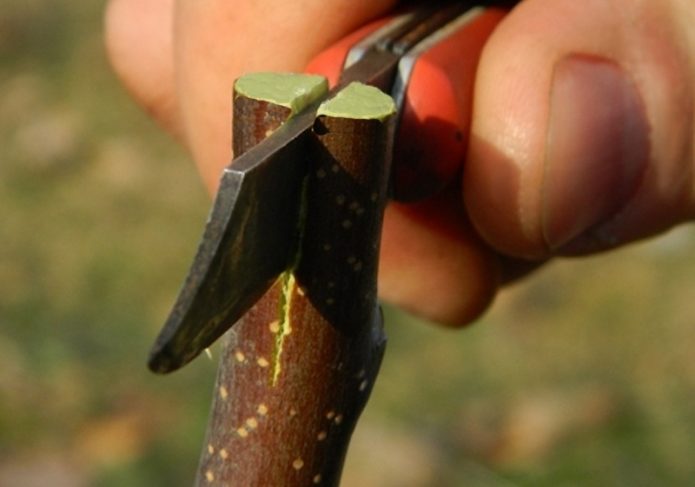
- After that, stepping back from the upper edge of the cut by 1/3 of the length, make a "tongue" on the rootstock (cut 10-12 mm deep into the shoot).
- Make exactly the same "tongue" on the scion.
- Insert the scion into the stock, in other words, start the "tongues" behind each other.
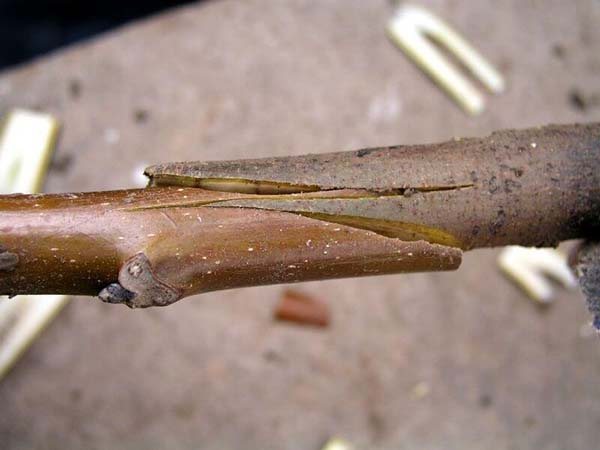


- Further, everything is the same: tightly wrap the graft site with foil, remembering to cut the scion over 2 or 3 buds, and process (cover) its upper cut with garden var.

Video: Plum grafting with improved copulation
Thus, the only difference between the two grafting methods is that small splits are cut out on the cuttings (they make "tongues" for better grip), the depth of which is equal to 1/3 of the length of the oblique cut.
Video: grafting trees - simple and improved copulation
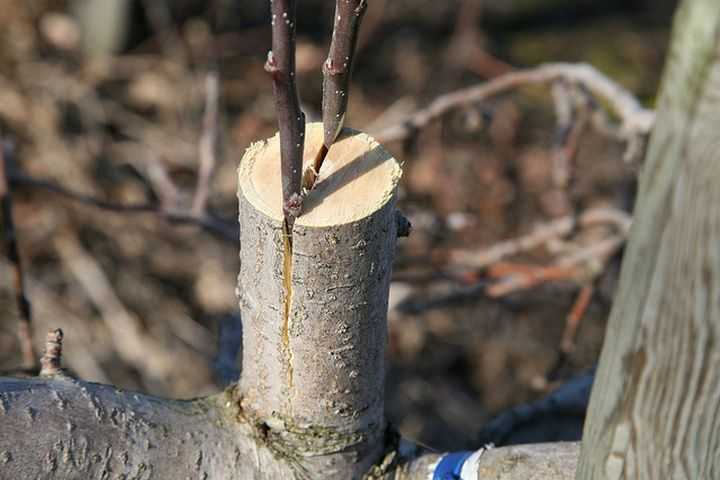
Into the cleft
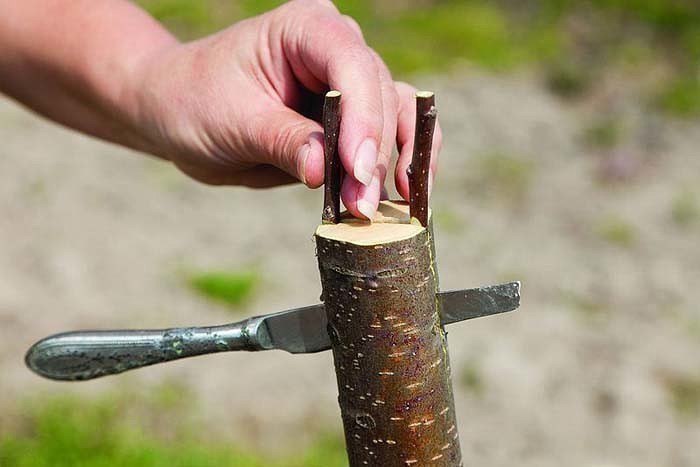
In the split, as a rule, adult (thick) tree branches are grafted, but it is quite possible to graft young ones with this method.
As for the timing, the grafting of the plum into the split is carried out while it is still sap flow did not start, i.e. when the tree is dormant.
Split grafting is performed when the stock is thicker than the scion (cutting). But in any case, the stock should not be thinner than the scion!
Moreover, if the rootstock branch is thick, then you can use 2 scions (cuttings) at once, placing them opposite each other (on opposite sides).
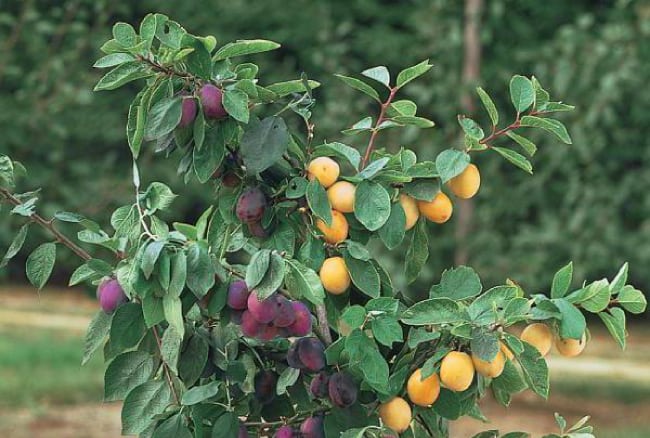
Grafting allows trees to rejuvenate, making them resistant to diseases. Up to 8 different varieties of plums can be grown on one tree, which saves space on the site. The procedure speeds up the fruiting time, increases the yield, improves the palatability of the fruit and strengthens the plant's immunity.
Taking care of the tree after grafting
Having grafted a plum, you can evaluate the result after 3 weeks. If the branch is elastic, a callus (growth) has formed in the connection mark, the scion has taken root. The electrical tape is gradually loosened so as not to overtighten the bark. When the first leaves appear, the harness is removed. For thin cuttings - after 2-3 weeks, for wide cuttings - the next year. When there are several scions, a few extra ones are removed, covering the cuts with pitch. Large branches are tied to supports.
When a tree is grafted in the spring, excess branches, fruits, leaves are removed in the summer, otherwise it will not have time to get stronger; in the summer - pinch the tops of established cuttings. This allows you to endure the cold winter and accelerates the onset of fruiting. The next year, a crown is already formed, directing the branches of the scion in the right direction, the secondary shoots are removed. Required dressing: in the fall - with mixtures of potassium and phosphorus, in the spring - with nitrogen and organic matter.
Optimal timing
If the spring time for grafting plums is missed, prepare to do so in the fall. A young scion cuttings need time to grow from 14 to 21 days, it must have time to get stronger before the cold weather arrives. The best autumn time for vaccination is the period of warm nights (not lower than 15 ° С) in September-October, when sap is still flowing. With the arrival of early frosts, the plant stops growing, at this time it is already useless to graft. Winter grafting of plums in southern Russia is possible, if the winter is warm, without severe frosts.
Read also: How to cook Baikal at home recipe


Plum grafting process
Rootstock selection
The basis of a plant for grafting in the fall is an adult tree with developed roots, strong branches, and a healthy trunk. The stock should be:
- frost-resistant;
- zoned, adapted to the weather conditions of the area;
- unpretentious to unfavorable soil indicators, such as waterlogging, acidity;
- have good resistance to diseases and pests.
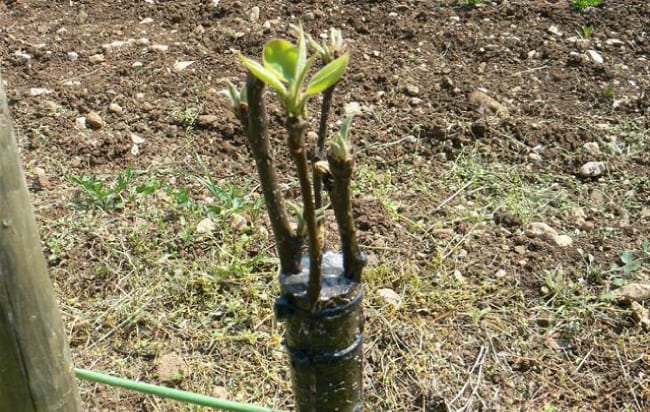


The established cuttings after plum grafting
Plum grafting in autumn can be on two types of rootstock: seed and clonal. Seed trees are grown from seed, and clone trees are grown by rooting cuttings. The growth activity, the quality of the crop and the duration of the growing season of the grafted plum depend on the characteristics of the main plant. As a seed stock used:
- Local thorny plum - unpretentious, frost-resistant, stunted, good yield;
- Plum seedlings - maximum compatibility, good survival rate, resistant to adverse weather factors;
- Home cherry plum is the best stock for heavy soil with high humidity, high survival rate. Grafting on wild cherry plum is compatible with many varieties of stone fruits.
- Apricot - increased winter hardiness, suitable for heavy soils, easily tolerates drought. Some plum varieties are not compatible with apricot stock.
- Felt cherry is undersized, frost-resistant, difficult to take root with some varieties of plums, and is susceptible to disease.


The results of grafting plum on apricot
Clonal, vegetatively propagated rootstocks, compatible with almost all varieties of plum:
- For the southern regions they use "Alab-1", "Druzhba", "Kuban-2".
- For the middle lane, own-rooted varieties "Vengerka Moskovskaya", "Tula Black" are suitable.
- "Ussuriyskaya", "Canadian" plum. Distributed in the Far East and northern latitudes of Russia, they can withstand large frosts and cross well with other varieties.
Why do unusual grafting of garden plants?
You will find the answer in our table. In it, we indicated the correct combinations of rootstocks and scions and the result that you will receive after vaccination.
Graft (stalk)
Rootstock (plant to be grafted onto)
Achieved effect
Hawthorn, Japanese quince
Early maturity, decrease in tree height
Early maturity, the ability to bend branches to protect against frost
Increasing winter hardiness, reducing gum flow
Every gardener would like the trees on his site to please with a plentiful and high-quality harvest every year, never grow old, and any variety that he likes to take root easily and quickly. It is quite possible to make all these dreams come true if you are an ace in grafting fruit crops. Let's figure out the nuances of this delicate and very fascinating case.
The main rule of breeders is to plant like on like. In this case, a successful result is guaranteed, since intraspecific grafts always grow together easily and bear fruit well.
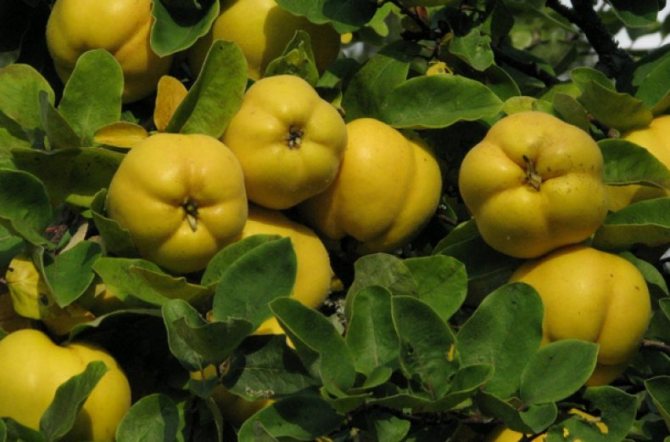


The desired result can be obtained not only by crossing varietal and wild quince, but also in tandem of interspecific specimens. Recently, gardeners have been experimenting more and more, planting a pear on a quince.
Such a combination is attractive by the special taste characteristics of the fruit, which become more pronounced. It is almost impossible to achieve this when growing into a wild game.
Experts emphasize that in most cases quince is used as a rootstock for pear and apple trees. - a plant on which the stalk you like takes root.
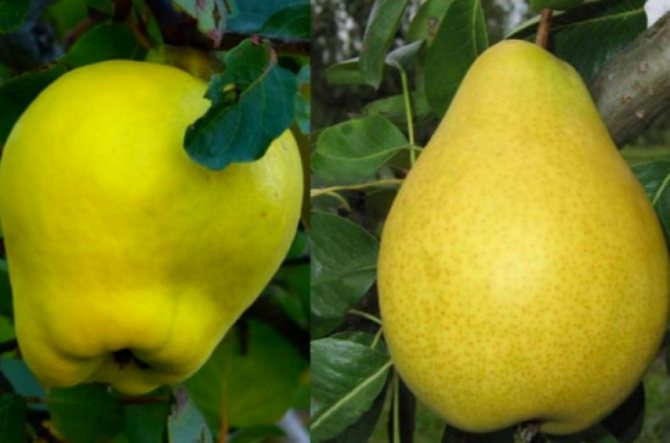


This variation is very successful for interspecific and interspecific combinations, since the tree provides good nutrition for the scion, which, in turn, assimilates useful microelements faster and forms an improved yield.
But it is impossible to grow quince sprouts on a pear, apple tree, hawthorn. This is extremely rare even for professionals.
Scion selection
A good cutting is a lignified, one-year or two-year-old shoot. Take healthy and developed branches without lateral branches on the south side of the tree. They are cut in spring before bud swelling or in autumn after leaf fall. Cuttings are stored in a dormant state at a temperature of about 0 degrees, a relative humidity of 70%. It is advisable that during the storage period the processes are hardened, a short-term temperature drop to -10 degrees. The cuttings are stored in wet sand under the snow, tops outward or on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator.
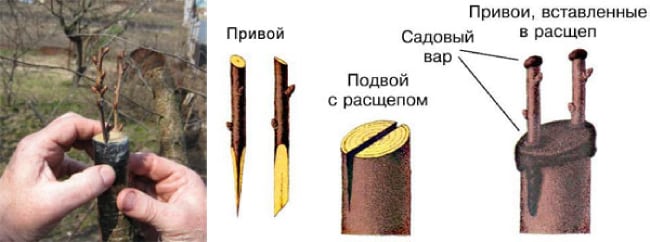

Graft and stock in the plum grafting scheme
Several options for choosing the right cuttings:
- only a healthy and well-fruiting plum will do;
- the branches are carefully examined, they must be free of damage and disease;
- buds are green, well developed and dormant;
- if the layer bends easily, then it is alive;
- look for suitable layering along the edges of the plum and in the middle of the crown;
- optimal length 40 cm, diameter 0.8 to 10 cm;
- to check the viability of the branches, the tip is cut, if the cambial layer is fresh, the bark is green - suitable for grafting.


Cuttings correctly selected for grafting on a plum tree
Characters and performers
They take part in the sacrament called "inoculation"
... There is also a fourth character - a man, but about him later, but so far only about the three main characters.
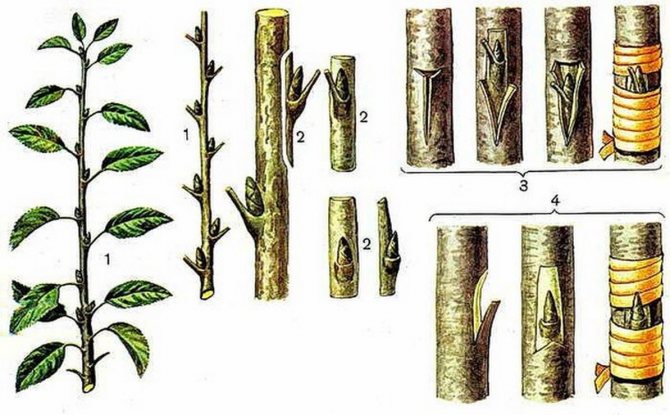
A graft is a part of a varietal plant that takes root on another plant. It can be a small piece of a stem, or even a single bud. The graft will form the upper part of the tree (bush) and "be responsible" for its varietal characteristics.
A rootstock is a plant or part of a plant on which a scion takes root. The rootstock is the lower part that will be responsible for nutrition, resistance and adaptation to local conditions.
In order not to confuse which is which, we remember this:
- a scion is a part of a plant that takes root on another plant;
- the stock is UNDER the scion.
And if the scion and stock are the main participants in the process, then
- this is the main performer, it is thanks to him that everything happens.
Copulation
The method is used when the rootstock and scion have the same cross-section. For better survival, it is desirable that the shoots have a diameter of no more than 1.5 cm. Disadvantages: it is very difficult to make the same cut. During the winding of the graft site, the stalk may move, then the cambial layers will not coincide. There are two types of copulation of plums:
- Simple - consists of the following steps:
- At the end of the scion and on the branch of the stock, cut an oblique corner, 3-4 cm long.
- Attach the slices to each other so that the cambial layer matches exactly.
- Tightly wrap the grafting site with plastic tape, and grease the top of the cutting with garden varnish.
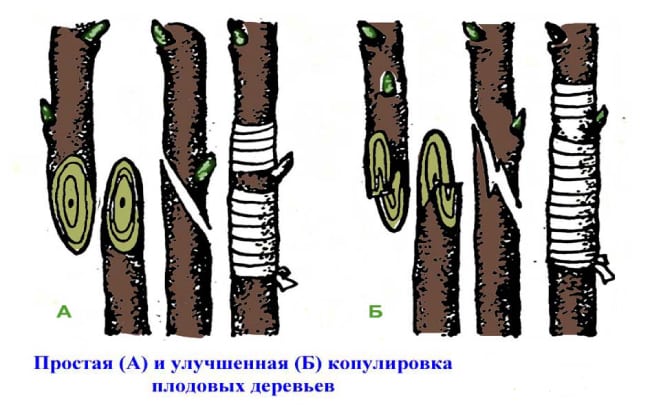

Simple and improved copulation of plums in the diagram
- Improved grafting - used in the fall more often than simple copulation, promotes a closer contact of the cambial layers. The main steps are the same, only a small split is made in the middle of the cut of the cutting, 1/3 deep from the oblique cut. Correct execution guarantees the formation of callus at the junction, the two parts of the plant will join and the cutting will take root.
Grafting technique step by step
Let's look at the instructions for the cleft vaccination. What is the advantage of this method? First, it's a pretty straightforward way. Secondly, it gives a high percentage of cherry accretion on the plum.
Step-by-step instructions for cleavage vaccination
Getting an improved cherry with the qualities of a rootstock is the result of a competent algorithm of actions.
- Grow a young plum as a rootstock.The best age for the procedure is 1–2 years, the trunk of the tree is about 6–8 cm. It may not be a specially grown plum, but quite a living and blooming young sapling, which was planted a year or two ago and feels great. Remember, grafting is not carried out on a diseased tree!


Grafting is carried out only on a healthy tree, preferably no more than 2 years old.


Cherry cuttings are prepared in advance - in the fall
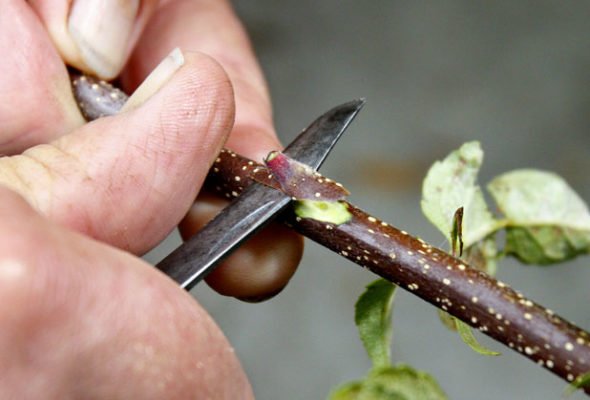


Summer grafting involves green scion cuttings
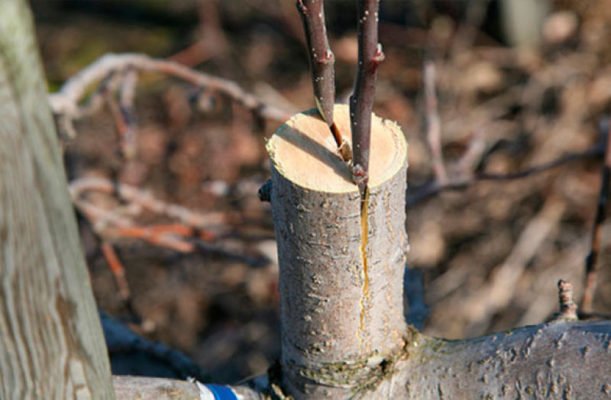


Cleavage is a safer and less difficult method of vaccination


The cut of the rootstock branch must be clean and neat, as well as the split in it.
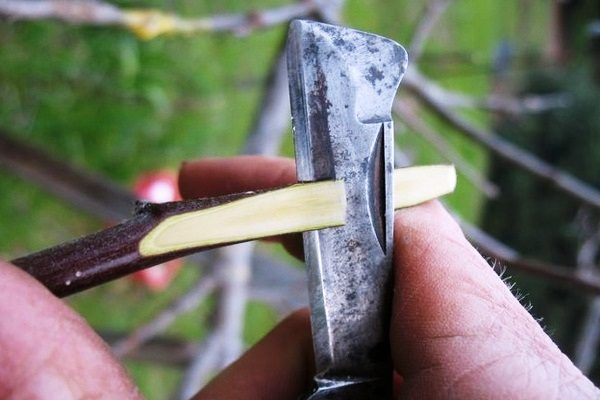


Two cuts should be made on one side so that the cutting becomes wedge-shaped.
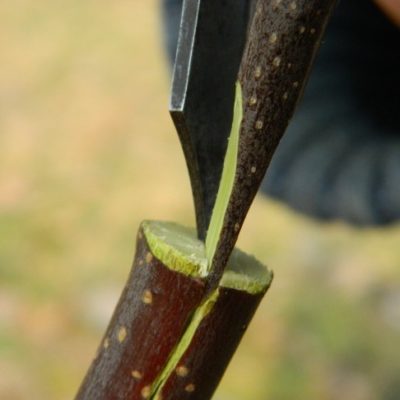


Carefully place the cutting into the cleft so that the cambial layers of the wood match and grow together
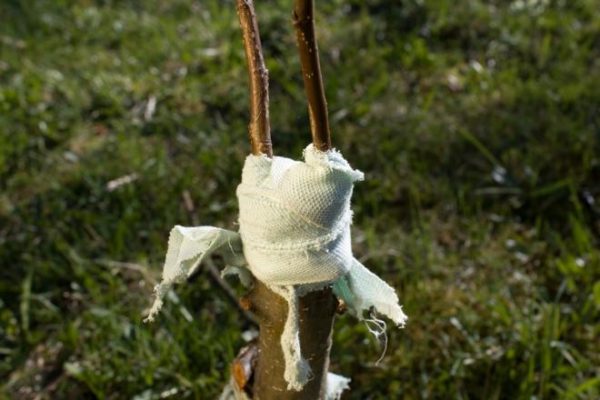


Tying the incision sites and treating with garden pitch is important, as this will help the excess juice not to leak out, and the tissues to take root faster
So that the split does not close while you are making side cuts on the cuttings - leave a hatchet in it or put a screwdriver, a strong stick, etc. It is advisable not to remove the item until you make sure that the handle is placed securely and correctly.
Video: cleft grafting technology from an experienced gardener
Budding
The kidney implantation method is performed in spring, summer and autumn.Suitable for large mature trees, but works best on young plants. Disadvantages of vaccination: painstaking work. You need a fresh kidney, neatly cut off from the scion with a sharp knife, with the capture of the cambial layer.
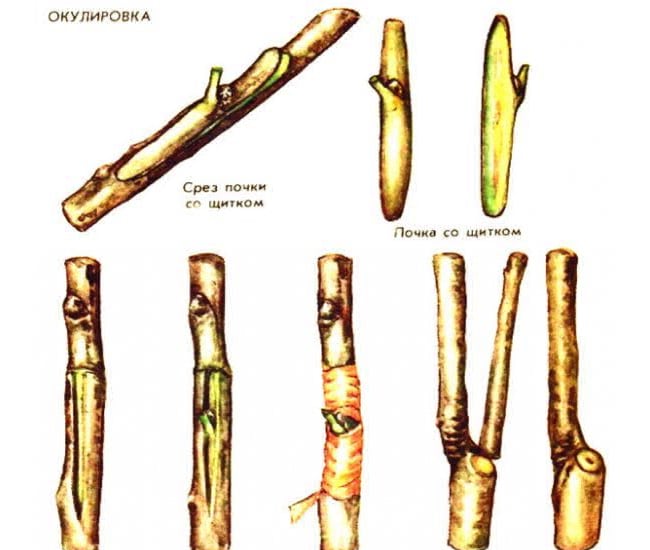

Plum budding
Step-by-step implementation of budding:
- Make a transverse incision on the branch of the scion 1-2 cm above the bud.
- Then cut downward, going a little deeper into the wood.
- Finish the cut at a distance of 1-2 cm below the kidney.
- A T-shaped incision is made on the bark of the stock to fit the size of the cut bud. The kidney is inserted inside and tightly wrapped with plastic tape from the bottom and top of the eye.
- After 2 weeks, you need to remove the winding and check the survival rate of the kidney. If it is fresh and firmly attached to the trunk, it means that it will soon grow. If the grafted eye is dry, budding has failed.
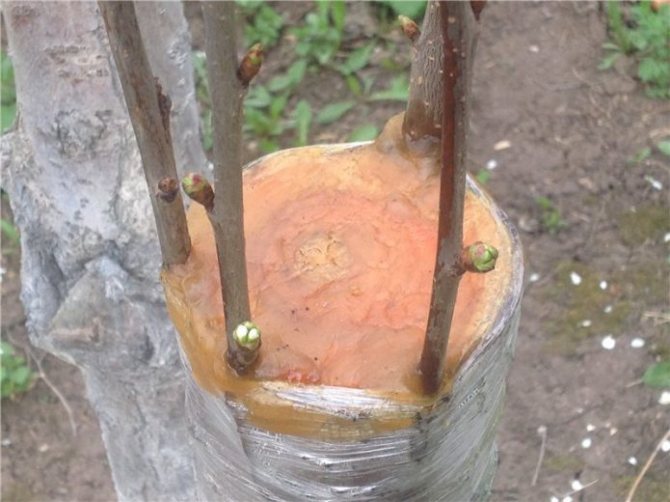
Into the cleft
The method is used during a small flow of sap, in early spring, and in the southern latitudes of Russia - in the fall. Plum grafting on plum is suitable when the rootstock is much larger than the scion. Step-by-step instruction:
- Choose healthy branches on the rootstock, cut at a height of 40-100 cm from the ground. From above, the cut diameter should not exceed 5-7 cm.
- In the center of the cut, with an ax or a sharp knife, make a depression 2-3 cm down.
- One or more cuttings with a wedge-shaped cut, with a thickness of 1 to 10 cm, are inserted into the resulting hole.
- The grafting site is tied with twine and lubricated with garden varnish. The cut is covered with plastic wrap to reduce moisture evaporation.
Video
Grafting of fruit trees is used by those who are not afraid to change the varietal characteristics of the plum. After all, cuttings from different trees can be grafted onto one tree. Then, after the procedure, fruits are harvested, different in shape and taste. And for the culture it is an opportunity to recover, to become more resistant to adverse weather conditions. But before you start any actions, you need to know everything about how to plant a plum, which crop is better and in what way.
What time of year to carry out the procedure
It is necessary to determine the timing of vaccination taking into account the region in which the stone fruit culture is grown. Spring grafting is most common, since the tree will recover faster due to increased sap flow. But autumn and summer also cannot be written off.
The phases of the moon also determine when it is best to vaccinate. The procedure is more successful in the growing month. Weather conditions are also taken into account. It is necessary that the day of the vaccination is not too cold or hot.
In the spring
The most chances for the success of the procedure will be in the first months of spring. The end of March - the beginning of April is considered optimal. At this time, the tree is full of strength, and the plum will recover quickly. Operation can be performed in May, but only in cold weather. Otherwise, the plum may wither away, or there will be no sense from vaccination.
In summer
A summer operation takes place only if it was not possible to carry it out in the spring. Often the spring grafting does not always go well, the stalk does not take root. Then it is worth postponing the procedure for the summer. The ideal time is June or July for temperate regions. Then the survival rate of the scion will increase before the onset of a cold snap. In warm areas, it is possible to plant plums in August as well.
In autumn
It is not recommended to plant plums in the fall. Even if the operation is carried out in September-October, the tree will not have time to recover after the procedure. And the vaccination will be ineffectual.
Cherry
The unspoken rules of gardeners speak of a successful combination of all stone fruit crops. They can be combined as rootstock and scion. Deciphering these instructions, experts call a combination with cherries and bird cherry, as well as varietal cherries, successful for cherries.
These are the most common amateur level variations. Moreover, tandems of wild animals with hybrids and different varieties are allowed.


But this is still an incomplete list of what can be grafted onto cherries.Amazing berries are obtained by combining it with currants, cherry plums and plums. In addition, in these cases, the opposite option is also allowed.
And if you want to get a dwarf, very winter-hardy tree with a branched variegated crown, try to grow a cherry with a thorn.


In regions with moderate climatic conditions for grafting, Vladimirsky, Korostynsky cherry varieties, as well as cloned rootstocks Izmailovskaya (PN), Rubin, AVCh-2, VP-1 are ideal.
How to prepare cuttings
As a scion, cuttings from lignified shoots of one or two year olds are used. It is better to cut from the side branches and from the sunny side of the tree. This should be done in the fall, before the first drop in temperature occurs. Cuttings ready for hibernation will be better preserved and remain viable until spring. They can be saved:
- in grooves lined with spruce branches, covered with earth and straw on top;
- on the balcony, tied in bunches;
- in a basement or cellar;
- on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator.
Read also: Peach Laika variety description
The main requirement for storage is an air temperature of at least 0 degrees and a humidity of 70%.
As many cuttings as possible should be harvested, as many can come out of storage with damage and rot.
Types of rootstocks
It is best to plant plums on related trees. Better if it is a wild or semi-cultured. The resulting tree will have the taste of the grafted cultivar, but it will be characterized by winter hardiness and durability. In addition to stone fruit crops, pome fruit can be used as a rootstock, but the survival rate of the cuttings will be worse. So you can use the types of rootstocks that are close to plums. These include bird cherry, cherry, apricot and peach varieties.
Plums on plums
One of the successful operations is when one variety of plums is grafted onto another, resulting in a wonderful hybrid. The best qualities of the parents will be a feature of the plum obtained. You can not limit yourself to one handle, but use several. Then the variety of fruits on the plum will be interesting.
On the turn
The closest relative of the plum is characterized by the fact that the shrub is unpretentious, resistant to low temperatures. If you want a plum variety that bears fruit in the southern regions, then you can graft a stalk from it onto a thorn. The success of the operation will be in any case.
Into the wild
Wild plum varieties are used for rootstock when it is necessary to improve such qualities as strong immunity to diseases and pests. Wildlife is characterized by persistent tolerance to cold climates, temperature extremes, and high humidity.
Novice gardeners need to use this type of rootstock for training in vaccination.
For bird cherry
Although it is possible to use a bird cherry tree as a rootstock, the vaccine will not give a positive result. The resulting fruit tree specimen will not produce good fruit. And the plant will hurt, develop poorly.
Cherry
Of all types of cherries, it is better to choose felt cherries for grafting plums. But at the same time, the operation requires precision and accuracy. Only then will the plum stalk take root. The advantage of the operation will be the short stature of the hybrid, its early maturity.
Apricot
If the vaccination is successful thanks to the correctly selected varieties of plum and apricot, their compatibility, then the summer resident will receive a wonderful hybrid. Although the wood will be more suitable for warmer climates, the aroma and taste of the fruit will become superior.
On yellow
The unusual color of the fruit is obtained after inoculation of the variety with blue plum and yellow. The operation is usually successful, and the stalk takes root quickly. But it is best to graft not on a seedling, but on an adult tree.
On a peach
To carry it out correctly, you need a variety that is ideal for merging with a plum. It is best if it is a semi-culture. Still, the peach tree rarely serves as a rootstock. It is better to graft a peach stalk on a plum, then the sense will come out more.
On cherry plum
A short stock is suitable for cutting a plum and the operation is successful. The survival rate is high, since both cultures are related.
Recommendations
Experts say that in the entire vaccination procedure, most of your attention and care should be given to the stock, that is, the plum. Choose a tree that is healthy and strong with a good root system and immunity to common diseases. For example, it can even be a wild-growing plum.


Often, it is wild trees and shrubs that have excellent properties that are so difficult to achieve from domesticated counterparts bred in captivity.
Vaccination methods and technology
There are many ways in which plum inoculation can be carried out step by step. It all depends on the experience of the gardener, his practical skills. For beginners, it is better to choose easy methods of vaccination, then move on to more complex ones.
Ablactation
Ablactation is also called a method of bringing horticultural crops closer together. The method can be used when you need to create a row of plum hedges. On the shoots growing nearby, incisions are made, connecting the scion together with the stock. Having folded the layers of cadmium correctly and securing the place of convergence with electrical tape, a new hybrid is obtained.
Copulation
One of the common and simple methods of grafting plums is that:
- The thickness of the rootstock and the scion should be almost the same.
- Cuttings with 3-4 buds, cut from annual shoots, are suitable for scion.
- At the top, the cutting is cut over the kidney.
- Cuts are made obliquely with the length of the cutting diameter - 3-4 centimeters. On the back side, the scion should have a bud.
- On the cuts, a tongue is made from the bark with a length of 0.5 centimeters. Cut from top to bottom under the middle lobe of the plane.
- Bending back the tongue, the scion and rootstock sections are connected with the coincidence of the cadmium layers.
- Tightly connect the place with a washcloth and adhesive plaster.
As soon as there is an increase, the winding material is cut across.
Budding
Budding is carried out by grafting a peephole or bud of the selected plum variety. The thickness of the stock should be 1 centimeter, a recess is cut out on it and a shield with a bud is inserted into it. The junction is fixed with a special tape, leaving the peephole open. Vaccination can be carried out in the fall, then in the spring the bud will sprout. A peephole taken in the spring is suitable for a summer procedure.
Shank
It is also possible to graft a plum with a cutting when the thickness of the rootstock is 2 times greater than the scion. Then an oblique cut is made on the tree, and then the width of the cut plane is reduced by a second cut at an angle of 30 degrees. In this case, the width of the remaining plane will correspond to the thickness of the cutting. The rest of the procedure is carried out as in copulation.
By the kidney
They are inoculated with a kidney or an eye on a bark shield, and so:
- make a T-shaped incision on the stock;
- fold back the bark layer;
- insert a shield with a kidney there;
- the vaccination site is rigidly fixed with PVC tape.
It is better to vaccinate on young plum shoots in August.
For the bark
If the thickness of the selected rootstock is from 2 to 4 centimeters, then grafting technology for the bark is suitable. The bark is incised across the length of 2-3 centimeters. With a thin cuttings, the bark is separated from one side. For a better connection of cadmium in a thin cuttings, the bark layer is removed. A stalk is inserted by the bark, the grafting site is tied up and coated with garden varnish. Be sure to make sure that the entire oblique cut of the scion goes under the bark.
Into the cleft
This technology will allow several plum cuttings to be planted. The rootstock branch is cut down transversely and straight. In the middle, slices are split perpendicularly. A wedge is made at the bottom of the cutting, with which it is inserted into the split so that the cadmium layers coincide. Then there is a varnish processing and strapping of the junction.
Side cut
This method is needed when the thickness of the stock is at the level of 2.5-3 centimeters. The cut is made with a sharp knife, placing it at an angle of 20-25 degrees relative to the rootstock axis. It is enough to cut to a depth of 5-8 millimeters.Turning the knife, bend back the trimmed part. Then a wedge is made down on the scion, which is inserted into the side cut. When the planes coincide, the strapping is made and covered with pitch.
By the bridge
In the butt, or with a bridge, the stock is prepared by cutting it across with a slight inclination of the end to one side. On the higher side, the bark and part of the wood are cut longitudinally, and the tongue is cut. The slice width corresponds to the thickness of the grafting cuttings. And the length will be 2-3 centimeters. Having connected the stalk with the stock, tied it with a washcloth, covering it with garden pitch on top. The upper end of the plum stalk and the end of the rootstock are also coated.
Features of grafting apricot
All methods of grafting trees have been developed in the main and are described in textbooks for apple and pear. If they are applied to stone fruits, the survival rate of cuttings can be: in plums and cherry plums, at best, 30-50%, and in cherries and peaches, nothing may take root.
Cuttings of all fruit species are harvested at the beginning of winter, before the onset of severe frosts. Apple and pear cuttings are well preserved in ordinary cellars in wet sawdust. It is better to store stone fruits frozen, for which, on a frosty day, wet sawdust is poured onto a piece of film on a frosty day, cuttings are placed on them (you can wrap them in a damp cloth), then covered with wet freezing sawdust with a layer of 20-30 cm.
Even on thaw days, heat does not penetrate under the sawdust for a long time. For grafting stone fruit, it is better to harvest thicker cuttings, since thin ones usually take root less well or do not take root at all. It is better to plant stone fruit cuttings in early March, during thaw days (at positive temperatures).
We offer you to familiarize yourself with: Ornamental trees and shrubs Siberian hawthorn
The film under the sawdust will help you to pull off the cuttings along with the sawdust and bring them into the house for thawing. For several days during grafting, cuttings can be stored in a damp cloth under the refrigerator in a regular refrigerator (it is better to set it to extreme cold). The day before grafting, the ends of the cuttings should be cut off and placed in water for no more than a day.
If an apple tree and a pear can be grafted at any age, if only the tree is healthy, then it is advisable to graft stone fruit only on young trees, not older than 5 years. Re-grafting at an older age can kill the tree.
The method of grafting into the butt for the bark, in mid-April. Saddle grafts for the bark in dry conditions often break, do not grow together in the upper part of the cutting.
When grafting, the compatibility of the scion and the rootstock should be taken into account.
Thank you very much for the information on stone fruit vaccination. I still have a large nut at my grandfather's dacha. I would like to re-graft. I would love to read tips for grafting nuts. I heard that there are some nuances. If in the course, advise how to vaccinate? An old tree with a hollow is about to bend. I wish I could be in time ... Thanks in advance.
What kind of nut, walnut? If so, I can describe the technology!
If you decide to propagate the apricot on your own site, you need to know about all the intricacies of this process. If there are already several fruit trees in the garden, use grafting. The main advantage of this method is the ability to cross different fruit trees: the apricot is grafted onto thorns, cherry plums and even plums.
Grafting allows you to cross the apricot with other fruit trees
Grafting is a vegetative propagation method in which one or more plant cuttings are attached to another. The material to which they are grafted is called the stock, and the grafted material is called the graft. With the correct connection, processing and fixation of the scion and rootstock, they grow together.
Most often fruit trees are planted. Grafting of apricots is especially popular. The main goal is culture propagation. Grafting of apricot can improve the varietal qualities of the plant.Often, such an operation leads to an increase in the frost resistance of the crop and better yield readings.
The vaccine was most widely used in central Russia. Apricot is a thermophilic crop, therefore, growing it in harsh climatic conditions is difficult, but if you choose the right stock, you can get an excellent frost-resistant tree. And the best performance is plum. Such a rootstock for an apricot would be ideal.
Grafting will help increase the yield of the tree
- Choose the right material.
- Prepare the tool.
- Choose a suitable time and carry out the operation itself according to the instructions.
- In the spring. Vaccination during this period is most effective. The plant wakes up after wintering. With warming, the sap begins to fill the branches of the trees, therefore, the grafted material will take root faster.
- In summer. No less favorable time. It is best to carry out such an operation in June. Such terms allow the graft to take root in a new place.
- In the autumn. Effective only in regions with warm climates. The first autumn frosts will destroy all chances for two parts of the plants to grow together.
- Side cut. One of the easiest but most effective ways to vaccinate. On the rootstock, a small incision should be made in the bark, into which the prepared cutting is inserted. The junction is coated with garden varnish or other healing agent, fixed with a tissue splint.
- Into the cleft. A simple and effective method used in case of large differences in rootstock and scion thicknesses. In the mother plant, a split incision is made into which a pointed stalk is inserted.
- Copulation. It is used when the thickness of the scion and rootstock is equal. The gardener only needs to make oblique cuts on the cuttings and connect them tightly together.
- Budding in the crown. This is a known vaccination method that uses the kidney engraftment method. The scion stalk is prepared for the operation by making an oblique incision just above the kidney. On the rootstock, budding incisions (usually T-shaped) are made, into which the scion with a small piece of wood (shield) is later inserted.
- For the bark. The peculiarity of this method is the implantation and pressing of the cuttings with the rootstock bark. A deep incision should be made in the bark of the mother tree, gently bending back the separated part. A scion is inserted into the formed space.
- improving the quality of fruits of interest to the gardener;
- increasing the level of winter hardiness of the plant.
The tools must be well sharpened. The use of low-quality materials can not only worsen the quality of the vaccine, but also negate all the chances of the success of the procedure.
Experts believe that the vaccine is best done in the afternoon or early morning.
Vaccination tools must be well sharpened
The simplest breeding option is grafting apricot to apricot.
It is best to plant a stalk grown from the bone of the mother tree. A feature of this vegetative propagation is the preservation of the varietal qualities of the culture.
We must not forget about the importance of processing the cut sites with garden pitch. They allow the grafting to proceed faster, speeding up the process of engraftment of one material to another.
From the video you will learn how to plant plums and cherries.
One of the methods of vegetative propagation of plants is grafting. It is often used for growing fruit crops, as it allows the grower to obtain a plant that will meet his requirements for yield, endurance, fruit taste, etc.
Grafting is one of the ways of vegetative propagation of plants
It should be noted that grafting is an effective agricultural technique, during which two crops are combined, one is called a scion (usually a cutting), the other is a rootstock (main tree). The result of vaccination is the fusion of two parts into a single whole.
The combination of a scion, which is less resistant, with a rootstock that can withstand severe frosts, allows you to achieve the second goal, which is especially relevant for those who grow crops in central Russia.
The grafting of an apricot does not require an exact varietal or species match of the two plants used. The main thing is that a stone fruit culture is used as a rootstock, and not a pome one (this means that it is inappropriate to plant an apricot on an apple tree or a pear).
Need to know: apricot should not be grafted onto an apple tree