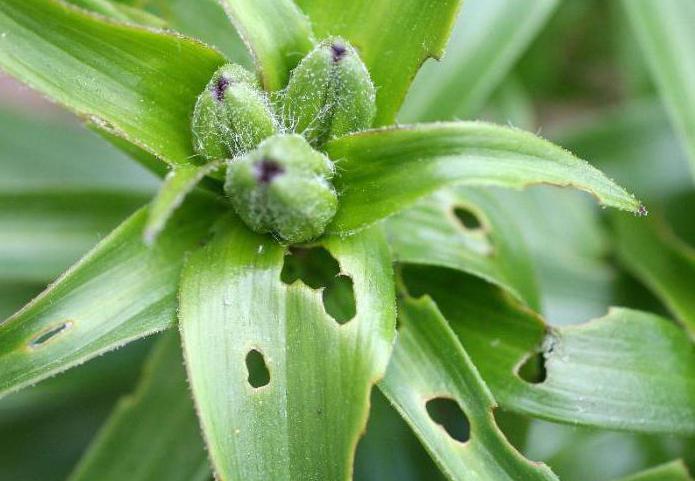
Lilies are one of the most beautiful flowers in a flower bed. And they also get sick sometimes. This is facilitated by poor living conditions, improper care of the bushes, as well as pests that love to feast on fresh leaves, stems or bulbs. Let's find out what diseases are found in lilies, what insects harm them, and what needs to be done to save the flowers.

Diseases of lilies and their treatment with a photo
The fragrant lily has always been the main decoration of flower arrangements. They also love her for a simple planting method and unpretentiousness in care, but they often forget that only compliance with the rules of agricultural technology ensures a full-fledged healthy flowering.
In addition, the resistance of a crop to diseases depends on the geographical origin of the plant. For example, people from the tropics can hardly endure winter and may even die due to insufficient air humidity. Therefore, plants planted in unsuitable climatic conditions grow weakened, get sick more often and longer and die faster.
The reasons
Most often, lilies are susceptible to fungal and viral diseases. So, in thickened plantings or with prolonged cultivation in one place, there is a risk of developing fungal diseases, among which are distinguished (Figure 1):
- Gray gil;
- Fusarium;
- Rust;
- Sclerocial rot;
- Root and bacterial rot.
Viral diseases are transmitted by insect pests or through infected garden tools. The most common among them:
- Variegated virus;
- Rosette disease;
- Mosaic.


Figure 1. The main symptoms of diseases in flowers
Let us consider in more detail the diseases of lilies, their symptoms and methods of treatment with a photo.
Symptoms
To start the correct fight against diseases, you need to familiarize yourself with the characteristic symptoms of each pathology from the photo and description.
- Gray rot (botris)
It is manifested by rapidly growing brown spots on the lower leaves, which soon form large patches of plaque-covered mucous tissue (Figure 2). The affected stems die very quickly, so it is recommended to carry out preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of this disease.
Ways to deal with gray rot are as follows:
- Preliminary disinfection of the bulbs before planting in a solution of foundation;
- Change of planting site of bulbs every 4-5 years;
- Compliance with sparse landings;
- Watering in the morning by the root method;
- Construction of a protective shed over the flower bed in case of a rainy period;
- Preventive spraying of seedlings in early spring with a solution of copper sulfate (0.5%), Bordeaux liquid (1%) or copper oxychloride (0.3%).
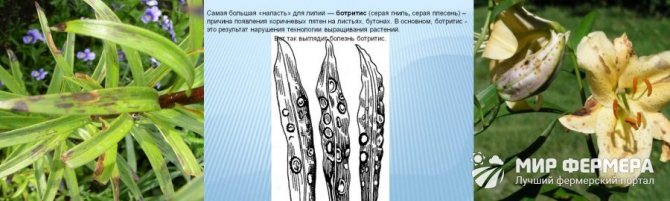

Figure 2. Symptoms of gray mold
When a disease is detected, the solutions are used in turn with an interval of 10 days, the affected parts of the plants are destroyed.
- Fusarium
Appears on mechanically damaged bulbs. The disease manifests itself most clearly during the storage period. Symptoms are yellow-brown spots appearing at the attachment points of the scales (Figure 3). Subsequently, these spots turn into soft, rotten areas and the bulb disintegrates.
Note: The disease is most active in hot weather with high levels of humidity.The spores of the fungus that causes fusarium can persist in the soil for about 3 years.
The fight against the fungus of fusarium consists in the release of the bulbs from the affected scales with a mild degree of disease and in the destruction of the bulbs with their severe damage.


Figure 3. Signs of fusarium
In addition, the soil is disinfected 2-3 weeks before planting with a solution of 40% formalin (250 ml of substance per bucket of water) and the soil is sprayed with basezol (0.1%), euparen (0.2%), bavistin (0.05% ) in early spring.
- Rust
Spores of the fungus that causes rust can overwinter in stems and leaves as well as in bulbs. Rust, as a disease, is manifested by the appearance of small colorless spots on the leaves, later they turn yellow, and the leaves and stems dry out (Figure 4). The dark growths remaining on them contain a large number of fungal spores, which can infect other plants in spring.


Figure 4. Manifestations of rust
Therefore, for preventive purposes, pre-sowing treatment of the bulbs and frequent top dressing with the introduction of potassium-phosphorus fertilizers are recommended. In addition, at the beginning of spring, prophylactic spraying of seedlings with Bordeaux liquid or copper oxychloride is carried out. When the first signs of the disease are detected, ditan, polycarbacin, cineb are used. If the lesion is still insignificant, then its infected parts are removed and destroyed. In the case of a severe defeat, the entire plant, together with the bulb, is removed and destroyed from the site.
- Sclerocial rot
The first sign is called uneven seedlings in spring. Lagging bulbs have a thick white bloom at the neck of the bulb or at the bottom of the bulb. The developing disease leads to the death of roots and leaves (Figure 5).
Note: Most often, sclerocial rot develops at an air temperature below +13 degrees in conditions of high humidity. Therefore, with an increase in temperature and a decrease in humidity, the disease stops its spread.


Figure 5. Symptoms of sclerocial rot
Prevention of sclerocial rot is similar to the methods of combating fusarium and botris. Diseased plants are removed along with a lump of soil, and foci of infection are treated with wood ash or bleach. In addition to lilies, daffodils, tulips, hyacinths, gladioli are also susceptible to this fungal disease, so it is not recommended to plant lilies after these decorative bulbs.
- Root rot
In accordance with its name, the disease affects the roots of the plant, as a result of which it begins to lag behind in growth, and then loses its buds. A signal about the onset of the disease is the yellowing of the tops of the leaves, which soon spreads to the entire stem and leads to its drying out (Figure 6).
To prevent plant disease with root rot, the following set of protective measures should be carried out:
- Carefully select planting material;
- Pickle the bulbs before planting;
- Disinfect the soil with a solution of colloidal sulfur (0.4%).


Figure 6. Signs of root rot
All affected plants must be removed from the flower bed and destroyed in order to prevent the spread of rot to other crops.
- Bacterial rot
Leads to decay and fall of leaves and peduncles. The bulbs of the plant are also affected by rotting depressed spots.
To combat this disease, the following procedures are taken:
- Regular inspection of bulbs during storage in order to timely detect and further destroy infected planting material.
- Presowing treatment of the soil and the bulbs themselves.
- Spraying seedlings with fungicide in early spring, and if bacterial rot is detected, such spraying is repeated every decade.
If fungal diseases can be prevented by various preventive measures, then the same cannot be said about viral infections.In addition, this type of infection is not only impossible to prevent, but also very difficult to diagnose and treat. Viral infections are transmitted by insect pests and with plant sap through untreated equipment. Such diseases manifest themselves in different ways, and the fight against them consists in the destruction of the affected plants. The most widespread viral infections are variegated, rosette and mosaic.
The main symptoms of viral diseases are as follows (Figure 7):
- Variegated virus causes a spotted color of a flower, unusual for lilies. This disease can be carried by aphids, and it is transmitted through gardening tools.
- Rosette disease provokes the action of a whole complex of viruses. It is manifested by a delay in the growth of peduncles, deformation of the stem, and the formation of irregularly shaped leaves. The carrier of this disease is aphids.
- Mosaic - a viral disease that has symptoms similar to botris. In this case, the leaves are covered with oblong spots of a pale gray color. The viral mosaic of aphids is also transmitted through a garden tool.


Figure 7. Viral diseases: 1 - variegation, 2 - rosette, 3 - mosaic
Methods for combating viral diseases are preventive examinations of the stored bulbs and the removal of specimens with unusual discoloration of the aboveground parts. Since the mosaic can be transferred with plant sap through the inventory, a set of blades should be used when cutting flowers, which is disinfected after use. It is also necessary to fight aphids by spraying lilies with karbofos or ragor.
Lily diseases: video
If you want to keep blooming lilies in the garden or pots, we recommend that you watch the video, which describes in detail the main diseases, methods of dealing with them and effective means of prevention.
https://youtu.be/082ezZyQqEE
Root onion mite
This pest damages a lot of bulbous plants. Its length is not even one millimeter. The mite feeds on the scales of the bulb, as a result of which it causes rotting of the latter.
A lily affected by a tick stops its growth. Its leaves turn yellow and gradually wither. A weakened plant is exposed to various other diseases and eventually dies. The spread of the tick occurs through the soil along with the planting material or through a soil cultivation tool.
Before treating lilies from pests, it is necessary to establish which one has affected the plant. When inspecting bulbs affected by a tick, you can find many passages and cavities in which a brown powder is located. These bulbs should be removed after digging up. All plant residues are carefully collected and destroyed. If the presence of this pest is suspected in the planting material, then all the bulbs must be kept in the Karbofos solution for fifteen minutes or sprinkled with chalk. Chalk adhering to the body of ticks leads to their death from desiccation. If the pest has been identified during the growing season, then the lilies should be sprayed with a solution of rogor, but it is better to destroy all diseased specimens. If your site has been infected, then you cannot grow bulbous plants on it for four years.
Asiatic lilies: diseases
Lilies belonging to Asian hybrids are the most unpretentious, and therefore the most common. They can be grown practically all over the world, even in Alaska.
In cold climates, the flower stalks of the plant are cut at ground level so that they do not rise above the snow cover. However, Asiatic lilies are more susceptible to certain fungal and viral diseases than others.
The reasons
A fungal disease known as botris affects flowers in cold weather with high humidity levels. Therefore, when choosing a site for planting, you should choose a place that is well ventilated.
Rotting of the bottom of the bulb is also caused by a fungus and is called fusarium. The reason for its occurrence is stagnation of water as a result of poor drainage or its absence, the use of fresh manure as top dressing, and the drying out of the earthen coma.
Viral diseases
Lily blossoms can be completely destroyed by viruses that infect the plant literally overnight. Symptoms can be quite different, but the most common change in the color of leaves and flowers - usually it becomes variegated, unclean. Viruses are transmitted through the bites of insect pests, and pathogens overwinter in the ground, having got into it with infected seed. Such plants are not subject to treatment, and the sooner you get rid of it, the more chances you have to save the rest of the garden. In this case, the affected flowers should not be thrown into the compost heap - they must be burned.


Lily pests and control
The bulbs of the culture contain a large amount of nutrients, therefore they are a delicacy not only for rodents, but also for various insect pests.
They not only weaken plants by eating leaves and bulbs, but also carry dangerous viral diseases. Consider some types of pests of lilies x and methods of dealing with them.
Lily pest control: red beetle
The red lily beetle is similar in appearance to a firefighter, and in fertility and gluttony - to the Colorado potato beetle. The adult insect and its larvae eat the leaves, flowers and bulbs of the plant (Figure 9). Adults appear on flowers already in April, and if you do not take protective measures, then it will be extremely problematic to cope with the larvae that hatch soon.


Figure 9. Larvae and adults of the red beetle
Therefore, as soon as pests of red beetles appear on the plants, you need to immediately start fighting them. It is best to manually collect and destroy insects. If time was lost, it is necessary to spray the plants with any insecticide that is used to combat the Colorado potato beetle, for example, actor, confidor, decis.
Onion leaf beetle
Orange oval beetles with two dozen dots on the elytra are onion leaf beetles. Adults and their pupae overwinter in the soil and come to the surface at the end of April. The onion beetle mainly damages lilies by eating leaves from the edges or gnawing holes in them. The onion beetle larva is able to skeletonize leaves (Figure 10).
As a preventive measure, it is recommended to regularly destroy weeds in the flower garden, on which leaf beetles can lay their larvae, collect adults by hand and destroy them, spray plants affected by larvae, chlorophos or infusion of herbs from wormwood and larkspur.


Figure 10. Flowers affected by the onion leaf beetle
To prepare the herbal infusion, you will need a bucket of finely chopped bitter wormwood or 800 g of dried wormwood, which is filled with cold water and infused for a day, then boiled for half an hour and immediately before spraying, diluted with water twice. Spraying with wormwood is repeated several times at weekly intervals.
Larkspur infusion is prepared at the rate of 1 kg of chopped grass per bucket of water. The agent is infused for 2 days, then filtered and used immediately.
Aphid
Aphids are insects that not only harm plants themselves, but also carry viral diseases (Figure 11).
For this reason, this insect must be quickly destroyed in order to prevent its reproduction. In the fight against aphids, inta-vir (1 tablet per bucket of water) and fufanon solution (10-15 ml per bucket) have proven themselves well.
In the video, you will learn more information about pests of lilies and methods of dealing with them.
Spring frosts
If suddenly there were late frosts, and you did not have time to cover your flower bed, then the lily will be the very first to respond to this. The description of the frostbitten plant says that it is similar to the consequences of a viral disease. The top layer of cells peels off, the leaves become blistered, bent, and the gardener may well destroy the planting, considering it a serious disease.
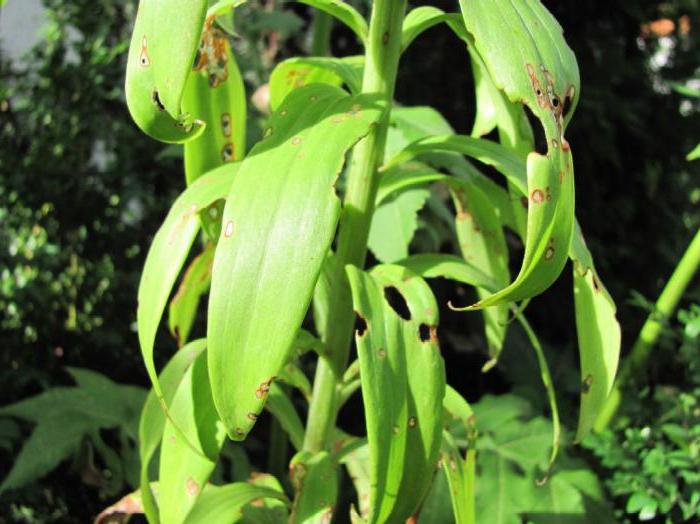


Processing lilies in the spring from diseases and pests
Unfortunately, lilies often get sick, they are damaged by many pests. Experienced gardeners know that the best way to fight is prevention and timely assistance. After all, the sooner a disease is discovered, the easier it will be to treat it, and the more chances are to preserve the entire blooming collection. That is why it is strongly recommended to spill emerging seedlings with special solutions. For example, a mixture of soda, ammonia and copper sulfate or Bordeaux liquid and copper oxychloride.


Figure 11. Lilies infested with aphid colonies
In addition, immediately before planting, it is advisable to treat the bulbs with a 0.2% solution of foundationol or a solution of karbofos (1 tablespoon per bucket of water). You can also disinfect the bulbs in a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Aphid
This pest is very small and forms whole colonies on the leaves. It weakens the plant greatly, and also carries a large number of viral infections.


In order for a beautiful and healthy lily to grow and bloom on your site, pests (beetle, aphids and others) must be mercilessly destroyed. In particular, aphids can be defeated with Karbofos, Fitoverma and other insecticides.
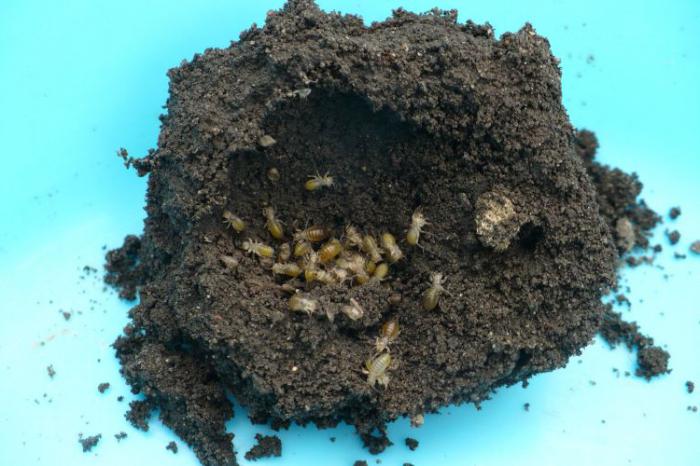
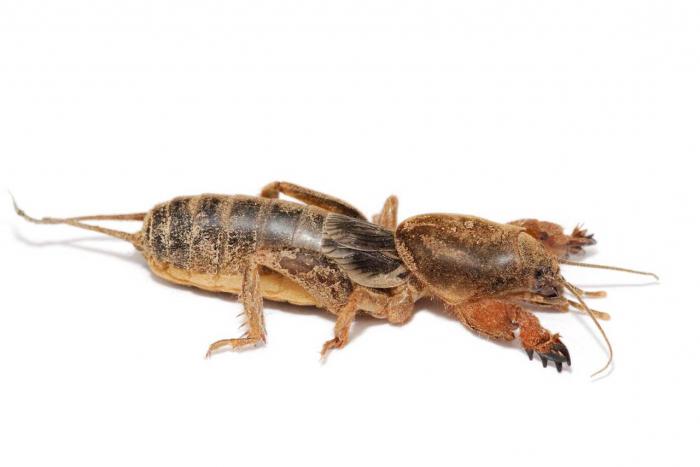
Wireworm (Click Beetle Larvae)
This typical potato pest eats lily bulbs with pleasure. As a result, the bulbs rot and the plants die.


Control measures. There are a lot of wireworms on acidic soils, so lime or wood ash must be added to such areas before planting lilies. Once every 2 weeks, it is useful to water the plants with potassium permanganate (3-5 g per 10 l of water). Of the drugs, Provotox, Medvetox, Vallar and Pochin help well.
Potato scoop
Lily pests such as the scoop eat up the plant trunks from the inside. As a result of such damage, the flower breaks or withers. The caterpillar is reddish-purple in color and has a bright red line that runs along its back. The eggs of these caterpillars spend all winter time on wild cereals, and in the summer they move to flowers and other cultivated plants. Pupation occurs in the soil next to damaged plants at a depth of five to fifteen centimeters.
To prevent the invasion of scoops on lilies, you must thoroughly clean your area of weeds, as well as all kinds of plant debris. All this must be collected and destroyed.




















