Description
The Khabarovsk apricot variety was bred back in 1949, and today it is one of the most deserved types of fruit trees. Until now, this variety is very popular among gardeners - and all thanks to its simple agricultural technology, high yield, and wonderful taste of the fruit.

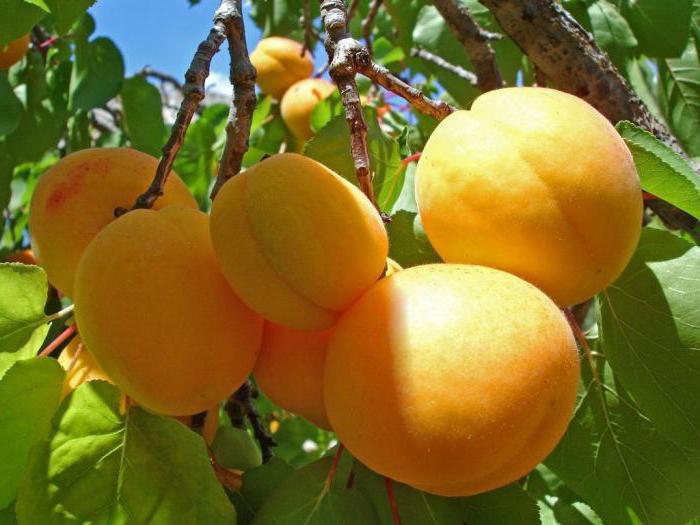
Apricot Khabarovsk
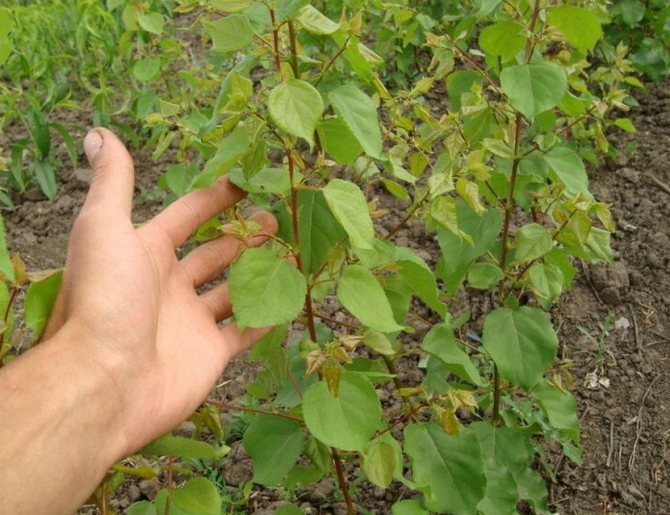
Note that the tree grows very tall, reaching 4-5 meters. His crown is rare, but rather spreading, which facilitates harvesting and ripening of fruits. Leaves are medium in size, oval-elongated, the lower part is lighter than the upper one. As for the main thing - the fruits, in this case they grow large and juicy.
It may also be useful for you to learn about what self-fertile pear varieties are for the middle lane.
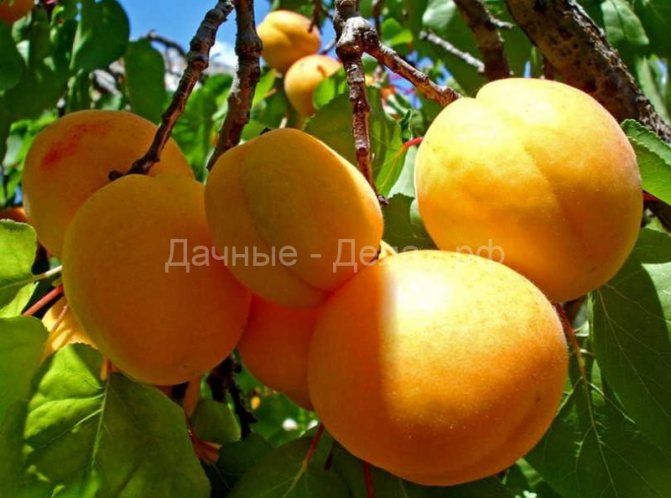
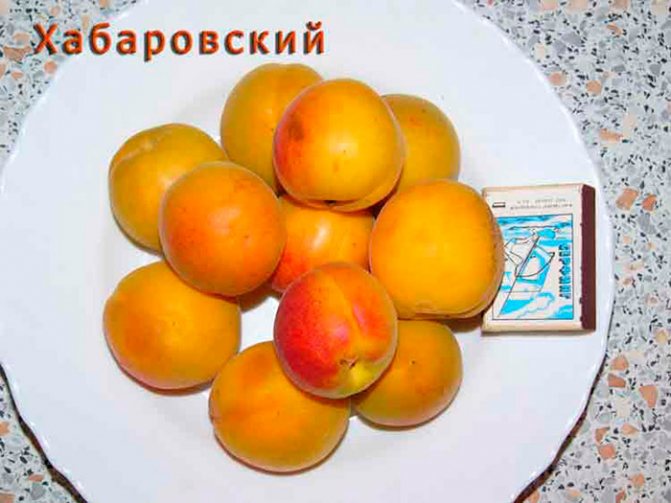
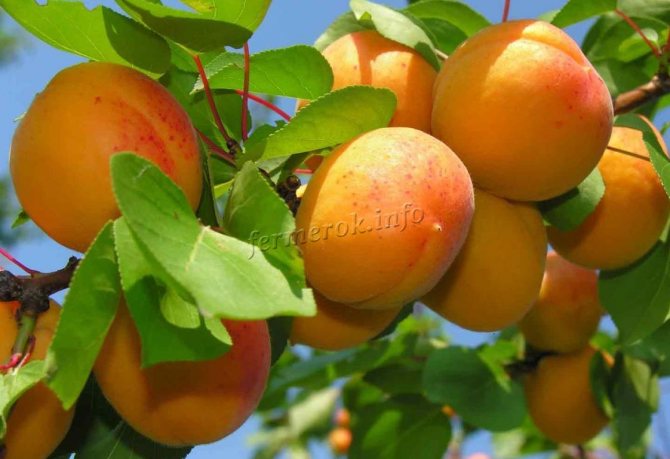
The mass of one berry, on average, is equal to 30 grams, sometimes it can reach 45 grams. The shape of the fruit is round, slightly conical, flattened from the sides.
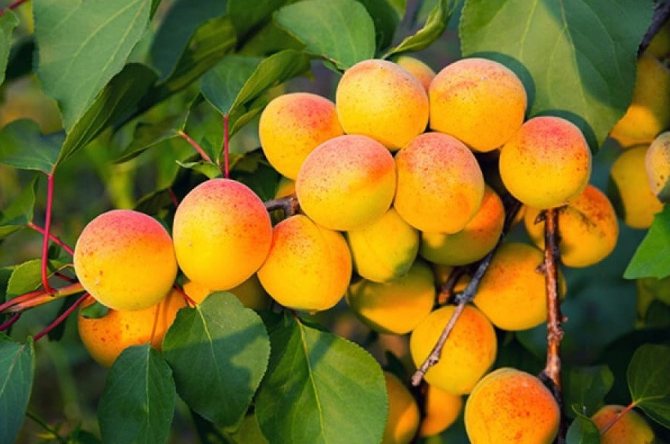
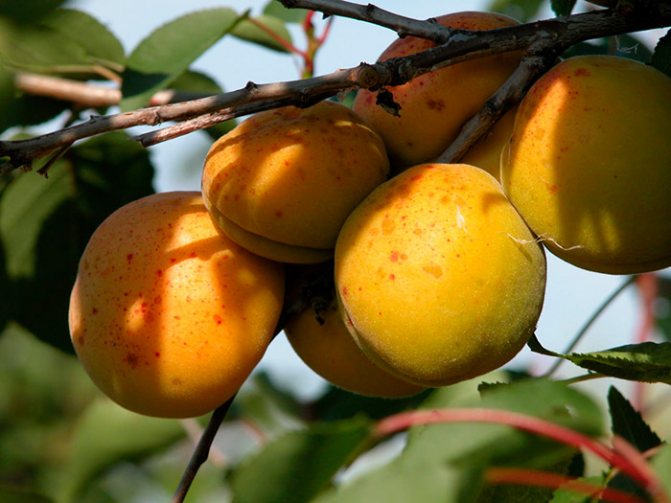
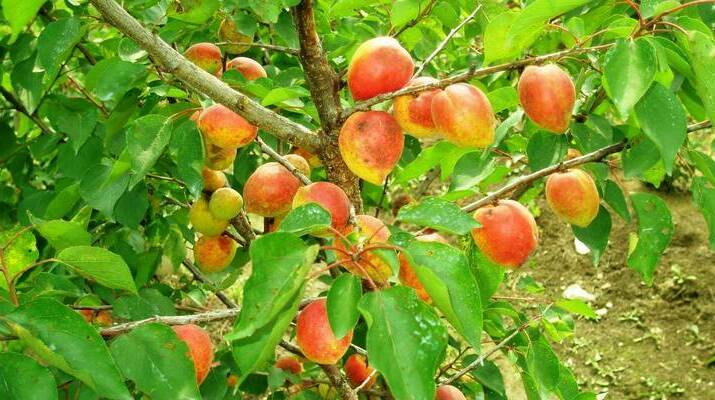
The surface of the skin is slightly bumpy, does not lag behind the pulp. The ripe fruit has a beautiful orange color with a pronounced red blush. The pulp is dense and juicy, has a yellowish tint, a pleasant sweet taste with pronounced sourness. In terms of taste, the variety is more a table variety than a dessert one. The tasting evaluation of the fruit is a four on a five-point scale.
The fruits of the Khabarovsk apricot contain a large amount of useful trace elements, especially a lot of potassium. Regular consumption of these fruits prolongs life by strengthening the heart muscle and cleansing blood vessels.
The video shows a description of the apricot variety:
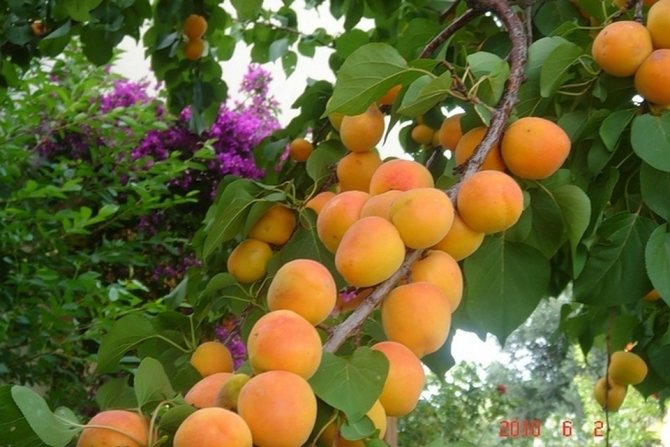
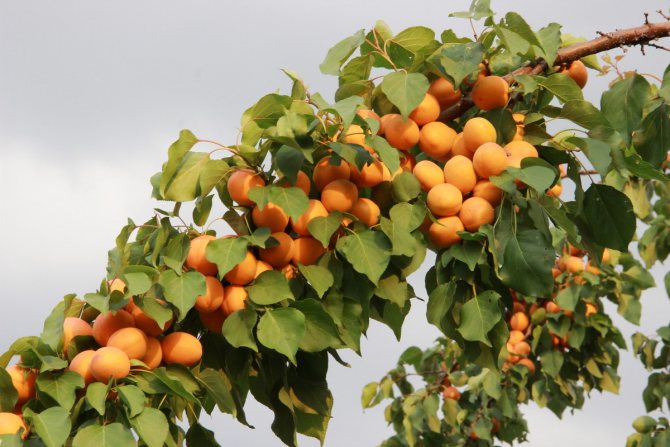
Note that the tree begins to bear fruit in the fourth or fifth year after grafting. And after the first giving birth, the apricot consistently yields a good amount of fruit annually. Fruits ripen by July 28-30; as a rule, about 35 kg of fruits are harvested from one adult tree.
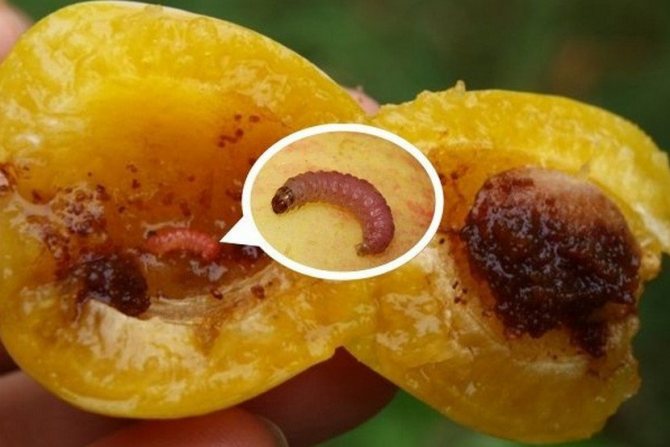
The variety is resistant to drought and waterlogging. In addition, the Khabarovsk apricot is resistant to such characteristic types of diseases as clasterosporia and monilosis. However, it is not resistant to damage by the moth. The winter hardiness of the variety is average.
Breeding history
Khabarovsk - has long been known It was obtained in the Far-Eastern Research Institute of Agriculture by breeder Kuzmin G. T. This variety was bred by pollinating the flowers of the Best Michurinsky apricot with the pollen of Krasnoshchekiy - a European variety.
To this day, the Khabarovsk apricot is popular, but mostly in the southern regions, as it blooms early. However, during cultivation of the variety in other parts of Russia, no falling off of flowers and their damage during late frosts was noticed.
Khabarovsk is a well-known variety of apricot for a long time. It was obtained in DalNIISH by breeder Kuzmin G. T. This variety was bred by pollinating the flowers of the Best Michurinsky apricot with pollen from Krasnoshcheky, a European variety.
The father of the Khabarovsk variety can be called the breeder G.T. Kazmina. It was he who bred this variety in 1949 on the basis of the Far Eastern Research Institute of Agriculture, crossing Krasnoshekiy and Best Michurinskiy apricots. The representative of the crop obtained as a result of selection is intended for cultivation in such regions as the Khabarovsk and Primorsky Territories.
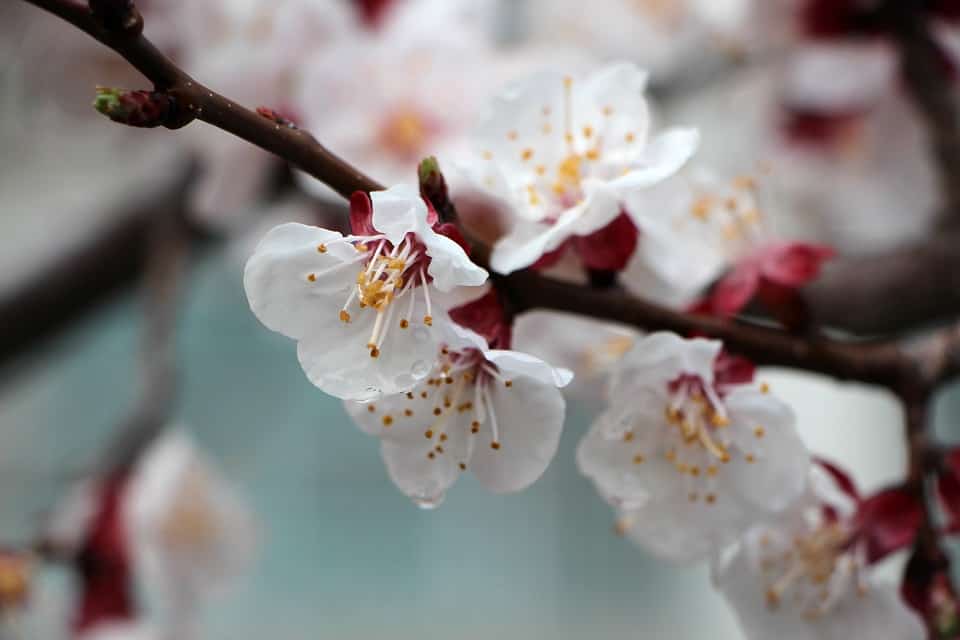
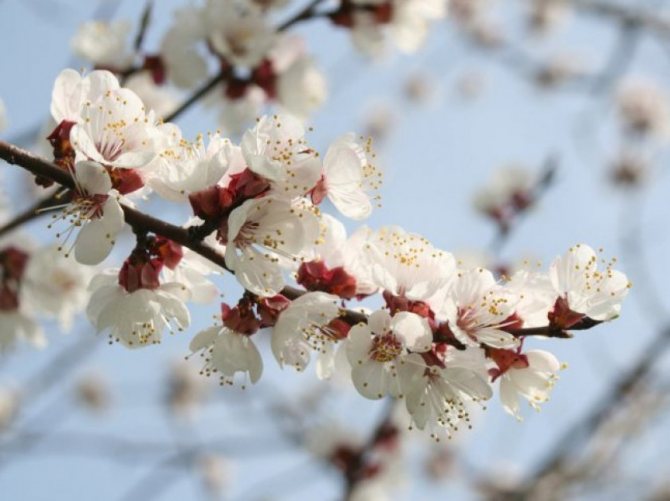
The Khabarovsk variety has its own distinctive feature - very early flowering. Therefore, it is popular in the southern regions.But when grown in the middle lane and other areas where late frosts are frequent, shedding of flowers from trees was not noticed. This means that the variety is cold hardy.
A distinctive feature of the Khabarovsk apricot variety is early flowering
Apricot Khabarovsk begins to bear fruit at the 4th or 5th year of life. For a good and bountiful harvest, the tree needs proper care, but it is worth noting that the variety has good tolerance to both prolonged drought and waterlogging.
Apricot varieties Khabarovskiy have a relative resistance to diseases such as clotterosporia and moniliosis, but there is a likelihood of damage by the moth.
All of the above features of the variety have made it very popular among gardeners in many regions of Russia.
Apricot fruits are rich in vitamin C, sugars and malic acid. The Khabarovsk variety ripens at the end of July. If you provide proper care, the tree will endow you with a crop weighing up to 36 kg.


Work on the creation of more frost-resistant varieties of apricots began in 1933. In Chelyabinsk, the experiments were carried out by Mikhail Nikolaevich Salamatov. A little later, they were continued by Grigory Tikhonovich Kazmin at the Far Eastern Scientific Research Institute of Agriculture (abbr. DalNIISH). The breeder decided to pollinate the previously bred frost-resistant variety Best Michurinsky with southern apricots (Alexander early, Korolevsky, Overinsky early ripening and Krasnosheky).
The collection of seeds was carried out in 1950, and already in the next year, several new seedlings appeared in the breeding nursery. For 13 years, the trees have been actively growing and giving a stable harvest. Successful trials allowed the hybrid to be included in the State Register of Varietal Crops.
The variety is also known as Far Eastern, Ussuriyskiy or Amurskiy early apricot. It is distinguished by its exceptional frost resistance. During the tests, the branches did not freeze by more than one third of their length, and the wood was almost not affected by the cold at all.


Apricot Cupid
In addition, the hybrid is equipped with high immunity to various fungal diseases. The yield has remained consistently high for many years. All this makes apricot Cupid ideal for cultivation in the Central and Far Eastern regions of the country.
Plant qualities
Apricot Khabarovsky, the description of the variety of which is given above, has the following qualities:
- fruiting occurs in the fourth or fifth year;
- transportability is average, so the fruits are not recommended to be transported over long distances;
- abundant fruiting every year;
- the variety tolerates both drought and waterlogging well;
- frost resistance is average, but it can be increased by grafting winter-hardy rootstocks into the crown, also by covering a young tree for the winter;
- beautiful presentation;
- high resistance to clasterosporium and moniliosis.
In general, not a bad variety. Apricot Khabarovsk is popular in many regions.
Advantages and disadvantages
This variety has gained popularity among domestic gardeners due to the presence of the following advantages in the description:
- large-fruited;
- apricots have a table purpose;
- excellent presentation of fruit;
- the presence of a bone that has a sweet core inside;
- annual and high yield of trees;
- reproduction with seeds is possible.


Also, the advantages of this species include relatively early fruiting. Experts refer to the obvious disadvantages of the variety as poor cold resistance in low locations and poor transportability of fruits.
Khabarovsk is an excellent apricot variety that, with simple care, will delight you with a bountiful harvest.
Landing rules and step-by-step instructions
Apricot varieties Khabarovskiy are grown, as a rule, in regions with a harsh climate and unstable weather conditions. He does not tolerate dampness and stagnant water in the soil.If snow melts in the near-trunk circle during the winter thaw, then it will surely freeze and form an ice crust. This crust will injure the bark of the trunk, and in the case of repeated repetition of this phenomenon (which usually happens at the end of winter), the tree may die. From this it follows that the site for planting must be chosen elevated, without accumulations of water and with a deep bed of soil waters. Apricot grows well on slopes, especially southern and southwestern ones, since excess moisture never stagnates there, it just flows down.
Any apricot does not like cold northern winds - you will have to look for a place protected by natural barriers for it. Such protection can be walls of buildings, a fence or tall, dense trees located to the north or northeast of the planting site. But you should not make a mistake - place the tree in the shade. In this case, the gardener will not wait for the harvest, since the apricot does not bloom in the shade. In the absence of natural protection, an artificial one should be equipped. To do this, knock down wooden shields and paint them white, for which you can use a lime solution. The white color reflects the sun's rays, creating additional illumination and warming the crown of the tree.


Apricots grow well on hillsides
Step-by-step instructions for planting an apricot
When planting an apricot tree, the following steps are sequentially performed:
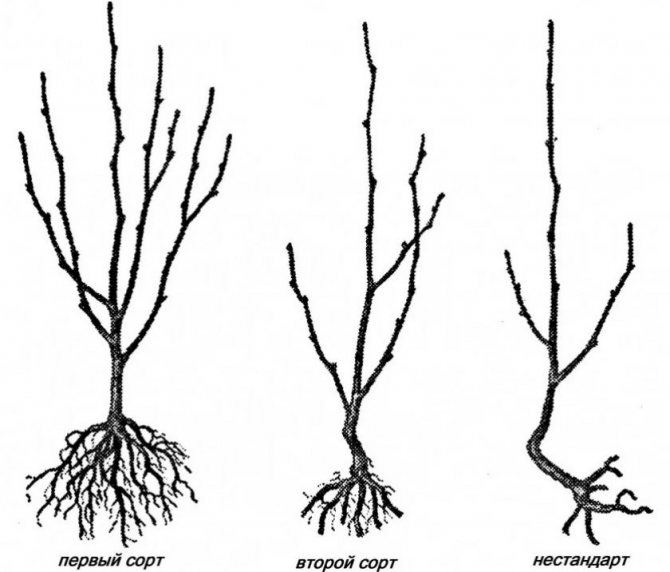
- In the fall, seedlings are purchased. Choose one or two-year-old plants with well-developed roots and healthy wood.
- They are laid for storage in the basement or buried in the ground. Before this, the roots are dipped in a mullein and clay mash, then wrapped in wet burlap or moss.

Until spring, the seedling can be kept buried - In the fall, a planting pit is prepared in the following order: They dig a pit measuring 90x90 cm and a depth of 60-80 cm.
- Drainage from crushed stone, broken brick, expanded clay, etc. is laid at the bottom.
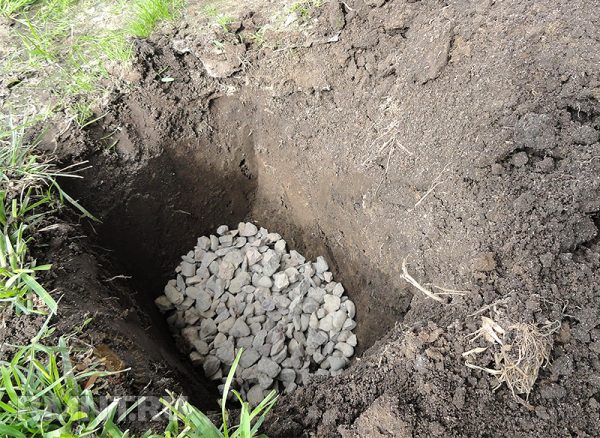


Drainage from crushed stone, broken brick, expanded clay is laid at the bottom of the planting pit - Then the pit is filled with a nutrient mixture consisting of
- black soil;
- humus;
- peat;
- sand - these components are taken in equal parts;
- superphosphate 300-400 g;
- wood ash 2-3 liters.


The planting pit is filled with nutrient mixture - A wooden stake is driven in at a distance of 15–20 cm from the center of the pit. Its height above the ground should be at least one and a half meters.
- Cover with waterproof material until spring.
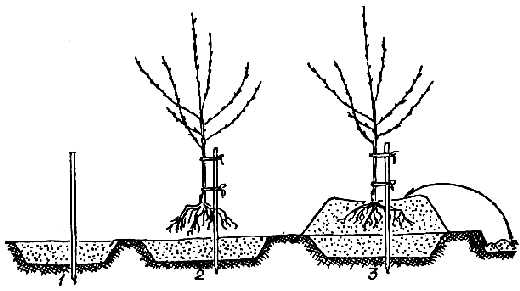

Planting an apricot on a hill will save the plant from stagnation of water and drying out of the roots.
General information about culture
Apricot Khabarovsky was obtained as a result of experiments by the breeder G.T. Kazmin.In the Far Eastern Scientific Research Agricultural Institute, in the second half of the 40s, Kazmin crossed the Best Michurinsky and Red-cheeked apricots. The result of this selection was to obtain a variety suitable for cultivation in the Primorsky region, as well as in Khabarovsk.
A distinctive feature of the Khabarovsk variety is the early onset of flowering. It is for this reason that it is popular in regions with a southern climate. The middle lane and other areas with frequent late frosts are also suitable for growing the crop because no shedding of buds was recorded during the flowering period of the tree. This suggests that this species is resistant to cold weather.
For the first time, the Khabarovsk apricot bears fruit after 5 years after landing in the ground. In order to get a bountiful and high-quality harvest, the tree needs to be surrounded with care and proper care. When growing, it is worth remembering that the variety perfectly tolerates prolonged heat and heavy rainfall.
Important! The Khabarovsk variety is distinguished by its high winter hardiness, but frosts below 30 degrees are a mortal danger for the tree. Young annual seedlings must be additionally covered for the winter, since frost affects the fragile trunk and the not yet fully strengthened root system of the tree.
Apricot varieties Khabarovskiy differs in relative resistance to moniliosis and clotterosporium disease, but sometimes it can be struck by such a pest as the moth. Taking into account all of the above features of this species, we can conclude that the culture is popular among gardeners living in many regions of the Russian Federation.
As for the composition of apricot fruits, it includes the following components:
- Apple acid;
- vitamin C;
- sugar.
Ripening of the Khabarovsk variety occurs in the second half of July. And if, when growing, you surround the tree with appropriate care, then from one seedling you can get a crop, the weight of which will be up to 40 kg. It is worth noting that this variety needs pollinators.
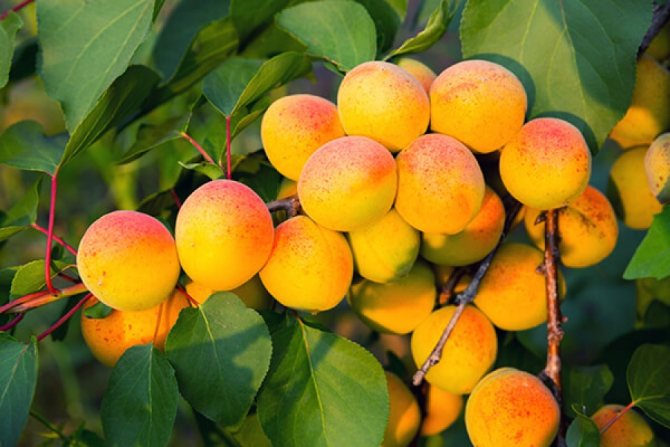


Apricot Khabarovsk
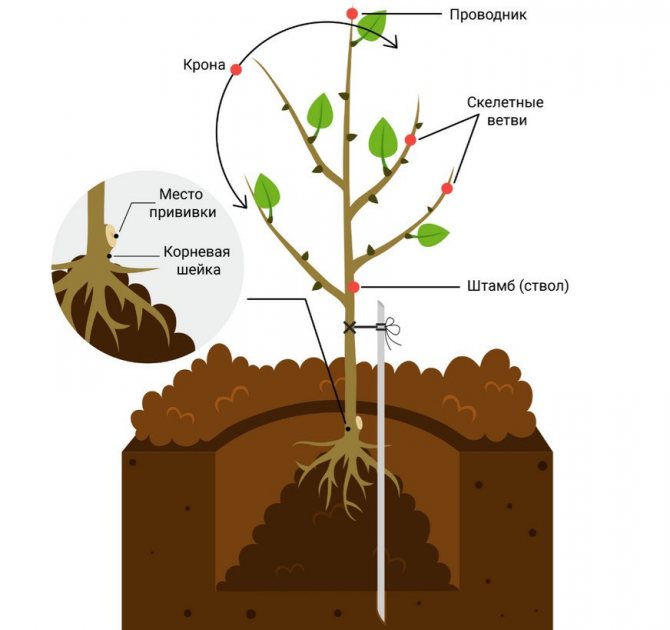
Characteristics of the tree
It is a vigorous, rather tall apricot tree. An adult plant reaches a height of almost five meters, the same amount in width. The crown is spreading, but rare. The main branches (skeletal) are powerful, straight, thick, the bark on them is dark purple, decorated with many longitudinal stripes of a whitish shade. Fruit buds are large, oblong, arranged in two and three together, but they can also be single. Leaves are medium in size with a pointed tip. Their lower part is light green, the upper one is dark, matte, serrated edges, burgundy petiole, long. The flowers are white, large, with oval petals, which are weakly closed. The stigma of the pistil is almost on the same level with the stamens, therefore, the Khabarovsk apricot is considered relatively self-fertile. He does not need pollinators, but for higher yields, the Snezhinsky and Amur varieties can be planted.
Features and subtleties of growing and care
The cultivar in the process of cultivation requires the observance of the usual rules and techniques of agricultural technology, but some of them have features associated with the region of cultivation of the cultivar. Let us remind the reader briefly about these rules, dwelling in detail on the points that are important for this sort.
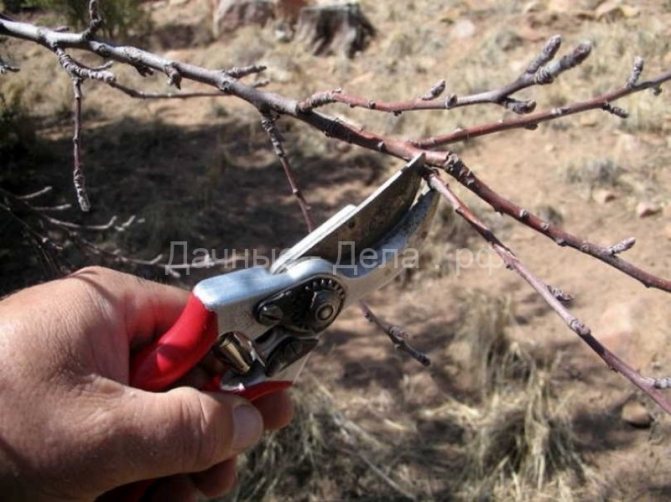
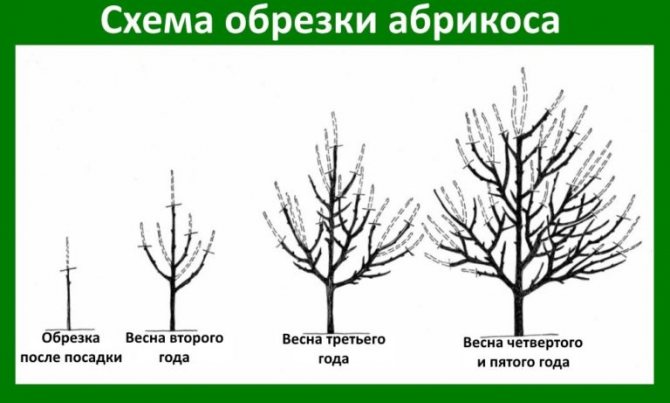
Trimming
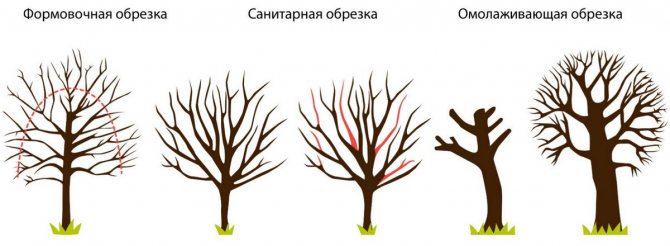
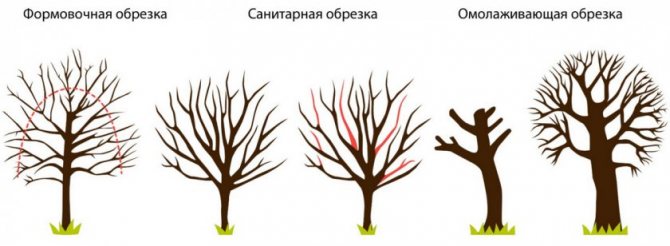
There is an opinion that apricots can grow by themselves and if pruning is carried out, then sanitary, cutting out dry and diseased branches. This is fundamentally wrong. Any fruit tree (and apricot is no exception) needs various types of pruning to increase productivity. Khabarovsk does not require any special approach in this regard. Therefore, in short:
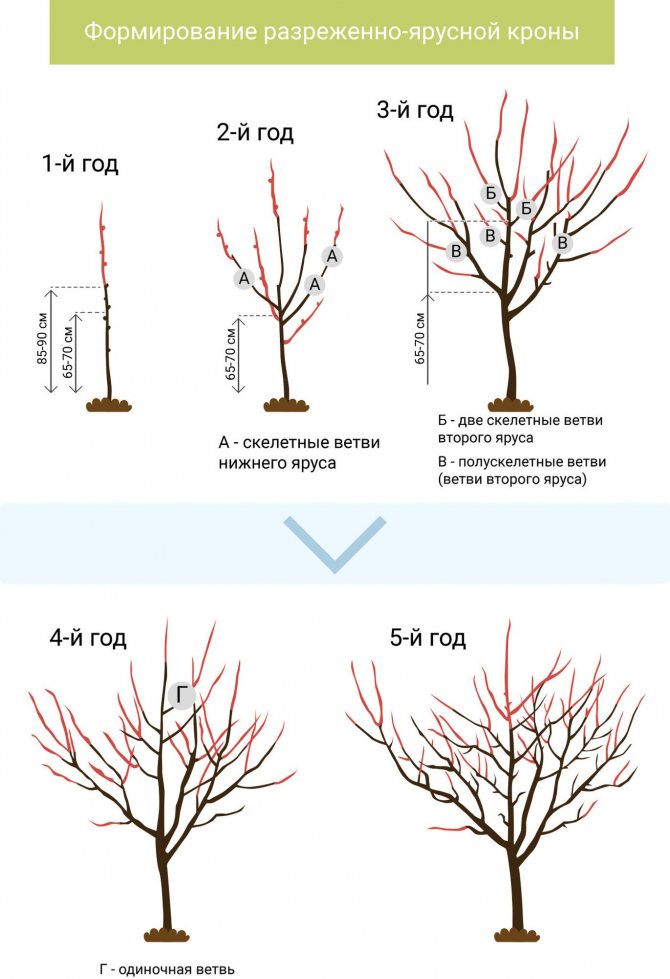
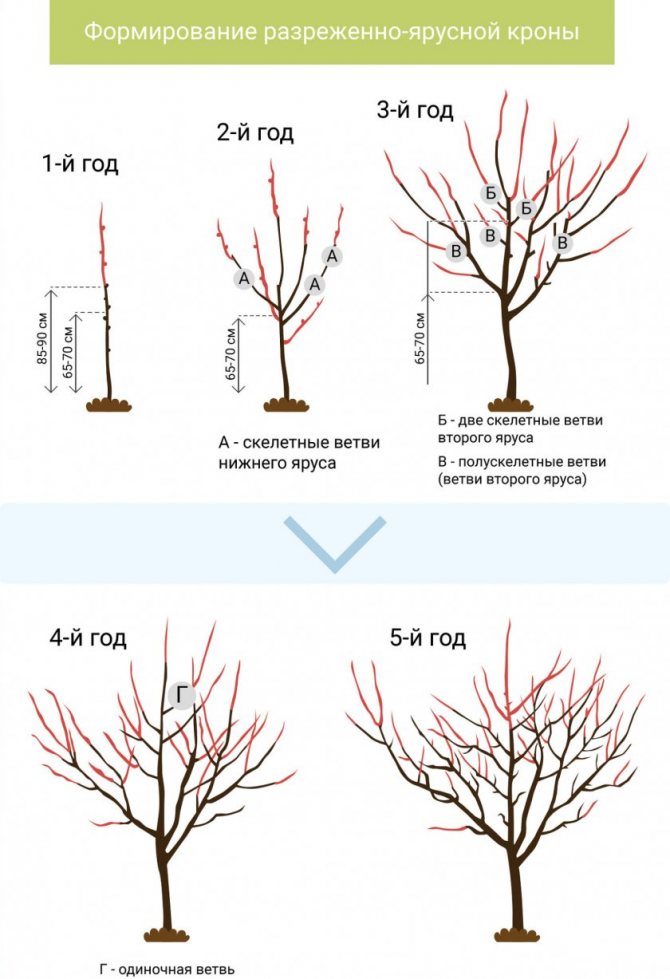
- Crown formation should be carried out in the first 4–5 years of the tree's life.
- Due to the rather high growth, it is better to use a sparse-tiered crown shape.
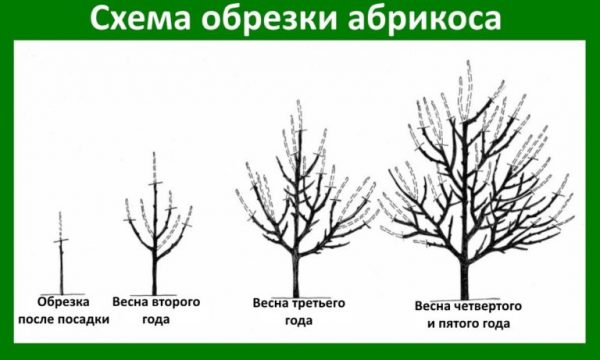

Apricot Khabarovsk forms a sparse-tiered crown - Sanitary pruning is carried out annually in late autumn.
- Since the crown of Khabarovsk is rare, regulatory pruning is unlikely to be required.
- No one exempted one-year-old shoots from the summer minting. This will increase yields.
- Well, in the mature age of the apricot, the gardener may think about rejuvenating pruning.
Watering
An important agrotechnical technique. The degree of growth of young shoots and fruits depends on it, especially in the first half of the growing season. We must not forget:
- Apricot is a drought-resistant plant. But, if there is not enough moisture in the soil, he will devote all his strength to preserving the tree. The growth of young shoots and fruits will slow down, the yield will decrease.
- Apricots are rarely watered, but abundantly, moistening the soil to a depth of 30–40 cm.
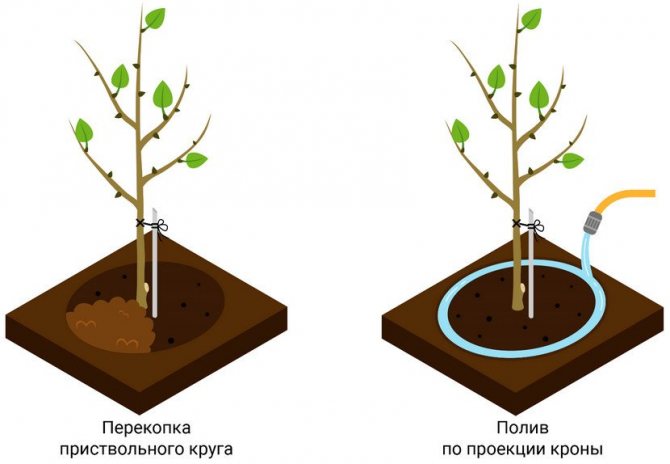
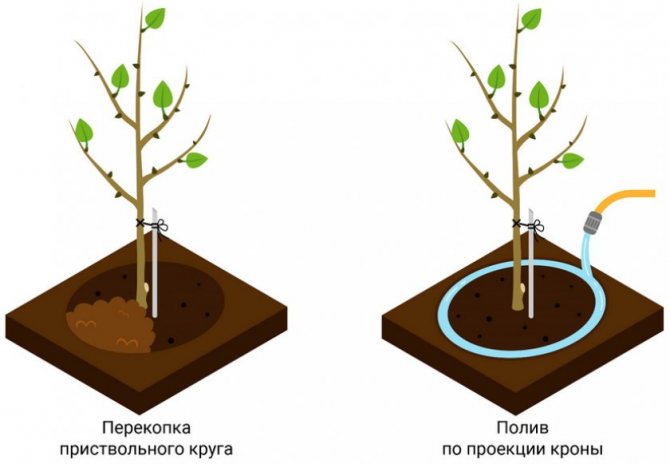
- After watering, the trunk circle is loosened and mulched.
- After the autumn water-charging irrigation, the roller of the near-trunk circle is removed, giving the mound a cone-shaped appearance. This technique will not allow moisture to stagnate in winter, after possible thaws, melt water will run down.
- Watering is especially important for young (3-5 years old) trees, the root system of which has not yet reached the aquifers.
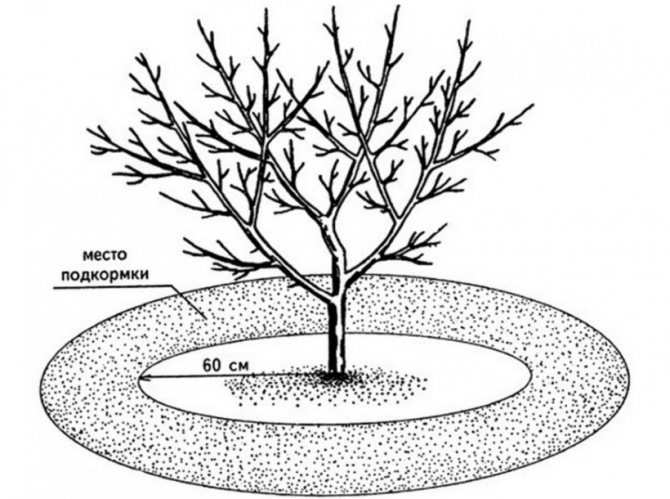
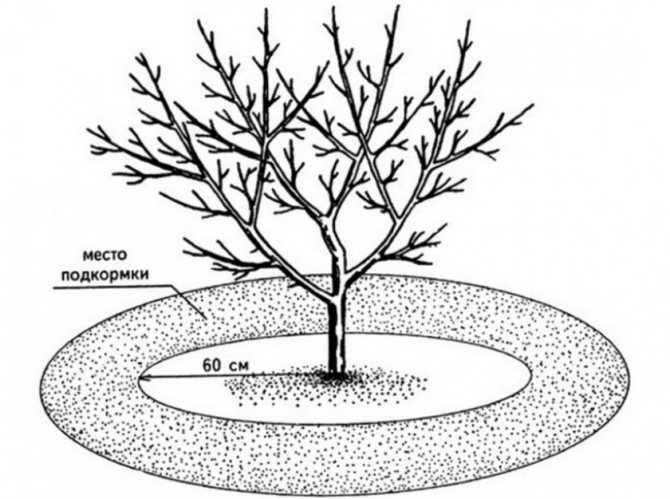
Top dressing
Needed to maintain a high yield of the tree. They start with them the next year, after the first harvest. It is important to keep them balanced.
An excess of fertilizers, especially nitrogen fertilizers, will do more harm to the apricot than a deficiency.
Table: approximate fertilization schedule for apricot
| Fertilizer type | Terms and intervals of application | Method of application and dosage |
| Organic | Every 3-4 years, in autumn or spring | Digging, 5 kg per 1m2 |
| Nitrogen | Annually, in the spring | Digging, 30-40 g / m2 |
| Potash | Annually, at the beginning of summer | Dissolving in water when watering, 10-20 g / m2 |
| Phosphoric | Annually, in the fall | Digging, 20-30 g / m2 |
| Complex | Follow the directions of the instructions for use | |
| Liquid infusions | For plant maintenance in case of a large number of ovaries. In the period of growth of fruits and shoots, make 2-3 times with an interval of 2 weeks. | An infusion of one of the components is preliminarily prepared:
Pour in a bucket of water and leave for 5-7 days in a warm place. Used for watering, diluting one liter of infusion in a bucket of water. |
Video: how to feed an apricot
Fruits and their taste
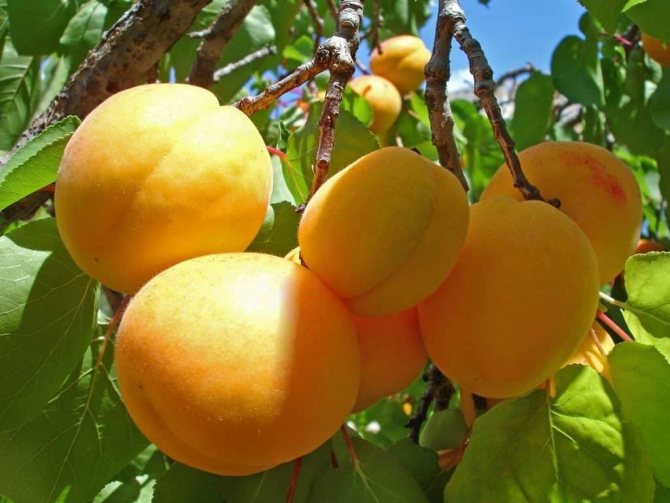
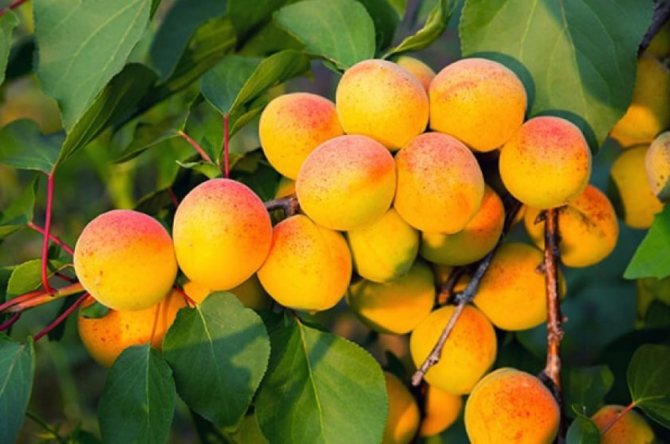
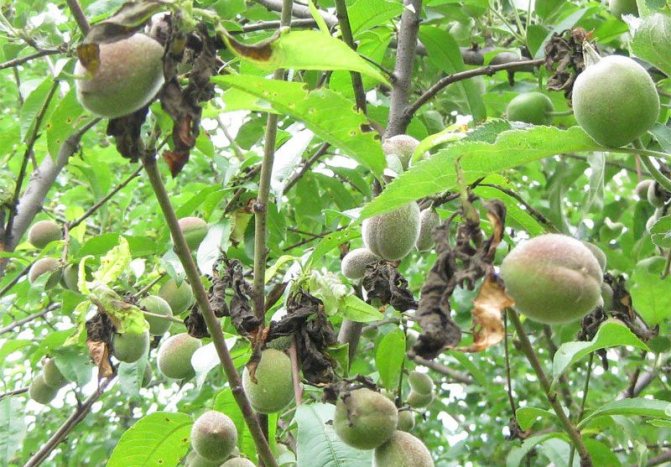
A good crop can be harvested from one adult tree, up to 36.6 kilograms. The fruits are of high quality, large, the average weight of one is 30 grams, and the maximum is 45 grams. The shape is rounded, conical, slightly compressed on the sides, outwardly resembles a heart - the upper edge is pointed, in the lower there is a deep fossa. The fruits are lumpy on the surface, the skin does not lag behind. The color is pale green, yellowish, in some places there is a red dotted or solid blush.
The pulp is yellow-orange, medium-juicy, thick, with a pleasant sweet-sour taste. In terms of taste, the variety belongs to the table. The fruits contain vitamin C, malic acid, sugar. The tasting grade received 4 points out of five.
The stone is round-elongated, has grooves. It is small, only 1.2 grams, well behind the ripe pulp, its heart is sweet.
Characteristics and description of the variety of apricot Khabarovsk
Check out these articles as well
- Tago strawberry variety
- Melon Torpedo - variety description, cultivation and care
- Planting cucumbers in open ground
- How to increase egg production in chickens
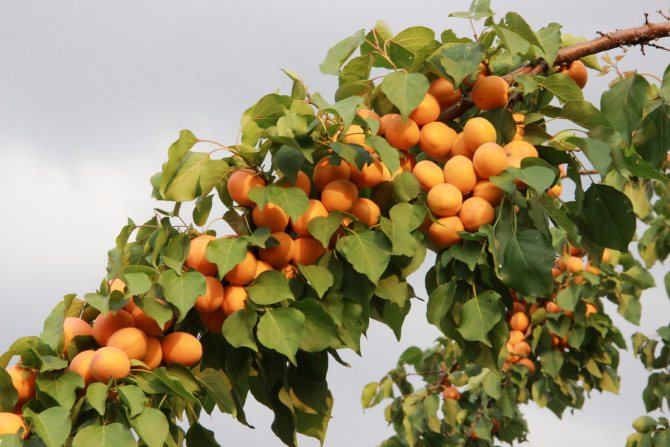


Apricot branch
The Khabarovsk variety is partially self-fertile, but if pollinators do not grow nearby, the yield will be low, therefore, to obtain a bountiful harvest, you need to have at least 2-3 varieties on the site. It begins to bear fruit in 4-5 years of development after planting in a permanent place. The ripening time of the crop is July 28-30. Yields are annual, consistently high. Up to 36 kg of apricots are harvested from the tree.
Apricot varieties Khabarovsk is characterized by high growth.The tree grows up to 5 meters in height if not controlled. The crown is spreading, but rare, so there are usually no special problems with pruning. Skeletal branches are almost straight, thick, dark color, slightly purple with white, longitudinal stripes. Young twigs (1-2 years old) are also thick, straight, can reach up to a meter in length.
Interesting! The main advantage of the Khabarovsk variety is the resistance of flowers to spring frosts, so its yield is always high.
The leaves are medium, of a typical oval shape with a pointed end. The front side is dark green, matte, and the back side is light green. The petioles, to which the leaves are attached, are burgundy and medium in length. The tree gives flowers large, white.
Harvesting apricot Khabarovsk
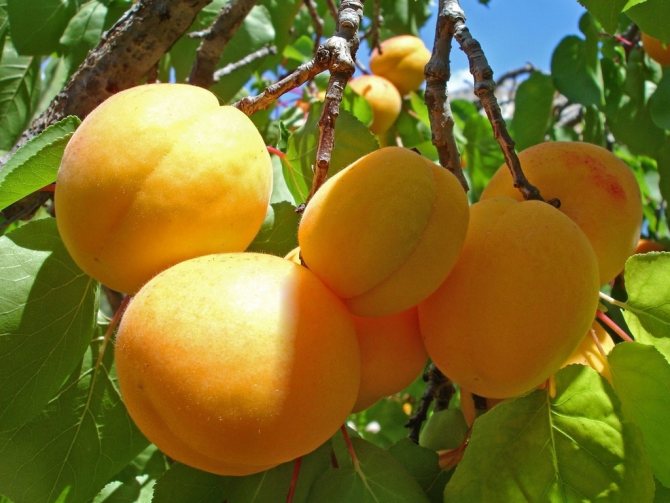


Apricot fruits Khabarovsk
Apricots usually ripen by the end of July. At this time, they may begin to fall off or simply gleam with a bright blush on the tree branches. It is advisable to collect them immediately, without delay, so that they do not start to deteriorate.
After harvest, the fruit should be used immediately for processing or transportation. They can be transported over short or medium distances, since the transportable qualities are not very high, on the way the fruits can crumple, let the juice start and start to rot. If the apricot is used for homemade preparations, then it needs to be processed in the first 1-4 days. Apricot Khabarovskiy is suitable for fresh consumption, preparation of sweet dishes, preservation (compotes, juices, purees, preserves, jams).
Testimonials
We will find out what opinion domestic gardeners have about this variety of apricot.
- Alexey, Belgorod: “Apricot Khabarovsk has been growing in my garden for 25 years already. It bears fruit annually, well, gives large fruits - you can eat them fresh, as well as make delicious preparations. Care is simple, standard. I recommend this proven variety, it will definitely not let you down. "
- Lydia, Evpatoria: “Our family has a small apricot orchard - we grow the fruits for sale. There are several varieties, there is also Khabarovsk. I can only say good things about this variety - it bears fruit every year, I am always confident in it, resistant to diseases, tolerates winter perfectly. We sell the fruits fresh, and from the leftovers we make canned food: compotes, jam. This is an old and trustworthy variety. "
And here you can read reviews of gardeners about the Northern Triumph apricot.
So, we examined the features of growing Khabarovsk apricot. As you can see, this is a rather old variety, which does not prevent it from remaining one of the most popular today. The Khabarovsk apricot, proven over the years, implies simple agricultural technology, and gives stable annual yields of a decent volume. These and its other positive qualities make this variety very interesting and noteworthy.
Landing features
We will learn how to properly plant the Khabarovsk apricot.
Timing
You can root a young seedling both in spring and autumn: both options have their advantages and disadvantages. If in the fall it is easy to get a high-quality seedling, but winter is ahead and, possibly, frosty, then in spring, on the contrary, there is a problem with planting material, but there is a long warm season ahead, useful for the successful rooting of the plant.
If you plant an apricot in the fall, then it is better to plant it in early October, so that the plant can take root in the ground before it freezes. In the spring, it is advisable to plant in April, trying to be in time before the start of the active growing season.
Seat selection
Apricots are best placed in a sunny area of the garden, well sheltered from the winds, and not located in a lowland. Sour soil is not suitable for apricot, therefore, in this case, it is necessary to first lime the earth. The tree will feel best in loamy soil, but not too dense.
Make sure that the groundwater table in the selected area is not too close to the surface. Otherwise, rotting of the roots of the tree is possible, which theoretically can also serve as the reason for its death in the future.
It is better to choose a hill - as a rule, on hillocks, the soil does not contain too much moisture. If your site is located in a lowland, you can form such a mound yourself, pouring the required amount of land.
Sapling selection
It is recommended to purchase a Khabarovsk apricot seedling in an official nursery, but not from the hands on the market. The fact is that when buying a seedling without the appropriate documents and vaccinations, you can run into another variety of apricot at best, and at worst - at a sick, affected, unvaccinated seedling.
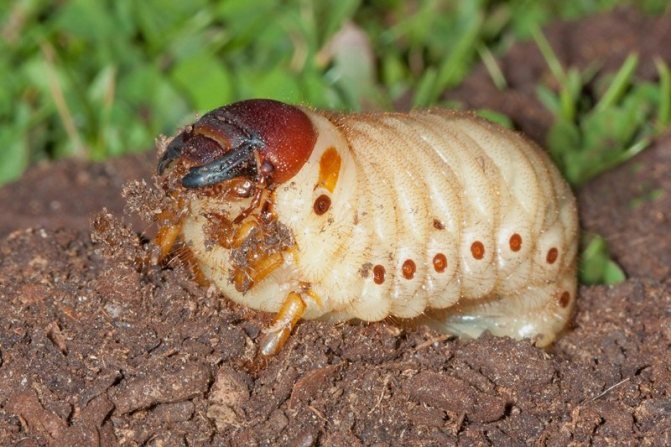
Diseases and pests, how to deal
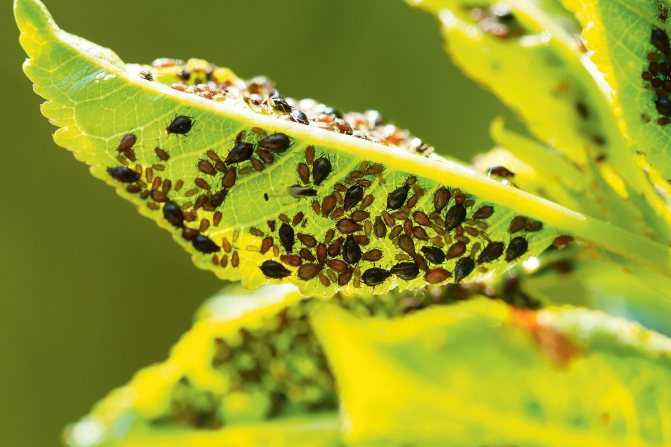
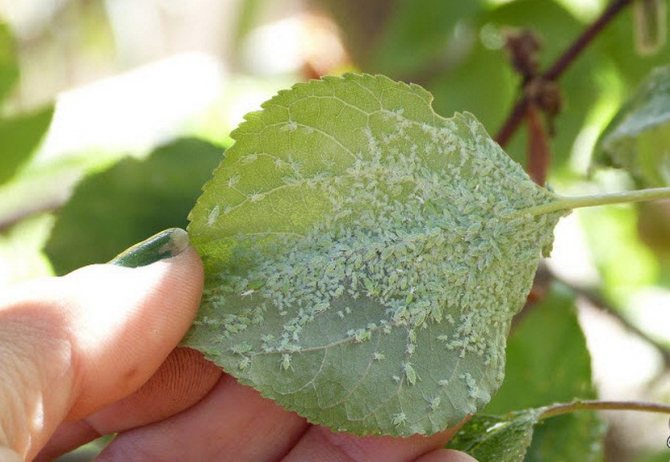
Most apricots are not too susceptible to diseases and pests. Under favorable weather conditions - sunny summers and the absence of prolonged rains - apricots rarely get sick. The rainy season promotes the development of fungal diseases. The most important factor in confronting troubles of this kind is the regular implementation of simple preventive measures.
Table: sanitary and preventive measures to combat diseases and pests
| What are they doing | When do | How do |
| Collection and disposal of fallen leaves | In autumn | — |
| Sanitary pruning | Late autumn | Cut out dead, diseased and damaged branches |
| Digging of trunk circles | In autumn | Produced with the overturning of earth layers, the roller of the near-trunk circle is removed. |
| Bark cleaning | In autumn | Deep roughness is cleaned with a metal brush. If cracks are detected, they are cut to live bark and wood, treated with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden varnish. |
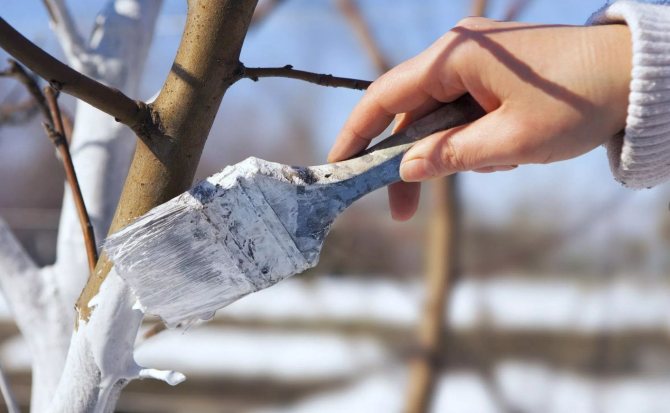
| Whitewashing of boles and branches | In autumn | For whitewashing, a solution of slaked lime is used, to which 1% of copper sulfate is added |
| Preventive treatment of the crown with a 3% solution of copper sulfate | In autumn and spring | Can be replaced with 5% Bordeaux liquid solution or 5% ferrous sulfate solution |
| Installation of trapping belts | In early spring | Fishing belts are placed at a height of 30-50 cm from the ground |
| Treatment with complex potent drugs | In early spring | They use drugs that affect all pathogens and insects:
|
| Regular treatments with systemic fungicides | After flowering and before harvest | Treatments are especially important in rainy summers. They should be carried out immediately after the rains, when the leaves are dry. If there is no adhesive in the preparation, it should be added. It can be a laundry soap solution or dish detergent. Immediately before harvesting, preparations with a short waiting period are used. For example, Horus (used 7 days before eating berries), Quadris (used 5 days before eating berries). |
The main diseases to which the Khabarovsk apricot is susceptible
With strict implementation of the recommendations for prevention, diseases in the vast majority of cases can be avoided. But you still need to know what the signs of the manifestation of the main possible diseases look like.
Clasterosporium disease
Hole spotting is the second name of this dangerous disease, often found on apricots. Fungal spore infection usually occurs for the first time in spring. It is carried both by the wind and by insects. In the future, fungal spores can overwinter in the bark, fallen leaves and the upper layers of the soil.
It primarily affects leaves on which dark red or burgundy dots appear. Then the dots grow, reach significant sizes (up to 5–10 mm), the inner part of the spots dries up and falls out, forming holes. Then the leaves turn yellow and fall off.If the plants are not treated with fungicides in time, in August the gardener will be able to observe the phenomenon that is popularly called "summer leaf fall". A weakened tree may not withstand the coming winter and die.


With clotterosporia, holes form on the leaves
In addition to leaves, the fungus affects fruits and shoots. Similar dots appear on the affected fruits, growing to spots. Further, a continuous covering of berries with a scab is possible.
Treatment consists of regular fungicide treatments. The sooner you resort to treatments, the better the result will be.
Moniliosis
Has a second name - monilial burn. The first infestation usually occurs in the spring during flowering. The spores of the fungus on their paws are carried by bees along with the pollen. The process is pretty fast. The fungus begins with a flower, through the stalk penetrates the shoot, leaves. The affected parts of the plant droop, then turn black, giving the impression of a burn.
Inexperienced gardeners may confuse moniliosis infection with early frostbite of a tree or with an overdose of chemicals during preventive treatment.
Having diagnosed moniliosis, they immediately cut out the infected shoots with a part of healthy wood and treat the tree with fungicides. Apply them according to the attached instructions. In the summertime, the fungus affects the fruit in the form of gray rot.
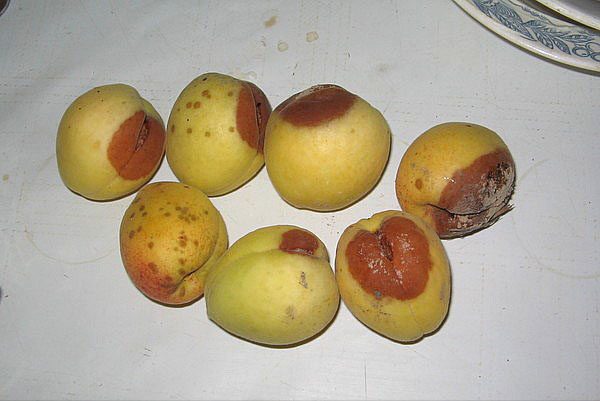


In the summer, the fungus infects fruits in the form of gray rot.
The pathogen, like other fungi, can winter in the bark of a tree, leaves and soil.
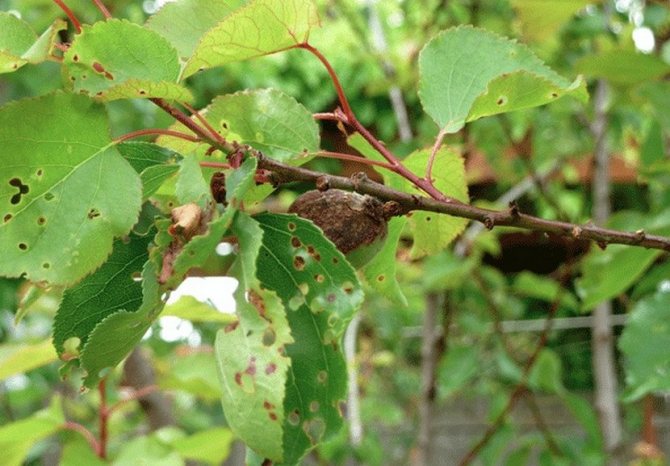
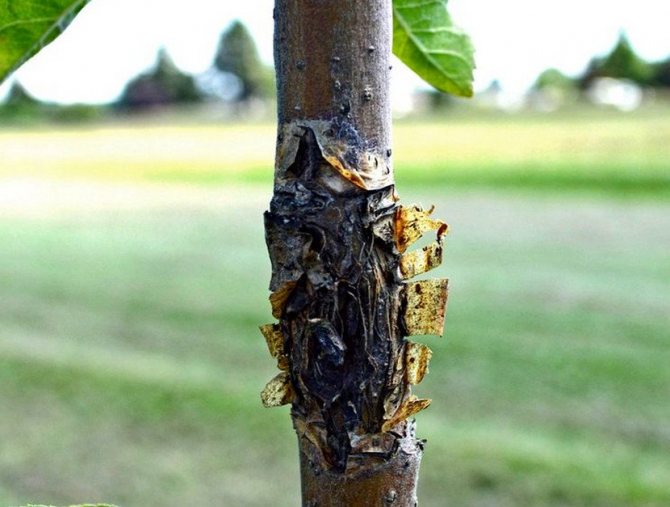
Cytosporosis
Fungal infection of the bark of a tree. It is facilitated by the presence of unhealed cracks, into which the spores of the pathogen fall. As the fungus develops, it eats away at the bark, it loosens and becomes rotten. Abundant gum flow occurs from the crack. Treatment, like prevention, consists in cleaning damaged areas to healthy bark and wood, disinfecting with 1% copper sulfate solution, treating with fungicides and protecting the wound with garden varnish.
Preparing for winter
It is important to keep an eye on the weather forecast throughout the season. In case of frost, it is worthwhile to surround the tree with a smoky ring, burning the straw.
Preparing for wintering, you need to remove and burn all the fallen leaves. This will protect the seedlings from pests and pathogens. The tree trunk is covered with whitewash to a height of 1 m, it will protect the plant from rodents. It is useful to spray the plant with Bordeaux liquid
An earthen mound is poured around the trunk, the trunk is wrapped in non-woven material, and the trunk circle is covered with it. A properly prepared plant will calmly endure the winter and quickly start growing with the first spring sun.
How to care
Consider the features of the care of the Khabarovsk apricot.
It is important that the soil in the apricot trunk circle is always cleared of weeds. This condition is of particular importance when the seedling is still small. In addition, after watering, it is also necessary to loosen the soil to allow the roots to "breathe" oxygen.
Watering
The plant needs watering, however, infrequent. Water the Khabarovsk apricot more abundantly in early summer and in the middle. At the end of the warm season, watering must be reduced so that the shoots do not grow much.
In the spring, it is important to ensure that melt water does not accumulate near the tree trunk, as waterlogging can lead to the death of the roots.
Wintering
Apricot Khabarovsky tolerates winters quite well in southern Russia, and under cover it can be grown even in the middle lane and in the Volga region. However, in any case, it is necessary to prepare for the coming winter.
After the leaves fly from the tree, they must be removed and burned. This measure will destroy microbes and larvae of harmful insects that were found in the foliage. The trunk of the plant must be whitewashed to protect its bark from being eaten by rodents for the winter.But how to care for a honey apricot, this video will help you understand.
The video shows how to care for a planted apricot:
If the apricot grows in an area with cool winters, it is recommended to cover it. To do this, pour a mound of earth around the trunk, and cover the trunk with non-woven material. Make sure that the trunk circle, where the roots of the tree are located, is well covered.
Pruning
Apricot Khabarovsk in the first years of life needs pruning forming a crown. And, in addition, every spring it is necessary to carry out sanitary pruning, removing diseased, damaged and frozen branches during the winter. It is also worth learning more about how fruit tree seedlings are pruned.
Top dressing
Apricot responds gratefully to organics and "chemistry". In the spring, it is important to supplement the tree's diet with nitrogen-containing fertilizers so that the crown quickly becomes thick and abundant. In summer, the plant needs phosphorus for fruit ripening.
Since initially the rooting of the tree takes place in a fertilized nutrient soil, fertilization is started only when the apricots reach the age of three from the moment of planting. And from the age of five, the amount of dressing must be doubled, since during this period the fruiting of the tree begins. But how red-cheeked apricots are fed, this information will help to understand.
Prophylaxis
Although the Khabarovsk apricot is resistant to fungal diseases, it still needs preventive spraying. For this purpose, for example, Bordeaux fluid is suitable. Spraying is best done in the spring after the entire crop has been harvested and all the leaves have been burned.
Care
Apricot Khabarovsk is not the most picky plant, it will not require anything special from you.
In the spring, after the snow has melted, loosen the soil so that moisture does not accumulate. Watering in warm seasons is needed moderate, only in the dry season. If there is a frost, then it is better to play it safe, and at night near the tree create warm smoke by burning straw. From the third year after planting, fertilizing in the form of mineral and organic fertilizers will be required.
Stably remove all unnecessary, diseased, weak and dry shoots, carry out prophylaxis against pests and fungal diseases with special preparations. If you grow Khabarovsk apricot not in the southern region, then sprinkle the roots with additional soil for the winter and wrap it over with a covering material. Young seedlings must be covered completely.