Category: Houseplants
From a tropical plant, the orchid gradually became indoor or indoor. Representatives of the Orchid family decorate offices, shopping centers and our homes. In many apartments, whole orchid plantations feel great. And the owners of these mini-greenhouses are easy to understand: when you receive or buy your first orchid as a gift, you immediately understand that you are hooked. After all, they are so beautiful! Each variety is completely original. They differ in shape, color, size. And every time it seems that a new orchid is more beautiful than those that already exist. Until you see the next one ...
Aging of orchid leaves is a natural process
Each leaf has its own life cycle, at the end of which the color of the plate changes to yellow and it dies off. As a rule, this happens with the lower layer of leaves. If the rest of the plant is in order, there is no point in worrying: this is an absolutely natural process.

Figure 1. Natural yellowing of leaves
It is important to consider that age-related yellowing depends on the variety. So, in varieties Phalaenopsis, Cattleya and Pafiopedilum, the color of the lower tiers changes, and in dendrobiums, the color of the upper leaves may also change. In addition, there are cases that after flowering is complete, the entire plant completely sheds its foliage.
Plant age
Most orchids do not flower until the second or third year after planting, although by this time the plant already has several fully formed leaves. The natural aging process affects only a few leaves, while the culture itself retains a completely attractive appearance.
If the yellowing is due precisely to the age of the plant, no special action is necessary: the leaf will gradually dry completely and separate on its own. But there are other factors that can trigger yellowing. Most of them are associated with improper crop care, therefore, in order to maintain the health of the plant, it is necessary to accurately determine what caused the pathology and revise the rules for caring for the flower.
Photo
You will see a photo of black and other dots on the flower:
Violation of irrigation regime
One of the most common causes of yellowing of leaves is considered to be a violation of the irrigation regime, and the pathology can be caused by both excessive and insufficient moisture.
Since orchids live in the tropics, they are very sensitive to moisture, so the irrigation regime should be clear and fully consistent with the characteristics of the plant. Consider what happens to flowers with excessive and insufficient moisture.
Excessive moisture
To give the flower enough moisture, it is recommended to put the plant pot in a larger container filled with water. In this case, the pot should be submerged in water by about a third. However, it is not recommended to leave the plant in water for a long time, since in this case the soil moisture will be increased.
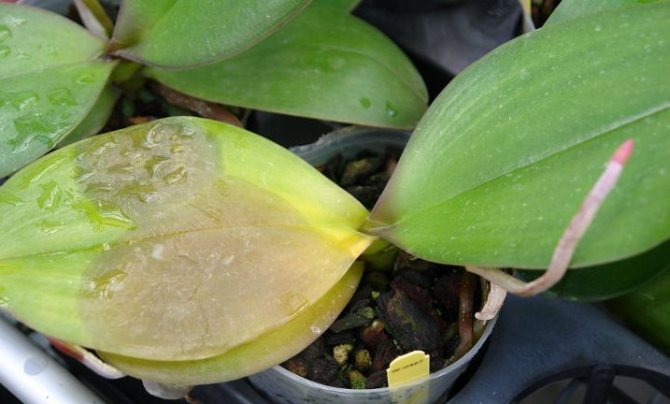
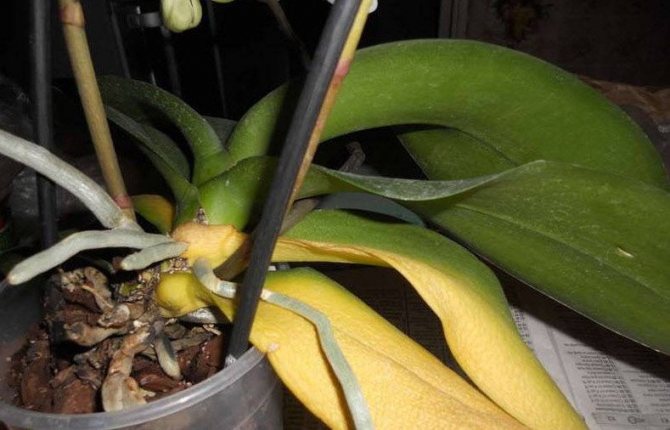
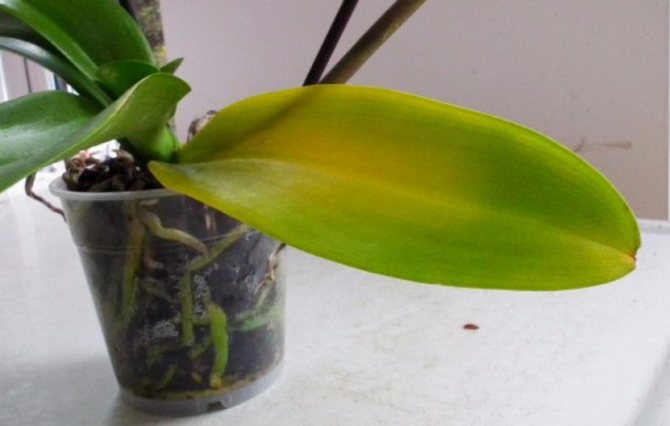
When over-watering, the following happens: the soil is so saturated with moisture, and sufficient oxygen does not flow to the roots.As a result, the root system simply cannot supply the aboveground parts of the plant with useful substances and the leaves of the flower begin to turn yellow (Figure 2).


Figure 2. Signs of excess moisture
In addition, it should be borne in mind that in a humid environment, fungi and bacteria often begin to develop, provoking various diseases, which can also change the appearance of the flower.
Insufficient watering
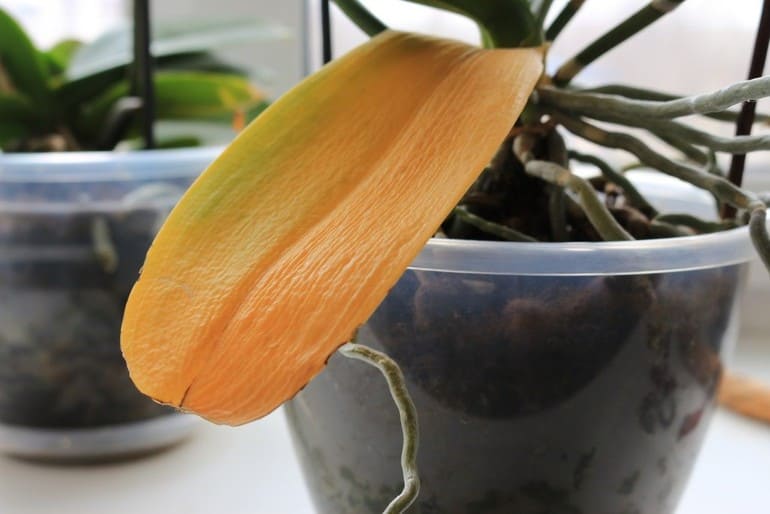
Not only an excess, but also a lack of moisture can provoke yellowing of the leaves in an orchid (Figure 3).
Note: If the flower does not have enough moisture, its leaves become lethargic, gradually wrinkle and dry out.
Moreover, this process is much less common than a change in the color of a plant due to excessive watering, and to eliminate it, it is enough to add enough moisture to the soil. But before the procedure, you need to check whether the plant really does not have enough water. If your crop has an opaque pot, simply remove a few pieces of bark to gauge the moisture content of the soil inside. You can also pierce the ground with a wooden stick: if it becomes wet, then your flower does not need additional watering, and the reason for the yellowing of the leaves is an excess of moisture.


Figure 3. Symptoms of lack of moisture
It is easier to assess the degree of soil moisture in a transparent pot: it is enough to assess the color of the roots. They should be light green and pearlescent. Over time, you will learn to determine the need for watering simply by the weight of the pot: if it is light, then the soil inside is dry.
Features of care and cultivation of phalaenopsis
Felonopsis cannot be called a capricious plant, but it must be borne in mind that its homeland is Southeast Asia and the northern regions of Australia. Accordingly, the flower needs certain conditions of detention, as close as possible to the natural conditions of these geographical regions.


Proper watering... Felonopsis refers to epiphytes, which means that the flower develops on other plants, and this plant is not a donor, all the moisture and nutrients of the epiphytes are obtained from the air through photosynthesis.
Important! The orchid suffers greatly from excessive soil moisture. It is much more difficult to save a flower, the state of which is undermined by severe waterlogging, than to bring it back to its normal state, slightly dried out from lack of moisture.
There are several ways to properly water your orchid:
- Strait. The substrate is watered near the sides of the pot, the water flows through large-diameter drainage holes into the pan. The method is used mainly after planting a flower in a new place.
- Immersion... The flower pot is lowered into a basin of water for 20-30 minutes, during which time the water will saturate the substrate well, from where the root system pulls it out. The method is used for healthy strong orchids that grow in a moisture-absorbing substrate.
- Watering in a closed container. Apply to flowers that are grown in containers without drainage holes. Water is poured into a pot to the level of the root collar. After half an hour, the liquid is drained. During this time, the substrate absorbs enough moisture for the normal life of the plant.
Absolutely any plant needs watering, without exception. However, even such a vital procedure can harm the orchid.


In order to prevent this from happening, when moistening phalaenopsis, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- do not water the orchid leaves, as this leads to wilting and loss of brightness of the flowers;
- water of low temperature or with a high level of hardness can cause the appearance of yellowness on the foliage, lead to necrosis of the roots;
- when moisturizing by immersion, each flower must be individually treated with clean water, otherwise, when water is reused, a healthy plant can be infected from a sick plant.
Important! For watering phalaenopsis, it is necessary to use settled water, mixed with distilled water in a 1: 1 ratio, with a temperature of + 30 ... + 35 ° С.
Lighting... Another important factor that should be given special attention. Lighting is one of the prerequisites for the normal course of the photosynthesis process. Experts say that sufficient daylight hours stimulate orchid flowering, while lack of light leads to the growth of green mass.
For normal development and flowering, the plant needs a sufficient amount of light, if not solar (which is quite problematic in our latitudes), then artificial. Moreover, it should be borne in mind that the flower grows in natural conditions, mainly in the shade, which he needs to create at home.


It is best to place the plant on a windowsill located on the south or east side. A north-facing window is the least viable option, although using phytolamps, you can create good conditions in such a situation.
Important! On average, phalaenopsis should be in daylight for 12
–
15 hours daily. For varietal orchids, sick, recovering from illness, as well as young plants, the recommended duration of daylight hours is 17
–
19 hours.
Temperature. The significance of the temperature regime for normal photosynthesis is no less than the level of illumination. For orchids growing in their natural environment, the optimum temperature is in the range of + 18 ... + 30 ° C. The same temperature regime is required for varietal species that could hardly grow normally at + 18 ... + 20 ° С, in a room with artificial heating and a lack of lighting for 4–6 months (typical Russian winter). But hybrids perceive such conditions quite normally, they are well adapted to them.
It is best to provide the flower with an average daily temperature of + 21 ... + 25 ° C and sufficient lighting. If you create the specified conditions, the rest of the care will be expressed only in watering and fertilizing.
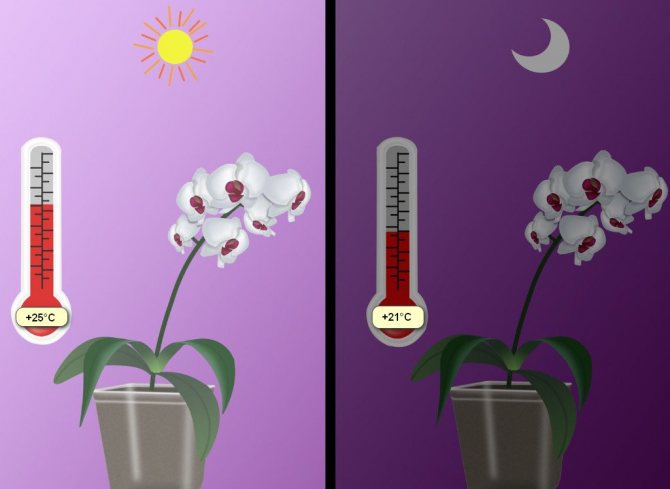

Regular temperature drop within 3-5 degrees stimulates the flowering process. However, when creating such conditions, it must be remembered that the temperature should not be allowed to drop by more than 5 degrees. Otherwise, the likelihood of developing fungal diseases is high.
Air humidity... Orchids require high humidity (75-100%) during normal periods of their life cycle and moderate (50-65%) during dormant periods. It is quite simple to provide such humidity in the warm season, much more problems with this indicator arise during the heating season, this is especially true for plants located on the windowsill, under which there are heating radiators.
Did you know? Phalaenopsis was first discovered at the end of the 17th century by the German traveler G. Rumph on Ambon Island, part of the Moluccan Archipelago. In 1752, the Swede P. Osbek on one of the islands of the same archipelago found another flower, which he sent to the founder of the modern classification of plants, Karl Linnaeus, who described Epidendrum amabile in his work "Plant Species".
It is best to purchase an electric humidifier to solve the problem, however, such expenses are not always acceptable for novice florists. Water containers placed around the plant will help, although not so effectively. The most suitable for these purposes are containers with a wide diameter that do not have a neck (bowls, shallow pots, plastic containers).
Top dressing. For normal growth, development and flowering of phalaenopsis, it must be regularly fed.


When applying fertilizers, you should follow some simple rules:
- fertilizers are applied only when the plant is absolutely healthy, it has strong roots and greens;
- during the flowering period, it is undesirable to fertilize phalaenopsis, since top dressing stimulates metabolic processes, respectively, the orchid will bloom faster;
- during active growth, fertilizers are applied every week, unless some special schedule is indicated in the instructions for the product, and at rest it is enough to feed phalaenopsis twice a month;
- transplanted orchids should not be fed for 1 month;
- observe the correct dosage and concentration of fertilizer solutions.
We advise you to read in more detail about the features of feeding the Phalaenopsis orchid.
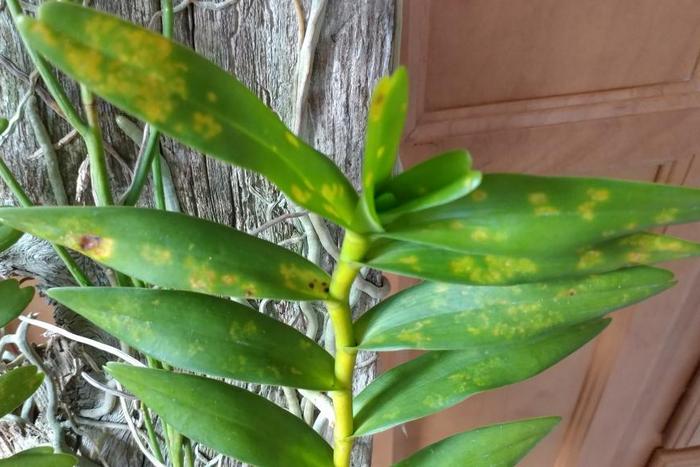
Flower lighting problems
An equally common cause of yellowing is improper lighting, or rather sunburn. If your flower is on the south or west window, then the plants can get sunburn during the summer.
With this pathology, not the entire leaf turns yellow, but only that part of it that has been in the sun for a long time. To fix the problem, you just need to rearrange the flower to another place. There is no need to remove the damaged parts of the plant: they will either recover or dry out on their own, and then it will be possible to carry out sanitary pruning of the flower.
How to care for a plant that has undergone this procedure?


An orchid in a stressful state requires increased attention., and also - care and maintenance. But you shouldn't be too zealous: a capricious flower may “not understand” overprotection. In order for the period of flower recovery to be successful, after transplanting, the plant must create an atmosphere of rest so that it can recover after the stress experienced: the orchid is placed in a shaded room, without transferring from place to place, watered moderately according to a certain scheme.
Fertilizer problems
Despite the fact that there are special feedings for orchids, they should be used carefully, and when choosing a fertilizer, focus on the crop variety, since each type of flower has its own preparations.
It should also be borne in mind that all fertilizing must be used carefully and in strict accordance with dosages, since an excess, as well as a lack of fertilizers, can change the appearance of the plant.
Lack of feeding
Leaves and can turn yellow if the plant lacks potassium or iron. With a lack of these elements, the aboveground parts of the culture lose their natural color.
But before you buy and apply fertilizers, you should make sure that the problem really lies in the lack of nutrients. The fact is that yellowness can be caused not only by a lack of nutrients, but also by their excess.
Supersaturation with minerals
It is not worth feeding the plant too often. To do this, it is enough to apply special fertilizers only during the period of active growth and flowering of the crop, and the frequency of fertilizing should not exceed once every three weeks.
You can determine that a culture has useful substances by the appearance of the leaves: if their tips began to turn yellow, it means that the soil contains too much potassium. It should also be borne in mind that in flower shops orchids are deliberately intensively fertilized to build up green mass. At home, when the feeding regime stabilizes, the leaves may begin to turn yellow or even fall off. It is also possible that you yourself accidentally exceeded the dosage of fertilizers. In this case, you need to remove the culture from the pot and thoroughly rinse the root system under running water for 3-5 minutes. The procedure must be repeated every week, as a substitute for watering.
Relapse prevention
To avoid such unpleasant situations is possible only with proper care of the orchid.


Maintaining a comfortable temperature in summer: + 22-25 ° C, in winter + 16-18 ° C. The difference in temperature differences should not exceed 5 ° C.- Lighting is required diffused, with a daylight hours of 14 hours.
- Choose a pot that matches the size of the flower.
- Humidity in the range of 50-60%.Be sure to regularly ventilate the room.
- Renew the substrate every 2-3 years.
- Water once a week, in between, the soil should dry out completely.
- The water temperature should be 35-40 ° C.
- Spray 5 times a day. Exclude the procedure during the flowering period.
The reasons for the deterioration of the appearance of an exotic flower, as you can see, are varied. Or perhaps a combination of factors is to blame. Therefore, follow the rules for caring for orchids, because deviations can lead to serious trouble. It is better to anticipate negative consequences than to eliminate them later.
Inappropriate pot size
The reason for the yellowing of the leaves can be quite simple: your flower may just be cramped in the pot. This requirement is especially true for flowers that were just purchased from a store. Their pots often do not match the size of the root system, and the plant requires a mandatory transplant.


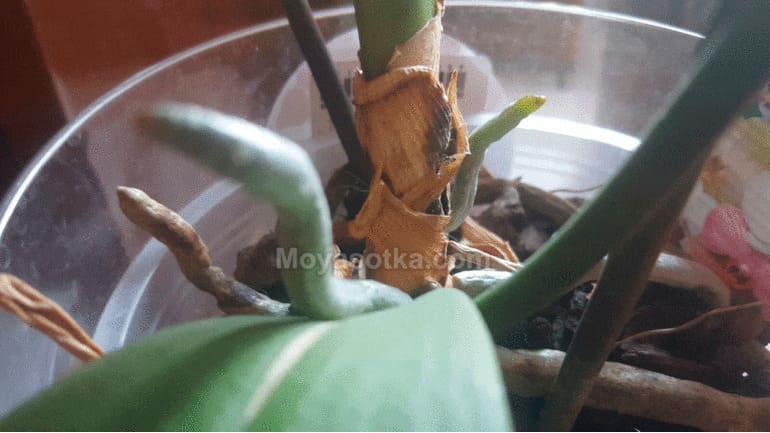
Figure 4. Examples of improperly selected pots
You can determine that your orchid needs to be transplanted into a larger pot not only by the color of the aboveground parts, but also by the roots, which will begin to protrude strongly from the container and dry in the open air (Figure 4).
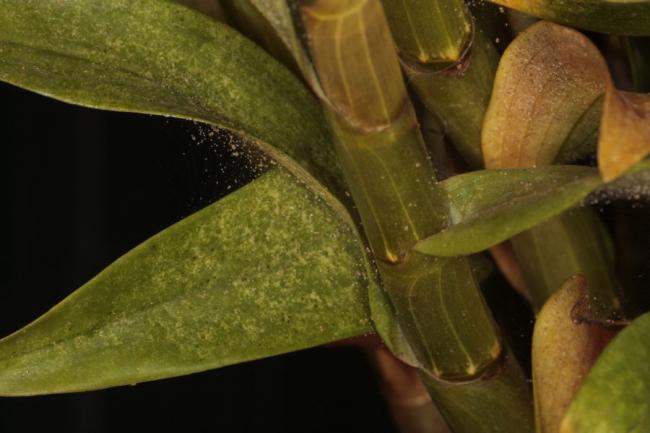
Types of pigmentation
Pigmentation can be distinguished by several types of characteristics:
- the size (there may be absolutely inconspicuous specks, which in large numbers at a distant distance seem to be one large spot, and sometimes very large blotches appear);
- color (all shades of yellow, brown, dark and black are found);
- the form (most often these are round spots, however, the edges are not always even; there are even, convex or, conversely, concave).
Major pests
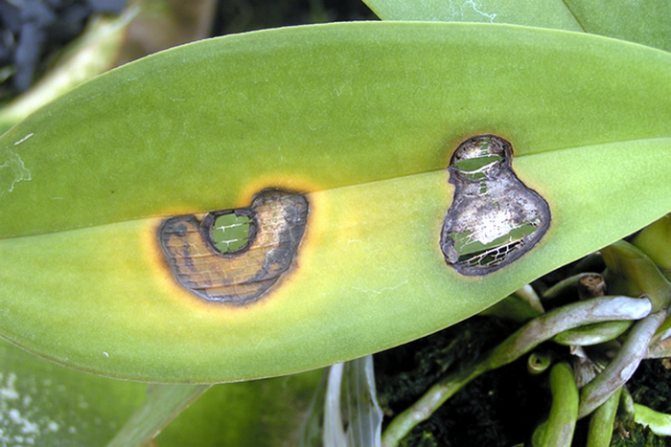
The green aboveground parts of the plant are very delicate, so they often become a tasty morsel for a variety of pests, which can also cause yellow leaves (Figure 5).
Among the common pests of indoor orchids are:
- Spider mite feeds on plant sap, and the stems of the leaves are covered with small dots (bite sites) and cobwebs. A sick flower must be immediately isolated from the rest so that the pests do not spread, and all the leaves of the affected specimen are thoroughly washed with a solution of laundry soap.
- Aphid not only changes the color of the leaf plate, but also causes the appearance of a sticky plaque on its surface. To eliminate aphids, you need to wash the orchid with soapy water and spray with Fitoverm.
- Shield - an insect that is difficult to eliminate, since its body is covered with a dense shield. It is easy to find a pest: when a scabbard is damaged, characteristic growths appear on the surface of the plant. To combat the pest, you can use folk remedies, such as ammonia or a mixture of water with vegetable oil, but it is better to use special preparations for this purpose, for example, Actellik.


Figure 5. The main pests of the flower (from left to right): spider mites, aphids and scale insects
Preventive measures
In order to minimize the risk of yellowness on the leaves of your phalaenopsis (as well as other diseases), you must follow some preventive measures:
- Water the plant properly... For a healthy flower, the immersion method is most acceptable. Use the “right” water to moisturize. Try not to overmoisten the flower, because the plant tolerates moisture deficit more easily than excess moisture.
- Do not water the leaves of the flower, do not use cold water... When humidifying, do not immerse different plants in one container, this can lead to massive diseases.
- Try to maintain the necessary air humidity, use any available means to moisturize. With a high dry air, it is sometimes possible to spray the plant from a spray bottle using the finest spray bottle.
- Only fertilize the plant if it is completely healthy.... During flowering, top dressing is not recommended. Observe the dosage when applying fertilizer. Feed according to your schedule. Orchids need timely fertilization not only for beautiful flowering, but also to create conditions close to their natural environment.
- You cannot transplant during flowering, and after flowering you need to cut the peduncle... This is done with a clean, disinfected instrument, after which the trimming site is processed. Do not forget to water the phalaenonopsis immediately after transplanting.
- Keep young plants separate from those that have been with you for a long time.


Orchid diseases
Orchid diseases are considered a common cause of yellow leaves, and at home, the culture is mainly affected by fungi. In this case, the leaves of the plant are covered with yellow spots.
To cope with the problem, you need to carefully remove the affected parts, and spray the culture itself with any fungicide. But even after such treatment, certain measures should be taken so that the fungus does not return. First of all, you need to inspect the flower for pests and revise the watering schedule, since an excess of moisture is a common cause of fungal diseases.
From the video you will learn even more useful information about the causes of yellowing of leaves in orchids and how to deal with this problem.
How to save if they lose turgor, turn yellow and fall off?
If the orchid leaves not only began to turn yellow, but also to fall off, then the plant urgently needs to be reanimated:


Analyze the conditions for keeping the flower and identify possible causes of the problem.- Change the mode and methods of watering.
- Move the flower pot to another location.
- If the orchid is next to yucca, peperomia, cordilina or ararcaria, then it is necessary to remove them away.
- Replace soil and pot. Be sure to disinfect a new pot with a potassium permanganate solution before planting.
- Do not use fertilizers and growth stimulants for at least 14 days.
- If fungal or bacterial diseases have been found on the orchid, then it must be treated with fungicides.
Important! Use only soft water for irrigation.
Tightness
The problem may be related to the fact that the pet has long outgrown its "apartment" and needs a transplant. In an overgrown plant, the roots are compressed and severely deformed, therefore they cannot provide the delivery of nutrients to the leaves, which is why they suffer. The solution is an emergency transplant into a container that is 2-3 cm larger than the previous one. Too large a pot is not needed - with an abundance of substrate, water begins to linger, and the roots rot.
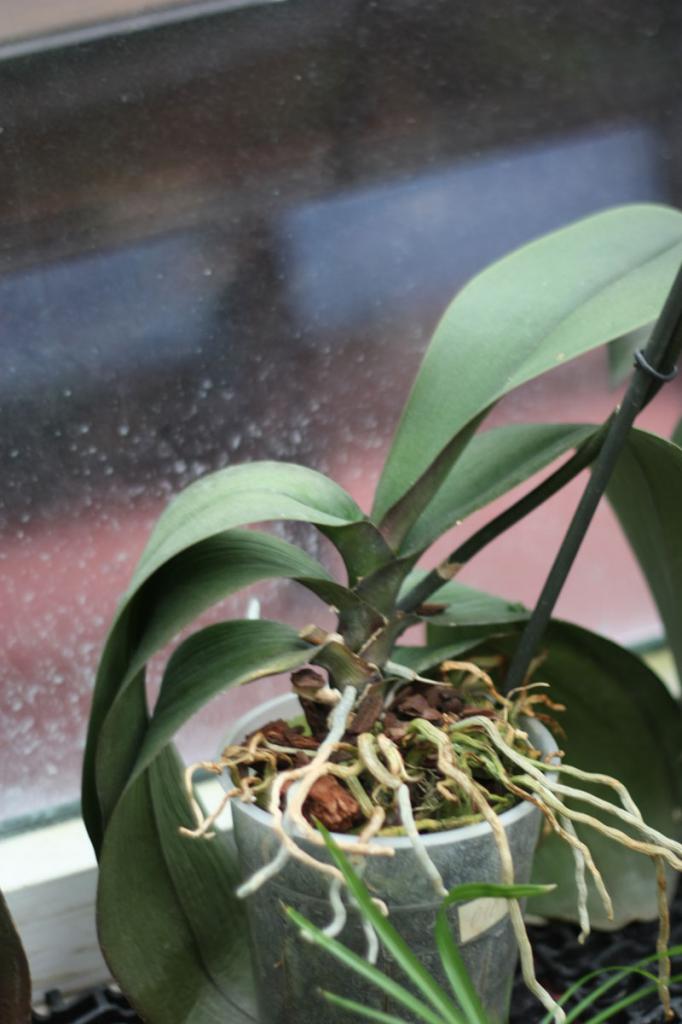


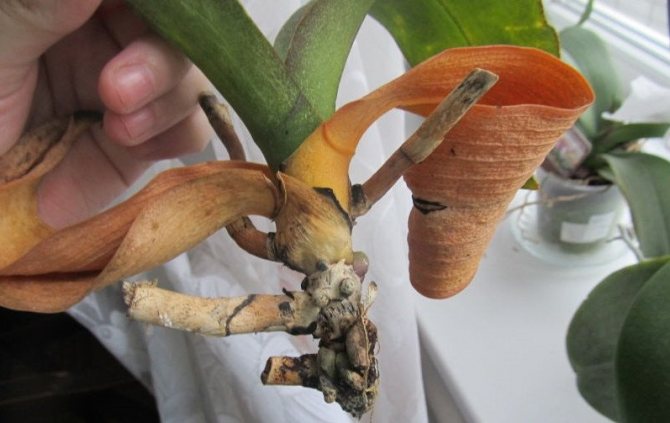
Root decay problem: signs and what to do?
Excessive moisture during watering can lead to root rot... A depleted and compacted substrate may be the cause. The roots cannot work at full strength. They pull moisture from the leaves. So they dry up.
Transparent containers allow you to verify the condition of the roots. Pay attention to their color. Act urgently. If the fears were confirmed:
- Remove the orchid from the pot;
- Free the roots from the old soil;
- Remove all damaged roots;
- Treat the cuts with brilliant green (crushed coal);
- Plant the plant in a new medium.
Falling foliage
Why do the leaves of an orchid turn yellow and fall off? Most often, this indicates an overabundance of fertilizers. Wanting to please the capricious beauty, flower growers unreasonably increase the amount of fertilizers applied and the number of dressings. An excess of mineral complexes with nitrogen-containing components has a particularly negative effect.
This is because the plant, driven by stimulants and nutrients, tries to quickly shed old leaves and grow new ones. The solution to the problem is to reduce the amount and amount of dressings.
Diagnosis of lesion
Orchid disease is determined by a change in the color of the leaves and the condition of the flower. Correct and timely diagnosis of the disease will help you choose the right treatment method, which means there will be a chance to save your favorite plant.
Table: external signs of orchid diseases
| Symptoms | Care errors | Disease | Pest |
|
| Brown bacterial spot | Phytopathogenic bacteria |
|
| Fusarium rot | Mushrooms of the genus Fusarium |
|
| Anthracnose | Colletotrichum orbiculare mushroom |
|
| Black rot | Aspergillus Niger mushroom |
| greenhouse effect: high temperature (over 25 ° C) and high air humidity | Powdery mildew | Powdery mushrooms (Erysiphales) |
|
| Gray rot | Mushroom Botrytis |
| weakened immunity or an excess of nitrogen fertilizers | — | Shield |
|
| — | Spider mite |
| the virus enters through gardening equipment or from another infected plant | Viral disease | Viruses ORSV, CYMMV, CACV, etc. |
| red spots with brown specks form on the lower part of the leaves |
| Rust | Rust fungus |
| dry air | — | Thrips |
| dry air | — | Mealybug |
| high air humidity | Root rot | Rhizoctonia, Pythium and Phytophthora mushrooms |
Brief information
Indoor orchids belong to a large family of plants called Orchidaceae. In their natural environment, they live mainly in tropical forests with a hot climate, high humidity and lingering downpours. Almost all decorative orchids in our country are derived from the phalaenopsis orchid, which prefers to settle on trees and rocks. In a temperate climate, representatives of this family are not so common, for example, in Russia there are just over 400 species. However, breeders have developed a huge variety of hybrid ornamental varieties that can be grown in a greenhouse or at home. But even for them, you need to try to create conditions as close to natural as possible.
Why do orchid leaves turn yellow? The leaves of any plant are an indicator of health. And if such an alarming sign has appeared, then you need to look for the reason.
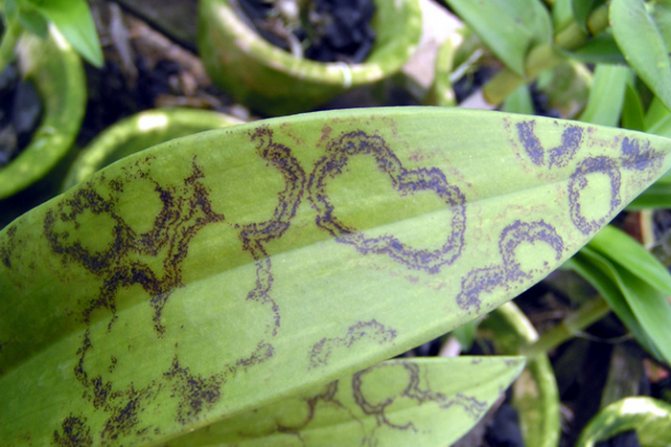
Which inclusions are dangerous and which are not?
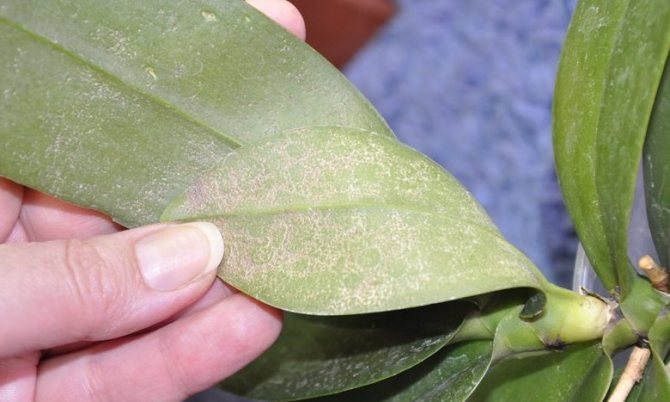
It is very difficult to say exactly what is dangerous for the plant. However, more often than not, if the blotches are hardly noticeable (small size or the color of pigmentation is not very different from the phalaenopsis site), this suggests that they are most likely not a cause for concern.
Reference! It is important to watch for such spots constantly, because they can develop into something more serious. The main thing is to notice the changes in time and take measures to eliminate them.
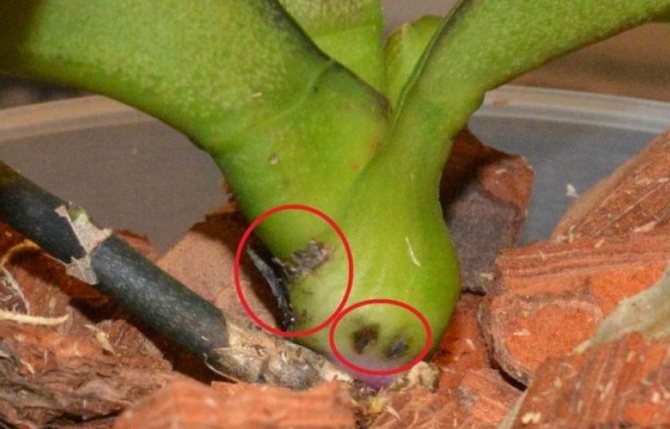
Bacterial spot
There are other reasons why orchid leaves turn yellow.Do the leaves turn yellow sharply and unevenly, and then lose their elasticity and wrinkle? Most likely, bacterial spotting is to blame. It can also be recognized by the characteristic wounds on the surface of the leaf, from which fluid is released. In this case, the orchid must be quarantined and treated: cut off the affected areas, and treat the cut sites with an antiseptic, for example, iodine. If new stains appear after pruning, you should use one of the special anti-bacterial stains.
The flower cannot be moved to healthy pets until it is precisely known that the disease will not return.


Useful Tips
Orchids can have yellow leaves for many reasons. But with a caring grower, this phenomenon can be observed much less often. In order for an exotic flower to feel good, several recommendations must be followed:
- Use a quality substrate.
- Keep the flower on a consecrated windowsill, but not in direct sunlight.
- Normalize the watering regime in accordance with the seasonality and phases of growth and rest.
- Keep the orchid only in special pots - transparent, with vertical slots and holes on the walls and bottom.
- Top dressing regularly.
- Transplant on time.
- Spray the plant regularly with warm water.
When to sound the alarm if orchid leaves turn yellow? The reasons for this problem can be different, and they all pose a danger (except for the natural process of withering away of the lower layer of greenery). Therefore, you should always pay attention to alarms and respond to them in a timely manner. And then the exotic beauty will delight with her flowers for a long time.



























