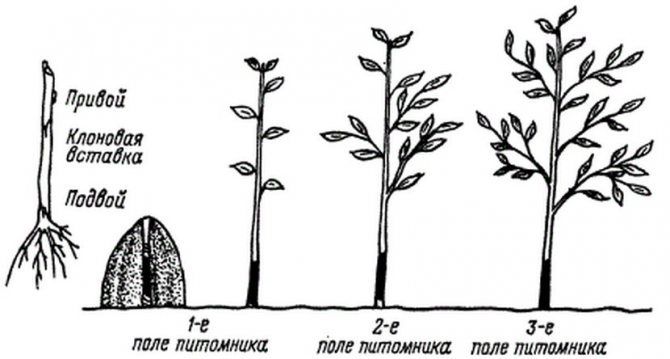
Gardeners are usually interested in planting varietal seedlings. You can buy varietal seedlings, or you can graft cuttings onto self-grown rootstocks. Most often, apple trees are grown in this way. But before that, you need to figure out what types of rootstocks are and how you can grow them yourself.
- 2 Types of rootstocks for apple trees
2.1 Seed stock
- 2.2 Clonal rootstock
- 3.1 Method one: from seeds
3.1.1 Video: growing apple stock with and without stratification
- 3.2.1 Video: how to grow a clone stock
What are scions and rootstocks for an apple tree?
In principle, from a biological point of view, seedlings can also be rooted. However, in many cases, unvaccinated trees do not have early maturity, that is, they begin to bear fruit relatively late.
But with the selection of rootstocks and scions is important to consider and know the compatibility of the components vaccinations in scion-rootstock combinations. The fact is that it strongly affects the productivity, mechanical strength and durability of trees.
What is an apple tree stock?
The rootstock is like the foundation of a fruit tree.It is also a plant on which a bud or cut from a cultivar is grafted.
IMPORTANT! The rootstock affects various qualities and properties of the aboveground part of the tree: growth strength, early maturity, winter hardiness, the number of flower buds laid, fruit set, productivity, regularity of fruiting and their appearance.

Rootstocks.
Apple varieties on a semi-dwarf rootstock for the Moscow region
For cultivation in the Moscow region, the most popular apple varieties are:
- Lobo is a mid-season variety with early fruiting. Indicators of frost resistance are good, apples are juicy and aromatic, large in size.
- Antonovka ordinary is a popular variety with abundant fruiting, as well as an above average life expectancy. The plant tolerates well the close location of groundwater relative to the surface of the earth.
- Imrus is a tree of winter ripening period, a characteristic feature is large-fruited. Apples have a sweet and sour taste, the structure is dense and juicy.
At each summer cottage, you can successfully grow popular varieties of dwarf and semi-dwarf apple trees, the main thing is to get acquainted with the peculiarities of planting and caring for such plants.
Most apple seedlings are the result of grafting. A stock for an apple tree is that part of a plant that is responsible for feeding a bud grafted onto it or a cutting from a fruiting tree (scion). When cultivating a horticultural culture, the choice of a rootstock variety is of great importance, because the future yield of the tree and its health depend on it.


Features of apple rootstocks
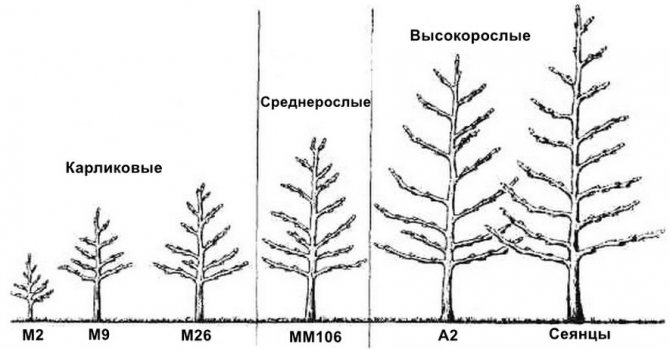
What are the rootstocks?
The impact on these qualities, depend on the strength of the rootstock growth.
On this basis, they are divided into:
- Vigorous,
- Medium-sized,
- Weak.
The last ones in terms of influence on the grafted variety are semi-dwarf and dwarf.
Moreover, by the method of obtaining and growing rootstocks are divided into:
- Seed,
- Clonal or vegetative,
- Insertable or intercalary.
The seed stocks of the apple tree represent seedlings grown from seeds of common varieties... Naturally, the strength of their growth as rootstocks is determined by the strength of the growth of a particular variety.
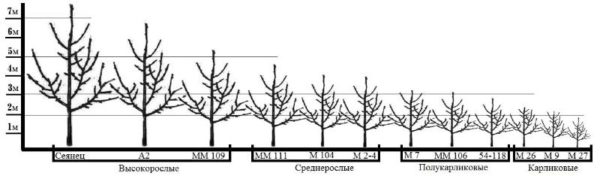

Graduation of apple trees depending on the strength of growth.
Most varieties with sufficient winter hardiness of the aboveground and root systems to be used as rootstocks in the Non-Chernozem zone, are vigorous.
For example, to obtain seedlings, the seeds of Grushovka Moscow, Antonovka ordinary, Borovinka and some others are often used.
Apple clonal rootstocks or vegetative
it original planting materialobtained by vegetative propagation of forms and species of plants used as rootstocks. Very often weakly growing hybrids of apple trees and other types of fruit trees are vegetatively propagated.
If you are thinking - is it possible to root a branch of an apple tree rootstock, then this is exactly the case when get a new seedling... In some farms, where there are greenhouses with installations that make it possible to obtain artificial fog, they are engaged in the propagation of rootstocks by means of green cuttings.
Feature of clonal rootstocks is a fibrous root system, consisting of adventitious roots.
They have their own advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages over insert rootstocks are in:
- Comparative homogeneity of the trees obtained in terms of the strength of growth and the time of the beginning of fruiting;
- The possibility of disembarking in areas with a close groundwater level.
disadvantages are also associated with the superficial location of the root system and are manifested:
- In the lesser stability of the tree in the soil;
- Mostly depending on the regularity of rainfall or artificial irrigation, since the surface layer of the soil dries out quickly during dry periods.
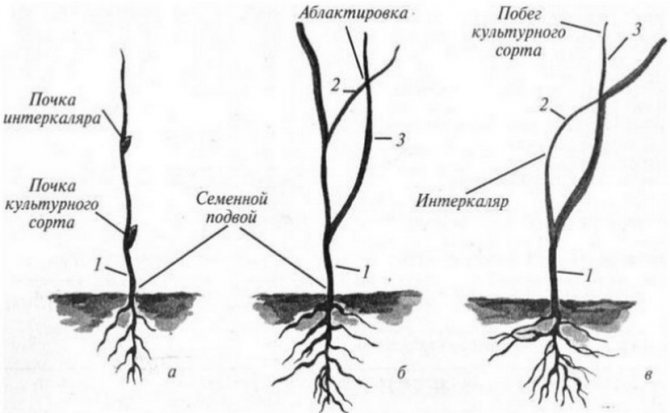
Intercalary or insertion
Represent a combination of seed stock and intermediate insert a weak rootstock or just a strainer.
It is a cuttings (a piece of stem) cut from a mother plant, as a rule, a weakly grown apple tree (dusen or paradizka) with a length of 12 to 22 cm.
The advantage of seedlings on such rootstocks is a combination of relatively short stature and early maturity with good stability in the ground.
Possible disadvantage is the insufficient mechanical strength of some dwarf forms of the apple tree, for example, Paradizka Budagovsky.
Determination of the dived culture
Today gardeners can choose from a wide variety of apple varieties. Most often, the summer resident selects for himself crops with larger and more palatable fruits. To grow an apple tree stock from seeds, you must first inoculate the material of the desired variety, it is on this that the further development of the plant and its fruitfulness will depend.
The material to be grafted (it can be a bud or a separate branch) will be called a scion, and the graft site will be called a stock. The grower should also consider a detailed classification of all types of vaccinations. There are several methods of growing stock - seed, vegetative:

With seed growing, everything is clear immediately from the name of the method. It is carried out by planting a seed. A gardener sows a seed into the soil and as a result gets a new crop, which becomes a seed stock.- The second way is clonal rootstocks. Their reproduction occurs by means of cuttings or cuttings, which is why this method is much more widespread than others, the procedure for growing a crop takes much less time. All clonal cultures are divided into two main groups - dwarf and medium-sized.
Thuja breeding methods at home
It is the apple trees of dwarf rootstocks that are much more attractive in appearance, but it is important to remember that such varieties require labor and money for the gardener.In this case, the owner will have to create special supports and regularly water the crop, as well as protect it from the attacks of possible parasites and disease. For beginner gardeners, it is best to plant large or medium-sized rootstocks.
How to grow wild apple trees for stock?
Usually in nurseries wilds are obtained by growing from seeds, which takes place in several stages: extraction of seeds, their stratification, sowing, care for seedlings, picking seedlings, digging seedlings, planting rootstocks.
Seed preparation. Depending on the size of the farm and nursery, it can be either manual or mechanized.
In private nurseries, it is made by hand, and in nurseries of large farms, ripe fruits are crushed in fruit grinders.
Good to know! Seed stratification is the effect of low temperatures on them.
In areas with light, non-floating soils, seeds can be sown in the fall. Thus, they will undergo natural stratification.
If the soil in the nursery is heavyswimming, artificial stratification in the sand is recommended. To do this, the seeds should be mixed with 3 parts of wet coarse-grained river sand and stored in boxes.
TIP! The boxes are recommended to choose the following dimensions: 60 cm in length, 30-40 cm in width and 25 cm in height.
Single seeds can be prostrated in a flower pot. It is recommended to store seeds mixed with sand in the basement at a temperature of + 3- + 5 degrees.
As the temperature in the basement rises, and even more so when signs of germination appear, the containers with seeds should be placed on ice or buried in the snow before sowing.
It is recommended to stratify the seeds of an ordinary domestic apple tree for at least 90 days, for a Chinese apple tree (for white apple) - from 70 days, for a Siberian berry apple - for at least 30 days.
Seeds should be sown on beds with fertilized and cultivated soil after physical maturation of the soil. It is recommended to plant seeds of apple trees to a depth of 2-3 cm, sowing them into grooves together with sand.
After sowing, the soil surface is recommended to be mulched and watered. A pick of seedlings it is recommended to carry out in the period from the beginning of the cotyledons to 2 true leaves. In this case, it is recommended to pinch the central root, leaving it 4 cm long from the root collar.
Plant seedlings it is proposed according to the scheme 15-20 x 7-8 cm. After planting, the seedlings must be watered, mulched and shaded for the first days.
Seedling care
In summer, seedlings are recommended to weed and loosen the soil under them.
In the first half of summer it is advisable to feed:
- Infusion of manure;
- Or with a solution of ammonium nitrate (at the rate of 40 g per 10 l);
- Or urea, spending ¼ buckets per 1 running meter of a row.
Growing: how to prepare and get a good stock
Healthy rootstock material can only be obtained if it is properly grown. It is easier, of course, to purchase ready-made seedlings in specialized nurseries. Nevertheless, you can prepare the stock yourself. Keep in mind that seedlings will be ready for grafting only a few years after planting. If grafting of a variety is necessary as soon as possible, it is best to give preference to the vegetative method.
Seed
It takes a lot of time and attention to prepare such material. The cultivation takes place as follows:
- remove the seeds from the ripe fruits of the variety selected for the future rootstock;
- stratify the seeds, mix the seeds with coarse sand in a ratio of 1: 3. In autumn sowing, stratification is carried out in a natural way;
- until spring, seeds are stored in boxes in a cool room with moderate humidity;
- sowing should be done after overheating the soil, before planting, the necessary fertilizers are applied and watering is carried out;
- seeds are introduced into warm soil together with sand, into grooves about 2-3 cm deep;
- after sowing, the garden bed is mulched;
- seedlings dive when the third true leaf appears, while the main root shoot is shortened to a length of 4-5 cm;
- seedlings are planted at a distance of 15-25 cm from each other, for the first time after the manipulations done, the plants are closed from the sun, the soil is mulched.
Read about the scion for the apple tree here.
Clone
Vegetative rootstocks are harvested from purchased ready-made material. The purchased stalk is shortened at the top and planted in the mother plant - a special place reserved for 10-12 years, during which it will give you new shoots. The soil in the mother liquor must be fertile, loam and sand are not suitable.
You don't need to grow a tree, but a bush. The process is as follows:
- make a groove in the soil 8-10 cm deep;
- plant the purchased stock in it, maintaining a distance of 100-120 cm;
- cut the cuttings by 30 cm;
- next spring, cut the rooted cuttings so that a stump remains 4-6 cm high;
- as soon as the shoots 15 cm long grow, spud the plants;
- carry out hilling 2-3 times per season.
From these shrubs, you can cut the right amount of rootstock material that will be identical to the parent plants.
Apple rootstocks and scions compatibility
Best Compatibility seen in most varieties with seedlings of Antonovka, Grushovka, Borovinka.
At the same time, there is a poor compatibility of many varieties of apple trees with seedlings of Chinese and purple raneta.
For example, with Chinese, as a stock, varieties are considered incompatible:
- Anises,
- Antonovka ordinary,
- Babushkino,
- Borovinka,
- Korobovka and many others.
Moreover, we can assume compatible varieties:
- Velvet,
- Cinnamon new
- Pepin saffron
- some others.
In most cases lack of compatibility is manifested in starvation and subsequent death of the root system.
In addition, lack of compatibility is manifested in apple varieties with other pome varieties: irgoy, hawthorn.
In this case, the reduced compatibility is expressed in the relatively short life of such scion-rootstock combinations.
Features of clonal rootstocks
This is the most popular type of rootstocks, since the material is much easier to obtain. During vegetative propagation, the variety retains all its qualities, while when growing seeds, cross-pollination and changes in the genetic base occur. The distinctive features of a vegetative or clonal stock include:
- fibrous root system with many adventitious roots located close to the soil surface;
- unpretentiousness to the state of soils, they are not afraid of the proximity of groundwater;
- weak fixation of the tree in the ground, instability;
- the need for constant watering or irrigation.
Vaccination site when planting an apple tree
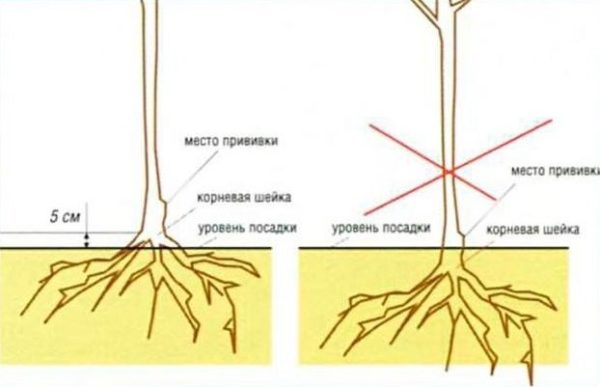
The position of the grafting site when planting an apple tree is of particular importance for seedlings on low-growing rootstocks, since to maintain low growth and early maturity it is important to plant the tree so that the vigorous scion does not touch the ground.
Otherwise, it can give roots and the influence of the weak rootstock will greatly weaken. Here it is worth paying attention to features of planting seedlings on clonal and intercalary rootstocks.
For example, when planting apple trees on clonal rootstocks, the grafting site should be about 3 cm above the level of the plot.
But when planting seedlings with inserts, the position of the grafting sites depends on the climate of your area.

Correct planting of the apple tree.
Particularly in areas with sufficient snowfall, the insert can be left above the soil surface. However, if winters in your area are not very snowy, then 1/3 to 2/3 of the insert should be buried in the ground.
The root shoot of an apple tree is like a stock. Mature apple trees grafted onto seed and intercalary rootstocks often produce root growth.Most of it should of course be cut out.
However, some stems growing at a distance of 15 cm and beyond can be used for grafting... So at a height of about 10-25 cm from the ground, you can inoculate by copulating in the spring or budding in the summer.
TIP! If the graft takes root, then in the fall the grafted tree can be transplanted to a convenient place.
Landing
After the cuttings are completely rooted, they are transplanted to a permanent place. The rooted cuttings are carefully separated from the mother plant. Planting of clonal rootstocks of an apple tree is carried out in a nutritious soil. The site is chosen light, closed and warm.
In cold regions, future rootstocks can be grown at home. Only a mature tree is planted in open ground. After that, a clothespin is made on such a tree, connecting the stock with the scion.
The care of the plant for the rootstock and for the grafted apple tree is practically the same. You need to regularly water the apple trees in the first years of life, mulch the tree trunk, apply fertilizer, and also prepare for winter.
Do not forget about molding pruning of the apple tree, which will help to create the correct crown shape. Treat trees with insecticides periodically to prevent disease.
How to determine on which rootstock the apple tree is?
In a grafted apple tree, only the type of rootstock can be determined.
For example, in a seed stock, the root system consists of a part of the taproot and five thick roots extending from it.
The clonal rootstock has a fibrous root system.
That is, it represents a large number of roots extending from the trunk.
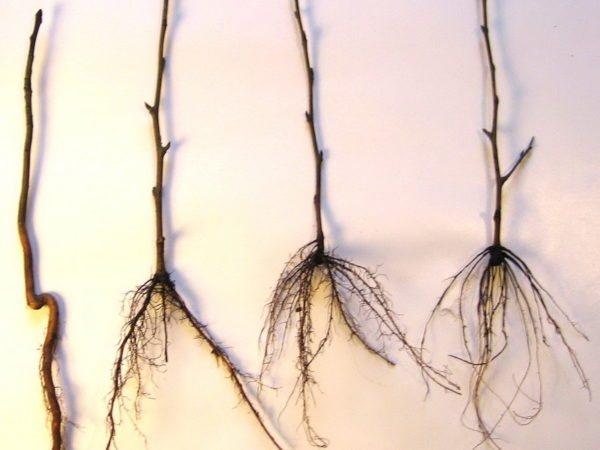


Seed and clonal stock.
In terms of the shape of the rootstock, it is usually possible to determine the origin of a particular shape of the rootstock, however, this requires being a rootstock specialist.
Preparation
Clonal stock can be grown using vegetative methods. For this, cuttings and layering are used.
Using apple cuttings for growing. Twigs with three leaves and dormant buds are cut from a healthy tree. Later they are rooted. You can do this in water, in potatoes, but it is easier to use boxes with plastic wrap.
Using layering. Here you can bend and fasten a low-lying branch to the ground or use root layers. They are covered with earth for root formation.


Features of different varieties of apple trees as rootstocks
Apple tree of Nedzvetsky
This type of apple has become quite widespread only in Central Asia and Kazakhstan. In central Russia, it freezes out.
Chinese woman
This kind of apple tree considered winter-hardy, drought-resistant, and resistant to fungal diseases. Can be used in landscaping. It is often considered as a rootstock, but it is only compatible with certain varieties, for example, Melba, Autumn striped, Renette Krüdner and some others.
At the same time she poorly compatible with Anise, Antonovka ordinary, Borovinka and many other varieties. Therefore, if at all to use it as a rootstock, then with great care, having previously studied the compatibility with propagated varieties.
Siberian berry apple
This species has various forms from medium-sized, reaching a height of 3-4 m, to vigorous with a height of 10 m. As a rootstock, it has become widespread in Siberia and the Urals.
They grow well on Siberian woods, like a rootstock:
- Antonovka saffron,
- Borovinka,
- Autumn striped
- Folding.
The roots of this apple tree are distinguished by good winter hardiness, but low drought resistance.
Propagated both by seeds and by segments of roots.
Seedlings of this species are recommended to be budded earlier than other rootstocks, since it ends the growing season earlier.
Apple tree purple
This species was obtained by crossing the Nedzvetsky apple tree with a dark red apple tree.
Winter hardiness is slightly higher than that of the Nedzvetsky apple tree, thanks to this it has become widespread in the southern and central and central chernozem zones of Russia.
Can withstand frosts down to -34 degrees... However, the degree of compatibility with domestic apple varieties is unknown.
Apple tree Raika
From the point of view of botany, a raika is a paradise apple tree or a bushy apple tree, called paradizka by fruit growers. The common people often confuse her with a Chinese woman, in fact, these are different types.
Relatively common dwarf rootstock for apple treeswidely used in rootstock breeding and used on an industrial scale. This type includes the best dwarf rootstocks M-IX, 62-396, 57-366, 57-491 and apple rootstocks 54 118.
Apple varieties on a dwarf rootstock for the Moscow region
The Moscow region belongs to the Middle lane. The varieties grafted on clonal undersized rootstocks are very popular in these places. The best varieties:
- Melba. It is grown in the Moscow region on an industrial scale, due to its high indicators of frost resistance and abundance of fruiting. The fruits ripen at the end of July. The weight of apples, subject to agrotechnical rules, is not less than 250 g.
- Zhigulevskoe. The fruits ripen at the end of September, each weighing approximately 300 g. It is characterized by excellent indicators of frost resistance, the tree is able to withstand temperature drops down to -30 ° C.
Non-standard rootstocks
Rowan
Sometimes used by gardeners in the absence of a more suitable rootstock. but such a tree is usually short-lived due to the large difference in growth rate in thickness between apple and mountain ash.
Hawthorn
Some gardeners use hawthorn as a dwarf rootstock for apple trees. True, they recommend planting an apple tree on it at a height of 50-60 cm.
On the one hand, experience shows that as a rootstock hawthorn can accelerate the entry of an apple tree into fruiting by a year. On the other hand, there are cases when an apple tree on other species could only live for about 8 years.
OUTPUT! Therefore, it is impractical to use hawthorn as a rootstock from a production point of view.
And if you are interested in how an apple tree will grow and develop on a hawthorn, then in the opinion of the author such a tree can only be grown as an exotic on a personal plot.
Irga
Irga can be considered an unpretentious breed, perfectly adapted to the natural conditions of the non-chernozem zone. The apple tree can take root on the irgahowever, in some cases, the apple tree as a scion may be thicker than the irrigated rootstock, which can contribute to the fracture of the tree.
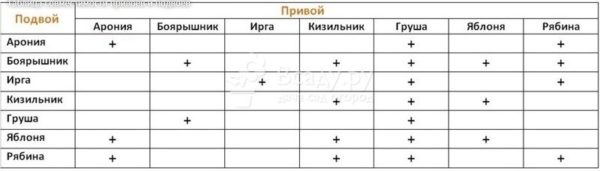

Scion and rootstock compatibility.
Variety selection
There are many types of rootstocks, and each has its own characteristics.
Dwarf
Dwarf ones have a superficial root system that is weakly attached to the soil layers, so they are unstable to drought and demanding on the condition of the soil. It is recommended to grow such trees on lands where groundwater passes high enough.
Saplings on dwarf rootstock varieties grow intensively and begin to bear fruit by the third year. These include:
- M8 is the lowest of the dwarf varieties, but also the earliest. Poorly tolerates drought and easily breaks under the weight of apples and snow in winter;
- M27 - rarely found in gardens, because has very fragile wood and requires careful maintenance, has a small crown, so the yield is low;
- M9 is compatible with all varieties, therefore it is popular among gardeners, apples grow early on it, yield indicators are high, refers to long-livers (average age is about 20 years), is drought-resistant, but picky about the quality of the soil, does not grow on sandstones, clay and heavy soil;
- D1071 - the result of M9 and Anis crossed among themselves, it is distinguished by high yield and moderate height; unlike other "dwarfs", it can endure short-term drought and slight frosts without consequences;
- 62-396 and 63-396 - clonal dwarf rootstocks are the most common in central Russia, any scion increases winter hardiness, grafted on a 62-396 variety will provide fruiting already for 2-3 years after planting, and from 63-396 yields 40 -50% higher than the popular M9.
Read also: We are going to live in the village
Semi-dwarf
Semi-dwarf varieties are more convenient for grafting procedures and breeding garden crops. The apple trees obtained on them are less demanding for watering and can grow without supporting structures, because they are more resilient due to the branched root system.
We started grafting apple trees on semi-dwarf rootstocks with M-2, M-3, M-4, M-5 and M-7. Having poor rooting, they soon lost their popularity, giving way to new rootstock varieties.
Today, the semi-dwarf variety MM-102 is widely used - the result of M-1 and the Northern Scout crossed among themselves. Shows good compatibility with all species, planting fast-growing and high-yielding trees. It has average indicators of frost resistance, withstanding a drop in temperature to -10 ° C.
Branched roots tolerate short-term drought without consequences. However, this species “does not like” waterlogging, waterlogging and grows poorly in lowlands.
Estonian developments E-56 and E-63 showed good results in the harsh conditions of the Urals with significant changes in winter and summer temperatures and the absence of precipitation. On infertile soils, they produce trees with strong wood and good rooting, which can withstand frosts down to -17 ° C. Fruiting occurs at 4-5 years.
Medium-sized
Medium-sized ones do not differ much from semi-dwarf ones and are also the best option for vaccination. However, they are much better adapted to the Russian climate, withstanding low temperatures. They do not immediately begin to bear fruit, but they give high yields. Among them:
- MM-104 is the result of crossing M-2 with the Northern Scout, a mid-season stock on highly fertile soils can grow to the height of a vigorous apple tree, seedlings on this stock begin to bear fruit early, but this affects the amount of harvest;
- MM-106 is a high-yielding rootstock variety, which produces trees with increased frost resistance;
- A-2 is similar to MM-106, has a deep-rooted system;
- M-111 - suitable for regions of the middle zone with a fairly warm climate;
- 54-118 - the result of Russian selection, bred for the harsh Siberian climate, compatible with most varietal species, begins to bear fruit from the 3rd year, the 54-118 root system is well developed, which allows trees to gain a foothold in the ground without additional supporting structures, apple trees on it take root quickly and immediately begin active growth, showing intense fruiting in the future.
Planting apple trees
Row spacings and aisles should be kept in consideration of the vigor of the variety and rootstock and the type of seedling. In addition, the planting pattern can be different in different climatic zones.
For example, in the non-chernozem zone:
- It is recommended to plant vigorous trees on seed stocks according to the 6x4 m scheme,
- On intercalary rootstocks 5x3 m,
- On clone 4-5x2-3 m.
In the southern zones of Russia between trees on dwarf rootstocks, it is recommended to leave 1-2 meters in a row.
The scheme for planting apple trees on a rootstock mm 106 recommends planting according to the scheme 4.6 x 1-1.5 m.That is, with a row spacing of 4.6 m and with distances between trees in a row from 1 to 1.5 m.
Correct fit and placement depth. If you did the vaccination yourself, then the planting rules will depend on how deep your groundwater is. When standing close, landing on a knoll is recommended.
Useful videos:
Watch a video on the correct planning of an apple orchard:
Watch the video for professional tips on planting apple trees:
For a normal planting, it is recommended to prepare a planting hole with a width of 50 to 80 cm and a depth of 50-60 cm, depending on the texture of the soil and the size of the root system of the seedling.
In this case, the root collar should be at a height of 5 cm above ground level on the site. The vaccination site, respectively, should also be above the ground.
What is a stock for an apple tree
The rootstock is the part of the plant located under the graft, that is, the entire root system and part of the trunk. The well-known Russian scientist breeder IV Michurin called the rootstock the fundamental basis of the plant.
Pay attention! The strength of growth, the beginning of fruiting, as well as cold resistance and resistance to diseases and pests, that is, almost all the individual characteristics of the tree, will depend on the quality of the stock.
Planting and leaving such apple "curiosities" is somewhat different from the classics.
The stock for apple trees has a list of advantages, and this is the reason for its popularity in recent years:
- trees begin to bear fruit after 2-3 years;
- the height of an adult tree does not exceed 2-2.5 m, undersized;
- the root system of apples readily responds to watering and feeding;
- due to the short stature, the fruits, falling to the ground, do not break, which greatly simplifies the harvesting process;
- due to the good illumination of any part of the crown of the tree, a high concentration of ascorbic acid and sugars accumulates in apples;
- apple trees on a dwarf rootstock are not afraid of the close location of groundwater to the earth's surface and are unpretentious to the composition of the soil.
However, do not forget about the shortcomings, which, unfortunately, also exist:
- shorter tree lifespan;
- some varieties of low-growing rootstocks are characterized by poor frost resistance;
- there is a predisposition to crop overload, which leads to crushing of the fruits and deterioration of their quality.
How to harvest apple grafts?
For cutting cuttings, you should know some rules:
- As the mother tree (or trees), you should choose those that are checked for belonging to the variety and yield;
- For cuttings, ripe annual stems (shoots) should be chosen;
- They must be chosen from the outer part of the crown, preferably facing south;
- It is better to cut the stems from the middle tier shoots;
- It is better to cut the stems in the second half of November or in the first days of December, the main thing is that they do not have signs of freezing;
- Cuttings are best made from powerful growths., the length of which is 40 cm or more, and the thickness is close to the pencil one.
Storage principles should be determined by the weather and climatic conditions of your area.
For example, in areas and edges where there is a lot of snow, it is recommended to store the stems in snow piles under a layer of snow 50-70 cm.
If there is little snow in your area or little has fallen by the time the scions are prepared, then the cuttings can be stored for a short time in the lower compartment of a conventional refrigerator.
In this case, it is recommended to cut the harvested shoots into 30 cm pieces and put them in a plastic bag, shifting them with wet peat, moss or sand, then close the bag hermetically.
IMPORTANT! In this case, the internal temperature of the refrigerator should, if possible, be 1-2 ° C.
Long-term storage of cuttings is not possible at other temperatures. In addition, cuttings should be checked frequently for the possible appearance of swollen buds (danger of premature awakening) and mold damage.
Watch the video for important information on how to prepare cuttings for further grafting:
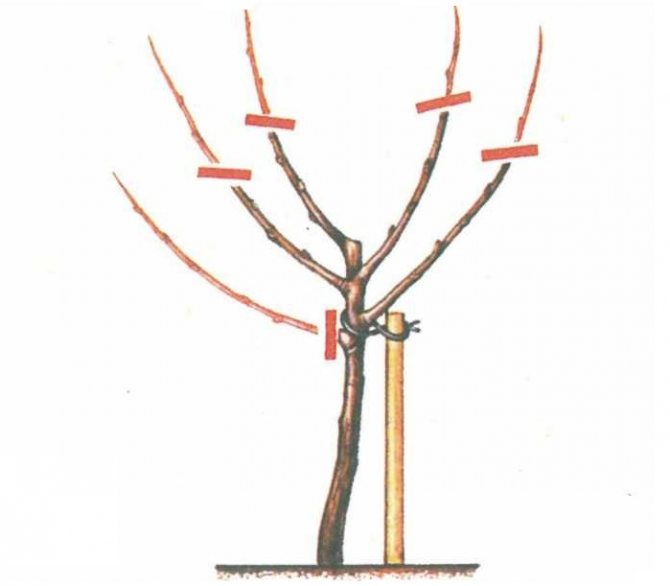
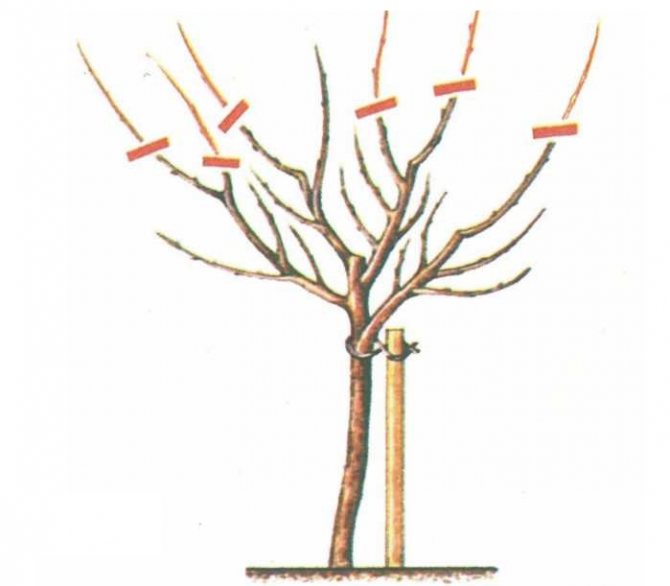
Apple tree formation
To grow a healthy and abundantly fruitful tree, you need to regularly carry out sanitary pruning, thanks to which the correct crown shape is formed.
Pruning for crown formation
After planting for the first year, the seedling builds up its root system.Numerous studies have shown that in the first year, the diameter of the root ball increases by approximately 35-40 cm, and the total length increases by 9-10 times.
In order for the branches to grow evenly in all directions, the upper conductor must be shortened by a quarter of the total length, thanks to this, the growth of the lateral branches will be stimulated.
You should pay attention to the uniform growth of branches throughout the crown. From thickened areas, you can bend the branches to bare ones and fix them; in a few weeks or months, the branch will remember the new direction of growth.
Important! Pruning adult trees consists only in thinning, as well as removing damaged, frozen and non-fruiting branches. Fat shoots should be cut off as soon as possible after they have formed.
Columnar apple trees
They are a separate apple culture with a very compact crown. Small-sized trees. They take up little space and therefore have become of considerable interest.


Important aspects of caring for columnar apple trees for an excellent harvest.
The following varieties are known as columnar:
- Vasyugan,
- Dialogue,
- Baby,
- Arbat,
- The president,
- Nectar.
The last 3 varieties are most widespread in the Non-Chernozem zone.
Below are their characteristics:
- Nectar. This is a summer variety, possessing early maturity. The trees are able to withstand frosts down to -42 degrees. Fruit weight varies from 100 to 140 grams. They taste sweet with a honey aroma. Maturity occurs by the end of August.
- The president. Early winter variety... Fruits taste sweet and sour, dessert, weight up to 250 grams. Productivity is 5-6 kg per tree. Fruit ripeness occurs in mid-September, and the shelf life is 1.5 months.
Varieties for the Yaroslavl region
In the Yaroslavl region, severe climatic conditions are observed, therefore, preference should be given to frost-resistant varieties. The fruits are usually small. The best varieties to grow in this region:
- Persian is a winter variety, the weight of each fruit does not exceed 150 g. Trees are able to withstand temperature drops down to -40 ° C. Poor scab resistance (fungal disease) is noted.
- In the local area, the Zhigulevskoye variety, which is also grown in the Moscow region, has shown itself well.
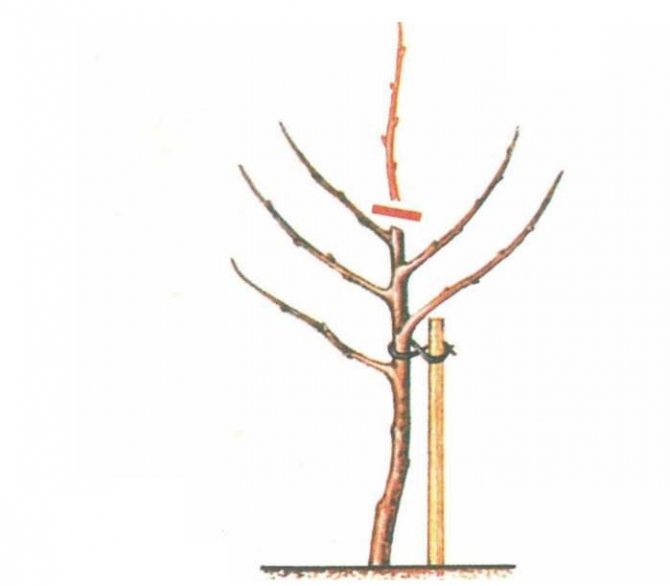
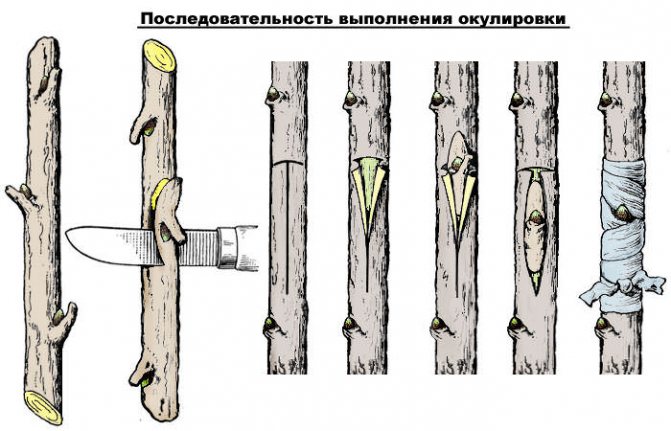
How to graft grafts?
Grafting of varietal material on rootstocks can be carried out using different methods.
In spring it is usually recommended graft grafting of the following types:
- Copulation,
- Cleft grafting,
- Grafting for the bark.
Copulation recommended in cases where the diameters of the rootstock and scion are the same or close. To carry it out, oblique cuts with a length of about 2-3 cm are made on the rootstock and scion.
The method has two options: simple and improved..
With simple copulation, the scion stalk is simply applied with the usual cut to the cut on the rootstock. Improved copulation implies a tongue-shaped notch on the cut surface.
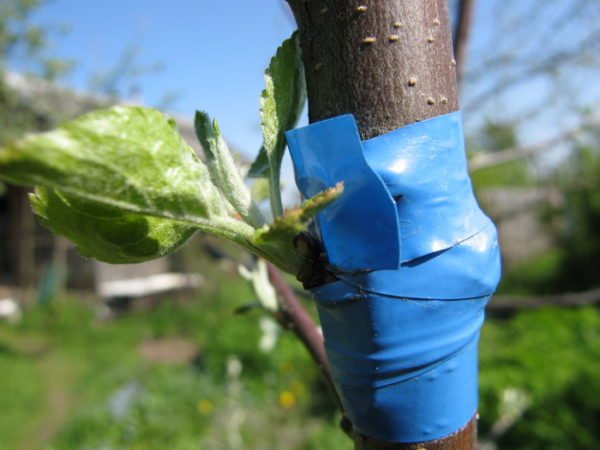
After combining the rootstock and the scion, the grafting site should be covered with pitch and tied with a film, PVC is best suited for this, sometimes it is possible to inoculate with electrical tape, as well as with modern Rostock and Svetlitsa films.
TIP! Spring grafting with a graft should be done before budding on the graft.
Watch the video for helpful tips from experienced gardeners on how to properly vaccinate:
Grafting for the bark and in the cleft recommended in cases where the rootstock diameter is greater than the diameter of the grafted cuttings.
For bark grafting in the bark of the rootstock, a cut should be made with a length corresponding to the cuts on the rootstock, about 2-3 cm, and on the graft of the scion, the same cut should be made as in copulation and inserted into the cut of the bark on the rootstock.
Thereafter cover the wound with pitch and wrap it with washcloth or PVC film... When grafting into the split across the cut, an incision is made on the rootstock, into which a wedge-pointed scion stalk is inserted. After that, the vaccination site is also smeared and wrapped.
Stock - what else do you need to know?
So, you want to plant an apple tree in your summer cottage, the variety of which you really like. If you just throw a seed into the ground, the chances are high that the fruits of the new tree will be small, sour, or even unripe. But you want to harvest those incredibly delicious apples! In this case, vegetative propagation of your favorite variety will come in handy, which will allow you to preserve all its properties.
Delicious varietal apples in the wild - it's real
Thus, you take a cutting from a tree of your favorite variety, for example, sweet Golden Delicious, and graft it into a stock that is more resistant to weather conditions and diseases. The result is a tree with the desired sweet and juicy fruit.
A stock is a plant (or part of it), to the stem or root system of which is grafted scion (a stalk or part of it with a bud of a plant of the variety you need). The rootstock plays a very important role: it provides adequate nutrition for the upper part of the plant, i.e. scion.
Read also: Scissors for cutting bushes
How to grow rootstocks?
Weak rootstocks, both apple trees on dwarf rootstocks and semi-dwarf ones are more often propagated by layering, less often by cuttings, for example, lignified.
For most rootstocks, the yield of seedlings is greater when propagated by layering..
However, rootstock 54-118 has a higher rooting rate with woody cuttings than other rootstocks.


Rooting of apple rootstocks.
Consider methods of obtaining and breeding low-growing rootstocks, including 54-118, M106 and others:
- To obtain vertical layers, a mother bush should first be grown. For this purpose, two-year-old seedlings must plant on a site with deeply cultivated soil... Before the start of frost, trees must be covered with sawdust, or peat, or earth.
- In the spring of next year, the base of the mother plant must be carefully freed from the soil and cut off the aerial part so that the top of the hemp is 3-4 cm below the top level of the soil.
- Soon from hemp shoots will appearthat will need to be spud and watered. At the end of September, the rooted shoots must be undone and cut off from the mother plant.
Growing seed stock in a container
This method of obtaining rootstocks involves stratification of apple seeds in a cool basement or refrigerator. It is necessary to plant the seeds with the expectation that they would open by mid-March. To do this, in three to four months, all the seed material is mixed with moistened sand and placed in a cold place.


The hatched apple seeds are planted in the prepared soil. To prepare such a mixture, you will need the following ingredients:
- Decomposed peat - 1 part;
- Garden land - 1 part;
- River washed sand - 1 part.
To this composition, at the rate of 10 kilograms, add 1 glass of wood ash, and 25 grams of potassium salt and superphosphate each.
The resulting mixture is filled with peat-humus pots, which can be purchased at specialized garden stores. In addition, as containers, you can use: ordinary milk bags, plastic cups or plastic bags. The size of the container for apple seedlings should not be less than 6x6x6 centimeters. In this case, at the bottom, it is necessary to provide holes for the drain of excess water.
In each, prepared in this way, a cup is planted with hatched seeds grown for apple rootstocks. The optimal amount per cup is considered to be two seedlings. This is dictated by the considerations that one of the two sprouts will necessarily be stronger than the other. It is he who is later left for further cultivation.
Timing of fruiting
The beginning of fruiting apple trees depends both on the early maturity of the variety itself and on the strength of the rootstock growth. For example, some varieties begin to bear fruit relatively early, others rather late.
Comparatively early-growing varieties include Narodnoe, Welsey, Goldspur, Student and others. At the same time, many old varieties on ordinary vigorous seed stocks begin to bear fruit at 6-8 years (Antonovka) and later.
On weak rootstocks, the same varieties can begin to bear fruit 2-3 years earlier..
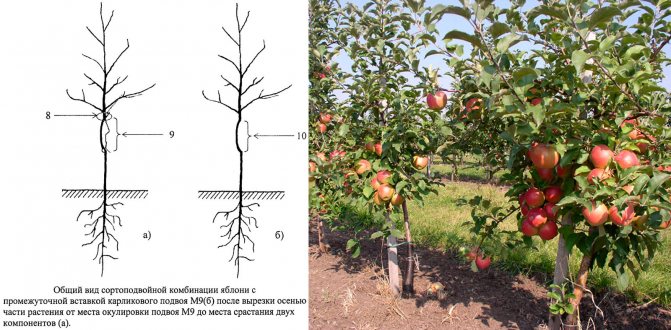
An apple tree on a semi-dwarf rootstock - what is it?
A semi-dwarf apple tree is formed after grafting to a specific vigorous variety on a special stock. Such plants reproduce in a clonal (vegetative) way. In this case, the most optimal stock for this culture is MM-106.
Read also: How white cabbage and cauliflower are processed
A semi-dwarf rootstock is understood as fruit-bearing trees, the height of which does not exceed 2 m. The crown diameter varies from 1.5 to 2 m. Despite the compactness of growth, these plants are quite capricious and capricious. The depth of occurrence is small, 0.1-0.4 m.
Pay attention! The life expectancy of apple trees on a semi-dwarf rootstock, subject to all care rules, is no more than 15 years.
Features of the dwarf apple tree


The dwarf apple tree is not a new type of apple tree. To obtain such a plant, a varietal cutting is taken, which is grafted onto a clonal dwarf stock. The resulting apple trees do not exceed 250 cm in height. The average life span of such apple trees, if properly cared for, is 20 to 30 years, while ordinary vigorous apple trees live slightly longer - from 35 to 40 years.
It happens that columnar apple trees are mistaken for dwarf trees, but these are different forms. Distinguish between medium-sized and vigorous columnar apple trees, however, there are also dwarf columnar apple trees, but this plant form does not have a crown. And in a dwarf apple tree, the crown shape is the same as that of an ordinary apple tree, only it is slightly smaller.