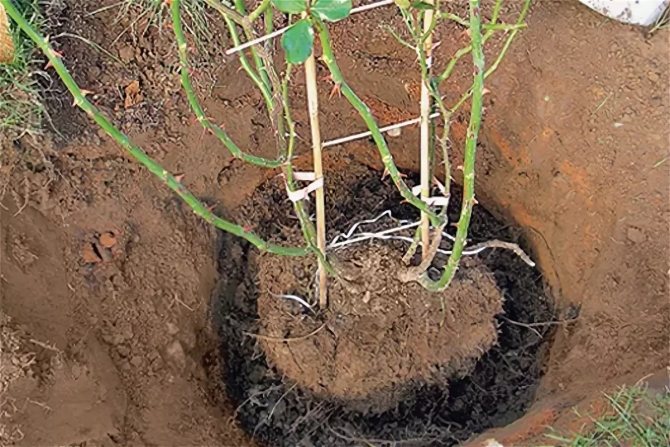
Before the onset of winter, many flower growers and summer residents are worried about the question: when, in what month can roses be transplanted to another place in the fall? After all, the capricious queen of flowers does not tolerate negligence and ignorance, and the climate in most regions of Russia does not indulge in a large number of warm autumn days in late autumn.
This nuance is especially true for the inhabitants of the northern regions of the country - where frosts bind the ground very early and then it snows altogether. In such cases, experienced flower growers recommend transplanting in the spring, so that over the summer the rose can take root, get sick, and gain strength.

When to replant roses
Let's take a look at when is the best time to replant roses. In fact, this can be done both in spring and in autumn, the recommendations below show not obligatory, but preferable terms for moving the bushes to a new place.
Autumn is the best time for replanting rose bushes in regions with mild climates. The soil is still warm and the roots will have time to grow before frost. In the south, roses are finished planting two weeks before temperatures drop below freezing. Usually in the month of November there is the height of earthworks. Regions with cool climates require October transfers, in cold conditions the best time is August-September.


But in areas with low temperatures, it is better to move the roses to a new place in the spring. The same applies to places where it often rains, strong winds blow, or the ground is very heavy.
Shelter for the winter
Since the transplanted plant is not quite strong, it will have to organize a shelter. There are several ways:
- the use of spruce branches;
- hilling with humus or peat;
- purchase of modern specialized materials;
- the use of sawdust and fallen leaves.
Each summer resident selects the material for the shelter, taking into account his own capabilities and planted varieties. It is recommended to cover the seedlings after the first slight frost, so that the plant is hardened.
In general, the transplanting process in spring and autumn is not so difficult. All that is required is careful observance of all the rules. Having settled in a new habitat, the rose will certainly bloom and delight you with the tenderness and beauty of the buds.
Rose transplant
The easiest way to transplant roses is at the age of 2-3 years. But sometimes it is necessary to move an adult, well-rooted bush. It is difficult to do this, but it is quite possible. We will tell you how to transplant a rose in the fall, correctly and without spending extra effort.
Seat selection
Roses are best planted in an open, well-lit area in the morning. It is then that increased evaporation of moisture by leaves occurs, which reduces the likelihood of fungal diseases affecting the bush. It is good if the plot has a small, no more than 10 degrees slope to the east or west - spring melt water in such a site does not stagnate, and the risk of damping out is minimized.
Before transplanting roses in the fall, study their lighting requirements - many varieties cannot stand the midday sun. Under the scorching rays, they quickly fade, the color fades, the petals (especially dark ones) burn and lose their attractiveness.Such roses are transplanted under the cover of large bushes or trees with an openwork crown, placing them at some distance from them so that the roots do not compete for moisture and nutrients.


For a flower, you need to provide protection from the north and north-east wind, and not place it in a deep shade. You can not transplant the bushes to a site where Rosaceae have already grown - cherry, quince, Potentilla, Irga, etc. for 10 years or more.
Almost any soil is suitable for this flower, except for swampy, but slightly acidic loams with a sufficient humus content are preferable.
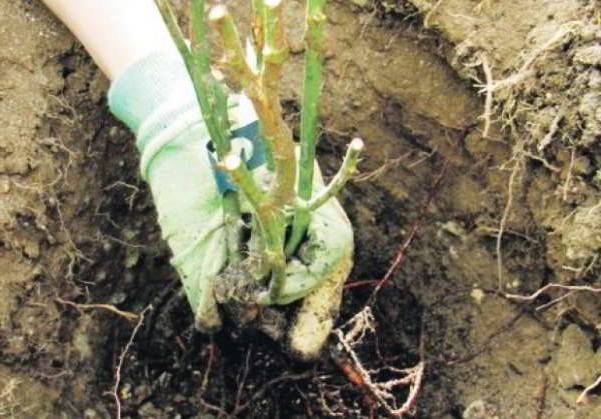
Digging and preparing roses for transplanting


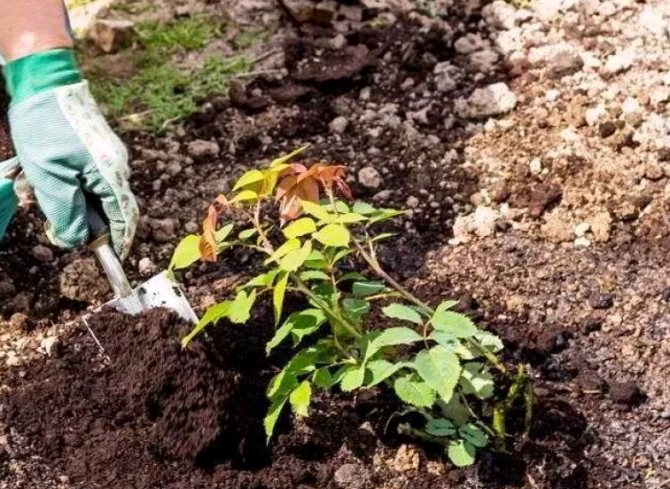
Before replanting roses in the fall, they need to be watered abundantly. After 2-3 days, dig out the bushes, stepping back from the base about 25-30 cm.Young roses will be easy to get out of the ground, but you will have to tinker with the old ones. First, they need to be dug in with a shovel, then loosened with a pitchfork, cut off the overgrown roots, and then transferred to a tarp or into a wheelbarrow.
When transplanting in autumn, the shoots are not touched at all or only slightly shortened, all leaves, dry, weak or unripe twigs are removed. The main pruning of the bush will be done in the spring.
But it happens that a rose has been dug up, and the planting site is not yet ready for it. Is it possible to somehow save the bush?
- If you postpone transplanting for less than 10 days, wrap an earthen ball or bare root with a damp cloth, or better with wet burlap or jute. Place it in a shady, cool place with good air circulation. Check from time to time to see if the fabric is dry.
- If the transplant is postponed for more than 10 days or indefinitely, the roses need to be dug in. To do this, dig a V-shaped moat, lay the bushes there obliquely, sprinkle it with soil and compact it slightly.
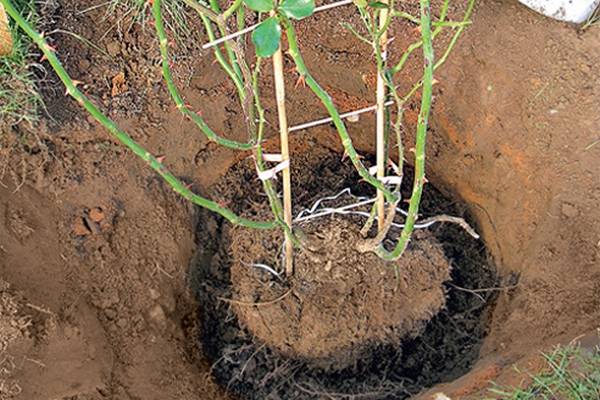
Preparation of planting holes
It is best to prepare holes for the autumn transplantation of rose bushes in the spring. But, frankly, you do this very rarely. Try to prepare the site at least two weeks before transplanting.


If your plot has good black soil or loose fertile soil, dig holes to the planting depth, adding 10-15 cm.On depleted, stony or unsuitable soils for growing roses, a deepening is prepared with a margin of about 30 cm.Prepare the soil for backfilling by mixing in advance:
- fertile garden soil - 2 buckets;
- humus - 1 bucket;
- sand - 1 bucket;
- peat - 1 bucket;
- weathered clay - 0.5-1 bucket;
- bone or dolomite meal - 2 cups;
- ash - 2 glasses;
- superphosphate - 2 handfuls.
If you do not have the opportunity to prepare such a complex composition, you can do the following:
- turf soil - 1 bucket;
- peat - 1 bucket;
- bone meal - 3 handfuls.
Fill the pits completely with water the day before transplanting.


Transplanting rose bushes
A good time to start work outdoors is a warm, calm, cloudy day.
Transplanting roses with an earthen ball


Pour a layer of the prepared mixture at the bottom of the planting pit. Its thickness should be such that the earthen lump is located at the required level. The planting depth is determined by the grafting site - it should be 3-5 cm below the ground level for bush and ground cover roses, and for climbing roses - by 8-10. Own-rooted plants do not deepen.
Fill the voids with the prepared fertile soil up to half, gently apply it and water it well. When the water is absorbed, add soil to the edge of the hole, tamp it lightly and moisten. After a while, repeat watering - the soil under the transplanted rose should be wet to the full depth of the planting pit.
Spring transplant of roses. How to properly transplant roses to another place
The main task when transplanting any plant is to keep the root system intact to the maximum. Please note that the structure of the roots of grafted and self-rooted roses is different.In the first case, the presence of a powerful taproot up to 1.5 m long is characteristic, which will still have to be chopped off; in the second, the root system is usually superficial, but branched in width.
The procedure for transferring a whole bush to a new place looks like this:
- Water the rose abundantly (at least 15 liters) two days before transplanting.
- Gently tie the stems with a rope, especially prickly roses can be additionally wrapped with matting or other coarse cloth to avoid injury.


If you first tie the shoots, the rose bush is much more convenient to dig in and remove from the ground
- Dig in the bush with a pitchfork in a circle approximately the same diameter as the aerial part of the plant. The depth of the "trench" is at least 20 cm. Loosen the soil inside well.


A rose bush is removed from the ground in much the same way as a loose milk tooth in a child.
- By loosening the bush to the sides, remove it from the soil. For taproot roses, cut the longest root with a sharp, clean shovel or other suitable tool.


It will still not work to extract a rose bush from the ground without losses - some of the roots will inevitably remain in the old place
- Transfer the removed earthen lump (ideally entirely) to a thick plastic wrap or cloth. Inspect the roots as much as possible, trim off any dry, decaying areas. Sprinkle all the cuts made immediately with crushed chalk, wood ash or cover with greenery.
- Transfer the rose to the planting site. If the procedure is not planned immediately, but within a week, moisten the cloth with water or spray it with an earthen ball, preventing the roots from drying out. If you postpone the transplant for more than 10 days, temporarily dig in the bushes, laying them obliquely in a V-shaped trench and slightly compacting the soil.
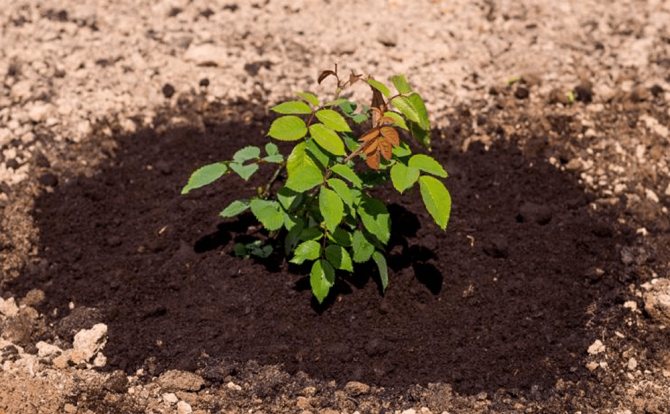
- Make a depression in the soil that filled the prepared hole, roughly the same diameter as the earthen lump. Put a rose bush in it and start filling the hole with soil, tamping it 3-4 times in the process and simultaneously spilling it with water. The root collar must be left at the same level as in the previous place.


Post-transplant care
We told how and when to transplant roses, now we need to figure out if we can do something else to facilitate their early rooting.
- If you transplanted the bushes at a later date, just before the frost, do additional watering.
- In warm, dry weather, water the roses every 4-5 days so that the soil is constantly moist, but not wet.
- In the northern regions, in the year of moving the bush to another place, make sure to make an air-dry shelter.
Watch a video describing the intricacies of transplanting roses:
Why you need to transplant roses: the main reasons
Often the roses grow wildly and obstruct the passage, etc. At the same time, a large shrub lacks nutrition, and it blooms poorly or dies. All this happens because of the wrong place for growing roses, or the flowers were planted at the wrong depth.
There are also external reasons for replanting plants. For example, when you need to build something on this place or create a rose garden in another place of the site.


In addition, all perennial plants and especially shrubs must be transplanted periodically.
Advice! When a rose is propagated by dividing the bush during transplantation, it is better to harvest the cuttings in the fall.
Why do you need to transplant roses
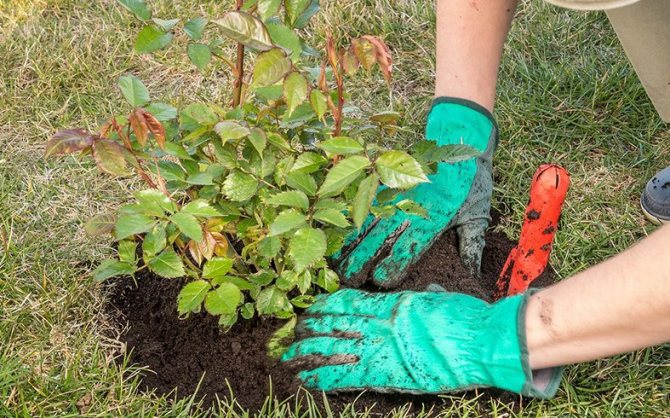


Before transplanting, you need to be sure that this process will not be harmful.
In most cases, replanting a garden rose is necessary in order to save the plant. It is not recommended to touch the flower unless absolutely necessary.
The main reasons for transplanting roses:
- Various diseases and lack of flowering can lead to the complete death of the plant. In this case, transplanting will help save the rose bush.
- If neighboring plants began to interfere with proper development, then moving the flower beds is a necessity.
- Dull shading of a flower bed by trees and buildings is unacceptable. The rose grows well in sunlight. Its absence will lead to illness.
- An adult plant may stop blooming beautifully. The inflorescences become small and lose their appearance. Everything is restored in a new place.
- It is necessary to transplant when groundwater is found near the root system. Otherwise, the root system will rot.
- If the soil on the site is depleted or its composition has changed, then transplanting can save the plant.
Site selection and site preparation for transplanting
Before you start transplanting plants, you need to find a new place for them and carry out preparatory work that is aimed at improving the fertile characteristics of the soil. Consider what you need to look for when choosing a new place for shrubs.


The area chosen for planting roses should not be blocked from sunlight. But it is very important that it is well protected from strong winds. If you plant plants in the shade, for example, near a fence, then they will bloom more slowly, so it is best to choose an open area for planting.
It is necessary to transplant the formed rose bushes to another place in such a way that they do not interfere with free movement around the site, especially since a calm zone, remote from busy places, will promote the development of plants and ensure good flowering. There are other requirements to consider.


For example, it is very important that the site chosen for transplanting roses is not located in a low-lying area. These plants do not like an excessive abundance of moisture, therefore, zones should be selected that do not suffer from this drawback.
Benefits of transplanting in the fall
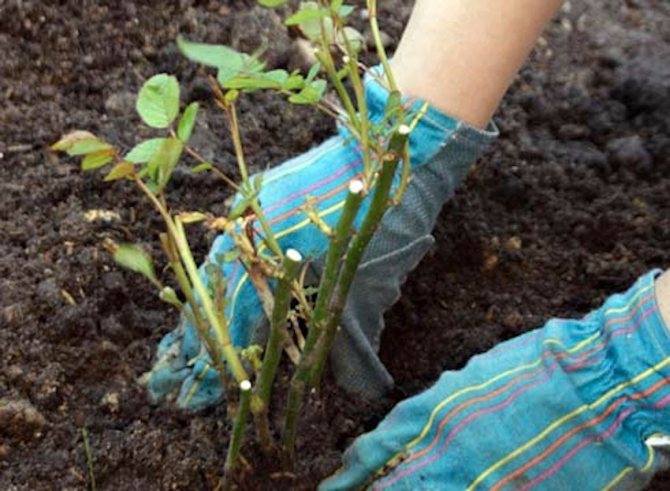


Autumn flower transplant is most favorable
Roses can be transplanted in spring and autumn. The plant should have time to get stronger in a new place before the onset of frost or heat. Experienced gardeners recommend choosing a transplant time depending on the climate and region. In the southern regions, it is recommended to plant in October or November. The main thing is to complete all work a few weeks before the temperature drops to zero. The best option for cold regions is September.
There are other benefits to replanting roses in the fall. During this period, flowers take root better in a new place. The mild climate and rainfall help the plant to take root well. In the spring it is difficult to predict favorable weather. In autumn, the soil remains warm after a hot summer. Long daylight hours will allow the plant to get enough sunlight and warmth. All these conditions will favorably affect the rooting of the bush in a new place.
Place and period of transplanting bushes
The most favorable time for transplanting is the period between the end of September and the beginning of October. Since it will be easier for the plant to take root at the moment when the influx of nutrients to the roots begins.
Preparation should start well in advance. In August, you need to stop feeding and reduce watering. In the Moscow region, transplanting roses to another place in the fall is carried out only with the use of mineral fertilizers, if the land has been occupied by other plants for a whole year. Any crops deplete the soil, so the flowers may lack some mineral components.
The transplant site should be in the sun for most of the day, in addition to this, there should be a good outflow of moisture. Otherwise, in winter, stagnant water will lead to overheating of the roots. This is especially true for those who live in the territory of the Kuban. In this region, warm climatic conditions have been created, which largely prevent the roots from freezing. If there is a lot of water, then rotting of the plant is possible.
Soil and site requirements
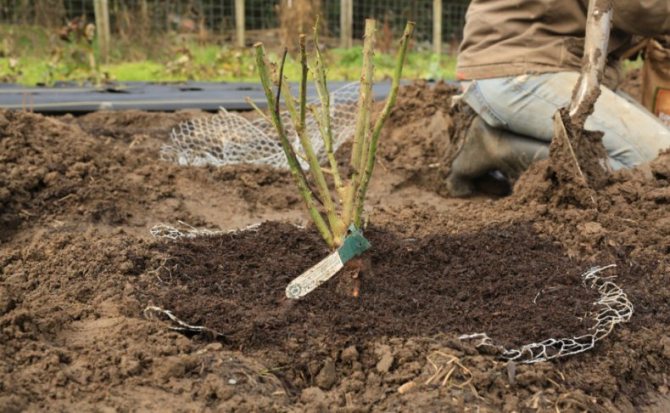


The new location should not be in complete shadow.
The plant will grow and develop properly in an open, sunny location in the garden area. Sunlight contributes to the evaporation of excess moisture, so the flower in such conditions is less susceptible to fungal diseases.... There should be no stagnation of moisture in the new place. It is recommended to choose terrain with a slope. A natural outflow of water is necessary so that there is no waterlogging of the soil and rotting of the roots.
When choosing a place for transplanting roses, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of the variety. There are plant species that can die from the aggressive sun at lunchtime. The petals become dull, flowering disappears, and the rose loses its appearance. For these varieties, prepare a place with light shading. You cannot completely deprive the plant of the sun. An area hidden from the sun under young trees is suitable. Plants should not interfere with each other's proper development.
The rose does not tolerate drafts. Cold winds can adversely affect flowering.
The soil is pre-fertilized and loosened. Sandy, clayey and muddy areas should be avoided. It is advisable if there have been no other plants on this site for several years. The content of nutrients in such soil will be higher. There will be an unfavorable neighborhood with rowan, bird cherry and cherry trees.
The earth must contain a sufficient amount of nutrients. The soil can be purchased ready-made, or you can prepare it yourself at home. For growing roses, you can make soil with different components. The simplest option is to mix a bucket of peat and a few tablespoons of bone meal. The more complex method includes garden soil, peat, a bucket of clay, several portions of ash and superphosphate.
How to transplant an old rose bush. Instructions on how to transplant a large or old rose
The conditions for growing a rose in a new place should be as close as possible to the previous one so that the plant experiences less stress. The new habitat of the rose can differ only if the current one does not suit her at all. But the site must be protected from the wind. And keep in mind that roses do not like deep shadow and soil in which moisture stagnates.
Carefully prepare the planting hole: remove all weed roots, put drainage on the bottom, fill the hole with fertile soil (you can add compost) and leave for 2-3 weeks to let the earth settle down a little. After that, start digging up the bush.
Try to dig a rose along the projection of the crown - with the largest possible earthy clod. To make this easier, water the soil under the bush with plenty of water. Then the earth will crumble less. To make it easier to approach the spreading plant, tie its shoots with a tight rope.
Dig a trench around the perimeter of the bush and gradually deepen it until you get a fairly deep ditch. Then tie the earthen ball back with any cloth or plastic wrap and continue digging under the base of the bush. If too long roots of the plant prevent you from reaching the earthy ball, chop them off with a sharp blade of a shovel. With proper care in a new place, they will quickly recover. It is advisable to sprinkle it with charcoal just before planting.
If the bush is very large, place a sturdy and fairly long object (such as a crowbar) under its base and use it as a lever to pull the plant out. Place the bush gently on the previously spread fabric and drag to a new location. To prevent the earthy ball from crumbling, tie it with twine.
If the rose has a long-term "relocation" (for example, to another site), then the earthen lump must be wrapped in wet burlap so that the roots do not dry out.
Place the rose in the planting hole so that the bush sprinkled with earth is at the same level as it was in the previous place. Remove the lining from the coma after filling half of the pit with soil.Then water the soil with water, wait until it is absorbed, and then fill the planting hole to the brim and water again. If the soil has settled, add some soil so that there are no air voids around the roots of the rose.
When transplanting a large bush, roses consume 1.5-2 buckets of water.
This method is suitable if you are looking for an answer to the question of how to transplant a tea rose, as well as any bush form.
In the first month after transplanting, the plant should be regularly, but moderately watered and shaded during bright sun. In spring and summer, daily spraying of the crown is also recommended. After transplanting, it is undesirable to disturb roses for several years so that they adapt to a new habitat.
How to prepare roses for transplanting
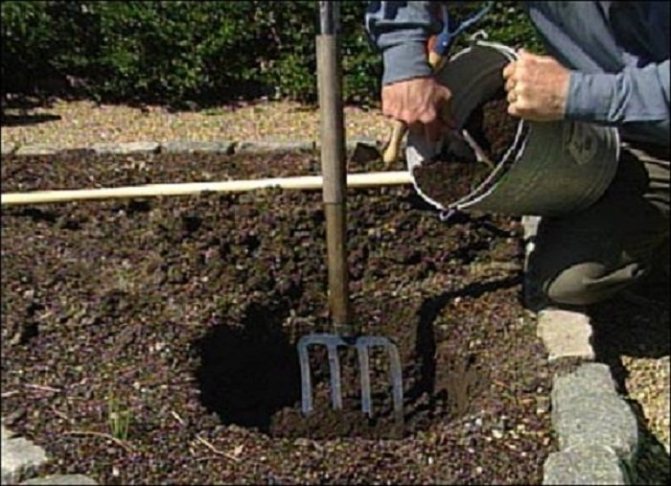


The place for the transfer should be prepared in advance.
In order for the flower to take root quickly, it is necessary to properly prepare the plant. The soil is fertilized in advance with autumn fertilizers. Useful substances and minerals will help to quickly take root and survive the cold. Immediately before replanting roses, abundant watering is required. You cannot immediately dig a bush from the ground, you need to wait a few days.
Plants with a small root system are not difficult to extract. Adult flowers are pre-dug at a distance of 30 cm. The overgrown root system cannot be completely removed from the ground, because it goes very deep into the ground. From tools you may need a crowbar and a large shovel. Damaged roots must be trimmed... As for the shoots, you do not need to touch them in the autumn. The main pruning occurs in early spring. Broken and diseased branches are an exception. It is important to be careful and careful when pruning.
How do I save the root system?
To preserve all the roots, water the plant abundantly before transplanting, which will lead to the creation of a clod of earth around the roots. Transplanting in this way becomes safer. If the plant is transported over a long distance, then a lump with earth should be carefully wrapped with a cloth and tied around the root collar. It will be possible to plant directly with this fabric, it will decompose, but do not forget to untie it.
When transplanting a rose bush to another place, they resort to trimming the roots, branches with leaves.
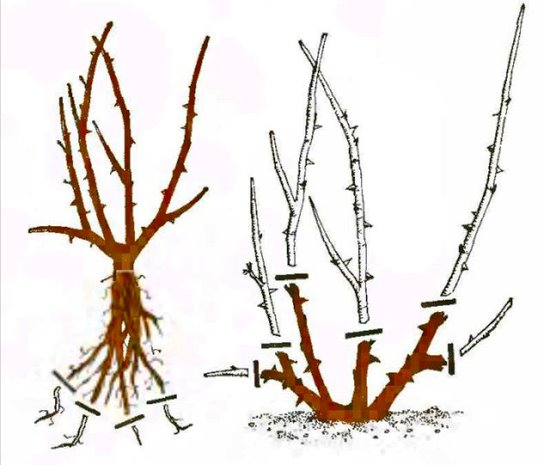

The bush must be dug wide in order to preserve the roots. If the main stem is long and deep in the soil, then it should be chopped off, trying to keep most of it. Correct transplantation of roses to another place in the fall using this technology will preserve all important parts of the root system.
Pruning
Pruning shrubs in the fall is done according to the climate in your area. Difficulties lie in the characteristics of the plant. Some species, after transplanting and pruning, begin to restore vital processes and may confuse autumn with spring. Therefore, in order to protect yourself from the death of the rose bush, it is best not to carry out this procedure. Only damaged or dry branches can be removed.
Pruning shoots is not always a good idea. If the autumn is warm and the air is humid enough, then cutting off the shoots can lead to the awakening of dormant buds, and this, in turn, will lead to the appearance of new branches that will die in winter. In this case, it is not recommended to touch the shoots.
The situation is the opposite: autumn is cool, and before the frost begins there is a time of about 20-30 days, then the shoots can be cut off and not worry that the planted bush will not have time to prepare for the cold weather. It all depends on the weather conditions and the region. It is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the weather that expects your city in the coming month in advance.
Types of transplanting roses in autumn
There are several methods for transplanting roses. Choosing a method is required based on the variety of the rose. More details about the technology and the benefits of each of them will be discussed below.
Classic method


This transplant method requires special care with the root system.
Transplanting bare-root roses is a classic method. The method is also suitable in the case when it was not possible to preserve the earthen lump during excavation. The root system must be carefully examined for diseased and dried roots. All damaged areas are immediately removed.
It is important to leave the length of the roots longer than the shoots.... Next, the root system is placed in a container with rooting solution. The procedure is necessary in order for the plant to quickly take root in a new place. Can be planted in two hours.
Then a hole is made with a small handful of fertile soil and the plant is carefully placed. Drainage can be placed at the bottom of the pit. It includes: river sand, small stones or gravel. Drainage will allow the roots to "breathe".
Next, you need to spread the roots well inside the flower bed. After that, the rose is watered and tamped into an intermediate layer of soil. Next, you need to water it again and fill the hole completely. It is important to compact the earth well so that there are no empty places and air congestion. In the presence of air, the plant may die. In the event of the onset of the first frost, the roots are reliably sheltered from frost.
Method for beginners


Transplanting a plant along with old soil is the easiest
The method of transplanting roses with a lump of earth is suitable for novice gardeners. The principle is also called "wet" and does not require special skills and knowledge. There should be enough soil on the root system from the previous location. It is important to prepare a hole larger than the roots of the plant. Further, water is poured to the bottom. You can add humate and soil with trace elements. Next, the rose is placed, dripped in and watered again abundantly. After that, you need to add the remaining earth and tamp the surface well. The appearance of air jams is unacceptable.
The advantage of this method is the absence of root damage. The plant is placed in a new hole in its usual soil, but from the fresh soil it will receive the necessary trace elements and substances. When transplanting with the "wet" method, there is practically no risk of dropping the buds. In the event that flowering continues during the transfer. When planting several bushes, you need to maintain a distance between the bushes of 60-80 cm. Thus, the roses will not interfere with each other.
How to transplant a blooming rose
Transplanting roses can be carried out at any time, if there is an urgent need. If you transplant a rose during flowering, you need to prepare for the fact that the bush will look sick and stunted for some time and only the next year will regain its former beauty. Such transplantation should provide for a particularly careful attitude to the root system of the flower: with minimal trauma and the preservation of all its sections, even if they seem excessively long. This should be taken into account when preparing the hole in width.


As for the rest of the technical points, they are no different from the rules that are given as an example of a spring bush transplant.
Rose transplant rules

The methods of replanting roses to a new place differ slightly from each other. All methods are described above. There are general guidelines that must be followed during the process so that the plant does not experience a lot of stress and takes root.
- The hole should be about 40 cm in diameter and up to 70 cm deep. It all depends on the root system.
- Transplanting a flowering plant is not recommended. If such a need arose, then attention should be paid to the roots and not damage them.
- Seedlings should have 2-3 shoots and a strong root system. Otherwise, you do not need to touch the flower.
- Shoots with an altered appearance must be carefully removed before planting.
- Curly varieties require special care.First of all, the branches should be removed from the supporting frame and the flowerbed should be carried along with the supporting devices.
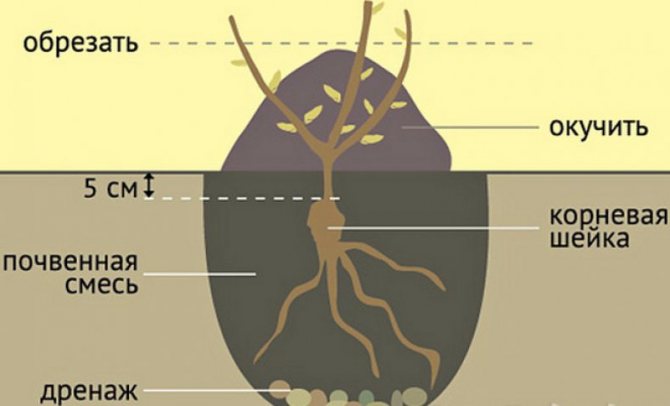
- The base of the root should be in the ground at a depth of 5 cm. The difference is made by wicker and own-rooted varieties.
- If the crown was tied, then after the end of the process, the branches should be freed and gently straightened.
- The grafting site of the bush should face south.
- A large earthen lump can be transported using strong film or burlap.
- It is recommended to water it with warm water to create favorable conditions for the weakened root system.
Ways to get new rose bushes
Climbing rose in the garden
Transplanting involves not just the process of moving to a new place, but also the reproduction of an overgrown flower. There are several methods for dividing a rose:
- The classical method is simple and time consuming at the same time. You will need to take the shoot, remove the leaves from it and cut the bud on its underside. A chip should be inserted into the cut and the shoot should be placed in a groove dug out next to the main bush to a depth of 10 cm. The shoot is sprinkled with a layer of soil, tamped and spilled with water. At the beginning of autumn, the young plant is separated from the mother plant, and after 3 weeks its top is cut off. Then they are transplanted to a permanent place of growth.
- The propagation method by cuttings is considered the most common and easiest to carry out. The best period for dividing by cuttings is June or July. To obtain cuttings, an area of a one-year-old rose shoot with a thickness of at least 5 cm is taken. In this case, cuttings should be cut so that each one has at least 2 buds. A cut from above must be made 2 cm above the existing kidney, and a cut from below is made immediately below it. The leaves are removed from the bottom, as well as all the thorns. The lower cut should be treated with a growth stimulator and planted in the prepared soil, while observing an angle of 45 °. If the seedlings were grown in a greenhouse, then after transplanting them into the open ground, the room must be treated with a sulfur checker.
- Reproduction by dividing the bush is possible if the plant has many shoots. A suitable bush will need to be dug, cut off its roots, shoots by 1/3. Each must have a part of the root and at least 2 buds. The resulting cuttings are dipped in a solution of mullein and clay, after which they are deepened into the ground by 5 cm and watered.
Reproduction is carried out by more laborious methods. These include:
- getting a rose from seeds;
- division by vertical layering;
- reproduction by root suckers.
Read more about the transplant in the video.
Follow-up care
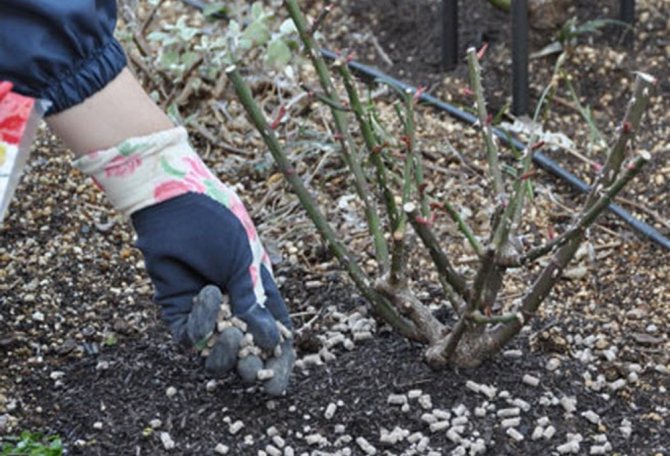


After transplanting, plants especially need feeding.
Roses require special care after transplanting. The plant is weakened and needs to be helped to recover in a new place.
Care instructions:
- It is necessary to feed only fertilizers containing potassium, and nitrogenous feeding should be excluded. It stimulates growth. This is not necessary in winter.
- Pruning cuttings should be done carefully. Cannot be pruned like in spring. New green shoots will not survive the cold and will die.
- Large shrubs need to be attached to a support to help the root system grow stronger.
- There is no need to water the plant. Too much watering can lead to waterlogging of the soil and death of the flower.
- Periodically in the autumn, it is required to weed and loosen the ground at the base of the plant. In winter, this procedure is not required.
- Before winter, it is necessary to cover the roots of plants and shoots to avoid hypothermia.
- After the rose has taken root, you need to cut off the damaged areas.
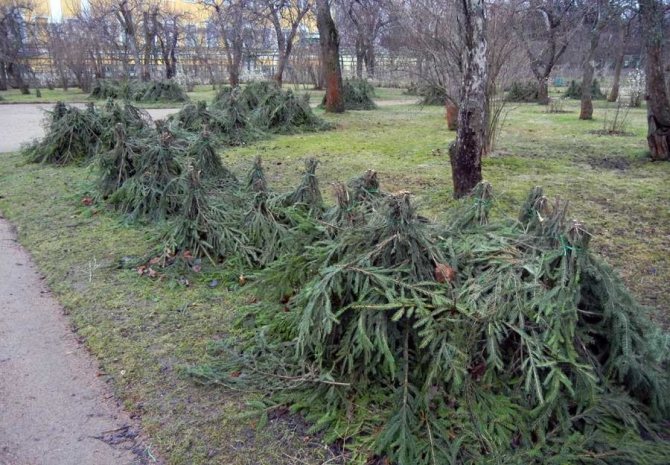


Covering roses with spruce branches is the most reliable protection against winter frosts
There are several ways that can help the plant survive the cold. Depending on the variety and climate, different methods are chosen. The most common cover is considered to be an additional layer of earth. But it will not be effective during severe frosts.In this case, it is required to additionally hide the roots under coniferous spruce branches, film or wooden shields.
It is important to remember that if the plant survives the first winter after transplanting, then rooting was successful. Light frosts are even useful as a preventive measure.
Suitable dates for transplanting roses and important nuances
The reasons why roses require transplanting can be different. But in any case, you need to choose the right time:
Spring. It is necessary to be in time until the leaf buds begin to bloom. The minimum soil temperature is 7–10 ° C. Dates, depending on the region, vary from early March to late April. Most likely, the rose will not bloom this season. Tear off the buds that have appeared so that the plant can form roots normally.


Summer. Risky procedure. The procedure is carried out on a cloudy day in the evening. Then the bush will need protection from direct sunlight, frequent watering and spraying.
Garden, vegetable garden and flower garden tips
Lunar calendar for august 2020 gardener and gardener
New moon in August 2020 when from what date to what time
Garden pests living in the ground photos and names
Fall. Such a transplant, if everything is done correctly, the roses are tolerated almost painlessly, since the plant is already going into hibernation. It is carried out 4–5 weeks before the first frost, when the leaves have already fallen from the bush. Approximate dates are from mid-September to the end of October.
Transplanting a rose to another place in spring may be required for several reasons:
- Unsuitable soil on the site. The rose does not like both too loose sandy loam and heavy clay soils; placement in such areas leads to the extrusion of the roots and the death of the bush.
- Depletion of the soil under the bushes. The rose garden has to be replanted every few years so that the flowering remains the same constant.
- The layout of the site was changed, and it was decided to move the rose bushes to another place.
- The rose bush has grown too much. In this case, it is not necessary to completely transplant the rose garden, it is enough to remove the extra branches and transplant part of the bush. An already developed root system will provide him with quick survival in a new place.
- If in the rose garden one of the bushes dies for any reason, a new plant must be transplanted in its place, while it is advisable to choose a similar variety.
- The question is often asked whether it is possible to transplant an old rose. If the plant is more than 5 years old, the number of suction roots begins to decrease, so the transplant will have to be carried out with extreme caution. To do this, you have to transfer them to a new place with an old clod of earth - this is a very time-consuming work. Young plants take root much better, therefore, for transplanting, it is still advisable to choose roses no older than 5 years.
Benefits of transplanting roses in autumn


Plants transplanted in autumn adapt faster to a new place.
The reasons are as follows:
- The soil is well warmed up. The root system of seedlings has time to give an increase before frost. In the spring, such roses immediately grow, they no longer need time to adapt. They bloom earlier than spring ones, are more resistant to unfavorable natural conditions.
- Soil temperature is stable. There is no threat of recurrent frost, which could damage the roots and buds. By the time the soil is frozen, the roses will be fully rooted.
- Humidity is higher in autumn than in spring, there is no scorching sun. Favorable conditions contribute to the rapid establishment of plants.
- Autumn rains moisturize the soil well. Additional watering is not required.
The time required for the full rooting of plants in a new place is 3-4 weeks.
Spring and autumn transplant technique
The transplant of an adult rose is most often carried out in September, but when choosing a date, one should take into account the region of growth of the plant. Spring transplanting roses in the garden will go well if you start work before the buds appear.The seedling will have enough time for root development and adaptation. An exception from the list is standard roses, it is more favorable to replant them in April. If the planned transplant of a rose in the spring for some reason was delayed, then for quick rooting, the seedling is shaded for a week.
The process boils down to several systematic stages:
- It will be necessary to prepare a proper indentation for replanting the bush. In this case, this must be done at least 2 weeks before the moment of planting. The hole should be dug at least 0.6 m wide. Next, you need to clean the depression from weed roots and lay out the bottom with compost. If several bushes are being prepared to change the place of growth, it is necessary to observe an appropriate gap between the pits of at least 0.8-1 m.


Landing in a prepared area
When to replant roses in autumn?
Fertilizer really gives more intensive growth of garden plants, and they bear fruit much better. Now you cannot grow a normal crop without fertilization, and this feeding increases the amount of vegetables, so I am very pleased with the result. "
Preparation of planting holes
Planting pits are prepared two weeks before planting. The volume of nutrient soil, size depends on the size of an adult bush.
| Rose type | Length, width, depth (cm) |
| Miniature | 30x30x30 cm |
| Roses patio | |
| Groundcover | |
| Floribunda | 40x40x50 cm |
| Tea hybrid | |
| Shrubs up to 2 m | 50x50x50 cm |
| Climbing | |
| Shrubs above 2 m | 100x100x100 cm |
If the site has good fertile soil, holes are dug according to the specified dimensions. On soil unsuitable for cultivation, add another 30 cm.
The ground for filling the holes is prepared in advance:
- flower soil - 2 buckets (24 l);
- humus, sand and peat - 1 bucket each (12 l);
- dolomite flour - 300-400 g;
- ash - 400 g;
- superphosphate - 50 g.
You can make a simpler composition:
- garden land, peat - 1 bucket each;
- bone meal - 100 g;
- ash - 200 g.
Transplanting rose bushes
Roses are transplanted on a cloudy, windless day.
The transplant takes place in three stages:
- Pour soil mixture at the bottom of the pit, level it. The thickness is 15-30 cm.The inoculation site should be 5 cm below the soil level, for standard ones by 10 cm.
- Prepared soil is poured around the earthen coma to half the hole. Squeeze, spill well with water.
- When the water is gone, the pit is completely filled with earth. Lightly tamp, watered.
Planting roses in open ground: nuances and technology
Planting roses can be carried out in spring or autumn, the main thing is to fully comply with the technology.
Sapling selection
The first stage of growing roses is the choice of material for planting. Flowers can be open or closed rhizomes and can be found in local or overseas nurseries.
Bushes with the first type of roots are planted immediately after purchase, as they are sold during the active growing season. With quality care, they easily take root.
Domestic samples are bought only in the fall and from trusted breeders. Foreign seedlings are carefully examined for bud growth, if any, then the plant is planted in spring.
Pay attention to the flowering period of the specimens, their frost resistance (relevant for the northern regions).
Location
Roses love well-lit areas, the more sun, the more active the buds appear. However, the places where direct rays penetrate are not suitable, since the petals turn pale and burn out, burns occur at the tips.
Shaded areas are strictly prohibited, as flowers tend to the sun, stretch and then weaken. This arrangement increases the likelihood of disease and pest attacks. Places with drafts are not suitable either, since gusts of wind break the stems of the roses.
The best option is the southeastern part of the garden.
Roses love to move away from buildings and other plants. These flowers should not be grown after stone fruit crops, as they severely deplete the soil, especially groundcover.


The soil
Roses prefer light, breathing earth.Water and oxygen are well supplied to the rhizome in chernozems and loams.
Sandstones and sandy stones are not the best option, in summer they are heated by the sun's rays, and in winter they freeze quickly. Such drops affect the rhizome. Professional gardeners correct the situation by adding peat, lime and rotted manure in equal proportions to such soil. When the soil dries quickly, clay is added, spreading it into the planting pit with a layer of 7-8 cm. In mid-September, in preparation for wintering, potassium monophosphate is introduced in the form of a solution.
Planting scheme of various varieties of roses
In September, bush varieties are planted deeper than in the soil of the nursery, since this way the seedlings do not bulge out during cold weather. Climbing varieties deepen even more, due to which additional root processes arise.
- When planting, the roots of the plant are evenly spread in different directions and sprinkled with earth so that it is in close contact with the flower and there are no voids.
- At the bottom of the pit, nutrient soil is poured with a slide, roses are placed on it.
- The hole is covered with soil, rammed and watered.
- Near the base of the shrub, a layer of earth 20 cm high is poured, this protects the roots of the plant from frost.
- Having compacted the soil, it is watered with several buckets of water (per bush).
- After evaporation of moisture, the surface is covered with dry soil, and holes are made around the seedlings for adding water.
The interval between park varieties is from 75 cm to 1 m, since in adult form they have a spreading crown. The distance between hybrid tea, polyanthus species and floribunda roses is from 30 to 60 cm.
Caring for roses after transplanting


All care after transplanting in the fall comes down to preparing the plant for winter. Watering is not needed because the soil is well moistened. But, if it is late, very warm weather without rains, the seedlings are watered every 4 days.
Additional feeding is not needed. The prepared soil contains enough nutrients until spring. It is strictly forbidden to introduce organic matter, nitrogen fertilizers, which stimulate the growth of the aerial part of the roses.
Low seedlings do not need to be covered for the winter. They are covered with dry soil to a height of 25 cm, as soon as a slight negative temperature is established. Do not use sand or sawdust for hilling. They absorb moisture, creating favorable conditions for the development of fungi and bacteria.
Rules for transplanting roses to a new place
For the correct planting of roses (so that they please with their flowering as long as possible and do not require re-transplanting), you need to adhere to simple tips, thanks to which the bushes will calmly and quickly take root in the flower bed:
- The main thing is to decide on the time of transplantation.
- It is necessary to prepare a new place for the rose. It is recommended to clear the land on this site from unnecessary roots and weeds. The pit is dug about 60 cm wide and 60-70 cm deep.
- The rose must be prepared for planting. Pruning of dried branches and flowers is carried out. If the bush has grown too much, it can be rejuvenated. This is done by dividing the root system.
- You need to dig out the bush as carefully as possible without damaging the root. Most likely, you will not be able to cut the root without damage. But there is nothing wrong with that. If you pay a little more attention to the bush in the future, the plant will happily take root in a new place.
- You need to transfer the flower with the remnants of the earth on the roots.
- It is not recommended to bury the bush deep into the finished hole. It's good if the landing level remains the same. Tall flowers must be tied up so that they do not break in the wind.
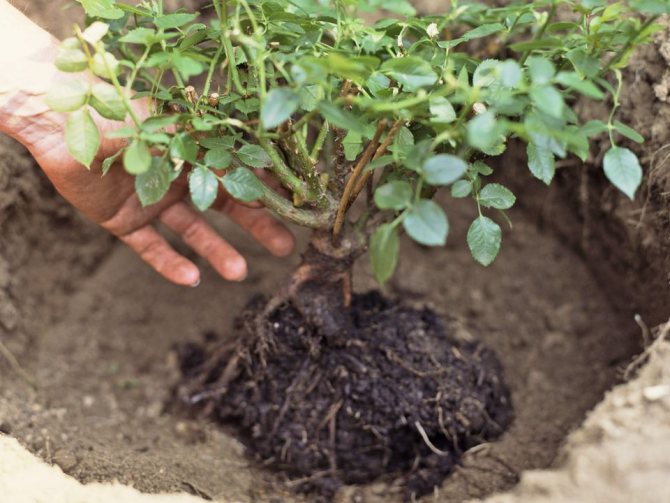


Care
Is it recommended to prune foliage, branches when replanting a plant? Some gardeners believe that everything should be left. Others are of the opinion about the need to shorten it to 10 cm columns, removing all the foliage. The decision is made by the weather. In a warm autumn, it is not recommended to touch the branches, the buds may awaken and the plant will spend a lot of energy on unnecessary growth.If you wish, you can cut the branches in late autumn, when the weather is cold.
If you are replanting a rose in a cool fall and about 3 weeks are left until frost, pruning can be done at the time of transplanting. With bare roots, this is done without fail.
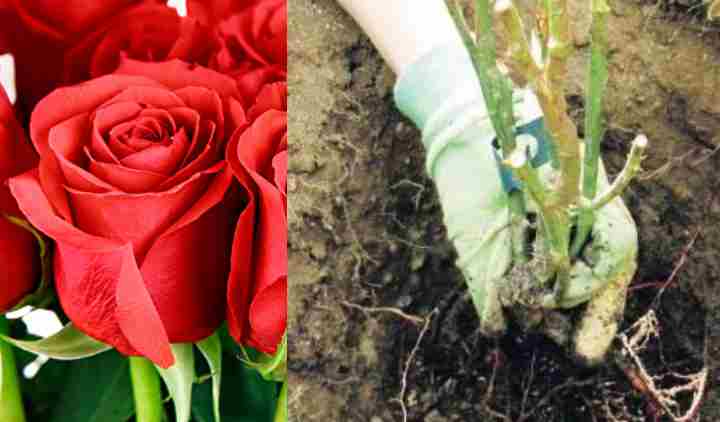


After transplanting, provide the plant with care, this will help accumulate the rose enough strength for the winter. Provide the seedling with extra watering before the first frost. If the weather is still dry and warm, then you need to water the rose every few days, the ground should be moist. No additional feeding is needed, the soil was already well fertilized before planting.
You will need to cover the weak roots of the plant. Suitable for this: wooden boards, simple hilling of the earth, modern films, materials, coniferous spruce branches. Gardeners recommend covering the rose after the first frost, because the first frost only hardens the plant. If you are not entirely sure of your experience, but a transplant is necessary, watch the video of professional gardeners who will reveal all the subtleties.
Thus, when it becomes necessary to transplant a rose bush in the fall, this will have a number of advantages:
- the ability to further refine the soil;
- take care of the root system and remove diseased processes;
- there is no danger of sudden frosts like in spring;
- wet weather provides natural watering and the roots are well strengthened, prepared for winter time.






















