Plants »Flowers
0
1004
Article rating
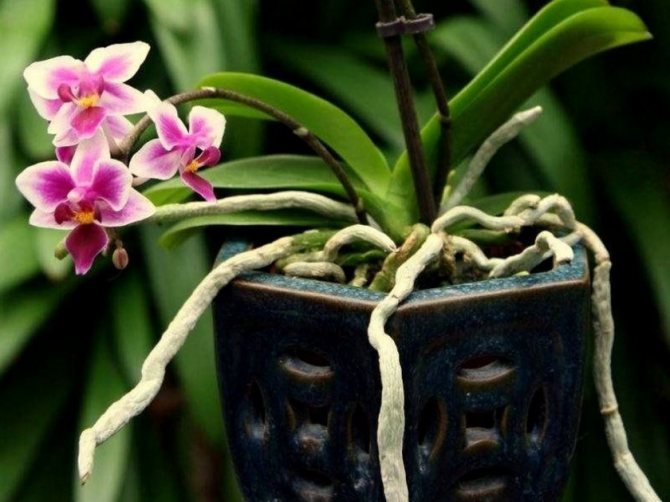
The orchid has become a resident of many houses. She is unpretentious in care and looks unusual. With minimal effort, the overseas beauty easily adapts to the microclimate of the apartment. Its flowers are pleasing to the eye for up to 10 months a year. For some growers, one stem is not enough, so they practice the propagation of an orchid with a peduncle.

How to reproduce an orchid with a peduncle
How do orchids reproduce with a peduncle?
The peduncle is formed in the leaf axil and at first it can be easily confused with the root. Only as it grows do clear differences appear. The peduncle is a green arrow with a pointed tip, and the root is always smooth and semicircular. Peduncle propagation is considered the safest way. This breeding method has a number of advantages:
- does not damage the mother plant;
- most of the plants grown in this way take root well;
- allows you to independently stimulate the appearance of kidneys;
- easy to use, and therefore available even to inexperienced growers.
However, for all the seeming simplicity, this method requires the mandatory observance of some rules.
For a new plant to be strong and strong, you need to follow these recommendations:
- choose only healthy specimens for reproduction;
- leave the lower sleeping bud on the peduncle;
- process all sections of the cuts with special means.
Cuttings after flowering
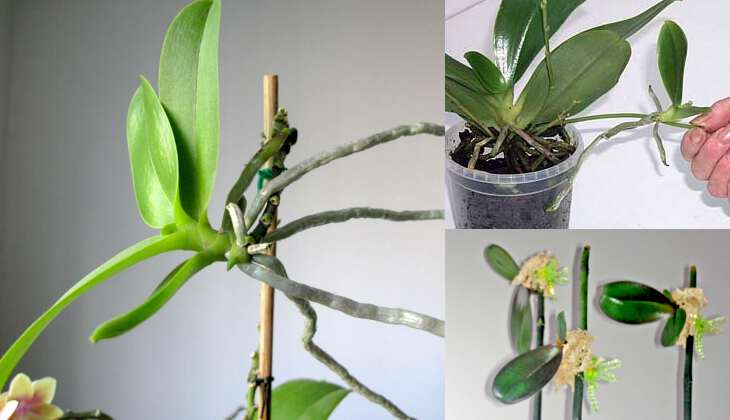
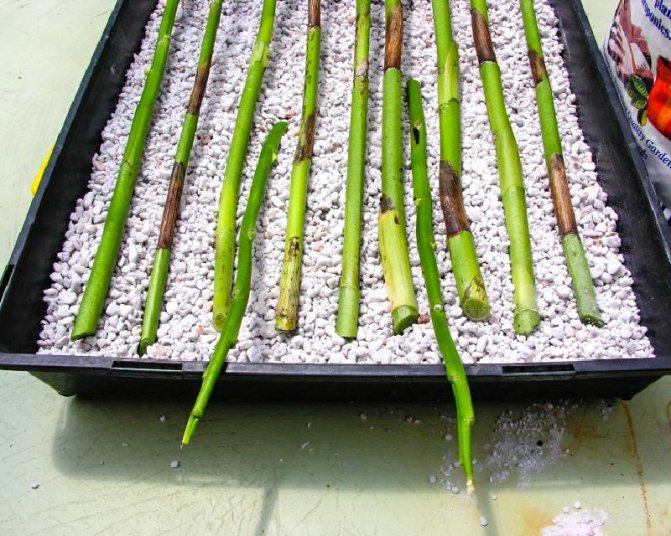
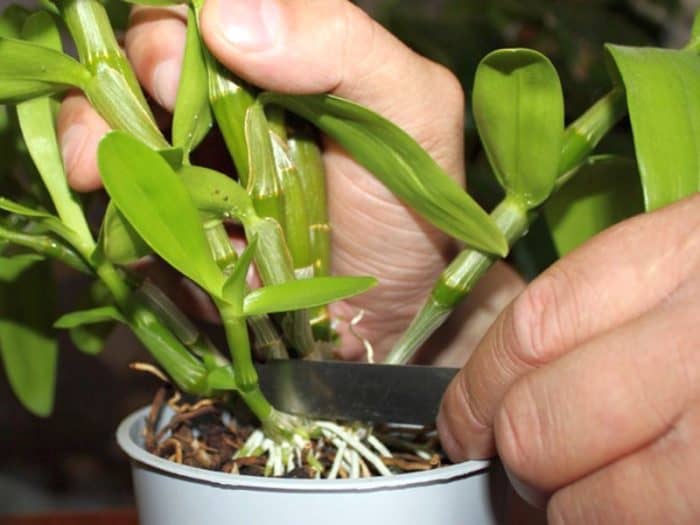
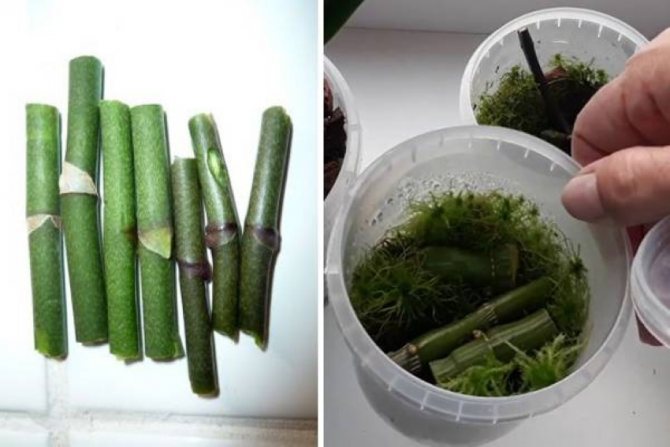
Cuttings are the most popular breeding method. The peduncle is cut off after the flowering period ends. This breeding method gives you the chance to root as many cuttings as there are buds on the cuttings. This operation is performed in several stages:
- Sterile instrument the faded shoot is cut off, but the lower bud is left. This enables the mother flower to form a new shoot.
- Cut stem it is divided into parts so that there is a kidney on each fragment. The distance from the lower part of the cutting to the bud should be at least 2 cm, from the bud to the upper part of the cut, not less than 0.5 cm.
- Top cuts dried and processed with ground coal. The same is done with the cut on the mother plant.
- Bottom sections cuttings are dipped in the rooting solution.
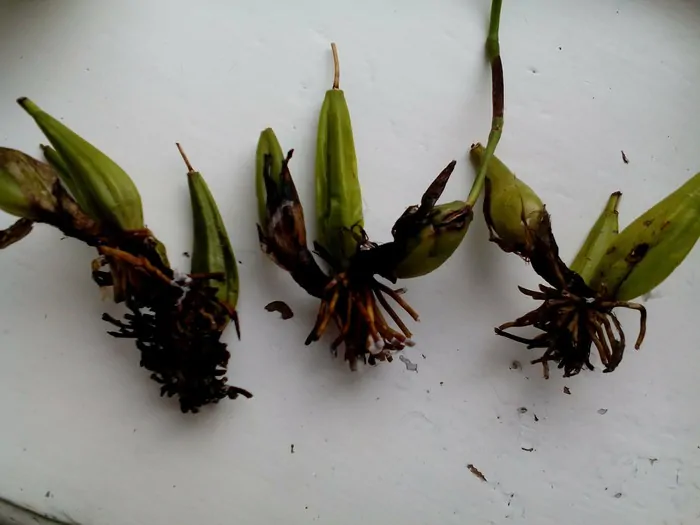
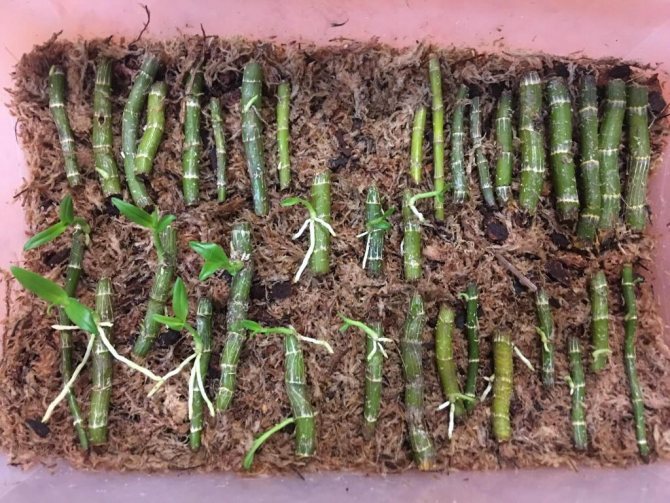
- Ready cuttings fit into a greenhouse with a moist substrate. The mini-greenhouse is tightly closed and placed in a warm and bright place.
You need to check the greenhouse every day with mandatory ventilation, otherwise the cuttings will begin to rot. Fresh shoots appear in about two weeks. When two leaves appear on them, and the roots reach a length of 4-5 cm, you can transplant the plants into separate containers.
Before flowering
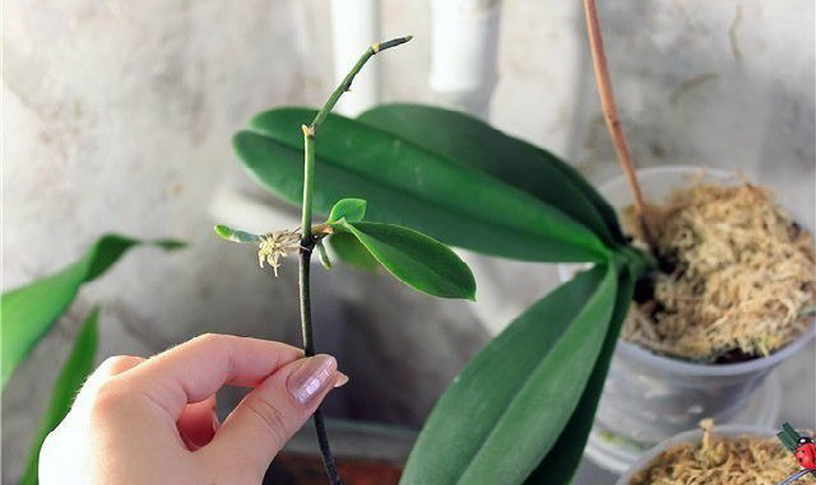
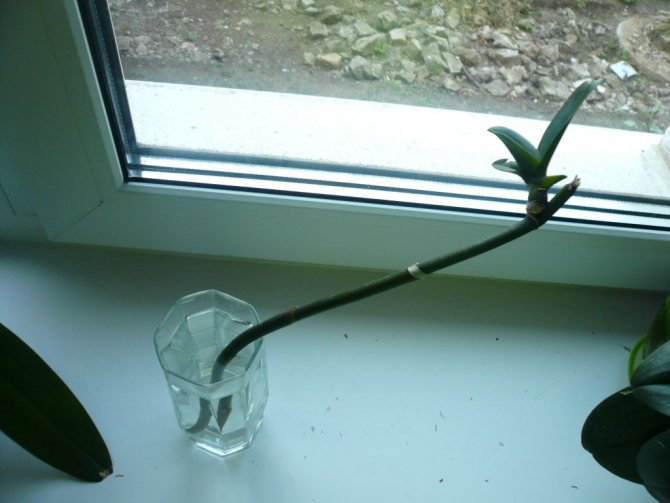
To reproduce with a whole peduncle, you will have to sacrifice the flowering of the mother plant. In this case, the arrow of the peduncle is cut off without waiting for a bud to form on it. When cutting off a shoot, it is important to leave the lower dormant bud, from which a new shoot will subsequently appear.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- The peduncle is cut so that about 1-1.5 cm of the stem remains from the bud to the lower cut.
- Dried sections are processed with crushed coal.
- The stalk is placed in a container with a pre-prepared nutrient mixture.
- The container is closed with a bag or lid and placed in a warm, bright place.
The greenhouse must be aired daily, and the peduncle must be sprayed with a biostimulator. In addition, the nutrient solution needs to be changed every 3-4 days. When the shoots sprout from the buds, they must be separated from the cutting. When at least two leaves appear on them and the roots grow up to 4-5 cm, they can be planted in separate pots.
Formation of a baby from a kidney
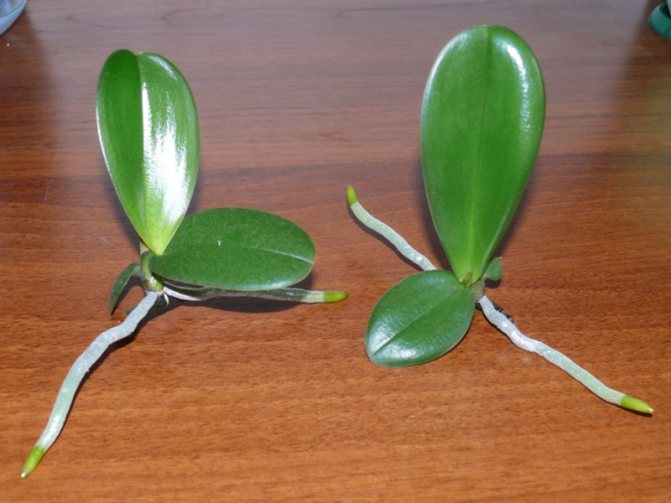
The baby is a young, independent plant that forms on different parts of the mother flower. The offspring of an orchid has its own root system, leaves and can even release a peduncle. Ripening lasts about six months and only after the roots grow back, the baby can be separated from the parent plant and transplanted into a separate flowerpot. Not every orchid grows babies, for this to happen, certain conditions are needed:
- After flowering is complete, the peduncle must be cut off, leaving the lower bud. Otherwise, the orchid may simply dry it out, trying to save nutrients.
- The formation of the baby is the result of the flower's desire to give new offspring. Such a need arises only in a stressful situation for a flower.
- Artificial stimulation of the kidney is possible. For stimulation, special hormonal preparations are used.
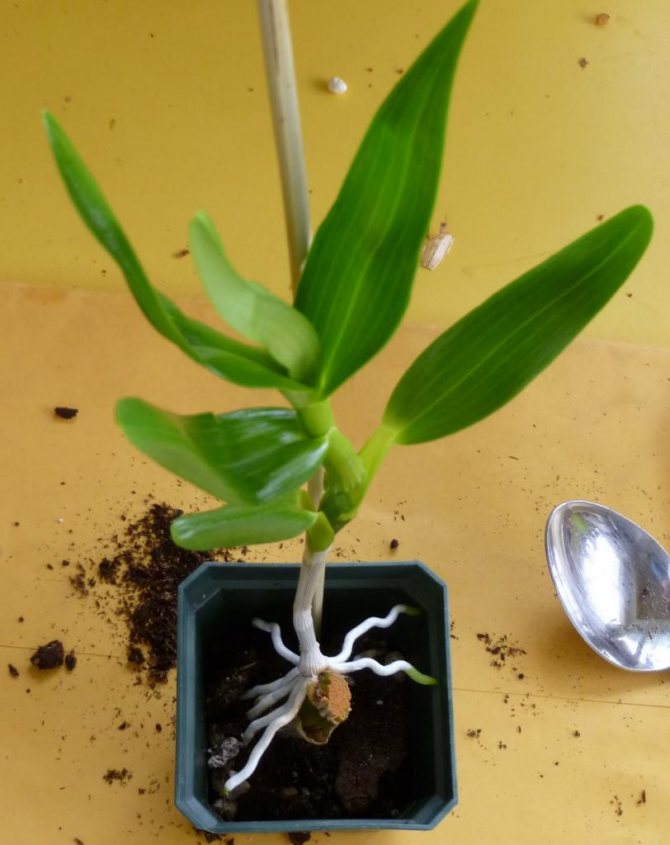
If the offspring does appear on the mother plant, then you need to separate it from the flower and transplant it into a separate pot. This can be done only when the young plant reaches a certain level of development. The operation should be carried out as carefully as possible and in compliance with all the rules, otherwise there will be a risk of ruining both plants.
Classification by type of height
All types of orchids, according to their characteristic growth characteristics, are divided into two large groups:
- Sympodial - plants consist of numerous shoots, which are interconnected by a rhizome. This is a modified stem, creeping along the surface of the substrate, from the nodes of which leaves and pseudobulbs with bunches of young roots are formed. They have several points of growth, and each new sprout turns into a pseudobulb (a thickened orchid stem with a supply of nutrients). This type includes "Lelia", "Cattleya", "Dendrobium".
- Monopodial - they do not have rhizomes and pseudobulbs, but contain one vertical stem and only one apical growth point. Growth is carried out by lengthening the stem and laying leaves at the top. In the axils, between the leaves, buds are laid. Lateral peduncles or axillary aerial roots are formed from them. Over time, from below, the leaves grow old and die off, and the young ones develop higher along the shoot. Representatives of this type are "phalaenopsis" and "vanda".


The type of orchid belongs to, to some extent, its method of reproduction depends.
Why is it necessary to root the shoots?
The rooting process is the creation of the necessary conditions for the germination of roots from parts of the plant taken for reproduction. New shoots can be planted in the substrate only after the roots have grown, otherwise the plant will not be able to receive nutrition. There are two ways to root cuttings: in soil and in water.
To stimulate the growth of root shoots, special hormonal preparations are used, on the basis of which solutions for rooting are prepared. These preparations contain acid, which has a beneficial effect on the formation of callus - plant cells that form new tissues.
The rooting agent is used for pre-soaking or one-time immersion of cuttings in it before planting., or added directly to the nutrient solution.Correct rooting is one of the most important stages in the reproduction of orchids, since the further development and growth of the flower directly depends on the formation of a healthy root system.
Summing up
Indoor orchid houses are propagated more often by children, stem cuttings, air layers. Seed planting is available only to experienced growers and is carried out mainly for breeding purposes. The choice of method and its step-by-step execution directly depends on what part of the orchid has for breeding.
With any technology, it is important to comply with the conditions of agricultural technology: to carry out all manipulations at the recommended time at a certain temperature and humidity. The new sprout is looked after as a simple adult phalaenopsis, providing watering, light and warmth. Only a healthy flower can be bred and stimulated to awaken offspring.
Suitable conditions
In order for a home orchid to produce offspring, you need to create special conditions for it. Plants that live in absolute comfort are not prone to reproduction, so you need to put the flower in a state of stress. The emergence of new shoots is most likely in the following environment:
- the presence of diffused sunlight for 10-12 hours a day;
- the difference between night and daytime temperatures is about 10 ° C;
- humidity level in the atmosphere 40-50%;
- rare watering;
- increase in nitrogen content in top dressing.
Cuttings and shoots sent for rooting also need special conditions for keeping. In the greenhouse, the temperature should be maintained in the region of 26-28 ° C and humidity at the level of 70-80%. The mini-greenhouse needs regular ventilation so that the scions do not rot. When rooting in the ground, watering is done every two weeks, when rooting in a liquid - the solution is changed every 3-4 days.
Raising children
The baby orchid is a natural clone of the mother plant. She, in fact, is a small formed orchid, which has a stem, roots and leaves, and in some cases produces a small peduncle. But it happens that after the end of flowering, it is necessary to stimulate the distillation of shoots. How to successfully grow an orchid baby from a peduncle? To do this, use the following methods:
- The difference between day and night temperatures. The night time is set at 18–20, and the daytime at 28–30 degrees. Moreover, they provide high air humidity by spraying and placing pebble trays filled with water. Daylight hours due to artificial lighting are extended to 12 hours.
- Sunbathing. For one hour a day in early spring, the orchid is exposed to direct sunlight. Care must be taken that the leaves do not become dark purple. In this case, the procedure is canceled.
- Artificial drought. For two weeks, the plant is not watered, but it is protected from direct sunlight. The roots become gray-silver in color, after waiting another two days, the soil is moistened. Thanks to the stress received, the plant is activated and releases shoots.
- Top dressing with fertilizer containing an increased dose of nitrogen. The method poses some risk, and the orchid sometimes dies from an excess of nitrogenous fertilizer. Therefore, use it with caution.
How to propagate phalaenopsis at home
In their natural habitat, Phalaenopsis reproduce by seeds. At home, pollination does not occur and independent seed reproduction is impossible. Growing a flower from a seed artificially is an extremely painstaking and long process, the process will take at least 5-6 years. Therefore, the most optimal way of reproduction is to grow babies on a mother plant or a cut peduncle.
Peduncle selection
For cultivation, you should choose peduncles of adult plants with at least 5-7 healthy strong leaves. If the method of grafting is chosen, then the peduncle should be cut off immediately after the end of flowering, without waiting for it to dry out.It is good if there are at least a dozen dormant buds on the layer.
Do not use flower stalks recently brought from the store for propagation. The tissues of these flowers may contain a high concentration of chemical fertilizers that interfere with the natural growth and survival of the shoots.
How to get the kidney to wake up?
In addition to creating a mild stressful situation for an orchid that does not want to multiply, awakening a dormant bud can stimulate the use of a special hormonal agent. Cytokinin paste, created on the basis of the phytohormone cytokinin, activates cell division, which in turn provokes the appearance of new sprouts.
When using the paste, you need to take into account the recommendations and contraindications:
- use is permissible in homeopathic doses, otherwise the kidney will dry out;
- do not apply on dormant plants;
- do not handle sick and weakened plants;
- apply to no more than three buds of one flower;
- create appropriate containment conditions after stimulation.
Kidney treatment is carried out in a warm room. Before applying, you should carefully remove the protective scales from the kidney. It is better to handle the buds that are closer to the ends of the peduncle.
Department of babies
When the baby grows on the mother plant and develops properly, it will need to be separated. In order not to harm any of the plants, you need to act very carefully:
- Prepare the necessary tools and materials.
- Disinfect the cutting instrument with alcohol or chlorhexidine.
- Carefully cut off the offspring from the peduncle, leaving about 1.5 cm of the stem on each side.
- Dry the cut points and treat them with crushed coal.
Before proceeding with the separation of the baby from the adult flower, you should prepare in advance the pot into which the sprout will be transplanted. The selection of a suitable substrate is also important.
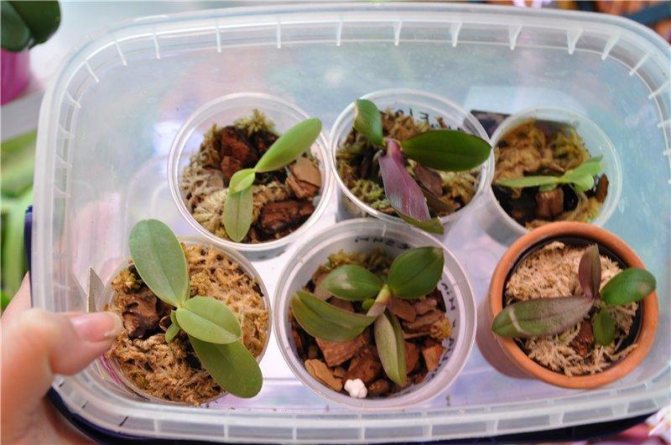
Pot and substrate preparation
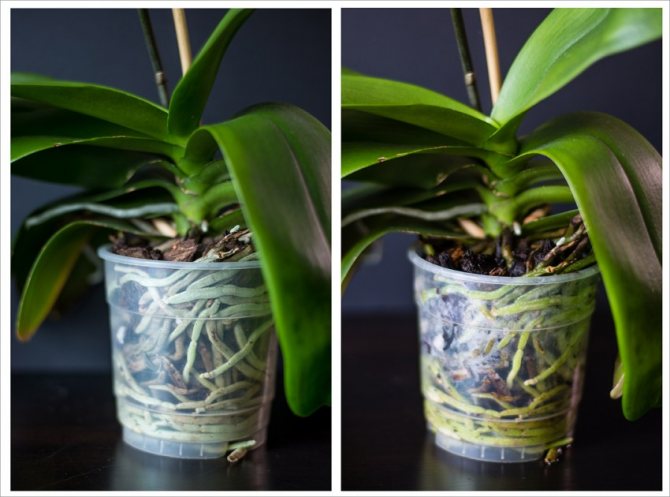
The pot for transplanting a new flower should be made of clear plastic. There should be perforations in the bottom and walls of the container to ensure the removal of excess moisture. The size of the pot should be very small; in large flowerpots, orchids begin to grow deciduous to the detriment of the rest of the flower.
The growing medium should consist of large to medium sized pieces of pine bark or coconut shells... In addition, drainage is needed, for the role of which expanded clay is ideal. For the top layer, sphagnum moss is required, which prevents the substrate from drying out.
Planting the appendix
After the sprout is separated from the mother flower, and all the cuts are properly processed, you can start planting it. The planting process is as follows:
- the plant is placed in the center of the pot, at the bottom of which there is a drainage;
- the flower adheres, and the container is filled with a moist substrate;
- sphagnum is laid on top.
The first watering can be done about 4 days after transplanting.... Before that, the bush can be sprayed from a spray bottle. The temperature and humidity of the atmosphere should be kept high.
Tips & Tricks
Experienced flower growers who have been growing orchids for a long time give the following recommendations:
- For good survival of cuttings, moist soil is needed until 2-3 leaf nodes appear.
- After the roots grow back 5 cm long, the sprouts are planted in new pots.
- When propagating, apical cuttings are often used.
- For the establishment and emergence of flower buds, the plant needs to arrange stress in the form of artificial drought or a sharp change in temperature.
- Bushy orchids of the sympodial type are most easily propagated by separating the rosette with roots.

- It is very important to observe the sterility of the necessary equipment and planting material during reproduction.
Reproduction nuances
The propagation of orchids by peduncles is not particularly difficult. With proper care and adherence to technology, this propagation method allows you to get several flowers from one peduncle. In addition, this method does not injure the adult plant that was selected for propagation.
Is it possible to grow a baby on a cut peduncle?
On cut peduncles, children grow out of dormant buds. In order for the buds on the cut stem to awaken, it is necessary to provide them with suitable conditions:
- the right choice of peduncle;
- treatment;
- rooting in water or soil;
- greenhouse conditions;
- diffused light;
- top dressing.
How to stimulate an orchid to sprout?
If the orchid does not give new shoots for a long time, then the first step is to diagnose its condition.
In the event that the flower is completely healthy, you can start stimulating:
- avoid changing lighting;
- give extra light in winter;
- ensure temperature drops at night and daytime;
- use a contrast shower;
If natural methods of stimulation have not helped, then you can resort to using special drugs. There is a wide range of root and foliar nutrition products on the market, as well as direct application to the buds to stimulate sprouting.
What if there is no flower stem?
Flowering is part of the life cycle of an orchid with normal development. If it is completely healthy, has an abundant deciduous mass, but at the same time does not release a flower stem in any way, the conditions of detention should be assessed. Among the main reasons that interfere with the appearance of the stem, the following can be distinguished:
- insufficient atmospheric humidity;
- lack of lighting;
- excessive or insufficient watering;
- unsuitable temperature.
What does the reproductive organ of a plant look like?
It is quite difficult for a novice florist to distinguish a peduncle from a root. At first glance, they are similar. That's just something starts to peck under the sheet, it is impossible to immediately give an unambiguous answer. The peduncle grows at the junction of the leaf with the stem... At the beginning of growth, it can wriggle, and then it grows vertically upward or to the side, directed towards the sunlight.
It happens that instead of the expected flowers, children appear. This phenomenon is possible with an inappropriate temperature regime in winter or due to problems with the root system.
Reproduction at home


Orchids are bred at home in the following ways: seedlings, children, dividing rhizomes. Breeding by babies that form on the peduncle is considered the safest and most reliable method.
pros:
- the mother plant is safe;
- a large percentage of established plants;
- you can wake up the kidneys on your own;
- the method is not difficult to execute, under the power of an inexperienced grower.
Indeed, the peduncle breeding method is simple, but everywhere there are pitfalls and various nuances:
- the flower must be an adult, have at least 4 leaves;
- a healthy root system;
- the method is applicable after the flowering period;
- the optimal time for breeding is the end of winter, lasts until mid-summer;
- a fresh peduncle with a strong bud is needed.
Fundamental rules
There is an opinion that babies appear on the peduncle at elevated temperatures and humidity. So, for the natural formation of sprouts in a dormant bud, certain conditions must be adhered to... In order to propagate the plant through the peduncle at home, it is important to create a stressful situation for the orchid.
- The duration of daylight hours is 10-12 hours. Sunlight should be diffused.
- Temperature drops: daytime temperature will be + 25-27 ° С, night temperature will be + 15-17 ° С, respectively.
- Indoor humidity is within 40-50%.
- Watering is minimal.
- Do not use top dressing and fertilizers.
- Lack of fungal diseases and pests.


If all else fails, even if you follow all the rules, you can apply artificial stimulation of the kidneys. Modern technology is based on the use of cytokinin paste. It contains phytohormones that provoke active cell division.
- Preheat the paste to room temperature.
- We choose a suitable peduncle, a lower, healthy bud.
- With the help of tweezers, separate the scaly skin, under it is a kidney of a light green hue.
- Moisten the area with water.
- Using a toothpick or a needle, evenly apply a thin layer of paste to the scratched kidney.
- After 7-10 days, we are waiting for the result.
Indications and contraindications
Experienced professionals recommend using Cytokinin Paste for demanding, whimsical flowers. The tool promotes:
- awakening sleeping kidneys;
- enhancing the growth process;
- normalization of metabolism;
- the imminent onset of the flowering phase;
- rapid recovery of the orchid after exposure to negative factors;
- extending the life cycle of the plant.
A stimulant is effective, but not always applicable. Before using cytokinin paste, you need to familiarize yourself not only with the instructions for use, but also with contraindications.
It is forbidden to process the orchid in the following cases:


recently transplanted;- is in the flowering phase;
- the flower is damaged by harmful insects;
- sick plant;
- orchids less than two years old.
If you do not adhere to the above recommendations, you can aggravate the situation, which will lead to the death of the plant.
Instructions
- We choose a healthy peduncle with dormant buds.
- We carry out a cut with a sharp disinfected knife, leaving a stump of 2-3 cm.
- Dry the cut of the mother plant, treat it with crushed activated carbon.
- To achieve the best effect, the kidneys can be treated with drugs to stimulate their development. Repeat the procedure weekly for a month.
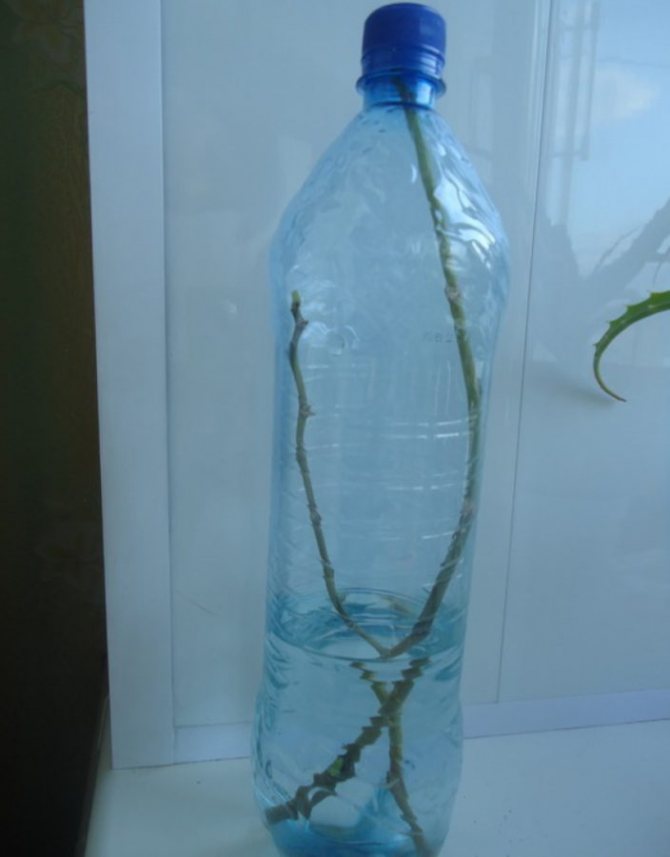
- We place the resulting flowering process in a transparent container; a plastic bottle without a neck will do.
- Pour clean, soft water with a temperature of + 1 ° C there. The liquid level should be 5cm.
- Throw 1 tablet of activated carbon at the bottom of the container.
- We arrange the greenhouse effect for the scion. We build a greenhouse, covering it with a plastic bag. Maintain the temperature in it at the level of + 25-27 ° С.
- We place the greenhouse, preferably on the windowsill from the southwest or west. Or in another well-lit place.
- Every week, the water in the container must be changed.
- We separate the resulting baby when 3 leaves are formed on it, and the roots grow up to 3-5 cm. It is better to perform the procedure with a sharp blade.
- We transplant a new sprout of an orchid into a transparent flowerpot with damp bark.
- We build a greenhouse on top again and leave it on a light windowsill.
- We moisten the bark periodically.
- We remove the shelter, after the appearance of at least two new leaves.
Next, you can watch a video describing the propagation of an orchid through a peduncle:



































