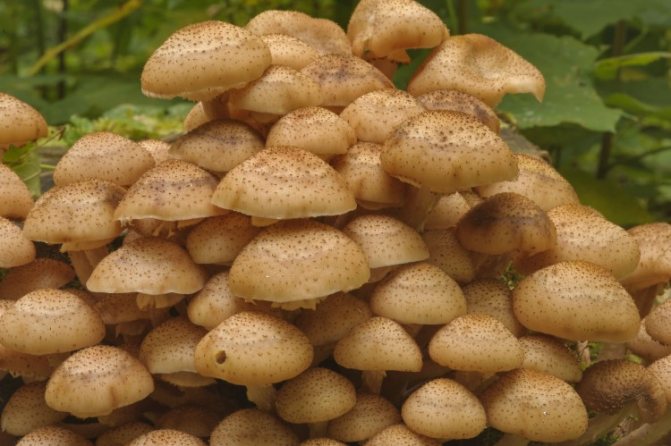
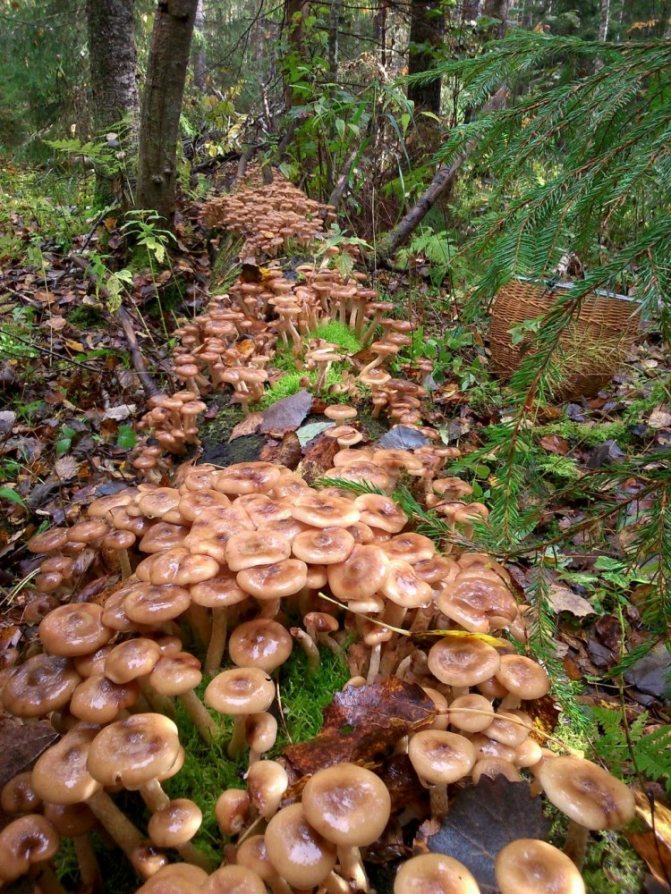
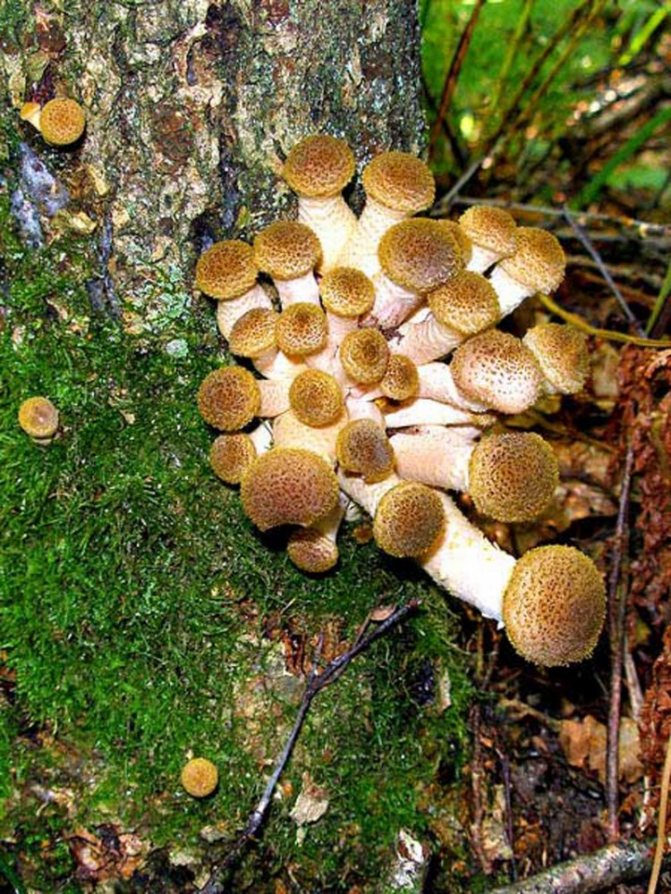
Honey mushrooms are not difficult to find in the forest, but you can also grow them yourself in a summer cottage, on a city balcony, or even just in a bank. If you choose the right conditions, then the beneficial properties of such mushrooms will be no worse than those of their forest counterparts. Of all the species of honey agarics, summer mushroom and winter mushroom have been domesticated.

There are several ways to grow.


How to grow mushrooms at home
Honey mushrooms are considered one of the most popular types of mushrooms adapted for growing at home. Their attractiveness lies not only in their excellent taste, but also in their rapid growth rates, which allow them to obtain high yields in a small area. This article will tell you how to organize your own mushroom garden.
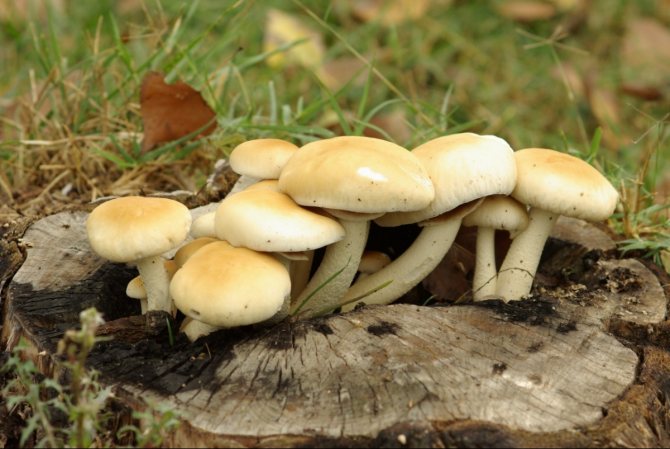
Among all types of honey agarics, winter and summer are called the most suitable for growing in artificial conditions. The first of them is appreciated not only for its good taste, but also for its medicinal properties, because this mushroom contains substances that increase the body's resistance to cancer. As you know, only a hat is taken from forest mushrooms for cooking, since the leg is too stiff. But with domestic mushrooms, both the cap and the leg are successfully used for food.
Growing conditions
Winter species can be grown both in an apartment and in a basement, as well as in a greenhouse or just in a summer cottage or in a garden. The main thing is to ensure the proper conditions under which the mycelium will grow and multiply (Figure 1):
- A constant temperature of 10 to 15 degrees above zero.
- High air humidity (70% -80%).
- Adequate lighting level.
- Heating the room in which the mushrooms are grown in the cold season and cooling it in the summer.
- Well-established ventilation.


Figure 1. Growing options at home
It is also necessary to ensure optimal phytosanitary standards so that fungi are not exposed to pests and diseases.
Growing methods
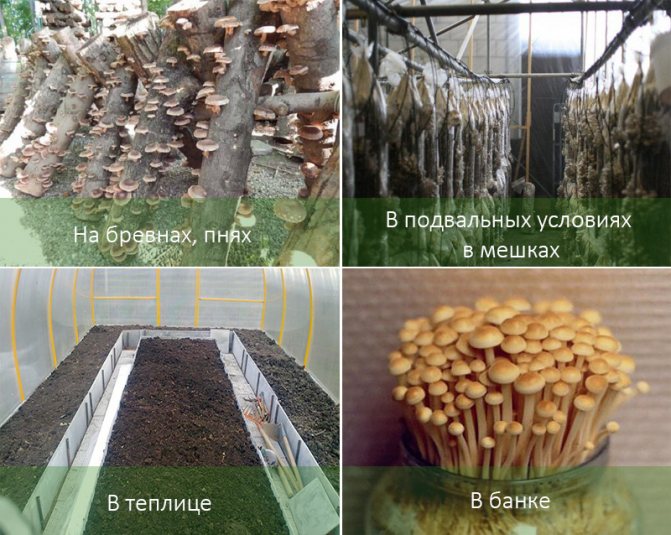
Growing honey agarics at home for beginners can be done in several ways (Figure 2):
- On stumps (felled logs);
- In banks;
- In the greenhouse.
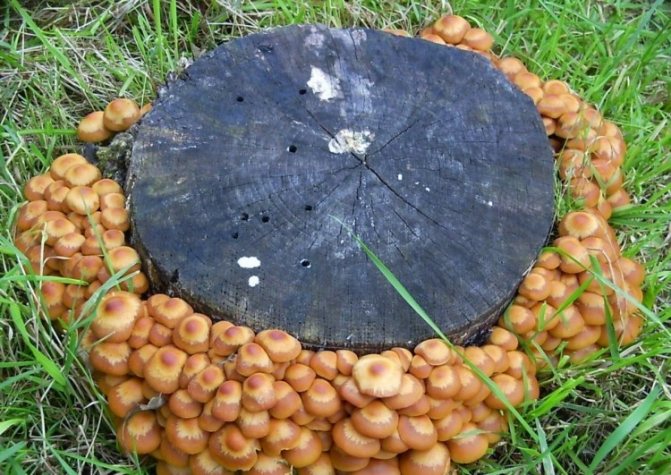
Consider the features of the technology of each of the methods. The most minimal cost is the method of growing on stumps. The essence of this method is that the mycelium of the mushrooms is introduced into small (1-2 cm) holes made in the wood, which are covered with moss.
Note: If the mycelium has been inhabited in growing stumps, then the ground around them must be watered periodically. If felled logs are used as a "container", then they must first be soaked in water for several days and only after that the mycelium should be populated.
To stimulate the growth of mycelium, the logs are placed in a basement with a constant temperature (+ 15-20 C) and covered with straw. Since mushroom cultivation requires a high level of humidity, it is recommended to wipe the floors and walls of the room where the logs are located at least once a day. As soon as they become overgrown with mycelium, they must be taken out to the site and dug in. The next year you will be able to get the first harvest of honey agarics, while the mushrooms will bear fruit until the stump (log) falls apart.
If the plot itself is not there, then there is a way of growing in banks in an apartment. The main task here is to properly prepare the nutrient substrate.
You will need small sawdust (seed husks) and the same small chips in a 2: 1 ratio. This chip-sawdust mixture must be boiled in water, then allowed to drain. After cooling, nutrients are added to the resulting gruel: starch, oatmeal and corn flour at the rate of 8 g of starch and 25 g of each of the two types of flour per 1 kg of sawdust.


Figure 2. Methods of home cultivation: in a jar, on stumps and in a greenhouse
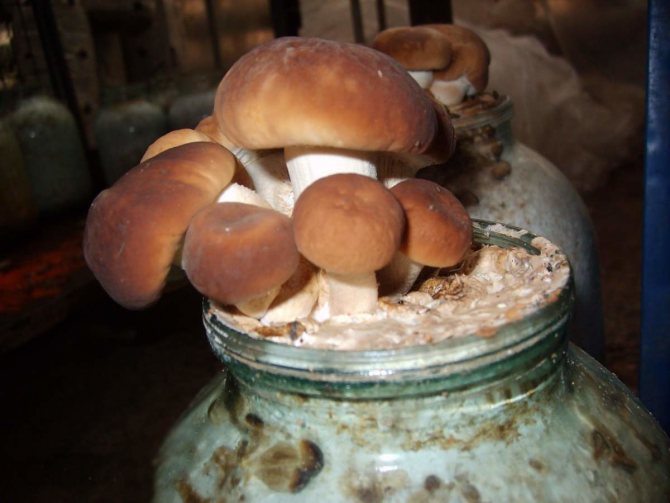
The resulting substrate is placed in jars (1-3 l) for two-thirds of the volume and compacted. Then the containers with the nutrient substrate are sterilized for 2 hours, and after it has cooled to room temperature, the mycelium is introduced into the hole 5-7 cm deep. Containers with mycelium are stored in a dark, humid room at a constant temperature of +24, and after germination of the mycelium, they are transferred to a cooler place or the temperature is reduced to + 14 + 16. For the convenience of harvesting, paper cuffs are put on the neck of the cans.
Owners of indoor facilities can use the greenhouse cultivation method. To do this, you will need special substrate blocks, which you can purchase or make yourself. Each block consists of hardwood sawdust (except oak), oats (barley) and chalk (limestone). 200 g of dry sawdust is boiled in 2 liters of water for 2 hours. After the gruel has cooled to +25, the remaining components are added: 70 g of oats (or its substitute) and 1 tsp. chalk. All components are mixed and placed in bags. Then, 20 g of mycelium is added to each such bag (block), gently kneading it.
Before tying the bag, it is necessary to put a sterile cotton plug so that the substrate inside does not dry out. The blocks are stored in a room with a constant temperature of +20 degrees. With the appearance of bumps on the surface of the substrate (this occurs within 30 days), the package is removed, and the temperature in the room is lowered to + 12 + 14 degrees. At the same time, high humidity (85%) should be maintained in the greenhouse and the room should be regularly ventilated.
Growing technology
The cultivation technology in the country and in the garden depends not only on the way they will be grown, but also on the method of obtaining raw materials for reproduction.
The most popular technologies for obtaining planting material are considered:
- The fruiting body of the fungus: for this, it is necessary to select the caps of overripe mushrooms, the reverse side of which is painted dark brown, and the diameter of the cap itself is at least 8 cm.The selected caps are kept in water for a day, then, without removing them from the aqueous medium, knead until a slurry is obtained, which filtered through several layers of gauze. Stumps (logs) are watered with the resulting talker from the spores. The wood must be pre-prepared by making small indentations on it, into which the liquid will fall. After settling the stumps, all the depressions are closed with wet sawdust or moss, and the ends of the stumps remain open.
- From the mycelium: this method is used mainly in the fall. A piece of the stump on which the mycelium grew in the forest is divided into small pieces 2x2 cm in size. These pieces of grafting wood are laid in the holes previously made on the sides of the hemp intended for cultivation. After that, the grooves are closed with sawdust or moss, and the end of the stump is covered with a dense plastic wrap, which will help maintain the desired level of moisture inside the stump. With the onset of a cold snap, hemp is additionally covered with spruce paws. In the spring, it is necessary to ensure that during the melting of snow, water does not fall on the ends of the stumps, since it can cause significant damage to the mycelium developing inside them.For this reason, it is necessary to regularly shake off the snow from the spruce branches so as not to damage the infected stump in case of a thaw. You can finally remove the branches immediately before the start of fruiting, that is, at the end of July, if we are talking about autumn mushrooms.
Remember that this type of fungus is a parasite, and therefore settles not only on dead wood, but also on living trees, shrubs and even herbaceous plants. Therefore, when growing autumn mushrooms on your site, take precautionary measures so that fungal spores do not infect fruiting crops. To do this, the stump infected with the mycelium of the fungus must be dug in a ditch 30 cm deep and 10 cm wide at a distance of 2 m.
Honey mushrooms are also well suited for growing indoors, where the required moisture level is always maintained. Therefore, the technology of growing in a greenhouse is so widely used. It involves populating half-rotted logs or stumps in bags with spore talkers. Infected logs remain in the greenhouse until the mushrooms germinate. At the same time, they must be periodically given to the sprinkling procedure. It is best to irrigate every hour from 12 to 5 pm. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. If this technology is followed, the first crop can be harvested in mid-June.
How to grow mushrooms step by step at home
Honey mushrooms are so popular among mushroom lovers that a method was invented to grow them not just at home, but in an apartment, even if it is in a multi-storey building. You will be able to harvest home-grown honey agarics after only a month and a half from the moment the mycelium is introduced into the substrate. At the same time, in one can, with a capacity of 3 liters, you can grow up to one and a half kilograms of mushrooms. The only drawback of this method is that only winter mushrooms can be grown in this way, the size of which is ideal for breeding on the windowsill (Figure 3).
So, how to grow mushrooms in the country or in an apartment, step-by-step instructions will tell you:
- Prepare a nutrient medium from bran and hardwood sawdust in a 1: 3 ratio.
- Soak the resulting mixture for a day in water, then squeeze and put in three-liter jars, filling them half the volume.
- Use a thin, long stick to make depressions in the substrate that reach the bottom.
- Sterilize the substrate jars over low heat for an hour. After the cans have cooled, repeat the procedure again. This procedure will kill all pathogens inside the containers and prevent mold from developing.
- After the second boil, let the jars cool to room temperature, then close them with plastic lids with holes up to 2 mm in diameter.
- Introduce the mycelium through the holes made using a medical syringe.
- Banks populated with mycelium must be kept in a room with a constant ambient temperature (not lower than +20) for about 30 days.
- As soon as the mushrooms sprout, you need to move the jar to a cooler place. This can be, for example, a window sill located on the north side, or a balcony, provided that the air temperature there does not drop below +13.
- After the mushrooms reach the neck of the jar, the lid is removed, and a paper cuff is put on the neck of the vessel, which will limit the place where the mushrooms grow.
- Spray the mushroom caps periodically to maintain optimal moisture levels.
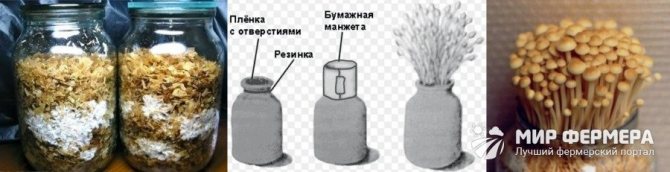

Figure 3. Features of growing honey agaric in a bank
Observing the above rules, you will be able to harvest the first harvest of winter agarics 2 weeks after germination. Mushrooms can be cut, or you can simply pull out, because in a few weeks a new wave of honey agarics will appear.
The video shows how to properly sow mycelium honey agaric when growing mushrooms in a jar.
Growing difficulties
The main difficulty in growing honey agaric is that their spores spread quickly and can settle on only rotten stumps, but also on healthy wood.
To prevent this from happening, you need to very carefully approach the procedure for sowing mycelium and cultivate mushrooms only in specially designated areas. In addition, honey mushrooms are very sensitive to temperature and humidity conditions, therefore, at all stages of growing, certain indicators must be maintained.
In the greenhouse
Greenhouses are a wonderful place for growing honey agarics. Stumps can be laid out in them. They are moistened, holes are drilled into which the mycelium is laid out.


In the absence of mycelium, the wood is watered with a talker from the fruiting body of the mushrooms. Banks, logs and substrate blocks can replace tree stumps.




How to store mushrooms - norms, rules, optimal conditions how to properly grow, process and store mushrooms (100 photos)

Home mycelium - growing mushrooms with your own hands. A step-by-step description of the technology for beginners (135 photos and videos)


Honey mushrooms at home - especially the cultivation and maintenance of mushrooms. 115 photos and videos of honey agaric cultivation technologies
How to grow mushrooms in the country
To grow winter mushrooms in the country, you will need a greenhouse or any basement room in which you can provide a constant high level of humidity. In addition, you will need to purchase a special nutrient substrate for growing mushrooms or prepare it yourself, as well as stock up on granular mycelium of mushrooms.
We will describe in more detail the features of growing at a summer cottage.
Features of the
It is easy to prepare a mixture for growing mushrooms on your own using dry sawdust (200 g), oats (70 g) and slaked lime (1 tsp). All of these components are mixed, then soaked for 5 minutes, then boiled for another 45 minutes. After that, the water must be drained, and the resulting mixture must be dried for 20 minutes over low heat.
The finished substrate is cooled to a temperature of +25 degrees, then laid out in prepared containers (jars, bags). 20 g of mycelium are poured into the same containers, the containers are hermetically sealed, after inserting a plug of sterile cotton wool. In this state, the substrate with mycelium is stored at a temperature of + 15 + 20 degrees for a month. After germination of the mycelium, the bags are transferred to the material where fruiting will take place.
Choosing a place and method of growing
You can grow geographically cultural mushrooms:
- in the apartment;
- on open air;
- in a greenhouse;
- in the basement.
To determine the method, you first need to choose the variety that is most suitable for the existing or created growing conditions. Of the numerous subfamilies of these mushrooms in an artificial environment, two types bear fruit best:
- summer mushroom;
- winter mushroom.
Winter mushrooms are the most productive, since they require a minimum area for growth. They can be cultivated in any way, without special financial costs. For the summer, you will need a specially equipped room in which suitable climatic conditions are created, or the territory of a garden, equipped with stumps.
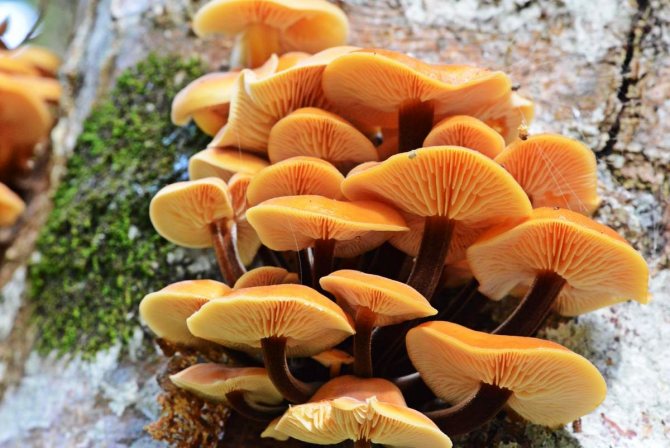
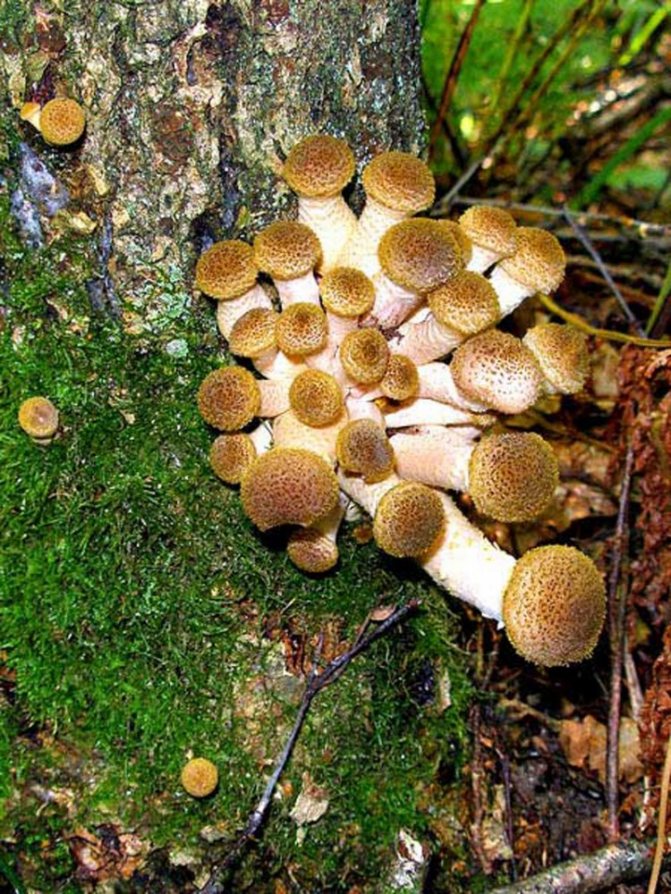
Winter mushroom (aka flammulina) is most suitable for cultivating at home. In nature, it is late. It differs from the summer one by a velvety leg and a light sandy cap, the diameter of which can reach 8 cm. The cap has a smooth skin. The pulp is light yellow.


In contrast to forest wild "congeners", the cultural honey agaric has a soft and delicate structure not only of the cap, but also of the legs.
If there is not enough lighting, for example, when growing at home, the color of the mushrooms can be very light, almost white, but this will not affect the taste and useful qualities of the product.
Breeding methods.
- On stumps.
- In the greenhouse.
- In glass jars.
- In bags.
How to grow honey mushrooms in the country from mycelium
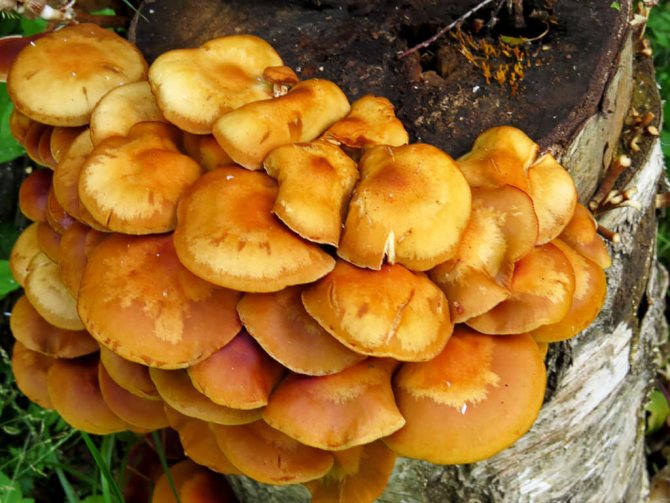
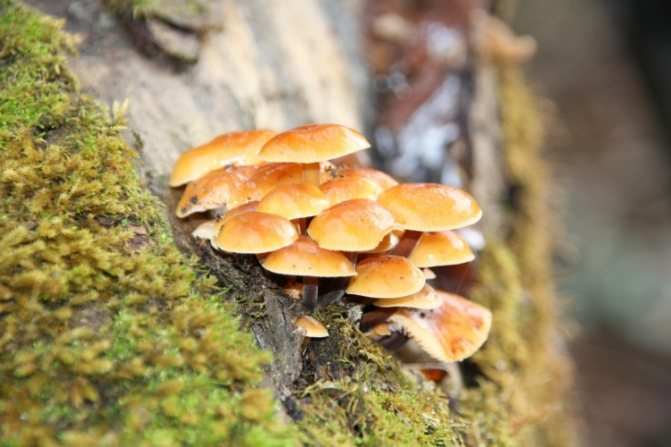
Summer mushrooms can be grown from mycelium at their summer cottage. The optimal substrate for growing them will be old stumps of deciduous trees such as maple, birch, aspen or damp boards, or trimming logs (Figure 4). Moreover, they are much easier to grow than mushrooms or oyster mushrooms.
Features of the
It is important to know that when growing honey agaric on stumps that are on the territory of the garden plot, there is a risk of infection with the mycelium of fruit trees, which leads to the destruction of their wood and, as a result, to the death of the tree itself.
Therefore, try to choose those stumps that are far from living plants, or grow mushrooms in closed ground.
The ways
In early May, when the optimum level of humidity and temperature is observed, it is necessary to irrigate the surface of the stump with sowing mycelium. It is recommended to pre-make small indentations in the hemp to better fill it with mycelium. After populating the holes, they must be sealed with moss. Experienced mushroom pickers also practice breeding summer honeydew by grafting small pieces of wood infected with mycelium. They are inserted into pre-prepared holes on the surface of the hemp.


Figure 4. Preparation of mycelium for growing honey agarics
Whichever way the mycelium is colonized in the stump, they must be covered with a dense film in order to create an optimal microclimate for the rapid development of the mycelium. One such mycelium allows you to harvest honey agarics for 3-6 years, while the first time you can remove the mushrooms in a year after the introduction of the spores.
You can also infect with fungal spores from trimming logs or even damp boards. For this, the spores of the fungus are added to a bottle of water, shaken thoroughly and poured over the material for growing with this solution. It is desirable that there are more gaps on the material in which the mycelium of the fungus can settle. Subsequent care consists in regular irrigation of the wood to maintain the required moisture level.
Hemp and fungi
Breeding on stumps is chosen by mushroom growers who do not have special rooms or large areas.


Not all hemp are suitable for this business, but only those that have dense wood. It is best to choose spruce or birch. Summer honey agaric grows well on deciduous trees, winter - on conifers.
The stump should be "fresh", not spoiled by bark beetles, with intact bark and core, not rotten, not infected with rot.
Growing up from spores


The stump must be moistened first. It will be good if it will stand for several days in the pouring rain. If rain is not expected, a long-term artificial shower will have to be arranged. You can water the stump from a watering can or dip it into a container of water. The main thing is that it is completely moistened to the core, darkens and moisture is released from a piece of wood extracted from the central part.
Planting can be carried out all summer - from early May to late August. Sowing is done by the fruiting body of the mushroom (cap), which can be bought in the store or obtained from the forest.
When collecting in the forest, it is advisable to take not only the mushroom itself, but also the stump surrounding the wood infected with mycelium, on which honey agarics grow. Choose hats that are mature, but not wormy. They should be darkened below.
Pieces of 20 hats, with a diameter of at least 10 cm, must be lowered into a bucket filled with filtered water. Bottled water, frozen and thawed water, well water, or rainwater can be used. From the water supply - not suitable, since it contains heavy metals and chlorine. Mushroom caps should be infused in a bucket for a day.
Then the fruiting body is kneaded with hands in water in order to obtain a mushy consistency as a result. The more thoroughly you grind the caps, the more spores will get into the water. Everything is mixed, filtered and passed through a sieve or cheesecloth.
A solution contaminated with spores is abundantly watered on moistened stumps, having previously made shallow incisions on their vertical surfaces with a sharp knife (about 10-12 pieces per stump in random order). The solution will take about a liter for each stump. After replanting the spores, the depressions are covered with wet sawdust, and the upper part of the stump remains open.
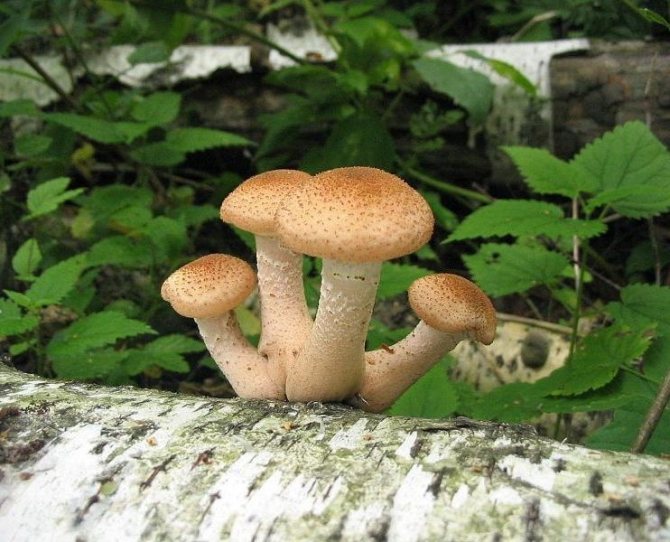


This method is one of the simple, but long-term - the first harvest can be obtained only the next year, or even one and a half. But then, within five years, the hemp will regularly and abundantly bear fruit. Then the stump will naturally begin to collapse, the mycelium will transfer to the ground and the roots of the nearest tree, if there is one nearby. You can spread other wood around, such as saw cuts or logs.
Growing from mycelium
The second way to grow mushrooms on stumps is sowing from mycelium. Unlike the spore method, the harvest can be obtained much faster, within 8-10 months.


The mycelium (mycelium) is collected in the forest. Most of all it accumulates on rotten old stumps covered with honey agarics. It is a filamentous cream-colored substance.- Collect the mycelium together with the pieces of wood and plant the pieces of about 2 cm² in the prepared grooves on the side surface of the stump.
- The stump also needs to be well moistened, and the crops should be covered with sawdust or moss.
- After sowing, the stump is covered with a film material, and with the onset of winter, it is insulated with spruce branches.
- Fruiting will begin in June.
In early June, you need to remove the shelter if summer mushrooms are grown. For winter, the spruce forest is removed at the end of the first summer month.
Important note. If you grow mushrooms on the site, it is necessary to limit their distribution area, since honey mushrooms are parasitic fungi and can infect fruit trees and grow over a large area. To limit the mushroom zone, a trench is dug around the circumference at a distance of two meters from the stump, where the spores or mycelium are planted. The depth of the ditch is 30 cm, the width is 10-12 cm.
Growing honey agarics at home on stumps
In your own garden or in your summer cottage, you can grow mushrooms on the stumps of deciduous trees: birch, poplar, aspen, apple, pear. The main thing is that the stump chosen for breeding is not affected by rot or tinder fungi. 2-3 days before the introduction of the mycelium, it is necessary to periodically moisten the stumps with water.
You can use both purchased mycelium and self-collected forest material. To do this, you need 10-12 mushroom caps, which must be poured with a bucket of rain (river, lake) water and kept like that for a day.
Note: It is important to know that water from stagnant bodies of water (pond, quarry, ravine) is not suitable for these purposes, since it can be contaminated with pathogens.
The present hats are kneaded with hands into a gruel, which is filtered through several layers of gauze. The end and side parts of the selected and prepared stump are poured with the resulting spore solution. To increase the likelihood of stump infestation with mycelium, it is recommended to make small holes with a diameter of 2 cm in the wood at a distance of 4 cm from each other. It will be much more convenient if the holes made are staggered. These recesses are additionally filled with spore gruel and covered with moss or sawdust. In this case, the end of the hemp is left open. Growing mushrooms in this way, you can get the first harvest of honey agarics in 2 years (Figure 5).
It is necessary to know that the mycelium of the fungus can infect other healthy trees in the immediate vicinity of an infested tree stump. Therefore, you need to take protective measures by digging in the infected stump with a ditch 30 cm deep and 10-15 cm wide at a distance of 2 m around it.


Figure 5. Features of growing honey agaric on stumps
The cultivation of honey agarics can also be carried out using wood sticks infected with mycelium, which are inserted into the prepared holes on the stumps. This procedure is carried out in April-May, when the sun is already active enough and can dry out the mycelium. Therefore, it is recommended to cover the inhabited stump with a layer of straw or dry grass. For the winter, the stump must be covered with spruce branches. In snowy weather, regularly shake off the snow accumulated on the branches, and with the arrival of spring, make sure that melt water does not fall on the end of the stump, since this greatly inhibits the development of mycelium, which means that you will receive a harvest much later.
The technology of self-obtaining mycelium


Considering how to grow mushrooms at home, it is worth dwelling in more detail on the methods of obtaining mycelium. It's easier to buy it, but if you want, you can get it yourself.
From the pulp of the mushroom
To obtain mycelium, old overripe mushrooms of a dark brown color are used, even wormy ones can be used. Only large caps with a diameter of about 8 cm are needed, since the mycelium forms between the membranes. The prepared raw materials are soaked in water. After a day, the whole mass is kneaded well with your hands to a state of gruel and filtered through cheesecloth. All mycelium will drain along with the liquid. Now you need to populate it immediately. Stumps or logs work best. The wood is drilled or grooved with a hacksaw. The liquid is poured onto the logs. The honey agaric mycelium will settle inside the grooves, which must be immediately closed with moss.
In the video, how to grow mushrooms in the country from independently collected mycelium:
From the growing mycelium
This method is better called how to grow mushrooms yourself, and it is more suitable for summer residents or villagers. The bottom line is that reproduction occurs by the mycelium from the growing mycelium. For planting material, you will have to go to the forest or any planting where there are old rotten trees. Having found a stump with growing mushrooms, they try to carefully separate a piece of wood. At home, the find is sawn into small cubes about 2 cm in size. Stumps or logs are prepared on the site, holes of a suitable diameter are drilled. Now it remains to place cubes with mycelium inside the nests, cover with moss.
In late autumn, the stumps are covered for the winter with straw, pine branches. In the spring, they try to clear the snow as much as possible. A large amount of melt water can wash out the mycelium of honey agarics. The autumn shelter is harvested from mid-June to obtain a summer harvest of honey agarics. To pick mushrooms in autumn, straw and branches are harvested at the end of July.
In the video, growing mushrooms on stumps:
Important! Artificial cultivation of honey agarics allows you to get only summer and winter crops. The second option is suitable for owners of small summer cottages, since mushrooms can be grown outdoors. To get a summer harvest, you need large, damp cellars with good ventilation.
Beginners are especially interested in the question of how long it takes honey mushrooms to grow from their own collected mycelium. If the technology is followed, after germination, the mushrooms are cut off after two weeks. Honey mushrooms can even be simply pulled out with your hands. The mushroom store will not suffer from this.
Another important question is how long it takes to grow mushrooms after harvesting the first wave of the harvest. Mushrooms grow quickly. If the dampness and temperature are maintained, a new crop will appear in 2-3 weeks.
Attention! When grown on the street, it is impossible to say exactly how much cut honey agaric grows. It all depends on the air temperature. If the humidity can be maintained artificially, then cold nights will not work. To accelerate growth, a greenhouse can be pulled over the mycelium.
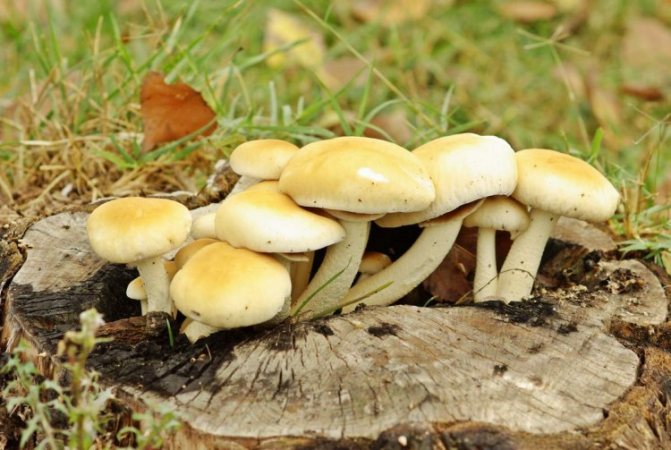
Winter honey agaric: growing at home
Among the edible species of honey agarics, it is easiest to grow winter mushrooms at home (Figure 6). Their small size allows them to be bred even in a three-liter jar on the windowsill. Various materials are used as a growing substrate: straw, buckwheat husks, sunflower husks, dry sawdust of deciduous trees.To give the substrate the necessary fertility, various additives are mixed into it, for example, bran, brewer's grains, corn cobs.
Then this nutrient medium is kept in water for 24 hours and squeezed out. Glass jars are filled with the prepared substrate to half their volume and closed with lids with holes made with a diameter of 2 cm. For these purposes, you can also use cotton-gauze plugs. The sealed cans are pasteurized for one and a half to two hours on low heat several times, after waiting for the cans to cool.


Figure 6. Methods of growing winter mushrooms at home
After the last pasteurization, when the jars with the substrate have cooled to +24 degrees, they begin to plant the mushrooms. To do this, with clean hands, pre-mashed pieces of mycelium planting material are placed in each jar. Closed jars are stored in a room with a temperature of + 20 + 24 degrees until the mycelium sprouts. After germination of mushrooms, the jar is placed in a cooler place: on the windowsill, loggias, facing north. When the mushroom caps reach the neck of the jar, it is necessary to put on it a paper cuff 5-10 cm high so that the mushrooms grow upward in the form of a bouquet. At this stage, it is very important to ensure high air humidity, therefore, it is necessary to spray the mushroom caps with water and moisten the cuffs. After the mushrooms have completely emerged from the jar, they must be cut off, and the jar must be closed again and taken out to a warm place. In a week or two, the second batch of mushrooms will ripen.
Basement, package, sawdust
For growing in a basement, garage, hangar, cellar - any cool closed room, the most suitable method of planting in bags filled with sawdust mixture.
- To fill one two-liter bag, you will need 200 g of dry sawdust. You can take pine and all deciduous ones, you should not only use oak.
- Fillers such as barley, barley oats, buckwheat or sunflower husks should be 30% of the substrate. A teaspoon of chalk is also added to the mixture.
- Everything is dry mixed and soaked in water for an hour.
- Then, in the same water, the substrate must be sterilized for ¾ hour by boiling.
- After draining the excess water, spread the mixture on a baking sheet and dry in the oven for about 20 minutes (low heat).
- Then the substrate, which should remain moist, is cooled and packaged in two-liter thick plastic bags.
- The mycelium, which must first be divided into small fragments with clean hands, is poured into a bag on the surface of the sawdust, about 20 g each.
- The mycelium is covered with cotton wool, the bag is tied.
All this economy is transferred to the basement or cellar. The temperature must be between + 12 ° C and + 20 ° C. You don't need to touch the packages for a month. Then, bumps should form on the surface, in places where the fruiting bodies of future mushrooms are formed.
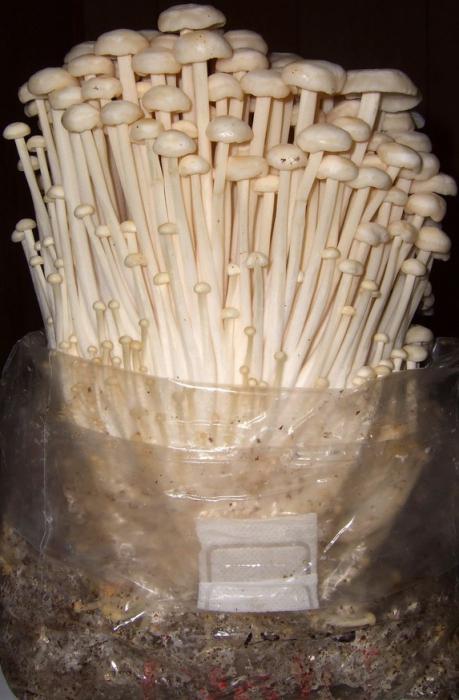


At this time, the packages are untied, the cotton wool is removed. The mushrooms will grow in the direction from which the air stream comes. Additional lighting will be needed to keep the legs short.
If you make holes in the bag in those places where the fruit bodies have formed, honey mushrooms will grow from there, but the bag will resemble a hedgehog, whose needles stick out in all directions, so it will be inconvenient to collect them.
Growing honey agarics at home or in the country is an interesting and rewarding activity. These mushrooms do not require complex care steps and special conditions. They grow on their own, actively and abundantly bear fruit, and the quality and taste are not inferior, even surpass the taste of forest mushrooms. Many mushrooms can be grown at home. Champignons, oyster mushrooms, chanterelles, even white ones. But honey mushrooms are the most productive of forest species in artificial cultivation.
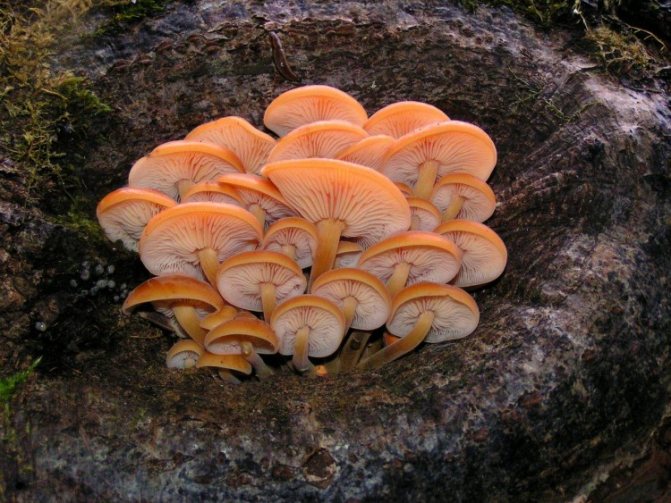
Poplar honey mushroom: growing
Poplar honey is highly prized for its pleasant nutty flavor and crunchy texture along with porcini mushroom and truffle.The main disadvantage of this mushroom is its short shelf life: raw poplar mushrooms are stored for about 20 hours, and frozen - no more than 6 days. For this reason, they cannot be purchased in the retail network. But poplar honey fungus can be easily grown at home, just in a flower pot (Figure 7).
First of all, you need a wet poplar or maple log from a healthy tree, free of branches. The height of the log should be about 30 cm, and its diameter should be 15 cm. It is necessary to make (drill) 2-3 holes with a diameter corresponding to the diameter of the sticks with mycelium. With clean hands, sticks with mycelium are inserted into the holes made, then they are sealed with wax, and the log is tightly wrapped in polyethylene, making several holes for ventilation. This kind of "container" with mycelium is stored in a dark and humid room until the mycelium sprouts (3-4 months). This can be determined by the white mycelium threads clearly visible in the holes. After that, the logs are placed vertically in flower pots, measuring 70x15x15 cm, filled with earth (mulch, poplar sawdust). In this case, the logs should be deepened into the pot by 8-10 cm. Thus, you can get 2-3 harvests of mushrooms per year, and the mycelium will grow within 5-6 years.


Figure 7. Features of growing poplar mushrooms at home
You can also grow poplar mushrooms in your own garden or in your vegetable garden. A piece of loose fertile land near trees is ideal. In the spring, in this area, they dig a recess of 10-12 cm, on the bottom of which corrugated cardboard is laid, then a centimeter layer of sawdust. All this must be spilled with water, and when it is absorbed, the mycelium is placed on the substrate on the sawdust. The mycelium is covered with a layer of sawdust mulch or wood chips and watered again. Level the edge of the recess to the general level of the site using a slightly mulched soil layer. So that the substrate in the hole does not dry out, it must be additionally covered with straw or tree bark and watered abundantly again. Subsequent care consists in maintaining the soil moisture level by watering it when it dries up to a depth of 3-4 cm.
During the fruiting of poplar mushrooms, it is recommended to collect mature mushrooms every day so that the mycelium does not get sick, and in the cold season, take care of additional shelter for it.
On the logs
This method is suitable both at home and in the country. A block of up to 0.5 meters is cut from a larch log. A dry log should be soaked for 2-3 days.
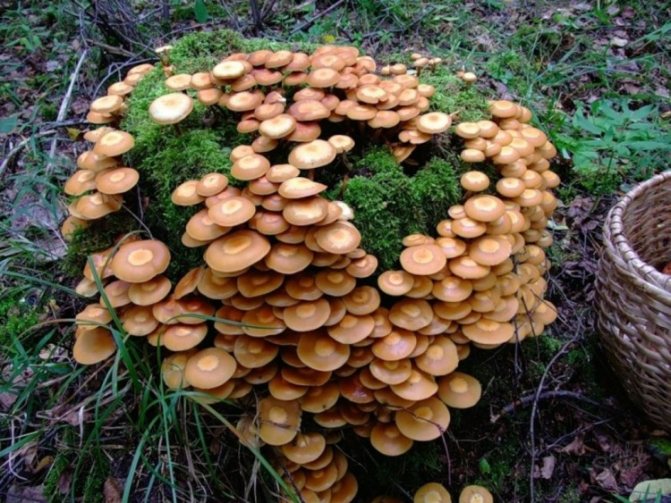


With a 10 mm drill, holes are made in the logs to a depth of 4 cm. The mycelium is inserted into them, then the logs are wrapped in a film, in which holes are made for the flow of air.
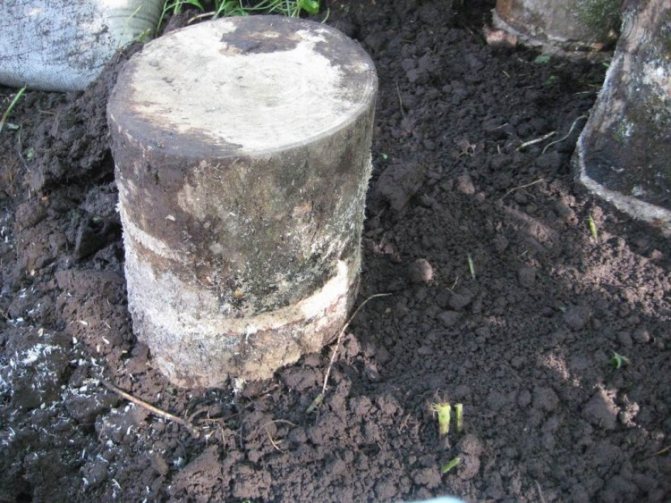


At the dacha, in a shady place, they dig a hole on the floor of a shovel bayonet and water it well. They put logs with mycelium in it. The landing site is sprinkled with ash to scare away slugs and snails. Further care consists in regular watering. In autumn, cover the log with fallen leaves.
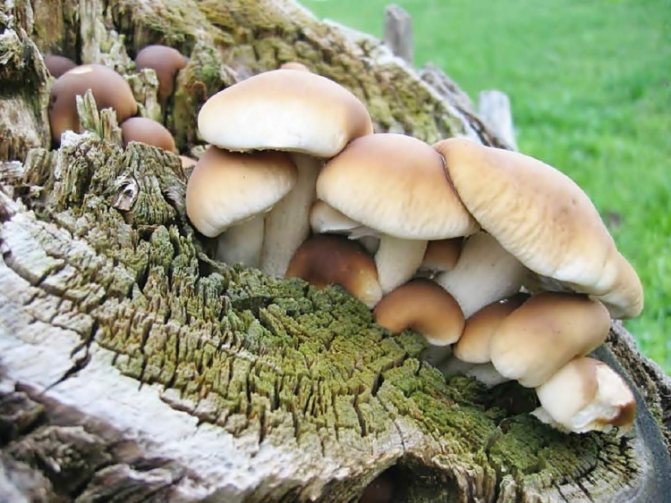


A log with mycelium can be placed on a loggia or balcony by placing it in a barrel with earth. Mushrooms will grow together if the soil is kept moist, and the temperature will be from +10 to + 25C.
Marble honey mushroom: growing at home
Marble honey fungus belongs to delicious mushrooms. When cooked, it has a sweet smell, a pleasant nutty flavor, and a slightly crunchy texture. In its raw form, this type of mushroom is stored in a cold place for up to 10 days.
Note: The difference between marble honey agarics and all the others is the fact that this species cannot be soaked in water, because, gaining moisture, they become brittle. In addition, marble honeydew contains a large amount of nutrients, with a complete absence of fat, which makes it possible to use dishes from it in diets aimed at weight loss, to stabilize metabolism. A positive effect is known in the treatment of anemia, asthma, diabetes, organs of the cardiovascular system and many other diseases using marble honey agarics.
For the cultivation of marble honey agarics, a substrate consisting of cotton waste (85%), rice or wheat bran (10%), sugar and gypsum powder (1% each), lime (3%) is used.Cotton waste is filled with water with lime dissolved in it. The resulting mixture is wrapped in a film for a day, then rice bran and gypsum are added to it, the acidity level is checked (it should be 6.5 - 7.5 pH).
The compost is placed in plastic bags or jars with a wide mouth, hermetically sealed and sterilized for 3 hours. The mycelium is populated into a sterile substrate, the bags are transferred to a storage room, in which the air temperature is + 18 + 26 degrees. After 40 days, the mycelium sprouts and ripens for another 30 days. Bags with ripe mycelium are placed on special racks in a cool room (+ 13 + 15). They must be opened, the substrate must be moistened, the bags must be covered with damp paper or cloth. After the appearance of mushroom caps, the damp cloth must be removed, further maintaining the necessary humidity by spraying air at the same temperature. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure the proper level of lighting in the room. If mushrooms are grown without the sun, they must be illuminated with a fluorescent lamp for 10-15 hours.
For harvesting, you need to gently cut off the bunches of mushrooms while pressing on the substrate around the root with your other hand. For the next mushroom wave, it is necessary to clean the substrate from the legs of dead mushrooms and add water to it. A new crop will appear in 2 weeks. In total, one such bag (package) gives 4-5 harvests of marble honey agarics.
Required conditions for breeding
The very name of the mushroom "mushroom" speaks of a suitable habitat - stumps, large branches, logs. It belongs to the category of parasitic fungi that attack wood and gradually destroy it. Under natural conditions, honey mushrooms are found not only on living and dead trees, but also near some shrub plants, as well as in meadows and forest edges. They grow in large groups, the fruiting period begins in the fall and lasts until the onset of frost.
In artificial conditions, it is not enough just to place stumps sown with mycelium and wait for rich harvests. A number of basic rules must be followed:
- to organize a place for growing mushrooms with a free area of 15–20 sq. m;
- achieve high air humidity (70–80%);
- maintain the temperature within 10-15 degrees in the winter season and 20-25 in the summer;
- provide uniform illumination and protection from direct sunlight;
- eliminate air stagnation by arranging a high-quality ventilation system (due to carbon dioxide, the mycelium will not be able to fully develop).
At a stable temperature and high humidity, mushrooms will be able to quickly adapt to new conditions and begin to grow.









































