The biologist advised mushroom places in the Moscow region: the map is attached
- Everyone posts huge baskets of whites, honey mushrooms, mushrooms on social networks ... Are there really anomalously many mushrooms this year?
- Not that there were more of them than usual, but they all got out at the same time and at an unusual time for them.
- And what's the reason? Is the notorious global warming to blame again?
- Yes, now we don't have to talk about the weather norm - every year is abnormal. Therefore, it is impossible to compare the year with the year, all the time there is an interesting situation of its own.
- This summer there was an unprecedented amount of precipitation, plus the temperature is below normal, but don't mushrooms need warmth?
- Moisture and heat are needed for the growth of the grass, and for the mushrooms, a cold snap is required, and the more powerful it is, the more mushrooms there will be. But, of course, within reasonable limits, if snow falls and frosts hit, nothing good will come of it. Several years ago we already had a summer with snow, but then there were few mushrooms. And now a very interesting phenomenon is happening. Two powerful waves of mushrooms met. The first one got a push because of the cold snap, which happened 2-3 weeks ago - in early July. Last week there was a second wave of temperature decrease, respectively, a new wave of mushrooms will soon follow, it will merge with the first in a week or two. And then we will get completely mushroom July and another half of August. This is really a very rare phenomenon, its uniqueness is that this year mushrooms of all seasons grow almost simultaneously. In the forests there is an abundance of both summer and autumn mushrooms. They went much ahead of time. From autumn - mushrooms, talkers, even winter mushrooms come across, which usually does not appear until October.
How long will this mushroom abundance last?
- A very correct question. After such a rapid growth, myceliums will retire for a long time. Therefore, most likely, there will be no mushrooms at all in the fall.
- That is, you can not go to the forest in September?
- I think that it is not worth waiting for new mushrooms before the second half of October - early November.
- Snow is promised next week - does this mean that new mushrooms may not appear?
- The maximum fruiting occurs three weeks after the cold snap, and, as I said, it began a week ago, so the second wave of mushrooms will begin next week.
- Where would you advise to pick mushrooms?
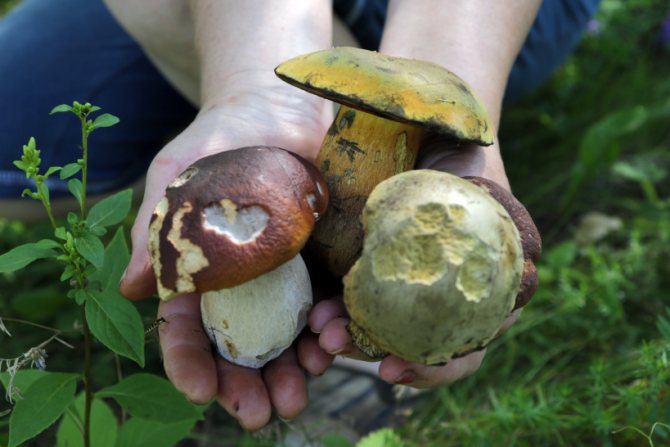
- Now the situation is wonderful - everything is growing everywhere. Collect even in the city, even in the field, even in the forest. Everywhere there are a lot of mushrooms: forest, field, forest, urban, marsh. A huge harvest of whites, butter, autumn mushrooms are everywhere and there are even a lot of mushrooms, oddly enough.
- What's so surprising about that?
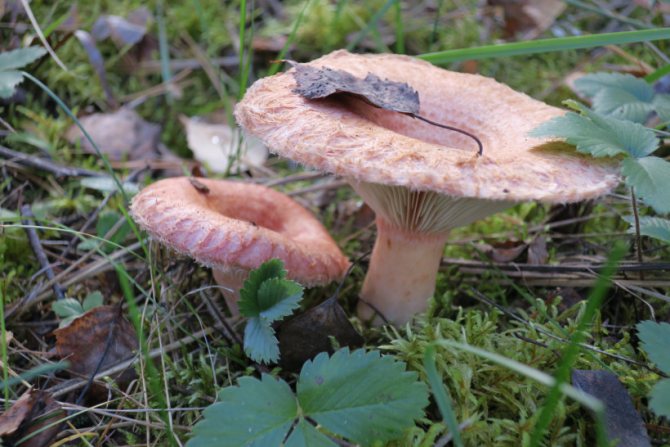
- Ryzhiks are very sensitive to the purity of the air, they do not like trampling, so you rarely meet them in the Moscow region. But this year, apparently, ideal conditions have developed for them. Because of the heavy rains, the air cleared up, and the mushrooms began to climb. There are also many mushrooms and umbrellas in the forests and fields. And fly agarics are collected in large quantities.

photo: Ivan Skripalev
- I used to think that whites love dry meadows, but this year the forests are oversaturated with moisture, nevertheless there are a lot of whites - how can this be explained?
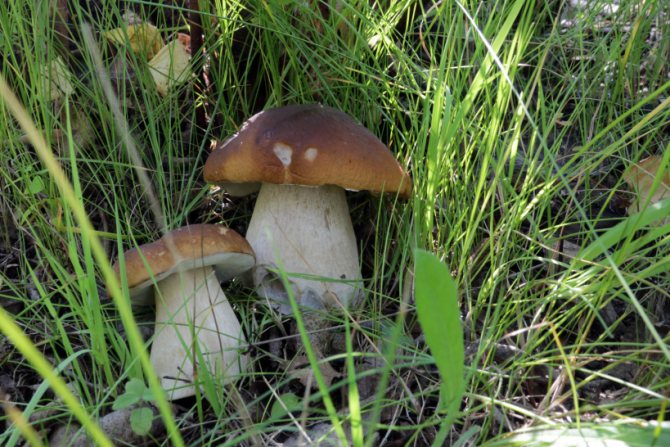
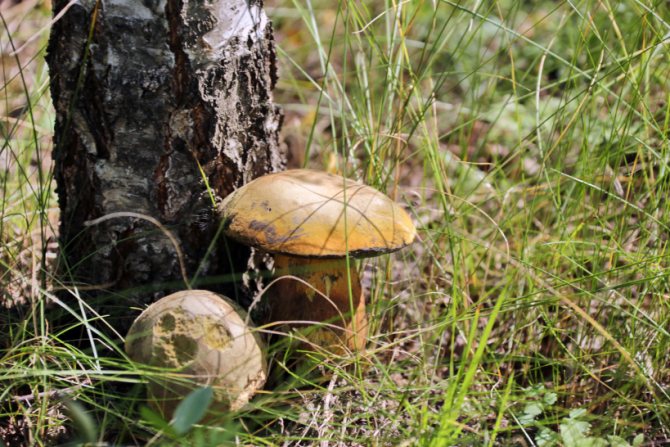
- If we talk about what certain mushrooms love, then porcini, boletus and many of their other brethren are actually attached to their partners - trees, in symbiosis with which they live. This is what determines the location of the mycelium. For example, boletus should be found in pines, and boletus - in spruce and birch forests. As for dry or wet areas of the soil, then, indeed, due to heavy rains, mushrooms this year need to be looked for where it is drier and lighter, in areas that are better warmed up by the sun. Therefore, I do not advise you to climb into the thicket, look for them on the edges, in the woodlands, on the slopes of the wooded hills. And the best suited for mushroom hunting are individual clumps of trees growing in the middle of the field, and forest shelter belts.
- They used to say that on forest edges, if they are adjacent to farmland, it is dangerous to pick mushrooms, since the fields are treated with various harmful chemicals, which mushrooms, like a sponge, absorb.
- Now this is no longer so relevant, because the MPC standards have been raised and strong toxins are no longer used in agriculture. This applies to both fertilizers and chemical warfare, which fights harmful insects. All of these products have become safer and are used in relatively small concentrations.
- So, you can not believe the horror stories about toxic mushrooms?
- If we are talking about the Moscow region, then yes. The worst thing that can occur here is the salts of heavy metals that settle on mushrooms growing along major highways. They get into them together with precipitation, because they are water-soluble. But as far as mushrooms easily absorb them, it is just as easy to get rid of them when boiled. Therefore, you can pick mushrooms even within Moscow, in Bitsa or Losiny Ostrov. Only when you come home, be sure to wash them well, then, even if they are white, no matter how blasphemous it may sound, they must be cut lengthwise and boiled for 10 minutes. Be sure to drain the water. In this case, 90–95% of heavy metal salts are removed. You don't need to soak the mushrooms at all.
Cook longer too - otherwise they will lose all their beneficial properties.
- Advise our readers about the most cherished mushroom places in the Moscow region.
- And this year is good because all the places have become mushroom, mushrooms climb even where they have not been seen for many years. But speaking globally, the most mushroom places in the Moscow region are the western direction (from Zvenigorod and beyond) and the southern (Serpukhov and its environs). I wish you all a successful hunt!
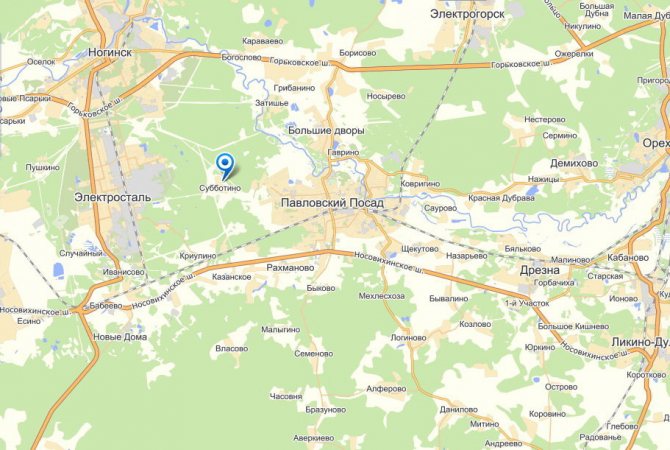
Mushrooms in the north of the Moscow region
People often pick mushrooms in the north of the Moscow region. The area has the advantage of being considered clean and easily accessible by transport. There is an accurate map of the places where mushrooms are found during the season and off-season.
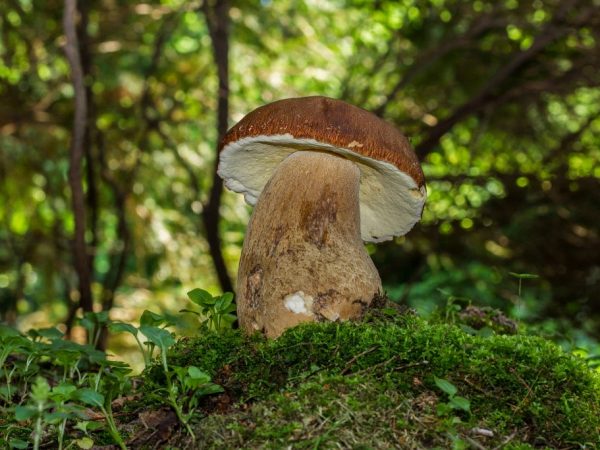


Mushrooms in the north of the Moscow region
Features of the region
The forest cover of the region is about 40%, a significant part of coniferous and mixed forests is in the north. Spruce forests predominate. The northern suburbs of Moscow are irrigated by tributaries of the Volga, there are shallow lakes, many reservoirs. swampiness is present in some places. There are no hills, few forest-steppe and meadows.
The outskirts of the city are considered environmentally polluted, which makes quiet hunting in and around the city dangerous. However, thanks to the developed transport system, it is not difficult to get to the remote corners of the region in a day. The weather and flora here are favorable for the growth of mushrooms.
Mushroom Sites Map
Places near settlements and villages are popular in the northern regions; there are especially many mushroom pickers here in autumn. It is important to calculate the distance so that you can get back from the forest about the onset of darkness. From the railway stations to the mushroom site, you will have to walk a few more kilometers.
By road
In the settlements of Kartamazovo and Troparevo, pine forests and deciduous glades are widespread, so most often they collect here:
In Kartamazovo there are minibuses from the Salaryevskaya metro station and buses from the Teply Stan AS. Minibuses go to Troparevo from the Sombrero and Viva shopping centers, as well as from the Anino metro station. The journey takes on average up to one and a half hours. By car, the distance is covered in 40 minutes.
Dubna is famous for the abundance of russula, butter and honey agarics. The Volga River flows in the city, and in the vicinity there is a pine forest. The distance from the city is insignificant - 120 km. Overcome it in several ways:
- Train. Inexpensive and fast form of transport. Travel time is up to 3 hours. They leave from the Savelovsky railway station. Electric trains run regularly, every two hours.
- Bus. A more comfortable and faster option. Coming from the SA of the Savelovsky station.
- Car. Motorists often take fellow travelers. They park near the places of boarding the bus at the Savelovsky railway station.
Tourism is developed in the city, so mushroom pickers who are late on the way will always find places to sleep.
By trains
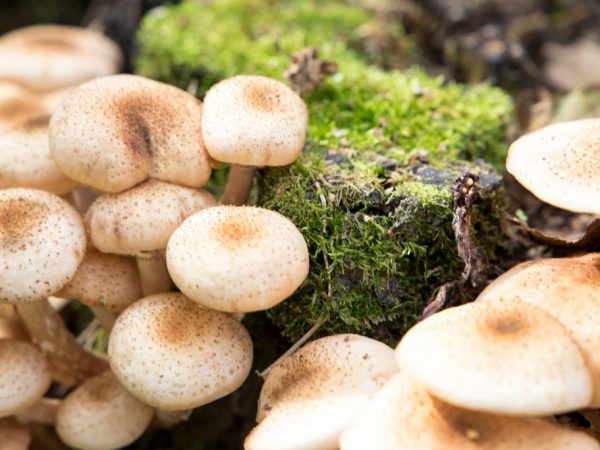


Suburban forests are rich in mushrooms
In the Moscow region, a system of suburban electric trains is developed, which makes the path easier for mushroom pickers.
On the northern branches (Leningradskaya, Savelovskaya, Yaroslavskaya) they get to mushroom spots in all corners of the Moscow region.
The Savelovskaya line starts moving from the city along the stations Lobnya, Nekrasovskaya, Katuar. There are many lakes, the area around which is rich in meadow gullies and swamps.
A spruce forest grows in front of Lobnya. The most mushroom place is the village of Khoroshilovo. Also advise the final stop Tourist and Lugovaya, located near the station. In these forests, chanterelles, honey agarics, aspen mushrooms are collected. To get to the place, on average, you will have to travel from 2 to 4 km in one direction.
On the Leningradskaya branch, the nearest mushroom points are located in Firsanovka and Podrezkovo. Here are common:
Not far from the stations Povarovo and Golovkovo, as well as in the vicinity of Frolovsky and Pokrovka, rare species are found.
On average, the journey from the station takes up to one and a half hours (from 1 to 3 km).
The Yaroslavl direction is also productive, there are four mushroom places:
- Neighborhoods of Zelenogradskaya station.
- Settlement Darino and neighboring Eldigino.
- Environs of the Kalistovo station.
- Station Abramtsevo.
If you leave Pushkino or move south from Darino, you can get into the complex of water bodies. The territory is located between the Savelovsky and Yaroslavsky directions. The path to the destination along the branch is up to 5 km. Honey mushrooms, boletus, white mushrooms, mushrooms, jaundice grow in these parts.
Collection time
It is important when hunting not to be mistaken with the time interval. Fruiting of species differs in time, therefore, it will not work to collect both white and winter mushrooms at the same time. Ceps, stitches, morels, May mushroom are considered spring ones. In summer, after heavy rains, it is time for honey agarics, boletus and aspen mushrooms. And in the autumn period (from August to mid-October) - the peak of the mushroom season. Winter mushrooms bear fruit at temperatures down to -6 ° C.
WHAT ARE THE FOOTWEARS ABOUT?
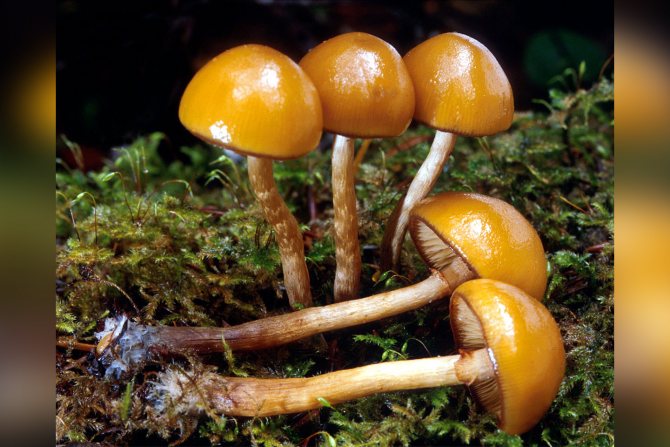


Fear in the spring-summer period is worth and honey agarics, experts say. Among these mushrooms there are also poisonous species that can lead to serious poisoning and even death.
- If we are talking about collecting honey agarics, it is better to wait for autumn, - continues Maxim Dyakov. - With the onset of warmth, there are a lot of false snakes. For example, the fringed gallerina is very similar to the summer mushroom, but contains deadly amatoxins.
Gathering season
The first boletus begins to grow in mid-July. At the beginning of the season, the harvest is small. The ripening peak comes at the end of August - beginning of September. Porcini mushrooms continue to grow until the end of October, after which the season ends.
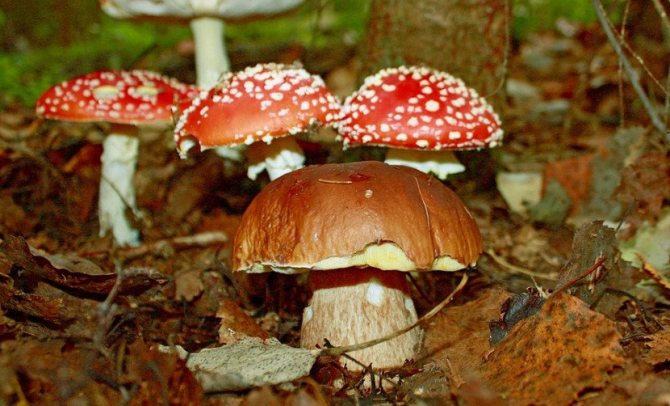


Avoid picking edible species if fly agarics, toadstools, or other inedible mushrooms are growing nearby. The spore powder of poisonous species can infect the good ones and make them unusable.
What mushrooms grow in a pine forest. Pine forest mushrooms


The species diversity of mushrooms in a pine forest depends on its age. The younger the forest, the easier the mycelium can grow into the roots of trees. In a two-year-old pine forest, a late oiler can already grow. Its growth begins in May, but it is most active in June. It can be found by the small tubercles that raise the fallen needles. Fruiting occurs throughout the summer. If conditions are favorable, three to six crops can be harvested in one season. After fifteen years, the activity of the oiler weakens, and new varieties of mushrooms come in its place.
Along with boletus, the following species are found in the pine forest:
- Ginger. It is found in lowlands and in open areas.
- The mucous is purple. As a rule, it grows near pine trees. Little known mushroom. It is versatile - it can be either prepared for the winter or prepared for direct consumption.
- Hericium is variegated. Considered conditionally edible. Has a characteristic aroma and bitter taste. Before cooking, you need to boil it for a few minutes so that the bitterness disappears. Only young mushrooms are suitable for food, since the old ones have increased bitterness and hardness. You cannot eat a hedgehog in its raw form. You can get food poisoning. It grows both singly and in several pieces.
- Greenfinch. A representative of the fungal family, growing in groups in lowlands and in open spaces.
- Rowing. Inhabitant of flat areas. It grows both singly and in groups. There are about a hundred of its varieties, and only about twenty of them are not poisonous.
- White. It differs from white from deciduous forests in that it looks like a gall mushroom. It is quite simple to distinguish it from gall: it is worth licking its cap. White is devoid of the taste of a bile mushroom.


Autumn honey fungus. It grows in groups on tree trunks and stumps.