What is fern
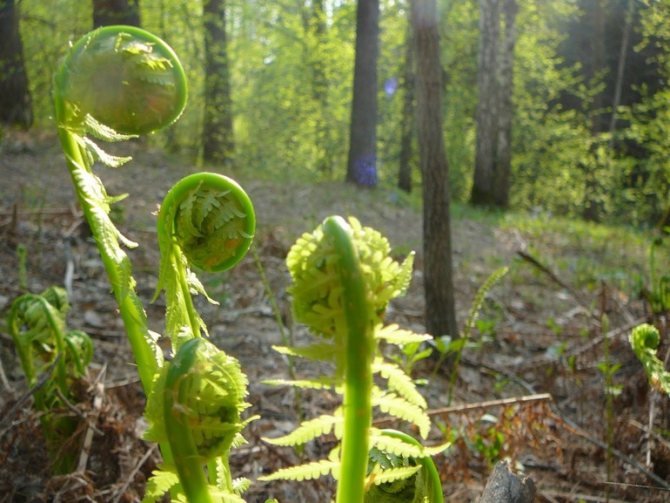
Along with the usual plant organ rhizome in ferns (Polypodióphyta), instead of stems, leaves, peduncles with seed pods, a leaf-like shoot developed, which received the scientific name frond. Spores form on fronds, with the help of which one of the ways of reproduction and development of ferns occurs.
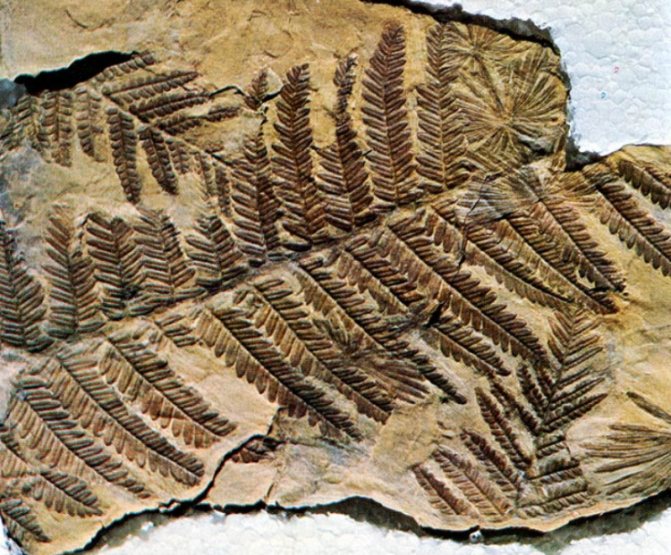

Fern print on stone
Currently, about 10 thousand perennial fern species have been identified on Earth. In the temperate climate of Russia, they grow in moist shady forests, they are grown as a garden crop. The most widespread European species of Polypodióphyta are the ostrich, bracken, and shrimp. Bracken fern is harvested in early spring, soaked, dried and used as a food product.
For your information! Growing bracken in a garden can negatively affect pets. The green parts of the plant contain toxic substances that are dangerous to them.
The tropical species Polypodióphyta are distinguished by a large variety of wai, and can have tree-like forms. Some of them grow high above the ground on the branches of other plants. In cold climates, the cultivation and reproduction of heat-loving ferns and fern-like plants (horsetail, lyre) is carried out at home.
Among the popular indoor ferns, the Aspelium stands out with shoots that resemble a green fountain; Blehnum, whose frond grows like the leaves of a palm tree; Nephrolepis is a lover of large free space; Disconia is a tall plant for office space; Platizerium, the fronds of which are like deer horns.
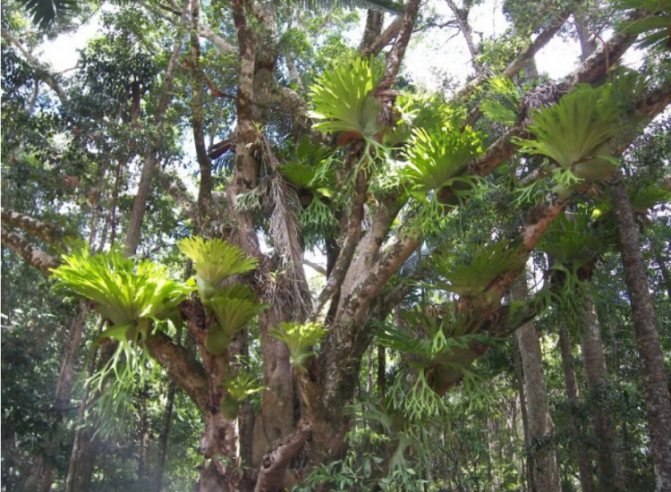


Tropical Platizerium on the branches of a tree
Plaunas - structure
Plaunas were widespread during the late Devonian and Carboniferous periods. Many of them were tall, tree-like plants. At present, a small number of species (about 400) has survived compared to the past - all these are small plants - up to 30 cm in height. In our latitudes, they are found in coniferous forests, less often in swampy meadows. The bulk of the lyre are inhabitants of the tropics.
The common species in our country is the club-shaped lymphoid. It has a stalk creeping along the ground, from which needle-branching lateral shoots extend vertically upwards. Its leaves are thin, flat, arranged in a spiral, densely covering the stem and lateral branches. The growth of lymphoids occurs only at the point of growth, since there is no cambium in the stem.
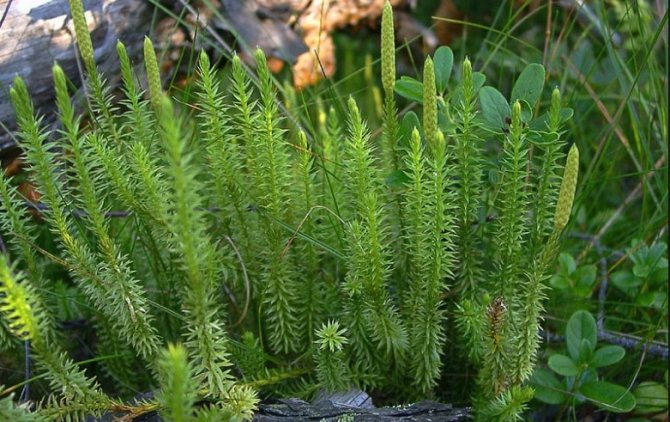


Year-old plow - photo
Reproduction of lymphoids
At the top of the stem are special leaves - sporophylls, collected in strobilus. Outwardly, it resembles a pine cone.
The germinating spore produces an outgrowth (gametophyte) that lives and develops in the ground for 12-20 years. It has no chlorophyll and feeds on fungi (mycorrhiza). The change of sexual and asexual generations in horsetails and lymphoids occurs in the same way as in ferns.
Fossil ferns formed thick coal seams. Bituminous coal is used as a fuel and raw material in various industries. It is used to produce gasoline, kerosene, combustible gas, various dyes, varnishes, plastics, aromatic, medicinal substances, etc.
How ferns reproduce in nature
Fern species and their classification
The reproduction of ferns has become a subject of study not only by botanists and plant breeders; pupils of grades 5-6 in secondary school are told about the spore, vegetative, asexual methods of fern breeding with diagrams and descriptions.
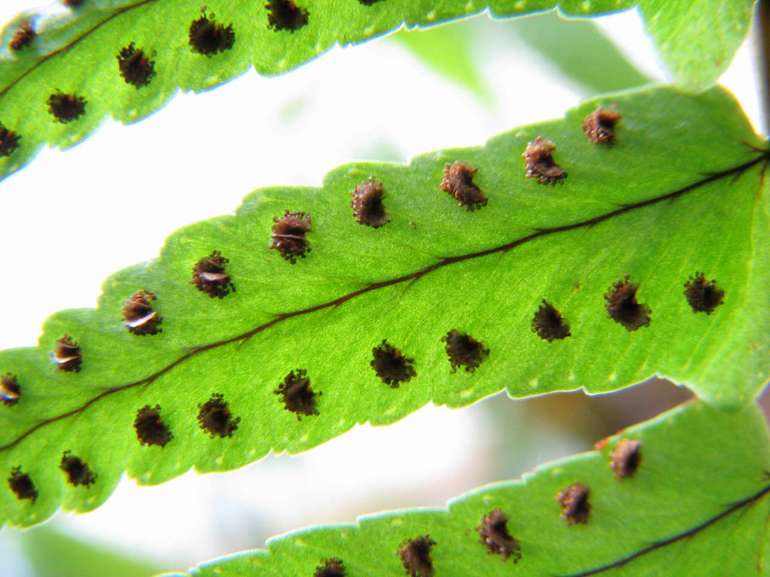
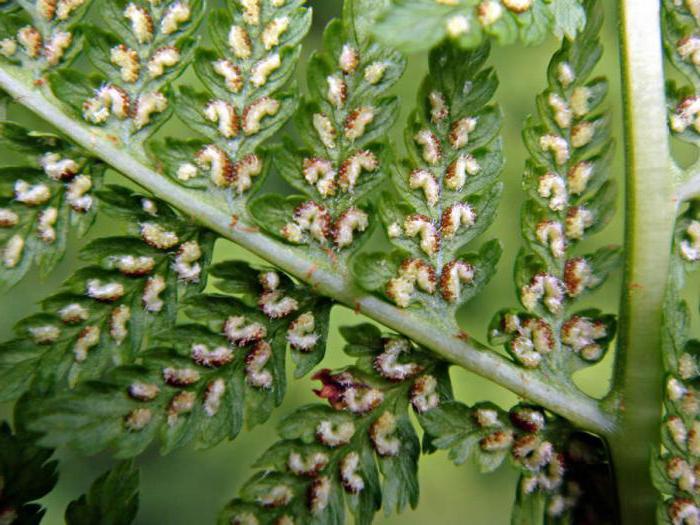
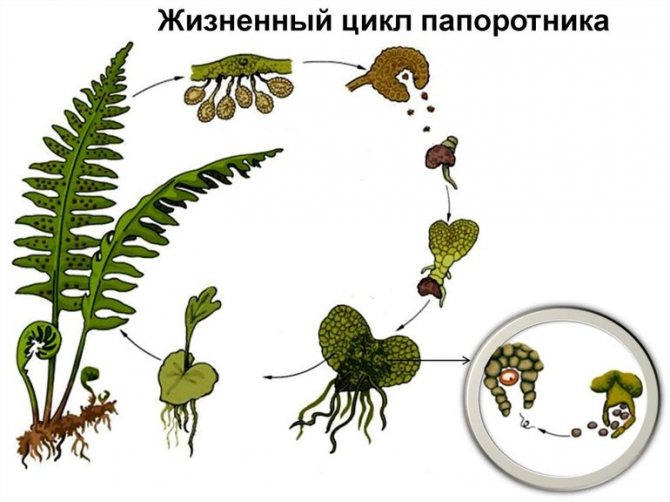
Spore reproduction of Polypodióphyta is subdivided into two cycles. They involve two genetically identical species of the same plant. At the first stage, frond grows from the rhizomes, sporangia form on the lower surface of the shoots, and spores form in them. Piles of sporangia with spores are collected in pouches (soruses). They are clearly visible on the underside of the wai. Spores from them spill out to the ground after ripening.
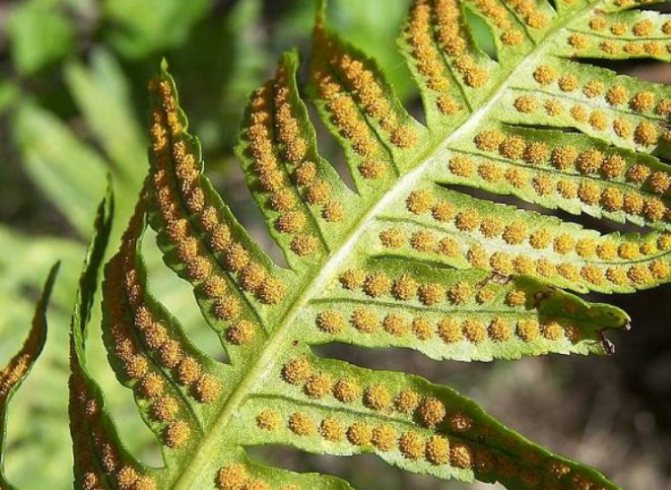


Sori with ripe sporangia on the back of the ostrich frond
At the second stage, a small, thin plant plate is formed from the spores on the surface of the earth - an outgrowth. It contains sperm and egg cells separated by plant fibers. They can unite into a single cell only under the external influence of water.
During rains, mature male cells swim up to the eggs and form zygotes. The strongest of these forms the embryo. The embryo draws strength from the germ, which gradually dies off. The embryo forms the root system, gives life to a new plant.
Note! The Polypodióphyta rhizome is the underground part of the stem in which plants accumulate nutrients.
In some fern species, spores are not formed on all fronds. In the Ostrich Feather fern, spores form in sporangia located on special fronds collected in the center of the plant. They differ in size, tissue thickness, and are collected in a bundle. Some people mistake these branches for peduncles.
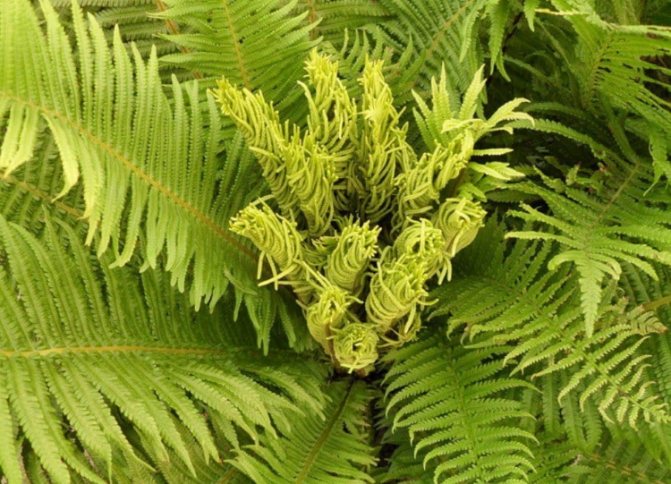


Ostrich with central fronds
How fern reproduces at home
Venus hair - description and care at home
Indoor reproduction and cultivation of Polypodióphyta is possible in several ways - by spores, planting outgrowths and vegetative methods:
- separation of rhizomes;
- rooting shoots;
- separation and rooting of brood buds.
The most common methods of reproduction are spore and separation of rhizomes and root processes. In open field conditions, fern crops are mainly propagated by separating the bushes during transplantation to a new growing site.
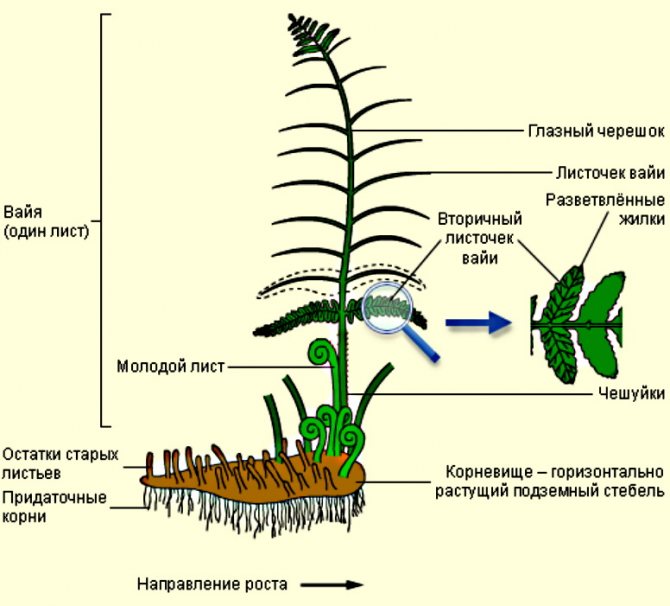

The structure of the root system and surface shoots of Polypodióphyta
How to propagate a fern by dividing a bush
Separation of root shoots and rhizomes of plants in the garden is carried out in spring or early autumn. Indoor overgrown ferns can be propagated throughout the warm period, combining transplantation with dividing the bush.
In the conditions of the garden, a site is preliminarily prepared for new parcels. For ferns, the best place to grow is an area of the garden where plants can be in partial shade.
Important! Bright sun and heavy shade are not suitable for fern-like crops.
The soil for plants should be loose, fertile, moisture permeable. You can buy a special soil mixture at a garden store or make it yourself from leafy soil, sand and peat (ratio 2: 1: 1). For indoor Polypodióphyta, a drainage layer is poured onto the bottom of the pots. Moisten the soil before transplanting plants.
The soil in a pot with a plant that is going to be planted is moistened 2 days before transplanting. The procedure begins by turning the container with the fern on its side and starting to roll it on a flat surface, thus separating the earthen lump from the walls of the pot.
Holding the plant with one hand, the pot is turned upside down, the bush is pulled out along with a lump of earth with rotational movements. Examine the condition of the roots, rosettes.The bush is divided in such a way that in each division there are 2-3 rosettes with well-developed roots and growth buds.
Note! Plants for good survival need to provide partial shade, regular watering, air temperature within 10-20 ° C.
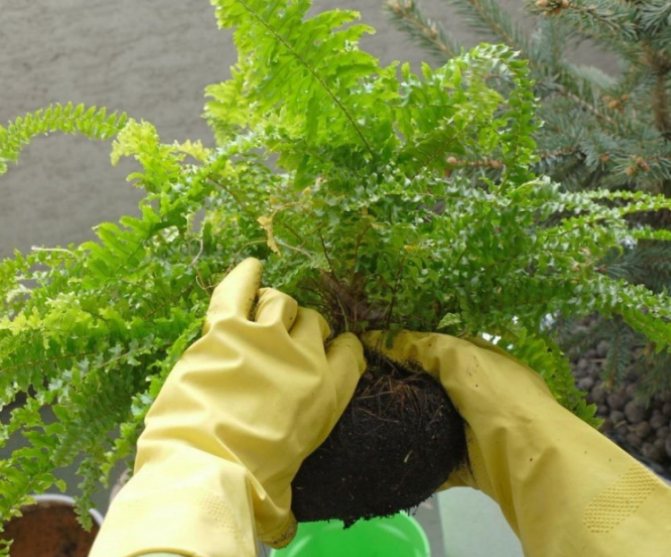


Splitting the bush
Views
Modern ferns are represented by more than 11 thousand different species, which are distributed around the globe. They grow in a wide variety of places: swamps, forests, fields and even deserts. Moreover, their appearance is as diverse as the places of growth. For example, in the tropical forests of South America, you can even find giant tree ferns that look like palm trees.
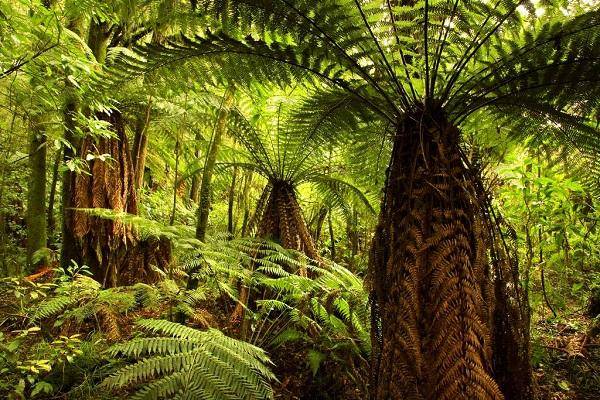


All ferns grown in the wild or grown in the garden and at home can be divided into two groups:
- gametophytes or sex plants. They are represented by females and males. These species often grow in the wild;
- sporophytes are asexual plants. Sporophytes grow in temperate and subtropical climates. Their characteristic feature is a sheet plate rolled into a spiral. It is these features that made sporophytes frequent residents of the house as decorative indoor flowers. This is due to the fact that the structure of the leaf of a plant can have a different appearance.
The following types of ferns are great for indoor growing:
- maidenhair. It is a graceful plant that forms feathery fronds, which are located on dark brown thin petioles. The leaves are characterized by fine dissection. Shades well. Has a simple care and rapid development, due to which the house quickly grows to a large size;
- asplenium. This indoor fern is characterized by a shiny leaf surface that has a light green color. The fronds have a solid, not divided into separate segments, structure. Therefore, they have a majestic and very beautiful appearance. A central vein runs in the center of the sheet. It darkens over time, which makes it more expressive;
- nephrolepis. Several species of this plant are grown at home, which differ among themselves in the size and shape of the leaves. Sori with spores are placed on their underside. Like Asplenium, it has simple home care;
- platycerite. The structure of this flower is characterized by two types of frond: sterile and spore-bearing. It is not recommended to touch the surface of the leaves, as this can disturb their silvery edge.


These are the most common indoor ferns in the home. But besides them, blehnum can be grown in the house. This flower, if the care was organized correctly, can reach a height of one meter. Leaves are formed quite dense and tough. Also dawallia or hare's foot often grows in pots at home. As an indoor flower, it is very attractive, as the plant forms beautiful shaggy rhizomes that hang from the pot. They look like a rabbit's foot, which gave the fern its second name. Growing this flower at home is also quite simple.
If desired, you can try to grow other types of ferns at home. The main thing is to know what kind of care they need at home.
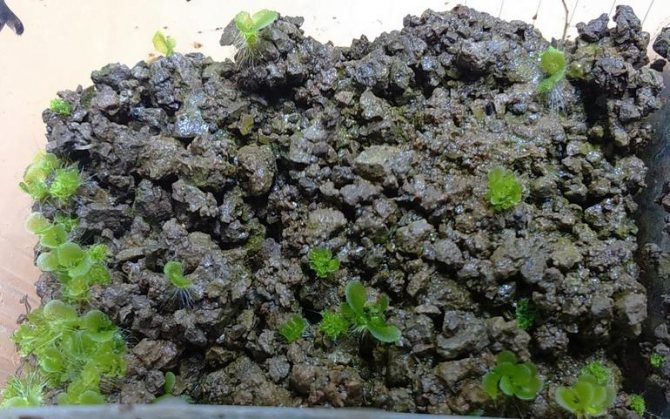
How to propagate indoor fern by spores
Many growers treat Polypodióphyta spores as seeds of common indoor and garden flowers. Spores in different fern species mature at different times. A sign that spores can be used as planting material is a change in the color of the sporangia to brown or brown.
Flowerbed with hydrangea - planting scheme of bushes
Sporangia, together with the spores, are cut from the frond and placed in a paper bag.Sowing can be started after the spores are completely dry.
Attention! They will start to spill out to the bottom of the bag as a brown powder, so you need to handle the bag with care to avoid spilling the seed.
For planting, shallow planting boxes and pots with drainage holes or a layer of expanded clay, small pieces of foam are prepared. A soil mixture is placed in boxes with the addition of coarse-grained river sand, leaf earth, and peat. Spores can also germinate well in violet soil.
The soil is well moistened a few days before planting. Before planting, the earth is tamped, the spores are placed on the surface of the soil, they are not sprinkled with anything. Transparent caps made of plastic bags are put on the planting containers or covered with pieces of glass, that is, conditions for mini-greenhouses are created. From time to time, the soil must be moistened, the boxes must be ventilated.
Important! The soil in the container with the sown spores must be constantly moistened, otherwise the process of fertilization of the eggs will not occur.
The spore germination process is very long. The first stage in the development of spores is the appearance of moss-like growths. The root system will begin to form in a few weeks in the formed embryo, and until then the germs receive moisture and nutrition through the rhizoids - the hairs formed on them after spore germination.
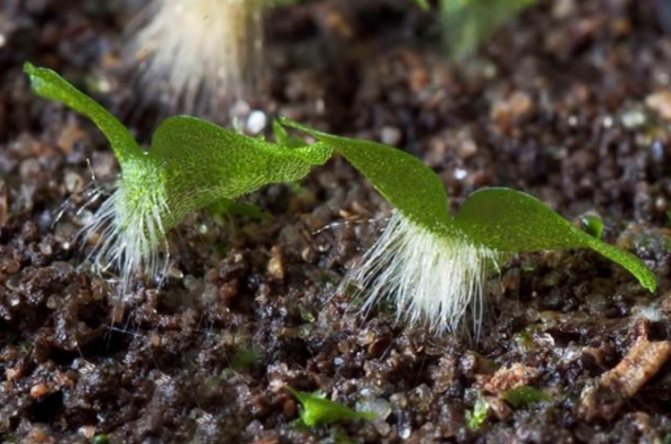


Rhizoids in the lower part of the outgrowth
Diseases and pests, the fight against them
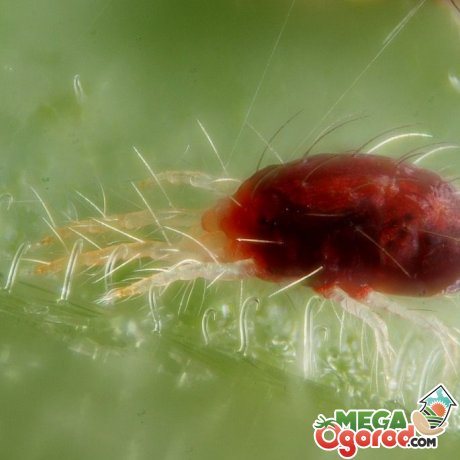


The fern is susceptible to disease, like any other indoor flower. In order to prevent the emergence of pathogenic bacteria and the invasion of parasites, it is worth following the conditions of care and constantly monitoring the condition of the plant.
The following diseases are distinguished, which most often affect the fern:
- Decay of the root system - initially the problem is reflected in the foliage, it begins to turn yellow, then turns brown. In order to prevent the formation of a fungal disease, it is necessary to correctly add the amount of nutrient moisture and prevent waterlogging.
- Gray rot - on any segment of the shrub, as well as on the soil substrate, there is a pile of gray plaque. To save the bush, you need to quarantine it, away from other plants from the collection. Remove all damaged parts. if possible, disinfect the soil and spray the branches with chemicals from mold.
- Anthracnose - Brown stains form at the ends of the leaf plates. All diseased leaves should be removed from the plant, and healthy ones should be treated with a fungicide. In this situation, it is recommended to reduce the introduction of nutrient moisture somewhat, and also to remove the spraying for a while.
- Spotting on leaf blades - brown oozing spots form on the foliage. To save the pet, it is worth completely removing all affected areas, also reducing watering to a minimum and spraying with chemicals.
In addition to diseases, the plant is affected by pests. Such parasitic insects include whiteflies, worms, spider mites, nematodes, thrips, and aphids.
If the colonization of parasites is detected at the initial stages, then it is recommended to remove the pests by hand. If the pest population exceeds the permissible limits, then chemical preparations must be used.
Most often, all problems are formed due to improper care and lack of control over the plant. Therefore, it is recommended to monitor not only the amount of watering, but also the dryness in the house, as well as the introduction of nutrients.
Fast fern breeding process
Ferns can be quickly propagated by separating brood buds and side shoots.
The side shoots are the thin whiskers that the fern forms along with the fronds. Their purpose is to provide the main plant with nutrients. The plant is capable of propagating with a mustache independently.When in contact with wet soil, shoots grow into it, taking root. Shoots take root within a month. They are separated from the mother bush and planted in specially prepared pots.
Brood buds are formed in some species of Polypodióphyta in the axils of leaf petioles. Under natural conditions, they fall off and take root in moist soil. At home, the frond with brood buds is bent to the ground, pinned with a V-shaped mount, sprinkled with moist soil. The buds release shoots. When 3 young leaves are formed on the shoots, they are planted in individual containers.
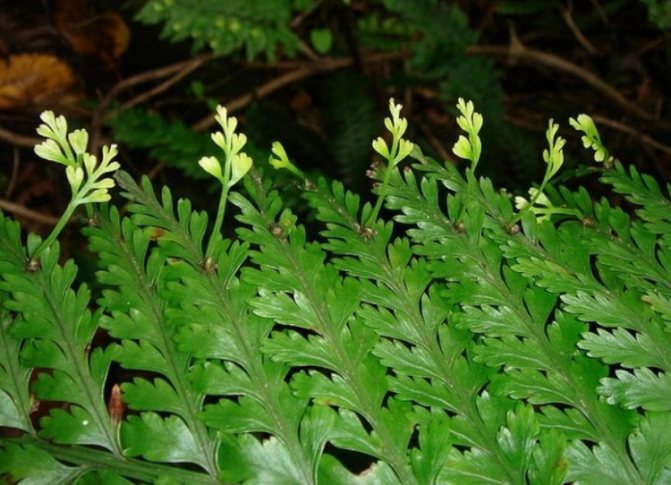


Brood buds in the axils of the petioles