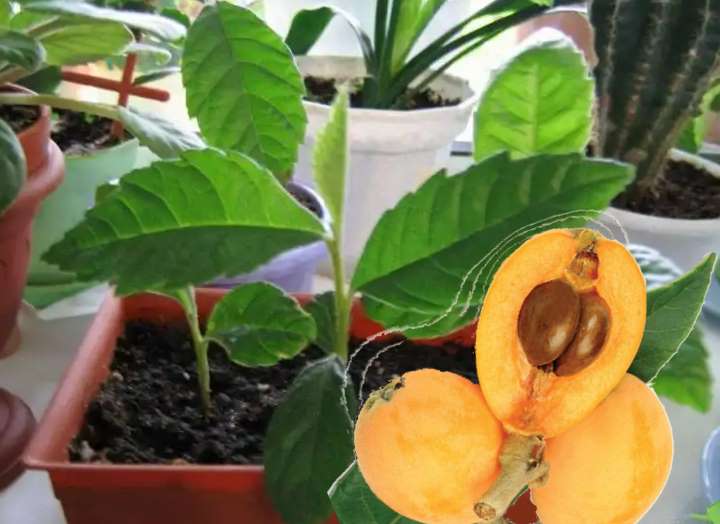
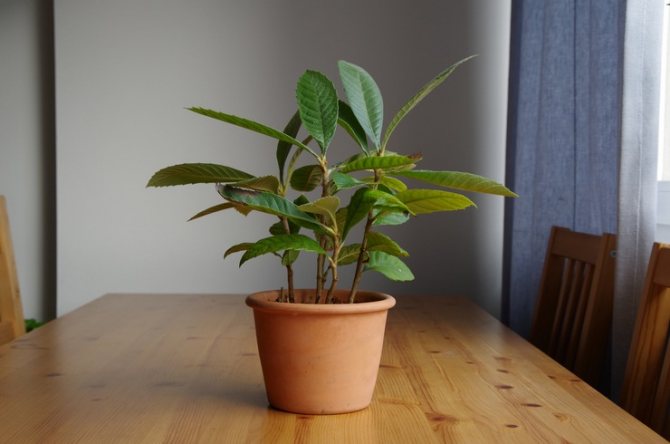
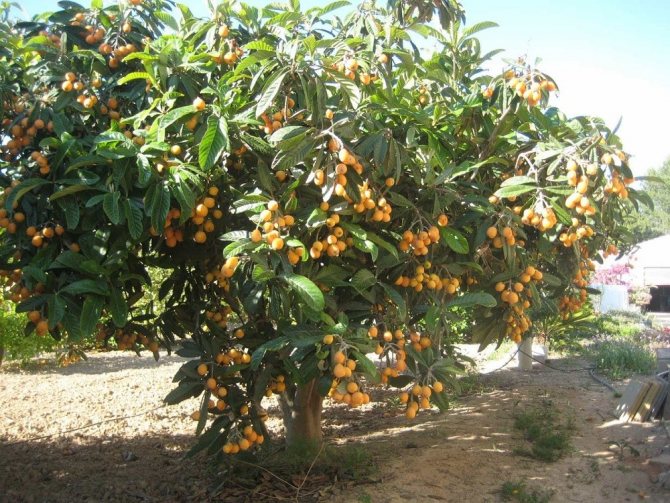
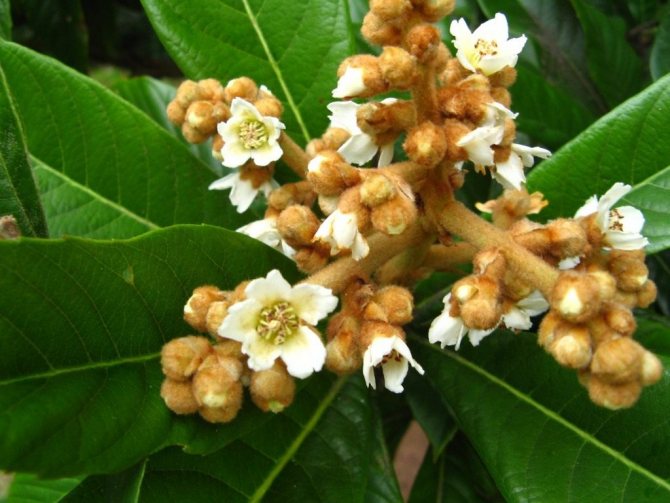
In our conditions, it is grown in the form of an ornamental indoor plant, from which a low tree is formed. In greenhouse conditions, it can reach 3 m. Hard, leathery, large leaf plates 20-25 cm long and about 8 cm wide.
Fruits are edible, pear-shaped, slightly sour, tied with tassels at the ends of the shoots. The pulp is juicy, sweet or with a slight sourness and flavor of pear and cherry. The number of large seeds is from one to five.
Also see how to grow fruit plants like lemon and pomegranate at home.
| High growth rate. |
| It begins to bloom in November to the end of January. |
| Easy to grow plant. |
| Perennial. |
How to grow German medlar, and how is it useful
Adding an article to a new collection
Important - let's avoid confusion right away. Often, in everyday life, medlar is understood as sweet yellow fruits - "apples" that you could pick from a tree and feast on, for example, on vacation in Turkey. And if you are going to grow this medlar in the middle lane, you will be disappointed.
This is an evergreen yellow-fruited tree - Japanese medlar (Eriobotrya japonica), she is eriobotria, she is lokva, she is shesek. There are many cultivars of this medlar, but, alas, it is possible to fully grow it in the open ground only in the subtropics, where the average temperature of the coldest month exceeds 0 ° C - the delicate plant does not tolerate a cold snap, because it blooms in September-November, and the fruits ripen late spring! This means that in Russia it is possible to successfully grow just such a tree only at the latitude of Krasnodar and on the South Coast of the Crimea, or cultivate it as an exclusively indoor potted plant, which is taken out into the air only in the summer.
Medlar japonica is the only fruit plant of the subtropics that blooms in autumn and ripens in the winter-spring period, which makes it the most valuable and, in fact, the only fresh source of vitamins during the spring beriberi.
What then is the article about? About a completely different culture - about the German medlar (Mespilus germanica), she is Caucasian, she is ordinary, she is Crimean, she is Caucasian, she is a cup tree. And also dzmartli, zykir or ezgil are in the Caucasian languages.
Although they are relatives with the Japanese medlar, they are quite different. And it is precisely the German medlar that it is quite possible to grow in the middle latitudes, at least in the same Moscow region - for decorative, culinary and even medical purposes. Let's figure it out together.
Medlar ... she is so different
It turns out that there are two types of medlar, in which even botanists are sometimes confused. One -
, which is an evergreen tree (less often a shrub).
Japanese medlar (lokva)
It belongs to the Pink family, the Yablonev subfamily, and its fruits resemble ranetki in shape. And the taste is a cross between a pear and a cherry, with a little bit of sourness.The Japanese capricious woman lives only in the south, blooms in autumn, and gives fruits in spring, so it is not at all suitable for growing in open ground in most of the Russian regions. It's a pity…
But there is a way out! This is German medlar (also called Caucasian), which is more loyal to the Russian climate and perfectly takes root in the gardens of the southern strip of Russia.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Rules for the construction of a drip irrigation system for greenhouses and greenhouses
Medlar

The German medlar is a deciduous fruit tree (or shrub), also from the Pink family, but it has nothing to do with the Yablonev subfamily. Here is such a confusing pedigree.
German medlar - what kind of tree
Medlar German is a deciduous fruit tree of the Pink family. This is the only species of the genus Medlar - the aforementioned Japanese variety belongs to a completely different botanical genus.
On the left in the photo are the fruits of the Japanese medlar, on the right - the German
This plant is also thermophilic, but not as much as its "eponymous" relative, loves warm summers and mild winters - in the wild, Germanic loquat grows in South-West Asia and South-East Europe. And today it can be found "wild" on the southern coast of Crimea, in Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan and the North Caucasus.
Why then is it “Germanic” and not “Asian” or “Black Sea”, for example, you ask? It is believed that this tree first of all got into European culture precisely on those lands - it was brought either by the ancient Romans, or by the same ancient Greeks.
There is evidence that in the ancient Roman and medieval eras, this plant was the most important fruit crop. However, by the XVII-XVIII centuries. interest in it gradually faded away, and it was replaced by other cultures, and at present it is cultivated quite rarely, although you can quite successfully try to “get” this exotic in your garden and taste its fruits.
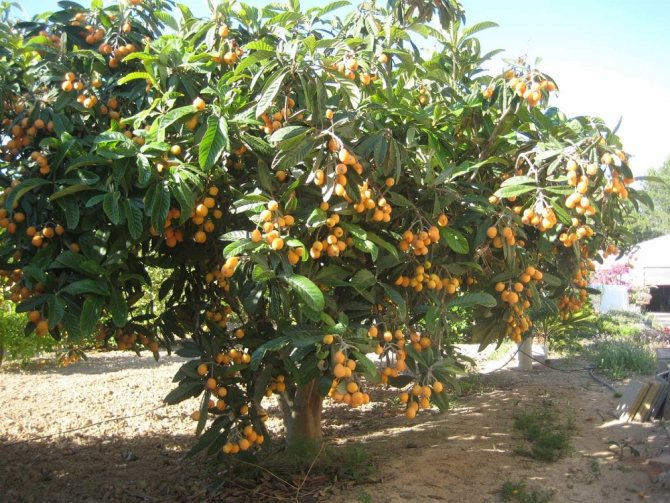
In Europe, the medlar is a small tree up to 3 m with a powerful superficial root system, although in ideal frost-free conditions it can grow up to 8 m in height. Her crown is wide, spreading, curved branches (in wild forms, thorny), leaves are elliptical dark green, glossy above and slightly pubescent below, changing a few days before falling off the color to brown-red. Flowers are solitary, white, five-petalled, appear in late spring.
General information about the medlar plant
Before moving on to growing, let's take a closer look at the fruit itself and all its beneficial properties.
Origin
Medlar is an evergreen shrub or tree of the Rosaceae family. Can be grown both outdoors and as a houseplant.
It should be noted that medlar has been cultivated since ancient times. The Roman Empire, Greek agrarians and Persians have been cultivating it for centuries.
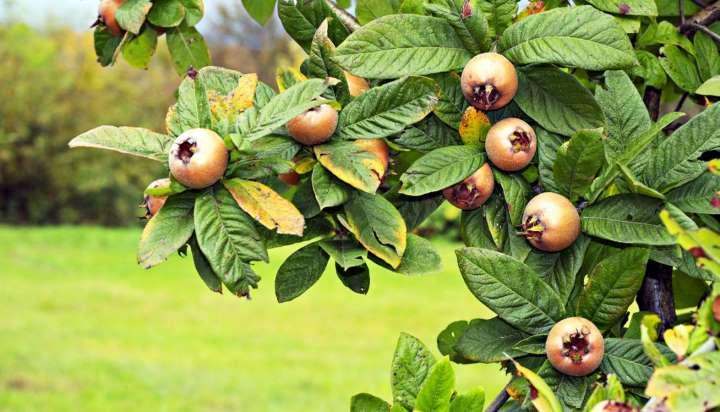


This fruit has been cultivated in Turkey for over 3000 years. Believe it or not, some 200-100 years ago, it was common for Europeans to eat fresh medlar. Jams and desserts were often made from it.
It is now in Europe that you can find medlar only in botanical gardens or among lovers of exotic flora. The fruit is popular in Azerbaijan, Iran, Japan, Israel, China, Crimea, Moldova and many other countries.
Appearance
There are a huge number of varieties more than 1000. The life of the tree is about 50 years.

Shrubs or trees grow in height from 4 meters to 8 meters.
Leaves predominantly oval or oblong in shape, and the color is solid dark green.
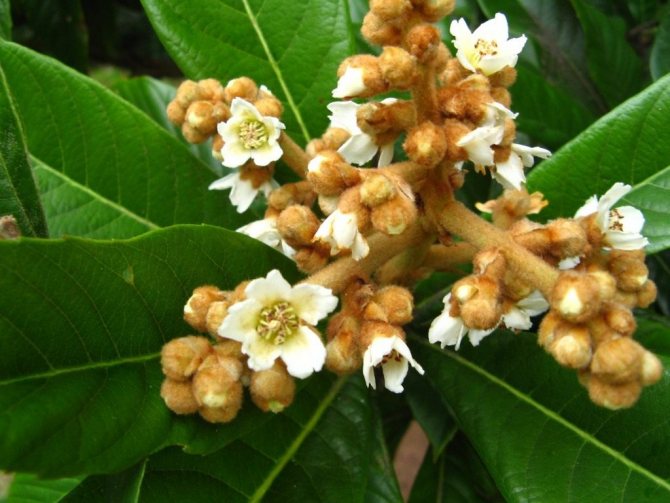
Flowers solitary, about 2-3 cm in diameter. The aroma of medlar flowers is sweetish with subtle hints of almonds.
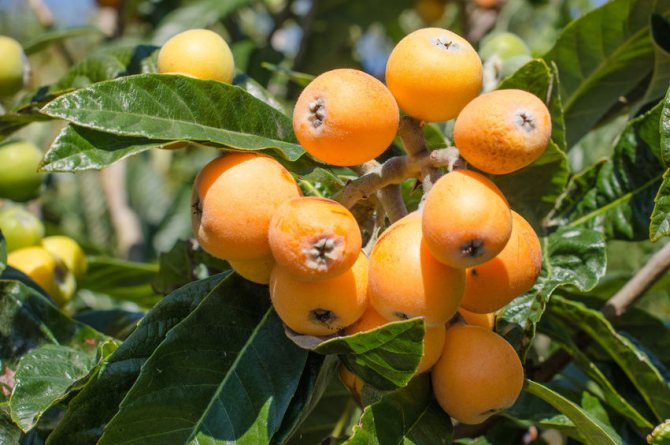
Berries edible and have various shapes with a diameter of 7-9 cm.
Fruit contain fleshy, juicy flesh, usually orange or yellowish in color. The taste of the fruit is sweet with a slight sourness.
Medlar is usually eaten fresh, its skin is thin and easily damaged, which in turn complicates transportation.
The main types of medlar
It was said above that medlar has a large number of species and varieties, but we will consider two main species that grow best in our summer cottages:
- German medlar, otherwise it is called "Caucasian".
- Japanese medlar, otherwise called "Lokva".
Medlar
Let's start with the first species, Germanic medlar (some also call it ordinary), has been cultivated for more than 3000 years, grows in Ukraine, Crimea, Moldova, as well as in Azerbaijan.
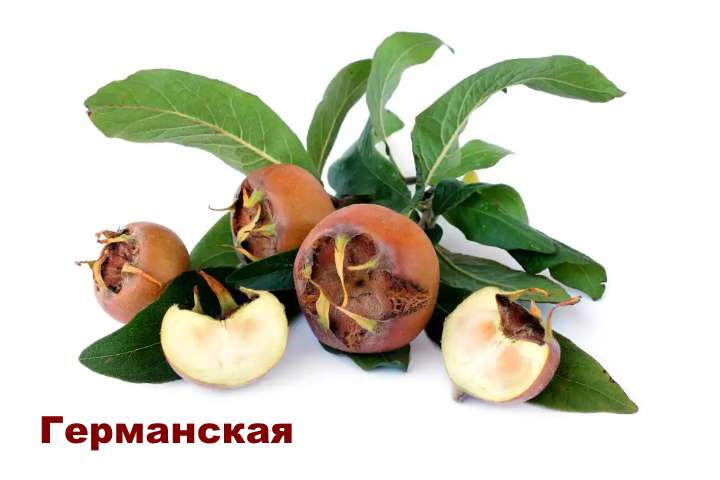


The plant grows on average 3-4 meters in height, in tropical conditions it can reach heights of up to 7-8 meters. Leaves are green in longitudinal-oval shape, turn red in autumn.
The fruits are usually dark brown in color and round in shape. Caucasian medlar should be consumed after the first frost, then the pulp becomes tasty, juicy and soft. It tastes like an apple.
If frost is not expected, then the fruits should be collected and soaked in a highly salty solution, so they can be stored for no more than two weeks, after which the fruits ripen and can be eaten.
This type of medlar is frost-resistant, it can be planted in open ground.
Japanese medlar
The homeland of this plant is Japan and China. Widespread in South and Southeast Asia. The Japanese medlar grows in the form of a spreading tree about 7-8 meters high.
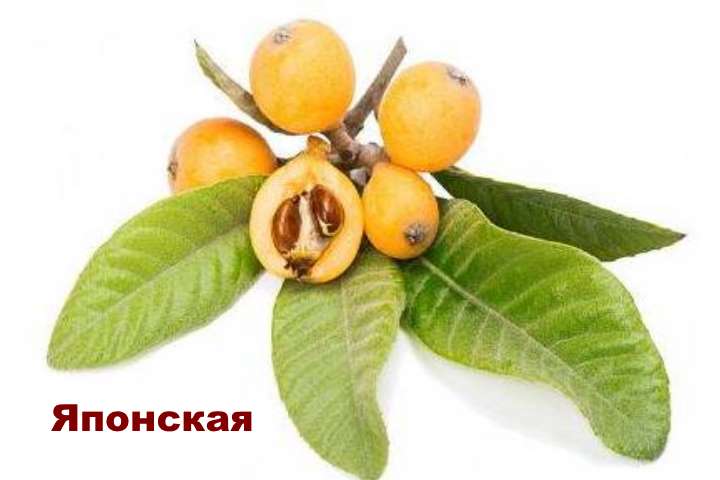


The fruits are orange in color and oblong in shape, very similar to the apricot fruit. The pulp is white, juicy. This type of medlar is thermophilic and does not tolerate frost (freezing temperatures).
The crop can be harvested in April or June. The size, shape of the fruit, as well as the color of the pulp and taste vary, depending on the type of medlar.
Varieties
Champagne - has yellowish fruits, fleecy skin and delicate pulp.
Tanaka - has yellow or orange fruits. The pulp has a pinkish tint, and the taste is sweet with a slight sourness.
Morozko - has unusually large fruits, reddish or brown in color.
Silas - has large fruits (about 80-100 gr.).
Structure
Why is medlar useful?
The valuable and useful properties of medlar have been known for a long time.
So, the ancient Romans made powder from seeds and treated stressed conditions, tremors and chills. And Hippocrates recommended eating fruits for people with diseased intestines and for removing sand and stones from the kidneys.
It is also interesting that the fruit consists of fructose, water, malic acid, citric acid, dietary fiber.
And for 100 gr. medlar has a total of 42 kcal.
Just think, the whole line of B vitamins is present in the medlar, as well as vitamins A, E, K, C. In addition to vitamins, there are also minerals - iodine, phosphorus, iron, calcium, potassium, magnesium, carotene, beta-carotene and much other.
Medlar properties
It is also striking that not only fruits are widely used, but also bark, leaves, wood.
Fruit
Eating fruits helps the body get rid of radionuclides, heavy metal salts and toxins. And the use for a long time, helps to normalize the functioning of the liver and pancreas.
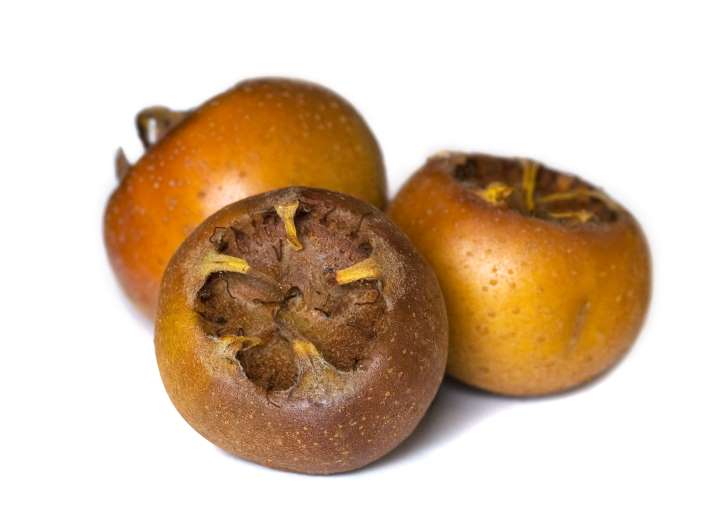


The fruits are rich in natural antioxidants that stimulate the immune system. Due to the high content of vitamins, it normalizes blood pressure, accelerates regeneration processes and has a beneficial effect on the work of the cardiovascular system.
An interesting fact is that during heat treatment of medlar, it does not lose its useful properties. The fruits should be eaten fresh, and do not forget to remove the skin. You can also prepare jam, compote and alcoholic tinctures.
Wood
Kitchen accessories and various fakes are made of wood.
Leaves and bark
The leaves and bark of the medlar are very useful.Decoctions are usually prepared from them. Antioxidants aid in the elimination of phlegm. Used for the prevention and treatment of intestinal diseases, ulcers, disorders, colic and infections.


Medlar leaves are able to fight diabetes mellitus, since the leaves contain triterpenes, which in turn produce a polysaccharide. And amygdalin, which is part of the foliage, helps the liver to get rid of poisons and toxins.
Infusions, decoctions
Water infusions of medlar seeds are used to treat dysentery, bronchitis and stomach inflammation.
A decoction of the leaves prepared according to the recipe is one tablespoon for one 250 ml. glass of water. Boil everything for about 5-6 minutes, then strain. Apply 50 ml., 3 times a day after meals. This broth helps to strengthen the immune system, as well as an antiseptic and hemostatic agent.


For the treatment of peptic ulcers, you can also use a decoction prepared according to the recipe above. But decoction from seeds helps the best. For 2 tablespoons of seeds, take 400 ml. water. Cook for 20-30 minutes. We apply 50 ml., For 30-40 minutes. before meals.
Contraindications
The medlar has a number of disadvantages:
- People with high acidity are not recommended to use medlar, as it is acidic in itself.
- Children and nursing mothers should be given in dosage, under supervision, so that there is no allergic reaction.
- A harmless dose for an adult is considered to be about 5 fruits a day, for children about 2 fruits a day.
- It is contraindicated to use for severe diseases of the duodenum, acute gastritis, serious peptic ulcer diseases.
German medlar - growing conditions, planting and care
In culture, mainly adapted species and varieties of German medlar are grown, which differ from the wild one in larger fruits, as well as in their increased content of sugars, vitamins, malic and citric acids. The fruits of such a medlar can be used both raw and in various preparations for the confectionery industry (jams, syrups, jellies, marshmallows, marmalade, etc.). The most popular varieties are Royal, Dutch, Nottingham.
How to grow this crop in mid-latitudes? Medlar German prefers sunny, dry places, protected from drafts, and weakly acidic well-drained fertile soil without stagnant water.
When planting, Germanic medlar seedlings are placed at a distance of at least 4 m from each other, bone meal and mineral fertilizer are added to the planting pit, the seedling is tied to a peg (especially weeping drooping forms) and mulched with peat or rotted manure with a layer of about 8 cm.
Seedlings begin to bloom 3-6 years after planting, at the same time they give the first harvest.
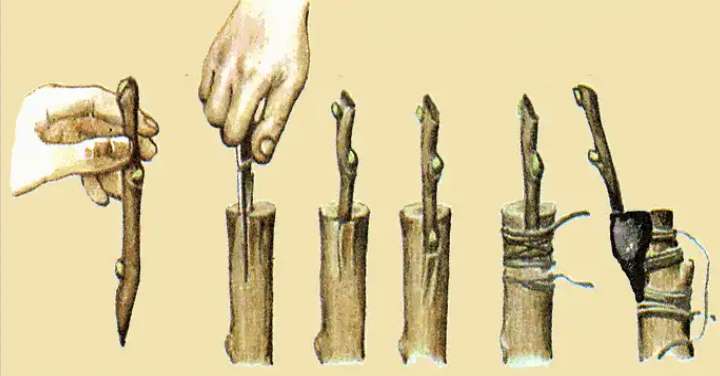
You can also propagate the German medlar by seeds, cuttings or grafting on hawthorn or pear.
In the first case, it is better to stratify the seeds, since they are very tough. They can be planted both directly in open ground in October-November to receive seedlings next spring, or grow a seedling in a pot at home for spring planting outside. In this case, everything is done as usual - the seeds are pre-soaked in a growth stimulator, sown in pots with a universal soil mixture around February, covered with foil and watered regularly. With proper care, the sprouts will appear in 1.5 months and in late May-early June, you can send them to a permanent place of residence.
The variant of propagation by grafting and budding is used for varieties and hybrids. In this case, hawthorns, less often pears, usually “work” as stocks - this way you can get an interesting standard shape. Medlar itself can serve as a drought and frost-resistant stock for other fruit trees (apple, quince, pear).
The most, perhaps, the most difficult way of reproduction of the German medlar is by cuttings, since the rooting rate of its lignified cuttings is quite low.
Caring for the German medlar is easy.This is rare watering during especially dry periods (the tree does not like waterlogging very much), timely removal of dry and damaged branches, feeding an adult plant 2-3 times per season (a young seedling - 1 time in 3 weeks), shallow loosening of the trunk circles.
Medlar responds well to pruning and actively releases new shoots, so you can safely engage in the formation of its crown. This is done in early spring before the start of sap flow. In the first 3-4 years, shorten the conductors of the main skeletal branches by a third of the annual growth along the outward-facing kidney. Subsequent pruning consists in removing branches thickening the crown.
Photo gallery
To begin with, we note that the medlar is divided into two types: Japanese and German (aka Caucasian). Japanese is an evergreen shrub or small tree. The fruits of this plant in appearance resemble ranetki, which are so familiar to each of us.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with: Potatoes rot in the cellar what to do
The Japanese medlar can only grow in southern countries. It begins to bloom in mid-autumn and bears fruit in the spring. Unfortunately, it is not suitable for the climate of our region. But the German one is an excellent option for Russia, namely for its southern regions.
In addition to being incredibly tasty, medlar is also very useful, which is of particular interest. The fruits of this plant contain a fairly large amount of vitamin C, which strengthens our immunity and improves the general condition of the body.
Medlar has a positive effect on human blood vessels, liver and muscle function. It is recommended for the prevention of blood clots, strokes and heart attacks; it can quickly bring your pressure and nervous system back to normal.
In order to grow seedlings, we need the seeds of this plant. In order for them to germinate and turn into sprouts, they must first be kept at low temperatures (for example, in the refrigerator) for 4 months. This will help speed up the growing procedure.
Before planting seeds in the soil, they should be placed in warm water and left there for 24 hours. Having planted the seeds in the ground, it is worth mulching the soil using peat or sawdust. You can cover the hole with plastic wrap.
If German medlar attracted you so much that you decided to grow a plant in the Moscow region, then the first thing to do is choose and correct the composition of the soil and its condition correctly. The soil should be loose and sufficiently drained.
Having dug a hole in which we will plant medlar, it is necessary to prepare a mixture of organic fertilizers. It should include: turf, sand, deciduous soil and humus in equal proportions. Having lowered the seedling into the hole, you need to sprinkle the roots with the prepared mixture.
The main care for this plant consists of timely watering and loosening the soil. It is worth remembering that medlar needs regular fertilization of the earth. This procedure must be carried out about three times a season. Fertilizers must be organic and mineral.
The condition of the branches of the plant should be monitored. Dry, damaged ones must be removed. Remember to shape the crown of the tree correctly. Medlar is one of the plants that are most susceptible to numerous diseases.
For their prevention, it is recommended to pollinate the tree with special insecticide solutions. These include Fitoverm, Insegar and Lepidocide. They will help get rid of both many diseases and pests.
We recommend that you familiarize yourself
Medlar is a subtropical plant belonging to the Rosaceae family. The most common are two types:
- Caucasian medlar (German).
- Japanese medlar.
This article will focus on the medlar, the photo of which is presented below.
The Caucasian and Japanese medlar are significantly different from each other. It reaches a height of six meters, but if grown at home, it can only grow up to two meters. It has sweet and tasty fruits that are high in vitamins and nutrients.
The Caucasian medlar is a tree with a well-developed trunk, 20 centimeters in diameter, shedding leaves in winter. May be in the form of a bush.
Its shoots contain thorns. The leaves have a beautiful dark green color, are large enough, which bloom at the end of April. Flowers with five petals form at the tops of the shoots. Initially, the flowers are white, later taking on a beautiful pink shade with a wonderful aroma.
It begins to bloom at the end of May. The fruits of this plant ripen in the fall, are red-brown in color and become edible after frost. The pulp tastes sweet and sour. The shape of the fruit is usually spherical or oval. One fruit has several seeds. They stay on the branches all winter.
What kind of medlar can be grown in the country?
When planning to grow medlar in the suburbs, it is very important to decide which variety you are going to purchase. Taking into account the fact that it is still quite cold in Russia and the Moscow region in winter, you should choose frost-resistant varieties that bloom in spring and give fruits in the autumn period.
Today there are about thirty popular plant varieties, each of which has its own distinctive features.
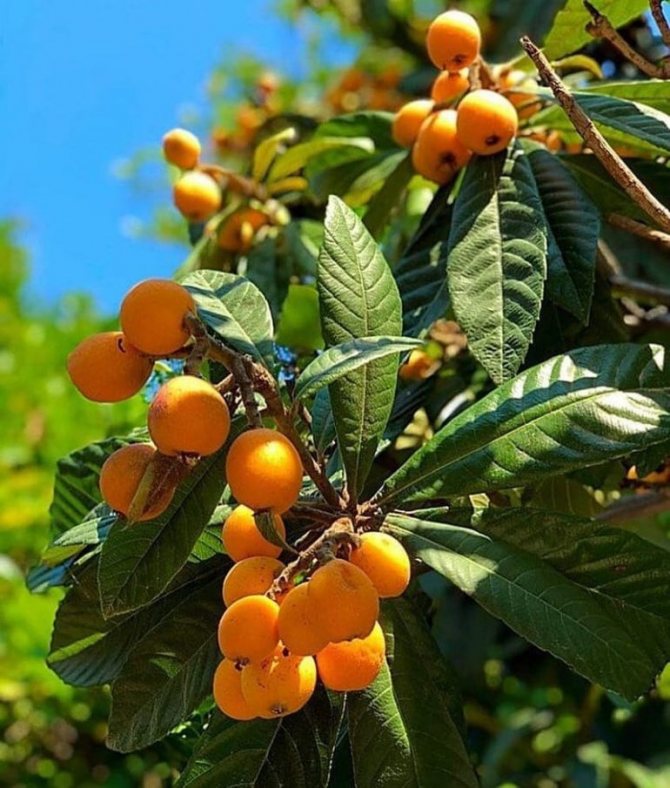
For example, the Japanese medlar is an evergreen plant variety that can reach a height of five to six meters. The flowering period begins in early winter, usually in January-February.
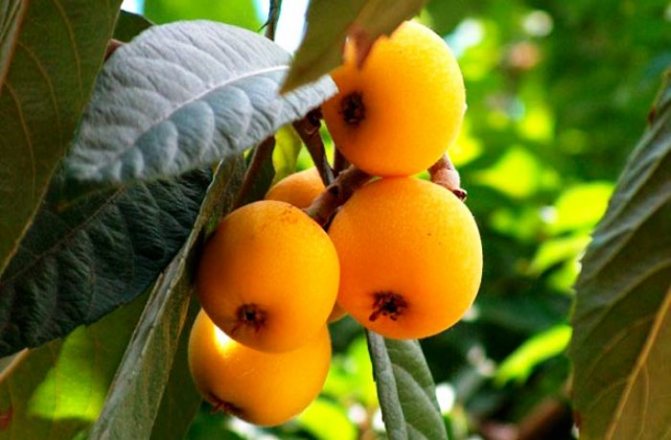


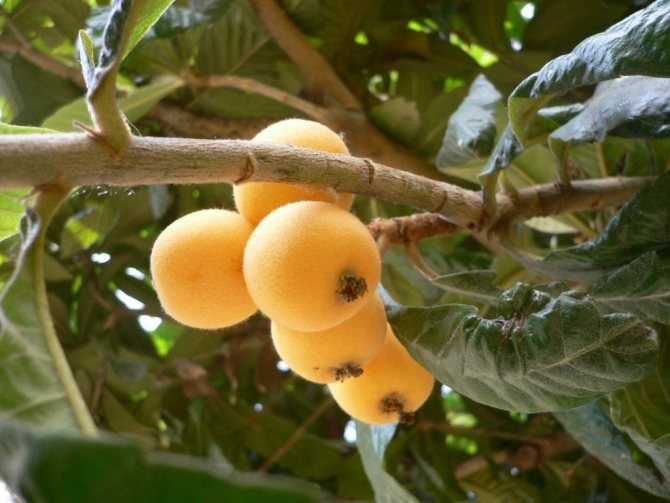
The Japanese medlar begins to bloom in the midst of winter, after the tree blooms, it takes about several months. The season of medlar and harvesting of fruits begins already by the beginning of spring. It is then that the fruits ripen - pear-shaped fruits, orange in color, resembling peach and quince outwardly.
Elongated pear-shaped fruits. The fruit tastes sweet, tart, somewhat reminiscent of peaches and strawberries. The Japanese medlar has taken root in the south of Russia, along the entire Black Sea coast. On the territory of the Moscow region, the cultivation of this variety is not successful due to the peculiarities of early flowering.
But you can grow the German or as it is also called the Caucasian variety of the tree. Loquat grows in cooler climates. Unlike the Japanese variety, it does not bloom in winter, but in spring, like most fruit trees.
Description of the types of medlar
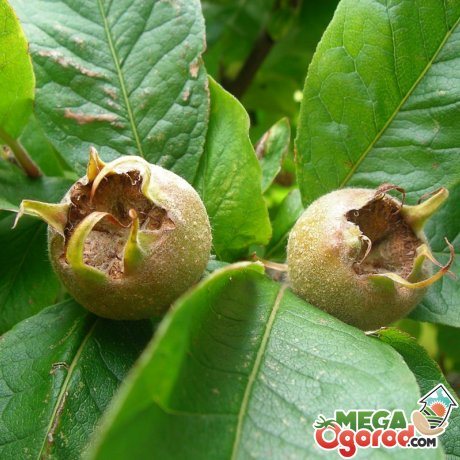


Medlar German (common) refers to deciduous fruit trees that grow up to eight meters. The culture has a developed and powerful root system, which is located close to the soil surface.
- Curved branches extend from the straight trunk, covered with cracked brownish bark, and form a spreading wide crown. Lignified parts of the tree are covered with small thorns.
- Medlar blooms in late spring or early summer. Flowers 2-3 cm in diameter are painted white or pink and are concentrated at the ends of the shoots.
- Fruits are round in shape, covered with a dense light brown skin. Their diameter does not exceed five centimeters and have a specific sour taste. The pulp contains several pits with seeds. The fruits reach maturity in the middle or at the end of winter, but they are harvested after frost or in spring - after freezing, the pulp softens and gains sweetness.
The leaves of the medlar are elliptical, painted in light green tones. The upper part of the leaf blade is smooth, and the lower part is pubescent. In the autumn, the foliage takes on crimson hues.
Medlar fruits contain about 90% water, 8-15% sugars, vitamin C, the content of organic acids (malic and citric), pectin substances, mucus and phytoncides has been revealed. Foliage, bark and unripe fruits are saturated with tannins.The fruits of the medlar can be eaten fresh or soaked, used in cooking. For medicinal purposes, they are used to strengthen the intestines and improve digestion.
Decoctions of green fruits help with diseases of the digestive system and urolithiasis.
Japanese medlar (lokva) refers to evergreen trees that do not grow taller than five meters.
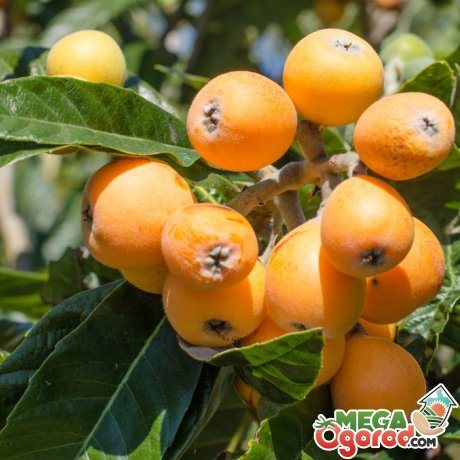


- The branches of the plant are covered with red hair.
- The foliage is large, up to 25 cm long, oval-oblong in shape. The upper part of the leaves is dark green, glossy, and the lower part is gray-green, pubescent.
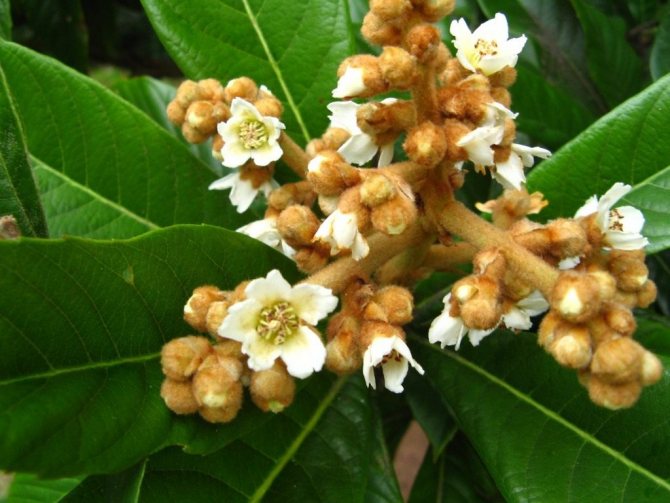
- Japanese medlar blooms from September to March. The flowers are collected in racemose inflorescences and are painted in white tones with shades of yellow or cream. During flowering, a strong, pleasant aroma spreads through the garden.
- The fruits are ready for harvest in May-June. They can be round, pear-shaped, oval and flattened. One brush can consist of 8-12 fruits, weighing from 15 to 110 grams. The pulp contains 2-3 large bones, in some varieties their number reaches 8 pieces.
- The flesh of the fruit can be tender or firm and vary in color from white to bright orange. The skin is predominantly firm and firm, but leaves the pulp with ease.
- The Japanese medlar grows only in warm climates, because it does not tolerate frosts of more than 14 degrees. But it can be cultivated as a greenhouse or pot plant.
Medlar of both species tolerates shade well, is drought-resistant, practically does not need watering and is capable of producing fruits without fertilization.
Eating and storing fruit
Gardeners often ask the question on forums: "How long to keep the loquat fresh?" Indeed, the preparation of canned food and cooking jams is familiar to every housewife, but not everyone knows how to enjoy the fresh taste of this fruit.
It must be remembered that eating medlar immediately after the fruit is plucked from a branch is not always favorable. It may contain a large number of enzymes that make it difficult for digestion. Better to let the berries lie down.
To avoid spoilage, each fruit must be wrapped in paper. So they should be stored in a cool, dark place. A cellar or a regular refrigerator is perfect. After the fruits lie down for several weeks and ripen, they can be safely eaten.
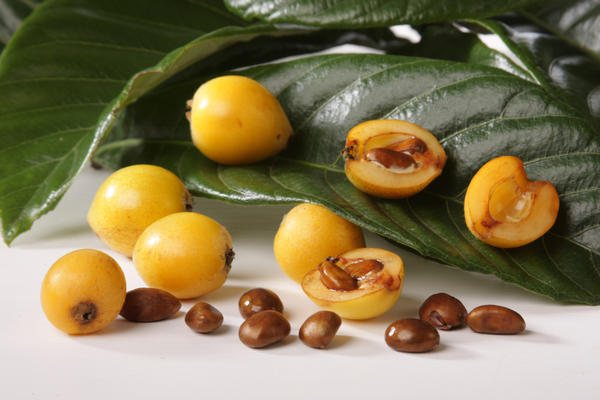


It is important to examine the fruits before this. There should be no traces of rotting, mold. The fruit becomes more flabby than the freshly plucked from the branch. However, this does not affect the taste; on the contrary, the fruits will be sweeter and more viscous.
Medlar is a beautiful guest in Russian gardens
The German medlar is very beautiful. Its spreading branches are strewn with long dark green leaves, which play with a crimson glow in autumn, unusually decorating the garden. It blooms in spring, releasing single white (less often - pink) flowers with bright red centers, very similar to rosehip flowers.
Medlar flower
The fruit of an adult tree is quite large, like a medium apple.
The fruits of the medlar are quite large.
They have a large shiny bone inside, are very dense and extremely tasty. Imagine a grated apple mixed with quince pulp, sprinkled with powdered sugar. This is roughly the taste of German medlar.
But the fruits of the medlar become sweet and soft only after freezing - defrosting or after keeping for 2-3 months in storage.
Medlar becomes sweet only after freezing-thawing
Then they soften, gain a healing bouquet of vitamins and are suitable both for food and for various preparations (jams, jams, jellies and others), and the smell is simply awesome!
How to grow medlar in the suburbs?
In the Moscow region, it is best to try to grow medlar from seeds. Other methods can be used, however, the guarantee of good germination and further strengthening of growth is lower with other methods.The process of planting and caring for seedlings is as follows:
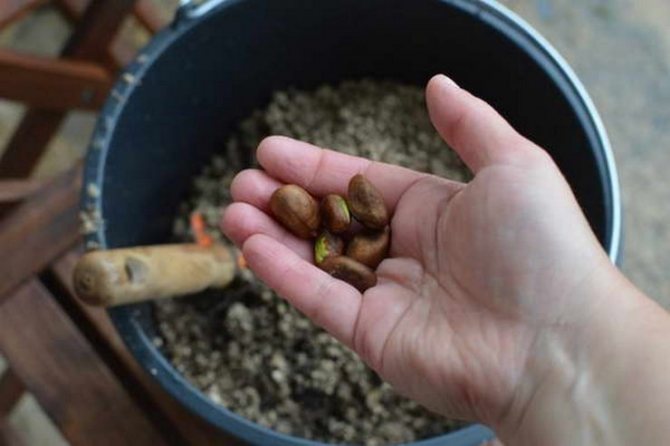
- It is necessary to select several seeds from well-ripe medlar fruits that are inside the fruit. They should be free of traces of worms and rot. They should be placed in a solution of root or other plant growth-promoting agent for five to seven hours.
- Prepare planting containers in advance. These should be tall pots, they need to be treated with a manganese solution. Then cover the earth and plant medlar seeds in pots.
- You should carefully choose the composition of the soil for planting. The tree loves slightly acidic soil, while the earth should be light and allow water and fertilizers to pass through.
- Do not plant more than three seeds in one pot. At the same time, they need to be buried no more than one centimeter underground. After planting, cover the pots with foil or glass.
- Sprouted seedlings should be watered regularly. Provide ventilation for the plants by regularly lifting glass or foil. Also, make sure the tree is on the sunny side. Medlar love well-lit and ventilated rooms.
- After the shoots have sprouted and strengthened, you can transplant each sprout into a separate pot. The bottom should be covered with peat or stones for a better outflow of water. In this state, the processes should hold out until the beginning of autumn.
- When autumn comes, the pots can be planted outdoors. It is better to plant the trees in a greenhouse so that the tree does not die in winter, then in the spring, after rooting, transplant it into open soil in the garden.
- The distance between seedlings should be at least three meters. Medlar can grow up to five to ten meters, while the crown of the tree is quite spreading.
To start bearing fruit, the tree needs to grow outdoors for four or five years. Only then can the trees form ovaries and fruits. Therefore, the gardener should patiently wait for this period and take care of the tree.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the cultivation of medlar in the Moscow region is gaining popularity among gardeners. Often the tree is planted for decorative purposes, they make a pretty bonsai from the crown.
However, if you approach the care with responsibility and diligence, you can get a healthy, fruitful tree in five years. As a result, the gardener receives not only a beautiful evergreen tree, but also an autumn harvest of tasty and healthy fruits.
Experiment Result
She carefully separated the grains from the shell, kept them in solution for half a day
(1 g in 1 L of water) and planted in small clay pots using potting potting soil. I put three grains into each one (what if not all of them will come up?), Buried them literally by 1 cm, poured them, covered them with polyethylene on top and put them in a warm place.
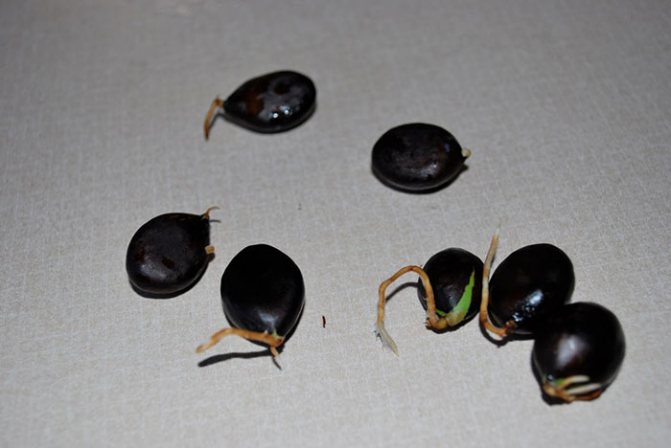
And what do you think? My medlar sprouted literally after a month and a half, released two leaves and reached for the sun. By the way, almost half of the seeds sprouted, and I had to carefully plant some of the bushes in separate pots.
And only later I learned that the seeds do not germinate in this way, because the plants grow weak (if they grow at all)), do not bloom and do not bear fruit. But at that time I did not know this, I wanted to see more quickly what kind of medlar is this?
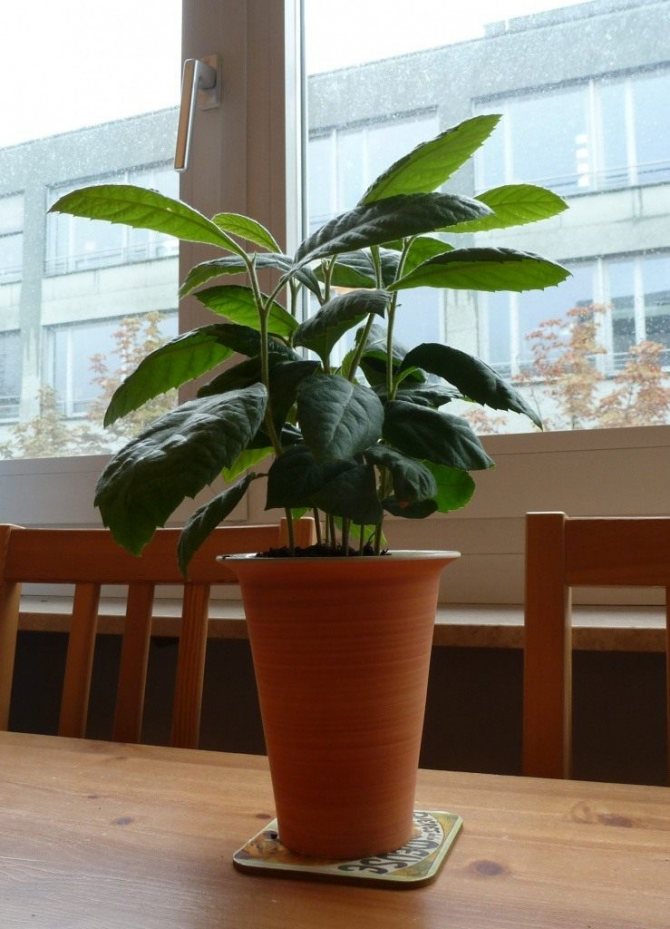
Medlar in a pot
I read on the Internet that the "babies" loquats need to be shaded, so I put the pots with seedlings in partial shade for a couple of weeks. And when my plants released 2 more leaves, I settled them on the windowsill.
Six months later, the fruits of my experiment grew up to 30 cm. Is it time to plant in open ground? But no ... it turns out that I got the seeds of the Japanese medlar, which - alas! - does not survive in the open ground of the central zone of Russia.
What to do? I gave some of the plants to my friends - my girls were happy.I left 5 bushes for myself, transplanted them into beautiful outdoor flowerpots and now I put them on the loggia in the summer, and in the winter they "return from vacation" to my apartment, where a bright place is equipped for them.
Website about the cottage
The popularity of the home medlar is growing every year, which is explained by its unpretentiousness in terms of cultivation and care.
Even a beginner can grow a medlar from a bone, and such a plant will decorate any summer cottage. In addition, there is always the opportunity to buy a ready-made seedling.
The medlar, or cup tree, belongs to the genus of deciduous plants in the Pink family. The medlar, currently cultivated, is subdivided into the following types:
- Germanic medlar, or ordinary;
- medlar Stern.
Diseases and pests
Medlar is not a very capricious plant, but systematic violations of the microclimate and improper care can lead to the disease:
- Decay of roots occurs with excessive soil moisture, stagnant water, especially in cold conditions.
- Medlar leaves curl and fade with a bacterial burn disease. The problem can arise when the plant is kept in conditions of low temperature, excessive soil moisture and high nitrogen levels in the soil.
- Medlar grows slowly in conditions of insufficient light or depletion of the soil.
Medlar can attack aphids, black fungus and scale insects.
General information
Medlar is very often called "nispero" or "shesek". This fruit plant forms the loquat fruit. The plant is often found in South-West Asia, as well as in the Caucasus. It gained particular popularity on the territory of Iran, Azerbaijan and Turkey, where the fruits of the medlar are very fond of. Medlar, the planting of which is popular in these countries, has been cultivated there for over three thousand years. In ancient times, it was grown by the Greeks and Romans.
The most famous varieties of the fruit tree are:
- medlar;
- Japanese medlar;
- medlar Caucasian.
The most common loquat is Caucasian, the fruits of which have unique beneficial properties and are successfully used in Caucasian cuisine.
Beneficial features
Germanic medlar and Japanese medlar are quite rare in our country, although the cultivation of these species is not difficult. Fruits have the following properties:
- in the composition of fruits - water, dietary fiber, protein, malic and citric acids, as well as fructose;
- significant content of vitamins and minerals, including beta-carotene, carotene, as well as components in the form of niacin, folic acid, vitamins E, B and A, calcium, phosphorus, iodine, iron, magnesium and potassium;
- one hundred grams of fruit contains about forty kilocalories.
In Spain, Japan and Israel, the Japanese medlar is highly prized. Fruit is most often consumed fresh. In addition, jam and jam are made from the fruits of this tree, as well as desserts, liqueurs and compotes are made. In Spain, the fruit is also used to make sauces and garnishes for meat dishes.
Medlar and Japanese medlar contain a small amount of calories and can be consumed with a diet. Medlar is recommended to be eaten by people suffering from kidney dysfunction, which allows them to increase their filtration capacity. The content of a significant amount of molecular water allows you to remove toxins from the body. German medlar and Japanese medlar perfectly maintain the vitamin balance in the body. The leaves of trees also have beneficial properties. They are used to prepare medicines.
We also recommend reading the article on growing medlar:
Various varieties
Currently, in the conditions of our country, it is possible to cultivate several varieties of medlar, among which are especially popular:
- seeds and seedlings of the medlar variety "Komun", which has rounded or slightly flattened fruits with a matte surface of the skin, which has pubescence and bright yellow color. Fruit weight does not exceed 30 grams;
- seeds and saplings of the medlar variety "Tanaka". Pear-shaped-oval fruits have a yellow color with a characteristic orange tint and a matte surface. The variety is large-fruited, and the weight of the fruit varies from 50 to 80 grams;
- seeds and saplings of the "Premier" medlar. Pear-shaped-oval orange-yellow fruits have a matte surface and pubescence. The average fruit weight is about 40 grams;
- seeds and saplings of "Champagne" medlar. The fruits of this tree are characterized by an oval or pear-shaped shape, dark yellow in color and pronounced pubescence. The average fruit weight is about 45 grams.
There are several more varieties, seedlings and seeds of which can be found in the garden markets of the country, but they are not very popular and do not always succeed when grown in conditions of central Russia.
Growing from seed and seedling
The main difference between medlar and other subtropical fruit crops is the ability to reproduce not only vegetatively, but also by seeds. To obtain seed, only the most ripe, as well as large fruits that have been grown in our climatic conditions should be selected. The inside of the fruit contains about three seeds, which, under conditions of proper planting and care, show a good level of germination. Seedlings that can be grown in this way are guaranteed to retain all the properties inherent in the mother plant.
As a rule, under standard growing conditions, seeds are kept in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for a day. It is possible to grow this plant from seeds with proper care in indoor conditions, as well as in winter gardens and in open ground. When the growth of the medlar is not limited, the tree can reach a height of one and a half meters. Plant care is quite simple. When the tree reaches sufficient height, pruning and crown shaping should be performed. Depending on which growing method is chosen, a fairly compact plant can be formed.
Growing a medlar from a bone is a rather lengthy process. Regardless of which fruit is used to extract the bone, it should be dried. At the next stage, the bone is scarified, which can be rubbed with sandpaper, followed by soaking in a solution of high-quality humus.
Care rules
Growing medlar is a simple process, but a consistently high yield of fruits can be obtained with proper care. As a rule, it is necessary to plant a medlar in the spring or in the autumn, in an area previously cleared of weeds. Bone meal, as well as complex mineral fertilizers, should be added to the planting pit.
The growing seedlings are tied to a wooden peg, which is installed in the planting pit along with the young plant. The soil around the seedling should be well crushed, and the light soil type should be mulched with compost or rotted manure. Under the mulch layer, the soil remains moist and cool.
Plant care is quite simple:
- transplanting an adult tree is performed once every three or four years;
- medlar is responsive to abundant irrigation with settled water;
- preventive procedures to protect plants from soot fungal infections;
- annual change of the topsoil around the plant.
In addition, care includes top dressing with high-quality complex fertilizers, which have a beneficial effect on the growth, development, and abundant fruiting of this amazing fruit tree.
The material was prepared in cooperation with the Dacha Decor portal
Japanese medlar or Lokba is a subtropical fruit. Nespera
Exotic care: where to put the pot
With the appearance of sprouts, the shelter is removed. The pots are placed in a warm, bright room, the best option is the sill of the south or southeast window. If there is not enough natural light, then daylight hours are extended artificially with the help of a lamp: abundant flowering is possible only in direct sunlight. The air temperature in the room is kept at + 18 ° C. In the summer, it is recommended to take the pot out to the balcony or to fresh air, this will promote active growth.
Advice Despite the fact that the medlar is photophilous, young plants should be protected from direct sunlight. Until the sprouts get stronger, they should be kept away from the sunny windowsill.