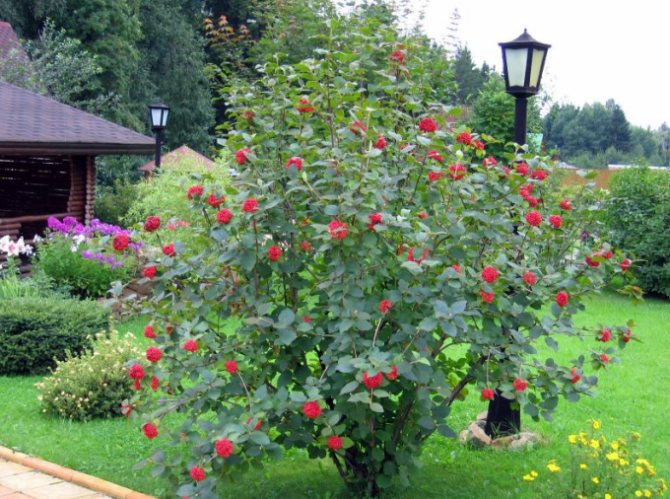
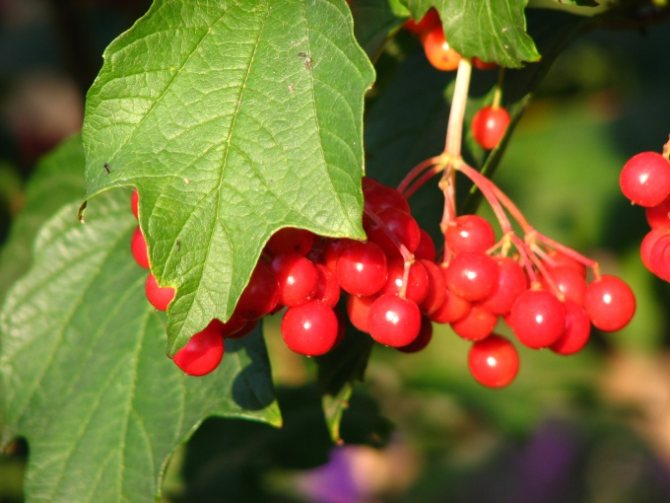
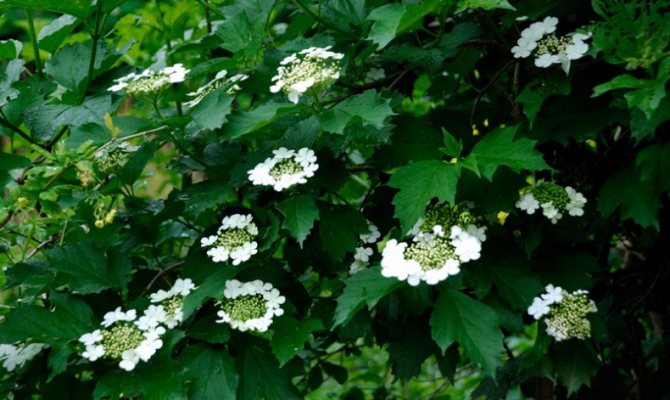
Growing viburnum on your own plot is a natural desire of any summer resident. With proper care, the viburnum bush will delight you with lush flowering in the spring, and with bunches of red berries in the fall. And the berry itself is so useful that you just need to have it on your site. Moreover, the reproduction of viburnum does not require any special efforts and knowledge.
How to grow viburnum
The plant loves partial shade, choose a place where the sun does not shine on it all day. It grows in a large bush, it is used to disguise unsightly master buildings. A bush is planted at a distance of 2-3 m from other plantings or a fence. Reproduction is best done in the fall, when the leaves on the trees have fallen, but the frost has not yet come.
Representatives of the Adoksov family take neutral and slightly acidic soils well. But soils of peat, podzolic, sandy type are not suitable for them. It is also important that the groundwater lies no less than 1 m from the place where the tree is grown.
Viburnum propagation can be done in several ways:
Viburnum can be diluted with berries, but it is not a fact that the harvest will be as large and abundant, the seeds do not convey all the properties of the mother plant.
Propagation by cuttings
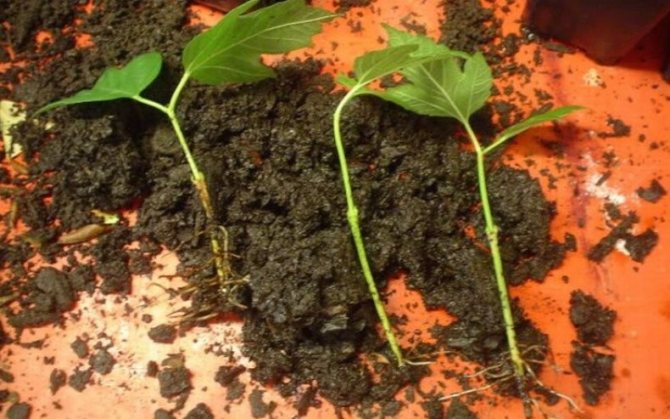
Cuttings are planted in spring or fall. When pruning a bush, remove unnecessary branches. Do not throw them away, but cut them off, leaving 3 buds on the shoot. Stick a few cuttings in a shaded area, cover with a 5 liter plastic bottle.
Green (young) shoots are planted in the summer when they reach a height of 15 cm. They are broken out with a heel. Plant in the shade, water, cover with a bottle. The cuttings will definitely grow back.


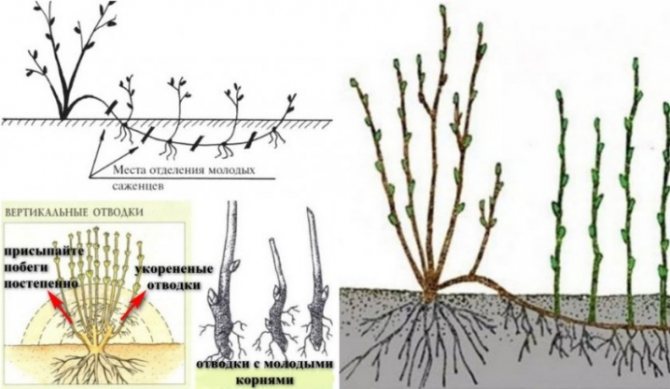
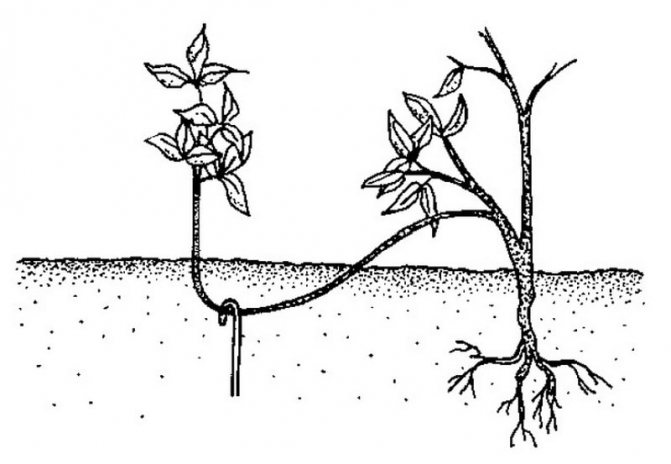
Reproduction by layering
Tilt the branch. From the place of the proposed rooting, count 3 buds and cut the branch. Pin the branch so that it touches the ground. Put cardboard, plastic under the twig, and a stone on top. How to do this, see this video.
Planting viburnum from a container
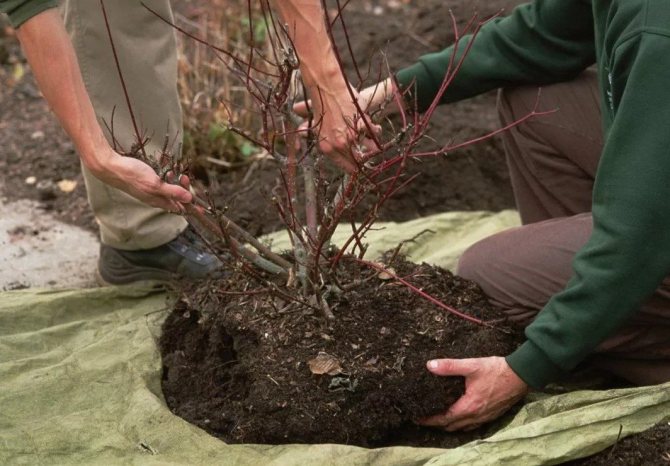
Now flower shops sell ready-made bushes in containers. How to plant them correctly on your site?
We find a shaded place where the viburnum bush will constantly grow. We dig a hole with a diameter of 60 cm, and to the same depth, you can even a little more. Add 1 bucket of rotted compost to the pit, mix it with earth so that the young roots do not burn. Embed the root collar a little, 5 cm below ground level. Over time, the ground will settle down, and the root collar will be at ground level.
We put the bush neatly in the prepared hole, pour abundantly with water. Pour out gradually at least 1 bucket of water. When the water is completely absorbed, cover the near-trunk hole with earth. Cover the soil near the planting with bark.
Further care
Proper care of it will help to grow a lush viburnum with excellent fruiting from a seedling. Full development will be ensured by sufficient moisture and fertilization, as well as preventive measures against diseases and pests. And in the future - regular pruning.
The shrub is hygrophilous. In the summer, in the evenings, seedlings need abundant watering. And the older they are, the more water will be required.
An adult bush can do without feeding. But for the better development of the seedling and increase the future yield, you need to use them.It is advisable to carry out top dressing together with mulching with sawdust.
Spring nitrogen fertilizers are applied before the leaves bloom. In the summer months - any mineral complex. In the fall, when preparing for winter, the bush is fertilized with a phosphorus-potassium mixture. The next autumn feeding with manure solution or potassium-phosphorus fertilizer is carried out 2 years after breeding, during watering or when digging up the soil.


The shoots must be protected from pests: aphids, leaf beetles, cap moth and comma-shaped scabbard. If necessary, plants should be treated with insecticides before bud break. The use of insecticidal plants is perfect: horse sorrel, dandelion, bitter wormwood.
In high humidity weather, young shoots can be attacked by a fungus. These are various types of rot, spotting and powdery mildew. Spraying with fungicides will help. You can process seedlings with folk remedies throughout the season. For example, solutions of household and tar soap with the addition of soda, tobacco, ash. In case of severe damage, the seedlings are treated with a Bordeaux mixture.
Preventive measures consist in the regular removal of weeds, loosening of the soil cover and the root zone of the seedlings.


For information on how to propagate viburnum by cuttings, see the next video.
Decorating the site with a beautiful bush or small tree is a common thing for gardeners. There are many factors to consider: from soil condition to maintenance. But the process of division and landing still remains decisive. Let's see how you can propagate viburnum.
Viburnum bush care
What is done to make the bush lush and the harvest abundant?
- Kalina needs to be protected from pests. In late May - early summer, a black aphid appears, it sticks to all the shoots and buds, sucks out all the nutrients from them, so there are few berries, and they are small. At the same time, a viburnum leaf beetle appears, it eats leaves so that only petioles remain.
To get rid of pests, the plant is treated before flowering with insecticides - Intavir or Iskra. 1-2 treatments will be enough to get rid of sucking and leaf-eating pests. It is important to inspect the bushes in order to identify insects in time.
- Viburnum is a very moisture-loving plant. Therefore, it is imperative to water in the summer. In the heat, 1 bucket of water is poured under a young bush, 2 buckets under an adult, at least 1-2 times a week.
- Form a bush, cut it off in time, do not let it thicken. A dense bush does not provide enough nutrition for all branches, as a result, fewer berries will grow.
- Top dressing of the bush. In the spring, nitrogen fertilizers are added, they cause good growth of the ovaries. In the fall, the bush is fed with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. This allows the plant to overwinter well and lay the buds for the next year.


Dear readers, plant viburnum in your plots, it is so beautiful, and the benefits of viburnum are very great. No wonder folk recipes from viburnum have been used for many, many years.
Dear Readers! Thank you for visiting me! I would be glad if you share in the comments your experience in growing vegetables, methods of combating plant diseases and pests. If you liked the article, please share this information with your friends. Please click on the social buttons. networks that are to the left of the article. I will be very grateful to you.
I really hope that we will communicate with you for a long time, there will be many more interesting articles on the blog. In order not to miss them, subscribe to the blog news. Good harvests to you!
We propagate the viburnum
Kalina is propagated dividing the bush, root suckers, horizontal layering, cuttings
or
seeds.
Do you want to have a viburnum in your garden? To do this, it is not necessary to go to the nursery or climb to a neighbor at night in order to dig up a shoot from his bush.Our mixed forests are full of the usual, so to speak, wild viburnum. Birds peck berries, seeds are spread at different distances, then young plants grow from them. Several times, when I went to the forest to collect raspberries (in August), I saw small viburnum plants. Since they grow on very wet soil, you don't even need a shovel to dig it out - you just pulled gently on the stem, and now the root is on the surface. The main thing here is not to dry out the root system during transportation. Since it was not far away for me (no more than half an hour), I used a regular plastic bag, in which I wrapped the root system of the seedling. You can take the exact same plastic bag, but put some earth in there and take a bottle of water. Dip the roots of the dug out plant in a bag, cover it with earth and water it so that it is moist. In this form, the viburnum will last even a day.
Do you want a forest viburnum? Welcome to the store - what varieties are there just not: Zholobovskaya, Zarnitsa, Red bunch, Ulgen, Garnet bracelet, Maria, Shukshinskaya.
There are even sweet-fruited varieties, for example
Red coral.
To divide or not to divide?
If you already have viburnum growing, then you can propagate it by dividing the bush, of course, provided that it is not very old. This is purely theoretical. In practice, it is unlikely that any gardener will sacrifice the only fruiting plant in the hope of getting some seedlings from him, which will bear fruit only after a few years. Usually, one or two shoots with a root system are simply separated from an adult bush (chopped off with a shovel). They look at their proportional ratio: if the root ball is very small relative to the crown of the new plant, then the stems are cut so that after planting in a new place the shoots do not experience a nutrient deficiency due to an undeveloped root system.
It is best to breed viburnum in autumn or early spring, when all vital processes in the plant are either greatly slowed down or have not yet been activated.
Root offshoots of viburnum take root very well in a new place. And there is a very simple explanation for this: the root shoot, as a rule, is very small, it also feeds on the mother plant, since it is associated with it, and at the same time it builds up its own root system. Root suckers grow at some distance from the main bush, therefore, when they are separated, the plant itself does not suffer, as happens, for example, when dividing a bush. To dig up a root shoot, you just need to chop off the common root and carefully transfer the plant to a new place with a lump of earth, water it well - and literally in a week the seedling will feel quite comfortable. It is most reliable to propagate viburnum with root shoots in early spring, while the leaves have not yet blossomed.
The viburnum has rather flexible branches, so this method of reproduction, such as dropping in shoots to obtain rooted horizontal layers, is great for it. If the viburnum bush has a young shoot, then it can be rooted. Strong annual shoots take root best. A groove with a depth of 10-15 cm is dug in the ground, a shoot is laid in it (you can first furrow it from the bottom along the internodes and dust it with some substance that stimulates root formation). The laid stem is pinned, leaving the crown above the ground, and covered with fertile soil.
During the summer, the cuttings are watered, earthed, and weeds are removed around. By autumn, it will take root, it can be separated from a large bush and transferred to a specially prepared place for growing. If the branch was not very young, and the process of root formation was slow, it is better to leave everything as it is, until spring or even autumn, and only then separate the resulting seedlings.
If the viburnum does not have young shoots, one of the branches (not older than 4-5 years) is cut off in the spring on a stump, leaving several dormant buds. Over the summer, renewal shoots grow from these buds.
The next year, in the spring, they are slightly shortened to stimulate the growth of lateral shoots, they are bent to the ground and laid in shallow grooves (about 5 cm), pinned tightly enough, but they are not covered with earth.
When the first shoots appear, they are slightly hilled and as they grow, the hilling is repeated so that by autumn each shoot has its own root system, and it can be separated and transplanted to a prepared place.
You can also use the traditional technology, in which an uncut branch laid in a deeper groove (10-15 cm) is pinned and covered with earth. In this case, the crown should stick out above the ground level. To stimulate the process of rooting, you can make a ring cut in front of each internode on the part of the shoot that will be underground, and dust them with heteroauxin.
The method of obtaining vertical layering is no less simple in the implementation of the propagation technology. In this case, annual shoots (the action takes place in the spring) are not bent to the ground, but left in an upright position, only huddled several times per season, so that the result is a mound with a height of at least 20 cm.The earth must be constantly kept moist. To stimulate rooting, an annular cut is made on the stem at the very bottom - at ground level - and this place is treated with a rooting machine and immediately spud. Or, under the lowest kidney, they make a constriction with aluminum or copper wire.
Organic fertilizing will stimulate the growth process, including the roots, and in this case will only benefit. By the end of the season, if everything was done correctly, there is a hope of getting self-rooted seedlings, which are separated from a large viburnum bush and transplanted to the place where they have to grow up for another year before they are planted in the garden.
There is an option of obtaining a seedling with its own root system directly on the branch of the mother plant. We choose a thin (preferably last year's) shoot, retreat from its upper part 25-30 cm and do ringing - a cut along the ring of a section of the bark with a width of 0.5 to 1 cm (under the kidney).
These works are carried out no later than June, otherwise the cuttings will not have time to take root before winter.
The cut can be treated with root stimulants. Instead of banding, you can use a soft wire tie of the shoot. Along the entire length (from the crown to the ring or wire waist), we cut off the side branches and leaves.
For rooting, we use humus earth or sphagnum moss. I would prefer moss - it holds moisture and is a good antiseptic. But the moss must be moist. If it was harvested a few days ago, it is better to soak it in water overnight. In the morning, lightly squeeze out excess moisture so that it does not flow down your hands, and make a dense lump of two handfuls of moss - try to roll it into a ball about 10 cm in diameter.Then stretch it a little so that you can wrap the stem around. The moss is tightly pressed to the shoot and fixed with a black film that wraps around the moss and is tightly tied on both sides or wrapped with tape and tape around the shoot. Air should not enter the constructed structure. The black film retains moisture and maintains an elevated temperature in the rooting site - it creates optimal conditions for root formation.
In mid-September (the latest date!) Shears cut off the layers below the film, which is carefully removed. The moss can not be removed so as not to damage the roots, but only slightly stretch it with your hands to make it looser, give more air and freedom to the growing roots. The seedling is planted in fertile soil and grown for another year.
Rooting cut shoots of viburnum
You can also try this method of obtaining additional planting material, such as rooting cut shoots.They are separated from the mother plant in early spring, before bud break. Then they are laid in grooves dug obliquely, so that the lower part of the shoot is below the surface of the earth at a distance of 15 cm, and the upper part is within 2-5 cm.They are covered with fertile soil, watered from a watering can with a fine spray, and straw is laid on top or hay to keep the soil from drying out. Watering is carried out daily.
When the shoots appear, the shelter is gradually removed, accustoming the seedlings to the natural growing conditions. The percentage of rooting in this way is low, but, nevertheless, there is a chance to get at least one seedling. I would not specially cut off the shoots so that they can be rooted later (although I do not mind a couple of branches for the experiment), but if the viburnum bush was pruned and formed and you still have unnecessary branches that you still throw away, why not try?
Viburnum, like many other shrubs, reproduces well by cuttings. But the best rooting rate is given by green cuttings, and not lignified ones. Cuttings are harvested in June (flowering period) from the middle of the shoot. Each stalk should have 2-3 nodes, an oblique lower cut under the internode and a straight cut above the upper bud within 1 cm from it. The lower leaves are completely removed, and the upper ones are shortened by half. The cuttings are treated with stimulants (using powder or soaking solution) and planted in the ground. The soil mixture is prepared from equal parts of sand and peat. Depending on the number of rooted cuttings, they use a special greenhouse under film or glass, or choose a place in the shade, but with fertilized soil, and plant the cuttings in open ground under cans or plastic bottles. Caring for viburnum cuttings is the same as for any others. The main thing is warmth, high humidity and lack of direct sunlight.
For the winter, young seedlings are covered so that they do not freeze, but they are transplanted in the spring if they grow in a greenhouse. Cuttings planted separately under banks can not be touched - they have enough space, so let them grow up for another year. And then the already formed plant is transferred to where it is to grow.
Sowing viburnum seeds
By sowing seeds, non-hybrid forms of plants are propagated. Ordinary viburnum can be grown from a seed, but the percentage of seedlings will not be very high: from 20 to 60% of the number of seeds sown.
You can sow seeds both in autumn and spring. For spring sowing, seed stratification is required - they are mixed with sand and stored in the refrigerator until spring. But in both cases, seedlings will appear only after a year.
To deceive nature and get earlier shoots, gardeners have come up with a cunning method. The seeds extracted from the fruits are mixed with wet sand, poured into a container and stored in an apartment at room temperature for two months, and then sent to the refrigerator on the lower shelf. After such storage, the seeds are sown in April (as the soil thaws), and they will sprout in the same spring. The seedlings will have to be cut once, so that they are more evenly distributed over the area of the garden (approximately at a distance of 10-15 cm from each other). And then grow in one place for at least two years. Viburnum, grown from seeds, enters the fruiting period no earlier than 5-6 years later.
Unless you are obsessed with the idea of growing viburnum from a seed, it is better not to use this method. It is troublesome and takes a long time to get a good seedling. And it will take several years to wait for the first berries from him.
Viburnum is undemanding to growing conditions, but it grows and develops best on light fertile soils with a neutral reaction. A planting pit is made 50 × 50 cm, filled with rotted manure or humus, mineral fertilizers (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) are added by handfuls, everything is thoroughly mixed, a seedling is planted, watered, and mulched on top so that moisture evaporates less.
To get good yields of viburnum, 2-3 bushes should be planted nearby at a distance of 3 m from each other. Young plants need regular feeding: in the first half of the season, nitrogen fertilizers or organic matter are applied, in the second - phosphorus and potassium fertilizers. With the entry of the plant into the fruiting period, the amount of nitrogen fertilizers is reduced.In the spring, the buds have not yet blossomed, but the earth has already thawed, 2 tbsp is scattered around the entire perimeter of the trunk circle. l. urea. Fertilizer is embedded in the soil, loosening it.
The second complex feeding is carried out before flowering, and the third - after the flowering of the viburnum. Use nitrate, superphosphate at the rate of 30 g per 1 sq. m before flowering and nitrophosphate and potassium salt - after the plant has faded.
In the fall, potassium salt, superphosphate are introduced, on acidic soils, 300 g of lime are added, if possible, then they spread manure under the bushes in about a bucket.
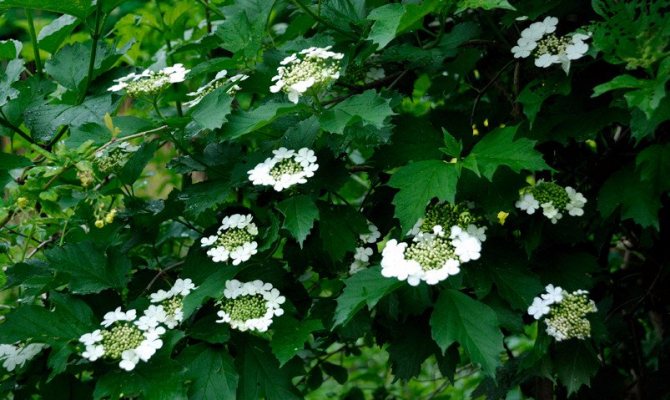
Along with the common viburnum, decorative terry viburnum began to appear in our gardens Buldenezh.
It is unusually decorative in spring: small white flowers are collected in dense spherical inflorescences from 8 to 12 cm in diameter, which cover the entire bush, turning it into a lacy cloud for almost two months.
Terry viburnum
also loves moisture, like her sister, but does not tolerate shade. Grows well and blooms in open sunny areas. For the rest, the methods of vegetative reproduction and agricultural techniques for growing these plants are almost identical. But the decorative viburnum requires a little more attention, even in terms of pruning the bush. The usual viburnum is especially not formed: weak, sick, broken or very old branches are cut out.
Buldenezh
with the help of trimming, you can give any shape at all. Pruning is carried out after flowering, all thin branches growing inside the bush are cut out, usually leaving 5-7 skeletal branches.
The viburnum has a very aggressive enemy - the leaf beetle, which eats the leaves, leaving only streaks. The invasion of this pest greatly weakens the plant, it gives small growths, blooms poorly and bears fruit the next year.
From viburnum leaf beetle and aphids, spraying is carried out before flowering. They use special preparations for this, sometimes they still recommend karbofos, but not everyone knows that this drug is prohibited for use in personal subsidiary plots. The fact is that it is able to accumulate in the soil, and therefore there is a risk of developing cancer in people who will eat vegetables and fruits grown on this land.
By the way, always be careful about what you use in your garden and in the beds. If you do grow something, then make these products safe for you and your family.
There is Federal Law No. 109-FZ of 19.07.1997 “On the Safe Handling of Pesticides and Agrochemicals”. According to this law, the circulation of pesticides and agrochemicals that are not included in the State catalog of pesticides and agrochemicals permitted for use on the territory of the Russian Federation is not allowed. In accordance with SanPiN 1.2.2584-10, pesticides registered in the State Catalog under the letter "L" can be used in personal subsidiary plots.
By the way, the well-known and often used on garden plots for weed control Roundup, BP is not included in this Catalog and, accordingly, is not allowed for use. In the State Catalog, you can also find plant growth regulators, pesticides, insecticides, herbicides, repellents, etc. approved for use in garden plots.
Returning to the pests of viburnum, I note that you can fight them not only with chemicals, but also with other means, for example, spraying with an infusion of hot pepper (1 kg of fresh chopped fruits or 0.5 kg of dry fruits per 10 liters of water). Another effective remedy is tobacco infusion. 0.5 kg of makhorka or tobacco leaves (who grows) is infused in 5 liters of water for 48 hours. Then it is filtered and the resulting product is diluted with water (1 part of the infusion for 4 parts of water). For better adhesion to the leaves of the plant, add 40 g of either liquid or grated ordinary soap and spray.
Able to scare away the viburnum leaf beetle and garlic solution (300 g of garlic are chopped, pour 10 liters of water).Spraying with this folk remedy also gives a good result.
If you alternate spraying the viburnum with infusions of pepper, garlic and citrus peels, then leaf-eating pests will have no chance. Tincture from the peels is prepared in this way: take 1 kg of fresh peels of orange, tangerine, lemon, grapefruit (you can all together, or you can do something alone), pass it through a meat grinder. This amount is enough to prepare one bucket of infusion: 1 kg of crushed crusts goes to 10 liters of warm water. The mixture is infused in a dark place for three days and then filtered. It can be sprayed on plants at intervals of about a week.
The viburnum leaf beetle lays eggs in young juicy shoots so that the larvae have enough nutrition. By the fall, these damaged twigs dry up. They must be cut and burned. In the spring, you should inspect the viburnum bush and, having found such branches, be sure to remove them. Thus, timely preventive spraying and mechanical harvesting will help you defeat pests.
<2014. All rights reserved. The publication of site materials is allowed provided that links to Rural Life
Decorating the site with a beautiful bush or small tree is a common thing for gardeners. There are many factors to consider: from soil condition to maintenance. But the process of division and landing still remains decisive. Let's see how you can propagate viburnum.
Kalina: planting and care in the open field
How to plant viburnum correctly? After preparing the ground for planting viburnum, a pit is prepared for disembarkation. Its depth and width will depend on the roots of the seedlings: they must fit freely into it and not deform. A mound is made at the bottom of the pit, where the seedling is installed and its roots are straightened. After the seedling is filled up, abundant watering is carried out and the planting site is covered with mulch from peat or humus. When planting and caring for Viburnum vulgaris, it is worth considering that the distance between neighboring trees should be at least 3 m.
Cranberries: planting and care in the open field
In the second year of cultivation, the viburnum is pruned: the aboveground part of the seedling is cut off, 2-3 nodes are left to form a shrub or 1 node to form a tree. Before you cut the viburnum, it is worth remembering that the process is carried out in the spring before the first leaves appear.
Note! Since viburnum is a moisture-loving tree, it must be watered at least once a week, with a volume of water from 15 to 20 liters for each adult tree. In a dry and hot summer, watering is worth at least 2 times a week.
For a bountiful harvest, viburnum needs good feeding. How to feed viburnum? In the spring, before the growing season, nitroammofoska is introduced, and in the fall, potassium and phosphorus. Fertilizers are dug up with the soil around the tree and watered.
Viburnum is a tree that is rarely attacked by pests. However, at the first sign of their appearance, you should immediately take action. It is also worth carrying out preventive treatments in the spring.
Viburnum can suffer from the larvae of the viburnum leaf beetle or aphids. Spraying with Aktellik, Inta-Vir and other similar preparations will help from them. Usually 2-3 sprays are enough with an interval of 10-12 days. All damaged shoots and inflorescences should be burned to avoid contamination of the entire tree. If pests are found during flowering, when it is impossible to treat the tree with chemistry, you can try to wash them off with a strong stream of water from a hose.


Viburnum pruning
In recent years, cases of damage to berries by bacterial diseases have become more frequent. For example, with endomycosis, the viburnum brushes become flabby, the color and density of the berries changes. To carry out proper care of the viburnum, gardeners are advised to spray the bushes at the beginning of the growing season with a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture.
In the last couple of years, complaints from gardeners have become more frequent that they have to harvest without waiting for the first frost, after which the berries lose their inherent bitterness and acquire a unique taste.The following happens to them at the time of ripening - unripe berries in the cluster become flabby, soft, the color inherent in mature fruits changes. Symptoms are very similar to endomycosis, but laboratory analysis is necessary for an accurate answer. To prevent the development of bacterial diseases, as with endomycosis, it is advised to spray the bushes at the beginning of the growing season with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid or analogs.
Attention! By winter, a layer of humus is poured under each viburnum bush, which will protect the root system in case of snowless frosts.
For flowering viburnum, props are made to prevent heavy branches from breaking. Broken and dry sticks are being cleaned. During this period, the wood must not be treated with chemicals. After flowering, the tree must be fed.
Propagation by cuttings
This is the most effective, but at the same time, quite complex method. Agronomists know that this procedure can be carried out in two ways: "high-speed" and more measured.


- In winter, annual shoots are cut 15-20 cm in length.
- They are dipped in water for 2-3 hours, after which they are placed in a regular bag, tied and stored until spring at low temperatures. For this, the workpiece is taken out to a dry basement.
- Planting is done when the soil warms up to at least + 10 ° C to a depth of 10 cm.
- This scheme provides for planting in a row, with an interval of 10-15 cm between cuttings. At the same time, they try to place them at an angle: one kidney is above the ground, the second is exactly at the level of the ground.
- The soil is watered and compacted abundantly. Further "classic" - watering and weeding.
- In the fall, the seedlings are transferred to a permanent place.
Viburnum propagation by cuttings with further planting in spring can be done in another way. It is conventionally called "green" or scientific. Looking ahead, we note that after such work bushes grow better:
- During flowering (June - early July), green cuttings are harvested. You can take those that have already begun to grow rustic. The main thing is that they must be elastic. If, when bent, they sprung, and did not break, you were not mistaken with the choice.
- The shoot is cut with the first two buds (this is about 7-12 cm) and divided into cuttings. The lower oblique cut is 1-1.5 cm from the base of the cutting above the kidney (cut at an angle of 45 °), and the upper one is made already over the next pair, cutting straight.
- Then the lower leaves are cut off from the cuttings. The top ones can be cut in half.
- The blanks are placed in a "root" stimulator. At the same time, the tips are immersed 1.5-2 cm. The liquid should not get on the leaves, so be careful. The best drug is still "Heteroauxin" (100 mg / 1 l of water);
- Such "baths" are placed in a dark place for 10-16 hours.


- For planting, small greenhouses are prepared in a shady corner of the site. Direct sunlight is undesirable for such plantings. The optimum temperature is + 27 ° C ... + 30 ° C.
- A light substrate is laid. The bottom layer of 10 cm is a mixture of turf soil, peat and coarse sand (in a ratio of 3: 1: 1). Peat can be replaced with humus. The top layer of 3-5 cm consists of equal proportions of peat and sand (here already without "organic matter").
- Planting is done according to the scheme: 7 cm row spacing and 5 cm between cuttings. They are placed obliquely, to a depth of 1.5-2 cm and covered with a film or greenhouse frame.
- The next 3 weeks are rooting: at this time, the plant is sprayed with water 3-4 times a day. After such a time, the greenhouse is opened on one side, and after a couple of weeks the cover is removed altogether.
- Cuttings overwinter in the same place, they are covered with spruce branches or dense lutrasil. If there are no such materials, dry leaves will come off.
- In the spring, after removing the mulch, they can be moved to a permanent place. But some are left for another season. So the seedlings are finally strengthened.
- Dig deep holes, leaving a small mound at the bottom.
- A seedling is placed on it, the roots are bred to the sides. The root collar deepens by a maximum of 7 cm.The general planting pattern is 50 x 15 cm.In a couple of years, there will be young strong bushes here.


For all its laboriousness, this method has one indisputable advantage - thanks to it, you can get a large number of plants, and cuttings are accepted better.
Features of cuttings
Cutting is the best agricultural technique to preserve the varietal characteristics and decorative properties inherent in the mother plant. A feature of the grafting method is to obtain an unlimited number of planting specimens, but this is associated with high labor intensity. When grafting, winter already lignified or summer green cuttings are used. Each type of cuttings preparation has positive aspects.
The easiest way is to propagate winter cuttings. Suitable for harvesting 20 cm annual shoots, cut from the bush in the winter months. You can distinguish a one-year-old by a lighter shade of the bark.
To preserve the prepared cuttings until spring, they are pre-soaked in water for several hours. After that, wrapped in foil, they are perfectly preserved until transplanted on the lower shelf of the refrigerator.
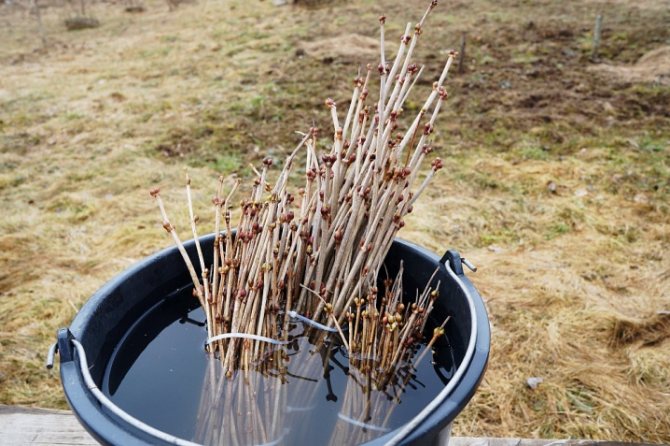


Transplantation into the ground is carried out in the spring, when it warms up well. They are planted in rows. Finish the planting process by loosening the soil around the cuttings and watering. This is done regularly, until the already rooted shoots are transplanted at the onset of autumn.
There is another technique when the cuttings are soaked for several days and then planted in the cuttings. The soil in it is moistened and covered with polyethylene. A month later, the root system will grow, and by autumn the seedlings will be ready for planting on open soil.
A more common agricultural technique is planting viburnum in summer with cuttings, harvested when cutting perennial, already faded bushes, since elastic green cuttings have the best survival rate. From a young branch, 15-centimeter pieces are cut, with two upper leaves previously cut in half. This will help reduce moisture evaporation.
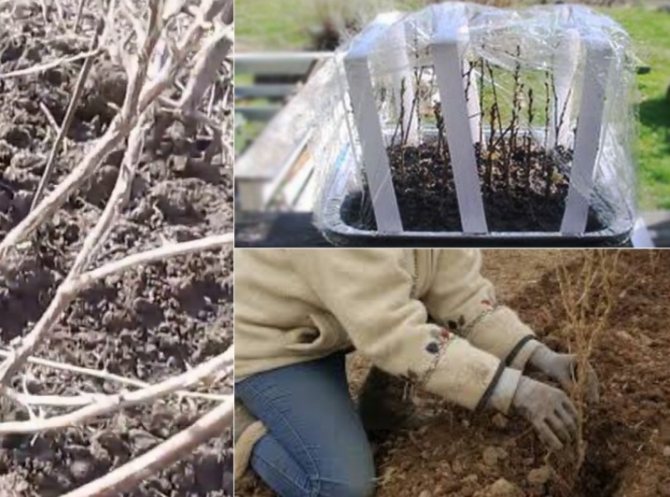


The cuttings are soaked for some time in a growth stimulator and planted in small greenhouses. Cover with foil from above. Cuttings that have released roots are gradually hardened, giving access to open air, regularly opening the film before removing it completely.
In the spring, without removing the earthen lump from the container, the shoots are moved to the garden bed for growing. After that, they are transplanted to a permanent place. Young bushes grown from seedlings will bloom only after a few years.


Propagation by vertical layers
This is a simple method that does not require extra effort:
- In autumn, the lower branches are cut on young plants, leaving 3-4 buds on them. The "trunk" is spud higher.
- In the spring, new shoots grow from the same buds. When they reach 8-10 cm, they are earthed up to a height of 4-5 cm.
- The shoots that have reached 25–30 cm are “grabbed” at the base with copper or aluminum wire and again cut to 1/3 of the height.
- After 10-14 days, the hilling is repeated.
- Until the fall, the shoots will have time to take root, then they are dug up, separated from the mother bush and planted in the designated place. It is undesirable to process the place of division: garden var or other compositions form a film on the cut that almost does not allow air to pass through.
- The landing is traditional. The hole is dug, it is moistened, the seedling is first wound up a little at an angle, digging in the root collar by 5-7 cm.
- Closer to frost, a mulch shelter is made.
As you can see, everything is simple here, no greenhouses and solutions. They are not needed for the next method on our list.
K alina: methods of reproduction
Viburnum vulgaris can be propagated by layering, shoots, simple dividing the bush and cuttings (green and lignified).
Reproduction by layering
Obtaining seedlings using layering is perhaps the simplest way that does not require much time and effort. It is held in the spring months.

For rooting, both young and perennial shoots that are located horizontally to the ground are suitable. For a perennial branch, the soil is carefully loosened to remove all weeds, and then attached to its surface using wooden or metal studs.
Young one-year-old shoots are laid out in specially prepared grooves with a depth of 3 to 5 cm. The apical bud of this shoot must be cut off, and sprinkled with leaf humus, but at the same time buds must be left free, from which young shoots will appear.
As they grow, they are huddled several times throughout the spring and summer. And in the fall, the rooted cuttings are carefully dug in and divided by the number of shoots. With this reproduction option, several seedlings of viburnum ordinary are immediately obtained.
Reproduction by shoots
Shoots or root suckers can be dug up in spring or fall. With the autumn division, it is better to insulate the seedlings for the winter. To obtain a seedling, they take a sharply sharpened shovel, and with a sharp movement separate the baby from the mother bush. It is better to leave the baby in the same place after the cut, so that the root system of the seedling develops better. If you are in a hurry with the transplant, when planting, spill the planting hole with heteroauxin, and cut the shoot in half.
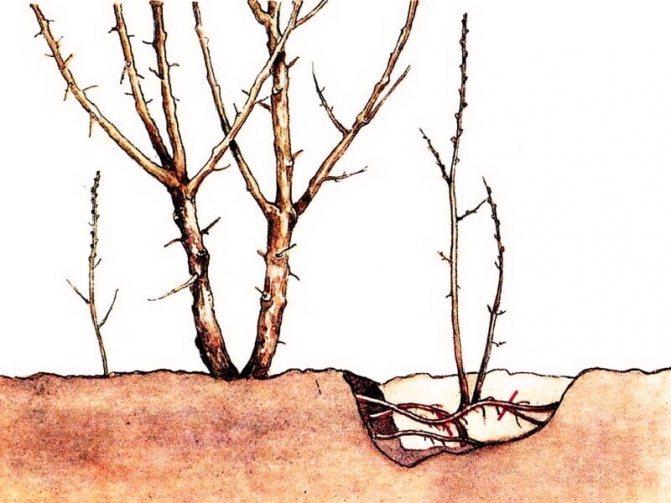

Dividing the bush
Propagating the viburnum bush by dividing the bush is still the work. To do this, the bush is dug in around the entire perimeter, and a bush with a rhizome is taken out. Then, with a hacksaw or an ax, they cut the bush in half or into several parts. When planting a delenka, a planting pit is prepared in the same way as described here.
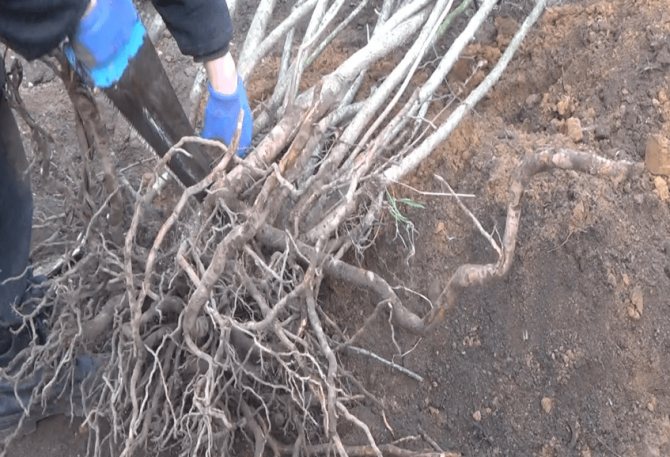


Photo <>
Cuttings
Also, quite quickly and without problems, you can get a large number of plants using green cuttings. Shoots for this breeding method are harvested at the end of flowering. In the area of Moscow and the Moscow region, it falls in June. During this growing season, the shoots begin to gradually become covered with bark and stop breaking.
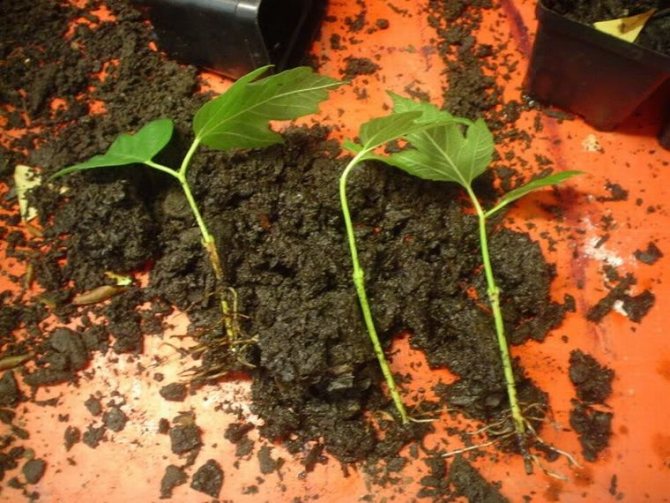


Photo
The optimum length of the cuttings is small, since it should have from 1 to 2 internodes (2-3 pairs of leaves). The leaves in the lower part of the cutting are completely removed, and in the upper part they are halved. It is worth remembering that cuttings taken from the upper part of the shoot root best.
On the beds intended for cuttings, the top layer of soil 12-15 cm high is removed. Instead, 10 cm of a mixture of peat soil, sand and turf or good garden soil, taken in equal shares, is poured. A small layer of sand (2-5 cm) is placed on top of the mixture. The beds must be covered with foil. For single reproduction, an ordinary glass or plastic jar is enough.
Before planting, the cuttings should be kept in a solution of heteroauxin (a substance that stimulates the appearance of roots) for 10-16 hours. Rooting of green cuttings takes 20-25 days. Throughout this time, the soil in the beds should be wet.
Viburnum seedlings can also be obtained with the help of lignified cuttings. They are harvested both in spring (before the buds swell) and in autumn (after leaf fall). Autumn cuttings for rooting are planted next spring, and until then they are stored under a layer of snow or in wet peat at a temperature of 3-6 degrees Celsius.
On this, perhaps, this is all that can be said to novice gardeners about the methods of vegetative propagation of viburnum bushes. We hope that our tips on how to propagate viburnum are useful to you, and you yourself will receive planting material for your site. I wish you success and excellent health!
Propagation by horizontal layers
The works begin in spring and cover two seasons:
- 2-3-year-old branches are cut from the bush (some of them also remove “four-year-olds”, but not older). A stump with 3-4 buds remains. That's all for the current year, we leave the viburnum alone until next spring.
- After a year, young shoots are cut off by about 1/5 of the entire length and bent to the soil.
- They are laid in a prepared groove (5-6 cm deep) and fastened with hooks.Please note: such layers are not immediately buried! We'll have to wait until the buds beat off shoots of at least 10 cm.
- Then the hole is covered with a substrate of humus and peat in equal proportions. The tops should remain on the surface. The first hilling is done with powder about half the height of the shoots.
- In the summer, make 2 hilling with an interval of 2 weeks. The maximum filling height should be 20-25 cm.
- With the onset of autumn, the cuttings are cut off from the main bush, and shoots are already separated from it, which by that time have become stronger and rooted. They are transplanted to another location.
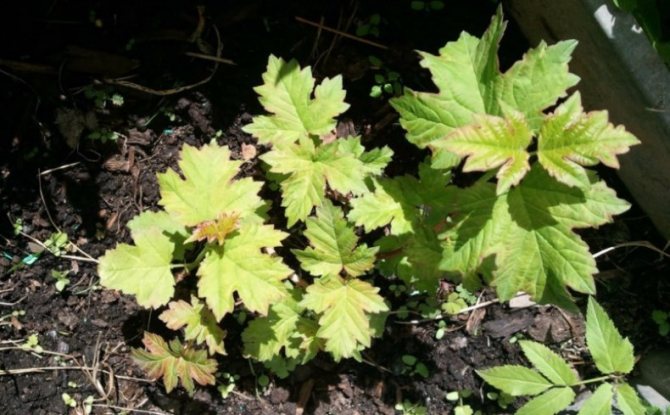


Pruning
You can prune the plant both in autumn and early spring. Kalina definitely needs sanitary and rejuvenating pruning. In addition, pruning forms the volume of the plant. Pruning in early spring each year limits the size of the shrub and increases the light in the crown. Weak diseased branches are also removed.
This is interesting: How to feed the rabbit from the moment of birth to complementary feeding
Next, the old 7-9-year-old branches are cut out, which have already borne fruit. Only strong, annuals are left. Low flowering bushes are cut completely. Stumps remain, protruding 15-20 cm above the ground. Sleeping buds give young shoots and viburnum very soon recovers.
If the plant is grown for fruit, the inflorescences at the edge of the shoots should not be shortened to avoid loss of yield.
When the bush is not cut for a long time, it thickens, loses its beauty. Rejuvenating pruning is done after the kidneys have awakened. Old branches are cut or cut with pruning shears, small hemp five centimeters long remain. Young shoots appear from the stumps. Over the summer, weak branches are removed on the shoots.


Overgrown viburnum bush, requiring pruning
Propagation by root shoots
Another simple trick that does not take a lot of time:
- In the last decade of May - early June, shoots that have grown up to 20 cm are looked after. To stimulate the growth of roots, they are pulled with a soft wire (at the very base).
- Hilling is done immediately to a height of 7-8 cm.
- The same procedure is repeated 2-3 times in the summer. By the fall, you should get a 20-centimeter mound. This year they no longer touch it, leaving the bush for the winter.
- But next spring, such a growth is separated from the viburnum and transferred to a prepared place. The planting technology is familiar to this plant and does not require any other operations. Just try not to deepen the root collars too much.
There remains one more approach that raises many questions for gardeners. We will try to answer them.
Growing from seeds
Enthusiasts should listen to the advice of agronomists and think about whether they are ready to take on such work. The fact is that viburnum seeds have poor germination - only 12-20% of the total sowing germinates. It is advisable to use such material in the first, maximum in the second year after harvest: viburnum seeds have a 2-year germination capacity.
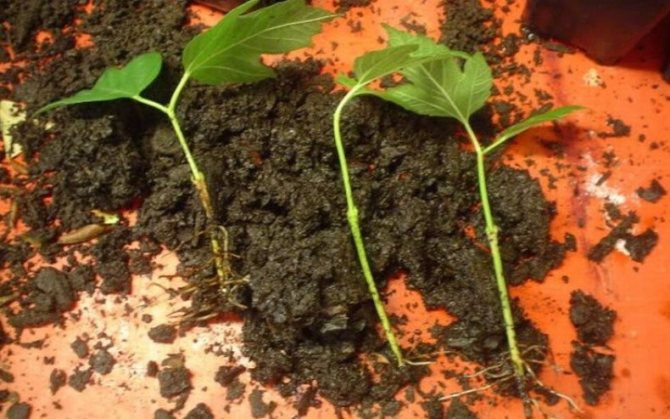


If you are determined to try this method too, then actions will be as follows:
- Juice is squeezed out of ripe berries, the seeds are washed.
- After drying, they are placed in a nylon stocking stuffed with wet sawdust. Two months at room temperature will be enough for them to start germinating.
- Then they are left to "winter" in the refrigerator for a month at a temperature of 0 ° C ... + 5 ° C.
- After such "hardening" the seedlings are placed in cassettes, pots or boxes, pressing the seeds 3-4 cm. It is enough just to lay them out and sprinkle them with a substrate. Seedlings will appear quickly, then a dive is made. It is repeated when the seedling grows to 5 cm.
- In April, when frost is no longer threatened, you can transfer the seedlings to an open area.
- Growing lasts 2 years, and only then such seedlings are transferred to a permanent place. All this time, the young are watered, fed with "organic" and complex "mineral water" in moderation, and also mulched.
Before planting viburnum, keep in mind that "seed" seedlings will begin to bloom only for 5-6 years, while with vegetative division this period is 2-3 seasons.
Now you know how you can propagate viburnum on the site. We hope this knowledge will be useful in practice, and in a couple of years the site will be even more pleasing to the eye. Happy experiments!
How to choose quality seedlings
It turns out that thanks to the efforts of breeders, the culture we are used to today differs from that sung in folk art and is very diverse. Therefore, first you need to decide what exactly you want to see in your garden.
https://youtu.be/eJZmG9gh5NQ
You will have to choose from decorative varieties, which never have berries, fruitful, tree-like or bush-like, tall, dwarf and ground cover species.
Did you know? Even in Kievan Rus, viburnum was revered as a special plant. Healers believed in its magical power, which gives women a happy fate. Therefore, viburnum inflorescences were woven into maiden wreaths and considered them an integral wedding attribute.
When choosing planting material, one should be guided by the condition of its stems and root system. Carefully inspect all the details, study if there are spots on the root processes, moldy and putrefactive areas, any mechanical damage, sagging and gall formations.
All roots must be fresh, uniform, smooth and clean. To make sure the seedling is fresh, lightly scratch the bottom of the rootstock. If fresh greenish wood appears at the site of the wound, it means that the viburnum is suitable for planting.
Its shoots must also look healthy. Choose small specimens, as they take root faster and more easily adapt to new conditions, and are easy to care for.
https://youtu.be/35uveFX_QMA
Experts respond positively to the seedlings obtained by the vegetative method. They say that such samples begin to bear fruit already in the second year after planting, it is advised to prefer exclusively the seed technique when breeding plants at home. They also recommend choosing two-, three-year-old seedlings for planting.