The world of orchids is something beautiful. Plants like to call flowers of seduction, they write poems and sing songs about them. And the mystic writer from Australia G. Meyrink, impressed by the enchanting appearance, called them the flowers of Satan.
Everyone is familiar with indoor flowers, but few have seen orchids in the wild.
Many types of these flowers are a stunning sight: they bloom in large inflorescences in different variegated shades. The easiest way to find such a beautiful picture is in the tropics and temperate regions. Various species of the Orchid family are found all over the world, except for Antarctica. Today there are more than thirty thousand species.
Care features
- During the period of active growth - in late winter and spring - orchids need good lighting and regular watering.
- During intensive development - in summer - orchids need careful watering and feeding. To supply the plant with the necessary nutrients during the growing season, there are special fertilizers.
- At the end of summer, pseudobulbs begin to ripen and flowers are laid. At this time, the temperature should be reduced to 4-6 ° C and watering should be reduced.
- In autumn and winter, orchids enter the dormant and flowering stage (how to care for an orchid in the autumn-winter period?). Many species bloom at the beginning of the dormant period or during dormancy. In winter, care involves an increase in lighting and a decrease in watering.
We talked more about the secrets and intricacies of caring for orchids at home here.
Where were the orchids brought to Russia from?
The first wave of interest in sensational flowers came to Russia in the 19th century. Flowers were brought from England and Germany for the royal family and noble families. The second wave captured the country after the Second World War, when the greenhouses of famous German collectors were brought to Russia. At the end of the forties, the era of industrial cultivation of representatives of orchids began in Russia.
For your information! It was during the orchid fever that a new profession was invented - the plant hunter.
How is the plant grown on an industrial scale?

Orchids grown in greenhouses and greenhouses in Thailand and Holland are mainly sold on the Russian market. (You can find out more about what to do after buying an orchid and how to care for it at home here). Recently, cultivation of orchids in the greenhouse has become common practice. It takes about a year from the moment of planting a plant to its appearance on the shelves. Growing orchids is possible in several ways:
- vegetative (by dividing parts);
- "Kids" (bulbs);
- family (from seeds);
- generative (due to tissue division in the laboratory).
The plant growth process starts from the "baby" stage:
- The babies are placed in trays in which they grow for 30 weeks under the supervision of greenhouse workers.
- Then they are manually transplanted into a transparent pot, in which they will grow directly in the greenhouse.
- A label is placed on the pot with information about the plant (type, color) and sent to the greenhouse, where they will be grown for 10 weeks.
- The orchids are then transferred to the workshop and placed in a special plastic pot, in which they are kept for 16 weeks.
- After this period, they are placed in a larger pot and are in it until the growth of the peduncle (3-4 weeks).
- At the last stage, orchids are placed in a special "cold" part of the greenhouse, with a temperature of 19 ° C.
The general rule of thumb for growing orchids is: a good ventilation system, providing the air with the correct temperature and humidity; sufficient lighting to increase the efficiency of the photosynthesis process; providing quality soil and fertilizers.
Where do orchids grow?
How ginger grows at home and in nature
An orchid grows in nature where it can receive enough light, air and moisture. Epiphytes take root best in the tropics. They are often found in Africa and South America. Terrestrial flowers are often found in temperate climates. They choose steppes and plateaus, most of all terrestrial orchids grow in Europe and the United States of America. Wild phalaenopsis is most commonly found in the Andes, as well as in the mountains of Brazil and southeast Asia.
Note! To contemplate carpets made of these flowers, you can go to Thailand, orchids have practically taken over this country.
What should be the conditions for domestic species?
- Temperature... Orchids differ in their thermophilicity. Domestic species prefer an average temperature: in summer - 18-23 ° С, in winter 15-18 ° С.
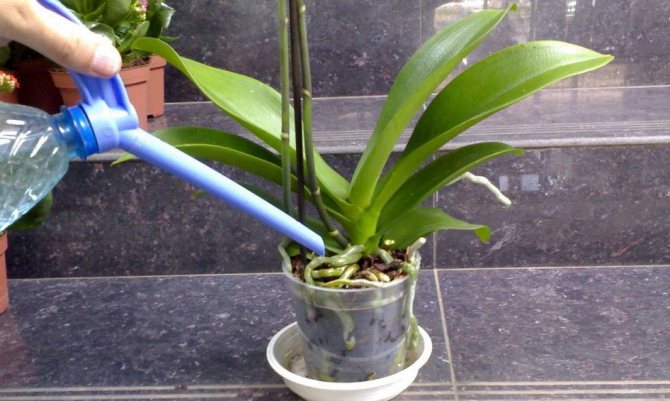
- Humidity... For irrigation, settled (soft) water is used, which is several degrees warmer than the room temperature. Watering is preferable to moderate - from one to three times a week during the growth period, so that the roots do not start to rot. Water should not stagnate in the soil. Air humidity should not exceed 70%, if it is insufficient, the plant must be sprayed from a spray bottle.
- Lighting... Orchid is a light-loving plant. In summer, it feels great on a slightly shaded windowsill - to avoid getting burned, a special opaque film is used (you can find out where it is better to put orchids in an apartment here). To intensify the cultivation in winter, orchids are supplemented with artificial lighting lamps.
Important: With a lack of light, the leaves are brightened and stretched.
Read more about the rules and conditions for keeping an orchid in this material.
Conditions for growing orchids
Orchids love light, but only if the sun's rays are not direct, but scattered. If the windows are located on opposite sides of the world, it is best to give preference to the east side. But in winter, it is imperative to create artificial lighting, since the daylight hours of the orchid should be at least 12 hours. Otherwise, the leaves of the flower will simply begin to wither and fall off.
Now about the air temperature that is suitable for plants. The minimum possible temperature can be 12 degrees, but it is better not to bring it up to that. The most optimal temperature should fluctuate around +20 - +25 degrees.
The air humidity should be optimal, approximately 50%. In general, the ideal condition is when the air humidity is 70%, but such figures are possible only in a greenhouse. Therefore, artificially humidifying the air is still at least periodically, but desirable. In addition, it is imperative to ventilate the room so that the air is not stagnant, otherwise the plant can get sick with various infectious diseases. In addition, in no case should drafts be allowed, otherwise the plant will immediately die. It is worth humidifying the air by spraying so that water does not fall on the plant flower. It is worth carrying out the procedure at least 3 times a day, especially in the summer. You should not spray orchids at night if they are in a well-ventilated area so that they do not freeze from temperature extremes. In winter, even when the air is humidified, it is not recommended to spray the plant itself.
Step-by-step instructions for beginners on how to grow a flower correctly
Preparation of soil and containers


A plastic (preferably transparent) or ceramic porous pot with enough space for the root system, equipped with holes for water drain, is suitable as a container. The bottom of the pot is lined with a drainage layer (small pebbles, tile chips).
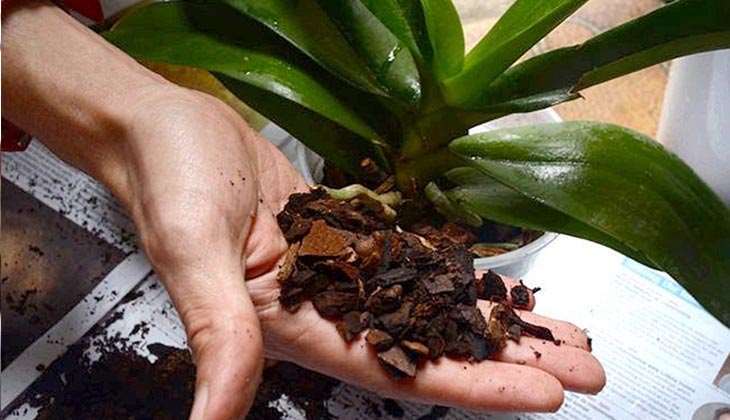
The soil substrate should consist of components that do not retain moisture: moss, pieces of tree bark, coal, cork, granular clay. Garden soil is not added to the soil.
Technology
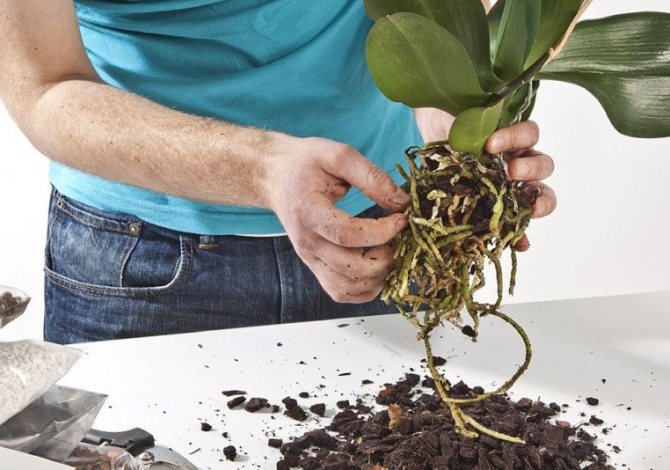
- From the root (or by dividing the bush)... How to grow a plant from a root? The division is usually combined with a planned transplant of an adult bush. The plant is completely removed from the pot, the roots are cleared of soil. The main (large) bulb is determined, which is divided with a sharp knife so that at least 4 pseudobulbs remain on each of the parts. The sections are processed with charcoal and dried. Each plot is planted in a separate pot. At first, instead of watering, spraying is carried out.
- Bulb orchid... How to grow it from store-bought bulbs? All small pseudo-bulbs are cut off with a knife; the cuts are powdered with charcoal and the bulbs are placed in the moss.
- From the cutting... With a sterile knife, a shoot (10-15 cm) with two or more air roots is cut off from the plant. Sections are treated with fungicide and charcoal. The cuttings are laid horizontally in a plastic container filled with moss. When roots appear, the segments are planted in pots. The procedure is carried out in the spring.
- From baby... The baby appears on the stem at high humidity and temperature (over 28 ° C). The baby is separated when its leaves reach a size of 3 cm, and is wrapped in moss. As soon as a 5 cm root sprouts from the base of the baby, it is placed in a pot with soil. It usually takes a baby about six months to grow its own roots. You can stimulate the appearance of children with the help of a hormonal drug - cytokinin paste.
- From seed... The most time consuming and rare way to grow an orchid. The seeds ripen within 8 months, then germinate in a sterile flask lined with moss or filled with an agar-agar base. If the seed has sprouted (it takes from 3 months to a year), the seedlings are planted on a mixture of pine bark and moss, on which they can wait for transplanting into a pot for about a year.
How orchids grow in the wild
Orchids are of the following types:
Saprophytes
This species has no leaves. They take root deep underground and feed on humus. Saprophytes also do not have chlorophyll, so they can live comfortably in the shade. They feed on substances produced by the fungus.
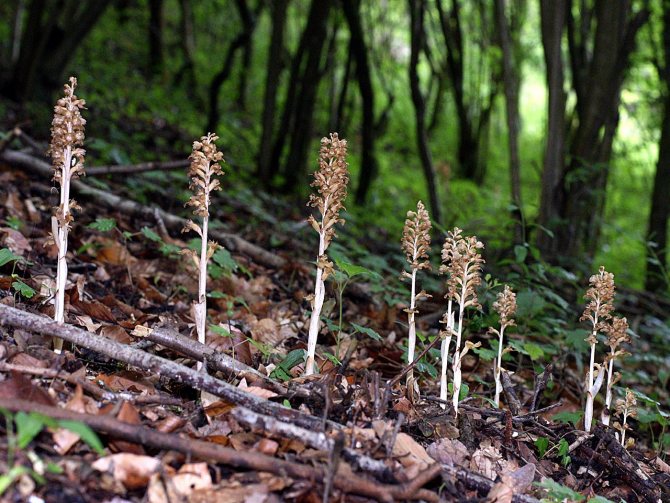


Saprophyte orchid
For your information! Saprophytes are considered the most unsympathetic plants in this family, but they are of great interest to collectors.
Epiphytes
This type of orchid grows on trees. Phalaenopsis and wanda, the most common species in this family, are of this type. The function of retention on the surface is performed by their open root system.
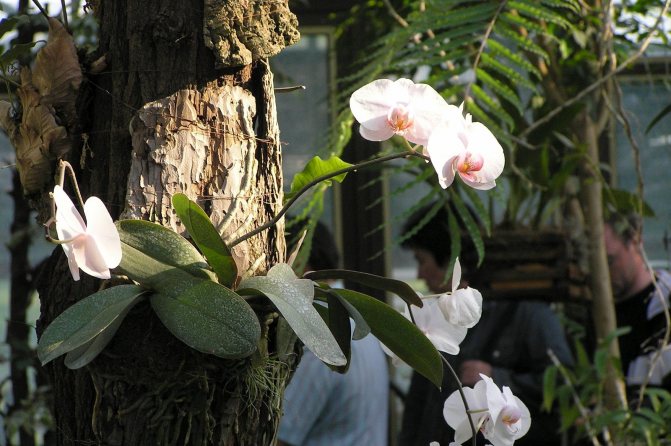


Orchid epiphyte
Important! Epiphytes are not parasites, but feed on fallen leaves, pieces of bark, etc. They do not cause any harm to the trees on which they live.
Lithophytes
Flowers growing on stones are called lithophytes.
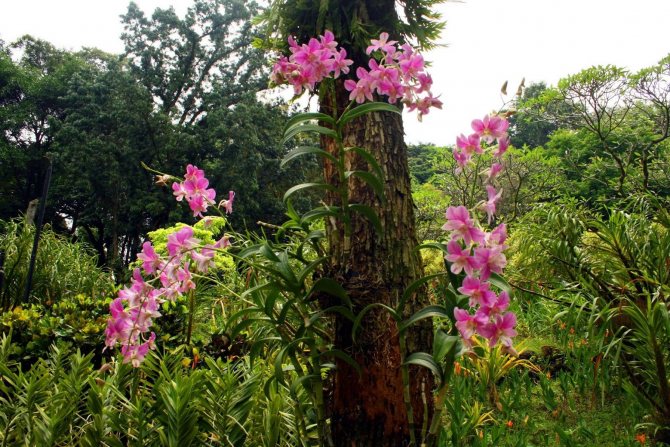


Ground orchid
Terrestrial representatives of the Orchid family grow on loose, air and moisture permeable soil. In Europe, they grow up to half a meter, in the tropics they grow wider and longer and resemble a spreading bush.
Difficulties and difficulties


With a lack of moisture and light, buds or leaves may fall off.- With excessive watering, the leaves become sluggish.
- If the temperature of the content is exceeded, the leaves will ripple.
- If the orchid does not bloom, it is necessary to arrange "heat stress" for it - to increase the difference between day and night temperatures by 8-10 degrees.
- When the roots are peeking out of the pot, this means that the plant does not have enough space and needs to be transplanted into a larger container.
Distribution in the world
When purchasing a beautiful flower in a store, we can not always even imagine the habitat of orchids. Where they just do not grow.
There are many types of orchids - about 35 thousand. They are so different. And their natural habitats are far from the same. Even very different. So what is the difference between them?
Representatives of orchids surprise not only with their beauty and originality. But also its ability to survive in different climates:
- Hot and harsh;
- Rainy and dry;
- Forests and steppes;
- Mountains and plains.
The continents are easier to list. And we can say that all continents. Except for one - Antarctica. But the countries will have to be named for a long time. Below we will name some.
Tropical epiphytes
The very word epiphyte means a plant growing on another plant. Or attached to another plant - forophyte. So they grow:
- On trees (branches and trunks);
- On stumps and snags;
- In the crevices of the stones;
- And even on sheer cliffs.
Such plants live off moisture, air and remnants of the bark. Their roots are also called airy:
- With their help, they are attached;
- These roots absorb moisture from the air and damp wood surfaces;
- And they also participate in the process of photosynthesis.
Herbaceous species of temperate latitudes
Can such an orchid grow in the ground? So to speak - they cannot do without soil... They have underground rhizomes or tubers. They find a kind of soil - breathable and moisture-permeable pieces of bark, stone chips, roots.


Some species - on the surface of the earth in layers of fallen leaves, branches and bark of trees, overgrown with moss and small stones. Such orchids have few leaves. Quite often, only one.
Conditional division by climatic latitude
The variety of orchids required some analysis and systematization. They were divided into five subfamilies:
- Herbaceous perennials. Each of them includes many tribes: Apostasy;
- Cypripedia.
- Vanilla.
- Epidendric.
- Orchids or Orchids.
There is also a division by climatic zones and territories. It is more conditional. And it includes four groups:
- Tropics. Bright and ventilated places near rivers. On the slopes of the mountains. Epiphytic species grow predominantly: the coast of Africa, South and Central America, eastern and northern Australia;
- Adjacent areas of the Amazon and Congo rivers.
- Foothills of the Himalayas;
- Highlands and arid zones. With their temperature fluctuations (hot days and cold nights), they are suitable for many types of terrestrial orchids. And some epiphytic ones. And they grow near rivers and reservoirs.
- North America;
Diseases and pests
When grown at home, orchids are attacked by pests and can even get sick.... Consider what is harmful to the health of flowers:
- scale insect (dark spots and mucus appear on the leaves);
- worm (leaves turn yellow and fall off);
- whitefly (the plant is dehydrated).
- powdery mildew (flowers are covered with a white bloom);
- anthracnose (characterized by the appearance of brown spots);
- rot.
We recommend watching a video about pests and diseases of orchids:
First mentions
Forest violet in the wild
Today, an orchid can be grown in a house without difficulty, but where did it come from in megacities? The very country of origin of the flower is not known for certain, but the first mentions are found in the manuscripts of China, dated 500 BC. e. According to historical references, the famous philosopher Confucius wrote that the smell of a flower resembles the words of love of loving hearts.
Also in China, scientists found a manuscript dated 700 BC. BC, which describes in detail how the artist V. May cultivated a flower in a small pot. Since then, people all over the world have learned about this amazing flower, about its beauty, smell and medicinal properties.
But, probably, the most beautiful name for the flower was given by the ancient Greek Theophrastus, a philosopher and thinker, having found a plant with pseudobulbs, he named it "Orchis". Translated from the language of the ancient Greeks, this translates as "testicle". And all this happened in the 300th century. BC e.


The first mention of an orchid was recorded in China
Secrets
- To maintain proper humidity, a special watering technology is recommended: a pot with a flower is placed in a container filled with water, when the soil is saturated (after 3-5 minutes), the container is listened to and placed on a grate to drain excess water through the drainage holes.
- The orchid needs to be planted at an average depth, since at a low planting, the buds begin to rot, and at a high planting, the plant is unstable in the pot. In both cases, growth retardation occurs.
- It is better to replant an orchid in a state of new growth, when it has faded and rested a little. It is necessary to remove all damaged and soft areas and treat the sections with charcoal. After transplanting, it is not recommended to water the plant for a week (after 3 days, you can start spraying).
- You can put a clove of garlic in the pot to scare off flower gnats.
- Orchid roots take part in photosynthesis, so a transparent pot would be the best planting container.
- Growing should start with disease-resistant and standard-care species.
- Top dressing is applied during the months of active development along with watering.
Transplanting a home orchid


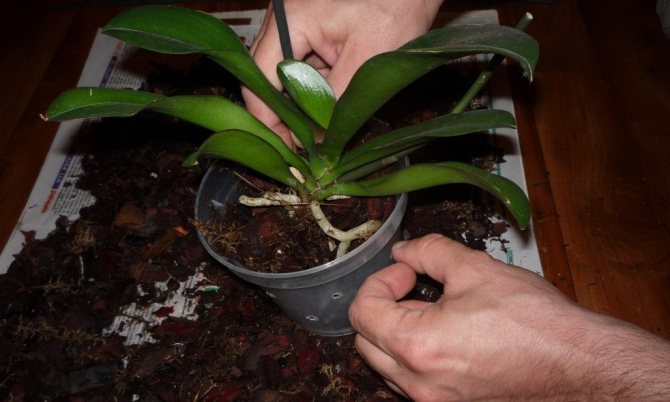
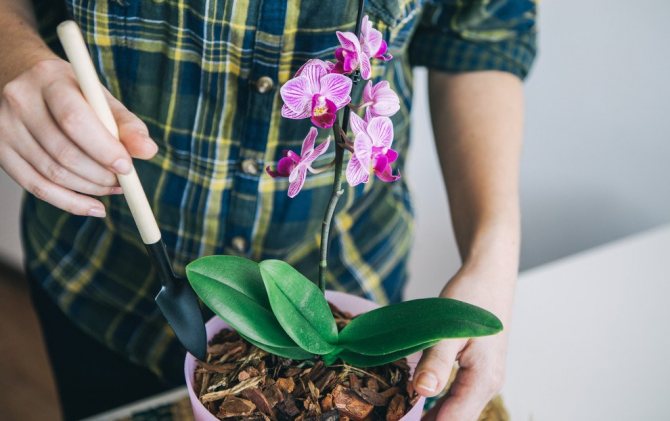
Orchid transplantation is not at all as complicated as it seems to beginner growers, but it still has rules, and you need to know them. The orchid is transplanted when the old pot becomes small or when the substrate is "eaten" by the plant. Half an hour before transplanting the orchid into a new pot, water it well so that the roots can be removed more easily from the pot. Then the plastic pot needs to be crumpled a little in your hands, so that a clod of earth with roots is easier to remove. In an earthen pot, insert a knife between the earthen lump and the wall and wiggle it so that the earthen lump easily comes out of the container. Then try to remove the old substrate from the roots of the orchid: for this, it is enough to shake off what is crumbling by itself, the remaining substrate will help the orchid to adapt more quickly to the new soil. Now remove dead, rotten and damaged roots with a sharp sterile instrument, and treat the cut sites with charcoal powder. Take a pot with large drainage holes, put a few large pebbles in it for counterweight, pour drainage, a little coarse bark, then lower the orchid roots into the pot, gently spread them and cover with the substrate on top, distributing it evenly in the pot. You can water the transplanted orchid the next day, if the substrate is already dry by that time.
Basic landing principle
I hope you have already understood that epiphytes cannot be planted in the same way as plants with a taproot system.
In a pot with an ordinary houseplant, the soil begins to dry out from above, and in the depths it remains moist for some time. And if for most plants this is normal, then for epiphytes it is completely unacceptable.
Therefore, such dishes should be considered only as a stand, but no more.
The main principle of the correct planting of orchids is that the substrate in the center should dry out as quickly as on top.
Let's look at a few options:
First option
The first option will be on the example of phalaenopsis. This method of planting is suitable for all orchids, whose conditions of detention are similar to those of the phalaenopsis and the entire tribe of the Vandans.
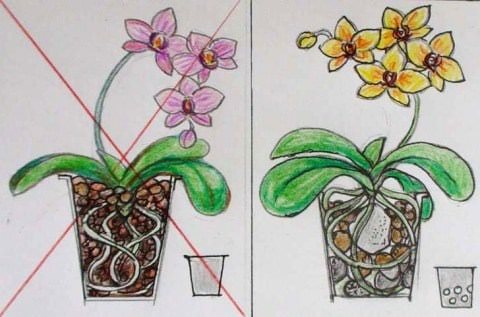

Left wrong fit:
- The container is solid, without holes;
- There is no drainage;
- The substrate is small and takes up the entire space, there is no air exchange;
- The base of the plant is located in the thickness of the substrate.
An orchid planted in this way will sooner or later begin to hurt.
On the right is the correct one:
- Container with holes;
- Large drainage from crushed granite;
- A fairly large substrate in which voids are visible, which means that air exchange is ensured;
- The base of the plant is slightly raised above the surface of the substrate;
- The most dangerous area in terms of waterlogging has been eliminated - the center of the pot, where a large piece of foam is placed, right under the base.
Second option
The second method (for example, Masdevallia) is suitable for relatively moisture-loving orchids that like to be watered more often, but, nevertheless, they also do not tolerate stagnant water and their roots also need good aeration. These are Bulbophyllum, Dracula, Miltonia, Masdevalle, oncidium group and other orchids similar to them in terms of keeping conditions.
Features of landing on the block
This is a fairly common way of growing orchids, gaining more and more popularity every year. For planting, any suitable material is used to which the plant can be attached. For example, a piece of oak, pine or tree fern bark is excellent.
The dimensions of the material are selected taking into account the size of the plant itself and the specifics of its growth. Choosing the right base size is a very important step. After all, if it does not fit, the flower will have to be transplanted, which will negatively affect its development and condition. Remember: every transplant for a plant is a lot of stress.


What is good about planting orchids on a block? First of all, the fact that the roots of the flower dry out quickly after each watering. Plus, they get a lot more oxygen, which is very beneficial.
And the plant on the block looks more natural and beautiful. In this way, orchids can be planted, which in the future will be moved to the greenhouse. In such conditions, they will not have a lack of moisture, therefore they will not lose it during the rest period.
What should be the substrate
For plastic dishes, it should be as water-absorbing as possible: the bark of trees of medium or large fraction, polystyrene.
Flower shops sell a special substrate for orchids. Sadly, but for the most part this substrate is as "special" as "special pots".
It is better to prepare the substrate yourself. But if you do not have such an opportunity, and you have to use the store, select the largest elements from it and use only them. There should be no peat or sawdust. Leave all the little things for other plants.
Watering after planting. When?
After planting, the orchid is not watered for as long as possible - 5-10 days, sometimes 2 weeks, depending on the condition. However, it should be in a shady, cool place.
At this time, instead of watering, it is recommended to spray the leaves and the air around them (not the substrate), but only in clear warm weather. And at the first watering, it is recommended to add phytosporin to the water.
These tips will help you plant your orchid properly and avoid common beginner mistakes. If you have anything to add to them, share your experience in the comments.
Even a child can plant an orchid in a pot. It is very simple and does not require colossal efforts.
It is enough to adhere to basic rules and everything will work out.Otherwise, there is a risk of losing a plant specimen and not learning anything.
What should be the pot
If it is transparent, this is good and convenient for you, but transparency alone is not enough. The container should have many holes not only in the bottom, but also in the side walls. If they are not there, then you need to do it yourself, for example, using a sharpened soldering iron or a burner.


Without holes, and therefore without air exchange, uniform drying of roots in plastic dishes is practically unattainable. In addition, good air exchange reduces the risk of fungal and bacterial infections.
For moisture-loving orchids, it is enough to make holes in the bottom 1/3 of the pot. But for most, you still have to make holes almost around the entire perimeter.
It is very good if the flowerpot has legs, then there will always be an air gap between the bottom and the surface on which it stands, and this is an additional plus.
The size of the container should match the root system, neither too large nor too small.
Plant adaptation after planting
Adaptation and rooting on average lasts 2-4 weeks, depending on the conditions of keeping and the habit of the plant itself.
Orchid can be sprayed with stimulants and placed in a humid environment - mini greenhouse. In extreme cases, you can simply cover it with a plastic bag, creating a greenhouse effect around the leaves, which in turn will reduce moisture evaporation and the overall load on the plant.
It all depends on what kind we are talking about. In general, it is necessary to ensure bright diffused lighting for 12-14 hours a day, optimal temperature and its drops, as well as proper watering. However, these are only general recommendations and each type of orchid should be approached individually, trying to achieve conditions that are most similar to natural ones.


The care for different types of orchids will also vary.
Major mistakes
The main mistake is the wrong size of the pot. Too much - it is more likely that the roots will start to rot, too small - the plant will dry out faster. The substrate, correct in moisture capacity, also plays a role. All these little things need to be considered.

























