Often there are people who are used to living one day. In principle, this is not bad. Make plans, but be prepared for various circumstances that may change these plans. However, this principle of life is not always suitable for gardeners. Or rather, it practically does not fit. Circumstances, of course, can change with them, like any other person, but whether the gardener tries to do the planned work at a different time depends on whether something grows for him or does not die. Not easy. But eating your berries fresh or in the form of compotes or jam, as well as stewing your own grown vegetables is a very big reward.
One of the useful and healing treasures in the garden can be raspberries. There is probably no person who would not be treated with raspberries when a sore throat or a fever has risen. Raspberries are very useful and can prevent colds if consumed regularly during epidemics in the form of compotes or jam. But in order for this wonderful berry to be enough fresh for the whole family, and even for the winter there would be enough reserves, it is necessary to grow the required amount in the garden. Therefore, the women's online magazine Pretty Secrets offers tips for growing and replanting raspberries.
If your site is already equipped with raspberry bushes, and you want to plant or transplant them, then it is better to plan this event in the spring. This is due to the fact that the root system, and the whole bush, will be able to take root better, since it will have more time before winter in order to get stronger and survive it.
Why transplant raspberries to a new location?
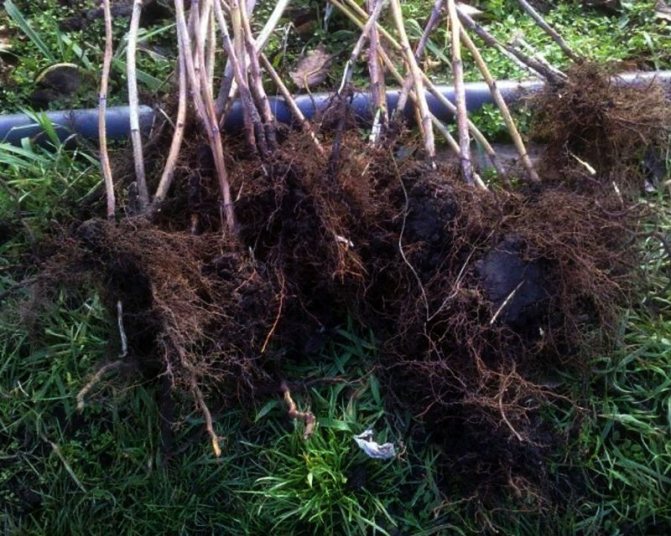
When growing a shrub in the same place for more than 10 years, the soil under the bushes begins to thin out, lose nutrients, it gets tired, needs a break. Although the bushes are becoming powerful, the berries are getting smaller every year, the yields are decreasing. The roots stick out, densely intertwine each other, they have nowhere to grow further. A depressed root system gives little young growth, becomes more vulnerable to temperature extremes, and is more likely to be affected by pests and diseases. As a result, the raspberry plant stops developing, yielding crops, and turns into dense, gloomy, useless thickets.
However, raspberries are transplanted to another place, not only for its rejuvenation in the new fertile soil. An incorrectly chosen place initially - insufficient illumination or swampiness of the site, strong drafts, strong soil contamination and much more can be the reason for transplanting raspberries to a new place, regardless of how long it has managed to exist in the old one.
When is the best time to transplant?
You can transplant raspberries throughout the season, it depends on the climatic zone, the nature of the planting material, the variety, and also on the reason for the transplant. It is important to remember the rule that cannot be ignored when transplanting - there should be warm, cloudy weather, and such periods can be found in spring and autumn. It is under such conditions that any seedlings will take root as quickly as possible, without culling.
Features of transplanting in spring
A spring raspberry transplant is best suited for the Midland and Northeastern regions.There is a lot of melt water in spring, the ground remains wet for a long time, and hot days in spring, as a rule, are few. Also in the spring it is better to transplant non-repaired raspberries. It will bear fruit anyway only for the next season, and over the summer the roots will get stronger, adapt to the new soil, the bush will gain strength.
Features of the transplant in summer
In the summer, it is advisable to transfer young basal processes to a new raspberry tree. Old large bushes have a powerful root system, it will be difficult for it to take root in a new place in the heat, and the small roots of the young growth will not require a large clod of earth with them, and it is easier to cover such seedlings from the heat than large ones. It is important to remember that before digging out the bushes for a summer transplant, the raspberry tree should be well watered to minimize root trauma when separating them.
Features of transplanting in the fall
Transplanting raspberries in the fall is best done in the southern regions. Autumn is warm there until the end of October, but the intense heat is gone. A month before the cold snap, you can begin to transfer the bushes. It is important that the vegetative growth of raspberries has already stopped, then all the force will be directed to the root system. The bushes will take root in a month, during the winter the plant will rest, and in the spring, with the first heat, the shoots will immediately grow into growth. It is also good to transplant remontant varieties of raspberries in the fall. Having rooted in the fall, in the spring, young shoots will have time to grow and give a crop.
Planting raspberries in fall fertilization. What to put in the hole when planting raspberries in the fall. The best fertilizers


Planting raspberries this year.
With the onset of autumn, you need to do a lot of work in the garden, including planting new raspberry bushes. For raspberries to take root well, you need to fertilize. I will tell you in more detail what you can get into the hole when planting raspberries.
Place for raspberries.
Raspberries need to be planted in a well-lit area, then the berries will be larger and they will be larger. For raspberries, it is better to choose a site that is protected from the winds, since this shrub does not like weathering. Therefore, you can plant raspberries near the fence, buildings.
When planting raspberries, crop rotation must be observed. The best precursors for raspberries are dill, onions, parsley, garlic, marigolds, and legumes.


I plant a prepared raspberry bush in a planting pit with fertilizers.
Raspberries will take root well after planting and will yield bountiful crops at a soil level of Ph 6-6.5. Of course, raspberries will grow best on light loamy. But this shrub can also be planted on a sandy one, subject to the introduction of regular fertilizers and dressings.
Soil preparation.
From my own experience, I know that raspberries are best suited for organic fertilization. Before planting, I prepare the soil as follows: when digging, I bring in humus, wood ash and superphosphate. For 1 sq. m. it takes me 10 kg of humus, 1 liter can of wood ash and 500 g of superphosphate.


I bring in wood ash when planting raspberries.
If before planting it is not possible to prepare the soil and fertilize. Then you can plant raspberries differently. That is, when planting, we add fertilizers to each hole.
What can be put into the hole when planting raspberries.
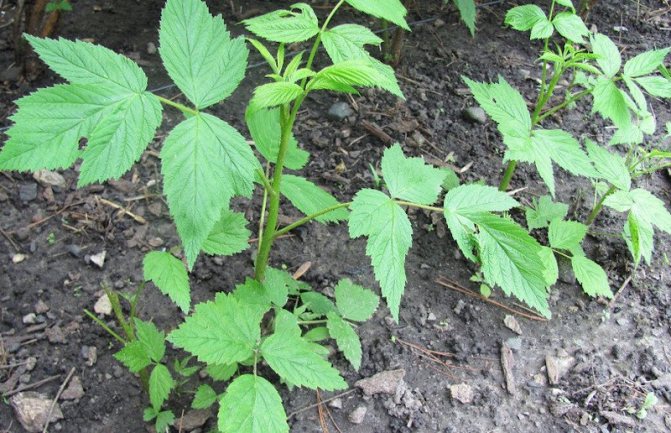
When planting raspberries, I must add humus and wood ash to each hole. I mix everything well right in the hole with the ground. Then I pour in water and plant a raspberry bush, deepening it by 2-3 cm.After that, I sprinkle the raspberry with earth. The surface of the soil around the planted bushes I mulch the bush with straw.


Raspberry bush.
And do not forget that you need to plant raspberries in the fall, taking into account the weather conditions. That is, so that the planted raspberries do not fall under the autumn frosts for at least two weeks.
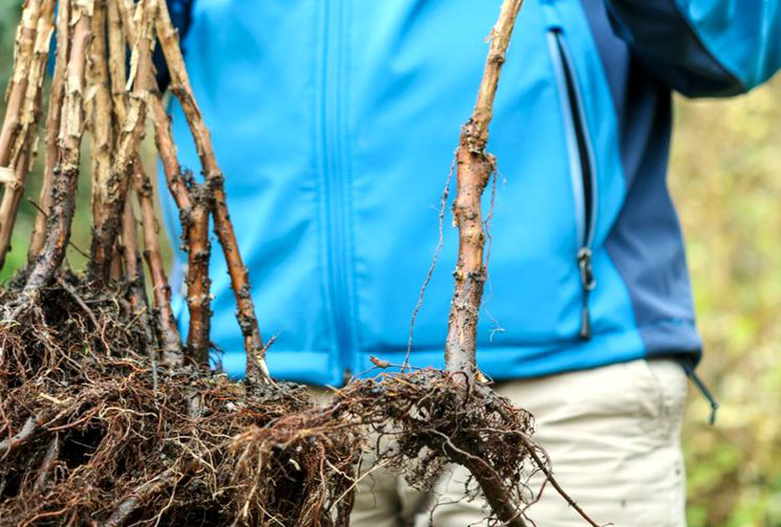
How to select planting material?
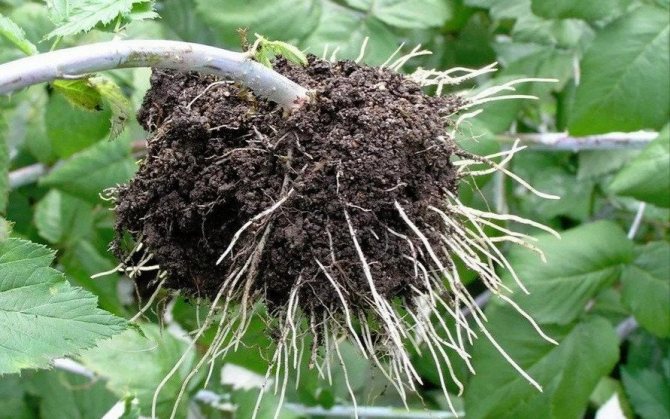
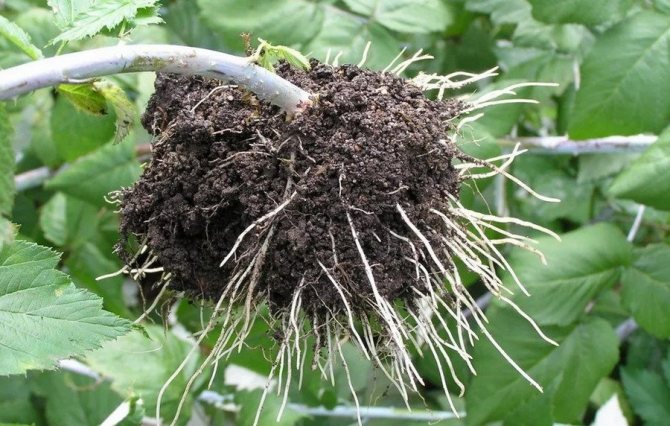
If you have a large raspberry tree and have the opportunity to choose, then transfer more young shoots and 2-3-year-old bushes to a new place. Young bushes are easier to divide, they will take root faster.However, the thickness of the shoots at the base should be at least 1 cm in diameter. The rhizome of the bushes should be fibrous, up to 30 cm long. Select bushes with healthy roots and stems, no growths, cracks, or signs of pest infestation. Trim suspicious areas to a healthy spot. If the bush is dividing, then each cutting should have several viable roots. Before planting, large branches are shortened with pruning shears to 40-50 cm so that food and moisture in the soil is not spent on leaves and stems, but gets to the roots.
Shrub or pit planting method
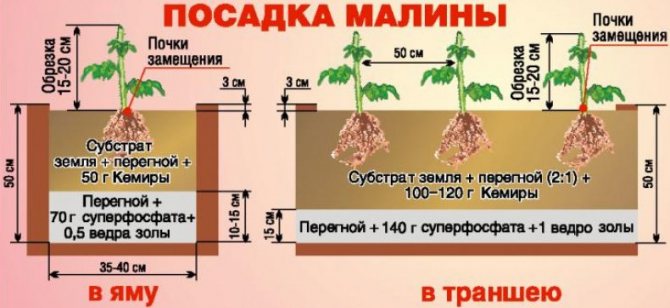

Most experts believe that the bush method, or as it is also called the pit method, is the most effective. Transplanting raspberries using this technology assumes the presence of a planting depth and width of approximately the same, as with trench technology. The rows should be done at a distance of 1.5 m, and between the bushes up to 70 cm. A separate hole is prepared for each plant, they should be staggered.
Previously, in 2-3 weeks, the site intended for transplanting raspberries is dug up. The required amount of fertilizers is introduced at the rate of 10 kg per square meter of humus, 250 g of superphosphate and potassium. Planting rules are the same as for the trench method. Raspberry transplanting involves dipping each seedling into a solution made from mullein and clay. There is an opinion that it is better to replant the offspring, and not the whole bush.
Preparing a new place
Basic principles of site selection
When choosing a new place for a raspberry plant, it is important to take into account your positive as well as negative experience of growing raspberries in the same place, the main thing is to follow the basic rules, namely:
- the area should be illuminated with sunlight throughout the day, with the exception of the area for some varieties of raspberries, in which the berries are baked in the sun, partial shade is suitable for such raspberries;
- if the raspberry plant is transplanted on a personal plot, then on the north side there should be buildings or a hedge, if on a gardening plantation, then on the north side there should be a forest or forest belts, a settlement. They will protect plantings from winds, as well as retain snow for shelter from frost and melt water in spring;
- if the soil characteristics of the area are not ideal for raspberries, then it is necessary to carry out a soil correction: dig up the acidified soil with slaked lime, ash, you can use old cement. Heavy clay soil must be dug up with humus, peat, sand.
- when digging a site, you need to remove roots, old branches, debris from it.
- if the site was previously used for other crops, then you need to add cow or pig manure, wood or straw ash, if this is not possible, then you can bring forest land or plant green manure in advance, which will improve the structure of the soil and saturate it with nitrogen.
- do not transfer the raspberry to the area where nightshade crops, as well as strawberries or strawberries, used to grow.
In pits or trenches?
It is important to remember that a new raspberry patch is prepared a month before transplanting.
With bush cultivation of raspberries, pits are prepared, and with tape cultivation, trenches. Several single cuttings, root shoots or a bush can be placed in the pits at once, the distance between the pits is left 80-90 cm. Single branches or cuttings are placed in the trenches, but more often. The distance between them is 40-50 cm.
With the tape arrangement of the raspberry plant, it is more convenient to control the growth of daughter offspring, it is more convenient to tie up and handle the shoots, especially when it comes to industrial plantings, where cultivation is carried out mechanically. With this method, it is easier to organize drip or trench irrigation, but expensive mineral fertilizers are spent more wastefully, which, during bush cultivation, are applied more rationally, directly under each bush.
Features of transplanting remontant raspberries
Experienced gardeners transplant remontant raspberries in the fall, so that in the spring the bush does not waste time on survival, but immediately begins to grow, because it needs to have time to grow and give ripe berries by the end of summer. It is important to correctly navigate the timing, they are different in each climatic zone. The main rule of a successful autumn transplant is to accurately "catch" the moment of transplanting, so that the cuttings and shoots have time to take root, but do not begin to give young shoots that do not have time to get stronger, deplete the already weak bush and die in winter. In the fall, remontant raspberries still bear fruit in full, but when transplanting, you do not need to spare the berries. Shoots can be safely cut to 10-15 cm from the ground, so that all forces are directed to rooting the plant.
The technology for transferring raspberries to a new place does not differ much from the usual planting of a bush. The main thing is that the soil in the new site is fertile and when transplanting plants, do not repeat the mistakes made when cultivating the old plantation.
Further care of plants
After planting the bushes, it is recommended to immediately take care of the supports that the grown bushes will need.
Since raspberries are a thorny plant, you will not get hurt by making support in advance.
Usually, wire is used to maintain the stems in an upright position, or lacing stretched between the posts.
In addition, in the fall, you need to prepare the plant for wintering. Too long stems need to be cut and covered.
Used as a covering material:
- film;
- spruce branches;
- straw;
- compost.
During the growing season, plants need regular watering, feeding and weeding. In addition, the bushes should be periodically treated against diseases and pests.
It is recommended to enclose the raspberry plant along the perimeter with slate, which is slightly buried in the ground.
This will help prevent unwanted spread of the plant throughout the area.


























