I, a novice gardener, having read many books on the topic, self-confidently considered myself a professional. And he began his experiments in the garden. In particular, plant trees. Alas, theory and practice are different things. Therefore, it is not surprising that many endeavors ended in failure.
It turned out that there are several ways of grafting trees, and for a positive result, you need to choose the optimal time. Otherwise, both the rootstock and the scion can be ruined.
Now, after a while, I, by right, can rank myself among the experienced craftsmen. So I decided to write an article. Suddenly it will help someone avoid my mistakes in the subject of vaccinations.

What is a rootstock and a scion
Grafting trees in spring, ways of grafting fruit trees for beginners
To grow new plants, gardeners use grafts and stocks to inoculate them. In plain language, this is the implantation of the tissue of one plant into the tissue of another.
The main tree on which the cuttings or buds will be grafted is called the stock. Accordingly, buds and cuttings from another tree are called grafts.
Gardeners recommend carefully studying the properties and characteristics of plants before grafting. You cannot combine two plants at will. There must be a family connection between them, so before grafting a tree, you should find out which rootstocks are suitable for this procedure.


Inoculation of a cultivated plant on the wild
Nursery workers do not have absolutely accurate information about the required compatibility, but grafting is considered successful if different varieties are grafted onto the same plant species. That is, you need to plant an apple variety on an apple stock, and a pear variety on a pear stock. There are some exceptions. For example, a graft of a plum stalk takes root well on cherry plum, a lemon stalk - on a bitter orange.
Attention! When creating ornamental plant species, distant related crops can be grafted.
Why is it so important to choose the right time?
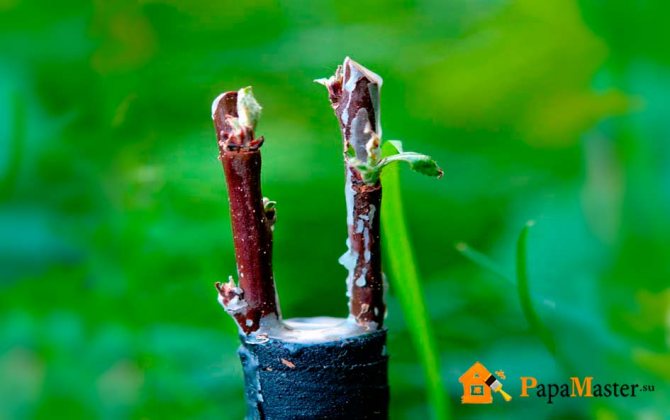
Often the basis for the reproduction of a garden tree is not a seed or a stone, but a stalk, that is, a small piece of a stiff young branch (not a shoot) with buds. Moreover, planting and rooting do not always give positive results, and if a tree grows up, then it will not begin to yield soon. This is why grafting is the fastest way to get a strong, fruitful tree.
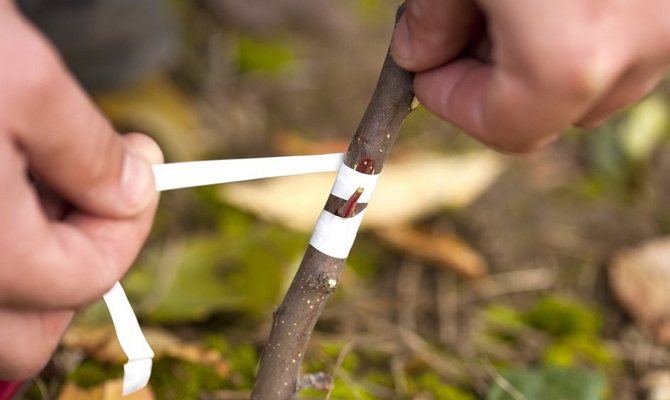


Grafting a fruiting tree
However, it should be remembered that this operation requires not only a scion (the same cutting), but also a stock, that is, a trunk or stem with a good root system. And the vital rhythms of both parts must be the same, otherwise, no matter how much you add up, they will not take root. That is why the optimal timing for different types of fruit trees and their individual varieties has long been tracked.
For example, stone fruits, such as cherries, plums and apricots, wake up in spring earlier than seed ones, and therefore you need to start working with them first. But if we talk about scions, the rootstocks also need to be selected according to the time when the juices begin to move in the cambium (fibers under the bark), which turns green during this period. If you graft a stalk before the roots start pushing nutrients down the trunk, it will most likely not take root.
How to choose a stock
Whitewashing trees in spring - treatment of fruit trees from pests
The rootstock stalk is selected so that it is compatible with the cultivar to be grafted. This is the foundation of the future tree on which the cultivar stalk will develop. The development and fruiting, as well as the taste characteristics of the fruit, depend on a properly selected stock.
The rootstock can be a broken tree that has retained its vitality, a stump with good roots, or a wild species of a related tree. The stalk takes root well on a tree that is more than two to three years old. It has a developed root system that supplies food to the petiole grafted to it.
Why are trees grafted?
For propagation: varietal plants cannot be propagated by seeds, cuttings of many crops root poorly, and self-rooted specimens may have a weak root system or form shoots.
For obtaining decorative standard forms and multi-varietal trees.
To solve problems. With the help of grafting, you can fix the crown, replace the variety you did not like with a new one, and even save a damaged tree.
Rootstock, scion and more
Grafting is an operation that allows you to combine 2 or more plants into a single organism. Usually, grafted plants consist of a lower part (wild stock) and an upper part (a scion of the variety we need).
WE CREATE DECORATIVE STAMP FORMS
Black currants are grafted on golden currants, black chokeberry - on mountain ash, many ornamental apple trees - on seedlings of home apple trees, weeping caragana form - on tree caragana seedlings (trying to choose those that are less prone to tillering).
Sometimes, to obtain the desired characteristics or to overcome incompatibility between the rootstock and the scion, an insert of a different variety or rootstock is added.
If it is not possible to remove a strong, even trunk, use a stem former.
The desired variety can also be grafted into the crown of a different tree variety.
How to choose a scion
Spraying fruit trees in spring before and after flowering
The graft should be chosen so that it corresponds to varietal qualities such as yield, frost resistance, and disease resistance.
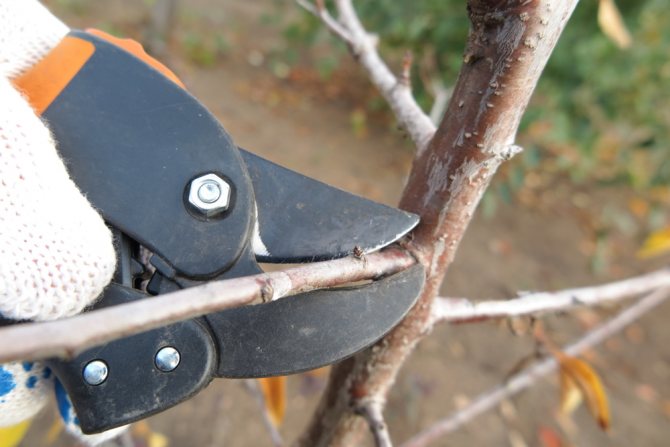


Best cuttings
Experienced gardeners are advised to take varieties that correspond to the growing regions as a scion. You can make the preparation of the scion yourself.
Preparing cuttings
The time to prepare cuttings for grafting is the end of autumn and the end of winter. Basically, gardeners prefer to do the autumn harvesting of cuttings after the leaves fall, with the onset of the first frost. At this time, disinfection from microbes and fungi occurs, the plant enters a phase of complete dormancy.
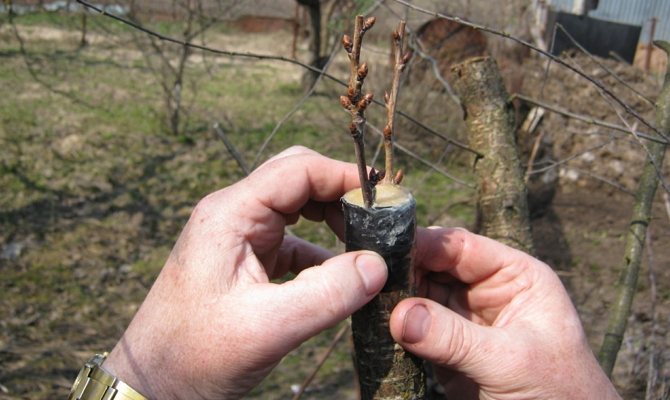
In the autumn harvesting, cuttings of a young fruiting tree are selected. Usually his age is from 3 to 7 years. The stalk can have a length of no more than 40 cm. Its diameter is about 5-7 cm. It should have growth and 4 developed buds. The distances between the nodes are short. In a small stalk, nature has invested the ability to give birth to a full-fledged tree with maternal properties transferred to it.
Attention! For grafting by cuttings, cuttings must be cut from the side of the crown of the tree, facing south, from the shoots of the middle tier.
If it was not possible to prepare the cuttings in the fall, they are cut in early spring. A favorable time for this is March-April, depending on the region where the grafted plants grow. Summer grafting of fruit trees with green cuttings gives good results. In summer, cuttings are cut before grafting. For beginners, experienced gardeners recommend taking cuttings from trees that are regularly pruned.
When to do it?
Spring grafting of trees with cuttings (copulation) is done during active sap flow, when plant tissues grow together best of all. This period begins approximately from the second decade of April.
A prerequisite: for grafting cuttings, annual shoots with dormant buds are taken.
Therefore, we harvest the cuttings in advance, it is possible at the beginning of winter and store them, wrapped in foil, in the cold until spring. When harvesting, cuttings are cut from the illuminated side of the crown - there they matured better.
Preparation for work
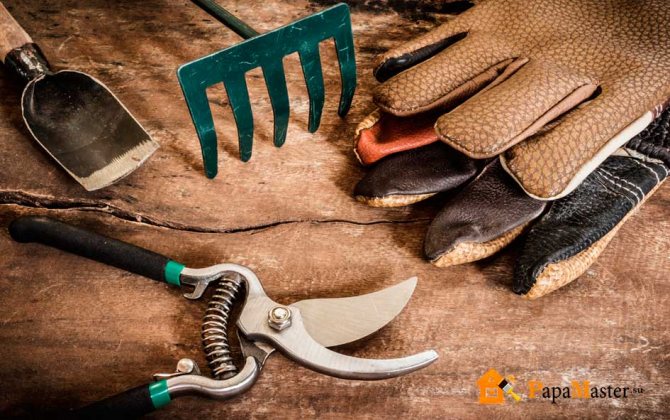
To perform the spring vaccination, you need to prepare:
- grafting (copulating) knife;
Before grafting, cuttings can be soaked in water. Garden var is sold ready-made in garden stores. But you can cook it yourself. To do this, take 6 parts of paraffin, melt it and mix with three parts of crushed rosin. Add 2 parts vegetable oil (mineral oil) to the mixture brought to a boil. Let it simmer for 10 minutes. Then the var is kneaded and laid out in jars
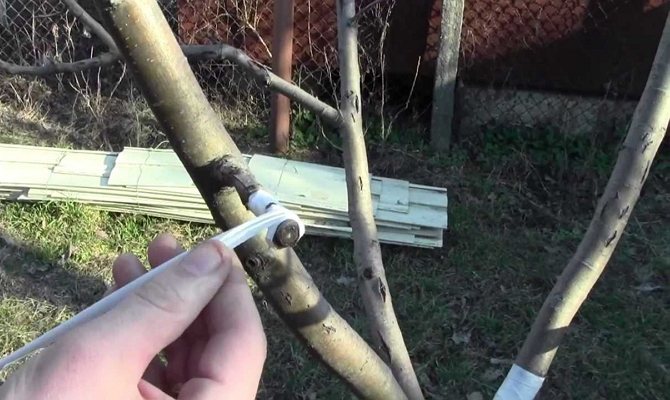
A special film for vaccinations is produced. It is elastic, tightly fixes the vaccination site and does not allow it to dry out. The special film can be replaced with insulating tape, polyethylene strips.
The grafting knife must be sharpened so that it can cut off the hair on the arm.
Vaccination tools and supplies
To prepare and carry out the vaccination procedure, certain gardening tools are needed. These include a suitably shaped knife that allows you to make the cut you want. For different types of grafting, there are special equipment and all kinds of knives, but not a kitchen knife, which can damage the bark of a tree without having a sharp enough blade. The quality of the inoculation depends on the knife.
To prepare the cuttings, garden shears are used - secateurs, thanks to which a smooth, clean cut is made. For grafting behind the bark, a special budding knife is used, in which there is an additional blade for separating the bark.
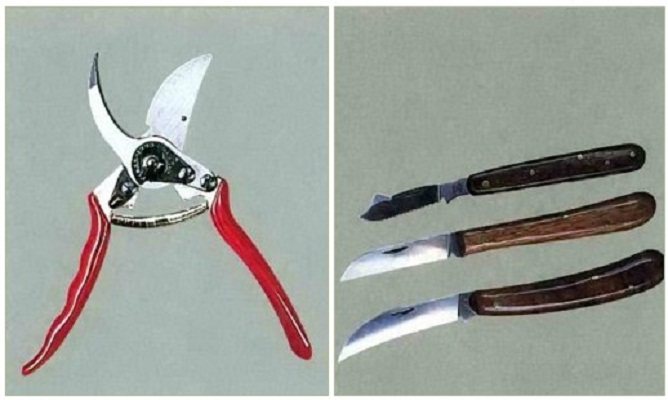

Vaccination equipment
For tying the grafted area, a special strapping material is used: elastic grafting strips, budding patches. Places of cuts are lubricated with light-permeable wood grease using grafting strips.
Optimal timing for vaccination
When is the best time to plant trees? Based on the experience of gardeners, it is better to vaccinate in a warm season, when there is the greatest likelihood of good engraftment of the cutting and tightening of the wound from the incision. Gardeners say that grafting trees is best done in the spring.
The best dates and times for vaccination are in May. At this time, sap flow occurs in the tree. If the stalk does not take root, it is possible to repeat the procedure again during the summer months: July-August.
Advice. Pros also draw the attention of beginners to the use of the lunar calendar, which indicates the most favorable numbers for this procedure.
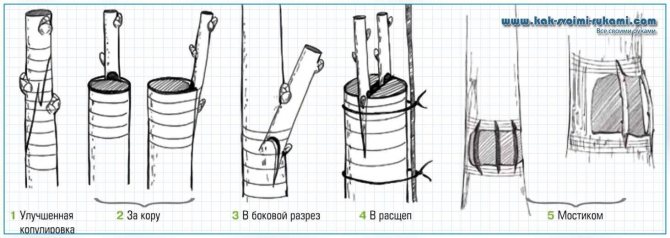
Grafting methods for fruit trees
Before starting the procedure for grafting fruit trees at home, you need to familiarize yourself with the rules for its implementation.
Important! It is necessary to carry out coloration of plants quickly so as not to expose the cuts in the scion sites to the influence of external factors.
A good result can be expected when young trees are grafted with good annual growth. Gardeners with extensive experience in coloration recommend grafting varieties with the same ripening period on the tree. If varieties ripen at different times, there is a chance to get a harvest of those fruits, the ripening period of which is earlier. Harvests with late ripening may not be obtained at all. Gardeners recommend grafting strong-growing varieties to the lower part of the trunk, and weakly growing to the upper part.
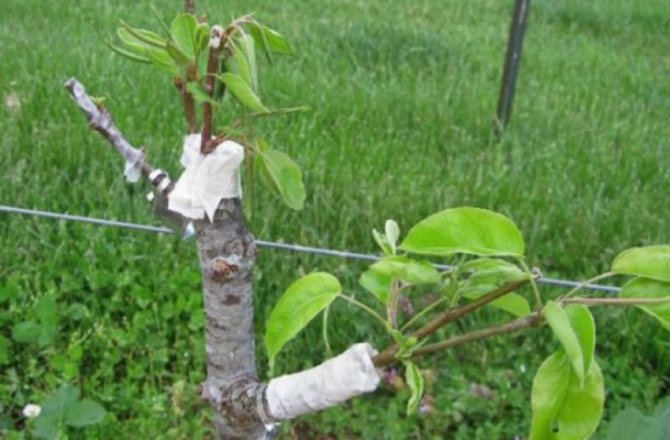


Grafted vigorous and low-growing varieties on a tree
Before you start grafting a fruit tree, you need to study and understand which method is best for a tree or shrub, what are its advantages and disadvantages.
For the bark
The simplest vaccination is for the bark. Best of all, it takes root during the movement of the juice, in the month of April-May. Then the bark is easily separated from the wood. The main thing is to make the correct oblique cut in the handle. It is made with a sharp knife, creating an ideal surface for joining the cambium of the rootstock and the scion. Next, the wrapping is done with film.
Side cut
This coloration is done on the side of a branch or seedling. The advantage of this type of gardeners consider early fruiting. For example, a young tree brings its first harvest in 5-7 years, grafted in this way - in 2-3 years.
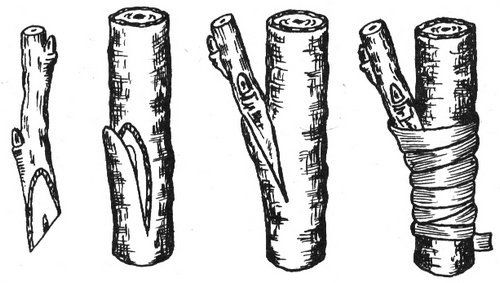

Graft to the side cut
This grafting is used by gardeners to align one-sided types of crowns.
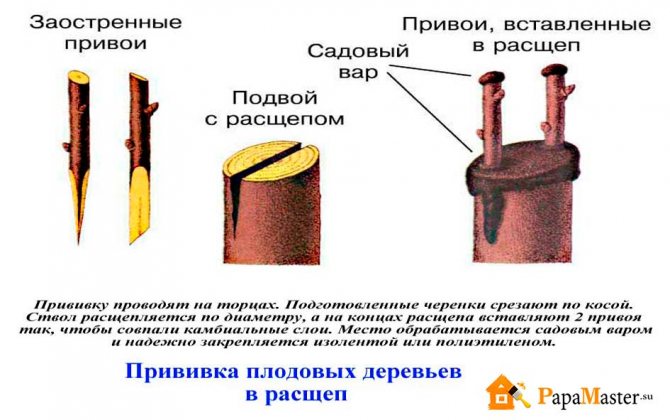
Into the cleft
Grafting in the cleft, gardeners use this method to renew their gardens. The top is cut off from the tree, the base is cut. A scion stalk is inserted into the slot. The time for vaccination is spring.
Additional Information! For this type of grafting, the diameter of the scion and rootstock is irrelevant and does not affect the result of the grafting. It is better to inoculate in the cleft together. The second pair of hands will help insert the stalk into the prepared cleft.
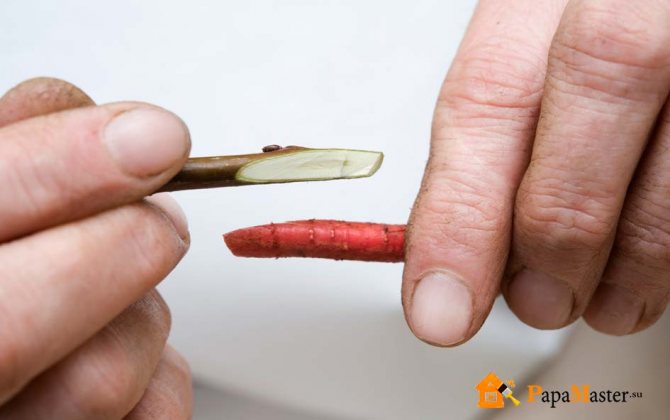
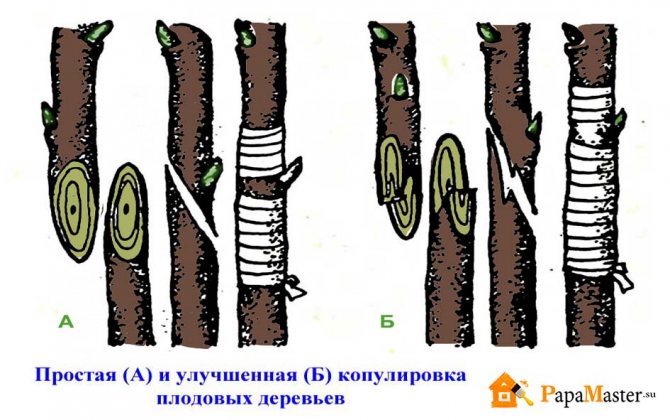
Copulation
This type of grafting is used when the rootstock and scion are fairly thin and of the same thickness. Both branches are cut obliquely at the same angle, the cut is the same length.
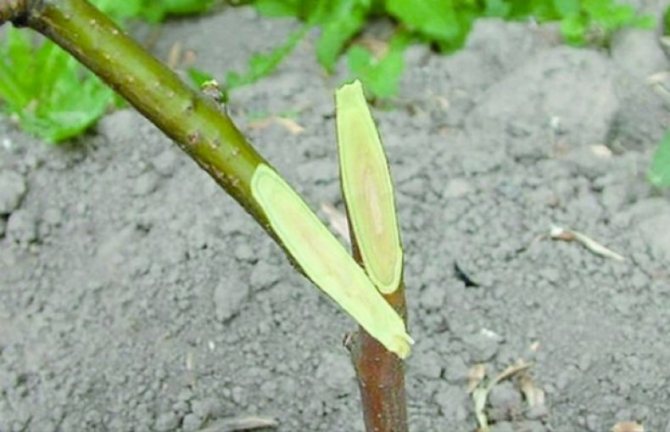


Copulation
By connecting the cuts, a winding is performed that fixes both branches. Copulation is usually done in April.
Ablactation
Ablation is rarely used today, although it is a simple vaccination method. For her, the bark is removed from the stock and scion, and the branches are applied to each other. The connection is wrapped with a special material and covered with pitch or plasticine.
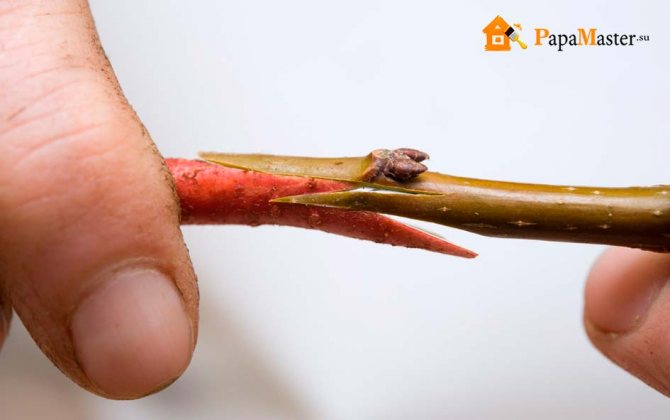
Budding
The most common method is the budding of a healthy kidney with a bark shield with a scion handle. The best time for budding is the summer months: from mid-July to mid-August. Usually the bud takes root in the fall, in the spring of next year it sprouts.
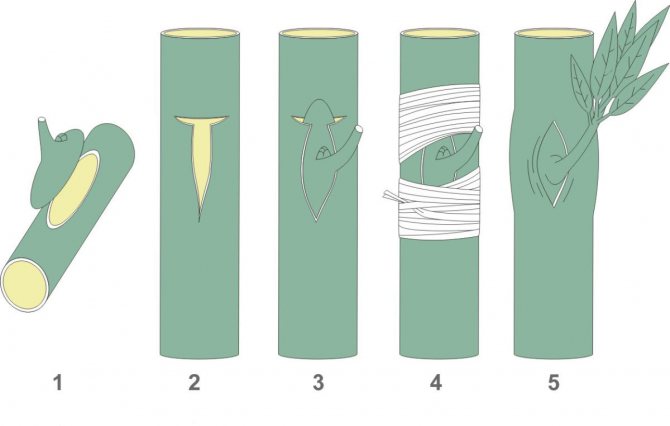

Diagram of the budding process
This type of vaccination requires a minimum of vaccine material.
Grafting a cutting with a drill
The essence of such an inoculation boils down to drilling a hole in a large tree with a drill, 8 mm in diameter to a depth of 4-5 cm. A suitable branch of the same diameter with four buds is taken.


100% survival rate of the cuttings
In it, the bark is cleaned from the edge, which will be inserted into the drilled hole. Planting the cutting should be such that the unpeeled bark goes a little into the hole.
The tricks and wisdom of the gardener
These tricks and wisdom from professionals will help to improve the results of vaccination work:
- A smooth cut is a challenge for novice gardeners. Plus, you need to make the right cut in one go. Therefore, before gardening, it is advisable to practice on pear branches: they have hard wood.
- A good garden pitch should soften in the sun without heating.
- Use a special, sharp, serviceable tool, treated with alcohol.
- Before work, rinse the cuttings with water and keep in a damp cloth.
- Avoid prolonged contact of the grafting material with air and do not touch it with your hands.
- The sections of the bark and cambium on the scion and rootstock should match as much as possible.
- The longer the length of the cut, the more successful the fusion is.
- At the bottom of the scion, it is recommended to remove 0.5 - 1 cm of bark to increase the area of accretion.
- Above the cut of the scion, it is desirable to have a healthy bud, since this stimulates the development of the branch. In addition, if the stalk breaks, a new varietal shoot can be grown from this bud.
- It is advisable to process not only the end of the stock with a garden pitch, but also the upper cut of the scion. This reduces evaporation, thereby ensuring better survival. In addition, a bag can be put on the place of fusion. Dissolving the buds will show when the vaccine bag can be removed.
- The bark peeling tool can be made from a regular 100 mm nail. To do this, you need to grind it half the thickness and 2 cm in length, and then sharpen the tip.
- If you tie several sticks towering over the scion to the graft, this will protect the escape from birds that like to sit on wrapped twigs.
Read also How to feed a two-week-old rabbit
How long does the vaccine take root
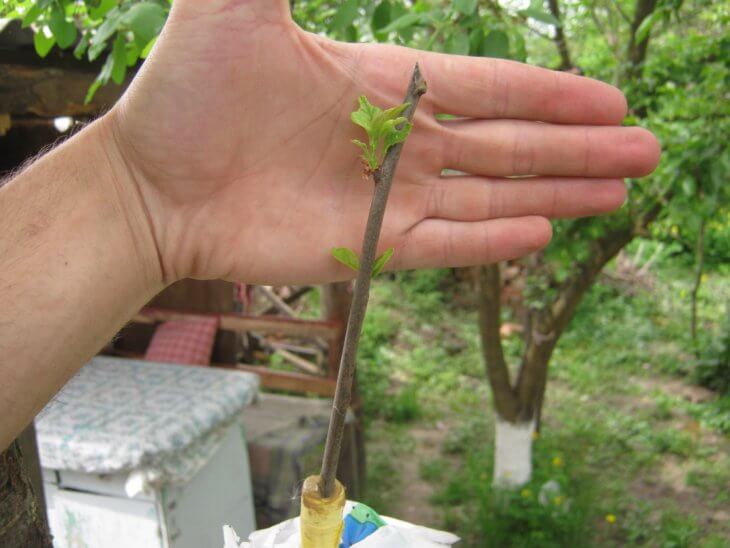
In order for a grafted cutting to take root on a new plant, an exchange of juices must occur between it and the main plant. The scions take root most successfully during the movement of the juice. This period falls in the spring and early summer.
If coloration occurs in the spring-summer months, after a couple of weeks you can observe the swelling of the buds on the scion, this indicates that the vital activity of the plant has intensified. For example, when coloring with eyes, you can make sure after 12-15 days that the peephole has taken root, while the petiole disappears, and you need to loosen the strapping.
It is not difficult to paint plants. The main thing is to follow the advice and take into account the experience of gardeners.
How to care for a tree after grafting
- Remember to remove the harness.
- About a month after vaccination, when growths appear on the cuttings, the strapping must be loosened, and after a few more weeks it must be removed completely. If the gain is weak, the harness can be removed later. The main thing here is to prevent the formation of constrictions. Otherwise, the vaccine will break off.
- In the first year, the fusion of the components is not too strong, and the graft site may not withstand a gust of wind or the weight of our feathered friends. Establish a strong support for the grafted plants and secure the growing shoot. If inoculated in the crown of a tree, tie a strong safety stick to the re-grafted branch. It should be 15 - 20 cm longer than the grafted cuttings.
- Remove overgrowths formed below the grafting site. Strong and sturdy, they take nourishment from the roots and do not allow the grafted variety to develop.
- Otherwise, the care of grafted plants is the same as for the rest. Stimulate good growth early in the season, and start preparing for a dormant period in mid-summer. Protect vaccinations from pests and diseases.