Do-it-yourself beautiful and productive beds
Home ›Bushes and trees› How to independently propagate lilac bushes by cuttings: step by step instructions
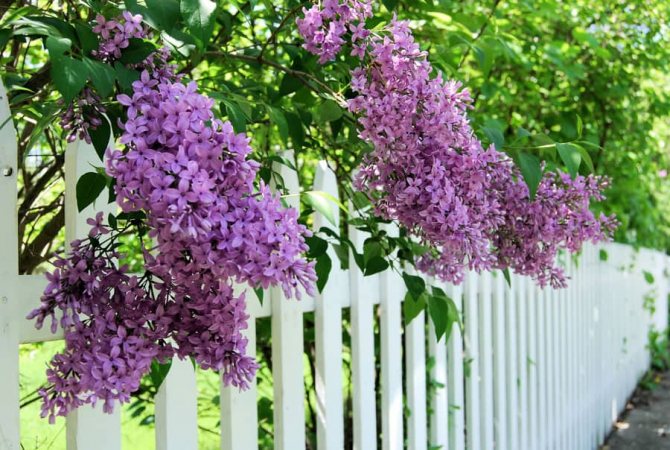
The owners of plots sometimes have the question of how to get hold of this or that plant on their territory. Lilac looks especially attractive. More than two hundred interesting varieties have been bred, which give unusual flowers on May days.
If you liked a particular bush, can you propagate it? - this question is asked by summer residents. - How to propagate lilacs by cuttings?
Probably, every summer resident dreams of having several bushes of this plant with a different color of flowers. Terry flowers are in particular demand; they look quite unusual and eye-catching.
Everyone can negotiate with neighbors who have unusual lilac bushes to cut a few branches. New plants will grow from them, which will decorate the territory with flowers. You just need to use a specific instruction, and then follow all the steps sequentially.

Where to start rooting lilacs
Procurement of material for future plantings can only be made in a certain period. The bush should be in a state of beginning flowering. By this time, the branches accumulate nutrients in the maximum amount.
Sometimes you can find recommendations where the authors argue that you need to wait for the flowering to complete. Unfortunately, after flowering, the nutritional concentration drops sharply, which noticeably reduces the survival rate of cuttings.
Preparation must be carried out two to three days before the start of blooming. It was at this time that the maximum of nourishment was concentrated in the plant. The rooting rate reaches up to 95%.
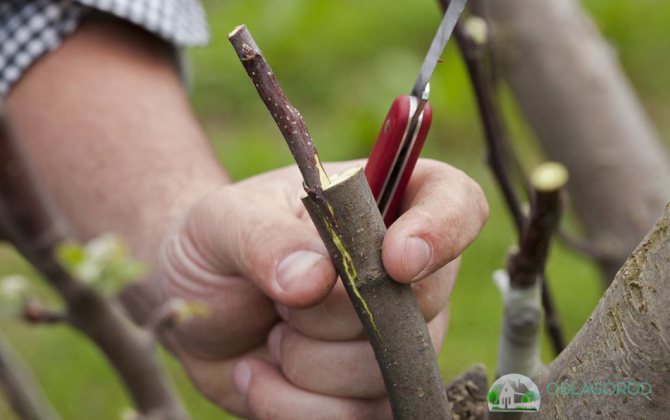
Small lignified shoots are selected, located near the flowers. The flowers themselves are not used, you need what is next to them. The cut branch must have at least 6 leaves - this is a sign of sufficient accumulation of strength for subsequent actions.
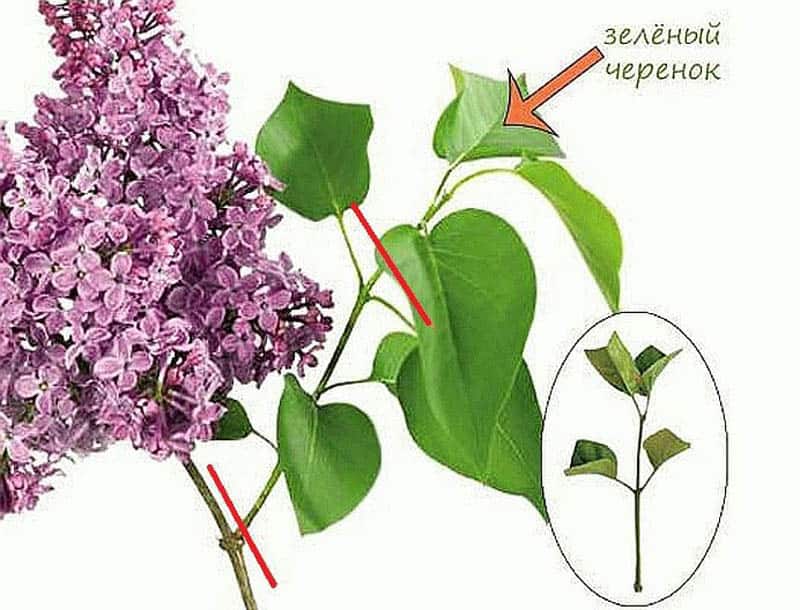

Harvesting cuttings
When formed on a lateral shoot, near the peduncle from four to six leaves, it can be used as a nursery. It is desirable to have a total length of 12 to 15 cm. The presence of three pairs of buds should be observed on the stem.
Attention! The use of shoots, next to which there are no peduncles, is useless. They cannot form roots. They lack nutrients.
As practice shows, you should not leave leaves on the harvested material. They evaporate moisture, so you only need to leave a part of the sheet plate.
Important! Many authors rewrite the same text many times. At the same time, they say that all available (4 ... 6) leaves must be cut in half. You can't do that! The plant will not be able to root and provide moisture to the remaining foliage.
Only one sheet is left, from which at least 60% of the surface is removed. Such a stalk has about 80 ... 85% for survival and rooting. From the bottom, it is cut at an angle of 45 ° below the kidney.
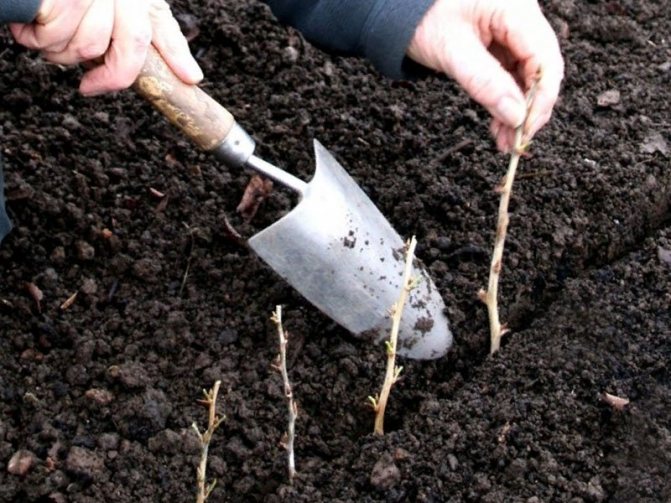
In order to be guaranteed to have future planting material, several such cuttings are harvested. They need to be prepared for planting on the day of cutting.
Popular garden plant
About 30 species of shrubs are described under the general name lilac, which grow wild in Asia, as well as in the south and east of Europe. Many of them have been grown in gardens for a long time, but varietal plants that differ in the shape and color of flowers are most widespread - more than 1,500 of them are now known.
The shrub looks like this:
- The average height of an adult plant is from 1.5 to 3 m. Branched shoots grow upward.
- The leaves are located opposite each other. Most varieties are whole. Pinnately dissected are less common. Leaves fall off for the winter.
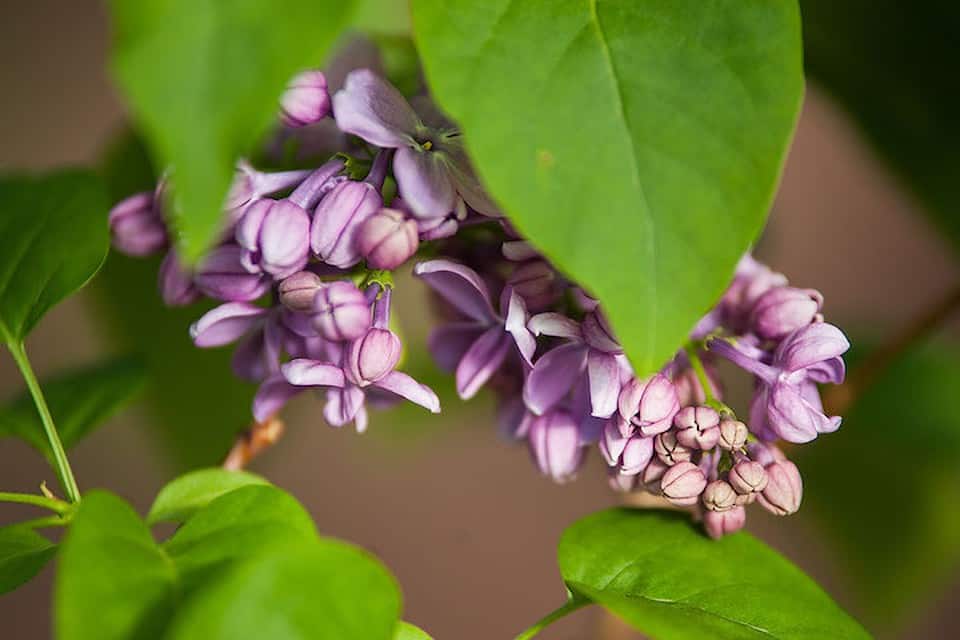
- Flowers are collected in panicle inflorescences. Most often they are painted in lilac (lilac) color of various shades.
- The fruit is a box with two valves.
The most common of the species is common lilac. This shrub is very hardy, thanks to which it is able to thrive both in the southern and northern regions. After planting, lilacs practically do not need care, therefore they are actively used in landscaping cities and towns. It is absolutely easy to propagate the bush you like on your own. This is done in several ways:
- by rooting cuttings;
- deposition of overgrowth;
- using layering.


All methods are quite productive and can be performed without much difficulty.
Advice. If the lilac needs to be transplanted, it is best to do this 2 weeks after the end of flowering. This period has been proven empirically.
Preparation of the substrate for rooting cuttings
Special nurseries are prepared for cuttings:
- Take a seedling box with a depth of at least 60 mm.
- There should be holes at the bottom for water to drain.
- Placed on a pallet.
- Lowland peat is poured.
- About 20 ... 25% of river sand is mixed with it.
- Perlite is added, about 50% of the peat volume.
- The whole mixture is stirred.
- Arcs are installed, you can bend it out of a wire and install it from edge to edge.
- Prepare the film. You can use polyethylene, or you can use a vapor barrier film recommended for wall insulation.
- The whole mass is spilled with a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate. It is desirable to heat it up to a temperature of 60 ... 70 ° С. There will be not only disinfection, but also moistening of the substrate.
Prepare in advance the place where the nursery for the cuttings will be installed. It is desirable to have a shaded warm corner. It should be exposed to sunlight only in the morning before lunch.


Description of the species
The Amur lilac came to us from Manchuria, the Amur region, the Khabarovsk and Primorsky regions, Korea and China.
The best conditions for the development of lilacs are mixed forests, wooded slopes, and shrubs.
Spreading in the mountains, it can rise 600 m above sea level. Amur lilac grows up to 10 m. In height, and occasionally up to 15 m., It is a multi-stemmed deciduous shrub. On the dark bark, white transverse lentils are clearly visible, young shoots are red-brown in color, a bit like cherry shoots.
Preparation and planting of lilac cuttings
You need to prepare:
- root growth stimulator "Epin Extra" or heteroauxin;
- wood ash or "Kornevin" in powder form;
- nursery for cuttings.
Preparation of a solution to stimulate root growth
- Recipe number 1 based on "Epin Extra"
- Dissolve 1 ml of "Epin Extra" in 1 liter of water (for 10 cuttings you need at least 200 ml of working solution).
- Pour the solution into a container, leaving 20 ... 30 mm from the top edge.
- Recipe number 2 based on heteroauxin
- Dissolve 1 tablet in 1 liter of water.
- Pour the solution into a suitable container (about 200 ml is needed for 10 cuttings).
- The prepared material for rooting is washed in warm water, an oblique cut is made under the kidney at 45 °, the remaining water is shaken off and placed in a solution for rooting. Cuttings are kept in solution for at least 16 ... 20 hours.
- Take out and dip in Kornevin powder or wood ash.
- The substrate is sprayed with a solution where the planting branches were kept.
- They are planted according to the scheme: the distance between the rows is 10 ... 12 cm, the distance in the row is 6 ... 8 cm.
- Deepen by 3 ... 5 cm (light touching of the cut leaves with each other is allowed).
- Cover the greenhouse with plastic wrap.


Vaccination procedure in different ways
It is recommended for a novice gardener to plant lilacs in the spring by a simple copulation method without cutting "tongues" of splits, so as not to damage the tissue of the shoots with awkward movements. Oblique cuts of the same size are cut both on the graft and on the rootstock, and then gently in these places they are applied to each other. It is advisable to do this with one confident movement and in no case rub the scion and rootstock slices against each other - this will damage their tissues, and the graft will not take root.
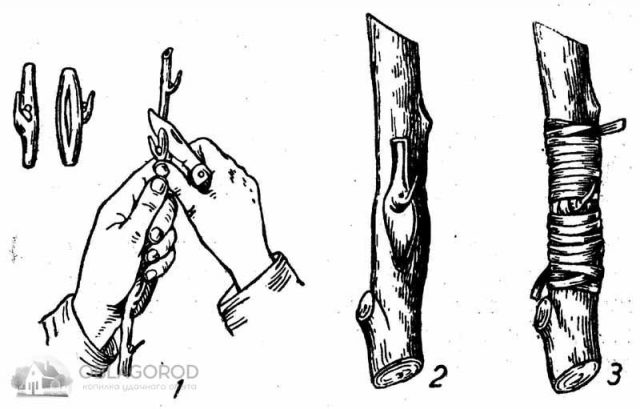

Inoculation by budding
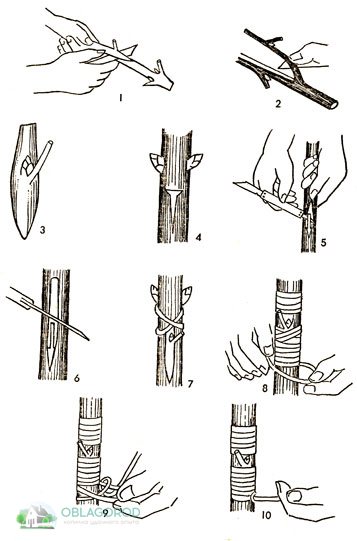

Detailed vaccination scheme
After that, the vaccination site is wrapped in polyethylene, and the opposite end is used to treat it with garden varnish to prevent it from drying out.
You can also plant lilacs in the cleavage. This should be done in early March, even before the start of the main garden work. This operation is performed strictly according to the instructions:
- The garden pruner is thoroughly cleaned of dirt and treated with alcohol.
- All buds are removed from the selected rootstock and the top is completely cut off.
- A vertical split 3 cm deep is made in the middle of the stock.
- A 3 cm long welt is cut obliquely from both sides so that it takes the form of a wedge.
- The graft is inserted into the rootstock split so that their cambial layers completely coincide on at least one side.
- The vaccination site is wrapped in polyethylene.
- Other damages on the rootstock and scion are treated with garden varnish.
- Before bud break, the graft is also covered with polyethylene - this will allow maintaining the optimum moisture level in the vaccination site.


Clean the sector from pollution


Cut to a length of 3 cm
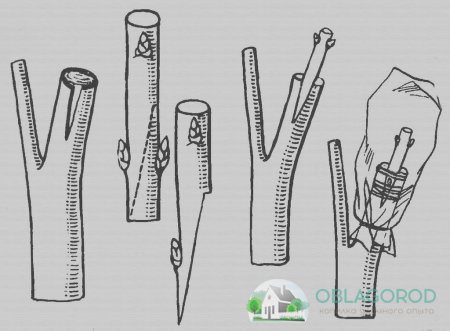

Vaccination scheme


Paste the habit into the cleft
In the spring, lilacs can also be grafted by budding, that is, with a sprouting bud or "sleeping eye" in the middle of summer.
Growing lilac seedlings
Two or three times a day you need to ventilate the greenhouse by lifting the film for a few seconds. After 30 ... 50 days, you can check how successful the rooting is.
Attention! If after 10..15 days the leaf turns black, the buds begin to darken and fall off, then you need to remove such a stalk. He did not take root and did not give roots.
The seedlings are taken out to an open place, the film is not completely removed, they are placed in a shaded place so that only part of the daylight hours fall on the greenhouse, preferably in the morning.
The film is slightly opened in the evening for 2 ... 4 hours. Be sure to close at night
During the rest of the summer, it is advisable to feed the growing bushes. They should already be giving foliage growth. At least two dressings are carried out. The frequency is about 20 ... 25 days.
Dissolve in a liter of water:
- 2.5 ... 3.0 g of ammonium nitrate;
- 1.5 ... 2.0 g of superphosphate;
- 0.5 ... 0.8 g of potassium nitrate.
The grown plants are watered with this solution. Can be sprayed from above by pouring some of the solution into a spray bottle. The jet should represent fine droplets in the form of fog.


After the second feeding, which will be at the end of August or the beginning of September, the film can be removed.
Important! The substrate must not be allowed to dry out. It is also not necessary to overmoisten. Watering is carried out once every three to four days.
In autumn, at the end of September or in the first days of October, it is advisable to insulate the box with seedlings for the winter. Use straw or hay. Some gardeners use peat, which is used to cover the seedlings from above.
Root shoots as planting material
Propagation by root shoots is a natural and convenient way. Most varieties of lilacs tend to form root shoots on their own. The daughter bush retains all the varietal characteristics of the parent plant. Another advantage of the method is a single transplant of a seedling.In this case, he receives the minimum amount of damage.
How lilacs propagate by root shoots, stages:
- Seating is carried out in autumn on a cloudy day no later than mid-October.
- Before dividing the shoots and the mother bush, the soil is watered abundantly.
- The main root is carefully separated at a distance of at least 15-20 cm from the mother bush.
- After transplanting, the soil is watered abundantly.
- The first year, seedlings will need shelter for the winter from spruce branches.


In this way, you can dilute lilacs in summer or late spring, so that the seedlings have more time left to adapt to a new place.
Works of the second year
In the spring (end of March, beginning of April) next year, an assessment of the grown seedlings of lilac bushes is carried out. Sick and weak bushes are discarded.
A place is being prepared in the garden or in the garden, where the school (as the plants that have grown from cuttings are called) will grow until autumn.


Requirements for the site:
- the place must be illuminated by the sun for at least 10 hours in summer;
- the soil is light, loose, fertilized;
- convenient watering with settled water that does not contain chlorine.
Attention! If there is an excess of chlorine in the irrigation water, as well as magnesium and calcium salts, then the color of the flowers may change. They may not match the parent plant.
The transplant must be carried out together with a clod of earth surrounding the plant. Try not to damage the small roots. Planted according to the scheme:
- the distance between the rows is 45 ... 55 cm;
- the distance between the bushes is 35 ... 45 cm.
Attention! Some gardeners who grow lilac bushes for sale use plastic buckets in which holes are drilled (diameter 6 ... 8 mm) from the bottom and in the side walls. The volume of buckets is 10 ... 12 liters. Buckets are added dropwise to 2/3 of the height.
Care in the second years of cultivation is simple:
- timely watering is necessary, depending on the weather and the condition of the soil on the school. It is advisable to soak the soil once or twice during the summer to a depth of 30 cm (summer rains of the Central Russia will do this work instead of a gardener);
- make three fertilizing with mineral fertilizers and one organic.


Mineral dressing for lilac school
Each plant will require:
- 3 ... 5 g of ammonium nitrate;
- 4 ... 7 g of superphosphate;
- 2..3 g of potassium nitrate.
It is advisable to dissolve the specified amount in 5 liters of water, and then water the growing bush.
Organic feeding
Experienced gardeners recommend using rabbit manure. It is used without additional training.
- Spread 200 ... 250 g of rabbit manure over an area of one square meter.
- Dig it to a depth of about 5 ... 8 cm.
Attention! Digging should be carried out, leaving a protective zone near the bush 7 ... 8 cm, so as not to damage the root part.
In the fall, after the leaves have fallen off, the lilac bush can be transplanted to a permanent place. For transplanting, the excavation is carried out at a distance of 35 ... 45 cm from the formed trunk. To facilitate the process, you can spill water, then most of the roots will remain intact.
Important! Approximately 35% of the planted cuttings finally take root.


Conditions for growth
Description and photos of the main species and varieties of spathiphyllum
When choosing a place for planting lilacs on your site, the following parameters should be taken into account:
- intensity and duration of natural light;
- type and composition of soil;
- humidity;
- the size of the allocated area for the growth, development and nutrition of the plant.
In the temperate climate of the middle zone, lilacs tolerate hot summers and frosty winters well.


Lighting and location
Lilac is an unpretentious plant, and it does not require special conditions. The most suitable place for planting it will be an area located on a plain or small slope with sunlight throughout the day.Bushes planted in the shade will not be lush, their development is slow, and flowering is very weak or absent altogether.
Soil for the bush
All cultivated garden soils are suitable for lilacs. Where fruit trees, berry bushes, ornamental plants grow, lilacs will feel good.
Heavy unstructured and highly acidic soils are not suitable for it. Acidic soil is neutralized with lime, dolomite flour or ash, but this tool will have to be applied annually.


Temporarily flooded, swampy or lowland areas are not suitable for lilacs. In such landscapes, it is necessary to create a separate fill mound for each bush, and not a traditional pit, as in a conventional planting.
Clay soil is also problematic. But planting a plant is possible provided the planting site is loosened with sand, neutralized peat, leaf humus or other organic additives. But since clay does not allow moisture to pass through well, care should be taken that rainwater does not accumulate in the pit prepared for the growth of lilacs in such an area. Areas with high humidity are detrimental to this plant.


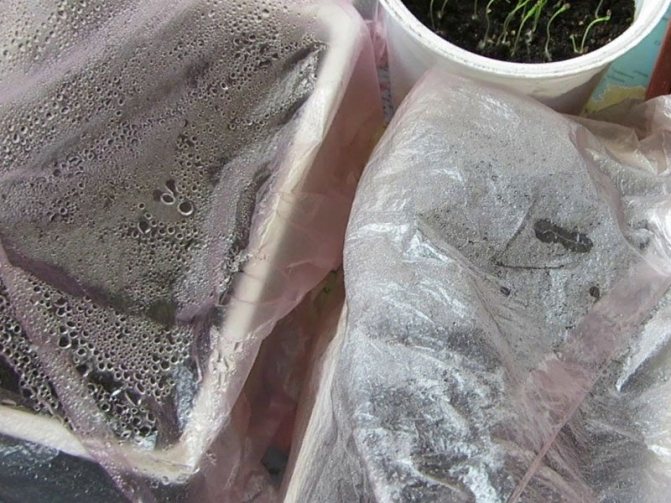
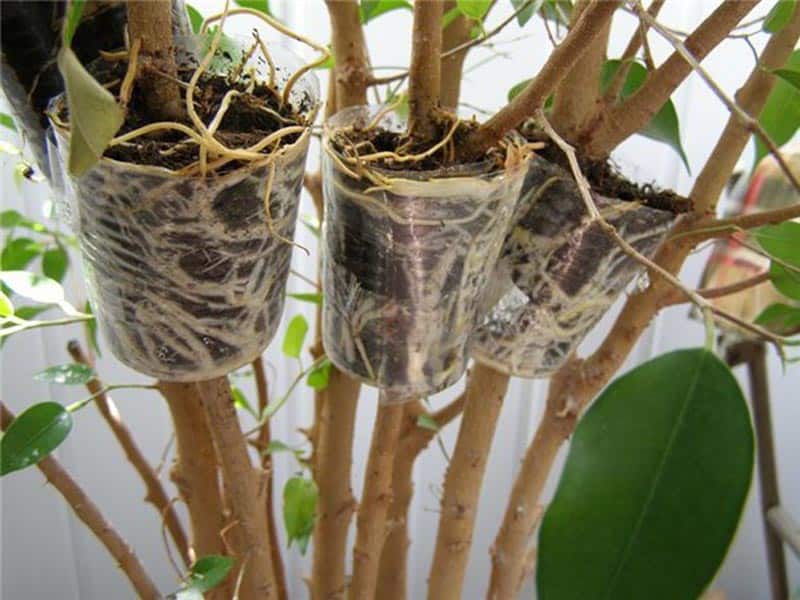
Growing a lilac bush from an air layer
In addition to cuttings, you can get a new plant if you form a cut. In this case, the survival rate is up to 90 ... 95%:
- A suitable branch is selected, which can be further cut off.
- A plastic container is being prepared, in it the future lilac bush will form the roots.
- On a branch, a small area of bark is removed with a ring and lubricated with phytohormone.
- A plastic bag is tied with a wire below.
- Put sphagnum moss down.
- Pour in the nutrient mixture (substrate).
- Watered with Epin Extra solution.
- Tied at the top.
- Roots are formed after 30 ... 40 days.
- A plastic container is put on a branch and fixed. Remove the plastic bag and add soil.
- In the fall, after the leaves fall off, the branch is pruned below the container.
- They are transplanted in the second year of rearing in a school.
- By the end of the second season, a new lilac bush is obtained.
- It is transplanted to a permanent place.


Some gardeners form several air layers on one bush. This method turns out to be more effective than growing from cuttings.
Root shoots
Reproduction of lilacs by young root shoots is the simplest and most natural method at the same time, because lilac tends to independently form shoots from the mother bush. In this case, the transplant is carried out only once, immediately to a permanent place, and the seedling receives minimal injuries.


The main advantage of this method is that the young plant will have all the varietal characteristics of the mother plant.
You need to plant lilacs in the fall, until mid-October, no later. The procedure is best done on a cloudy day. Before separating a young plant, you need to shed the soil well with water, the main root must be chopped off carefully, minimally traumatizing the fragile root system of a young bush, at a distance of at least 15-20 cm from the mother bush. After planting in a permanent place, it must be well watered and provide shelter for the winter.
Some experts advise to carry out this procedure in the summer, starting in July, in order to give time for the young plant to take root and grow stronger after transplantation.


















