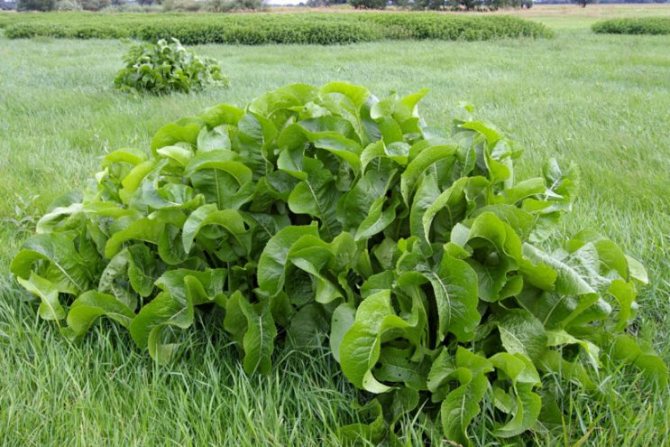
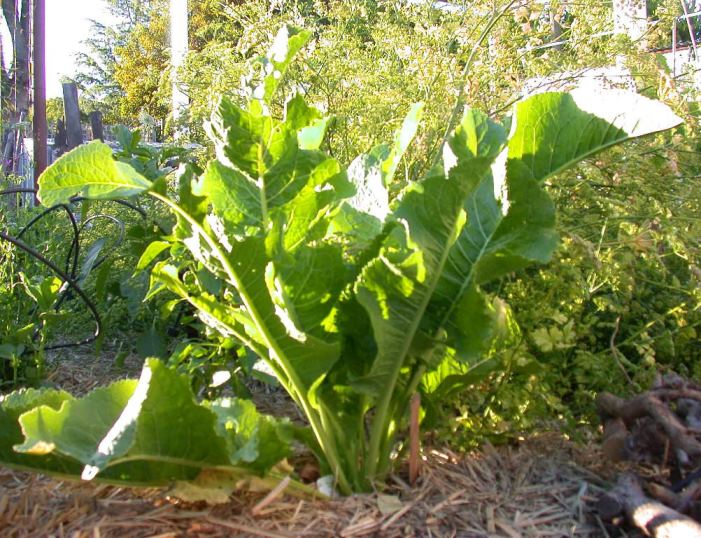
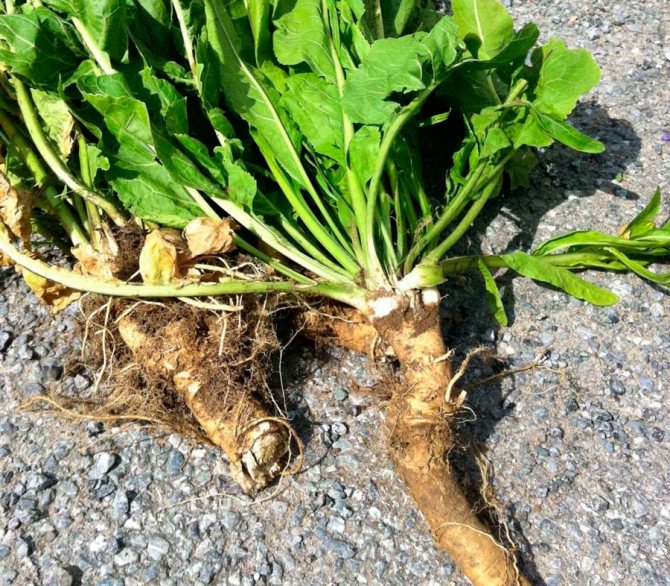
Planting horseradish
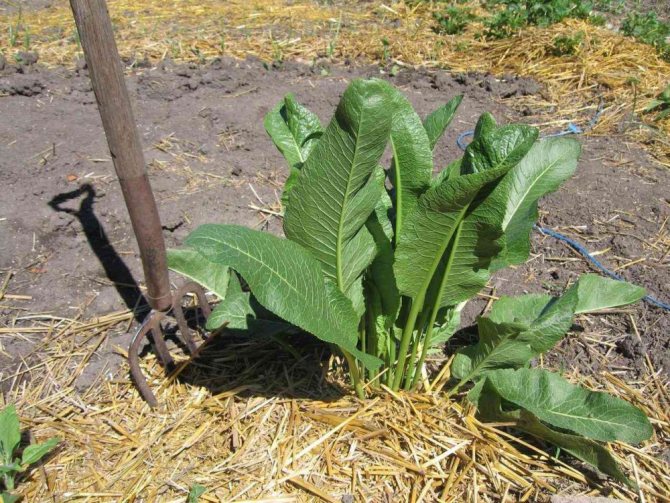
It is better to plant horseradish closer to the fence, on the sunny side having allocated a small area for this, especially if you plan to grow the crop for more than one year. From the rapid growth of roots, the land is clogged, which makes it difficult to carry out further crop rotation.
Getting a good horseradish harvest is possible on light soils:
So that the work does not turn out to be in vain, heavy clay lands need to be reanimated. To do this, before planting seedlings, peat, manure, sand are introduced into the beds and everything is carefully dug up. Horseradish is very responsive to organics. Or you can use mineral fertilizers per 1 sq. m .:
- 30 gr. or 1 tablespoon of ammonium nitrate;
- 30 gr. potassium salt;
- 25-30 gr. superphosphate.
Preparing cuttings
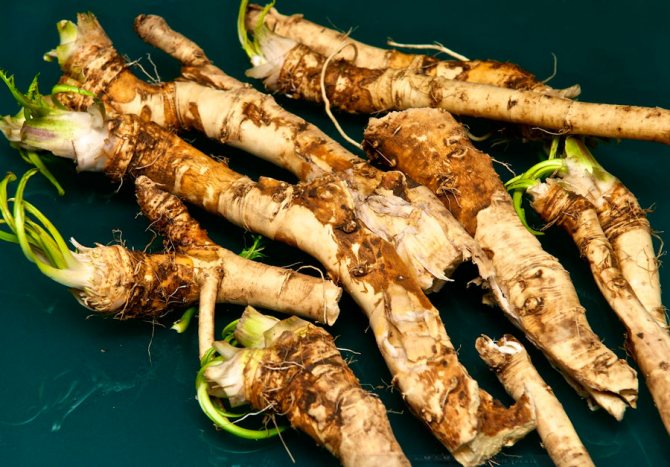
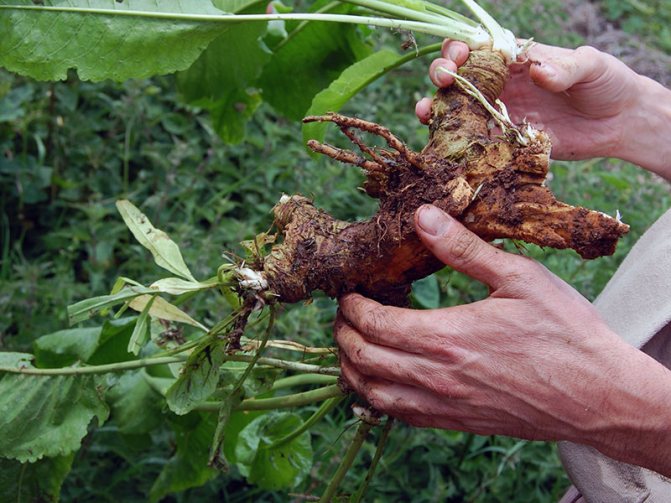
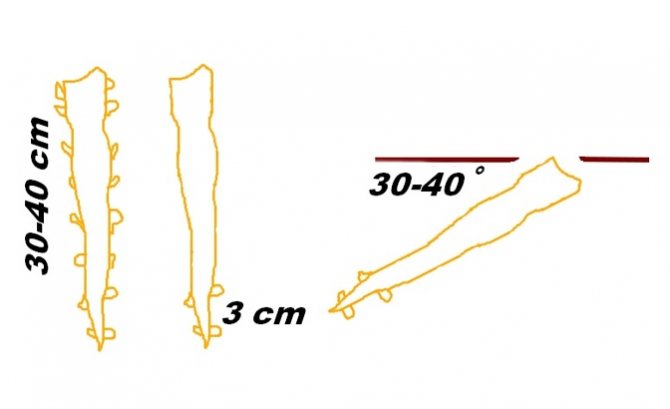
Horseradish is propagated by rhizomes, which must be prepared in the fall or purchased at a seed store. For planting, cuttings 10-15 cm long and at least 1 cm thick are used.
It is necessary to remove the middle buds from the rhizome, leaving two buds at the top and bottom, from which the root system and the aerial part will subsequently form. 2 - 3 weeks before planting, the cuttings should be placed in peat or wet sawdust and kept at a temperature of at least +18 degrees. In such conditions, the cuttings will germinate well and the buds will be better visible.
Landing in the ground
After the cuttings are prepared, you can start planting the plant in the ground. The depth of the planting hole should be equal to the length of the cutting. The seedling is placed in the hole at an angle of 45 degrees, leaving 2 cm of the cutting above the ground. The distance between the bushes should be 40 - 60 cm so that the roots can develop freely and do not interfere with each other.
Sprinkle the seedlings with earth, slightly compact the soil around them and watered with water at room temperature.
Horseradish can be propagated in spring and autumn. Spring planting can be done immediately after the snow melts. During this period, the soil is saturated with natural moisture, which contributes to better rooting. In autumn, horseradish is planted before the onset of frost, so that the plant has time to take root before the soil is completely frozen.
Horseradish breeding
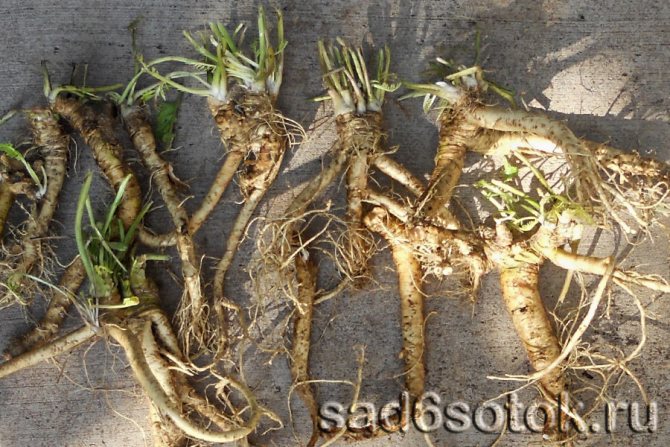


Cuttings are harvested in the fall during harvest. The lateral processes or "spider" are chopped off from the main root. From the whole mass, thin, healthy roots with a length of max - 25 cm and a diameter of 0.8 - 1.2 cm are selected. Long cuttings are cut into several parts. Their upper part is cut across, the lower part is cut diagonally or obliquely. Pruning is done before planting in the ground.
Then, until spring, the cuttings are placed for storage in the cellar, basement, sprinkling with dry or slightly damp sand, or sawdust. If covered with raw sawdust, the roots will begin to sprout. And the goal of the gardener is to save the planting material. Sometimes harvesting is done in the spring, until the leaves appear.
Diseases and pests
Horseradish is extremely resistant to diseases, unlike other cultures. In extreme conditions and poor care, it can be infected by white rot, leucorrhoea, verticillium and mosaic. Of the pests for horseradish, cruciferous fleas, rapeseed bugs and flower beetles, cabbage bugs and moths are dangerous.Diseases can also be transmitted from neighboring crops, which means that you need to check them too, in the process of a diagnostic bypass.
How to protect?
Viral diseases are not cured, so the plants that have been affected by the mosaic will have to be thrown away. Regarding leucorrhoea and white rot: these are fungal diseases, the causative agents of which can be eradicated at the initial stage of the development of the disease by treatment with preparations that contain copper - Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate, "Oxyhom", "Tiovit", "Jet" and others.
In the fight against insect pests, agricultural techniques are used (observance of crop rotation, weed control, removal of plant residues and deep processing of the site after harvesting), as well as treatment of plants with insecticides - Aktellik, Foxim in the case of flea beetles and bedbugs, Tsimbush, Etaphos or Zolon in the case of the flower beetle and moth.
The last processing of horseradish with chemical preparations is carried out no later than three weeks before harvesting.
Landing dates
It is better to plant horseradish in early spring. To do this, in 1.5–2 weeks, the seedlings are removed from the cellar, placed in a warm place and covered with a damp cloth or peat. After bud germination, cuttings are planted in prepared beds. For 1 sq. m. place from 4 to 6 plants. The distance between them should be 30-40 cm, between the rows - about 65-70 cm.
The purpose of planting can be different - getting a good harvest or planting material. If the gardener expects to get the first, then before planting it is necessary to clear the entire middle of the cutting from the extended buds. They are left only at the bottom for the formation of roots, and at the top for the leaves. To get good seedlings in the future, cuttings are planted along with all the buds.
Further care consists in loosening the soil and removing weeds. Do not allow the soil to dry out. Some horseradish varieties are susceptible to powdery mildew and other diseases, so timely processing is necessary.
How to get horseradish out of the garden
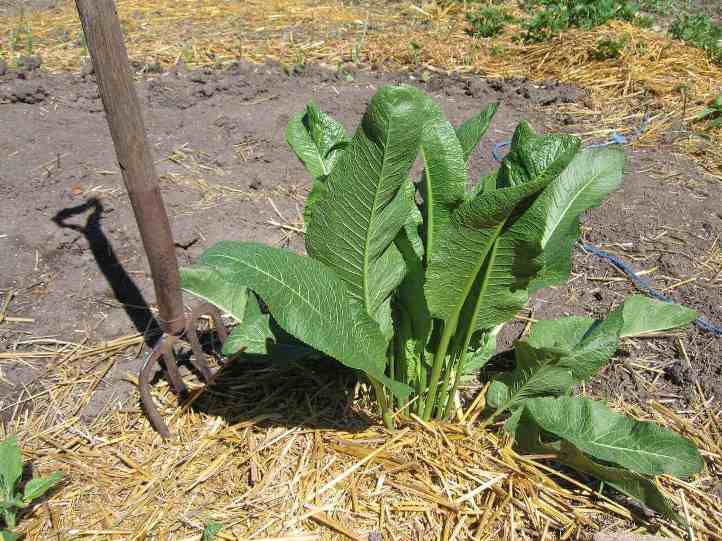
It should be borne in mind that sometimes horseradish can become a "pest" in the garden area, grow strongly and drown out other cultivated plants. Therefore, caring for it must necessarily include the timely thinning of the roots. It is better to use a pitchfork for this, they will not damage the horseradish roots and will not cut them into small roots, which in the future can grow and fill even more land.
You can also remove horseradish by covering it in early spring with roofing material or other opaque material. Horseradish will die from a lack of light, you will only have to dig up the vacated area in the fall.
A good horseradish harvest will provide the gardener with not only a special taste of dishes for the whole year, but also the prevention of various diseases for the whole family.
Types and varieties of horseradish
On the territory of Russia, horseradish is rarely cultivated on an industrial scale, therefore, out of the many (about 500) previously existing varieties in modern vegetable gardens, few are left.
It is interesting to know that in Europe, where horseradish spread in the Middle Ages, more than 2 thousand varieties of this plant were bred. In America, where he was brought in in 1900, there are already 3.5 thousand.
In summer cottages, local wild-growing forms of horseradish are most often cultivated. But there are also cultivated varieties, one of which - Atlant - is included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation, as a mid-season variety. Atlanta has a long (up to 50 cm), rather thick (up to 5 cm in diameter) grayish-white root. Its mass can reach 380 g, it has a dense milky flesh. The plant does not bloom, propagates only by cuttings. The variety shows good keeping quality and high commercial qualities, resistance to heat, drought and frost, is universal in application and is recommended for cultivation in all regions of Russia, as well as in Belarus, Ukraine and Moldova.


The rhizome of horseradish of the Atlant variety is smooth, whitish-gray, with a small number of tubercles
Among the varietal forms of horseradish are the following:
- Valkovsky. A late-ripening variety with a yellowish cylindrical root and milky white flesh. Its mass can reach 150 g, its length is 60 cm, and the diameter of the middle part is 3 cm.
- Suzdal. For centuries, the variety was grown in the vicinity of Suzdal and was considered the most vigorous, juicy and fragrant. Annual roots up to 30 cm long, practically without side shoots, are valued. In older rhizomes, there is a lack of tenderness and juiciness.
- Tolpukhovsky. A late-ripening variety with a white-grayish cylindrical rhizome, about 35 cm long, about 3 cm in diameter, weighing up to 250 g, with white flesh. It is unpretentious, tolerates frost and lack of moisture well, therefore it is often grown on greens, leaving the roots in the ground for the winter.
Helpful information! Russian gardeners grow Alpo (Polish selection) and Malinsky (Czech selection) varieties on their plots, but many consider them not vigorous enough.
Katran and wasabi are relatives of horseradish
Horseradish, katran and wasabi are biological relatives, as they belong to the same Cabbage family. The last two vegetables can be called horseradish substitutes, since they are similar in nutritional and taste qualities to it.
The perennial herb katran has a powerful (up to 10 cm in diameter) root with white flesh, which contains many essential oils. The yield of root crops is 1.2–1.8 kg / sq. m, the plant is drought and frost resistant. Katran, like horseradish, is rich in minerals and vitamins. Its advantage is the shape of the roots, convenient for processing, as well as the absence of aggressiveness in clogging up the site.


Along with the root, young leaves of katran are successfully used in vegetable salads as an analogue of asparagus.
Wasabi, or Japanese eutreme, is called green mustard or Japanese horseradish. It is also a herbaceous perennial with a high content of horseradish-smelling essential oils. The Japanese believe that real wasabi grows only in the running water of mountain streams. The garden culture of the same name has only the smell and taste of an authentic Japanese eutreme.


For normal growth and development of Japanese eutreme, a moderately warm climate with a year-round air temperature within the range of +7 - +22 ºС is required
Reviews about katran
I would recommend growing not horseradish, but steppe katran (Tatar). It tastes the same horseradish (even better), but the roots are much thicker, smoother, fleshy, and seem to be not fibrous AND DOES NOT litter the garden. In the first year after sowing, the root thickness is up to 2 cm, in the second up to 7 cm in diameter, in the third it blooms and dies off along with the root. Therefore, you can not be afraid that it will grow in the garden and you will not bring it out.
mmm
My grandmother also raised Katran. It used to be quite popular, but over time, people began to plant horseradish instead. But it seems to me in vain. Unlike horseradish, katran does not spread throughout the entire area, the taste of the root is softer and more pleasant. I sow it in the fall, with several spring plantings, the seeds did not germinate even once. Probably they need to stay in the cold to germinate. I don’t dig up the first year, although in principle it is possible to put young roots in food, they are already tasty. But it's better to wait a year to grow bigger. In the second year I dig out, but not all. A couple of rhizomes must overwinter in the garden bed again so that the seeds can be collected next year. By the way, you can also eat leaves from katran. But they are not for everybody. I don't like it, but the neighbor is happy to break off the young leaves and put them in salads.
Artemida
Katran is a little more difficult to grow than ordinary horseradish and it has more pests.
tanja
Where is the best place to plant?
Planting horseradish does not require any special preparations, at least not more than any other plant.Try to choose a place where nothing has grown before or where early maturing crops grew. Beds of potatoes, beets, tomatoes, cucumbers are suitable.


The culture is unpretentious to the soil, but it is worth choosing a place on a site with loamy soil or drained peat bogs. Before planting, you need to properly prepare the soil. There are different methods of preparing the soil for the future shitty plantation. In one of them, you will need 6-8 kg of humus, 2 tbsp. spoons of nitrophoska, 3 tbsp. spoons of wood ash. All this must be mixed, dug up, diluted with water, and then the roots must be prepared for planting.
Read also: Planting roses in autumn
Another “recipe” is applied in the fall. 5-10 kg of manure, 70-100 g of superphosphate, 50 g of potassium chloride are imported to the selected site. Remember: the thicker the prepared soil layer, the better the horseradish will grow.
What are the mistakes and how to overcome them?
The most common mistake is planting horseradish near plants, as it will take away nutrients from them. Excessive care and an attempt to manually cultivate the plant can also be attributed to mistakes. In the wild, it sits between common plants and stronger, "dominant" crops. Also, poor surface preparation can be called the cause of the crop failure.
Many, believing that horseradish is a wild plant, do not even clean the corner or the outskirts of the garden from all sorts of debris (including household ones), and decomposing polymers will harm any plant. Also, do not water the plant too often, otherwise it will simply drown in the water and the roots will not be in close contact with the ground.
Planting in the garden
The cultivation of this crop requires preliminary seed preparation. Before planting seedlings, you need to take them out into the light for 35-40 days in order to awaken the buds. Cover the middle of the spines with tape and place in a warm place. Thus, many lateral roots are not formed and the plant will grow strong and powerful.
The roots sprouting from the seeds should be sorted out - it is better to put small roots into cooking, and cut large ones, 15-20 cm long. An incision is made from above - cutting off the top to make a ring, and from below - obliquely. So it will be more convenient to disassemble where is the top and where is the bottom of the horseradish. Next, the selected roots are wiped with a hard cloth or glove to remove small shoots, thereby controlling the multiplication of the culture.


In the spring, approximately in the second half of April, the cuttings are placed in the ground at an inclination of 30-40 °. Make sure that the distance between the roots is 20-30 cm, and between the beds - about 60 cm. Sprinkle the upper end of the cutting with earth and stamp it with your foot, creating a tight contact with the ground. Remember that this crop does not like shading, so do not allow densely growing fruit or berry plants to be adjacent to it. Best planted outdoors. By correctly planting seedlings on the site, you will receive a first-class product at home. In addition, transplanting this plant is a chore.
When to land?
At home
Basically, it doesn't matter what time of year to plant horseradish at home, unless the "bed" is on the balcony or in another cold place. Place the pot with the plant in a neutral place, where there is not a lot of light or temperature changes.
In the garden in the country
Like other plants, horseradish is planted in spring.so as not to disrupt the natural life cycle. Horseradish also needs to prepare for the winter by moving all energy systems closer to the soil to retain more heat and water in the winter.
Growing and care
Caring for a plant is not difficult - it is extremely unpretentious. Water the plants regularly, do a thorough weeding, and loosen the soil between the beds. In the spring and summer, feed the plants with a mixture of urea, superphosphate, potassium chloride fertilizers - this will help propagate large, fleshy roots.


Another way to get thick roots is to remove the roots and cut the leaves. The ideal month is July, when the deciduous part grows to 18-20 cm. Carefully expose the upper part of the root, cut off all the shoots, and then carefully return the soil back and water the beds well.
Include pest control in plantation maintenance. Babanukha willingly reproduces in the garden next to horseradish to huge populations. Insects eat away the leaves and rhizome of the plant. It is easy to destroy them, but you will have to do the rescue procedures several times per season. Prepare a warm mustard-pepper solution, in a ratio of 100 g of hot spices to 1 bucket of water.
Spray the leaves in the garden beds generously until the insects are completely eliminated. This will help you grow a good crop. When can you dig up horseradish? At the end of October, the rhizomes are already formed enough to send them to cooking.


How to grow?
Horseradish, in principle, grows easily in any soil, but if you want to get a juicy root, then you need to plant it in a light and warm soil that is rich in humus. You can fertilize with manure, compost and mineral complexes, as well as other root crops.
The purpose of planting and growing horseradish is to grow a well-developed, smooth, thick and straight root. This is possible only when growing horseradish in an annual culture.
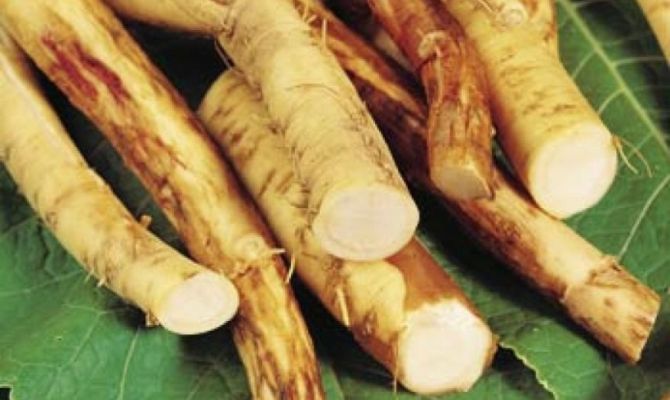
For planting, choose pieces of root with a length of 30-40 cm (root cuttings). The roots need to be cooked in the fall, or bought in the spring just before planting.


Horseradish is planted in April.
- Before planting, the cuttings are wiped with a damp cloth, removing the dormant eyes - this is necessary so that the root does not branch.
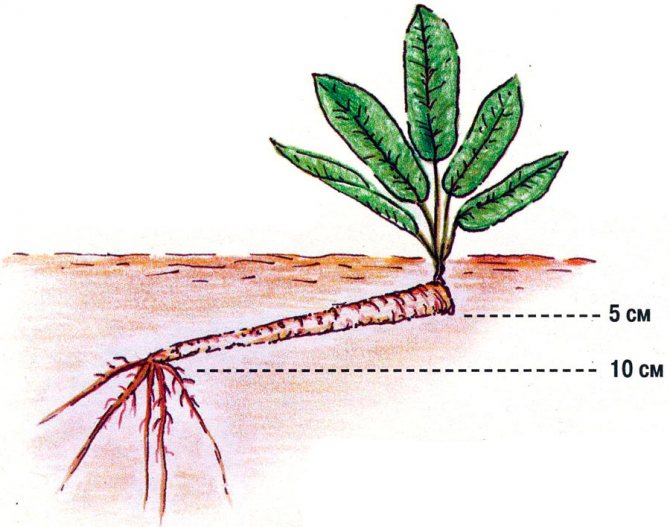
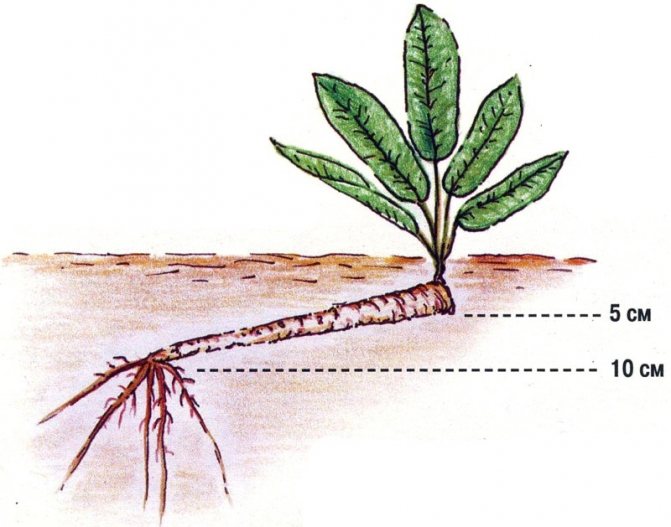
- The roots are planted in holes 10 centimeters deep at a distance of 50-60 centimeters from each other. It is necessary to plant at an angle, so that the upper part of the root is submerged by 5 cm, and the lower - by 10 cm. On the lower part, horseradish will start up a new root system.
How to limit horseradish
Care for the beds should be started long before planting the roots. The entire preparatory process takes place at home, without requiring special skills. There are several ways to isolate the horseradish growing area from the rest of the vegetation:
- old slate is suitable, which is cut into narrow strips, and then dug into the ground;
- before preparing the land, the pit is lined with roofing material or linoleum;
- the least expensive option is plastic bottles, which are dug in with their neck down by 20-30 cm, tamp them well, sprinkle them with earth on top to make a neat fence;
- an elegant way is to plant horseradish in a barrel, small buckets or boils are suitable, where cuttings are planted, this method will greatly facilitate the care of the plants and prevent them from growing into neighboring beds.
Planted and carefully grown horseradish will thank you for your care and work with a rich harvest.
Read also: Potassium sulfate (potassium sulfate) as fertilizer: application in the garden
How to choose the right variety?
You need to make sure that the variety is suitable for the type of planting and soil, coincides with the planting season and moisture level. Also pay attention to the incompatibility of plants, which will be discussed below.
Where to locate and what is adjacent to?
If in most cases the restrictions are a minus, in this case it is a big plus, because they will not allow the horseradish to spread into closed areas. It is necessary to choose plants that inhibit the growth of other crops in the same way.such as garlic, ivy.
It will be rather strange to see ivy in the garden next to the vegetable patch, nevertheless, such a “living fence” will allow you to keep the planned borders of the horseradish site.
Fuck friends:
- cucumber;
- onion;
- garlic;
- cabbage;
- parsley;
- dill;
- tsawel.
Enemies:
- tomatoes;
- potatoes;
- pepper;
- beans;
- booths;
- zucchini.
What is useful
Usually horseradish and its leaves are used a year or two after planting. The usefulness of this plant is well known.Both leaves and rhizomes are eaten.
The plant contains a large amount of sugars, resinous substances, fatty and mustard oils, as well as proteins and carbohydrates. The leaves and roots of horseradish are useful because they contain B vitamins, and it contains more vitamin C than other vegetables and fruits (5 times more than lemon).
Has antimicrobial effect, improves appetite, promotes the secretion of gastric juice. Eating foods prepared with horseradish helps to improve the functioning of the digestive system.
Bactericidal and antimicrobial properties allow to preserve products for a long time using grated roots or horseradish leaves.
Description of the plant
Horseradish is a herbaceous perennial plant belonging to the Cabbage family. Under natural conditions, it grows in Europe, Siberia and the Caucasus, brought to the countries of the Asian and American continents and is widely cultivated there. Wild horseradish forms are often found along rivers, lakes and swamps. They mastered wastelands and dumps, as well as backyards of vegetable gardens.
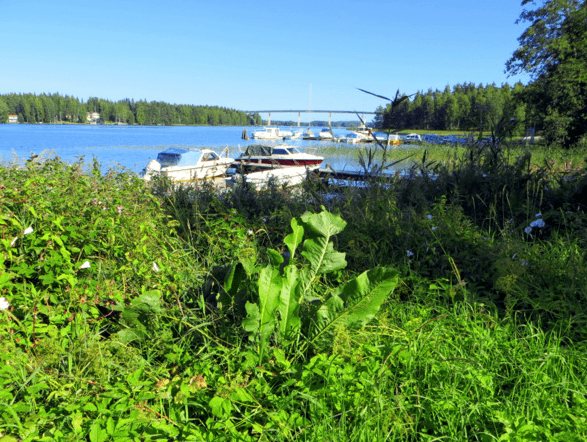


Although horseradish is considered a cultivated herb, it can often be seen growing in wilderness, such as on the banks of rivers and swamps.
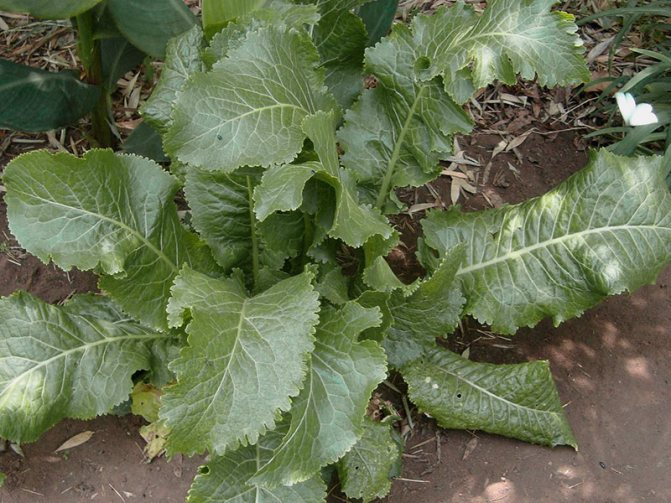
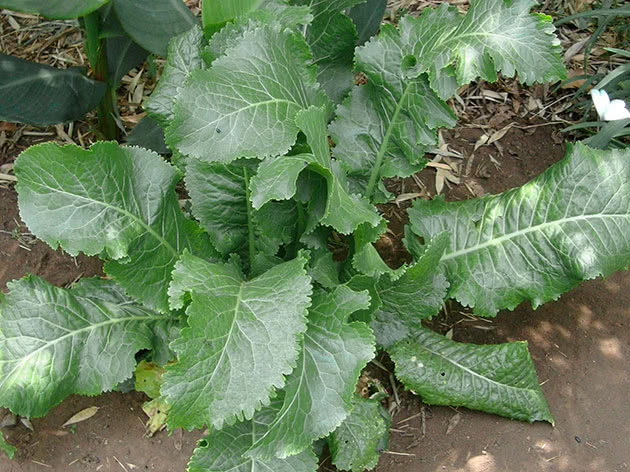
Horseradish can grow up to one and a half meters in height, has an erect branched stem, elongated basal leaves, a large, fleshy root. Small, white inflorescences form fluffy brushes. Horseradish seeds ripen in small pods.
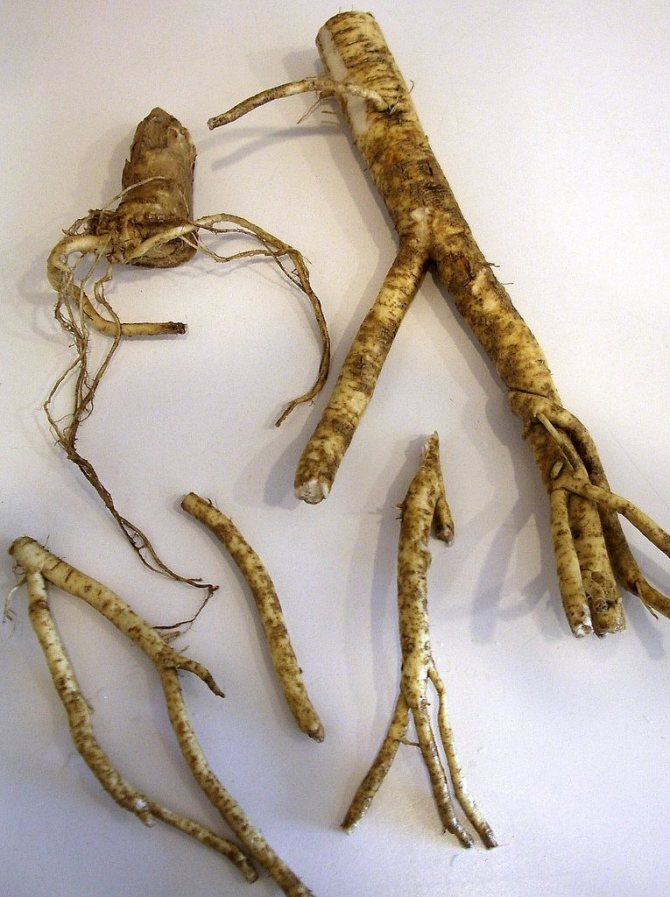
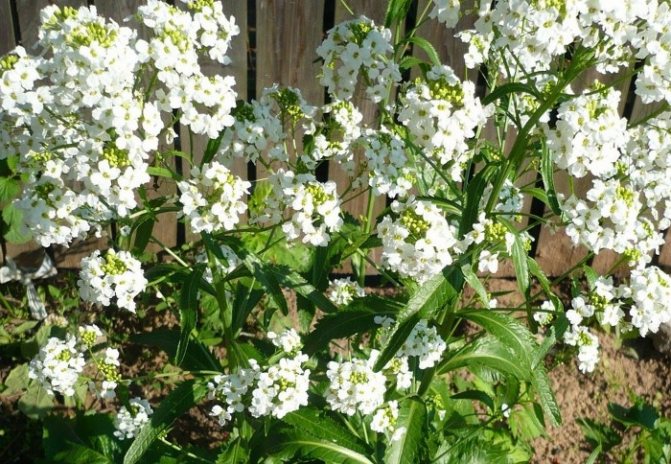
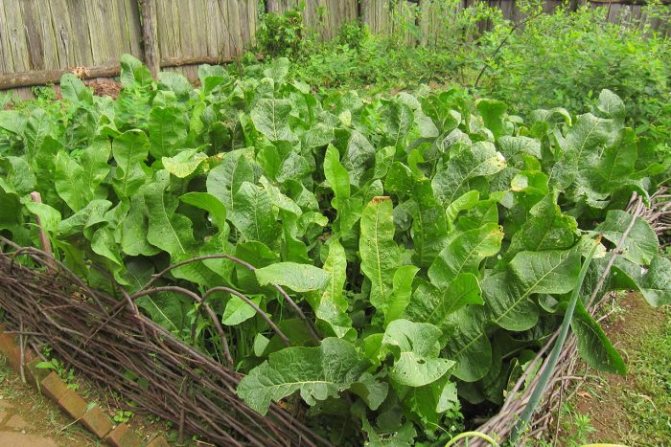
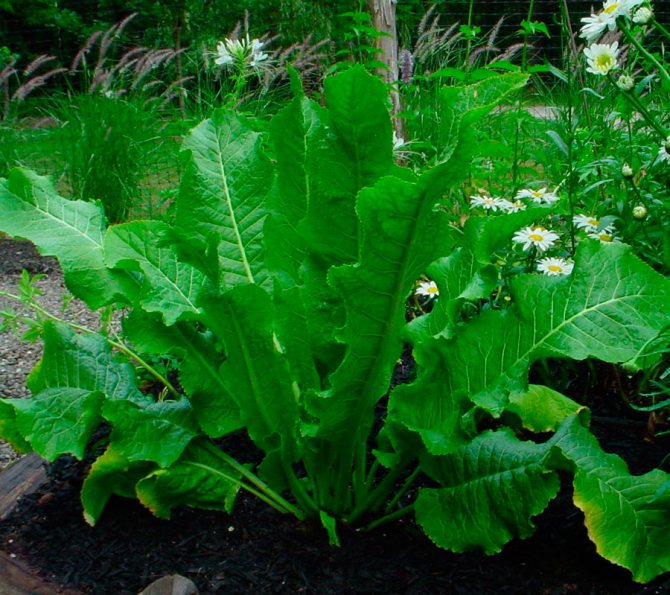
Photo gallery: leaves, flowers and horseradish root


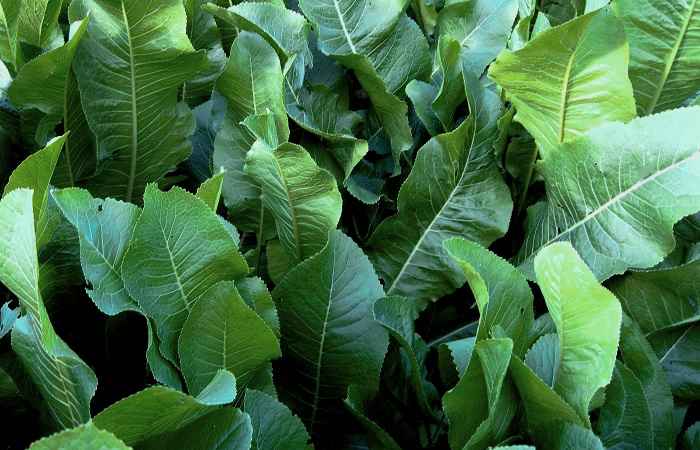
Horseradish leaves are large, oval, long-petiolate, oblong, serrate along the edge


Horseradish has a powerful, thick, fleshy rhizome


Horseradish blooms in small white flowers, collected in racemose inflorescences
A bit of history
The nutritional and medicinal properties of the plant have been known since the ancient world. In Russia, horseradish has been cultivated presumably since the 9th century. There is a laudatory record about this plant in the Russian herbalist. The ancient Slavs used horseradish for eye diseases and to increase love. In the Middle Ages, the culture began to be grown in the countries of Western Europe. As a spice, it became popular in Germany and the Baltic countries, and the British grew horseradish for medicinal purposes.
Application
Horseradish is used as a spicy additive to many dishes, pickling and salting vegetables, mushrooms, pickling cabbage, making drinks (kvass, horseradish) cannot do without it. Seasonings with grated horseradish root can be served with almost any dish: ham, fried and boiled meat, sausages and sausages. Horseradish with sour cream or apples perfectly complements fish dishes. They eat cottage cheese with it, prepare dressings for vegetable salads.


Horseradish seasoning goes well with poultry aspic, cold boiled beef, veal and beef offal
Horseradish has long been actively used in folk medicine. Known antibacterial properties of juice from the roots of horseradish, so it is used for colds, rinse the mouth and throat with angina (tonsillitis), it also helps with toothache.


Horseradish root juice is used to make homemade tinctures
Horseradish decoction has a diuretic and vasodilator effect, so it can be used for hypertension and vascular atherosclerosis. Compresses and lotions from root gruel are effective for ear inflammations, radiculitis, bruises and fungal skin lesions. Known and the whitening properties of horseradish, which are actively used in cosmetology. Root tincture is used to remove freckles, unwanted sunburn, age spots on the skin.
Video: useful qualities of horseradish, popular recipes
Interesting fact! In the United States of America, horseradish is classified as a particularly important product for the medicine, defense and space industries.
How it grows and its features
The plant belongs to the cabbage family, with a powerful thick, branched root.When growing in natural wild conditions, it can annually grow new rhizomes up to 50 cm.
Often, the root system is located compactly, to a depth of 30 cm and a radius of about 60 cm. An adult or old plant can take root from 1.5 to 4-5 meters in depth. The leaves grow up to 1.5 meters, usually bright green in color, rather large, oblong in shape.
In the second year after planting, the plant blooms. In early summer, the flowers open, flowering can last up to a month. By the end of the period, a fruit is formed - a pod, about 2 cm long. Horseradish seeds are small, low-viable. Usually no more than 25% of all planted germinates.
Plants sown in spring and emerging from seeds catch up with shoots grown by another method in autumn. But in varietal plants the seed-fruit does not grow at all.
The most common method of vegetative propagation. To do this, cut off a piece of rhizome and root it in the soil.
With a longer period of time, the root becomes woody, becomes coarse, loses many nutrients, therefore, on an industrial scale, it is cultivated for no more than two years in one place.
A frost-resistant plant, therefore, it is grown practically throughout the entire territory of Russia. It can withstand significant changes in winter temperatures, especially in February-March, when the difference between day and night values can be more than 20 degrees.
The optimal temperature regime for a good horseradish harvest is from +17 to +20 degrees. At higher temperatures, the plant reduces the growth of root mass, the likelihood of disease increases, the leaves begin to coarse and dry out.
Picky about the composition of the soil, he loves moist nutritious soils, with a neutral or slightly acidic reaction. Prefers periodic watering, but the root system can rot when waterlogged.
It can grow with a slight lack of moisture, but at the same time, the taste of both the leaves and the roots of horseradish decreases.
Follow-up care
The plant must be periodically watered, loosened and weeded. Remember that horseradish is very aggressive in the garden. Remove shoots in the spring, leave strong shoots. In early summer, remove the topsoil of the soil, cut off the side branches from the top (25-30 cm). Then tamp the soil back so that there are no voids left.

Loosening the soil after planting horseradish
You need to water regularly, 15-20 liters of water per 1 m2 of plot is enough. In dry weather, water the roots more often, and in case of precipitation, stop, otherwise the roots will rot.
The plant will not grow well without good nutrition. Use a complex mineral fertilizer when the first leaves appear. Mix superphosphate, ammonium nitrate and potassium salt in a 1: 1: 1 ratio. Take the amount in the calculation of 5 g of each component per square meter of the site. Do the next fertilization in July in the same way or with the addition of manure. If you grow horseradish for winter storage, then increase the dosage.
Growing
You can grow horseradish in your garden without much difficulty. It is important to observe a number of conditions and then the plant will give an excellent harvest.
To grow it, you need to allocate a site with a high fertile layer without a close occurrence of groundwater.
Loamy or sandy loamy soils with good moisture absorption or drainage properties of the soil are suitable.
A good harvest is obtained on drained peatlands.
Planting in heavy clay soils should be avoided.... Horseradish root grows branched, coarse. When harvesting, small roots may remain, which can grow back the next year, which will clog the area.
If you plan to grow horseradish for two to three years in one place, then it is better to allocate a separate area for it.
For annual cultivation, can be planted after vegetable crops in well-fertilized soil next to other green plants or vegetables. The predecessors can be cucumber, tomatoes, legumes.
Read also: How to propagate Kampsis at home
After the horseradish, it is better to plant potatoes. It will be able to drown out and prevent the remaining one-year roots from growing.
A plot for planting horseradish is prepared in the fall. Even if the soil is fertile, rich in humus, it will not be superfluous to introduce humus, compost with the necessary amount of mineral fertilizers, such as superphosphate and potassium chloride. Strongly acidic soils are limy.
In the spring, the soil is once again dug deeply and horseradish is planted in warm and moist soil. The best time for planting a plant in central Russia is late April-early May.
The place for growing horseradish can be anything: sunny, with partial shade or in the shady side of the cottage, but it is worth noting that the best yield will be when planting in a sunny area.
To obtain an excellent harvest with smooth, even and juicy rhizomes, the site is well fertilized in autumn and spring when digging, and horseradish is grown for no more than two years in one place.
Horseradish instead of ficus
It's great if the hostess always has fresh herbs on hand. At any time, you can pick parsley, dill and make a sandwich with a green onion. These plants feel great not only in the open air, but also in pots on windowsills and balconies of city apartments. Horseradish can be grown in the same way. What is needed for this:
- large planting capacity: a tub or pot for ficus is perfect;
- soil: you can buy it in a specialized store or bring it from the garden;
- horseradish cuttings.
The rules for planting and caring for horseradish in indoor cultivation are similar to those in open ground. And if you take into account the unpretentiousness of the culture, the normal tolerance of shading, then with minimal care you will get excellent greens that can be added to soups and salads. Lightly salted cucumbers cooked with horseradish leaves will be appreciated by your family and guests in winter. Useful green leaves and horseradish roots for the treatment of colds and other diseases.
Good to know! A tub with planted horseradish will decorate your apartment. Its large, bright green, expressive leaves grow quickly and look no worse than a ficus.
The tub is filled with soil mixed with compost, holes are dug inside and roots are planted
It is also possible to grow crops in planting containers (barrels, large boxes) that limit the spread of roots in the country. In this case, the main problem is eliminated, because of which many are afraid to plant horseradish - its massive distribution throughout the site. And autumn harvesting is simplified to a minimum: just turn the container over and shake out its contents.
Preparation of planting material
Horseradish can be propagated by grafting.
When examining the planting material, it is necessary to remove all lateral buds and branches.
For planting, you can take the apical processes, on which there is a growth point.
If the cuttings are taken in the fall, then until spring they are stored in the basement, in boxes with slightly damp sand. Correctly prepared roots will well endure the rest period and in the spring, after planting, they will grow.
After winter, you need to inspect each root and trim it:
- the upper cut is made across;
- bottom - obliquely, at an angle.
In early spring, cuttings are placed in moist peat crumbs or dripped in a greenhouse. This should be done in early April.
At the end of the month, before transplanting into open ground, the plants are dug up and with a hard cloth they try to clean off all the filamentous processes in the middle part of the root, thus "blinding" the buds. This procedure will prevent the horseradish from branching strongly in the ground, but only the main root will grow.
The top and bottom are not cleaned.Roots grow from the bottom, and a rosette with leaves grows from the top.
Where and when is it better to plant horseradish
Planting horseradish in the fall should take place on fertile soil, then the plant will grow really tart and tasty. For this, chernozems, dry peat bogs are suitable. The culture does not grow well on clay, stony soils. The roots of the plant will be weak, and the taste will be expressionless. More often, experienced gardeners grow horseradish on sandy loam, loamy soils.
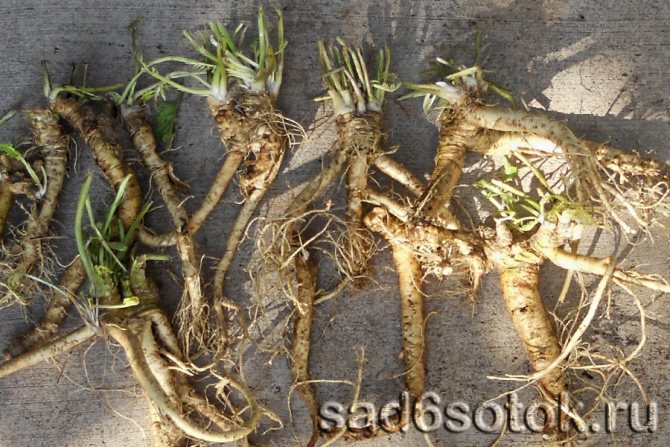
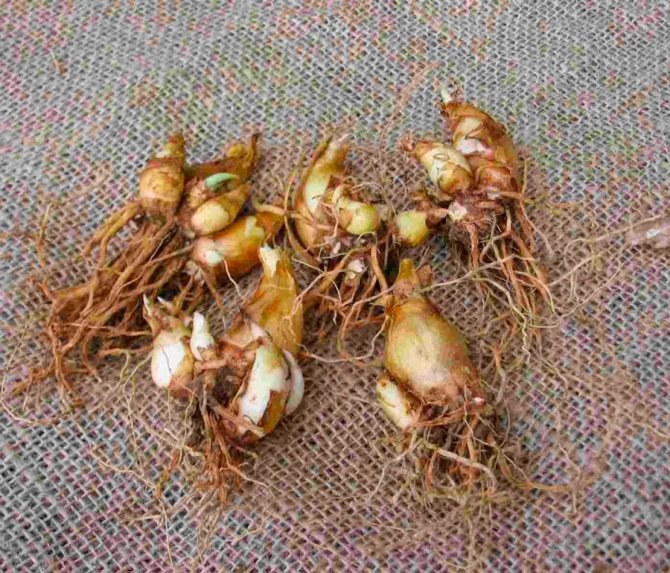
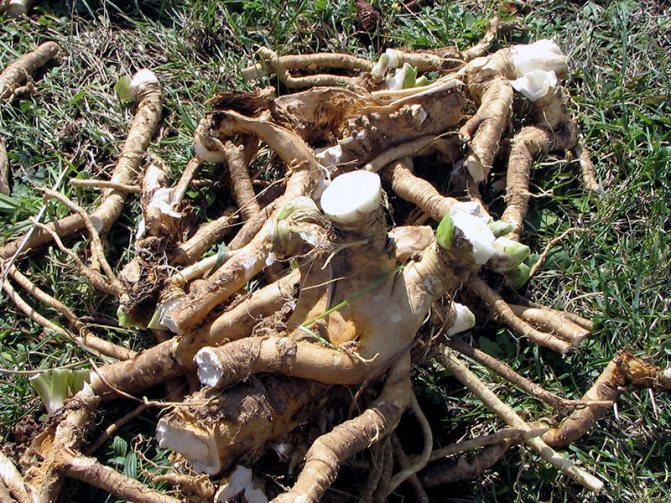
Horseradish propagation in the fall occurs vegetatively. An adult plant is dug in with a pitchfork and 2-3 thin root cuttings are selected for planting. The length of each spine should be 15-30 cm.


Horseradish roots before planting
Prepared cuttings need to be cut at the bottom at an angle. So during planting it will be possible to distinguish the upper part from the lower one. Until planting, the roots are recommended to be stored in the basement, in boxes with dry sand. Root vegetables need to be rubbed with coarse burlap to separate the lateral buds. The rhizomes will grow evenly, without branches.
For Russia, the optimal planting time is considered to be from the first half of September to mid-October. Although the plant is hardy, planting horseradish before winter is not the best solution.
Care and harvesting
Cuttings are planted in well-dug and fertilized soil with a peg, which is stuck into the ground at an angle.
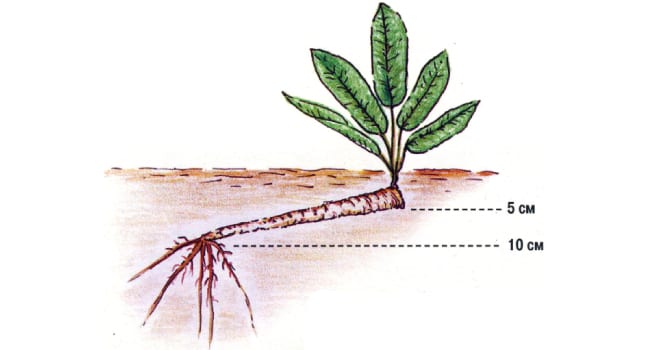
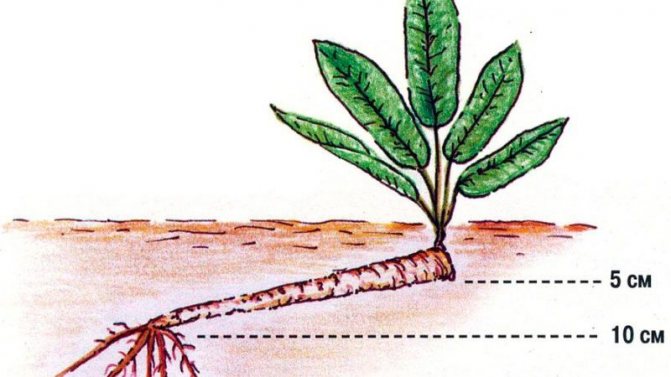
The roots should fit into the ground with an oblique cut down. The apical bud is covered with earth 3-5 cm.
The distance between plants during planting is maintained - 30 cm, row spacing - 70 cm.
Wide row spacings make it possible to care for plants and grow them without hindrance.
Plant care is simple. It consists in timely loosening during weeding and watering in dry conditions. It is worth noting that the depth of loosening should, with the growth of leaves, increase to 7-8 cm. After top dressing and timely loosening, the plants look more vigorous and increase the root mass faster.
To combat pests, you need to dilute 100 g of red ground pepper and 200 g of dry mustard powder in a bucket of water. Regularly, once a week, you need to spray the plantings with this drug.
If the lower leaves turn yellow, the horseradish roots can be dug out. It is more convenient to dig horseradish with a pitchfork.
All roots are sorted, setting aside separately intended for future planting.
Harvesting and storage
Horseradish leaves can be cut off throughout the season and used as additives in salads, first courses, when pickling and pickling cucumbers and tomatoes. Full harvesting is carried out in late autumn before the soil freezes (approximately at the end of October). It is by this time that the roots accumulate the maximum amount of nutrients, have good juiciness and taste. Yellowing and dying off of leaves serves as a signal for harvesting. Before harvesting, they are completely cut off, and then they dig in the bush with a pitchfork, take out the rhizome, sort out the soil in order to select all the remnants of the roots from it.
Important! It is better to clean the rhizome from the ground and cut it not in the garden, since in this case it is possible to clog the area with fragments of roots, which in spring can germinate and clog the area.
Horseradish is a high-yielding culture. About 1.5-2 kg of roots are obtained from one square meter. About 60% of them (with a diameter of 1.5 cm) can be used for storage and processing, thinner ones (about 1 cm in diameter) are left for planting for the next season. Smaller spines are unusable and go to waste.
Horseradish greens retain their commercial qualities at room temperature for three days. If you put it in a plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator, then the shelf life will increase to three weeks.
The processed roots are immediately sent for processing and storage, otherwise they will lose their elasticity. They store horseradish roots in the basement, covered with sand.It is very practical to store dried horseradish, a powder which is great for making sauces and seasonings. Drying can be carried out in natural conditions, as well as using an electric dryer or oven.


Dried horseradish roots can be ground with a coffee grinder or food processor, finely grated or ground in a mortar
Many housewives freeze the vegetable and use it as needed. When stored in a freezer, the nutritional properties of horseradish are preserved for six months.
Growing horseradish at home
Table horseradish is an unpretentious plant that does not require much effort during cultivation. In order for the harvest to be good, it is necessary to periodically update the culture.
The best option for growing would be an area with light shading, since the leaves may turn yellow in the sun, and it is not advisable to grow it in the shade due to its slow growth in the absence of optimal lighting.
Growing technology
If you are interested in the question of how to grow horseradish from seeds, first of all you need to know that the plot for it, as well as for other crops, is prepared in the fall. The earth is dug up and fertilized, and in the spring it is additionally loosened immediately before the start of planting.
Agricultural technology, varieties, planting scheme, blank recipes
Horseradish is an amazing culture. Some consider her to be almost a weed that does not have the right to permanent residence in a decent garden, others adore and take care in every possible way. Having studied the experience of FORUMHOUSE participants, we will tell you about how to care for horseradish, how to easily remove it from your site, about popular varieties of horseradish and recipes for delicious preparations from it.


FORUMHOUSE participant Elena Miss complains: horseradish refuses to grow in her garden, although the soil is fertile and the place is moist. The leaves are barely enough for pickling cucumbers. And it turns out that this is not such a rare occurrence.
Elena MissFORUMHOUSE member
Maybe there are modern varieties, otherwise I have a bush from neighbors ... It's already two years, but it grows 5-6 leaves and does not multiply ... And I really want to make grated horseradish!
Good horseradish grows only from good planting material.
Landing
Root cuttings are planted in previously well-loosened soil, in narrow planting holes made with wooden pegs. It is important that the depth of the planting hole is 5-7 cm greater than the length of the horseradish root prepared for planting. The petiole is placed in the hole with an oblique cut down (the main thing is not to confuse the top and bottom when planting!). On top of the holes with planted horseradish, they are covered with a small amount of earth and moderate watering is performed.
For every 1 m2, 3 to 6 horseradish stalks are planted. So that over time they do not begin to capture the nearby space, slate is dug into the ground along the perimeter of the plantings, which will limit the growth of roots underground.
How to care for horseradish
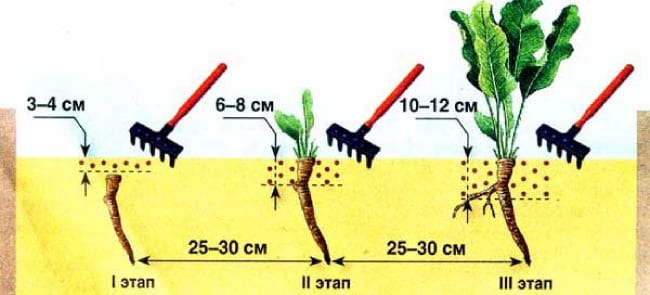
Horseradish care is reduced to weeding, regular loosening. The first time is loosened a week after planting to a depth of 3-4 cm, after the emergence of seedlings, the depth of loosening is increased to 6–8 cm, at the third stage it is brought to 10–12 cm. A total of 5–7 loosening is carried out per season. Watering is necessary in dry weather with a water consumption of 3-4 l / m2.
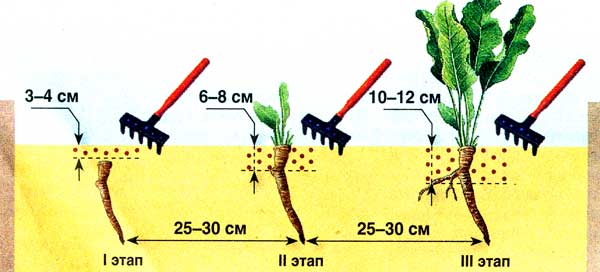

Loosening horseradish is done carefully, at a short distance from the plant, so as not to damage the roots.
Top dressing and loosening
Horseradish is not picky about fertilizers, it grows well without them. You can feed the plantings once a month: 50 g of complex fertilizers per 10 liters of water. At the same time, loose soil is very important for horseradish, as for all root crops. Loosening the ground should be done carefully, taking care not to damage the roots.
Pest and disease control
Horseradish is used in salads and preparations. Unfortunately, not only people love it, but also insects, despite the sharp and even bitter taste, which greatly harm the plant. How can you help him?
Table: horseradish pest control measures
| Pests | Manifestation of harm | Control measures |
| Wavy flea | Females lay eggs on the soil surface, feed on leaves, gnawing holes in them | Loosening will help. Vegetable insecticides containing tobacco can be used. Spraying with preparations "Foksim" and "Actellik" is carried out. During spraying it is necessary to observe safety precautions! |
| Cabbage fire | Females lay eggs on the underside of the leaf. Gluttonous larvae gnaw leaves | Planting early before the appearance of butterflies. Insecticide treatment |
| Cabbage bug | Leaves turn yellow and later die off | Means with a deterrent effect (treatment of leaves with soapy water). Dry processing with wood ash with the addition of tobacco. Treatment with decoctions of chamomile or onion husks helps |
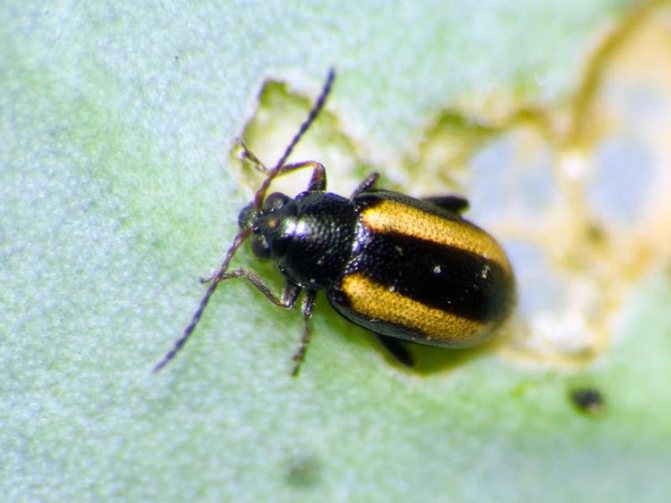
| Babanukha (horseradish leaf beetle) | They gnaw the leaves of horseradish, like other cabbage | With minor lesions, mechanical treatment is possible (shaking off beetles on the litter, glue traps). Processing with decoctions of yarrow, wormwood, chamomile is possible |
Photo gallery: horseradish pests
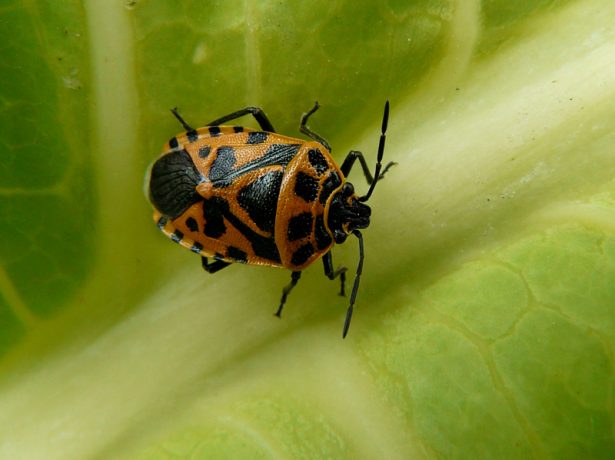


Treatment of the leaves with soapy water helps well against the cabbage bug.
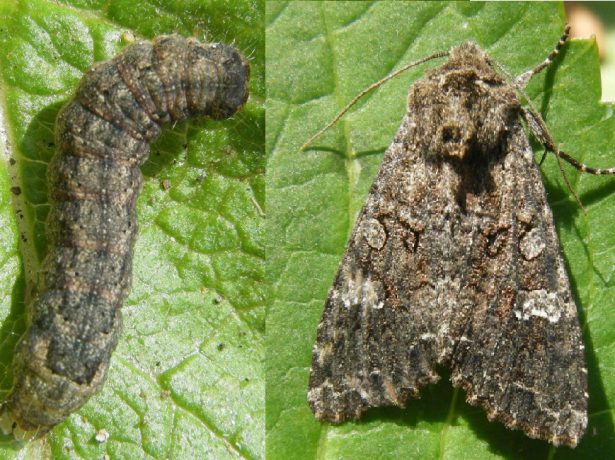


To combat cabbage fire, insecticides are used
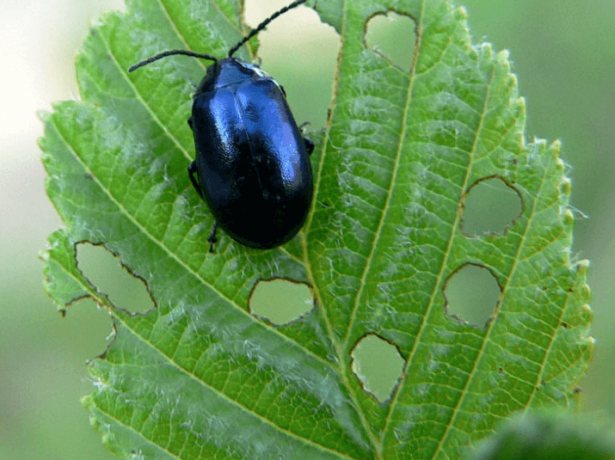


Babanukha gnaws horseradish leaves, and it becomes unfit for eating
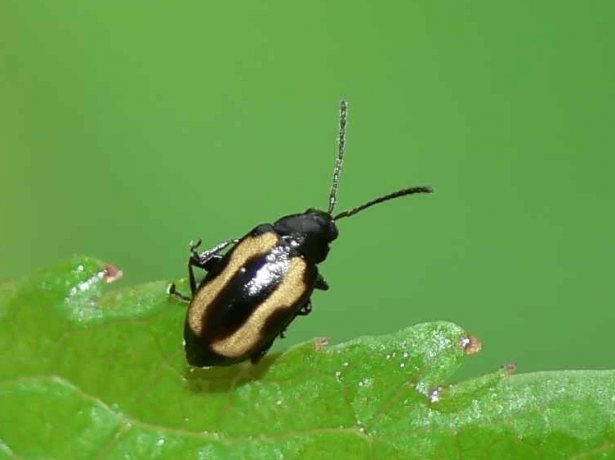


To combat the wavy flea, the leaves are sprayed with insecticides containing tobacco
Horseradish is a useful and unpretentious plant, it is used not only for food, but also in the treatment of many diseases, but sometimes it can itself be affected by diseases.
Table: horseradish diseases
| Name of the disease | Cause and manifestation | Control methods and prevention |
| White rot | Appears at high soil moisture, excess nitrogen in the soil. White bloom on roots | Fungicides containing copper Ordan, Previkur, Acrobat MC. Liming, deep digging |
| Belle | Occurs upon contact with diseased plants in the garden. The leaves look like they are covered with white oil paint. Then they dry up | Spraying with copper-containing preparations, timely removal of diseased plants from the garden, compliance with the rules of crop rotation |
| Ascochitosis | The reason is high soil moisture. Brown spots with a yellow tint | Bordeaux liquid treatment. Compliance with crop rotation, deep digging |
Video
Horseradish is considered to be one of the most traditional spices in Russian cuisine. Spicy, pungent and incredibly healthy, it awakens the appetite and makes even relatively bland dishes tasty. Good horseradish, this is when he smeared mashed gruel on bread, took a bite and shed a tear - "I saw Moscow."


Read on Dacha6.ru:
It is not difficult to grow horseradish on the site, this cultivated plant will give odds to many weeds in terms of vitality. On our backyard, horseradish has been growing near the household block in a rather shaded place for the second year and still grows very well. When it bloomed in the summer, many acquaintances who came to the site doubted that it was horseradish - it became so powerful with us.
Horseradish vegetable - description
The horseradish root crop is thick and fleshy, the stem is straight, but branched, reaching a height of 50 to 150 cm. The leaves are basal, very large, oblong-oval, crenate, heart-shaped at the base. The lower leaves are pinnately separate, and the upper ones are linear, entire. The flowers of the plant are white, with petals up to 6 mm long. The fruits are swollen, oblong-oval pods 5-6 mm long with a mesh-veined pattern on the valves. Inside the pods are nests with four seeds.
Horseradish is a surprisingly unpretentious plant, and if you once plant it on your site, then it will be forever - this perennial winter-hardy culture behaves aggressively, like a real weed.
All parts of the plant contain an essential oil with a pungent taste and aroma. Horseradish root juice contains ascorbic acid, thiamine, riboflavin, carotene, starch, carbohydrates, fatty oil, resinous substances and lysozyme protein, which has antimicrobial action.Horseradish root contains mineral salts of calcium, potassium, magnesium, sulfur, phosphorus, copper and iron. The healing properties of horseradish have long been known to medicine: it improves bowel function, has antiscorbutic, choleretic and expectorant properties, heals colds, liver, gastrointestinal and bladder diseases, rheumatism and gout.
- Conditions for growing beans in the garden: what you need to know


In this article, we will tell you how horseradish growing outdoors is carried out:
- when and how to plant horseradish;
- how to water horseradish;
- how to fertilize horseradish;
- what horseradish is sick with;
- how to treat horseradish from diseases and pests;
- when to dig the horseradish;
- how winter horseradish is planted;
- how to store horseradish until the next harvest.
Ways to multiply horseradish
To prevent the soil from clogging up with many horseradish root branches, the plant should be dug up annually, and then propagated in one of the known ways.
These include:
- seed method;
- reproduction by tops;
- cuttings.
So that the overgrown horseradish does not greatly clog the soil, it should be dug out annually
Seed method
Horseradish will bloom and give seeds if it is not dug up for 2 or 3 years, the leaves are not plucked from it.
When planting seeds in autumn, they are sealed to a depth of about 3 cm at a distance of 10 cm between them.In order for the plant to develop normally, 70 to 90 cm are left between the rows.When the seeds collected in autumn are sown in the spring, they are mixed with wet sand in ratio 1: 3 and placed for 3 months in a cool place (refrigerator, basement).
Periodically, the mixture is stirred and sprayed with water if the seeds dry out in the sand. Then the container is placed in heat. For seed germination, the ideal temperature is 21 ° C. In the 2-leaf phase, the sprouts dive into boxes or pots.
When the seedlings have 4-5 leaves, they are planted in a permanent place (after a month and a half). With this method of reproduction, the rapid development of the bush will begin only after a year, and it will be possible to dig up the root at the end of the third season after planting. Since this method is quite time consuming, horseradish is rarely propagated by seeds.
Horseradish can bloom and give seeds in 2-3 years
The planting material for this simple method is the green tops of the main or lateral shoot of horseradish. These are short (1–2 cm) petioles of the upper root part of the plant with a growth bud at the end. To propagate a plant:
- A furrow is buried in the ridge to a depth of 5 to 7 cm.
- After 10-15 cm from each other, the planting material is laid out vertically.
- Water the seedlings and sprinkle them completely with earth on top.
- on a raised bed,
- in a bucket or barrel,
- into a "sleeve" made of polyethylene film.
Most often, horseradish is planted in high beds. This planting method is especially recommended for soils with a thin fertile layer or excessive moisture. The height of the beds should be 25–30 cm: with such a planting, the plants are not flooded with water during heavy rains and, moreover, it is easier to dig out rhizomes in the fall.
Planting horseradish on a raised bed is suitable for soils with a thin fertile layer or excessive moisture
Horseradish is planted in a bucket or barrel to limit its "creeping" in the garden. The difference between planting in a bucket and in a barrel is only in the number of plants that fit in these containers.
Grow horseradish in a barrel or bucket as follows:
- A nutrient mixture from compost or humus with soil is poured into an old bucket (barrel).
- The filled container is buried in the ground so that the sides rise above the surface by 2-3 cm. 2-3 rhizomes can be placed in each bucket, 5-6 in a barrel.
If you plant horseradish in a bucket, it will not creep over the site.
Watering and feeding plants in a barrel or bucket in summer is carried out according to the general scheme.
When growing beans and caring for them in the open field, you need to know that beans are not very demanding on the quality of the area on which they are sown.They grow well on loamy soils, peat bogs and chernozems, but they are especially successful on heavy clayey soils. Acidic soils must be limed, since otherwise nitrogen-fixing bacteria are almost not formed, plant growth is greatly inhibited.
When growing and caring for beans, don't worry about harsh winters. The beans are extremely hardy. Their seeds begin to germinate almost immediately after the soil thaws. Seedlings easily and without damage tolerate spring frosts down to -5-7 ° С. In the Mediterranean countries, they are grown even in winter crops.
In central Russia, beans are usually sown in the second or third decade of April, depending on the condition of the soil. Sowing is carried out to a depth of 6-8 cm, the distance between rows is 40-50 cm, between plants in a row is 10-12 cm.
When growing beans from seeds, soaking the beans before sowing is not recommended, since after soaking, active biochemical processes begin in them. If seeds get into insufficiently heated or moisture deficient soil, these processes may slow down or stop altogether and the seeds will die. During germination, the beans do not carry the cotyledon leaves to the soil surface; a real leaf appears immediately.
The beans are demanding on the presence of moisture both in the soil and in the air, especially during the period from germination to flowering. The highest yield is given with sufficient moisture supply during this period. On sandy loam soil during dry summers, they need abundant watering. In such a summer, the beans are often tied only on the lower flowers, the upper buds fall off.
When planting and caring for beans, you need to know that this plant is self-pollinating, although cross-pollination is possible. Flowers usually begin to open around 2 pm, after sunset they close until the next day. They are eagerly visited by bees, bumblebees. At the beginning of flowering, the growing point of plants is pinched, removing the upper part of the stem by 10-15 cm. This will increase the flow of nutrients into the growing seeds and at the same time relieve the tops of the shoots from aphids settling there.
The density, firmness and flavor of the roots depend on the growing conditions and the time of harvest. As a leaf culture, rosettes are planted in pots, in winter at home, horseradish is grown on a windowsill. A decoction of the leaves helps with angina, acute respiratory viral infections, it is used to rinse mucous membranes. It is an excellent antiseptic for treating household cuts and burns.
Horseradish grows in any soil, does not require intense light. It grows well in confined spaces. It is often cultivated as an annual crop to keep the site from clogging.
Landing dates
An unpretentious culture survives in any conditions, is not afraid of frost on the soil. Horseradish planting is carried out throughout the spring-summer season, in the fall, depending on the timing when the harvest of leaves or roots is needed. In agricultural technology, there are no restrictions on planting:
- in the spring, cuttings are planted or seeds are embedded in the soil when the soil warms up to a depth of 10 cm, the plant grows at a temperature of 5 ° C;
- for mechanical cultivation, the second half of April is considered the best planting time in Central Russia; with strong return frosts, the roots may not take root;
- horseradish is planted and transplanted in summer, when there is no severe drought, air humidity is not lower than 70%, on sunny days the first 5-7 days plantings require shading, intensive watering;
- in autumn, the last planting date is 2 weeks before the onset of regular matinees (mid-October or early November), if the autumn is dry, it is necessary to saturate the soil well with moisture, the cuttings are deepened into the soil 3-4 cm deeper than in spring.
Planting methods
Horseradish is grown in open and protected ground, for summer distillation of roots, cuttings are planted in greenhouses when the first thawed patches appear (early and mid-March). Landings are deepened by 3-4 cm, mulched, covered with snow 15-20 cm in height.The greenhouse is tightly closed, left for a month. The snow will melt and gradually moisturize the ground.
When warmth comes, the roots are planted in isolation:
- On a high ridge (at least 30 cm). This planting method is suitable for areas with a high groundwater table, the ridge will serve as a drainage. The roots quickly gain mass, are easily dug out in the spring.
- In the "sleeve" of dense or reinforced polyethylene, a thin film of rhizomes is broken through. The culture is not grown in such a “screen” for more than 3 years, the rhizomes germinate to a depth of 2.5–3 meters, the plant runs wild and turns into a weed that is difficult to exterminate.
- In a large container, it is dug in at a level of 5 cm from the edge of the edge. There should be holes at the bottom so that water does not stagnate.

In the fall, the containers are removed, it is not difficult to get rhizomes from them. New cuttings or superficial buds are embedded in the ground. With limited cultivation, the use of fertile soils, it is possible to obtain a large yield of horses with valuable pulp. The agrotechnology of horseradish cultivation in an isolated space is no different from ordinary care.
New breeding varieties of horseradish with distinctive taste properties and ripening times are constantly emerging. Cultivation of roots from purchased seeds is carried out in early spring, when the soil warms up to 5 ° C or in late autumn, “before winter,” 12-14 days before stable frosts. The seed is buried in the soil to a depth of 2.5–3 cm.
Planting by cuttings
They prefer to propagate horseradish by cuttings, the seed material is well stored in the cellar, the refrigerator, the main thing is to moisten the substrate in time where the cuttings are buried. It should not dry out too much. Sometimes the buds at the roots wake up during storage, in which case they are taken out into the light. Allow to germinate well. After pecking "blind" - remove the extra kidneys with a dense tissue, they appear in all internodes of the root. Leave sprouts from below and above: for a leaf outlet and small roots.
Horseradish easily tolerates a transplant. Cuttings are placed at a distance of 40 cm; in the first year, a large leaf rosette grows. The next year, the plant develops rapidly, in the fall the rhizomes are ready for digging, and reach technological maturity.
Use as cuttings:
- thin lateral roots;
- uneven areas of the root, inconvenient for processing.
The recommended length of cuttings is 20 cm, but any fragments of the rhizome can take root. They are usually planted immediately after harvest. You have to keep cuttings at home when buying them in the cold season. When there is a free pot at home, it is better to dig horseradish, young herbs are used in soups and salads. In the spring, it is enough to "blind" the dug-in stalk, and then plant it again.
Horseradish benefits and uses
Useful properties of horseradish
As a medicinal plant, horseradish can help with rheumatism, gout, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, stimulates the intestines, stimulates appetite, has bile and diuretic effects. And this is not the whole spectrum of its action.


Culinary business in Russia was not complete without horseradish. Its leaves were used to prepare vegetable supplies for the winter. The sauce made from chopped horseradish root was traditionally served with meat and fish dishes. Young horseradish leaves that have not yet hardened are good in salads and summer soups.
Also, horseradish acted as a kind of antiseptic. It was crushed and poured into products. As a result, they did not deteriorate for a long time.
Horseradish is a useful plant not only for us, but also for our gardens, as it protects nearby plants from pests.
In our time, horseradish, as a garden culture, is not as popular as in the old days. And why bother yourself, because it can be purchased in a store or on the market. But here it is worth thinking about what we take in the store? As you know, any vegetable contains those substances that it received from the soil with which it was "fed".It is known that vegetables grown on an industrial scale do not always contain only useful substances. And is it really bad to have such a useful and necessary, especially during the salting period, a vegetable within walking distance. Means, it is worth trying to grow horseradish yourself on your site.
How to plant horseradish on the site
Horseradish is a vegetable plant related to perennial herbs. It has powerful, well-developed rhizomes and large oblong leaves. Differs in excellent winter hardiness, drought resistance and general vitality, therefore it is grown both in European and Asian countries. Often, gardeners grow non-selective ("folk") varieties of horseradish (Suzdal, Valkovsky, Latvian, Rostovsky), although there are also cultural varieties - Atlant and Tolpukhovsky, which are distinguished by a softer taste and less tendency to spread over the site.
Care after landing


Cuttings planted in autumn do not need shelter for the winter, they can withstand temperatures down to -45 ° C.
In the spring, regularly loosen and water the beds, remove the flower stalks (so that they do not take away the strength from the leaves and rhizomes). Adult plants almost do not need additional care.
Choosing a suitable site and preparing the land
Horseradish loves the sun, so it is best to plant it on the south or southwest side of the garden. It can grow in the shade, but with a lack of sunlight, it develops and matures more slowly.
A good place to plant horseradish will be a piece of land on which nothing has been planted for 1-2 years. Often this is a corner of a vegetable garden or a place near a fence. It is not recommended to plant beans, carrots and tomatoes next to horseradish, and rhubarb, dill and potatoes will become its best neighbors.
The soil for the plant should be selected fertile and soft, because in clay and hard ground, the rhizomes will become hard and will not be juicy, but dry.


Before planting, the selected area should be dug up and fertilized with 1 m² of soil with double superphosphate (50 g) and potassium chloride (20 g), mixing them with the soil. 1 bucket of humus is also introduced into the ground. Fertilizers are best added to the soil in the fall. Immediately before planting, the bed is loosened and watered abundantly.
Although horseradish is a perennial plant (it grows up to 5 years in 1 place), it is recommended to eat it at one year of age, when it is most juicy, and plant the plant again the next year. For 2-3 years of life, the roots become hard, branch out and become smaller.
Watering and fertilizing
Although horseradish belongs to drought-resistant crops, in dry years the taste of the roots deteriorates: the pungency and piquancy decrease. In a period of severe drought, the plant is moistened so that the central part of the rhizome grows. With insufficient watering, the yield will be less, many lateral thin roots are formed, coarse fibers grow. An excess of water leads to decay of the center of the rhizome, it acquires an unpleasant aftertaste of rotten hay.
It is not necessary to water the horseradish regularly, it is enough to shed the bush once a week. The roots will absorb moisture from a great depth. They use the osmosis method: the soil is covered with a film, then moisture from the lower layers of the soil rises up. The method is effective when the groundwater is close to the ground.


Top dressing improves the chemical composition of horseradish. Complex mixtures are annually embedded in the soil in the spring in the amount of ½ indicated on the package. During the rains, after the morning dew, they gradually dissolve. If desired, you can water the plant with fertilizers prepared for vegetables in open or closed ground.
Optimal timing
The optimal timing for planting horseradish in central Russia is from the second half of September until mid-October. The plant is winter-hardy and almost always takes root well and tolerates the subsequent winter without problems.


Horseradish is one of the favorite spices of Russian cuisine.It not only gives an original note to the taste of meat and fish dishes, sauces and marinades, but is also rich in various vitamins. Any gardener can grow horseradish, even a beginner.
Horseradish cleaning
Leaves are used for canning vegetables. They begin to take them off the horseradish in late summer and early autumn. They start harvesting horseradish rhizomes in October, or even leave them before winter. In early spring, the green mass has not yet begun to form, you can also dig out the rhizomes.
When digging horseradish in autumn first, all the leaves are cut off, then carefully prying the rhizome from several sides with a garden pitchfork, manually remove it from the ground. This must be done carefully, trying not to leave small roots in the ground. Otherwise, the cultivated plant can turn into a malicious weed.
Compatibility with other plants
Horseradish is a rather aggressive plant. He himself easily withstands the proximity of other plants, only tomatoes, beans and strawberries are undesirable for him. And it is also advisable not to plant horseradish near trees and shrubs, because tree roots will interfere with the extraction of horseradish rhizomes.
Fragrant herbs and potatoes are considered good neighbors for this vegetable. It is even recommended to plant horseradish next to potatoes as a means to scare off the Colorado potato beetle. Rhubarb tolerates horseradish well, and for broccoli this plant is good as a precursor.
They can't stand the neighborhood of horseradish:
- artichoke;
- swede;
- turnip;
- carrot;
- sweet pepper;
- scorzonera (Spanish goat, or black root).
In general, it is best to plant a vegetable that is "no sweeter than a radish" away from other plants - on the border of the plot or in the corner of the garden - and limit its ability to creep to the sides.
How to prevent excessive horseradish overgrowth
If horseradish is not taken care of, it begins to grow and run wild, gradually turning into a weed. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly thin out the roots of the plant. In order not to damage them, it is better to do it with a pitchfork. An opaque covering material will help to remove excess plants. At the beginning of the spring season, you need to cover the overgrown horseradish bushes. After some time, they will die from lack of light. So that horseradish does not grow much, you can plant it in a bucket or barrel without a bottom. You can dig a wooden box without a bottom at the planting site. You can also close the pit walls with plywood before planting the cuttings and cover it with soil with fertilizer. Proper care will ensure a good harvest. This will allow you to enjoy the spicy taste of dishes, increase immunity and protect the body from various diseases.


Mr. Dachnik informs: what to do if horseradish flooded the site
A healthy vegetable often turns into a noxious weed. When harvesting, the root is crushed, then all the pieces germinate.
The main measures for the prevention of uncontrolled reproduction of horseradish:
- it cannot be placed next to perennial crops, shrubs, trees, it is difficult to remove roots;
- the soil with the remnants of small roots, seeds cannot be used for bedding other crops, it is enriched and used again for growing horseradish or placed in compost;
- young unnecessary shoots are "salted": cut off, covered with fine salt, isolated from water so that sodium chloride is absorbed into the rhizome;
- annual shoots die after treatment with Roundup, but the root will germinate again, multiple applications of the decomposing chemical will be required to thin it;
- peduncles break, do not allow seeds to form.
Problems do not arise when planting isolated crops in large containers, growing horseradish as a two-year culture.
Planting plants in open ground
Horseradish is a plant that grows strongly and, if grown incorrectly, can develop into a weed that is difficult to remove. Its roots can grow up to 2 m into the ground, while reaching 10 cm in diameter and forming lateral roots.Therefore, horseradish growing in one place for many years is very difficult to remove. Even a small piece, not removed during digging, can become the basis for the emergence of a new bush. Therefore, the plant should be grown as an annual, adhering to some rules.
When to plant horseradish
The spice is planted in spring, autumn and even summer. The main thing to remember are the following points:
- Spring planting should be carried out as soon as the soil thaws. Thanks to such an early planting, it will be possible to use the young roots for canning in the summer. You need to completely dig out the rhizome in October. Store in a cool place, preferably in a basement or cellar.
- Autumn planting is carried out a month before the onset of cold weather, so that horseradish has enough time to root. When planting a plant in the fall, there is no need to store planting material throughout the winter. Having dug out the rhizome, thick roots are selected for use in food, and cuttings are harvested from thin ones, which are immediately planted.
- With summer planting, it will be possible to get a good yield only in the second year. The reason is that horseradish, planted in summer, can take root, but does not have time to grow a strong rhizome.


Choosing the right place
Horseradish is an undemanding plant that will take root both in the sunlit area and in the shade. It grows on any soil. But in order to get healthy thick roots, it is better to plant horseradish in a nutritious and light soil, water and fertilize. It is not recommended to grow the plant next to tomatoes, carrots, turnips, legumes and strawberries. It grows well among potatoes, but does not clog it and does not affect the amount of potato harvest.
Planting methods
Horseradish is planted using the roots, rooting the top or seeds. Cuttings are harvested from the root. Then, grooves are made in the garden allotted for planting. It is important to take into account that there is a distance of 30 cm between the seedlings. Between the beds the gap should be 70 cm. The petioles go deep into the ground at an oblique angle so that the cutting goes 10 cm deep. Then they are covered with soil, watered and mulched. The easiest method is to root the tops. They have small roots of 1-2 cm, short cuttings and buds. Therefore, the tops are excellent planting material. They are placed in grooves 5-7 cm deep, watered and covered with soil. The distance between the planted bushes should be 10-15 cm.


Seed breeding is practically not used, since horseradish almost does not produce seeds, and it is difficult to buy them. If you still manage to purchase them, you need to sow according to the instructions indicated on the package or according to the principle of sowing cold-resistant crops.
Harvesting
The fact that it is time to harvest horseradish is indicated by yellowed leaves. The harvesting takes place at the end of October - beginning of November. Before removing the rhizome, the foliage is cut. Then the roots are dug up with a shovel and removed to the last piece. In order not to injure the root, you can use a pitchfork. The remaining leaves and lateral processes are removed from the plant.


Planting material should be taken from the dug roots. Prepare it for storage and place it in the sand. Keep planting material in a basement or cellar. Storage temperature should be approximately +3 degrees.
Useful properties of this plant
Horseradish has long been grown in the gardens in Russia. This herbaceous plant of the cabbage family is distinguished by very large leaves with a straight stem and a thick root with a pronounced taste, which is traditionally used for food. The homeland of this plant is the countries of the Mediterranean coast. In Siberia, as well as in the Caucasus, horseradish grows in the wild. Currently, in nature, it can be found mainly in places with high humidity (on the banks of reservoirs), in addition, horseradish is successfully grown in many garden plots.


The pungent spicy taste of the root of this plant will come in handy for preparing sauces, savory snacks and seasonings for a variety of meat and fish dishes. Its roots and young leaves are indispensable for preparing various types of vitamin preparations for the winter. Horseradish root juice contains significant amounts of B vitamins, ascorbic and niacin, phytoncides, carotene, mineral salts and organic compounds, as well as lysozyme, which has antimicrobial activity. For a long time, horseradish root is considered one of the most valuable antiscorbutic agents, in addition, it is known for its antitumor activity, as well as for its properties of a natural antibiotic. In the cold season and during the spread of infections, it is very useful to eat a small amount of horseradish daily to prevent flu and colds.
The characteristic smell and specific burning taste of horseradish is due to the content of allyl mustard oil in all parts of the plant. Horseradish root has the ability to stimulate appetite and stimulate the secretion of gastric juice, improves digestion and normalizes metabolism. In addition, the numerous healing properties of this plant (choleretic, light diuretic, anti-inflammatory and expectorant) are successfully used in folk medicine for external or internal use. Horseradish will help eliminate a hangover, it is useful in the treatment of colds, gastritis with low acidity, migraines, diabetes mellitus, mild hypertension, joint aches and sciatica, skin diseases and many other ailments.
Is it possible to plant horseradish in the fall before winter
The best time to collect horseradish is October, then the ideal time comes for grafting and planting it.
Planting before winter provides the plant with characteristic properties: horseradish will grow with increased pungency and sharpness, the rhizome (its main valuable part) will gain the required mass, will be strong and large.
Advantages and disadvantages of autumn planting

With this type of planting, the earliest harvest is obtained. This is especially important for regions with late spring and short summer. In this case, the horseradish crop is ready to be harvested not at the end of autumn, but at the height of the canning season. It is then that it is especially needed - it is used for home preservation everywhere, without it it will not be possible to make adjika, horseradish, properly pickle cucumbers and tomatoes.
The culture does not like return frosts. But plants planted in autumn are not afraid of spring frost. Winter landing is good hardening.
There are practically no drawbacks to winter planting, and another plus - in the spring you get extra time, which is so precious, for other urgent work in the country: in the garden or in the garden.