Plants of the family Cereals (monocotyledonous class) are distributed on all continents and are represented by about 10,000 species. Among them there are both wild and cultural varieties that have played a large role in the development of mankind and the animal world. Modern man uses cereal plants not only for food, but also for decorative purposes. To better represent the world of cereals, we offer a selection of different types with photos and names.

List of cereals
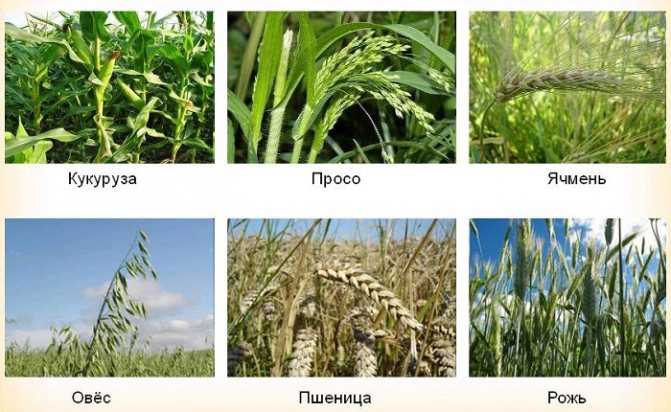


The list of cereals cannot be complete, since most of the plants on the planet belong to them:
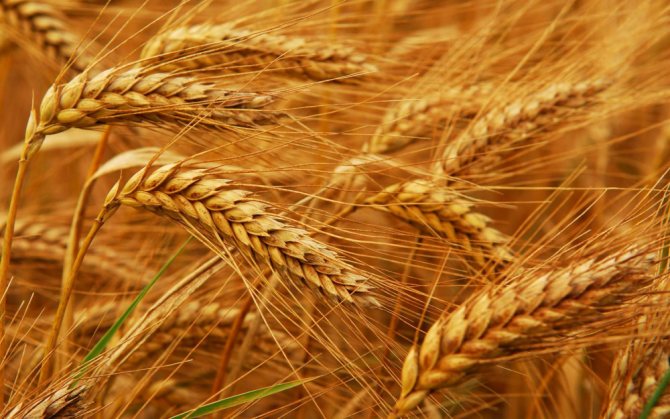
- Wheat
- the main agricultural crop on Earth.
- Rye
- is cultivated along with wheat and is characterized by high resistance to unfavorable climatic conditions.
- Rice
- grows in the eastern part of climatic zones and is not inferior in importance to wheat and rye.
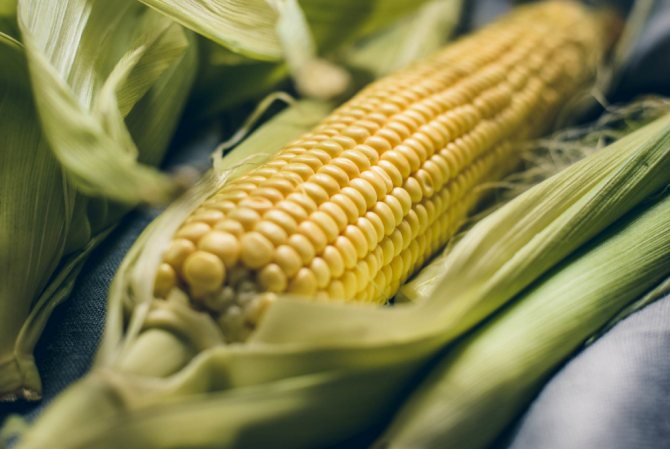
- Corn
- in many countries it is the basis of national cuisine.
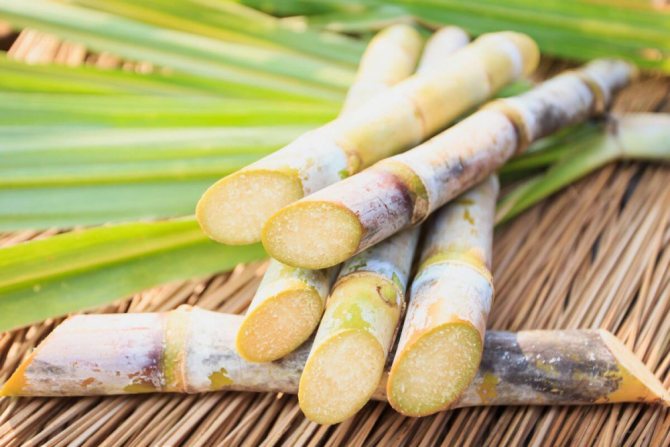
- Sugarcane
Is one of the main sugar derivatives on the planet.
- Bamboo
- a perennial cereal that is used for food (young shoots) and for the manufacture of furniture.
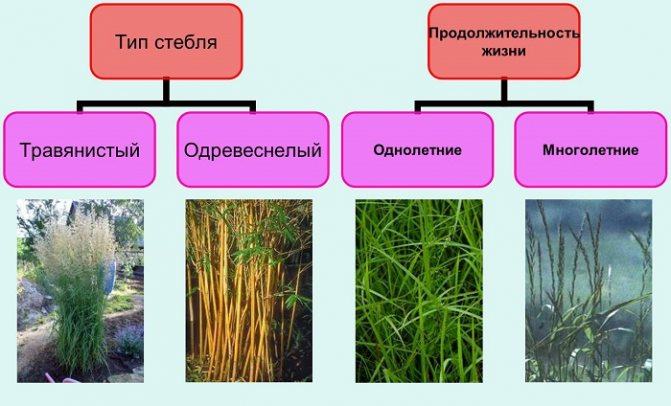
Classification
Scientists have discovered and examined over 350,000 plant species. Only 60 thousand of them make up the class of monocots, which is subdivided into 2 families: liliaceae and bluegrass (or cereals).
Signs
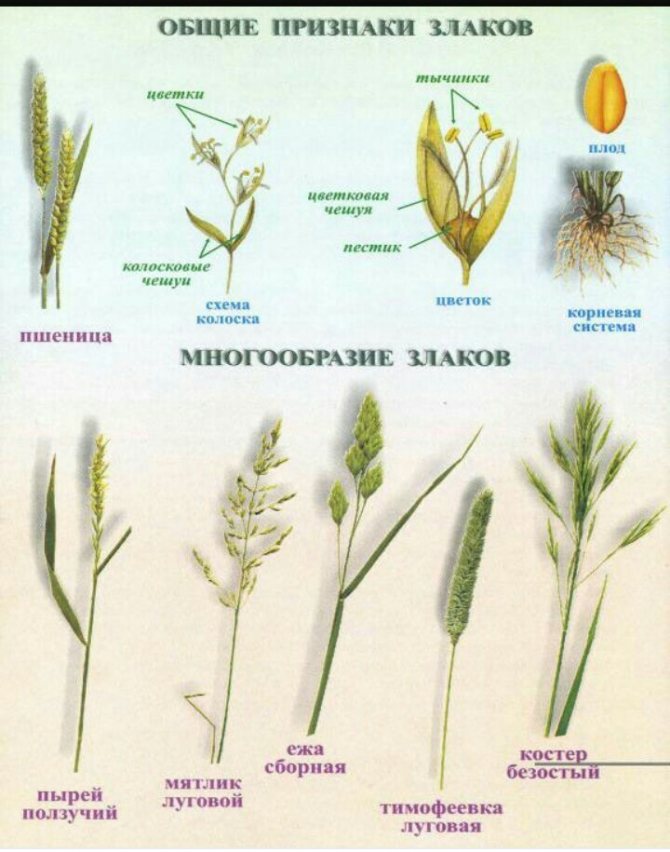
All cereals have external similarities, so sometimes they can be confused. They are distinguished by the structure of the stem: empty inside in the form of a tube. However, there are other distinctive morphological features.
Signs of the family of cereals:
- They have dense nodules on the stems.
- Leaves on stems grow together, have a linear plate with characteristic parallel veins.
- Between the leaves and the stem are the "near-stem parts".
- A tongue is located at the base of the plates.
- Fibrous root system.

Representatives
The classification of cereals includes ornamental and cultivated grasses, the distribution is based on the intended use and the quality of processing.
Decorative:
- Hedgehog.
- Feather grass.
- Wheatgrass.
- Zhitnyak.
- Fescue.
- Wild oats.
- Bonfire.
- Timofeyevka, etc.


For cultivars, their growth is influenced by environmental conditions. To get a high-quality harvest, crops had to be domesticated. Comprehensive care was established for them on agricultural land.
Pets:
- Wheat.
- Rye.
- Millet.
- Sugarcane.
- Barley.
- Corn.
- Rice, etc.
Add sorghum to this list. He has the same symptoms, and instead of a fruit, there is grain. However, it is impossible to meet him on the territory of Russia. Sorghum loves warmth very much. The fruit is used to grind and receive flour, the stem and leaves are used as livestock feed.


According to the quality of processing, they are distinguished:
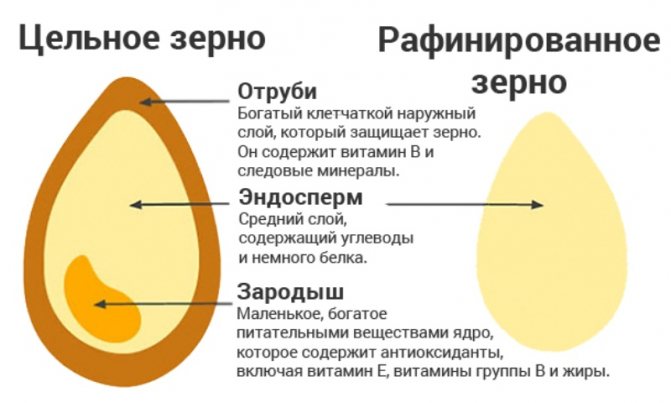
- Refined. These are bran and germ. After refining, they acquire a fine structure. This allows the grain to be stored for a long period. However, this treatment destroys all available nutrients. First of all, fiber is lost.
- Complex. Grains that have retained their shell during processing. Its components, bran and germ, are preserved at the time of grinding. Therefore, together with them, all the nutrients remain in place: potassium, magnesium, selenium.
- Enriched. Grains differ from the rest by the presence of trace elements added during processing. Despite the "artificial enrichment with vitamins," this type is in no way superior to the complex one, since the lost fibers cannot be restored.

Cereal Flower Formula
The flowering process is unattractive. At the moment of self-pollination or cross-pollination, the flowers lose their beauty and aroma. All inflorescences are simple, inconspicuous, small and pale.
Types:
- Ear of corn (corn).
- Complex ear (wheat).
- Panicle (feather grass).
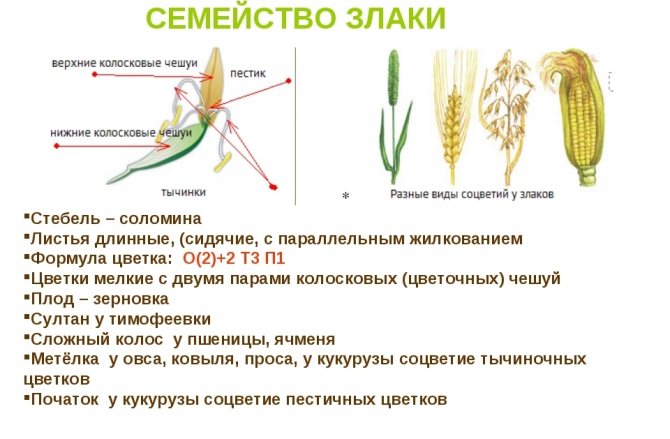
The flowers have the same shape. The flower formula of each of them is as follows: ЦЧ2 + П2 + Т3 + П1, where ЦЧ - flower scales, P - films, T - stamens, P - pistil. This formula confirms the nondescriptness of cereals at the time of flowering.

Common
Common cereals include cultivated grain plants, the names of which are known to everyone. They are used for the production of flour, sugar, cereals. In rare cases, these crops are used as components for building materials. Therefore, special conditions are created for their growth, which affect the nutritional value of the grain, as well as fertility and quality. These cultures are irreplaceable in human life.
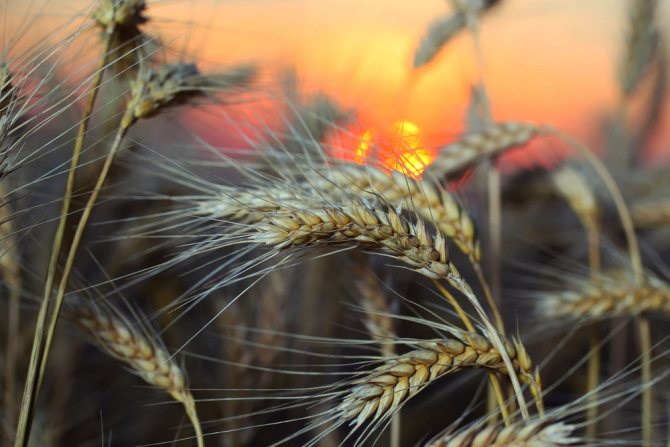
Rye and Wheat
These cereals are widely used in bakery. In addition, oils, alcohol, and medicines are made on their basis. Wheat yield directly depends on the climate of the area where it grows. Cold and frost may not have the best effect on the condition of plants. Since the soil quickly freezes, the side shoots and stems that are close to the ground also freeze. Due to the lowered temperature, their growth stops.


Rye is not so thermophilic and can fight weeds on its own. Its loosening properties help soften the soil and provide moisture for it. This contributes to the favorable and rapid growth of cereals. Rye is used not only in bakery. Bran delivers nutrients to the cells of the body and thereby increases immunity.
Areas of use for rye straw:
- Arrangement of roofs.
- Production of adobe bricks.


Wheat and rye belong to the perennial class and go through several stages of vegetation. Distinguish between spring and winter crops. They differ in sowing time: spring crops - spring, winter crops - autumn. Spring crops go through a full cycle of growth and maturation, and are ready for the autumn harvest. Winter crops are harvested in the second half of summer. They grow up to the beginning of frost, during the cold period they begin "wintering". The next stage of growth occurs in the spring-summer.
Corn
The plant has a high stem and a variety of grains: yellow and dark red. On the territory of Russia, the most popular is the first type. Other food products are obtained from these grains. The advantage of corn is that it is a row crop, that is, it fights weeds itself.
Grains contain useful trace elements for human health: phosphorus, magnesium, vitamins A and B, antioxidants, carbohydrates. Like rye bran, they have a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system, are used to prevent diabetes and heart disease, and cialicia.


Rice
Rice is most commonly used in the food industry. It only bears fruit in watery soil. This condition is key. Therefore, when deciding where to plant the cereal, it is better to choose fields near the river. If this is not possible, then you need to make regular watering.
There are several types of rice. They differ in color and grain shape (short, medium, large). Red has retained its color thanks to a plant-derived pigment. This was made possible by incomplete grinding of the rice. Only inedible hard scales are removed, and the colored shell remains intact.After industrial processing, rice comes to store shelves heat-treated (steamed), whole, refined (polished).
Types of rice by industrial processing method:
- Heat treated (steamed). Designed for pilaf. Main properties: soft, crumbly, rich in vitamins. Parboiled grains absorb moisture well and boil soft. Thanks to this, ready-made pilaf (porridge) is obtained in large quantities. The color after heat treatment acquires an amber-yellow tint. However, at the time of cooking, the grains change their color. All that remains is the unaccustomed nutty flavor.
- Refined (polished). After processing, it becomes crystal white, smooth. Complete grinding of the grains removes half of the beneficial trace elements. Such a fruit is suitable only for cooking porridge, but not pilaf.
- Whole (unpolished). Undergoes minimal processing. The grains retain their color, natural nutritional value and vitamins. The shell is tough. For this reason, the cooking can be long (40-50 minutes). Due to the weak grinding of the grains, the bran (flower) shell and grain germ are preserved, as well as all the nutrients and vitamins that nature has so generously endowed this variety. It is useful for everyone who cares about the health of their body.


Oats
Grain is rich in vitamins E, B1 and B2, as well as trace elements (iron, potassium, magnesium, zinc), useful amino acids, and fiber. Oats provide the body with energy and normalize sugar levels. Its advantages include the ability to control the amount of cholesterol.
Oats grow in moderately cold climates. The grain can be black, beige, gray and yellow. The color depends on whether it is refined or solid. On grocery shelves, it is sold in the form of oatmeal or cereal, and also muesli.
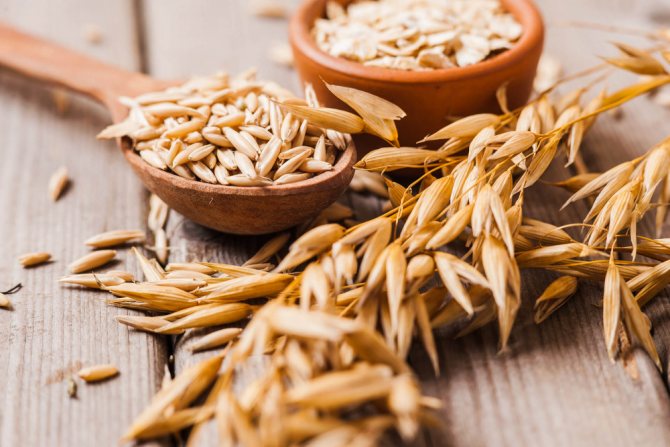


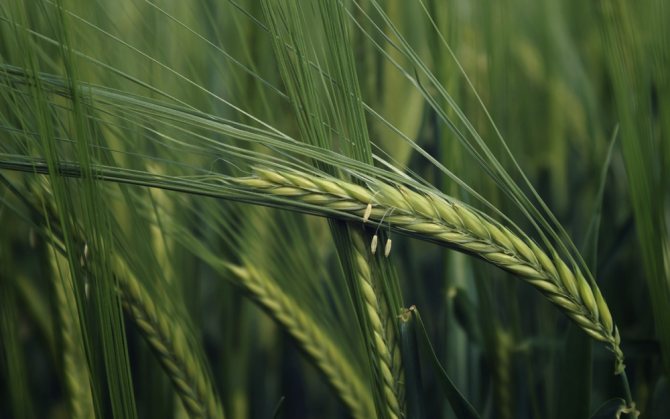
Barley
It is widely used for the manufacture of bakery products. On sale, it can be found in the form of flour or flakes. Barley adapts to any climatic conditions, has a light nutty sweetish aftertaste. Fruit color is brown, purple and light brown.
Unlike other cereals, it is used in the production of alcoholic beverages. It has more protein than wheat. Rich in vitamins, fiber, antioxidants and minerals.


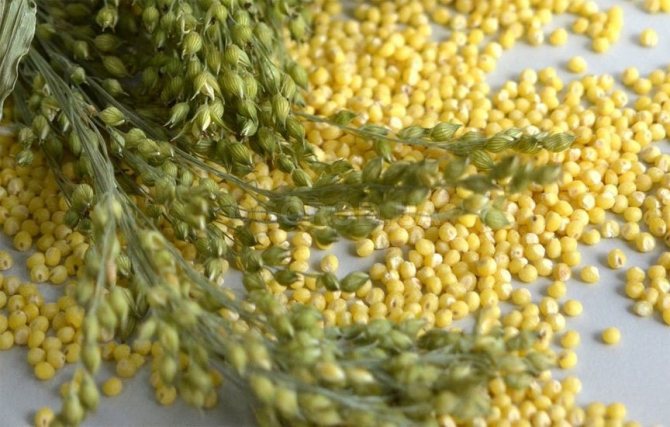
Millet
Popularly known as millet, it was first cultivated in India. Then it spread to the territories of the Caucasus, Iran and Pakistan. The nutritional value of millet has not gone unnoticed by the inhabitants of Central and Eastern Europe.
Millet is used for making cereals, soups, side dishes. The ground grains are used to make flour and baked goods. In villages and villages, boiled millet is used to feed livestock and poultry.
Millet is a genus of cereals, which includes over 400 varieties. Only eight are grown on the territory of Russia. The stems are cylindrical and divided into 10 sections. Leaves are advantageously glabrous and linear-lanceolate. The size of the leaves is half a meter long and 40 mm wide. The color palette is varied: from green to red.
At the time of ripening, round caryopses with a diameter of 2 mm appear in the inflorescences. They are white and red with a yellow tint. Reproduction lasts up to 4 months.


Dangerous
Among the cultural plantings, some are dangerous. Harmful are not so much the fruits as the products of their processing. Of particular note are rice, corn and oats. Wheat foods are not healthy.
Oats
Grains in their original form are useful, which cannot be said about oatmeal. They have the same disadvantages: an increased glycemic index, a deficiency of useful elements, and phytic acid completely flushes calcium out of the body.
As for the fruits of rice, it is worth clarifying here: only white is harmful. It is a high-calorie product with a glycemic index of 70%. There is little protein in rice - 7 grams per 100 g of product.
Wheat
The first dish in terms of harmfulness is semolina porridge. People from childhood are used to hearing about the benefits of this product. However, few people know how harmful it can be. In the manufacture of semolina, the grain is finely ground, during which all nutrients are lost. Thus, 70% of starch remains in cereals, and its glycemic index is 80%. In addition, semolina contains a complex mucopolysaccharide. It is not broken down in the child's body, which causes the digestive system to suffer.
Corn
The prohibitive norm of the glycemic index in corn is 80%. However, along with this disadvantage, corn is good for the heart, contains a lot of potassium and magnesium.
Another hidden threat is the presence of gluten. Because of it, the absorption of nutrients in the body is impaired. The gluten content is noted in fruits such as rye, spelled, barley, wheat, oats. It is absent in rice, corn, millet and buckwheat.
Gluten is a vegetable protein that causes allergies in 30% of the world's population, and can provoke intestinal disease or inflammation.
Rare
Wheat, rice, oats and their processed products have long become traditional. But there are rare species that are not found everywhere. They are also rarely used in food preparation.
Durum
It is commonly called pasta wheat. The first plants were discovered in the 7th millennium BC. Durum gained the greatest popularity in the Middle East. Flat bread is baked from it, and in northern Africa it is added as a spice to soups and pastries.
The Russian consumer may encounter durum when buying durum wheat pasta. The disadvantage of this cereal is the high content of gluten, which at the same time makes the dough soft and pliable.
The grains are large and amber. Durum is also used in the production of couscous, semolina, bulgur. He gained wide popularity in the west of Asia. It grows in Canada, from where it is exported to other countries. It is especially in demand in Italy, as it serves as an irreplaceable ingredient in a recipe for making pasta.
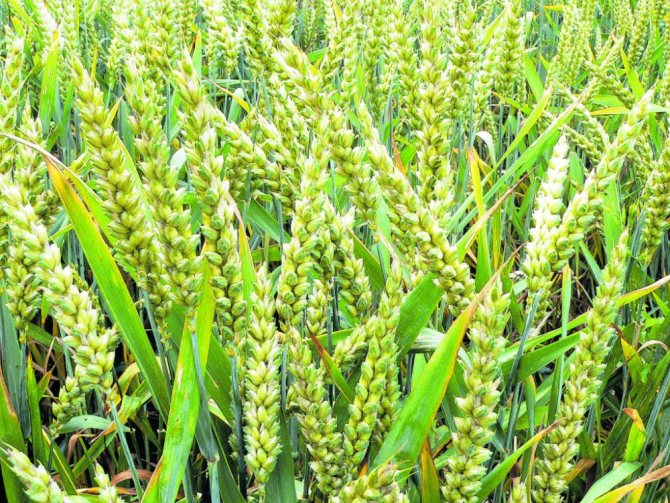


Chumiza
Habitat - Asian countries. The fruits are ground to make flour and cereals. After processing, feed for livestock is prepared from the waste. Asians add chumiza to liquid dishes, pastries, and sweets.
Some alcoholic beverages contain an ingredient such as black rice. Chumiz was widely used in the manufacture of food for parrots. In its pure form, it is sold only in organic stores or online stores.


Sago
This groats are very difficult to find. It is made from the sago palm tree, which grows in a tropical climate. In Europe, cereals are not grown. More fortunate are the inhabitants of Australia, Southeast Asia and India, as well as New Guinea. It is in these countries that sago is actively used in cooking: pastries, cereals, soups and chips.
During cooking, the cereal becomes stringy. This property makes it a thickener for the preparation of puddings and sauces. The distinguishing feature of sago is the presence of fiber and the complete absence of gluten. Due to complex carbohydrates, a person is charged with energy for a long time and the feeling of hunger is satisfied.


Teph
You can meet this cereal in the vastness of Russia only in health food stores. The plant is native to Ethiopia, where it serves as a staple food. The climatic requirements for growth imply a high air temperature, as teff grows on the tops of the mountains. An important condition for growth is abundant watering, so it makes no sense to import teff for cultivation.
The grains are used in baking. A flatbread similar to Caucasian lavash is baked and the filling is wrapped in it. Vegetarians will love this product because it contains not only proteins, fats and carbohydrates, but also iron.There is no gluten in the chemical composition.


Amaranth
One of the oldest cereals in South America and Mexico. It was first discovered on the American and Latin American continents 8000 years ago. It is used to make sweets, flour, drinks and bake bread. The nutritional value of the plant is great: it contains fats, proteins, carbohydrates, starch. Also amaranth is rich in acids, vitamins and minerals. Contains squalene - another trace element with antimicrobial and regenerating effect.


Small
The smallest cereal is golden lamarkia. This is an annual herb with a shoot height of 10–40 cm. It grows on sandy and rocky slopes, as well as in the subtropical territories of the Mediterranean and Asia.
Lamarckia has a lot of stems. They are all naked and erect. Leaves reach 12.5 cm in length and up to 1 cm in width. The ears are grouped in bunches of 4–5 pieces.
Flowers appear alternately. One fades and the other unfolds. Each inflorescence resembles a golden panicle, the length of which is 7 cm. You can wait for flowering only by mid or late summer.


Large
Large species include corn, which can reach gigantic sizes - 5 meters in height. For the first time, the giant cereal appeared on the American continent in Mexico about 3500-5000 years ago. Each corn stalk has several ears containing up to 1000 kernels.
The second highest stem is sugar cane, which grows up to 7, and sometimes reaches 9 meters. India is considered the first place of its growth. Sweets were made from condensed cane juice, which was called "sakkara" ("sarhara"). The name is consonant with the Russian word "sugar".


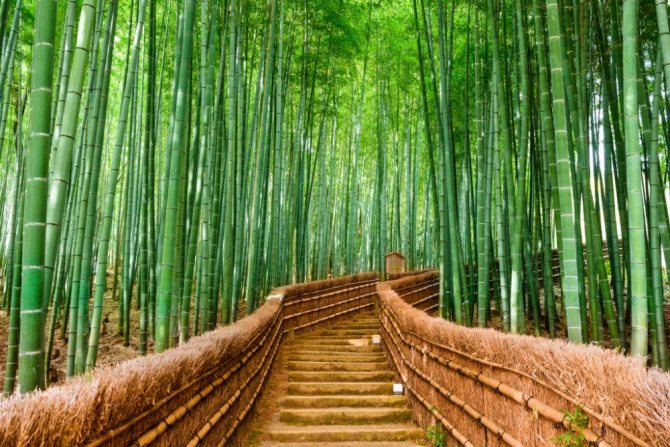
The leader among large cereals is bamboo, a fast-growing plant of the cereal family. Some of its species, common in South America, reach 30 meters. In a day, bamboo can add a whole meter in growth. Sharp and thin shoots reach for the sun and make their way even through the asphalt, often pushing stones apart. It is no coincidence that beautiful and durable stems are used in construction.
Bamboo flowering is a very rare phenomenon, observed once every 20 years. Some of its representatives can bloom once every hundred years. The stems are water-resistant, so they are used for making buckets and other household utensils. If holes are made in the partitions of the barrel, then water pipes will be obtained.


Life form
The life cycle of cereals consists of several vegetative periods (seasons). These are one or two-year herbaceous plants, less often shrubs.

The life form is the totality of all the plant's abilities for existence. In cereal plants, rhizomes play a key role, and the possibility of tillering them.
Distinguish:
- Long-rhizome perennial cereals
, which, with the help of long horizontal shoots, propagate vegetatively.
- Loose bush perennials
, which, having no long creeping roots, actively branch out overground shoots.
- Dense sod perennials
, growing mainly in the steppe zone and characterized by the location of young shoots close to the mother plants.
An annual plant bushes during the growing season, dies off, while forming many seeds for the next generation.
Caring for a sheep in the garden
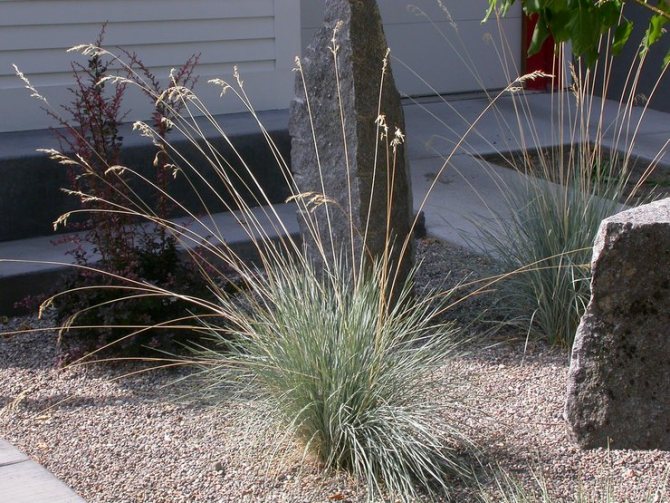


For high-quality flowering, oat plants need to create suitable conditions of detention, in which there will be no two factors dangerous for the cereal - high air temperature and high humidity.
Watering
The main enemy of the oat is excess moisture. "Excess" moisture can destroy plants. The first sign of a problem is the lack of new leaves and the drying of old ones. It is necessary to water the crop only during prolonged severe drought and very hot weather. Irrigation volumes are moderate.
Top dressing
Excess fertilizer also negatively affects the external characteristics of crops. In the first year, it is enough to feed the sheep twice.The first time is 7-10 days after planting the sheep in the open field, and the second time - after the end of flowering. As a top dressing, you need to use complex mineral fertilizers (in liquid form). In the future, plants will have enough once a season.
Pruning
The first pruning is done in the second fall after planting. Experienced flower growers recommend cutting off the entire aerial part. Subsequently, it is worthwhile to promptly remove dry leaves that have lost their green color and dried panicle inflorescences. The rejuvenation of the bush is carried out after 3-4 years.
Wintering
The winter-hardy perennial oat tolerates winter cold and is not afraid of frost. It doesn't even need to be covered.
Root system
All cereals have a fibrous root system.
Various types of cereals have the ability to form a large number of fine roots.
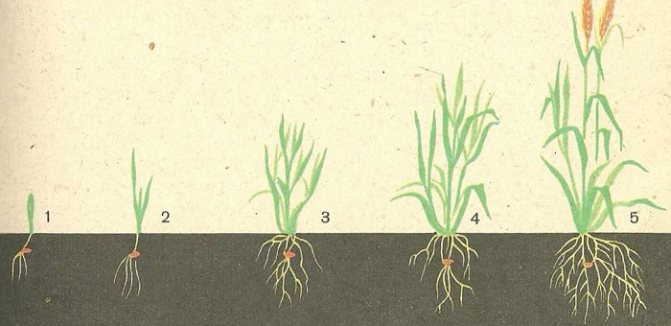

They actively absorb water and are the basis for plant survival. Sometimes underground shoots can turn into rhizomes. The root makes up the bulk of the plant mass.
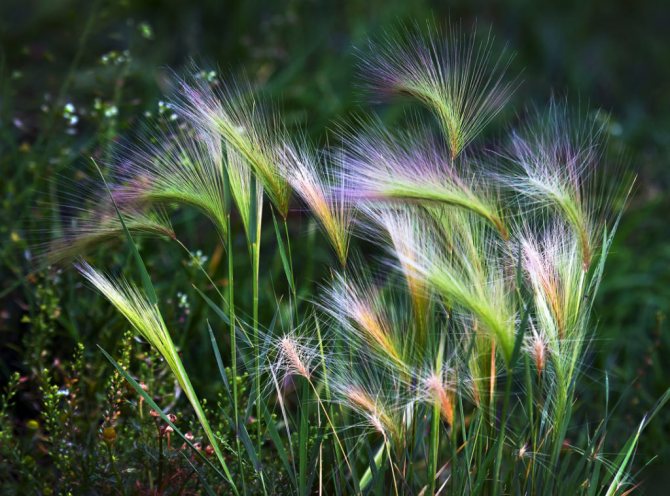
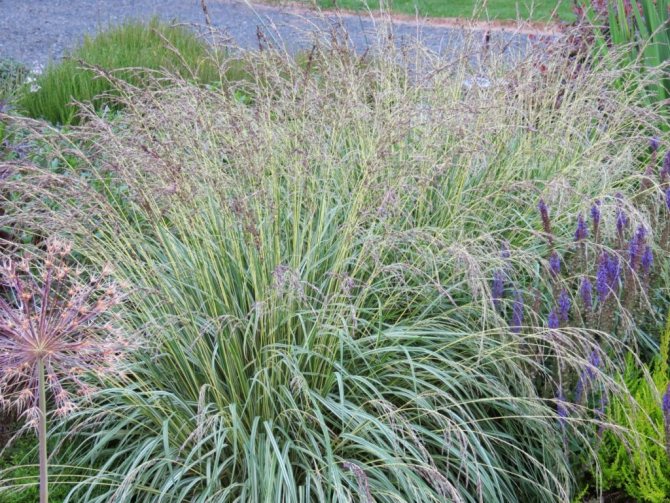
Decorative cereals: all the best from nature itself
Capricious, varietal flowers require a lot of attention, labor and care, they may refuse to bloom or even die if the weather conditions do not meet their needs. An alternative option for decorating flower beds is decorative cereals. Together with unpretentious zinnias and other annuals, they will create a stunning oasis of beauty. Ornamental grasses play an important decorative role in most landscapes, have a calming effect, while creating a coherent, colorful, blooming picture. Being a central accent in garden design, decorative grasses are able not only to complement flower beds during the summer expanse, but also to hide voids at the end of the garden season. These plants are versatile, they are suitable for decorating the shore of a pond, add brightness to a Japanese garden, they are indispensable for decorating an alpine slide or rutaria. If you plan on setting up a prairie-style garden, then a soft grass carpet is the perfect base. They will also perfectly decorate the terrace or containers on the balcony.
It is decorative cereals that have the property of magical effects on humans. They rustle so pleasantly in the wind that pictures of free steppes and lush meadows involuntarily come to mind. These plants do not leave us even in winter. Bumps of all shades, slightly crushed by snow, from greenish-brown to blue, brighten up the winter landscape. In the spring, old perennials will need to be mowed, and annuals will need to be removed and sowed again.


Leaves and leaf arrangement
Grass and bush plants of the family of cereals have a regular leaf arrangement. Narrow linear leaves prevail, which are located on hollow straws with nodular formations.
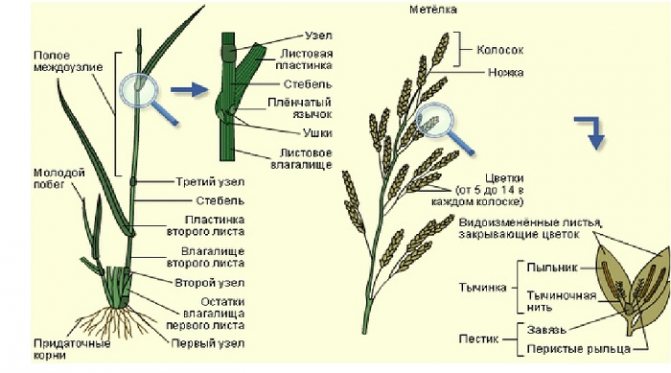

Educational tissue in the interstitial cavities of the stem is the basis for plant growth. Leaf vein runs parallel to the central vein.
The sheath of the lower part of the leaf does not completely cover the stem at the site of the node. This gives the leaves a convenient opportunity to open. Most of the transition of the leaf to the leaf blade forms a thin tongue.
Sheep breeding
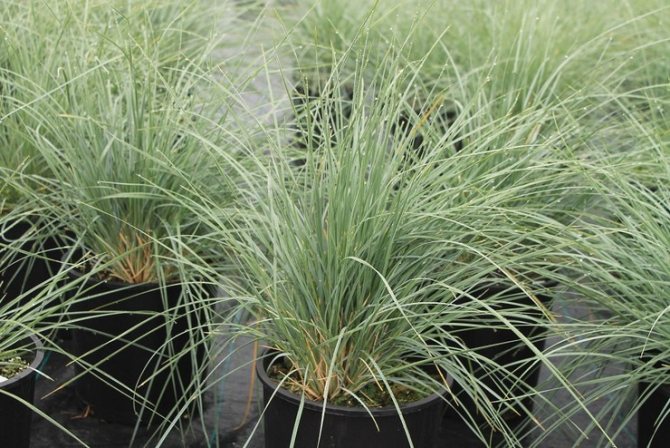


This method of breeding sheep is only suitable for plants that are three or four years old. At this age, decorative qualities are gradually lost and the attractiveness of the culture decreases. You can give cereals a second youth by dividing the bush into several parts. Only in spring is such a division made. Each new part should have several sturdy and strong roots. The resulting delenki must be immediately planted in a new place and watered. Three-year-old plants do well with this procedure.
Dividing and transplanting a sheep does not carry anything dangerous for the further growth and development of the plant.
Inflorescence

The family of cereals has a varied inflorescence shape:
- ear (simple and complex shape);
- brush;
- cob (corn);
- panicle (a type of paniculate cereals);
- sultan (spike-shaped panicle).
Cereals do not attract attention. They are characterized by inconspicuous flowers,
which usually open at certain times of the day.
Criterias of choice
In order for decorative cereals to take root well and successfully fit into the decorative composition on the garden plot, you need to carefully consider the choice of the variety.
When choosing a plant for landscape design, you should consider:
- future location (composition or separate flower bed);
- life span (annual or perennial);
- active flowering phase;
- climatic zone;
- decorative period;
- the color of the plant and its flowers;
- the shape and size of the plant, its leaves and inflorescences;
- the ability to produce aroma;
- capriciousness to soil and lighting.
Often gardeners are afraid not to cope with the design of their site with decorative cereals, so they prefer to contact a professional landscape designer. But, in fact, there is nothing difficult in this, if you carefully study the varieties of plants, and draw up a plan for their location on the site in advance.
Flowers
Flowers in cereal plants are small. The ovary is located in one cavity of the ovule (monocotyledonous flowers). An ear serves as their basis.
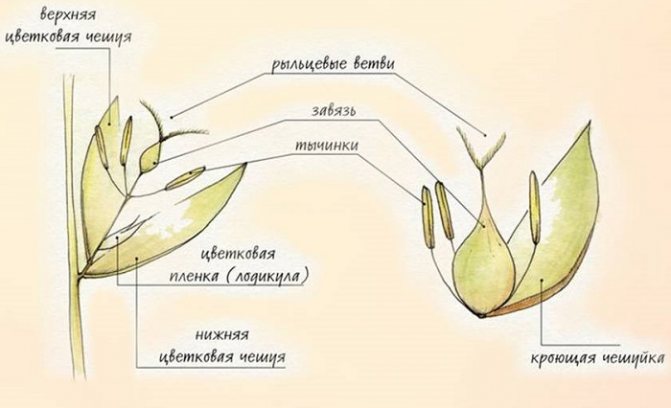

On both sides of the base of the spike, the axils of the bracts are arranged in rows. They are the bottom color scales. At the base of the flower, 2-3 scales are formed, which swell during flowering (dodicules). There are usually 2 to 6 stamens per flower on long stamen legs.
Cereal flowers are pollinated by wind and insects. Single plants are an exception. For example, in corn, the female flowers are on the cob, and the male flowers are on top in panicles.
Growing conditions
Among ornamental grasses, plants are distinguished that prefer dry places for growth; specimens that feel comfortable in wet soil, as well as varieties that are grown near water or in swampy areas. Therefore, to decorate the yard, choose plants from the first two groups, but the representatives of the third group will look spectacular by the reservoir. All these crops are unpretentious in care, only during severe drought do they need watering.
Choose crops for garden decoration taking into account periods of active growth. So, thermophilic species are active in summer, and cold-resistant ones - in early spring and autumn. Evergreen species adorn even the winter landscape. Knowing these features well, it is possible to provide a wonderful landscape almost all year round.
You will find more information about ornamental grasses in the video.
Care secrets
For the most part, ornamental grasses are perennials, and therefore they grow in one place for a long time and do not require special care, except for the spring pruning of last year's shoots.
However, there are some nuances, the implementation of which guarantees an attractive appearance and health of your plants:
- In spring, last year's leaves and shoots should be cut as short as possible.
- After spring pruning, the lawn can be covered with a layer of mulch, 5 to 10 cm thick.
- In order to further preserve the decorative effect of some plants, it is recommended to regularly cut off faded panicles.
If the plant loses its decorative effect, it is necessary to cut it to the width of the palm.
Distribution of the cereal family
Representatives of the family of cereals are mostly unpretentious and spread throughout the planet. Even in Antarctica there are two plants (bluegrass and Antarctic pike) that belong to this species.
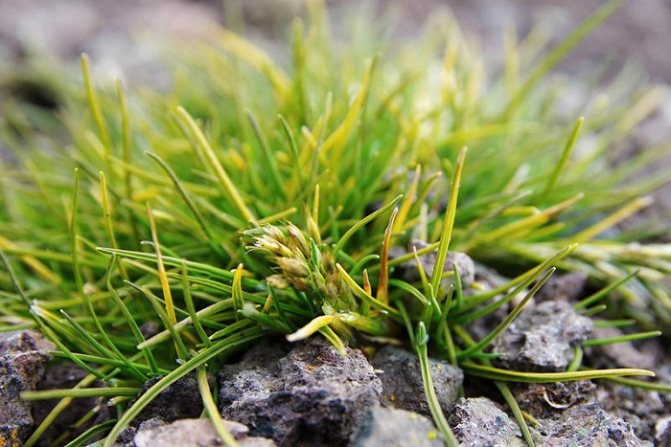


Antarctic pike
The vast majority of steppes and shrouds are inhabited by wild grains that serve as food for all living things.
On all continents, people cultivate cereals for food and as forage crops for pets.
Value
Cereals are irreplaceable in pasture and hayfields.Among all the others, it is worth highlighting creeping wheatgrass, meadow fescue and awnless bonfire.
The importance of cereal crops in the economy is explained by the microelements necessary for human life. For example, sugar is extracted from tropical sugar cane. Bamboo is used as a building material; the inhabitants of the tropics and subtropics make the roofs of houses from it. Furniture and decor items are also made from bamboo. Rice straw can be used to make hats, baskets, some paper and furniture.
In addition, in some areas, representatives of the bluegrass family are grown in unusual places: ravines and gullies. This is necessary to strengthen sand and soil, which may crumble. The roots loosen the soil from the inside and saturate it with nutrients.
Features of the
The peculiarities of growing cereal crops include the timing and time of their sowing. Cereals sown in autumn are called winter cereals. They need low temperatures to start growing. Spring crops are sown in early summer when the ground warms up.


Cereals are not only the main food for humans and animals. They are widely used for landscaping. There are examples and photos of the use of cereals to strengthen the soil in the fight against erosion. However, cereals as a weed plant often reduce wheat yields and can cause disease in livestock.
The beneficial properties of cereal plants cannot be overestimated. Products based on them are the main supplier of vegetable protein and carbohydrates in the human diet.
Planting sheep in open ground


How to plant sheep correctly
Planting sheep in the ground is carried out in pre-prepared holes, which must be pre-moistened. It is important not to damage the seedlings, so the plant does not need to be pulled or tugged. A seedling with a lump of earth is placed in the center of the hole and all the free space in it is sprinkled with the remaining soil.
The sheep planting site should be open, sunny or slightly shaded at certain hours, but always in the southern part of the land. You can not choose areas in the lowlands and with a close location of groundwater. To grow sheep as a hedge, seedlings are placed at a distance of about 50 centimeters from each other. For a group composition, it is recommended for one square meter of a flower garden - no more than four young oat plants, and in a single planting, a cereal may have no neighbors at all at a distance of more than 1-1.5 meters. It all depends on the available land space.
The preparatory work is not required only for poor and depleted areas. It is recommended to pre-dig up heavy soils and add gravel or coarse river sand during the work. The soil should be light, loose and moderately dry.
The lack of nutrients in the composition of the soil will not affect the decorative effect of the oat and its full development.
Pearl barley ciliate
This long-rooted perennial grass loves sunny places and light moist soils. It grows in dense bumps that form narrow light green leaves. Flower stems, about 60 cm high, appear in late spring or early summer, forming a whole cloud of creamy white graceful drooping panicles, for which the cereal is valued. Spikelets are decorative for a little more than a month.
The plant is quite unpretentious, the pearl barley reproduces by dividing the bush or seeds, in August it requires pruning.
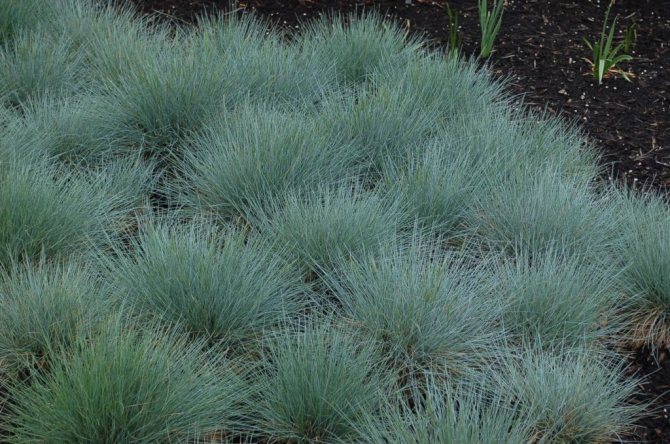
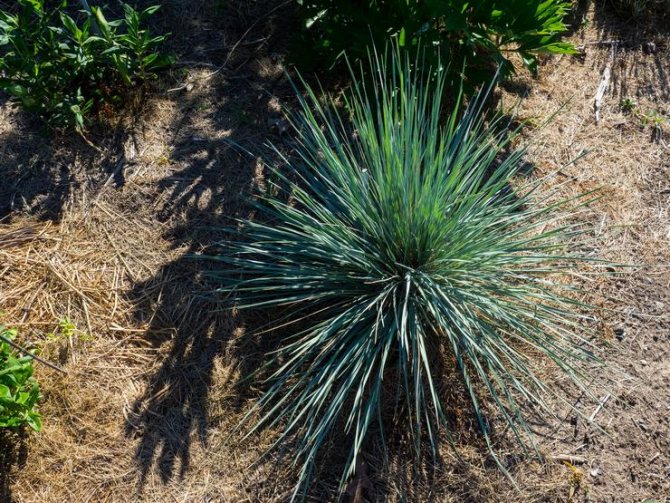
Evergreen sheep
Heliktotrichon, evergreen oats, viviparous oats - this cereal has many names and one essence. Its bright, lush bushes can be the perfect border, blend into any flower bed, or grow in a container. Frost resistance and unpretentiousness make it a real find for our climate or beginner gardeners.
The most popular sheep varieties are Pendula, Robust, Saphirsprudel.
The main requirements of the oat are poor soil, sunlight and dryness.From an excess of nutrition, he gets sick, in the shade it loses the blue tint of the foliage, and when waterlogged, its roots begin to rot, and the leaves become covered with rust. For maximum decorativeness, the bushes need to be divided every three years.
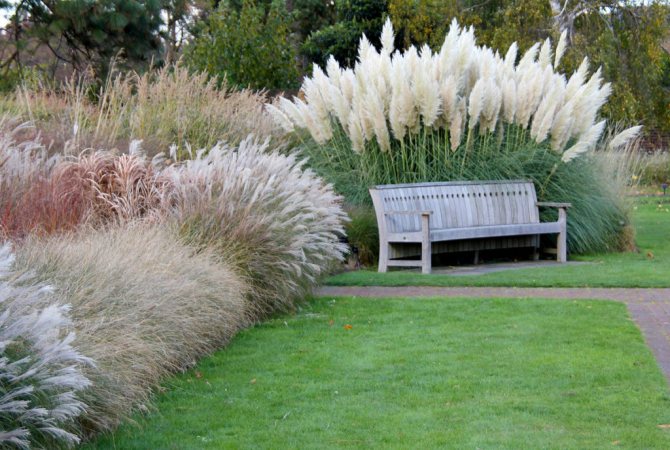
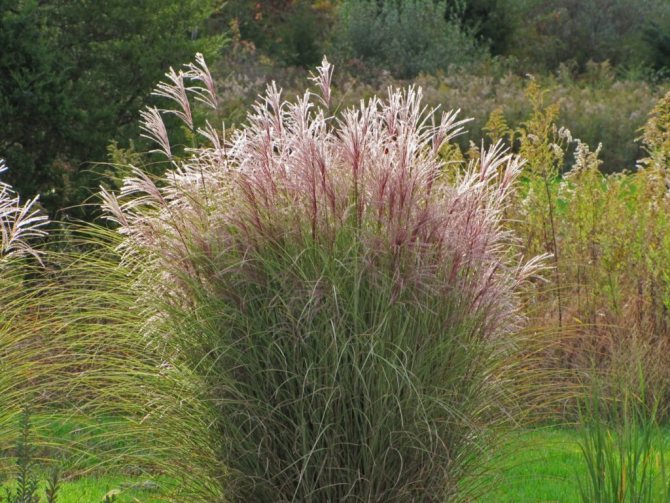
Cortaderia selloana ↑
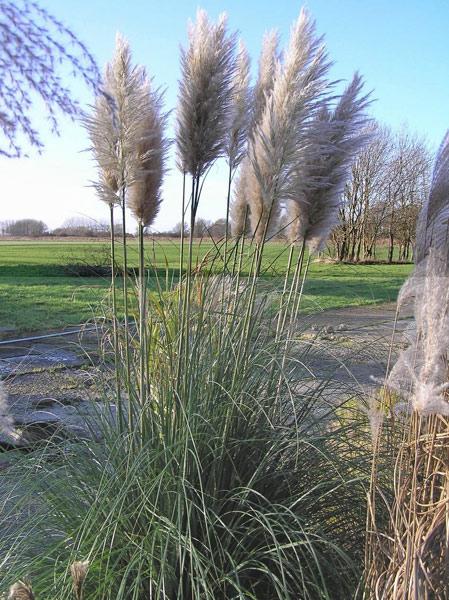


Many people grow a pampas grass in their garden - the cortaderia. It is a very large herb native to South America. It reaches up to 3 meters in height. The main advantage of this herb is its fluffy white panicles, which somehow resemble a fan. Only this herb is very fond of heat, so it is not suitable for a garden in cold regions.
Collection of herbs for your flower garden
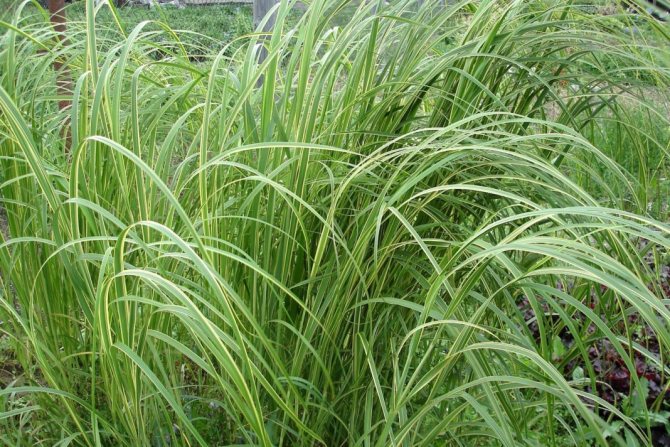
Tall and lush ornamental grasses work well for large gardens. A photo of such a flower garden will never leave indifferent any hostess. These species include spartina comb, canary reed and bearded Gerard. If you have a small flower bed or a front garden, then a large hakonechloa or a blue lightning is a good choice - these two variegated species are very beautiful, but they grow much slower than their large relatives.
A very beautiful composition can be obtained by choosing a pair for cereals, namely ornamental plants. Phlox, helenium, verbena, posconik, meadowsweet and burnet will look very beneficial in this combination. As a rule, if you are preparing an autumn flower bed, you need to take into account the color that decorative cereals will acquire by autumn. Species in harmony with yellow flowers are red-leaved and cylindrical impera, as well as copper-red rod-shaped millet.
If your flowerbed is kept in red tones, then the best option would be to shade it with viviparous sheep and blue fescue. These plants acquire a bluish color of leaves and stems, which perfectly complements the autumn crimson and gold.


Molinia
Until recently, this unpretentious decorative cereal was more often found in swamps than in personal plots, but now designers have appreciated it. A modest plant only needs minimal maintenance in the first two seasons, and then remains attractive for decades without your participation.
The easiest way to grow blue lightning, however, if you want maximum splendor and bright colors, you should pay attention to reed lightning and varieties such as Bergfreund, Fontane, Staefa.
The lightning is propagated by dividing the bush, leaving is reduced to watering during dry periods, and she will cope with weeds herself. Lightning wakes up late, so do not rush to prune old leaves in the spring.
Bluehead
For winter bouquets, flat-leaved and alpine blueheads are used. Plants look spectacular. The stem is high, strong. Leaves are carved in gray-blue color. Inflorescences are capitate blue, bordered with spiny collars. Popular varieties: Blue Jackpot, Super Boom, Blue Star, Amethyst, Slive Donard.
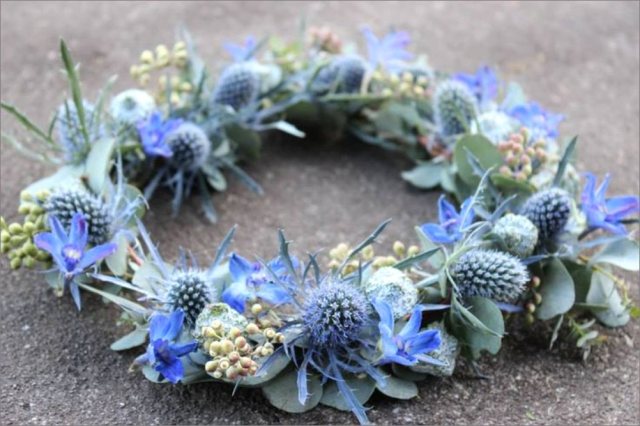


Bluehead
Gelichrizum
The birthplace of the flower is Africa and Australia. In our latitudes, an annual culture of Helichrysum bracteatum or Helichrysum bracts is grown. The most common variety is with large flowers. The basket grows up to 6 cm in diameter. The petals have multiple wrap. Thanks to this feature, Gelichrizum looks soft, velvety.
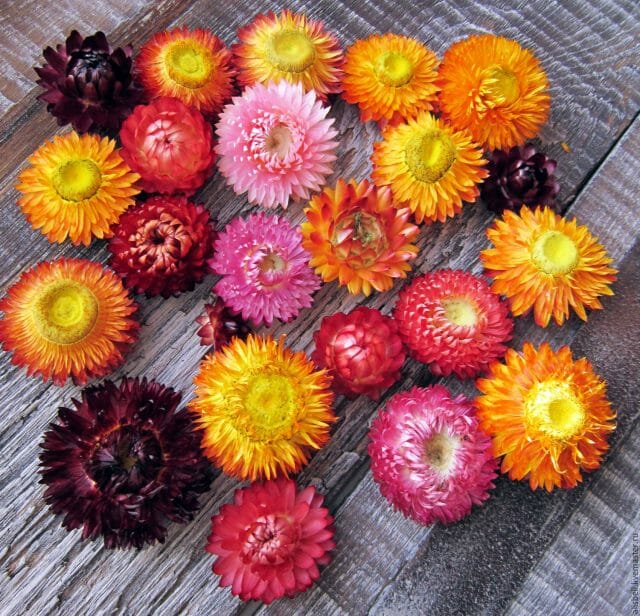


Gelichrizum
The stems are strong. They grow from 40 cm to 1 meter. Inflorescence baskets have different colors. The variety is represented by the following varieties: White, Fireball, Yellow, Lotus, Scarlet, Ogonyok. The largest is considered "King Size". It reaches a height of one meter. The undersized ones include: Hot bikini, Luteum, Moreska, Chico Red, Pink porcelain. Helichrisum helmet-shaped, daisy-shaped and Milford are also popular among gardeners.
Wild species
The importance of wild or meadow species of cereals is difficult to overestimate - they are both the basis for the breeding of new, more useful for humans, species of cultivated cereals, and food for animals.Among other things, many meadow species are widely used today for design purposes.
How to make a mini garden with your own hands at home
To understand what kinds of cereals are from wild varieties, it is necessary to consider their features that make them so tenacious and unsuitable for human food. Among these features are the following:


Wild varieties grow without human assistance. This suggests that they have the strongest adaptability to environmental conditions and they are often pests for other, weaker plants.- A characteristic feature of meadow species is their fertility and reproduction rate. This is especially well known to the owners of their own plots and summer cottages, who have to fight unkillable weeds every summer.
- People have always tried to improve the beneficial qualities of plants. It follows that the nutritional and other properties of wild varieties are much inferior to cultivated varieties. This makes them less valuable to people in this regard.
- Wild plants can contain useful qualities of a different nature - some can be used for the production of medicines or for the production of certain types of tissues and fibers.
Common wild species include timothy (a subfamily of bluegrass), wheatgrass (often used in medicine) and wild oats, named for its similarity to oats. Apart from them? often in the meadow, in the savannah, in the steppe or in the forest, you can find wheat grass, feather grass, bristle grass and hedgehog.
It is also necessary to mention those species that are called "revived", that is, they were used in antiquity, but then, with an increase in the quality of life, they fell out of use. In the XX and XXI centuries, these wild plant species found their "rebirth", once again becoming cultivated varieties.
Among them, it is worth mentioning one of the ancient types of Kamut wheat, Emmer two-grain wheat (which was used by mankind until the 18th century), as well as Polenta corn grits.
Bulbous ryegrass
Small striped bushes of bulbous ryegrass were loved by designers for their easy molding and low aggressiveness. They spread much less than most cereals, they can be given any shape, and after a couple of weeks after cutting "to zero" they turn green again.
Caring for ryegrass is simple: it is sheared three times a season, fed once a year with diluted compost and watered during dry periods. Diseases and pests do not encroach on him, and he copes with weeds himself.
Xerantemum
First appeared in the Mediterranean and southern Russia. Bears the name Xerantemum annual, strongly branches. It reaches a height of 60 centimeters. Baskets grow up to 4 cm in diameter. They can be pink, white and lilac. There are semi-double and double varieties. The most popular of them are: Violetpurpur, Carmine, Rose and Kazachok flower mix.


Xerantemum
Anafalis
Anafalis pearl is found in the middle lane. It has narrow leaves. The stems reach a height of 45 centimeters. Fully covered with down. This creates a silvery veil effect. The baskets are small, up to 8 millimeters. The silvery-white flowers are arranged in inflorescence cords. Anaphalis is spreading rapidly. Cold resistant. It continues to bloom in light frosts. The plant is perennial.
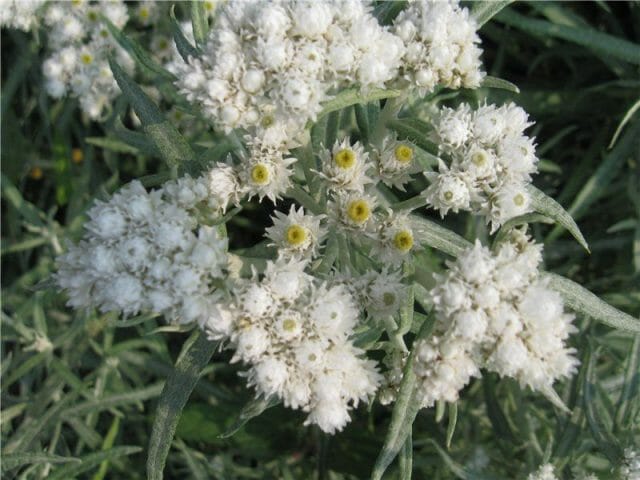


Anafalis
Veinik
Huge reed bushes can be found all over the world. Its height reaches a meter, so it is perfect for the role of a tapeworm or a vertical part in a group planting. Used in curbs and hedges. In summer, the stems and spikelets of reed grass are green, by autumn they partially turn yellow, and in winter, covered with frost, they become pearl and continue to decorate the garden.
The most popular varieties of reed grass are: Avalanche, Waldenbusch, Karl Forster, Overdam.
The reed plant is propagated by dividing the bush, in May, every 5-7 years.If this is not done, the bush will outgrow and become disproportionate. It grows well on any soil, but if you allocate a sunny and fertile area for it, it will become the pride of your garden in a couple of years.
Yarrow
To create compositions and dry bouquets, two types of yarrow are used:
- Yarrow meadowsweet. One of the largest perennials. It reaches a height of 1.2 meters. Inflorescence scutes are flat and dense. Painted golden. This gives the yarrow a dressy look. The flowering period is from July to August.
- Yarrow ptarmica. Has a popular name - pearl mussel. The perennial plant has a creeping rhizome. Shoots reach a height of 80 centimeters. Baskets are pure white. Up to 1.5 cm in diameter. Decorated in loose shields. Blooms from July to August. This yarrow variety is used for bouquets. With its help, other elements of the composition are set off, as well as create airiness and delicacy.